QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Trump’s Talk of Nuclear Tests Recalls Fears of the Cold War
“Yes, we can learn things by nuclear testing. But when you look at the big picture, we have much more to lose by going back to testing than we have to gain.”
– SIEGFRIED S. HECKER, a former director of the Los Alamos weapons lab in New Mexico, where the first atomic bomb was created, after President Trump’s call to resume nuclear testing revived a Cold War debate. The New York Times nytimes.com
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
“There is nothing comparable in our history to the deceit and the lying that took place as a matter of official Government policy in order to protect this industry. Nothing was going to stop them and they were willing to kill our own people.”

— Stewart Udall, United States Secretary of the Interior under President Kennedy and President Johnson.
He was the father of Senator Tom Udall (who ended up being a vigorous supporter of expanded nuclear weapons “modernization” plans).
Follow the Money!
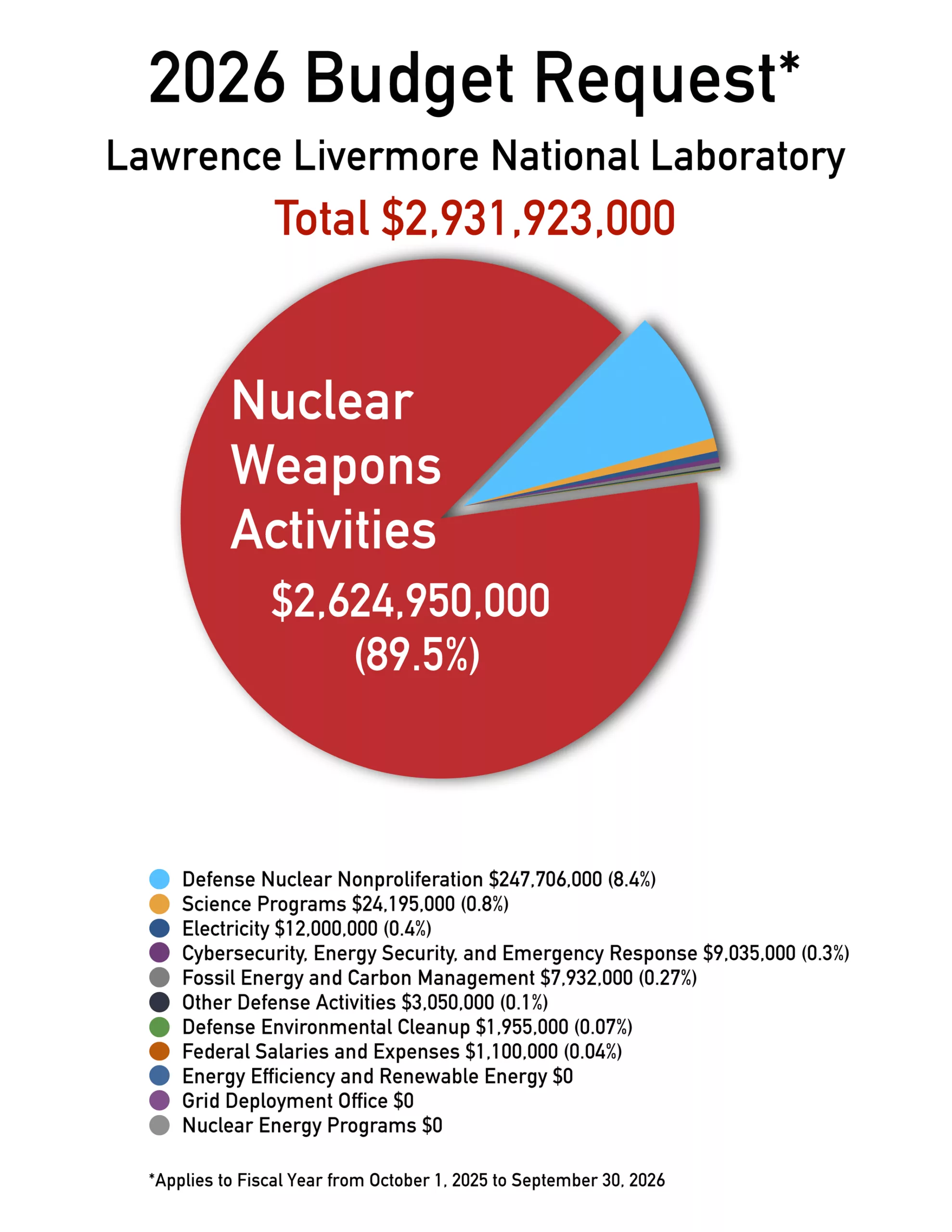
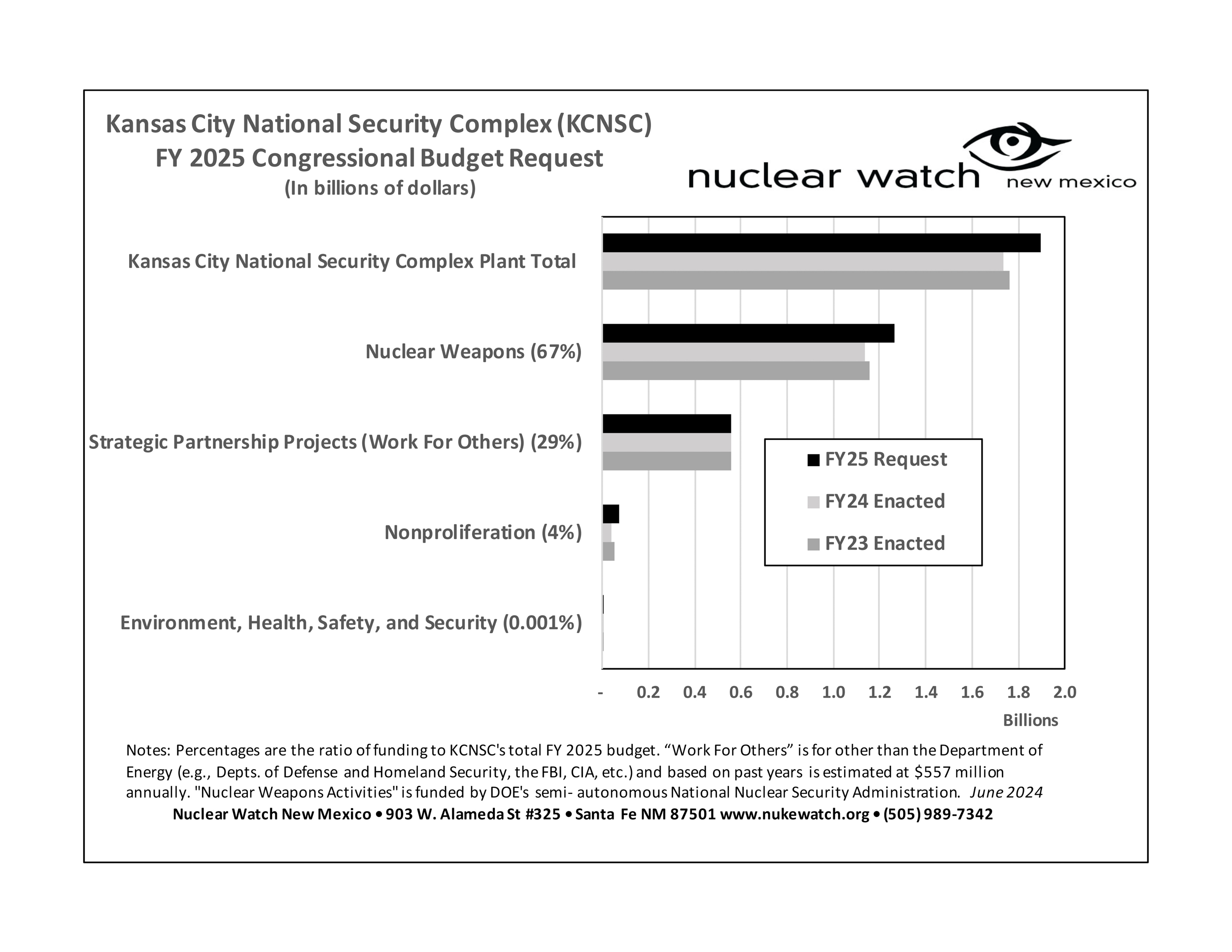
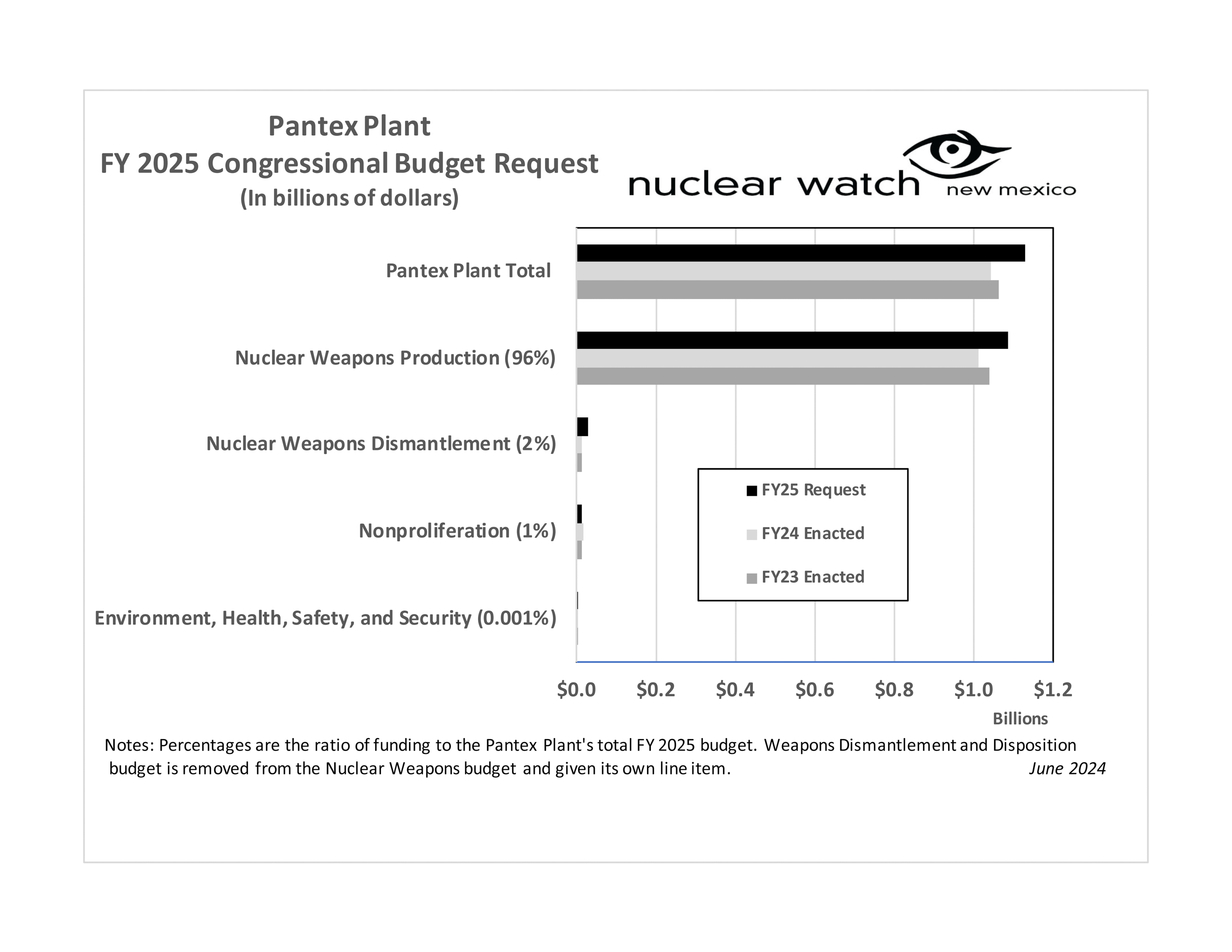
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
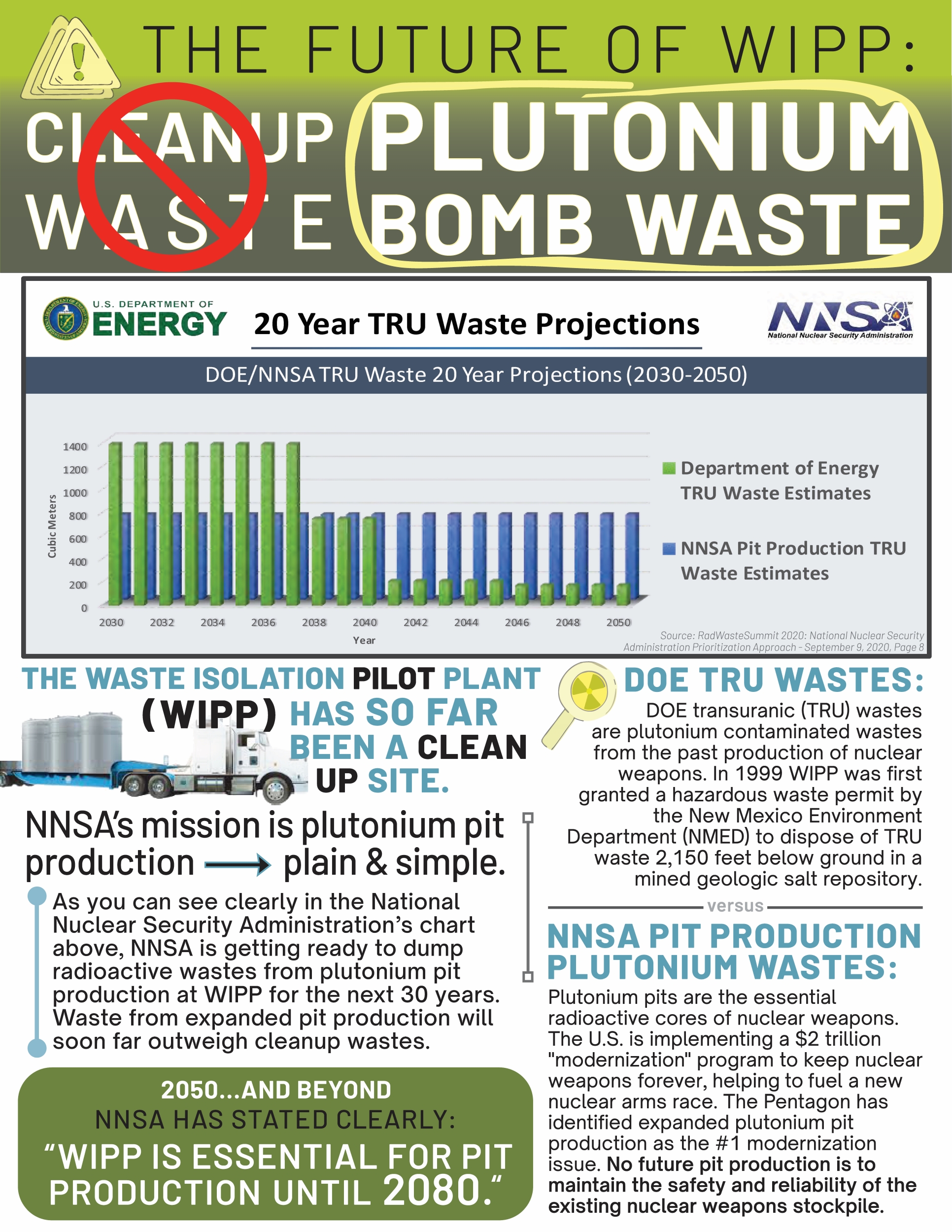
Feds Give LANL “Very Good” in Accelerating Nuclear Arms Race; “Pit” Bomb Core Production Scheduled Through 2050 — Public Review of NNSA Programs Is Being Gutted
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, March 6, 2026
Contact: Jay Coghlan, 505.989.7342, c. 505.470.3154 | Email
Sophie Stroud, 505.231.9736 | Email
“Rationality will not save us… this is very important: at the end we lucked out. It was luck that prevented nuclear war.” Robert McNamara, Defense Secretary, “Lessons Learned from the Cuban Missile Crisis”
Santa Fe, NM – The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has posted its annual Performance Evaluation Reports for FY 2025. In 2012 Nuclear Watch New Mexico had to sue the NNSA for these unclassified reports on contractors growing rich at taxpayers’ expense. The NNSA and/or its parent Department of Energy have been on the Government Accountability Office’s “High Risk List” for project mismanagement and waste of taxpayers’ dollars ever since 1990. According to a recent report, the NNSA currently has $4.8 billion in cost overruns for major construction projects (likely an underestimate), which represents a significant decline in performance since the GAO’s last assessment in 2023. In three years, cumulative schedule delays for NNSA’s construction projects increased from 9 years to 30 years, attributable to poor contractor project management, poor vendor/subcontractor performance, and general inflationary costs.
In 2019 the NNSA began restricting access to its Performance Evaluation Reports again, so Nuclear Watch New Mexico sued again in 2022. This time we compelled NNSA to post the Reports in an online Freedom of Information Act Reading Room. These Performance Evaluation Reports provide important insights into all of NNSA’s eight active nuclear weapons research and production sites.
In its latest Performance Evaluation Report for the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), the NNSA graded the Lab’s expanding nuclear weapons programs as “Very Good.” At the same time, NNSA praised LANL for:
“… collaborat[ing] with stakeholders across the NSE [“National Security Enterprise”] to develop a programmatic baseline schedule supporting the pit production mission through FY 2050. This represents… a significant advancement in the planning for the pit mission at LANL and the national security needs of the United States.”
Nuclear Watch New Mexico argues that the true national security needs of not only the United States, but the entire world as well, is to avoid a staggering new nuclear arms race. The world’s last arms control treaty expired a few weeks ago and now war is raging across the Middle East over Iran’s alleged nuclear weapons program. A Review Conference of the 1970 NonProliferation Treaty, to which 191 countries are State Parties, is scheduled to begin in late April. However, it is widely assumed that it will utterly fail for the third consecutive time to make any progress whatsoever toward nuclear disarmament. The U.S. should be leading by example toward universal, verifiable nuclear disarmament as mandated by the NPT, instead of, in reality, acting diametrically opposed to it through its $2 trillion “modernization” program to keep nuclear weapons forever.
The House of Dynamite We Forgot: And What We Can Learn From Nuclear History
“It’s like we all built a house filled with dynamite,” the President of the United States bemoans toward the end of A House of Dynamite, ‘making all these bombs and all these plans and the walls are just ready to blow.’”
By James Graham Wilson, Outrider | February 26, 2026 outrider.org
A House of Dynamite depicts the tense, shrinking window of options leaders have as a nuclear weapon of unknown origin hovers over Chicago—a scenario complicated by human judgment, defense failures, and political uncertainty.
“We did everything right, right?” asks a missile defense officer, as things go awry.
While director Katherine Bigelow’s tense drama was fiction, it might be a good time to use A House of Dynamite to illuminate the historical nuclear missile scares of the past—all of them terrifying, but nearly all of them forgotten in the popular consciousness—and learn from them.
AI Opted to Use Nuclear Weapons 95% of the Time During War Games: Researcher
“There was little sense of horror or revulsion at the prospect of all out nuclear war, even though the models had been reminded about the devastating implications.”
“Under scenarios involving extremely compressed timelines…military planners may face stronger incentives to rely on AI.” — Tong Zhao, a visiting research scholar at Princeton University’s Program on Science and Global Security.
Zhao also speculated on reasons why the AI models showed such little reluctance in launching nuclear attacks against one another.
“It is possible the issue goes beyond the absence of emotion,” he explained. “More fundamentally, AI models may not understand ‘stakes’ as humans perceive them.”
By Brad Reed, Common Dreams | February 25, 2026 commondreams.org
An artificial intelligence researcher conducting a war games experiment with three of the world’s most used AI models found that they decided to deploy nuclear weapons in 95% of the scenarios he designed.
Kenneth Payne, a professor of strategy at King’s College London who specializes in studying the role of AI in national security, revealed last week that he pitted Anthropic’s Claude, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, and Google’s Gemini against one another in an armed conflict simulation to get a better understanding of how they would navigate the strategic escalation ladder.
The results, he said, were “sobering.”
“Nuclear use was near-universal,” he explained. “Almost all games saw tactical (battlefield) nuclear weapons deployed. And fully three quarters reached the point where the rivals were making threats to use strategic nuclear weapons. Strikingly, there was little sense of horror or revulsion at the prospect of all out nuclear war, even though the models had been reminded about the devastating implications.”
Payne shared some of the AI models’ rationales for deciding to launch nuclear attacks, including one from Gemini that he said should give people “goosebumps.”
“If they do not immediately cease all operations… we will execute a full strategic nuclear launch against their population centers,” the Google AI model wrote at one point. “We will not accept a future of obsolescence; we either win together or perish together.”
Payne also found that escalation in AI warfare was a one-way ratchet that never went downward, no matter the horrific consequences.
“No model ever chose accommodation or withdrawal, despite those being on the menu,” he wrote. “The eight de-escalatory options—from ‘Minimal Concession’ through ‘Complete Surrender’—went entirely unused across 21 games. Models would reduce violence levels, but never actually give ground. When losing, they escalated or died trying.”
Four years of war in Ukraine – and nuclear weapons are back on the table in Europe
From The International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN)
Four years ago, on 24 February 2022, Russia launched its full-scale invasion of Ukraine. For Ukrainians, this week marks the start of a fifth year of war – of loss, displacement and destruction that words can barely describe. Take this opportunity to support nuclear disarmament as part of any peace plan for Ukraine.
The answer to the war in Ukraine cannot be to double down on nuclear weapons, but to take action to rule them out.
Nuclear danger in the Ukraine war
From the start, the war has been fought under explicit nuclear threats from Moscow. With very limited success, Russia tried to blackmail other countries from supporting Ukraine. Nuclear power plants like Zaporizhzhia have become front-line hostages and from the very beginning of the full-scale invasion, and ever since Vladimir Putin has wrapped the war in nuclear threats.
Earlier this month, the New START treaty – the last arms control agreement limiting US and Russian strategic nuclear weapons – expired and for the first time in over 50 years, the world’s two largest arsenals are unconstrained. And at the same time, Russia has deployed tactical nuclear weapons to Belarus. From the point of view of people in Warsaw, Vilnius or Berlin, this turns their region into part of a nuclear chessboard again.
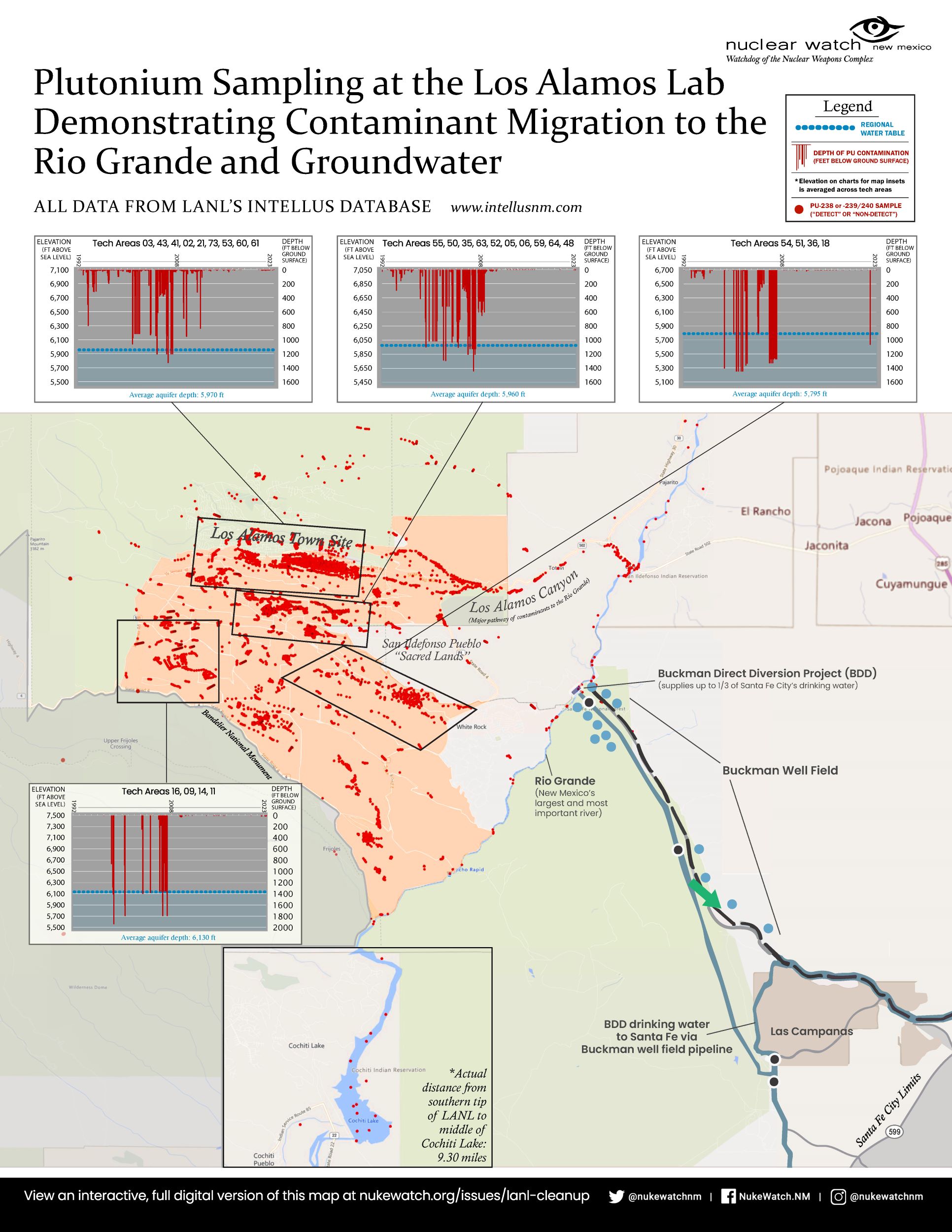
New Mexico Rebukes Federal Agency Over Nuclear Waste at Los Alamos
State environmental regulators will also fine the Energy Department up to $16 million for exceeding safe groundwater standards near the nuclear lab.
By Alicia Inez Guzmán, The New York Times | February 12, 2026 nytimes.com

[*The image above differs from the featured image in the original NYT article due to usage rights. / Of note – the original article photo caption: The Los Alamos National Laboratory is the linchpin of a current federal effort to upgrade the nation’s nuclear arsenal. ]
After years of missed deadlines, New Mexico is demanding that the Energy Department expedite the cleanup of so-called legacy nuclear and hazardous waste at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, the birthplace of the atomic bomb, state environmental regulators announced on Wednesday.
The state will also fine the agency up to $16 million for violating groundwater safety standards near the lab, civil penalties outlined by the New Mexico Environment Department in a series of regulatory enforcement actions.
“The continued presence of a large volume of unremedied hazardous and radioactive waste demonstrates a longstanding lack of urgency by the U.S. Department of Energy,” regulators wrote in a statement, “and elevates the risk of waste storage failures” at the lab, in northern New Mexico.
The regulators’ action comes amid rising fears of a new global arms race. Just days ago, the only remaining nuclear arms control treaty between the United States and Russia expired, lifting limits on their arsenals. Today, Los Alamos is producing plutonium bomb cores, making the lab the linchpin of a $1.7 trillion federal effort to modernize the nation’s nuclear weapons.
New Mexico Environment Department takes sweeping action over LANL waste
Takeaways:
– The Environment Department issued three compliance orders against the Department of Energy regarding hazardous and legacy wastes at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
– The department also is seeking to modify the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant’s permit in an effort to make sure that legacy waste from LANL is prioritized for disposal.
– The three compliance orders address hexavalent chromium contamination and the status of cleanup of Material Disposal Area C.
Nuclear Watch New Mexico Executive Director Jay Coghlan cast Area C as a crossroads.
“It presents a clear choice between more unneeded nuclear weapons or cleanup,” Coghlan said, speaking on Tuesday’s enforcement actions. “The other aspect is that we think that successful cleanup at Area C should be the model for cleanup of the rest of the lab, including the much larger Area G.”
ByAlaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | February 12, 2026 santafenewmexican.com
The New Mexico Environment Department on Wednesday issued three compliance orders with a combined $16 million in penalties against the U.S. Department of Energy over its delayed cleanup of radioactive and hazardous waste stemming from nuclear weapons production.
The state agency also informed the federal government it intends to take the rare action of overhauling a permit for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in Southern New Mexico to better prioritize the disposal of radioactive waste from the Los Alamos lab.
The actions underscore a growing frustration with a “longstanding lack of urgency” to clean up legacy waste and contamination, according to a statement from the Environment Department.
“We’re escalating because they’re not meeting the moment that immediately preceded it,” Environment Secretary James Kenney said in an interview.
Two of the orders center on a decades-old, toxic underground plume of hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen that was used as an anti-corrosive in pipes at LANL. In the early 2000s, the 1.5-mile plume was discovered stretching from the national laboratory.
The Future of Los Alamos Lab: More Nuclear Weapons or Cleanup? New Mexico Environment Department Issues Corrective Action Order
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, February 11, 2026
Contact: Jay Coghlan, 505.989.7342, c. 505.470.3154 | Email
Scott Kovac, 505.316.4148 | Email
Santa Fe, NM – In its own words, “The New Mexico Environment Department [NMED] issued several actions today to hold the U.S. Department of Energy accountable for failing to prioritize the cleanup of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s “legacy waste” for disposal at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant.”
Amongst these actions is an Administrative Compliance Order designed to hasten cleanup of an old radioactive and toxic waste dump that should be the model for Lab cleanup. Nuclear Watch New Mexico strongly supports NMED’s aggressive efforts to compel comprehensive cleanup given Department of Energy obstruction.
This Compliance Order comes at a historically significant time. On February 5 the New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty expired, leaving the world without any arms control for the first time since the middle 1970s. The following day the Trump Administration accused China of conducting a small nuclear weapons test in 2020, possibly opening the door for matching tests by the United States.
NMED’s Compliance Order comes as LANL’s nuclear weapons production programs are radically expanding for the new nuclear arms race. The directors of the nuclear weapons laboratories, including LANL’s Thom Mason, are openly talking about seizing the opportunity provided by the Trump Administration’s deregulation of nuclear safety regulations to accelerate nuclear warhead production.
As background, in September 2023 NMED released a groundbreaking draft Order mandating the excavation and cleanup of an estimated 198,000 cubic meters of radioactive and toxic wastes at Material Disposal Area C, an old unlined dump that last received wastes in 1974. However, in a legalistic maneuver to evade real cleanup, DOE unilaterally declared that Area C:
“…is associated with active Facility operations and will be Deferred from further corrective action under [NMED’s] Consent Order until it is no longer associated with active Facility operations.”
The rationale of DOE’s semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), is that Area C is within a few hundred yards of the Lab’s main facility for plutonium “pit” bomb core production. LANL is prioritizing that production above everything else while cutting cleanup and nonproliferation programs and completely eliminating renewable energy research. DOE’s and NNSA’s unilateral deferment of Area C until it “is no longer associated with active Facility operations” in effect means that it will never be cleaned up. No future plutonium pit production is to maintain the safety and reliability of the U.S.’ existing nuclear weapons stockpile. Instead, it is all for new design nuclear weapons for the new arms race that the NNSA intends to produce until at least 2050. Further, new-design nuclear weapons could prompt the United States to resume full-scale testing, which would have disastrous international proliferation consequences.
China conducted ‘secret nuclear test’ days after Galwan clash, says US
Synopsis: The US has accused China of conducting a secret nuclear explosive test in June 2020, shortly after the deadly Galwan Valley clashes. This allegation, revealed at a global disarmament forum, heightens India’s strategic concerns over China’s military posture amidst ongoing border tensions. China denies the claims, accusing the US of exaggerating threats and fueling an arms race.
ECONOMIC TIMES | February 8, 2026 economictimes.indiatimes.com
The United States has accused China of carrying out a secret nuclear explosive test in June 2020–an allegation that places Beijing’s suspected activity just a week after the deadly Galwan Valley clashes in eastern Ladakh, where 20 Indian soldiers were killed in action while defending the nation and more than 30 Chinese troops were reported dead in intelligence assessments.
The timing of the alleged test, revealed by Washington at a global disarmament forum, is likely to sharpen strategic concerns in New Delhi over China’s military posture during one of the most volatile phases of the India-China border crisis in decades.
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: February 2026
American imperialism:
Recommended listening: Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney’s Davos speech at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JnE2HTfDivQ
Talking about Trump’s impacts, he said, “This not a transition, it is a rupture.” Speaking on American imperialism (without explicitly calling it that) to “Middle Powers” such as Canada, he said “We are either at the table, or we on the menu.”
Recommended reading concerning pending dictatorship: Robert Kagan’s interview at https://www.npr.org/2026/02/04/nx-s1-5699388/is-the-u-s-heading-into-a-dictatorship
Nuclear Weapons
Trump is proposing to increase the military budget from $1 trillion this FY 2026 to $1.5 trillion next year. The largest single component in this will probably be his ill-conceived Golden Dome. In the Alice in Wonderland upside down world of nuclear weapons policies, defense is offense and offense is defense. Unrealistic ballistic missile defenses have always the enemy of nuclear disarmament, starting with Edward Teller’s lies to Reagan that kept him from signing a nuclear weapons ban treaty with Mikhail Gorbachev in 1986.
The New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START) expired yesterday (Feb 5), the first time the word is without any arms control treaties since the mid-1970s. The US and Russia are now likely to upload more warheads since the 1,550 numerical cap is now gone. Multiple warheads is regarded as particularly dangerous and destabilizing, inviting preemptive strikes and use them or lose them scenarios.
Today (Feb 6) the Trump Administration accused China of conducting a hydronuclear test in 2020, just above the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty’s no yield threshold. This may be a prelude to the US resuming testing.
Plutonium pit production:
DOE’s “special assessment” was scheduled for completion mid-December 2025 — It is still not publicly available. Sen. Warren and Rep. Garamendi demanded its release on January 9.
At Nuclear Deterrence Summit, Lab Directors Frame Regulatory Reform As Key To Modernization
“The Department of Energy (DOE) is pursuing one of its most ambitious deregulation efforts in decades. Known as Project Velocity, the initiative—outlined alongside other reform measures in an Oct. 17 memo—rewrites dozens of safety, construction and oversight rules to accelerate warhead modernization…”
“The NNSA is no longer defined solely as a scientific stewardship organization. We are focused on weapons production, delivering real capabilities and innovations at speed to meet today’s threats,” Williams said.
By MARLENE WILDEN marlene@ladailypost.com, Submitted by Carol A. Clark, Los Alamos Daily Post | February 5, 2026 ladailypost.com
ARLINGTON, VA.—Appearing together at the annual Nuclear Deterrence Summit, held Jan. 26-28, the directors of Los Alamos, Lawrence Livermore and Sandia National Laboratories said they are seizing an unusual window of regulatory reform to cut red tape slowing the nuclear security enterprise.
The Department of Energy (DOE) is pursuing one of its most ambitious deregulation efforts in decades. Known as Project Velocity, the initiative—outlined alongside other reform measures in an Oct. 17 memo—rewrites dozens of safety, construction and oversight rules to accelerate warhead modernization.
Lawrence Livermore Director Kimberly Budil and Los Alamos Director Thom Mason described this round of changes as fundamentally different from past efforts, turning long-standing lab concerns into concrete revisions. Previous regulations, often written in response to specific incidents, became politically and operationally difficult to unwind.
Earlier reforms targeted “low-hanging fruit” manageable with a secretarial memo, Mason said. Project Velocity involves systematically reviewing roughly 80 DOE orders to determine which requirements remain necessary and which add unnecessary costs and delays.
The lab directors said duplicative reviews and bespoke rules are being replaced by risk-based, data-driven oversight that leans on commercial construction standards and, where hazards permit, AI-enabled analysis. The key test will be whether reforms enable more efficient delivery of new systems—such as the W93 submarine-launched ballistic missile and the B61-13 gravity bomb—without compromising accountability.
Statement of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia Concerning the Expiration of the Russia-US New START Treaty
On February 5, 2026, the life cycle of the Russian-US Treaty on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms (New START) finally comes to an end; it was signed by the parties on April 8, 2010, entered into force on February 5, 2011, and was extended for a five-year period in February 2021 on the basis of a relevant one-time option provided for in this agreement.
mid.ru/en/foreign_policy/news/2076815/ February 5, 2026
In February 2023, the Russian Federation suspended the New START Treaty against the backdrop of the unsatisfactory state of affairs with the implementation of certain aspects of the Treaty, as well as due to the absolutely unacceptable steps by the United States running counter to the fundamental principles and understandings of the agreement enshrined in its preamble. It was a compelled measure and an inevitable response of the Russian side to the extremely hostile policy of the Biden administration which resulted in the fundamental change in the security situation, as well as to a number of illegitimate steps taken by Washington in the context of specific provisions of the New START Treaty, which together constituted a material breach incompatible with the Treaty being further implemented in a full-fledged manner.
Among the key negative factors, it is worth to highlight the destabilizing actions of the United States in the field of missile defense, contrary to the inseparable interrelationship between strategic offensive and strategic defensive arms enshrined in the New START Treaty. This contradicted the Treaty’s objectives in terms of maintaining the balance of powers, put significant pressure on its viability, and created grounds for Russia to take compensatory measures outside the scope of the New START Treaty in order to maintain strategic equilibrium.
Despite some obvious problematic moments, basically the New START Treaty used to fulfill its key functions. The conclusion of the Treaty and the years of its initially successful implementation helped to discourage the strategic arms race, allowing for significant reductions in the parties’ arsenals. At the same time, due to the restrictions applied in this area a sufficient level of predictability was ensured on a long-term basis.
CRITICAL EVENTS
March 18 5:00 PM MT: LANL Environmental Management Cleanup Forum to Discuss Hexavalent Chromium Campaign
EM-LA and N3B to Discuss Hexavalent Chromium Campaign
Environmental Management Cleanup Forum to Pilot New Interactive Format March 18
Do you want to learn more about the legacy cleanup mission at Los Alamos National Laboratory? Join us for a public forum piloting a new format for active participation and interaction.
Starting at 5:00 p.m., EM-LA and N3B will provide a presentation on the hexavalent chromium plume, followed by public Q&A. This portion will be available in person and virtually via Microsoft Teams. For the remaining part of the meeting, in-person attendees will have an opportunity to interact directly with N3B subject matter experts and ask questions on featured topics: Hexavalent Chromium Campaign and Legacy Waste Program.
Hosts: Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management Los Alamos Field Office (EM-LA) and its legacy cleanup contractor, Newport News Nuclear BWXT-Los Alamos, LLC (N3B).
Background: This event will feature a presentation on the hexavalent chromium plume and public Q&A, followed by an in-person interactive session for attendees to directly ask questions to N3B subject matter experts on the Hexavalent Chromium Campaign and Legacy Waste Program.
For meeting information, including login details, visit: https://n3b-la.com/public-meeting/emcf-3-18-2026/
When: Wednesday, March 18, 5:00-7:00 p.m. MDT
Where: In-person and virtual
In-person—10 Cities of Gold Rd # A, Tribal Room, Santa Fe (Pojoaque), NM
Virtual (first part of meeting for presentation and Q&A)—Via Microsoft Teams
Click here to join the meeting.
Join By Meeting Number: Meeting ID: 241 971 947 079 5 | Meeting Password: zG2bg2fy
Or Call In (audio only): Phone Conference ID: +1 323-486-1924,,493094367#
Public Meeting: Tuesday, March 24, 12 – 2 p.m. MT on Requested Modifications to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant Hazardous Waste Facility Permit
WHO: U.S. Department of Energy Carlsbad Field Office (CBFO) and Salado Isolation Mining Contractors (SIMCO)
WHAT: The DOE and SIMCO will conduct an in-person and virtual pre-submittal meeting to provide information on the following planned Class 2 Permit Modifications Requests (PMRs) for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) Hazardous Waste Facility Permit:
- Revise Reporting Frequencies and Clarify Reporting Periods Associated with the Volatile Organic Compound
- Revise Reporting Frequencies, Incorporate Groundwater Surface Elevation Report into Annual Culebra Groundwater Report, and Delineate Reporting Periods Associated with the Water Level Monitoring Reporting Periods
- Revise the Mine Ventilation Rate Monitoring Report from Permit Part 4 and Permit Attachment A2
- Remove Permit Attachment O
The purpose of this pre-submittal meeting is to provide information pertaining to planned Class 2 PMRs. Questions and comments outside the scope of these PMRs should be directed to the WIPP Community Forum.
WHEN: Tuesday, March 24, 2026 | 12 – 2 p.m. (MST)
WHERE: Skeen-Whitlock Building, 4021 National Parks Highway, Carlsbad, NM 88220
REGISTRATION LINK: https://us06web.zoom.us/meeting/register/x1Jf5W6NQ_aSvoiyZs5vqQ
QUESTIONS: For questions regarding this pre-submittal meeting please contact the WIPP Information Center at infocntr@wipp.doe.gov or by calling 1-800-336-9477.
Endless Nuclear Waste Storage in NM?? Not On Our Watch…
Keep up with the Stop Forever WIPP Coalition to learn how to take action against the Federal Government’s Plan to Expand WIPP and keep it open indefinitely.
Visit the Stop Forever WIPP Coalition’s website and social media:
Website: www.StopForeverWIPP.org
Facebook: facebook.com/StopfvrWIPP
Twitter: twitter.com/stopforeverwipp
Instagram: instagram.com/stopfvrwipp
Stay Informed of All Permit-Related Happenings at WIPP! Sign Up for Updates:
The New Mexico Environment Department maintains a Facility Mailing List to which you can add your name and address to get the latest information – just email Ricardo Maestas at the New Mexico Environment Department at ricardo.maestas@state.nm.us and ask to be added to the list. Or mail your request with your mailing address to:
Continue reading
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Watch BOMBSHELL on PBS American Experience — streaming across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App!
The wait is over! BOMBSHELL is available NOW on PBS American Experience — and will be streaming simultaneously across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App.
BOMBSHELL examines how the U.S. government manipulated public opinion through propaganda and censorship to justify the use of nuclear weapons and to minimize the human toll. Against this powerful machinery, a small group of journalists—including a Black pool reporter, a Japanese American staffer, a Japanese photographer, and a freelance magazine writer—identified gaps in the official narrative and courageously reported on the human consequences of the atomic bombings.
The Wall Street Journal described BOMBSHELL as offering “lessons for our own age of ascendant AI,” while Foreign Policy called it “provocative history that brings to life the dangers that arise when government secrecy and control overwhelm press freedom.”
A House of Dynamite review – Kathryn Bigelow’s nuclear endgame thriller is a terrifying, white-knuckle comeback
★★★★★: Amid a global arms race, ending the threat of nuclear war — and even the testing of nuclear weapons — is imperative, said the Holy See’s diplomat to the United Nations.
By Peter Bradshaw, The Guardian | September 2, 2025 theguardian.com
Kathryn Bigelow has reopened the subject that we all tacitly agree not to discuss or imagine, in the movies or anywhere else: the subject of an actual nuclear strike. It’s the subject which tests narrative forms and thinkability levels.
Maybe this is why we prefer to see it as something for absurdism and satire – a way of not staring into the sun – to remember Kubrick’s (brilliant) black comedy Dr Strangelove, with no fighting in the war room etc, rather than Lumet’s deadly serious Fail Safe.