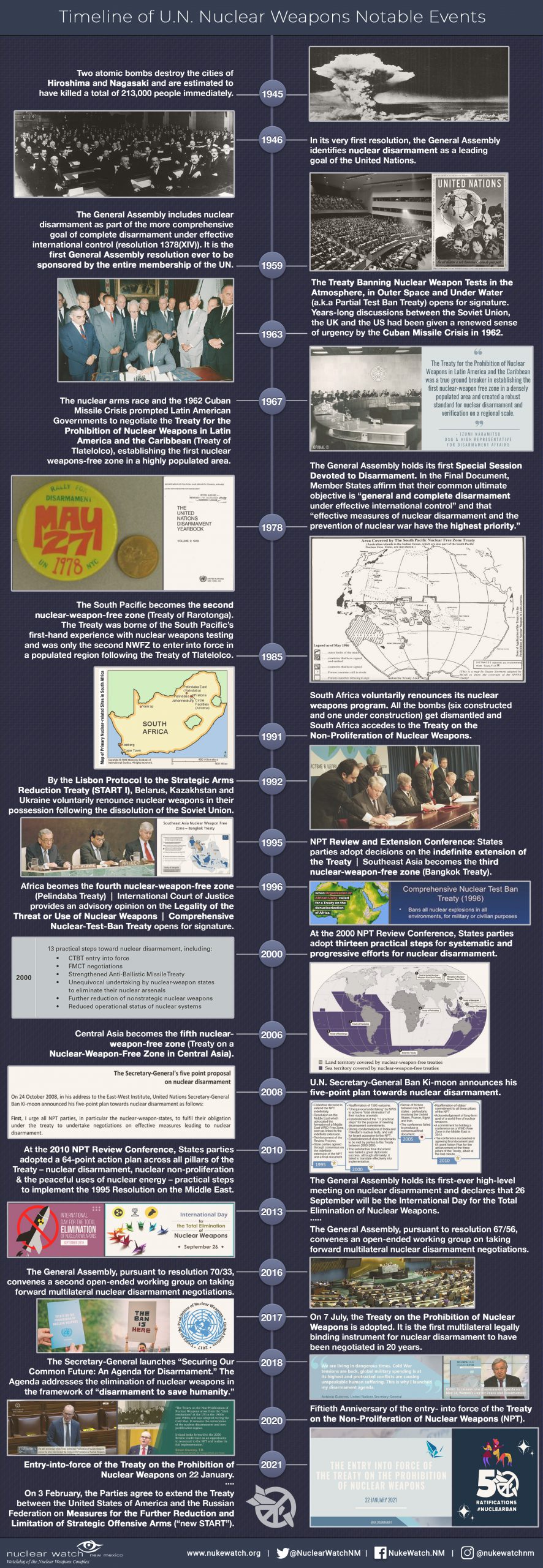
Recent News
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Abolishing Nuclear Weapons is a Moral Imperative
View Recording of the March 9th PDA CNM Community Gathering:
PDA CNM welcomed Archbishop John C. Wester, Archbishop of Santa Fe, and our own executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, Jay Coghlan, to speak at their March 9, 2022 monthly gathering: “[Archbishop Wester's] courage in speaking out against the proliferation of nuclear weapons inspires us at PDACNM to follow his example and continue the fight against this peril, especially given the threat of a possible imminent war between two nuclear powers.
Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, has worked successfully against radioactive incineration at the Los Alamos National Lab, and in Clean Air Act, Freedom of Information Act and National Environmental Policy Act lawsuits against the Department of Energy. He prompted a 2006 independent study that concluded plutonium pits last at least a century, refuting the NNSA’s assertion that we “need” new-design nuclear weapons and expanded plutonium pit production.”
The Nuclear Ban Treaty
Overview
The U.N. Treaty
on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
On 7 July 2017 – following a decade of advocacy by ICAN and its partners – an overwhelming majority of the world’s nations adopted a landmark global agreement to ban nuclear weapons, known officially as the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons. It will enter into legal force once 50 nations have signed and ratified it.
Prior to the treaty’s adoption, nuclear weapons were the only weapons of mass destruction not subject to a comprehensive ban, despite their catastrophic, widespread and persistent humanitarian and environmental consequences. The new agreement fills a significant gap in international law.
It prohibits nations from developing, testing, producing, manufacturing, transferring, possessing, stockpiling, using or threatening to use nuclear weapons, or allowing nuclear weapons to be stationed on their territory. It also prohibits them from assisting, encouraging or inducing anyone to engage in any of these activities.
Why a ban?
A nation that possesses nuclear weapons may join the treaty, so long as it agrees to destroy them in accordance with a legally binding, time-bound plan. Similarly, a nation that hosts another nation’s nuclear weapons on its territory may join, so long as it agrees to remove them by a specified deadline.Nations are obliged to provide assistance to all victims of the use and testing of nuclear weapons and to take measures for the remediation of contaminated environments. The preamble acknowledges the harm suffered as a result of nuclear weapons, including the disproportionate impact on women and girls, and on indigenous peoples around the world.
The treaty was negotiated at the United Nations headquarters in New York in March, June and July 2017, with the participation of more than 135 nations, as well as members of civil society. It opened for signature on 20 September 2017. It is permanent in nature and will be legally binding on those nations that join it.
Nuclear weapons are the most inhumane and indiscriminate weapons ever created. That is why it is time to end them, before they end us.
Nuclear weapons are the most inhumane and indiscriminate weapons ever created. They have catastrophic humanitarian and environmental consequences that span decades and cross generations; they breed fear and mistrust among nations, as some governments can threaten to wipe out entire cities in a heartbeat; the high cost of their production, maintenance and modernisation diverts public funds from health care, education, disaster relief and other vital services. Banning these immoral, inhumane weapons under international law was a critical step along the path to ending them.
With the adoption of the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) on July 7th, 2017, the world's majority took a critical step towards making that nuclear-weapon-free future a reality.
Nuclear Weapons Ban Treaty News & Updates
Nuclear-Weapon-Free States Demand Immediate End to Deterrence Policies, Start of Dismantling Atomic Arsenals, as First Committee Continues General Debate
Calling for swift remedies to mend a fractured non-proliferation landscape, nuclear-weapon-free States demanded an immediate end to deterrence policies and the start of dismantling atomic arsenals, as the First Committee (Disarmament and International Security) moved into the third day of its general debate.
UNITED NATIONS MEETINGS COVERAGE GENERAL ASSEMBLY FIRST COMMITTEE SEVENTY-SIXTH SESSION, 4TH MEETING (PM)
As thousands of atomic bombs located around the world pose grave risks to humanity, delegates implored nuclear-weapon States to steer the planet onto a path of peace. Some suggested such ways to do so, with delegates agreeing that dismantling nuclear arsenals must start now, in line with the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and under safeguards established by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Many urged all nations with atomic arsenals to sign, ratify and fully implement existing conventions, including the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, which entered into force in January, and some decried the quarter of a century delay in entering into force the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty. To rectify this, many called for nuclear-weapon States to sign and ratify it so that atomic bomb testing can become part of the past.
International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons 2021
Today, Sunday, September 26, 2021, marks the United Nations International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons. The United Nations has been working toward achieving global nuclear disarmament since the organization’s inception; it was the subject of the General Assembly’s first resolution in 1946, with a mandate to make specific proposals for the elimination of atomic weapons and all other major weapons adaptable to mass destruction. The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons has been observed annually since 2014, serving as a tool to enhance public awareness and education about the threat posed to humanity by nuclear weapons and the necessity for their total elimination. In 2013, the year the International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons was introduced, the President of the General Assembly noted that a “renewed international focus on the catastrophic consequences of nuclear weapons has led to a reinvigoration of international nuclear disarmament efforts.”
ILHAN OMAR SIGNS ICAN PLEDGE

April 30, 2021: Representative Ilhan Omar today submitted her signed ICAN Pledge to ICAN, becoming the eleventh member of the US Congress to sign the Pledge. Rep. Omar represents Minnesota’s 5th Congressional District in the US House of Representatives. Rep Omar also co-sponsor the H.R.2850 Nuclear Abolition and Economic Conversion Act of 2021 that Representative Eleanor Holmes Norton reintroduced on April 26, 2021.
Nuclear Weapons — They’re Illegal
“Remember that when your congressional members pitch expanding nuclear weapons production as jobs programs; you can respond that they are illegal. Tell them they should show visionary leadership and moral courage by helping to create cleanup and green energy jobs instead.”
By: Jay Coghlan / Santa Fe New Mexican

Jan. 22 will go down in history as the day when the tide turned against nuclear weapons. That was the day when the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons went into effect, signed by 122 countries.
It specifically prohibits nations from developing, testing, using or threatening to use nuclear weapons and assisting others in doing so. It reinforces existing international law obligating all states not to test, use or threaten to use nuclear weapons.
What immediate impact will it have here, given that the Los Alamos National Laboratory is the birthplace of nuclear weapons and now sole producer of plutonium pit triggers for the expanding U.S. stockpile? The brutally honest answer is no impact, not immediately.
But think about it. Nuclear weapons are now internationally illegal, just as horrendous chemical and biological weapons of mass destruction have long been. But nuclear weapons are the worst WMDs, potentially killing millions more while causing radioactive fallout and famine-inducing nuclear winter. Ask your New Mexican congressional members to explain why nuclear weapons shouldn’t be internationally banned just like chemical and biological WMDs, all of which cause agonizing, indiscriminate suffering and death.
ICAN IGTV
The international campaign to abolish nuclear weapons on instagram (@nuclearban) tackling some of the more technical legal questions of the treaty: what does entry into force mean, what happens now? Joined with experts, they dive into international law and the TPNW (without getting too technical!) through instagram chats to help break it all down.
View this post on InstagramTim Wright in conversation with Associate Professor Treasa Dunworth of the University of Auckland
A post shared by ICAN (@nuclearban) on
View this post on InstagramA post shared by ICAN (@nuclearban) on
View this post on InstagramA post shared by ICAN (@nuclearban) on
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Quotes
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
All Nuclear Arms Reduction and Non-Proliferation Updates & Recent News
Nuclear Weapons Have Always Been Immoral. Now They’re Illegal.
On 7 July 2017, the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) was adopted by the UN General Assembly. Just over three years later, the TPNW reached the 50 national ratifications needed to become international law. The treaty will enter into force on January 22, 2012, and nuclear weapons will become officially illegal under international law. This day will represent a culmination of years of campaigning for nuclear weapons to be reframed as a collective humanitarian problem, one which requires prohibition and elimination, rather than a national military defense asset that needs to be managed and even upgraded.
Nuclear Disarmament tops UN agenda
3 Oct 2020 – The United Nations General Assembly holds a high-level meeting to commemorate the International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons. Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, many leaders speak by pre-recorded video to call for a nuclear-weapon-free world.
Nuclear Ban Pact Should Not Erode Validity of NPT: Confab Chief
Noting that the current international security environment “is not very positive,” [Gustavo Zlauvinen, President-designate of the 2020 Review Conference for the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT)] said a lack of progress on nuclear disarmament will likely “play a big role, unfortunately” at the forthcoming NPT review conference.
By: KYODO NEWS | kyodonews.com

Questioning the effectiveness of a U.N.-adopted nuclear ban treaty, which involves no nuclear powers, the president-designate of an upcoming nonproliferation conference has stressed that the pact should not be allowed to undermine the legitimacy of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
“You can’t have nuclear disarmament without the nuclear weapon states in that system. And that’s why, for the time being, the only treaty that has been accepted by at least five nuclear weapon states, that includes obligations on nuclear disarmament, is the NPT,” Gustavo Zlauvinen said in a recent exclusive interview with Kyodo News.
There is a “huge difference” between the NPT and the pact, Zlauvinen said, adding that it is necessary to make distinctions between the two treaties and “try not to erode the validity and the legitimacy of the NPT.”
He also noted that some members of the NPT are opposed to any reference to the nuclear ban pact at the review conference to be convened early next year and indicated that a wide gap between nuclear power states and those pushing for the nuclear ban treaty could be an “issue of contention” at the NPT gathering.
US, Russia to hold latest nuclear arms talks in Finland
“The Finnish president’s office says the United States and Russia will hold a round of nuclear arms control talks in Finland’s capital, Helsinki, on Monday to follow up on negotiations in Austria this summer”
By: Associated Press | abcnews.com
HELSINKI — The United States and Russia will hold a round of nuclear arms control talks in the Finland’s capital, Helsinki, on Monday to follow up on negotiations in Austria this summer, the Finnish president’s office said.
“The round of discussions on strategic stability and nuclear weapons between the United States and Russia, which began in Vienna in the summer, will continue in Helsinki on Monday,” the office of the Finnish President Sauli Niinisto said in a brief statement late Sunday.
The office said nuclear arms negotiators from Washington and Moscow met a previous time in Finland in 2017.
“Finland welcomes the negotiators, this time (U.S.) Ambassador (Marshall) Billingslea and (Russian) Deputy Foreign Minister (Sergei) Ryabkov,” the statement said, adding that Niinisto would meet both representatives after the talks.
Ambassador: Time is right for new arms control agreement
“Arguing that its stockpile is small, China has said it would participate only if the U.S. agrees to nuclear parity among all nations. Russia has suggested that if China were part of the pact, other countries would need to be included as well.”
BY: The Associated Press, SUSAN MONTOYA BRYAN | apnews.com
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. (AP) — The Trump administration has sketched out a framework that it hopes will avoid a three-way arms race as a deadline nears for extending the only remaining nuclear arms control deal with Russia and as China looks to expand its nuclear forces.
Ambassador Marshall Billingslea, the special presidential envoy for arms control, spoke with The Associated Press about negotiations with Russia while touring some of the top nuclear research labs and production sites in the United States.
Citizen Scientist: Frank von Hippel’s Adventures in Nuclear Arms Control
For 50 years, Frank von Hippel has been working as a citizen-scientist to reduce the grave dangers to humankind from nuclear-weapon and nuclear-energy programs around the world. In this special collection of edited, illustrated and footnoted interviews, von Hippel describes in vivid personal detail the many policy battles he has taken on, the state of nuclear dangers today, and his hopes for a path forward.
Interviews by Tomoko Kurokawa | Journal for Peace and Nuclear Disarmament
Born into an illustrious scientific family that included his grandfather, Nobel laureate James Franck, a leader of the opposition within the Manhattan Project to the use of nuclear weapons against Japan, von Hippel got his PhD in physics from Oxford as a Rhodes Scholar. He was inspired by student activists opposed to the Vietnam War to move from teaching physics at Stanford into a career of policy activism based in Princeton University, where he co-founded the Program on Science and Global Security a leading international center for nuclear arms control, nonproliferation and disarmament research. During the 1980s, von Hippel joined the US citizens’ uprising to “freeze” the nuclear arms race.
Russian officials have already repeatedly warned in the past that its Eastern European neighbours’ decision to host US-made strategic systems, including components of America’s Aegis Ashore missile defence system, make them targets for Russia’s strategic nuclear response in the event of a war.
sputniknews.com
The redeployment of US nuclear weapons from Germany to Poland would be a direct violation of the Russia-NATO founding act of 1997, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov has said.
“This would be a direct violation of the Founding Act on Mutual Relations between Russia and NATO, in which NATO undertook not to place nuclear weapons in the territory of new members of the North Atlantic Alliance, either at that moment or in the future…I doubt that these mechanisms will be implemented in practical terms,” Lavrov said, speaking to reporters following a videoconference-based meeting of the Council of Baltic Sea States on Tuesday.
Earlier Tuesday, Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova said that the redeployment of US nuclear weapons from Germany to Poland would serve to further damage already-strained Russia-NATO relations and escalate tensions.
Trump Administration Determined to Exit Treaty Reducing Risk of War
Mike Pompeo and Mark Esper agreed to proceed with US withdrawal of Open Skies Treaty despite pandemic, sources say
ARTICLE BY: JULIAN BORGER | theguardian.com
The Trump administration is determined to withdraw from a 28-year-old treaty intended to reduce the risk of an accidental war between the west and Russia by allowing reconnaissance flights over each other’s territory.
Despite the coronavirus pandemic, which has put off a full national security council (NSC) meeting on the Open Skies Treaty (OST), the secretary of defence, Mark Esper, and secretary of state, Mike Pompeo, have agreed to proceed with a US exit, according to two sources familiar with administration planning.
Navy asks Lockheed Martin to build additional Trident II D5 submarine-launched ballistic nuclear missiles
The Trident II D5 is the primary U.S. sea-based nuclear ballistic missile, and is deployed aboard U.S. Navy Ohio-class ballistic missile submarines.
BY JOHN KELLER | tricityherald.com
WASHINGTON – Strategic weapons experts at Lockheed Martin Corp. will build additional UGM-133A Trident II D5 submarine-launched ballistic nuclear missiles and support deployed D5 nuclear weapons under terms of a half-billion-dollar order announced Thursday.
Political Battle Brewing Over New Nuclear Program
“Congressional leadership has yet to receive the military requirement or justification for another new nuclear warhead,” a spokesperson for HASC Democrats said in an email.
“As recently as July 2019, the Department of Energy projected it would begin work on this warhead in 2023. Work on this new warhead will add billions of dollars to an already strained nuclear modernization plan.”
BY JON HARPER | nationaldefensemagazine.com
The Trump administration’s proposal to begin work on a new nuclear warhead program to modernize the nation’s aging stockpile is expected to be hotly contested.
For fiscal year 2021, President Donald Trump requested $28.9 billion for the Pentagon’s nuclear enterprise. He requested an additional $15.6 billion for efforts by the National Nuclear Security Administration, which manages the stockpile, including $53 million for NNSA work on a new warhead, dubbed the W93.
2021 & Earlier
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Resources
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Quotes
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.