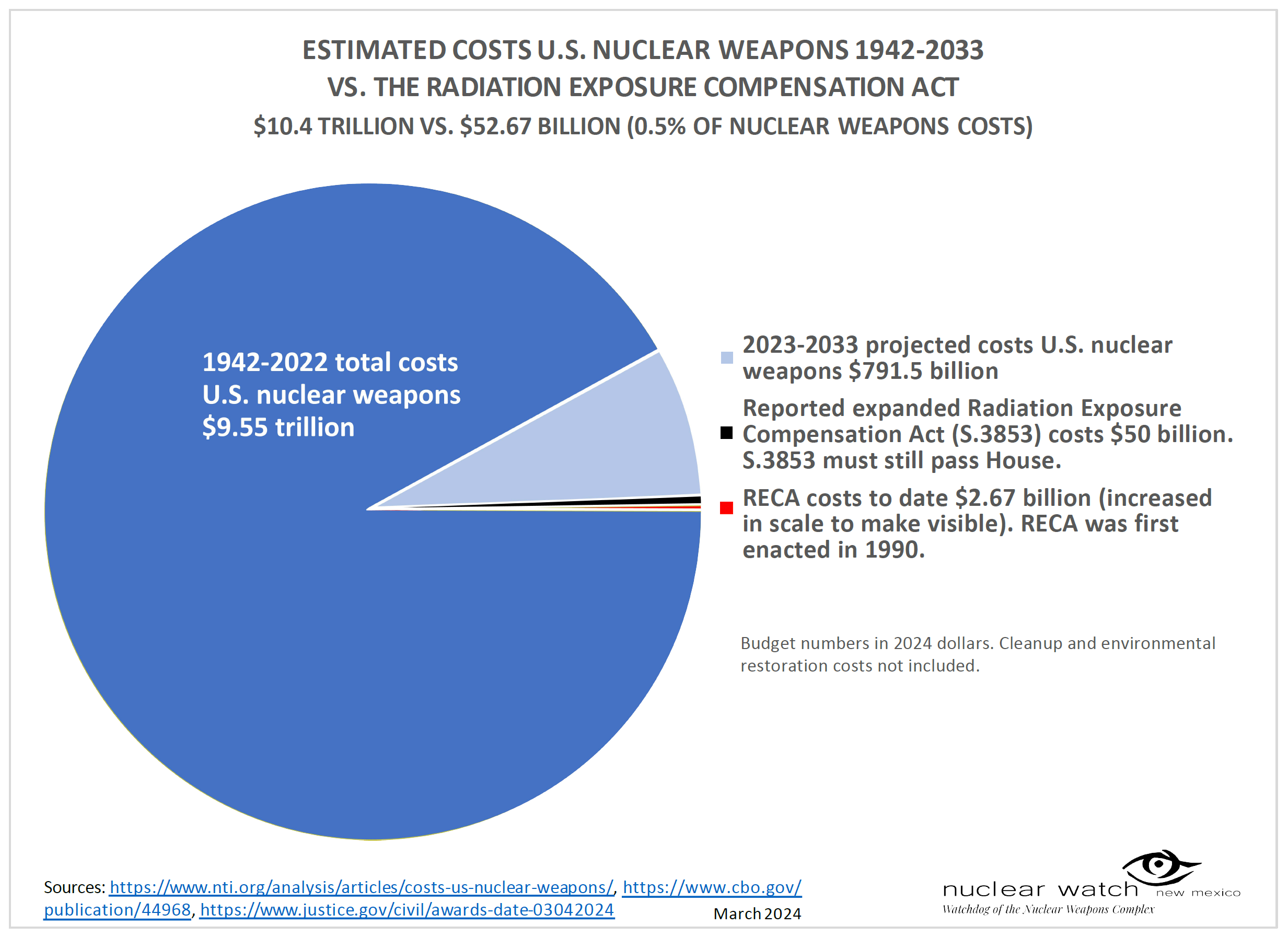
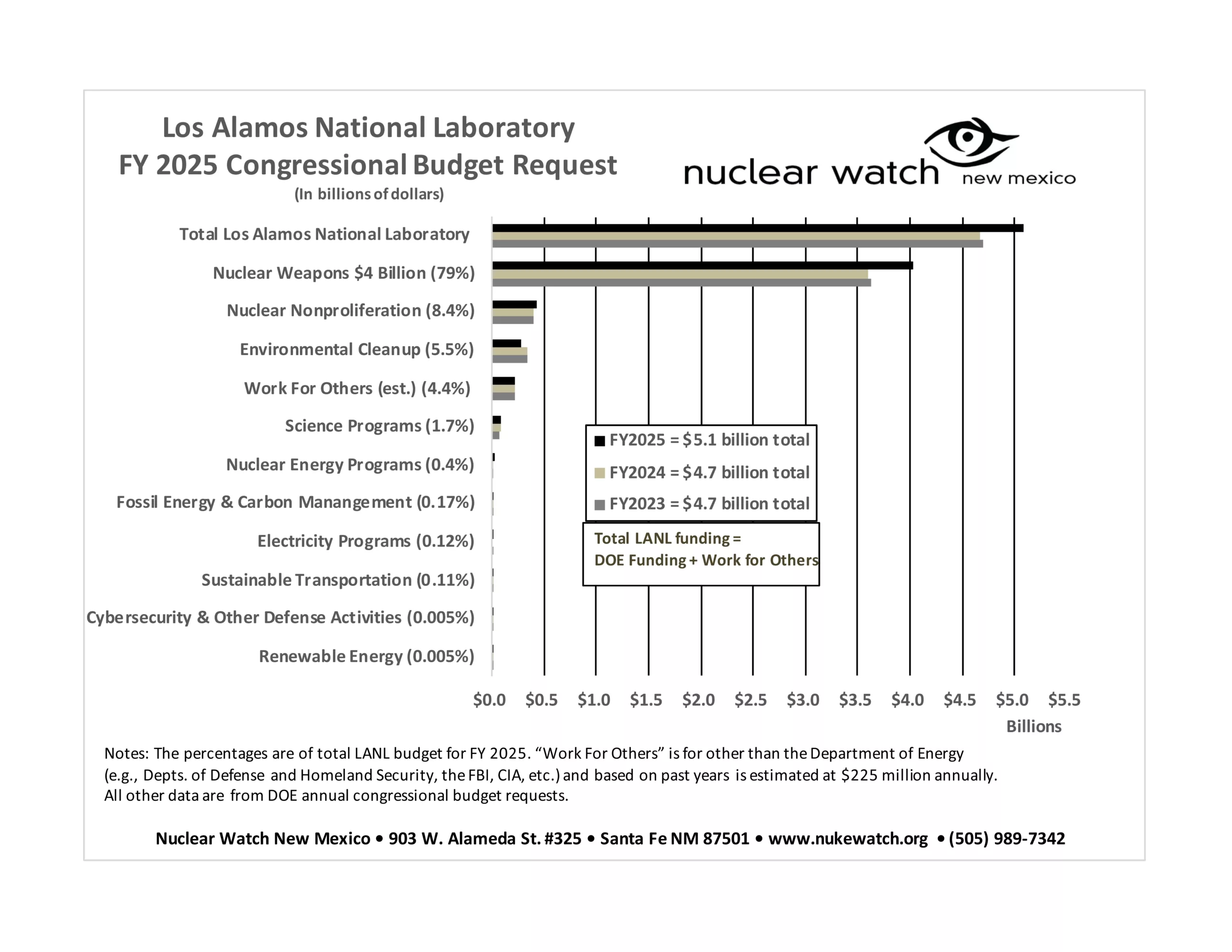
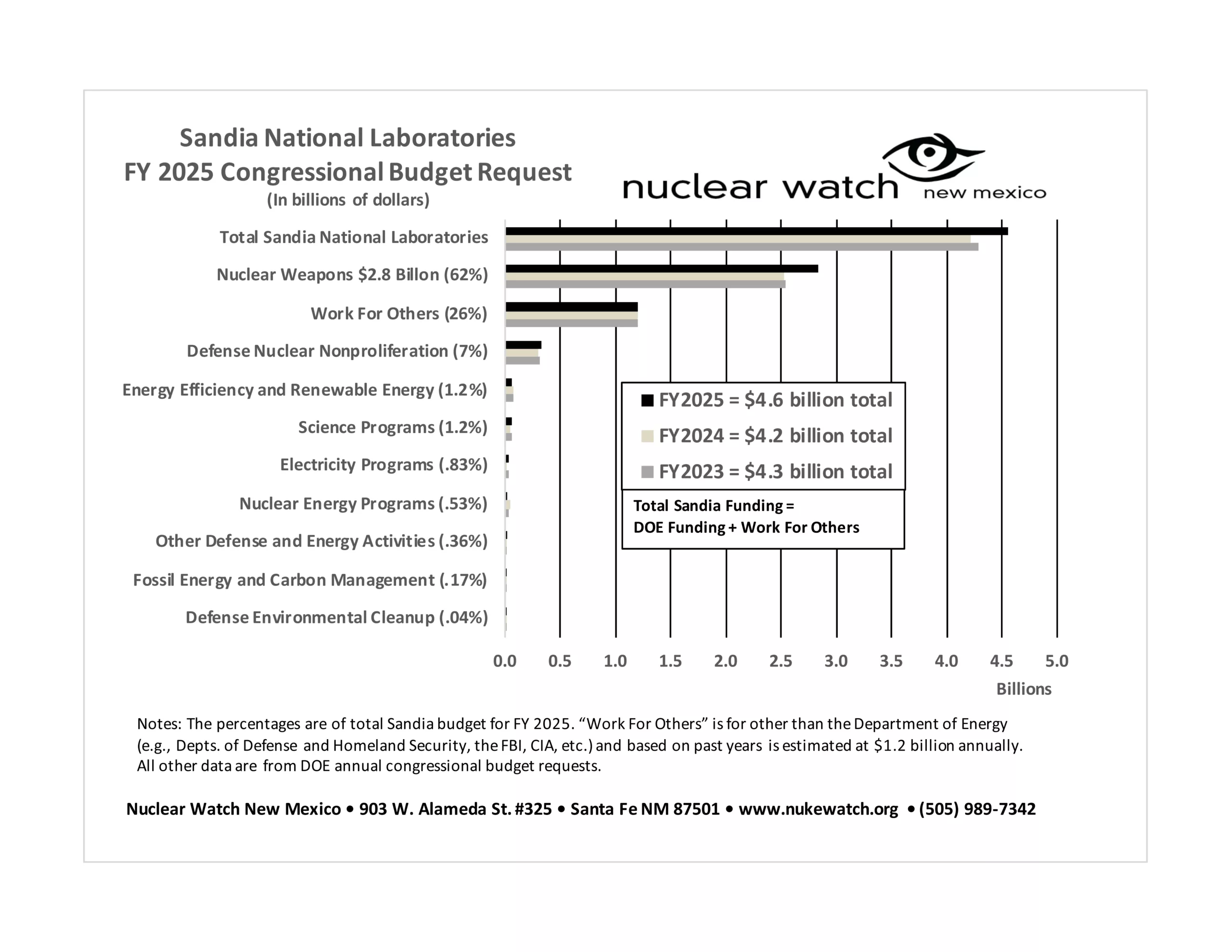
Source/Reference Documents
Map Spreadsheet Examples 2021-2023
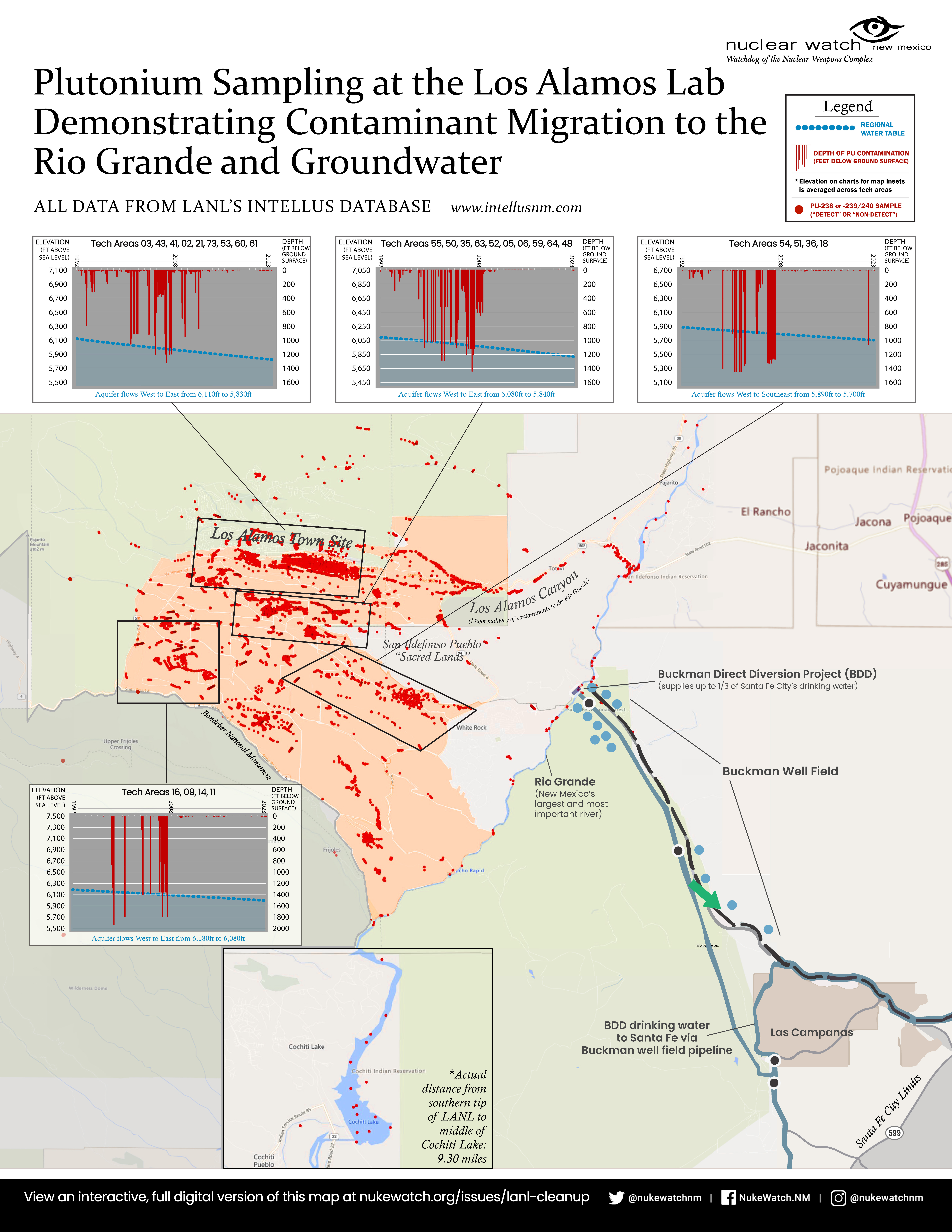
Below are examples of a spreadsheets created in Intellus, which is the environmental database at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The requests were for all soil and groundwater samples taken in, under, and around the Lab in 2021, 2022, and 2023. The spreadsheets were then sorted by “Report Result” (Column ‘F’), which lists the plutonium found in samples in descending order. It shows the highest sample for each year at top of the column.
Looking at the 2021 spreadsheet, there were 2043 samples analyzed for plutonium taken in 2021. There are approximately 100 detects including the high sample of 10100 pCi/g. Please read Dr. Ketterer’s report for a discussion of the ‘detects’ and ‘non-detects.’
Notice the latitude and longitude for each sample (columns ‘O’ and ‘P’). We used these coordinates to create the maps.
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New & Updated
NNSA Releases Draft Environmental Assessment for LANL Rad Lab; Raises Plutonium Limit 10 Times for Expanded Pit Production
Santa Fe, NM.
Today the National Nuclear Security Administration announced an Environmental Assessment to increase the amount of plutonium used in the Radiological Laboratory Utility and Office Building (aka the “Rad Lab”) at the Los Alamos National Laboratory from 38.6 grams of plutonium-239 equivalent to 400 grams. This 10-fold increase is significant because it will dramatically expand materials characterization and analytical chemistry capabilities in the Rad Lab in support of expanded plutonium pit production for future nuclear weapons designs. It also re-categorizes the Rad Lab from a “radiological facility” to a “Hazard Category-3” nuclear facility.
Trump’s Budget Dramatically Increases Nuclear Weapons Work
In keeping with the Trump Administration’s recent controversial Nuclear Posture Review, today’s just released FY 2019 federal budget dramatically ramps up nuclear weapons research and production.
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the Department of Energy’s semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency, is receiving a $2.2 billion overall boost to $15.1 billion, a 17% increase above the FY 2018 enacted level. Of that, a full $11 billion is for the budget category (Nuclear) “Weapons Activities”, 18% above the FY 2018 level.
Digging deeper under Weapons Activities, “Directed Stockpile Work” is increased from $3.3 billion to $4.7 billion, or 41%. Directed Stockpile Work is the hands on, nut and bolts operations that include extending the service lives of existing nuclear weapons for up to 60 years, while also endowing them with new military capabilities.
In addition, NNSA budget documents show “Weapons Activities (Reimbursable)” (parentheses in the original), adding another $1.76 billion to NNSA’s Nuclear Weapons Activities, for a total of $12.78 billion. It is not made clear where that additional money comes from, but most likely is from the Defense Department, as it has been in the past.
Of concern to the American taxpayer, DOE and NNSA nuclear weapons programs have been on the Government Accountability Office’s High Risk List for project mismanagement and fraud, waste and abuse since its inception in 1990.
Meanwhile, NNSA Nonproliferation Programs are budgeted at $1.86 billion, only 16% the size of the nuclear weapons budget. Further, the State Department is being cut by $10.4 billion to $28.3 billion (a 29% cut), while many senior diplomatic positions are left unfilled (such as the U.S. ambassador to South Korea), even as the possibility of peace on the Korean peninsula is breaking out.
The NNSA budget also reiterates the executive branch’s intent to terminate the Mixed Oxide (MOX) program, designed to “burn” military plutonium in commercial reactors. That program would introduce plutonium to the global market, contrary to its stated intent as a nonproliferation program. It has also been a debacle in terms of cost overruns, blown schedules and lack of contractor accountability, kept alive only by South Carolina congressional political pork interests.
However, the MOX program’s slow demise puts yet more pressure on New Mexico to become the nation’s radioactive waste dumping ground, with up to 35 tons of military plutonium potentially headed for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (which already lacks capacity for currently scheduled wastes). In addition, the Trump budget increases funding for so-called interim storage of spent nuclear fuel rods, the nation’s deadliest high-level radioactive wastes. There are two separate proposals for “interim” storage of 100 tons of spent nuclear fuel in either southern New Mexico or just on the other side of the border with Texas.
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) received an increase to $397 million, $106 million above the FY 2018 level. This starts the expansion of WIPP with a new ventilation shaft that has silently morphed from replacing the old contaminated exhaust shaft into being an additional intake shaft. Plans are underway for a new filter building, which will replace the capabilities lost due to the 2014 radiological release caused by an improperly prepared radioactive waste drum from the Los Alamos Lab. That closed WIPP for nearly three years, costing the American taxpayer at least $1.5 billion to reopen. The planned new intake shaft will greatly increase WIPP”s capabilities, allowing for expansion to take more of the nation’s radioactive wastes.
The cleanup request for Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) stays flat at $192 million. The basis for this is DOE’s woefully low lifecycle cost estimate for LANL cleanup, which in turned is predicated upon the New Mexico Environment Department’s revised cleanup Consent Order. Under Governor Susana Martinez, the revised Consent Order allows DOE and LANL to fund so-called cleanup at levels they choose, rather than needed cleanup driving the funding.
The Los Alamos Lab explicitly plans to leave permanently buried 200,000 cubic yards of radioactive and hazardous wastes in unlined pits and trenches, above our groundwater and three miles uphill from the Rio Grande. Once those wastes are “capped and covered”, LANL plans to claim that “cleanup” is completed.
Finally, under Trump’s budget, the Department of Energy cuts sustainable transportation, renewable energy and energy efficiency by 33% and zeroes out weatherization programs.
Jay Coghlan of Nuclear Watch commented,
The Trump budget prepares for nuclear war, in which even Ronald Reagan said there can’t be any winners. It finances a new Cold War arms race with Russia and indirectly increases the chances of a nuclear war with North Korea. It sets back nonproliferation and cleanup programs, and further hollows out our country by diverting yet more huge sums of money to the usual fat cat nuclear weapons contractors. Come November, voters should vote their conscience over how the federal government under Trump prioritizes their tax dollars for good or ill.
# # #
Nuclear Watch New Mexico will provide more budget information on our web site www.nukewatch.org and blog www.nukewatch.org/watchblog as it becomes available. The available budget documents are still not detailed enough for new issues and programs that we are keenly interested in, such as new, more usable mininukes and expanded plutonium pit production at LANL.
Trump’s Budget Dramatically Increases Nuclear Weapons Work
Santa Fe, NM
In keeping with the Trump Administration’s recent controversial Nuclear Posture Review, today’s just released FY 2019 federal budget dramatically ramps up nuclear weapons research and production.
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the Department of Energy’s semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency, is receiving a $2.2 billion overall boost to $15.1 billion, a 17% increase above the FY 2018 enacted level. Of that, a full $11 billion is for the budget category (Nuclear) “Weapons Activities”, 18% above the FY 2018 level.
Digging deeper under Weapons Activities, “Directed Stockpile Work” is increased from $3.3 billion to $4.7 billion, or 41%. Directed Stockpile Work is the hands on, nut and bolts operations that include extending the service lives of existing nuclear weapons for up to 60 years, while also endowing them with new military capabilities.
Testimony Calls Out Continued DOE Cost Estimating Mismanagement
Testimony Calls Out Continued DOE Cost Estimating Mismanagement
Given that DOE has challenges estimating almost all large projects, taxpayers must push to spend on cleanup first. Both nuclear weapons and environmental management estimates keep increasing. We can keep spending on dangerous nuclear weapons that we don’t need, or we can finally focus on cleaning up the Cold War mess.
Government Accountability Office (GAO) officials presented some of their recent work to Congress concerning management problems facing the Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and Office of Environmental Management (EM). NNSA is responsible for managing the nation’s nuclear weapons and supporting the nation’s nuclear nonproliferation efforts. In support of these missions, NNSA’s February 2016 budget justification for the Weapons Activities appropriations account included about $49.4 billion for fiscal years 2017 through 2021 to implement its nuclear weapons complex modernization plans. More recently, in November 2017, NNSA issued its Stockpile Stewardship and Management Plan, which included about $10.2 billion for nuclear weapons activities for fiscal year 2018.
Since the end of the Cold War, it is claimed that much of the nuclear weapons production infrastructure has become outdated, prompting congressional and executive branch decision makers to call on DOE to develop plans to modernize. The Department of Defense’s (DOD) 2010 Nuclear Posture Review identified long-term modernization wishes and alleged requirements. In January 2017, the President directed the Secretary of Defense to initiate a new Nuclear Posture Review to meet the Administration’s vision. This review was released in February 2018.
GAO has found that NNSA’s estimates of funding needed for its modernization plans exceeded the budgetary projections included in the President’s own modernization budgets. And the costs of some major modernization programs—such as for nuclear weapon Life Extension Programs (LEPs) — may also increase and further bust future modernization budgets.
The LEPs facing potential cost increases include:
B61-12 LEP. An independent cost estimate for the program completed in October 2016 exceeded the program’s self-conducted cost estimate from June 2016 by $2.6 billion.
W80-4 LEP. Officials from NNSA’s Office of Cost Policy and Analysis told us that this program may be underfunded by at least $1 billion to meet the program’s existing schedule
W88 Alteration 370. According to officials from NNSA’s Office of Cost Policy and Analysis, this program’s expanded scope of work may result in about $1 billion in additional costs.
EM is responsible for decontaminating and decommissioning nuclear facilities and sites that are contaminated from decades of nuclear weapons production and nuclear energy research. In February 2017, GAO reported that, since its inception in 1989, EM has spent over $164 billion on cleanup efforts, which include retrieving, treating, and disposing of nuclear waste.
GAO found that the federal government’s environmental liability has been growing for the past 20 years—and is likely to continue to increase—and that DOE is responsible for over 80 percent ($372 billion) of the nearly $450 billion reported environmental liability. Notably, this estimate does not reflect all of the future cleanup responsibilities that DOE may face.

As NNSA works to modernize the nuclear weapons complex, EM is addressing the legacy of 70 years of nuclear weapons production. These activities generated large amounts of radioactive waste, spent nuclear fuel, excess plutonium and uranium, and contaminated soil and groundwater. They also contaminated thousands of sites and facilities, including land, buildings, and other structures and their systems and equipment. Various federal laws, agreements with states (including New Mexico), and court decisions require the federal government to clean up environmental hazards at federal sites and facilities, such as nuclear weapons production facilities. For years, GAO and others have reported on shortcomings in DOE’s approach to addressing its environmental liabilities, including incomplete data on the extent of cleanup needed.
EM has some budget issues, too.
Examples of costs that DOE cannot yet estimate include the following:
DOE has not yet developed a cleanup plan or cost estimate for the Nevada National Security Site and, as a result, the cost of future cleanup of this site was not included in DOE’s fiscal year 2015 reported environmental liability. The nearly 1,400-square-mile site has been used for hundreds of nuclear weapons tests since 1951. These activities have resulted in more than 45 million cubic feet of radioactive waste at the site. According to DOE’s financial statement, since DOE is not yet required to establish a plan to clean up the site, the costs for this work are excluded from DOE’s annually reported environmental liability.
DOE’s reported environmental liability includes an estimate for the cost of a permanent nuclear waste repository, but these estimates are highly uncertain and likely to increase. In March 2015, in response to the termination of the Yucca Mountain repository program, DOE proposed separate repositories for defense high-level and commercial waste. In January 2017, we reported that the cost estimate for DOE’s new approach excluded the costs and time frames for site selection and site characterization.
Govt pulls full Nuclear Posture Review – Get it here!
The old link for the full Nuclear Posture Review
live on Friday February 2, 2018, now yields nothing.
The Defense Department’s new link
https://www.defense.gov/News/Special-Reports/0218_npr/
has an executive summary and some fact sheets, but not the full Review.
Interestingly, the executive summary looks like it’s translated into Russian, Chinese, Japanese, Korean and French. No doubt people around the world are looking at it.
But you now can find the full Nuclear Posture Review at
https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/2018-NUCLEAR-POSTURE-REVIEW-FINAL-REPORT.PDF
That won’t go away!
“Gateway Drug to Nuclear War” Feeds More Nuke Addiction
“Gateway Drug to Nuclear War” Feeds More Nuke Addiction
The Trump Administration’s high policy document, the Nuclear Posture Review (NPR), released February 2, includes recommendations for the deployment of lower yield, “more usable” nuclear warheads. This will only feed the US addiction to nukes.
An article on the same day in The American Conservative, “Trump’s Nuke Plan Raising Alarms Among Military Brass”, quotes one retired senior Army officer who tracked the NPR as saying that nuclear neocons were providing Donald Trump with “gateway drug for nuclear war.”
So while the [NPR’s] recommendations won’t necessarily be a surprise, what is less public is the bitter battle during its drafting that pitted senior Army and Navy warriors against nuclear wonks inside the Defense Department. That fight—over the exorbitant costs associated with the NPR, and charges that it could make nuclear war more likely—are bound to continue through implementation.
“It’s one thing to write a policy,” a senior Pentagon civilian privy to the NPR fight told The American Conservative, “and it’s another thing to have it implemented. What the NPR is recommending will break the bank, and a lot of people around here are worried that making nuclear weapons more usable isn’t what we should be doing. The conventional military guys have dug in their heels, they’re dead-set against it. This battle isn’t over.”
In effect, the congressionally mandated review calls for the U.S. to deploy two new types of lower yield nuclear warheads, generally defined as nuclear bombs below a five kiloton range (the one dropped on Hiroshima was 20 kilotons), that could be fitted onto a submarine-launched ballistic missile, and one, yet to be developed, that would be fitted onto a submarine-launched cruise missile. Additionally, the NPR calls for “recapitalizing” the complex of nuclear laboratories and plants, which, taken together with the proposed modernization program of the U.S. nuclear arsenal (the “triad”), will almost certainly cost in excess of the estimated price tag of $1.2 trillion over the next 30 years.
The article continues that Army and Navy officers worry that senior administration officials would promote massive new funding initiatives at the expense of badly needed funding for conventional military readiness. They also worry, more urgently, that the administration would put the nation on the slippery slope to nuclear escalation.
NukeWatch’s bottom line: Addiction to nukes is a potentially world-ending problem.
Trump’s Nuclear Posture Review goes in the opposite direction of meeting our long-term need to eliminate the one class of weapons of mass destruction that can truly destroy our country. It will instead set back nonproliferation and arms control efforts across the globe, and further hollow out our country by diverting yet more huge sums of money to the usual fat defense contractors at the expense of public education, environmental protection, natural disaster recovery, etc. Under the Trump Administration, expect Medicare and Social Security to be attacked to help pay for a false sense of military security. Trump’s Nuclear Posture Review is part and parcel of that.
Nuclear Watch New Mexico seeks to promote safety and environmental protection at nuclear facilities; mission diversification away from nuclear weapons programs; greater accountability and cleanup in the nation-wide nuclear weapons complex; and consistent U.S. leadership toward a world free of nuclear weapons. Please help support NukeWatch.
Draft Nuclear Posture Review Degrades National Security
Yesterday evening the Huffington Post posted a leaked draft of the Trump Administration’s Nuclear Posture Review (NPR). This review is the federal government’s highest unclassified nuclear weapons policy document, and the first since the Obama Administration’s April 2010 NPR.
This Review begins with “[m]any hoped conditions had been set for deep reductions in global nuclear arsenals, and, perhaps, for their elimination. These aspirations have not been realized. America’s strategic competitors have not followed our example. The world is more dangerous, not less.” The NPR then points to Russia and China’s ongoing nuclear weapons modernization programs and North Korea’s “nuclear provocations.” It concludes, “We must look reality in the eye and see the world as it is, not as we wish it be.”
If the United States government were to really “look reality in the eye and see the world as it is”, it would recognize that it is failing miserably to lead the world toward the abolition of the only class of weapons that is a true existential threat to our country. As an obvious historic matter, the U.S. is the first and only country to use nuclear weapons. Since WWII the U.S. has threatened to use nuclear weapons in the Korean and Viet Nam wars, and on many other occasions.
Further, it is hypocritical to point to Russia and China’s “modernization” programs as if they are taking place in a vacuum. The U.S. has been upgrading its nuclear arsenal all along. In the last few years our country has embarked on a $1.7 trillion modernization program to completely rebuild its nuclear weapons production complex and all three legs of its nuclear triad.
Moreover, Russia and China’s modernization programs are driven in large part by their perceived need to preserve strategic stability and deterrence by having the ability to overwhelm the U.S.’ growing ballistic missile defenses. Ronald Reagan’s pursuit of “Star Wars” (fed by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s false promises of success) blocked a nuclear weapons abolition agreement in 1988 with the soon-to-collapse Soviet Union. In 2002 George W. Bush unilaterally withdrew the U.S. from the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty, which has been a source of constant friction with the Russian government ever since.
More recently, at Israel’s request, the U.S. blocked the 2015 NonProliferation Treaty (NPT) Review Conference at the United Nations from agreeing to an international conference on a nuclear weapons free zone in the Middle East (Israel, an undeclared nuclear weapons power, has never signed the NPT). As an overarching matter, the U.S. and other nuclear-armed NPT signatories have never honored the Treaty’s Article VI mandate “to pursue negotiations in good faith on effective measures relating to cessation of the nuclear arms race at an early date and to nuclear disarmament…”, in effect since 1970. As a consequence, last year more than 120 countries at the UN passed a nuclear weapons ban treaty which the U.S. vehemently denounced, despite the fact that there have long been ban treaties on chemical and biological weapons which the U.S. has not only supported but also sought to enforce.[1]
With respect to North Korea’s nuclear provocations, that repressive regime is clearly seeking deterrence against the U.S. (North Korea’s infrastructure was nearly completely destroyed during the Korean War, and it witnessed the destruction of the Iraqi regime that did not have nuclear weapons). The bombastic statements of “fire and fury” and who has the bigger “nuclear button” from two unpredictable heads of state (Trump and Kim Jong Un) have put the entire world on edge, given the highest chance of nuclear war since the mid-1980’s.
Finally, the Nuclear Posture Review purports to be all about “deterrence” against hostile threats. However, the U.S’ true nuclear posture has never been just deterrence, but rather the ability to wage nuclear war, including possible preemptive first strikes. This is the reason why the U.S. (and Russia) keep thousands of nuclear weapons instead of the few hundred needed for just deterrence.[2] And keeping and improving the ability to wage a nuclear war is the underlying reason for the $1.7 trillion “modernization” program that is giving nuclear weapons new military capabilities, instead of prudently maintaining a few hundred existing nuclear weapons.
In addition to fully preserving and improving the enormous land, sea and air-based Triad, the new NPR calls for:
1) Near-term development of a low-yield nuclear warhead for existing Trident missiles launched from new strategic submarines.
2) New sub-launched nuclear-armed cruise missiles.
3) Keeping the 1.2 megaton B83-1 nuclear gravity bomb “until a suitable replacement is identified.”
4) “Provid[ing] the enduring capability and capacity to produce plutonium pits at a rate of no fewer than 80 pits per year by 2030.”
5) “Advancing the W78 warhead replacement to FY19… and investigating the feasibility of fielding the nuclear explosives package in a Navy flight vehicle.”
Obvious problems are:
1) An adversary won’t know whether a Trident sub-launched nuclear warhead is a new low-yield or an existing high-yield warhead. In any event, any belief in a “limited’ nuclear war is a fallacy that shouldn’t be tested – – once the nuclear threshold is crossed at any level, it is crossed, and lower-yield nuclear weapons are all the more dangerous for being potentially more usable.
2) Sub-launched nuclear-armed cruise missiles are inherently destabilizing as the proverbial “bolt out of the blue,” and can be the perfect weapon for a nuclear first-strike. Moreover, this is redundant to nuclear-armed cruise missiles that are already being developed for heavy bombers.
3) The National Nuclear Security Administration largely justified the ongoing program to create the B61-12 (the world’s first “smart” nuclear gravity bomb) by being a replacement for the 1.2 megaton B83-1 bomb. Does this indicate doubts in the ~$13 billion B61-12 program? And will it lead to a bump up in the number of nuclear weapons in the U.S.’ arsenal?
4) To date, the talk has been up to 80 pits per year, not “no fewer than.” Also, the 2015 Defense Authorization Act required that the capability to produce up to 80 pits per year be demonstrated by 2027. The NPR’s later date of 2030 could be indicative of longstanding plutonium pit production problems at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. That delay and hints of higher than 80 pits per year could also point to the pit production mission being relocated to the Savannah River Site, which is under active consideration. In any event, future plutonium pit production pit production is not needed for the existing nuclear weapons stockpile, but is instead for future new-design nuclear weapons.
5) “W78 warhead replacement… in a Navy flight vehicle” is code for so-called Interoperable Warheads, whose planned three versions together could cost around $50 billion. These are arguably huge make work projects for the nuclear weapons labs (particularly Livermore), which ironically the Navy doesn’t even want.[3] It is also the driving reason for unnecessary future production of more than 80 pits per year.
Jay Coghlan of Nuclear Watch commented,
“This Nuclear Posture Review does not even begin to meet our long-term need to eliminate the one class of weapons of mass destruction that can truly destroy our country. It will instead set back nonproliferation and arms control efforts across the globe, and further hollow out our country by diverting yet more huge sums of money to the usual fat defense contractors at the expense of public education, environmental protection, natural disaster recovery, etc. Under the Trump Administration, expect medicare and social security to be attacked to help pay for a false sense of military security, and this Nuclear Posture Review is part and parcel of that.”
# #
[1] Since then the U.S. has reportedly used strong arm tactics to discourage individual countries from ratifying the nuclear weapons ban treaty. See http://www.businessinsider.com/mattis-threatened-sweden-over-a-nuclear-weapons-ban-treaty-2017-9
[2] This was explicitly stated in a Department of Defense follow-on to the 2010 Nuclear Posture Review (NPR). It states: “The new guidance requires the United States to maintain significant counterforce capabilities against potential adversaries. The new guidance does not rely on a “counter-value’ or “minimum deterrence” strategy.”
Report on Nuclear Implementation Strategy of the United States Specified in Section 491 of 10. U.S.C., Department of Defense, June 2013, page 4 (quotation marks in the original), http://www.globalsecurity.org/wmd/library/policy/dod/us-nuclear-employment-strategy.pdf
[3] See https://nukewatch.org/importantdocs/resources/Navy-Memo-W87W88.pdf
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.