Source/Reference Documents
Map Spreadsheet Examples 2021-2023
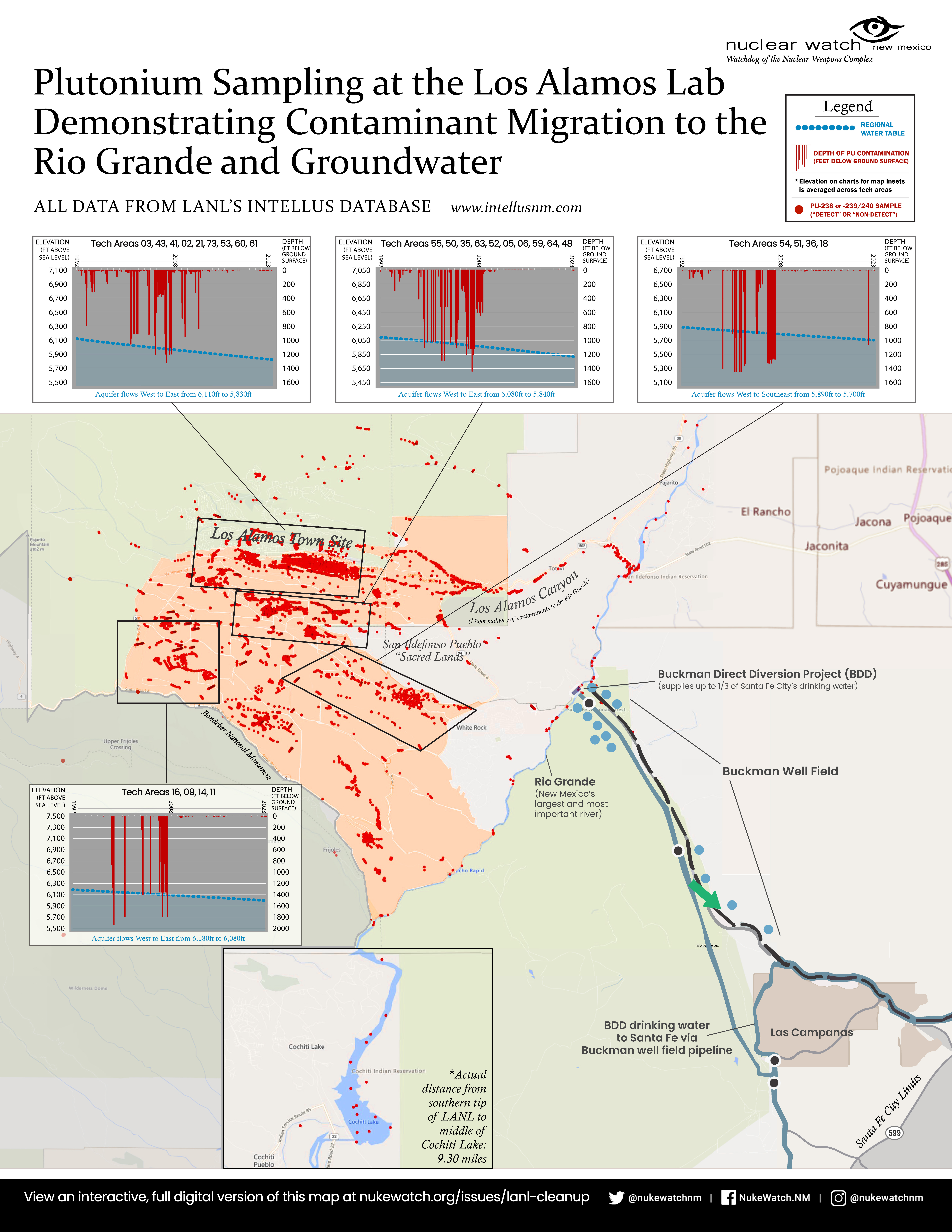
Below are examples of a spreadsheets created in Intellus, which is the environmental database at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The requests were for all soil and groundwater samples taken in, under, and around the Lab in 2021, 2022, and 2023. The spreadsheets were then sorted by “Report Result” (Column ‘F’), which lists the plutonium found in samples in descending order. It shows the highest sample for each year at top of the column.
Looking at the 2021 spreadsheet, there were 2043 samples analyzed for plutonium taken in 2021. There are approximately 100 detects including the high sample of 10100 pCi/g. Please read Dr. Ketterer’s report for a discussion of the ‘detects’ and ‘non-detects.’
Notice the latitude and longitude for each sample (columns ‘O’ and ‘P’). We used these coordinates to create the maps.
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
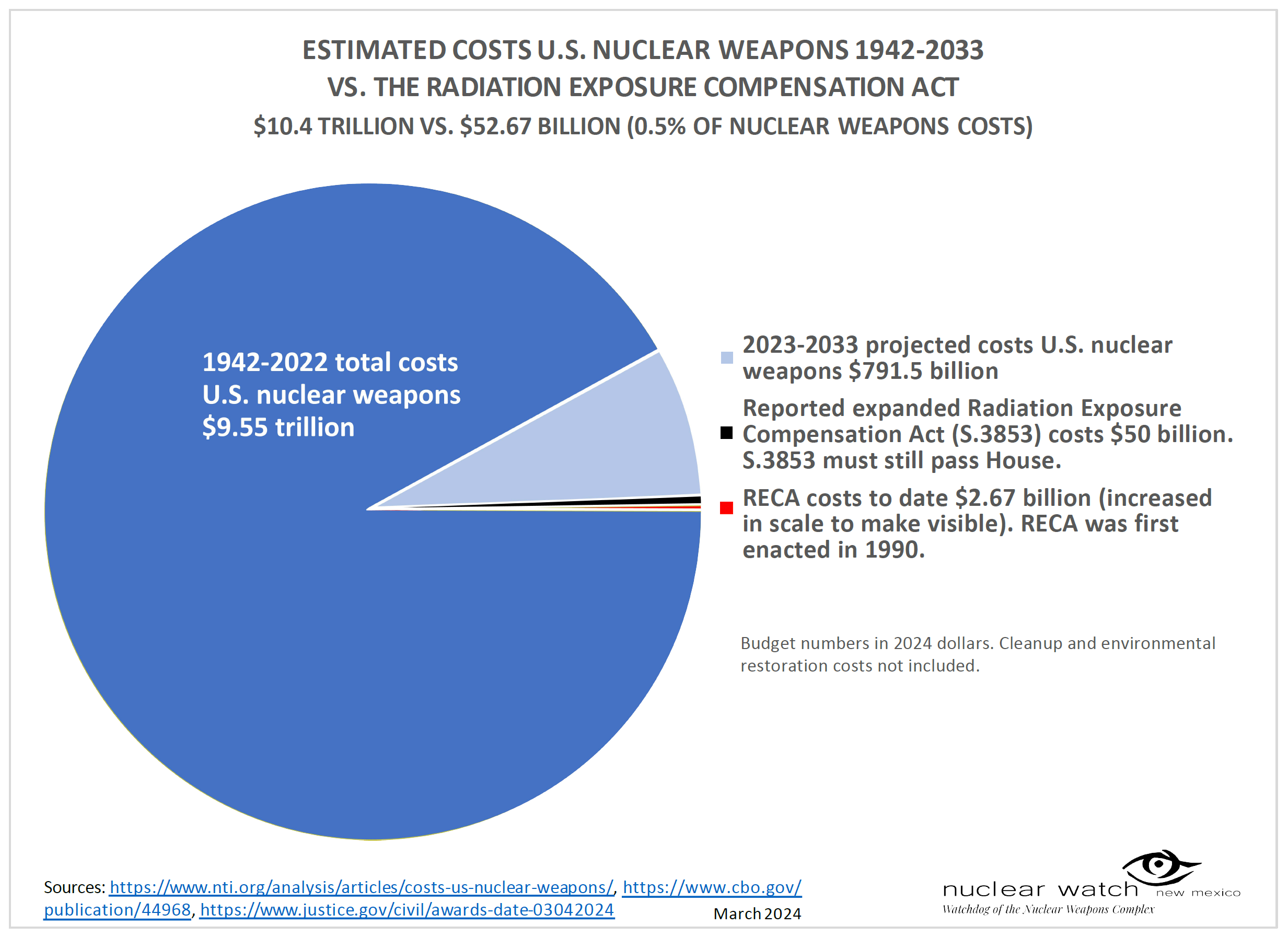
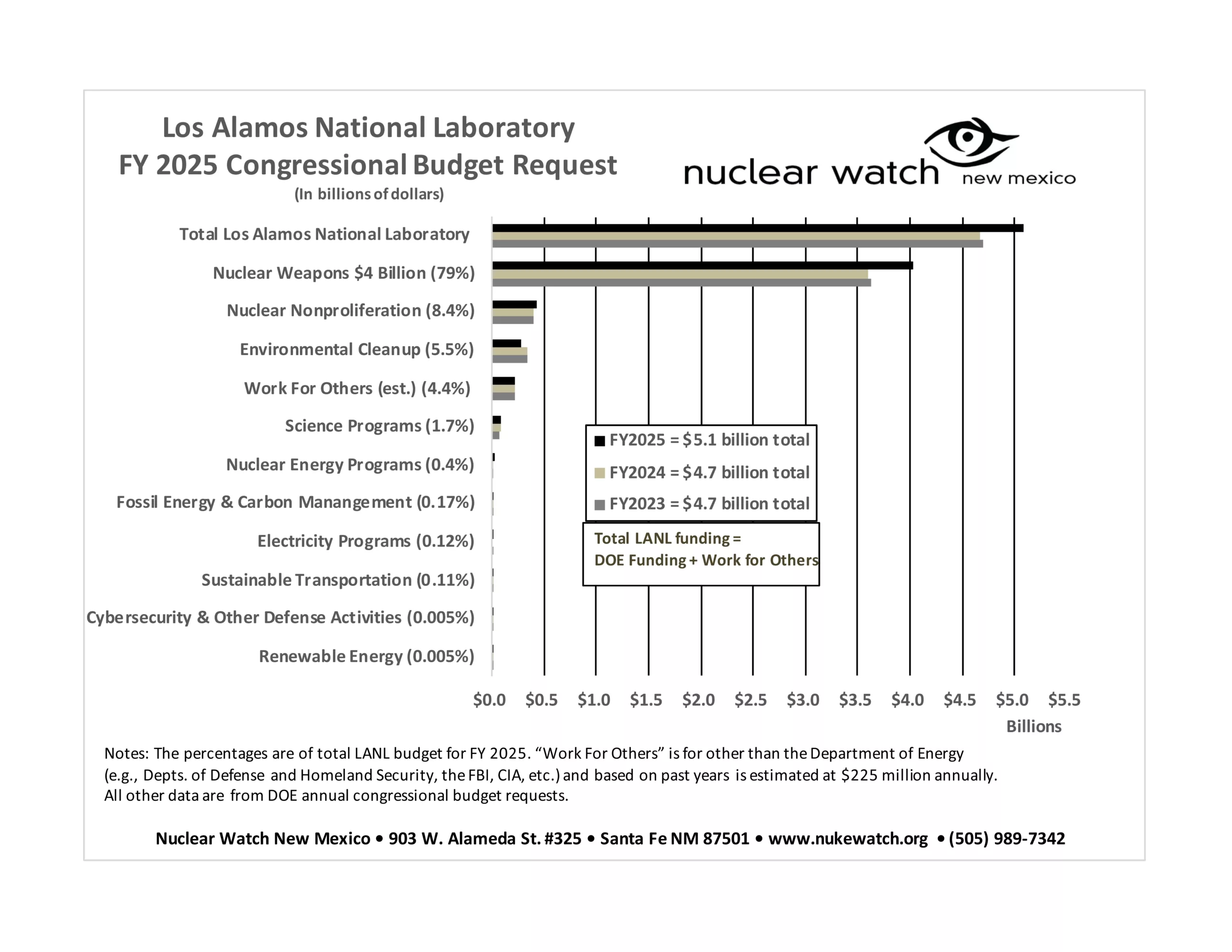
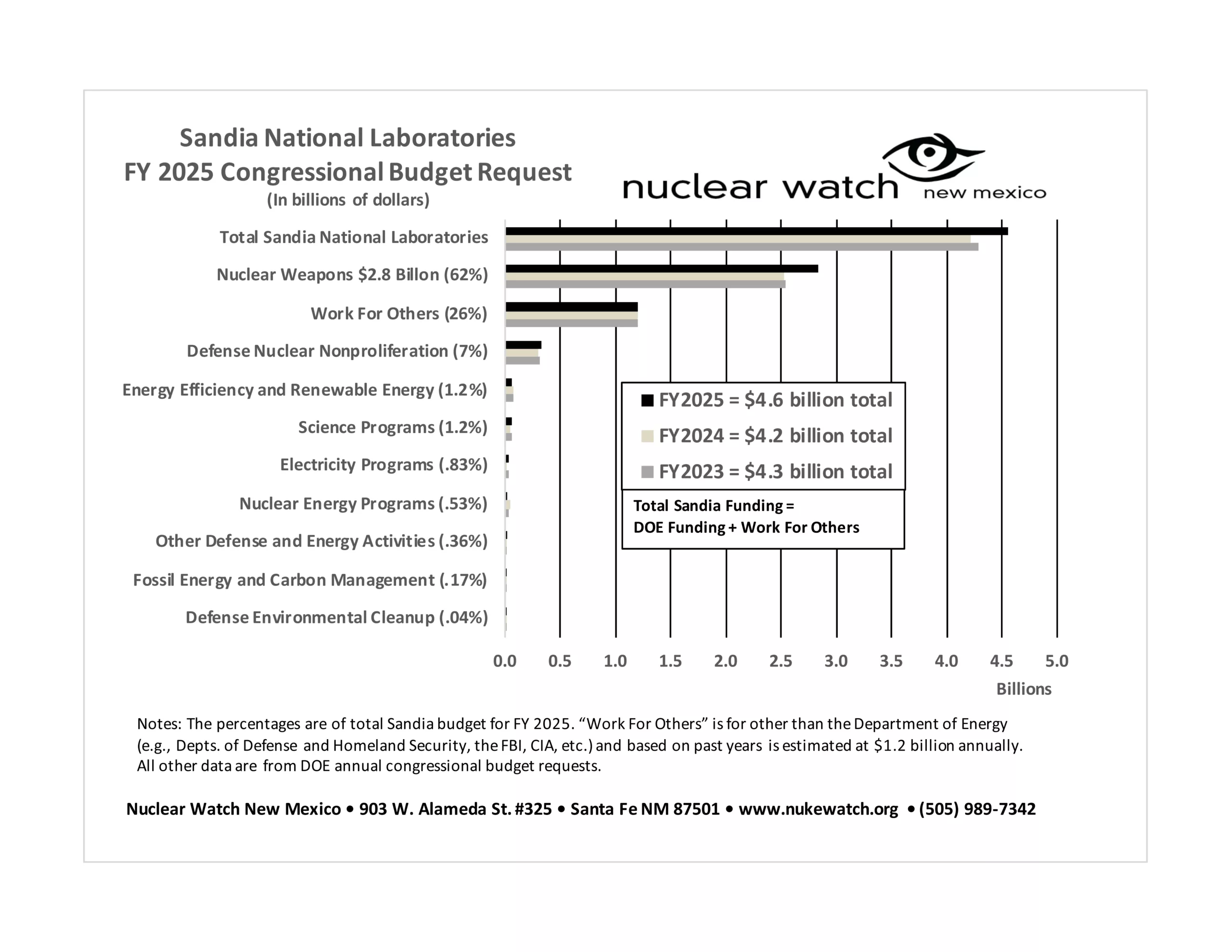
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New & Updated
The Risk to Waste Stored at Area G
We pride ourselves here at Nuclear Watch New Mexico on trying to stick to the facts as we best we know them and not being alarmist. That said, the Las Conchas Fire that has now crossed the Los Alamos National Laboratory’s (LANL’s) southwestern boundary is a real threat. For starters is the mind-blowing fact that in just 30 hours this fire has grown bigger than the notorious 2000 Cerro Grande Fire which burned ~48,000 acres (~5,000 acres within Lab boundaries), and traveled in a beeline 12 miles to get to the Lab. With forecasted days of strong winds and gusts and high temperatures it’s hard to say where this fire might go and what it might do. Pray for rain.
We are not so concerned about the hardened facilities at the Lab constructed of concrete and cleared of combustible materials (i.e., trees and brush) around their perimeters. We doubt that there would be any breech to their containment that would let contaminants escape (with one caveat below). But we do have concerns. One is the fact that over 6 decades the Lab has blown up a lot of uranium and depleted uranium in dynamic high explosives experiments in the general area in front of the fire. We don’t know to what extent the shrapnel or debris has been cleaned up and could possibly be aerosolized.
Another concern, given both the velocity and ferocity of the Las Conchas Fire, is whether any Lab facilities loose their power and back up generators failed to work for whatever reason. In that case containment systems could fail with unknown safety implications.

But our biggest concern is whether the fire could reach the fabric buildings (essentially very large tents) at Technical Area-54’s Area G that store some 20,000 barrels of plutonium-contaminated wastes from nuclear weapons research and production. We recommend that the public use satellite-based fire detection data and fire intelligence information published by the US Forest Service to monitor the situation (see related post for instructions on how use it). From that we can “see” that the leading edge of the fire is a little more than three miles from Area G.
The good news is that the fire should slow down if and when it heads toward Area G because it will have to leave the mostly ponderosa forest into pinon and juniper country (which doesn’t crown fire like ponderosa). Also, the Lab has cleared trees and vegetation around Area G, and the fire would have to jump some major canyons just to get there.
So here’s hoping the fire doesn’t get anywhere close to Area G. But watch out if it does. The public should be concerned and really pay close attention. It might be a good time to take a road trip somewhere away from being downwind. This is one fire that cannot be underestimated.
Extensive B61 Life Extension Serves Lab’s Self-Interest More than Weapon’s Mission
To add to the uncertainty surrounding the pending B61 Life Extension Program:
The NNSA’s FY 2012 Congressional Budget Request says that among other things the scope of the B61 LEP will include “implementation and maturation of enhanced surety technologies into the nuclear explosive package,” a major rationale for the program to begin with. B61 surety is especially sensitive given their forward deployment in Europe.
During the last few months I have learned the following from anonymous congressional staff:
• Prestigious consultants to the government (the JASONs) finished a study in January or February on the surety of US nuclear weapons. It is classified with no unclassified summary. One aim of the study (perhaps the aim) was to create baseline criteria for applying surety mechanisms to existing US nuclear weapons.
• In that study the JASONs raised some concerns that NNSA-proposed enhanced surety technologies could impact nuclear weapons reliability. NNSA is now in the process of responding that its enhanced surety technologies are maturing.
• Some congressional staff seriously doubts these new surety technologies will be mature enough for inclusion in the B61 LEP if it starts as scheduled in FY 2012 (which begins this October 1). If I understood correctly, these concerns revolve around multi-point safety and optical detonation. It’s not clear to me whether or not the JASONs share these particular concerns.
• The JASONs are also in the process of preparing a separate cost benefit study on the proposed B61 LEP.
To be clear, I have no way of independently verifying the above, nor do I have a full (or even good) understanding of their implications. It is obvious that the B61 LEP is a very big deal to the nuclear weapons labs. For example, Sandia calls it “the largest effort in more than 30 years, the largest, probably, since the original development of the B61-3, 4, a full-up weapon development effort that began in the late 1970s and entered the stockpile in 1979.” (“Launching the B61 Life Extension Program,” Sandia Lab News, March 25, 2011).
NNSA and the nuclear weapons labs seem anxious to rush the B61 Life Extension Program now before the political momentum of increased nuclear weapons funding as a condition of New START ratification begins to recede. To the contrary, we should hit the pause button on the B61 LEP instead of automatically following the labs’ vested self-interests. In order to prudently conserve taxpayers’ dollars, the B61 LEP should be delayed for a few years while new surety technologies and other issues (such as continuing forward deployment in Europe) are sorted out.
Replacement of Neutron Generators is Routine
At a town hall meeting this week in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, near the proposed location of the new “UPF” nuclear weapons facility at the Y-12 National Security Complex, the state’s junior senator, Bob Corker quipped:
It’s just about the fact that our nuclear arsenal is absolutely obsolete. I saw neutron generators, literally, out in New Mexico that will quit working in the year 2015, which means it renders the weaponry totally obsolete.
Whew. Stunning.
Neutron generators are “limited life components” (LLCs). The NNSA FY 2012 Congressional Budget Request has this to say: Many age-related changes affecting various nuclear warhead components are predictable and well understood. Limited life component exchanges are performed routinely to replace these components periodically throughout the lifetime of the weapon. Components such as power sources, neutron generators and tritium reservoirs deteriorate predictably and must be replaced before their deterioration adversely affects function or personnel safety. Page 50, emphasis added.
Changing out neutron generators in fact appears so routine that it seems the military changes them out in the field. A July 1995 Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists (p. 78) mentions “On April 11, [1995] Sandia delivered 36 recertified neutron generators to the Navy…” Emphasis added.
NNSA says under FY 2010 Accomplishments for Stockpile Systems: “Delivered all scheduled LLCs (GTS [gas transfer systems, meaning tritium] reservoirs and neutron generators (NG)) and alteration kits to the DoD and Pantex to maintain the nuclear weapons stockpile.” NNSA FY 2012 Congressional Budget Request (CBR), p. 61, emphasis added.
Also of interest on the same page: “Selected a common NG for the B61 and B83 that will reduce development, production, and maintenance costs.”
Neutron generators are testable, and the testing devices themselves are being improved. “FY 2010 Accomplishments Stockpile Readiness Nonnuclear Readiness… Deployed Neutron Generator (NG) Testers, which assures neutron generator test capability by modernizing testers as required to support NG production and shelf-life programs.” NNSA FY 2012 Congressional Budget Request, p. 135.

In the current Life Extension Program W76-1’s are being outfitted with new-design neutron generators (the MC4380). Corker is seeing neutron generators in New Mexico because Sandia produces them and loads tritium into the neutron target tubes that are a critical part of neutron generators. Production of neutron generators is being both improved and expanded.
This from Sandia Labs “Labs Accomplishments:”
During FY10, Sandia shipped more than twice as many neutron generator assemblies (NGAs) to its NNSA and military customers than in any previous year. This totaled 850 NGAs and 340 packaging requirement kits. Record completion rates were achieved in four different production areas within the neutron generator supply chain, in concert with a shift to a common neutron generator subassembly that improved production efficiency. Sandia established a balanced supply chain capacity approach to help meet future NG directive schedule challenges with a diverse neutron generator product mix supporting numerous weapon systems.
http://www.sandia.gov/LabNews/labs-accomplish/2011/lab_accomp-2011.pdf, p. 5
Neutron generators themselves are being continuously improved, for example:
In the early 1990s Sandia undertook to design a replacement neutron generator for the W76 nuclear warhead on the Mark 4 reentry body of the Navy’s Trident I system. There were several compelling reasons for doing so, including the need to increase the component’s design margins, simplify its manufacturability, augment its resistance to new profiles of hostile environments, and increase its life span.
http://www.globalsecurity.org/wmd/systems/w76.htm
In 1999 the MC4380 Neutron Generator and its MC4378 Timer, MC4705 Voltage Bar, MC4148 Rod, MC4437 Current Stack, and MC4277 Neutron Tube were qualified for use in the Navy’s W76 weapon system. This culminated a multi-year development effort which included the transfer of production capability from the Pinellas Plant to Sandia. This is the first weaponized neutron generator to employ a focused ion-beam neutron tube for higher reliability, the first produced at Sandia, and the first Sandia component with radiation hardness requirements to be qualified without underground testing.
http://www.globalsecurity.org/wmd/systems/w76.htm
The neutron generator business is very robust, and Corker’s claims of obsolescence are absurd.
Big Money for the B61’s New Ride
In a mid April report to Congress, the Pentagon stated lifetime cycle costs of the dual [nuclear] capable F-35 Joint Strike Fighter will exceed $1 trillion. The F-35 will have a lot to do with future forward deployment in Europe (or not) of the proposed heavily modified B61-12 tactical nuclear bomb.
According to Inside Defense, problems with development and production aspects of the F-35 program will delay the deployment of the aircraft another two years and require an additional $7.2 to complete the development phase.
Ironically, Lockheed Martin is the lead contractor for the F-35. It is also the contractor that runs the Sandia National Laboratories, which is the lead lab for the B61 Life Extension Program (LEP). One of the main purposes of that LEP is transform the B61 “analog controlled” bomb into a “digitally controlled” bomb that mates with the advanced electronics and avionics of the F-35.
The B61 LEP will begin in FY 2012 with $223.6 million in funding. Total cost is currently estimated at ~$5 billion
The Corporate Folly of Nuclear Power
Meltdowns at the reactors are not the biggest threat, as horrific as they are. Instead the biggest threat is the spent fuel rod pools if they lose circulating water.
The reactors at Fukushima were designed by US General Electric, whose corporate slogan is “bringing good things to life.” The Fukushima reactors had their back up diesel generators at ground level, hence a few feet above sea level, and their spent fuel pools on the “top deck” of the reactor buildings, the equivalent of 3-4 stories up. When the earthquake knocked out the electric power required to circulate absolutely essential liquid coolant the diesel generators kicked in as designed. So far so good.
But then the diesel generators were wiped out 55 minutes later by the tsunami (duh!, the Fukushima nuclear power complex is right on the coast – didn’t the “experts” think of that?). The resulting lack of circulating water has precipitated this crisis that is now on the verge of being an unprecedented catastrophe. A spent fuel rod fire can release far more radioactivity than Chernobyl (see below).
The pathetic irony is that to prevent this catastrophe Tokyo Electric MUST get circulating water UP to the spent fuel rod pools because the diesel generators were swamped DOWN below. The placement of the generators and the waste pools relative to each other was exactly and tragically back *sswards. Do not trust “EXPERTS!,” meaning that citizen activism is always required. IT IS A MUST!
I shun hysteria, but this situation is way serious, it could really get out of control. Pray for the Japanese people, already the victims of history’s only two (so far) atomic attacks. If the fuel rods go count this as the 3rd attack, albeit self-inflicted. Nuclear operations require perfect human operation 24/7/eternity (i.e., as long as we run them). Humans are fallible, and nature can shrug us off like flies.
Get rid of nukes, period (except medicine). It takes only once on the balance sheet to wipe out any potential benefits, and indebt seven future generations environmentally, economically, politically and genetically all at the same time. It’s NOT worth it.
To end on a cheery note (not!): “As flies to wanton boys, are we to the gods. They kill us for their sport.” Shakespeare’s King Lear, 4. 1. The gods may do what they want, but don’t let international corporate nuclear power interests kill us. Fight back!
Mother Earth Gives Nuclear Renaissance a Black Eye
Our hearts and prayers go out go out to the people of Japan.
As Japan is faced with the possibility of nuclear meltdowns in five earthquake-damaged nuclear reactors, the U.S. and other countries are re-considering nuclear plans. While it is unlikely that radiation that has leaked or will leak from the Japanese reactor accidents will reach the United States. This could change if there is an explosion and/or fire affecting one or more of the reactor cores or spent fuel pools. The accident at Chernobyl (25th anniversary is April 26th) affected the entire Northern Hemisphere because of a massive explosion in the core, and an out-of-control fire that burned for days. This same scenario is unlikely in Japan. But reactors have been damaged beyond repair and old questions are being raised again.
In the U.S., Sen. Joe Lieberman (I-Conn.) and Democratic Rep. Ed Markey of Massachusetts have made statements – “But I think we’ve got to kind of quietly put, quickly put, the brakes on until we can absorb what has happened in Japan as a result of the earthquake and the tsunami and then see what more, if anything, we can demand of the new power plants that are coming on line,” Lieberman stated. “Any plant that is being considered for a seismically vulnerable area in the United States should be reconsidered right now,” Markey said, adding that the Japanese earthquake registering 8.9 in magnitude was “a hundred times greater in intensity” than the level that U.S. plants are built to withstand.
Countries in Europe are pausing to re-consider, also. Japan’s nuclear emergency Monday prompted Germany and Switzerland to halt nuclear programmes as anxious Europe scrambled to review cross-border safety while safeguarding the powerful industry. More
Why were the Fukushima reactors at sea level? Japan’s nuclear accident exposes the dilemma of whether to build power plants on tsunami-prone coasts or inland sites where water supplies are unreliable, a problem likely to be aggravated by climate change, experts say. (More from Reuters)
What happened at the Fukushima plant? “Three of its six reactors were in operation when the earthquake hit. The reactors — which went into service between 1970 and 1979 — are designed to shut down automatically when a quake strikes, and emergency diesel generators began the task of pumping water around the reactors to cool them down. However, these stopped about an hour later. The failure of the back-up generators has been blamed on tsunami flooding by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).” More –
This event shows how Mother Earth can have her way with the best-made plans. The power company said that that 7.9 was the highest magnitude for which they tested the safety for their No. 1 and No. 2 nuclear power plants in Fukushima. The original magnitude was estimated to be 8.9, which would have been 10 ten times the magnitude 7.9 that the structures were tested for. The Japan Meteorological Agency up-rated Friday’s earthquake to 9.0 on the Richter scale, meaning that it was twice as powerful as initially thought. More
Here at home, we have no commercial reactors in New Mexico, but there are national nuclear weapons facilities, including Los Alamos National Laboratory, which currently has plans for a $5 billion addition to the Lab’s plutonium weapons production complex. This addition, called the Chemistry and Metallurgy Research Replacement project Nuclear Facility (CMRR-NF) is being designed to survive a 7.0 magnitude earthquake without releasing plutonium. Much of the estimated cost is to seismically qualify the CMRR-NF to be built on the fault-ridden Pajarito Plateau. The plans call for a storage vault with the capacity of six metric tons of radioactive materials, such as plutonium.
Now would be a good time to re-consider any plans that make us feel invincible.
CMRR FY2012 Budget Request – Blank Check or Black Budget?
CMRR FY2012 Budget Request – Blank Check or Black Budget?
The FY2012 budget request shows $300 million for the Chemistry and Metallurgy Research Replacement (CMRR) Project, which is now estimated to cost a total of $6.22 billion. $29.9 million is requested for equipment in the recently completed first building, the Radiological Laboratory/Utility/Office Building (RLUOB). But exactly how will the remaining $270 million be spent? That’s literally “TBD” (To Be Determined). What a great deal – receive $270 million and then decide what to do with it. How lucky the Lab must feel to get a blank check in this era of fiscal restraint.
Is the Lab planning to use some of the $270 million to begin construction of the huge “Nuclear Facility”? Because there is a Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) now underway for the NF, any construction funding now could prejudice any decision, or at least would smell like prejudice. A more likely scenario is that the Lab figures that it might be able to stash funds away in some black budget to use on construction later, in effect creating a slush fund that would insulate it from and possible future budget cuts.
Perhaps going back to last year will offer some clues. The FY2011 Congressional Budget Request projected that LANL would ask for a total of $322.1 million for FY2012.
The FY2011 breakout estimated for FY2012 was:
$29.9 million RLUOB Equipment Installation (REI) [This turned out to be exactly the amount requested for FY2012.]
$3 million for Other Project Costs (OPC) [This turned out to be “TBD” for FY 2012.]
$102.8 million for NF design [This turned out to be “TBD” for FY 2012. Not counting any FY2012 funding, $419 million has been spent to date on design of the NF.]
$186.4 million for NF construction [FY2012 was to be the first year that construction funds were to be requested for the NF. This turned out to be “TBD” for FY 2012. But it really should be “0” because there is a SEIS underway.]
If all of the $270 million requested for FY2012 is not for NF design, we deserve to know what it’s for.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.