Source/Reference Documents
Map Spreadsheet Examples 2021-2023
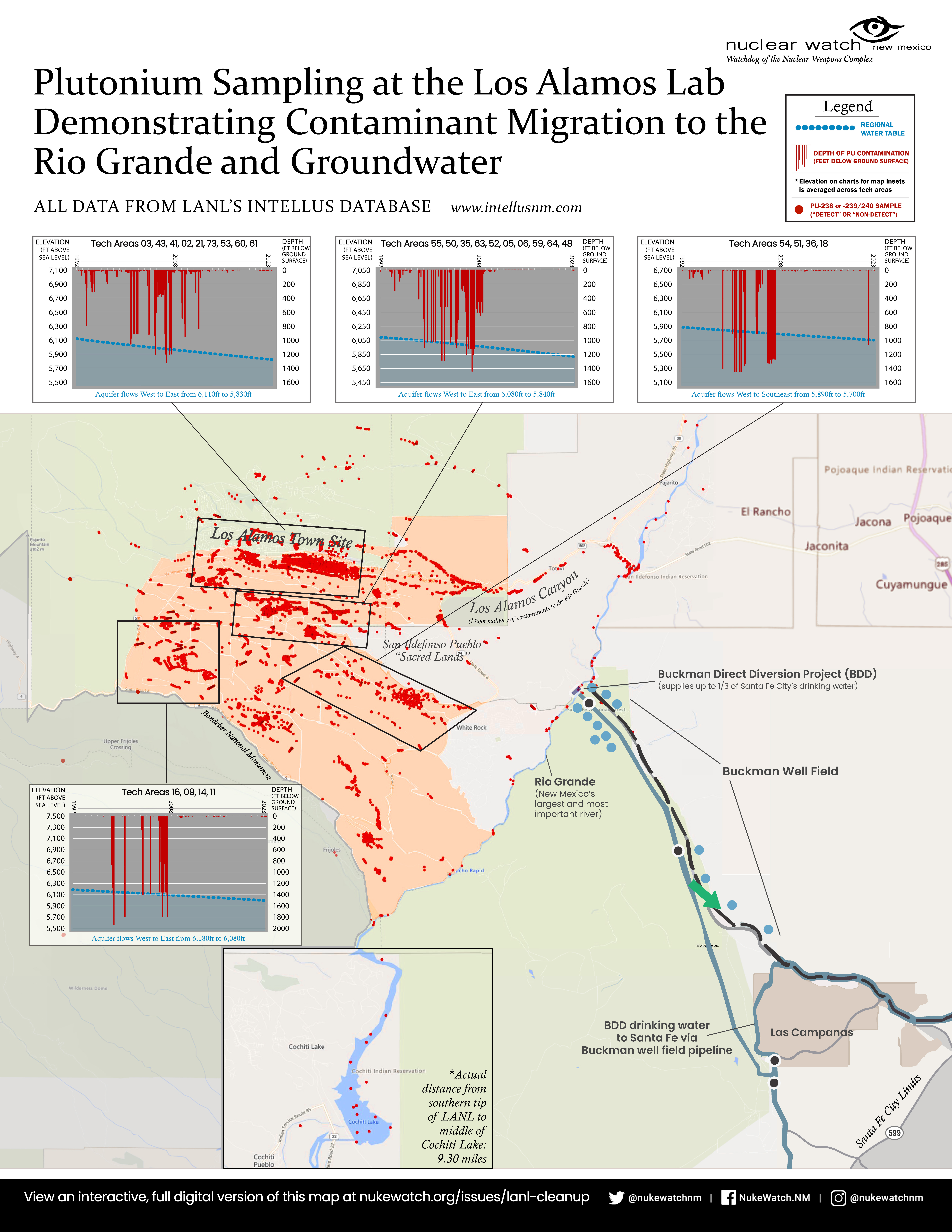
Below are examples of a spreadsheets created in Intellus, which is the environmental database at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The requests were for all soil and groundwater samples taken in, under, and around the Lab in 2021, 2022, and 2023. The spreadsheets were then sorted by “Report Result” (Column ‘F’), which lists the plutonium found in samples in descending order. It shows the highest sample for each year at top of the column.
Looking at the 2021 spreadsheet, there were 2043 samples analyzed for plutonium taken in 2021. There are approximately 100 detects including the high sample of 10100 pCi/g. Please read Dr. Ketterer’s report for a discussion of the ‘detects’ and ‘non-detects.’
Notice the latitude and longitude for each sample (columns ‘O’ and ‘P’). We used these coordinates to create the maps.
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New & Updated
Call to action! Comments Against WIPP Expansion Needed By April 3rd
Call to action!
Comments on WIPP Expansion Needed By April 3rd
Informational Meeting Is March 8th
New Mexico is under growing nuclear attack.
· Plutonium pit production increases are planned for Los Alamos.
· There are serious plans for all of the nation’s commercial spent nuclear fuel to head to NM.
· WIPP has a major expansion in the works to allow even more radioactive waste into NM.
Today we ask you to join with others to stop a proposed major Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) expansion. Officials at the WIPP are proceeding with a deluge of permit modifications to try to get as much weakening of the Hazardous Waste Permit as they can before 2019.
Because DOE is so far behind emplacing waste at WIPP, including because of the three-year shutdown from the 2014 radiation release, and they are running out of underground space, they want to change the way waste volume is measured. Since the 1970s, DOE has agreed that the amount of waste is the volume of the outer-most container. Now, DOE wants to estimate the amount of waste inside each container and use that lesser amount.
By April 3, we need You to submit written comments opposing DOE’s request. If possible, you can find out more at a public meeting (which isn’t for public comments):
“Clarification” of TRU Mixed Waste Disposal Volume Reporting
Thursday, March 8, 2018 3 – 5 p.m.
Courtyard by Marriott, 3347 Cerrillos Road, Santa Fe, New Mexico
DOE’s request is at: http://wipp.energy.gov/rcradox/rfc/Volume_of_Record.pdf
What to expect at this March 8 meeting:
· Interested people, including NM Environment Department officials, gathered to discuss this issue in one of the smaller conference rooms
· Optional sign-in sheet, and DOE handouts of their presentation
· A presentation of the proposed plan by DOE
· Question and answer period – Make sure you get all your questions answered
· No opportunity for formal public comments
WIPP is now filling Panel 7 (of 10 originally proposed), which is about 70% of the space. But WIPP has only emplaced ~92,700 m3 of waste (about 53% of the 175,564 m3 allowed). DOE has “lost” more than 30,000 m3 of space by its inefficiency and contractor incompetence. Measuring the waste the proposed new way decreases the ‘amount of waste’ emplaced to date by ~26,000 m3.
The proposed modification is controversial and is part of a larger plan to expand WIPP, but is submitted as a Class 2 Permit Modification Request (PMR), which has lesser public input opportunities. The public has opposed WIPP expansion for years and decades. There is significant public concern and interest in the WIPP facility. This PMR should be a Class 3, which includes much more public input, a formal public hearing — a process that could take up to a year.
We will provide sample comments by April 3rd, but your comments are just as important.
The complete Permit Modification Request is here –
http://www.wipp.energy.gov/rcra-com-menu.asp
Class 2 Permit Modification Request Clarification of TRU Mixed Waste Disposal Volume Reporting Waste Isolation Pilot Plant Permit, Number NM4890139088-TSDF dated January 31, 2018
http://www.wipp.energy.gov/rcradox/rfc/18-0308_Redacted_enclosure.pdf
By April 3, please mail or fax or e-mail comments to:
Mr. Ricardo Maestas
New Mexico Environment Department
2905 Rodeo Park Drive East, Building 1
Santa Fe, NM 87505
Fax: 505-476-6030
E-mail: [email protected]

The Regional Coalition of LANL Communities: Benefits for the Select Few
According to media reports, Andrea Romero, Executive Director of the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities, is accused of charging some $2,200 dollars of unallowable travel costs, such as alcohol and baseball tickets, while lobbying in Washington, DC for additional funding for the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). She in turn accused the nonprofit group Northern New Mexico Protects of political motivations in revealing these questionable expenses. Romero is running in the Democrat Party primary against incumbent state Rep. Carl Trujillo for Santa Fe County’s 46th district in the state House of Representatives.
Perhaps more serious is the fact that Romero was awarded an undisclosed amount of money by the Venture Acceleration Fund (VAF) for her private business Tall Foods, Tall Goods, a commercial ostrich farm in Ribera, NM. According to a May 8, 2017 Los Alamos Lab news release announcing the award to Tall Foods, Tall Goods, “The VAF was established in 2006 by Los Alamos National Security [LANS], LLC to stimulate the economy by supporting growth-oriented companies.”[1] LANS, primarily composed of the Bechtel Corporation and the University of California, has held the annual ~$2.4 billion Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) management contract since June 2006.
The Regional Development Corporation administers the Venture Acceleration Fund.[2] It states that the median VAF award in 2017 was $41,000, and that preference is given to companies that “Have an association with LANL Technology or Expertise.” [3]
It is, at a minimum, unseemly for the Executive Director of the Regional Coalition, which lobbies for increased LANL funding, to receive funding for her private business from LANS, who runs LANL.[4] Ultimately that funding for her private business comes from the American taxpayer.
Romero’s employer, the Regional Coalition, is overwhelmingly funded by the Department of Energy (DOE) and the Los Alamos County government, which receives more than $30 million dollars annually from the Lab through state gross receipts taxes. The Regional Coalition has been lobbying the New Mexico legislature to pass a state law requiring that LANL continue to pay gross receipts tax in the event that its management contract is taken over by a nonprofit university.[5] If successful, that would help to ensure the Regional Coalition’s funding stream.
Concerning the “adequate funding for LANL” that the Regional Coalition lobbies for, LANL’s annual ~$2.4 billion budget is now 70% for core nuclear weapons research and production programs, while much of its remaining funding either directly or indirectly supports those programs. In partial contradiction, the Cities and Counties of Santa Fe and Taos, which belong to the RCLC, have at various times passed resolutions against expanded plutonium pit production for nuclear weapons and/or called for genuine comprehensive cleanup at the Lab.
Despite its rhetoric on producing jobs through cleanup, the Regional Coalition has yet to take a position advocating for genuine comprehensive cleanup at LANL. Instead, the Coalition seems to condone DOE and LANL plans to “cap and cover” and leave ~150,000 cubic meters of radioactive and toxic wastes permanently buried in unlined pits and trenches at the Lab’s largest waste dump, Area G.[6] This will create a permanent nuclear waste dump above the regional groundwater aquifer, three miles uphill from the Rio Grande. Radioactive and toxic wastes are buried directly in the ground without liners, and migration of plutonium has been detected 200 feet below Area G’s surface.[7]
In September 2016 the Department of Energy released a 2016 Lifecycle Cost Estimate Summary[8] of proposed future cleanup at LANL, which RCLC Executive Director Romero hailed as:
The Lifecycle Baseline documentation provides our communities the necessary foundation to properly advocate on behalf of the best possible scenarios for cleaning up legacy nuclear waste at the Laboratory in the most time and cost-efficient manner. After years of requests for this document, we now have the tool that can get us to additional cleanup dollars to get the job done.[9]
However, at the beginning of the 2016 Lifecycle Cost Estimate Summary DOE declares that “An estimated 5,000 cubic meters of legacy waste remains, of which approximately 2,400 cm [cubic meters] is retrievably stored below ground”, a claim which was widely reported in New Mexican media. From there DOE estimated that it would cost $2.9 to $3.8 billion to complete so-called cleanup around 2040, which is woefully low. The DOE report omits any mention of the ~150,000 cubic meters of poorly characterized radioactive and toxic wastes at Area G, an amount 30 times larger than DOE acknowledges. As a partial result, DOE funding for cleanup at LANL remains flat at around $190 million per year, when the New Mexico Environment Department is on record that $250 million per year is needed.
Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch Director, commented,
New Mexicans often hear from the Department of Energy and our congressional delegation how nuclear weapons programs economically benefit us. If that’s the case, why is it that New Mexico has fallen from 37th in per capita income in 1957 to 48th in 2017? [10] Why is it that while Los Alamos County is the second richest county in the USA, Main Street Española hasn’t significantly changed for the better in the last 40 years? It’s clear that the economic benefits of the nuclear weapons industry go only to the select few, while to its shame New Mexico as a whole continues to be ranked as the second worst state for children.
# # #
[Copying URLs into browsers is recommended.]
[1] LANL’ s May 8, 2017 news release Six northern New Mexico businesses awarded funds to boost growth is available at http://www.lanl.gov/discover/news-release-archive/2017/May/0518-6-nnm-business-awarded-funds.php
[2] “The RDC [Regional Development Corporation] was incorporated in 1996 to serve as the Department of Energy (DOE) Los Alamos Site “Community Reuse Organization” (CRO). As a CRO, the RDC’s mission is to diversify the economy within the north central New Mexico region. As a result, the RDC maintains a special working relationship with both the DOE and Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL).” https://rdcnm.org/about/
[3] See https://web.archive.org/web/20190120214344/https://rdcnm.org/vaf/
[4] The mission statement of the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities is
… the Regional Coalition works in partnership to create one voice to ensure national decisions incorporate local needs and concerns. The organization’s focus is community and economic development, site employment, environmental remediation, and adequate funding for LANL. The Regional Coalition of LANL Communities is comprised of nine cities, counties and pueblos surrounding the Department of Energy’s Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). https://regionalcoalition.org/about
[5] Four universities are currently vying for the LANL management contract: Purdue (with corporate partner Bechtel), the University of California, the University of Texas, and Texas A&M (DOE Secretary Rick Perry’s alma mater). Corporate partners for the last three have not been disclosed.
[6] Estimated quantities of waste at Area G (in cubic yards) are from Table G3.41, MDA G Corrective Measures Evaluation, 2011, LANS, p. G-13. See excerpts at https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/Area_G_Pit_Totals_from_CME_rev3_Sept-2011.pdf
[7] Documentation of the plutonium detection 200 feet below the surface of Area G is at https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/AGCME Plate_B-3_radionuclides_subsurface.pdf
[8] The Department of Energy’s 2016 Lifecycle Cost Estimate Summary for LANL cleanup is available at https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/LBC-Summary-Aug-2016.pdf
[9] https://web.archive.org/web/20170124153124/http://www.santafenm.gov/news/detail/department_of_energy_release_important_baseline_study
[10] NM per capita income at https://web.archive.org/web/20161206084557/http://www.bea.gov:80/regional/bearfacts/pdf.cfm?
The Regional Coalition of LANL Communities: Benefits for the Select Few
Santa Fe, NM
According to media reports, Andrea Romero, Executive Director of the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities, is accused of charging some $2,200 dollars of unallowable travel costs, such as alcohol and baseball tickets, while lobbying in Washington, DC for additional funding for the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). She in turn accused the nonprofit group Northern New Mexico Protects of political motivations in revealing these questionable expenses. Romero is running in the Democrat Party primary against incumbent state Rep. Carl Trujillo for Santa Fe County’s 46th district in the state House of Representatives.
Perhaps more serious is the fact that Romero was awarded an undisclosed amount of money by the Venture Acceleration Fund (VAF) for her private business Tall Foods, Tall Goods, a commercial ostrich farm in Ribera, NM. According to a May 8, 2017 Los Alamos Lab news release announcing the award to Tall Foods, Tall Goods, “The VAF was established in 2006 by Los Alamos National Security [LANS], LLC to stimulate the economy by supporting growth-oriented companies.”[1] LANS, primarily composed of the Bechtel Corporation and the University of California, has held the annual ~$2.4 billion Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) management contract since June 2006.
Major LANL Cleanup Subcontractor Implicated in Fraud; Entire Los Alamos Cleanup Should Be Re-evaluated
On December 17, 2017, the Department of Energy (DOE) awarded a separate $1.4 billion contract for cleanup at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) to Newport News Nuclear BWXT-Los Alamos, LLC (also known as “N3B”).[1] This award followed a DOE decision to pull cleanup from LANL’s prime contractor, Los Alamos National Security, LLC (LANS), after it sent an improperly prepared radioactive waste drum that ruptured underground at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP). That incident contaminated 21 workers and closed WIPP for nearly three years, costing taxpayers at least $1.5 billion to reopen.
Tetra Tech Inc is a major subcontractor for N3B in the LANL cleanup contract. Tetra Tech is part of Tech2 Solutions, and will be responsible for the groundwater and storm water programs at LANL that are of intense interest to the New Mexico Environment Department and citizen environmentalists.[2] To date, these programs have been supported by several New Mexico small businesses that will be displaced by Tetra Tech.
Serious allegations of fraud by Tetra Tech were raised long before the LANL cleanup contract was awarded. The US Navy found that the company had committed wide spread radiological data falsification, doctored records and supporting documentation, and covered-up fraud at the Hunters Point Naval Shipyard cleanup project in San Francisco, CA. See media links and excerpts below.
The award of the LANL cleanup contract that includes Tetra Tech raises serious questions about the DOE’s contract evaluation and award process, and the Department’s due diligence in reviewing the performance histories of companies bidding for DOE work. To put this in broad perspective, the DOE’s nuclear weapons and cleanup programs have the singular distinction of being on the congressional Government Accountability Office’s High Risk List for fraud, waste and abuse since 1990.
Potential groundwater contamination is of intense interest to New Mexicans. As late as 1996 the Los Alamos Lab was officially declaring that groundwater contamination was impossible because the overlying volcanic tuff was “impermeable.” LANL even went so far as to request a waiver from NMED to not have to monitor groundwater contamination at all (which fortunately NMED denied). What the Lab, which advertises its “scientific excellence,” omitted to say is that the Parajito Plateau’s geology is highly complex and deeply fractured, providing ready pathways for contaminants to reach groundwater. Indeed, in just the last few months Nuclear Watch forced LANL to admit that its chromium hexavalent-6 groundwater contamination plume is much bigger than previously thought.[3]
Scott Kovac, Nuclear Watch Research Director, commented, “It took years for the DOE Environmental Management Office in Los Alamos to put a cleanup contract in place. We are seriously disappointed that there are major problems before the contract even starts. This situation shines a light on the cozy DOE contractor system, where every cleanup site has different combinations of the same contractors. Call it different trees, but the same old monkeys, where the real priority is to profit off of taxpayers dollars before a shovel turns over any waste.”
Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch Director, added, “The entire LANL cleanup program needs to be rethought.” In September 2016 DOE released a 2016 Lifecycle Cost Estimate Summary[4] of proposed future cleanup at LANL. At the beginning of that document the Department declared, “An estimated 5,000 cubic meters of legacy waste remains, of which approximately 2,400 cm [cubic meters] is retrievably stored below ground”, which was widely reported in New Mexican media. From there DOE estimated that it will cost $2.9 to $3.8 billion to complete so-called cleanup around 2040, which is woefully low.
However, the DOE report was far from honest. It intentionally omitted any mention of approximately 150,000 cubic meters of poorly characterized radioactive and toxic wastes just at Area G (LANL’s largest waste dump) alone, an amount of wastes 30 times larger than DOE admits in the 2016 Lifecycle Cost Estimate.
In reality, DOE and LANL plan to not clean up Area G, instead installing an “engineered cover” and leaving the wastes permanently buried. This will create a permanent nuclear waste dump above the regional groundwater aquifer, three miles uphill from the Rio Grande. Radioactive and toxic wastes are buried directly in the ground without liners, and migration of plutonium has been detected 200 feet below Area G’s surface.[5]
“In sum,” Coghlan concluded, “DOE should take a cue from the president and tell TetraTech “you’re fired!” Beyond that, after the current governor gets out of the way, the New Mexico Environment Department should completely reevaluate cleanup at LANL and force the Lab to genuinely clean up, which it is failing to do now.”
# # #
Media excerpts (copying URLs into browser is recommended):
June 29, 2017, well before the LANL cleanup contract was awarded- https://www.sfgate.com/bayarea/article/Ex-SF-Navy-shipyard-workers-allege-fraud-in-11257774.php
Ex-SF Navy shipyard workers allege fraud in radiation cleanup By J.K. Dineen Published 9:06 pm, Thursday, June 29, 2017 “The cleanup of radioactive contamination at the Hunters Point Shipyard was marred by widespread fraud, faked soil samples, and a high-pressure culture where speed was valued over accuracy and safety, according to four former site workers…” “Questions over the accuracy of the soil tests emerged in October 2012, when the Navy discovered that some results were inconsistent with results from previous samples collected in the same areas.” “In a statement, Tetra Tech spokesman Charlie MacPherson said the company “emphatically denies the allegations made by individuals at today’s news conference that Tetra Tech engaged in a cover-up of fraud on the Hunters Point Naval Shipyard.”
Jan 31, 2018: https://sf.curbed.com/2018/1/31/16956458/hunters-point-toxic-cleanup-navy-responds-san-francisco
Navy: Do-over of $250 million cleanup at Hunters Point necessary Unknown delay for city’s biggest redevelopment project By Chris Roberts@cbloggy “…According to a review of Tetra Tech’s data, triggered by allegations of fraud first made in 2011 and 2012, as much as half of Tetra tech’s work contains problems. That’s enough for the Navy to lose trust in all of the company’s data, Derek Robinson, the Navy’s coordinator for cleanup at the shipyard, said in an interview on Tuesday. “We’ve lost confidence” in Tetra Tech’s work, said Robinson. “All areas” at the shipyard where Tetra Tech did work will be re-tested, beginning as early as this summer… Problems with Tetra Tech’s data first surfaced in 2011 and 2012, when contractors and workers at the shipyard stepped forward with allegations of fraud…”
Jan 26, 2018 https://sf.curbed.com/2018/1/26/16916742/hunters-point-shipyard-toxic-cleanup Almost half of toxic cleanup at Hunters Point Shipyard is questionable or faked, according to initial review City’s goals for housing, affordable housing in doubt after fraud at city’s biggest redevelopment project “much worse” than thought By Chris Roberts@cbloggy,
[1] See https://energy.gov/em/articles/doe-awards-new-los-alamos-legacy-cleanup-contract
[2] See http://tech2.solutions/projects/lanl/
[3] The dangers of chromium-hexavalent 6 were made famous in the film Erin Brocovitch.
[4] The Department of Energy’s 2016 Lifecycle Cost Estimate Summary for LANL cleanup is available at https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/LBC-Summary-Aug-2016.pdf
[5] Documentation of the plutonium detection 200 feet below the surface of Area G is at https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/AGCME Plate_B-3_radionuclides_subsurface.pdf
Major LANL Cleanup Subcontractor Implicated in Fraud – Entire Los Alamos Cleanup Should Be Re-evaluated
Santa Fe, NM
On December 17, 2017, the Department of Energy (DOE) awarded a separate $1.4 billion contract for cleanup at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) to Newport News Nuclear BWXT-Los Alamos, LLC (also known as “N3B”). This award followed a DOE decision to pull cleanup from LANL’s prime contractor, Los Alamos National Security, LLC (LANS), after it sent an improperly prepared radioactive waste drum that ruptured underground at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP). That incident contaminated 21 workers and closed WIPP for nearly three years, costing taxpayers at least $1.5 billion to reopen.
Tetra Tech Inc is a major subcontractor for N3B in the LANL cleanup contract… Serious allegations of fraud by Tetra Tech were raised long before the LANL cleanup contract was awarded. The US Navy found that the company had committed wide spread radiological data falsification, doctored records and supporting documentation, and covered-up fraud at the Hunters Point Naval Shipyard cleanup project in San Francisco, CA.
Detailed NNSA Budget Documents Accelerates Nuclear Weapons Arms Race
Late Friday February 23 the Trump Administration released the detailed FY 2019 budget for the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency within the federal Department of Energy. Overall, NNSA is receiving a $2.2 billion boost to $15.1 billion, a 17% increase above the FY 2018 enacted level. Of that, a full $11 billion is for the budget category [Nuclear] “Weapons Activities”, 18% above the FY 2018 level. Of concern to the American taxpayer, DOE and NNSA nuclear weapons programs have been on the congressional Government Accountability Office’s High Risk List for project mismanagement, fraud, waste and abuse since its inception in 1990.
Under Trump’s budget, funding for nuclear warhead dismantlements stay flat at $56 million, (point).5% of NNSA’s total nuclear weapons budget, despite the fact that dismantlements save taxpayers by eliminating constant security costs.[1] NNSA’s Nonproliferation Programs are budgeted at $1.86 billion, only 16% the size of the nuclear weapons budget. Funding for DOE cleanup of Cold War legacy wastes remains flat, in a number of cases insufficient to meet legal milestones. Meanwhile, the Department of Energy cuts sustainable transportation, renewable energy and energy efficiency by 33%.
Some selected NNSA FY 2019 nuclear weapons budget highlights are:
- Funding is tripled from $218.76 million to $654.77 million for the W80-4 Life Extension Program for a Long Range Standoff nuclear warhead,[2] (slated for $804 million in FY 2022). This is for a new dual-use air launched cruise missile (ALCM), which is particularly destabilizing because ALCMs can evade radar by hugging topography. In addition, the targeted adversary has no way of knowing until it is hit whether the payload is conventional or nuclear. The LRSO nuclear weapon is arguably redundant to the new B61-12 nuclear bomb, to be delivered by the new super-stealthy new B21 Raider heavy bomber (whose astronomical costs are kept classified by the Air Force).
- Funding for the world’s first nuclear smart bomb, the B61-12, is increased from $611.9 million to $794 million, with a First Production Unit scheduled for March 2020. As part of the escalating Cold War II arms race, its main mission is to be forward deployed in NATO countries against Russia.
- The Obama Administration had delayed the Interoperable Warhead (IW) for five years. The IW-1 is very much back as a $53 million FY 2019 budget line item, up from $0 in FY 2018. The NNSA and the nuclear weapons labs are proposing three different types of interoperable warheads, which all together could cost more than $40 billion.
The IW-1 is supposed to be interoperable between the Air Force’s W78 intercontinental ballistic missile warhead and the Navy’s W88 sub-launched warhead. However, a 2012 memo leaked to Nuclear Watch and Tri-Valley CAREs shows that the Navy never supported it.[3] In addition, NNSA is beginning a $3 billion “alteration” to the W88 that will refresh its high explosives and give it a new fuze, making the Navy even less inclined to support the IW. The Interoperable Warhead is a huge make work project for the labs, particularly the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.
Nevertheless, the IW is the programmatic drive for expanded production of plutonium pits at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), which will incur many more billions in costs.
- Trump’s recently released Nuclear Posture Review proposed quick development of a low-yield sub-launched Trident missile warhead. While not yet a separate budget line item, NNSA’s FY 2019 hints at dedicated funding next year:
The 2018 Nuclear Posture Review states that the United States will modify a small quantity of existing SLBM [submarine launched ballistic missiles] warheads to provide a low-yield option in the near-term. As the Nuclear Weapons Council translates policy into military requirements, the Administration will work with Congress for appropriate authorizations and appropriations to develop options that support the modification. (P. 80)
- “Plutonium Sustainment” is nearly doubled from $184 million to $361 million. NNSA’s FY 2019 budget says this will:
[S]upport fabrication of four to five development (DEV) W87 pits… and the selection of a single preferred alternative for plutonium pit production beyond 30 war reserve pits per year… (P. 57)
The increase represents the following:
Supports additional personnel, equipment, and certification activities needed to ramp pit production to meet mandated pit production requirements.
Supports additional infrastructure investments to meet requirements by the Nuclear Weapons Council to produce no fewer than 80 war reserve pits per year. (P. 117)
This is significant for a number of reasons. First, as mentioned above, “plutonium pit production beyond 30 war reserve pits per year” is driven by the Interoperable Warhead, which the Navy doesn’t want and is a radically different design that could prompt a return to full-scale nuclear weapons testing. The existing stockpile does not need pit production. Future production is all about future new nuclear weapons designs.
The W87 pits mentioned above are for the Interoperable Warhead. Inside sources indicate that they will not be exact replicas, but instead may have additional built-in “surety” mechanisms to prevent unauthorized use. A serious concern is that any changes to the pit design could perturb the symmetrical implosion process of the plutonium pit, thereby potentially degrading confidence in weapons reliability.
Finally, there are serious doubts that the Los Alamos National Laboratory, the current site of plutonium pit production, is capable of more producing more than 30 pits per year.[4] This may lead to the relocation of the plutonium pit production mission to the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, or more likely in Nuclear Watch’s view production at both places.[5]
Despite the uncertainty of where future expanded plutonium pit production is going to be located, the Chemistry and Metallurgy Research Replacement Project at LANL is slated to be increased from $181 million in FY 2018 to $235 million in FY 2019. Increasing the plutonium limit 10-fold to 400 grams in the CMRR “Rad Lab” is the main priority, for which NNSA has just issued notice of an environmental assessment.[6] The purpose of the increase is to dramatically expand the Rad Lab’s capabilities for materials characterization[7] and analytical chemistry,[8] all in direct support of expanded plutonium pit production.[9]
- The Uranium Processing Facility (UPF) at the Y-12 Plant near Oak Ridge, TN, is increased to $703 million from $663 million, and is projected to go to $750 million in FY 2021, with construction to start soon. The UPF will produce future thermonuclear components that put the “H” in H-bomb. It was halted after a half-billion design mistake for which no one was held responsible, and a Defense Department estimate that it would cost $19 billion.
NNSA’s FY 2019 budget repeats the original claim that the UPF will cost only $6.5 billion. However, after downscoping the original UPF because of costs, NNSA now omits the costs of continued operations at two dangerous old facilities previously slated for decontamination and decommissioning.[10] Moreover, after a team of Lockheed Martin and Bechtel won the Y-12 management contract, it awarded UPF construction to Bechtel without competition. Bechtel is responsible for some of the biggest cost overruns in the DOE complex, for example the Waste Treatment Facility at Hanford (originally $3.5 billion, now $13.5 billion and may never work).
Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch Director, commented, “This rapid arms race build up is not going to make us safer. We don’t need thousands of nuclear weapons to deter North Korea. A new arms race with Russia is a giant step backwards. Further enriching the usual nuclear weapons contractors is the wrong priority when instead taxpayers’ money should be making our schools safe and rebuilding our country.”
# # #
NNSA’s FY 2019 detailed Congressional Budget Request is available at https://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2018/02/f49/DOE-FY2019-Budget-Volume-1.pdf
[1] Some 2,500 retired nuclear weapons are estimated to be in the dismantlement queue.
[2] “Standoff” means that a B52 carrying the LRSO nuclear weapon can position itself some 1,500 miles from the intended target.
[3] See 2012 Navy memo leaked to Nuclear Watch and Tri-Valley CAREs at https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/Navy-Memo-W87W88.pdf
[4] It should also be noted that major proposed federal actions are required to have public review and comment under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), followed by an agency’s formal Record of Decision (ROD). After completing a 1996 a Stockpile Stewardship and Management Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement to relocate pit production to LANL from the Rocky Flats Plant, DOE issued a ROD limiting production to 20 pits per year. Nuclear Watch believes that NNSA plans to expand production beyond 20 pits per year require a new programmatic environmental impact statement.
[5] An engineering study, reportedly based on an assumed production rate of 50 pits per year, is reportedly due this week, which may soon clarify this situation (however, it may be classified).
[6] The 30-day public comment period ends March 26, 2018. Comments should be sent to emailed to [email protected] or mailed to NNSA Los Alamos Field Office, ATTN: CMRR Project Management Office, 3747 West Jemez Road, Los Alamos, NM 87544. Nuclear Watch will post sample comments at www.nukewatch.org by March 16.
[7] Materials characterization ensures that the plutonium and/or highly enriched uranium are of sufficient “weapons-grade” to begin pit production to begin with.
[8] Analytical chemistry performs up to a hundred quality control samples per pit as it is being produced.
[9] For more, please see https://nukewatch.org/pressreleases/PR-2-22-18-CMRR_Rad_Lab_draft_EA.pdf
[10] In addition, the independent Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board says these two old facilities can never be brought up to modern seismic standards, while a few years ago the US Geologic Survey dramatically raised projected potential seismic risks in eastern Tennessee.
Detailed NNSA Budget Documents Accelerates Nuclear Weapons Arms Race
Santa Fe, NM.
Late Friday February 23, the Trump Administration released the detailed FY 2019 budget for the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency within the federal Department of Energy. Overall, NNSA is receiving a $2.2 billion boost to $15.1 billion, a 17% increase above the FY 2018 enacted level. Of that, a full $11 billion is for the budget category [Nuclear] “Weapons Activities”, 18% above the FY 2018 level. Of concern to the American taxpayer, DOE and NNSA nuclear weapons programs have been on the congressional Government Accountability Office’s High Risk List for project mismanagement, fraud, waste and abuse since its inception in 1990.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.