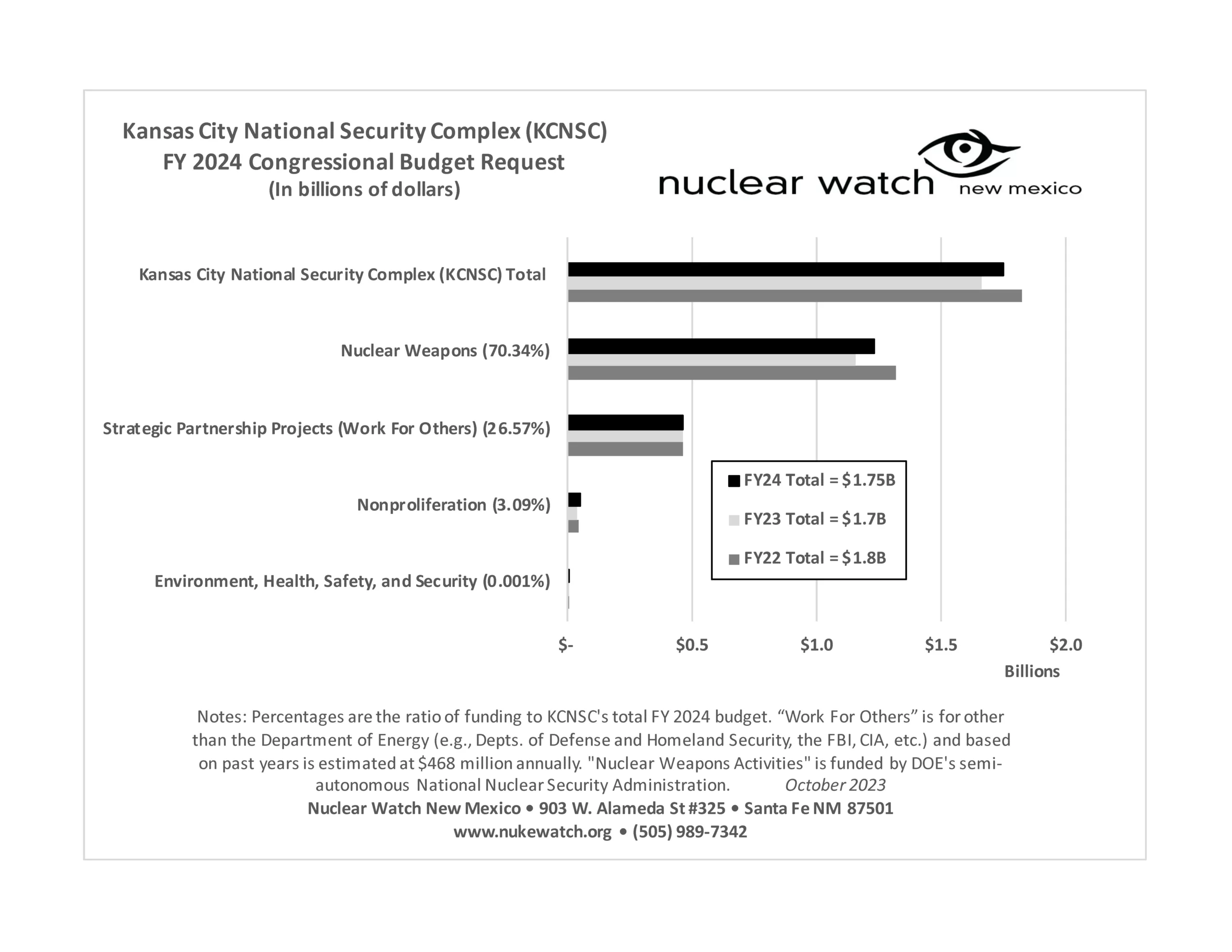
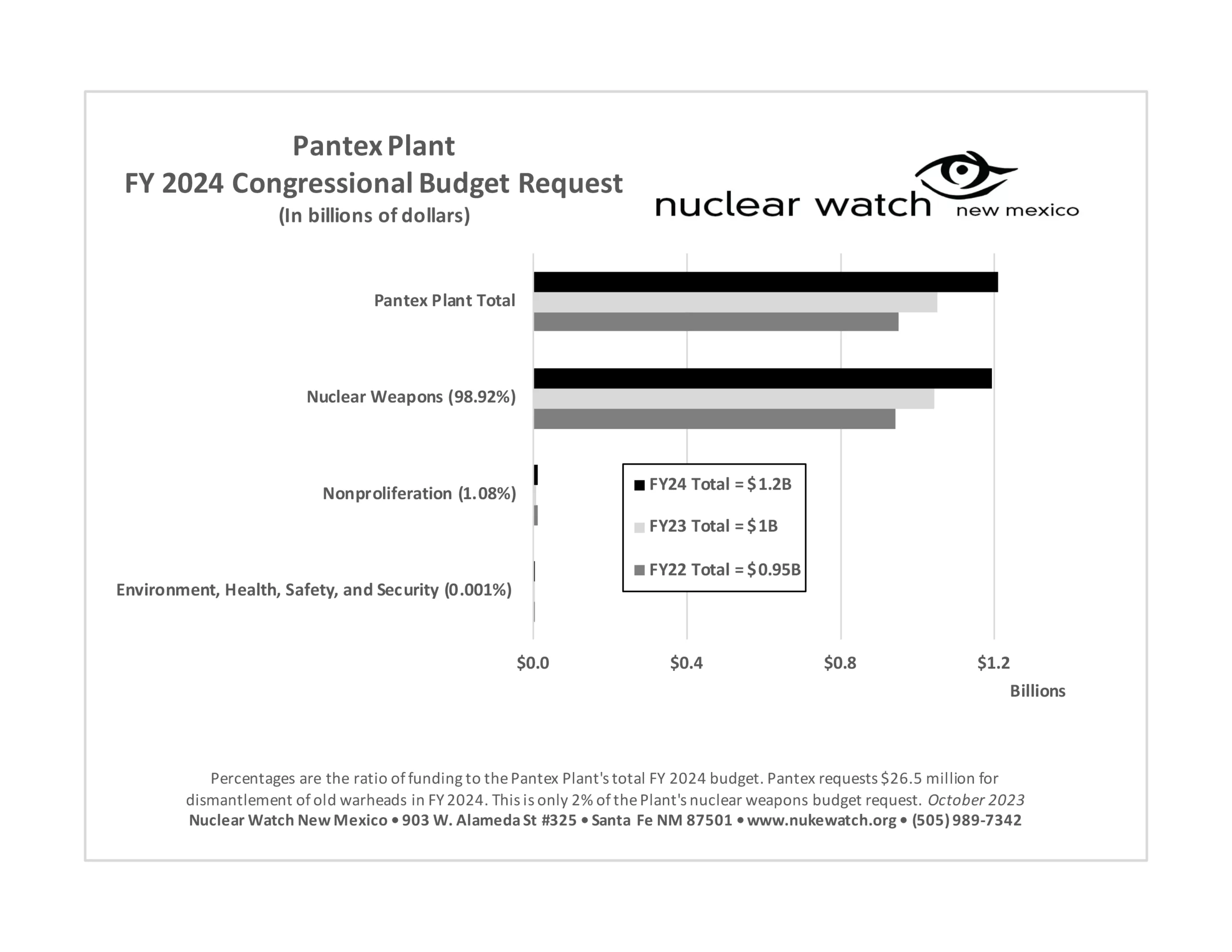
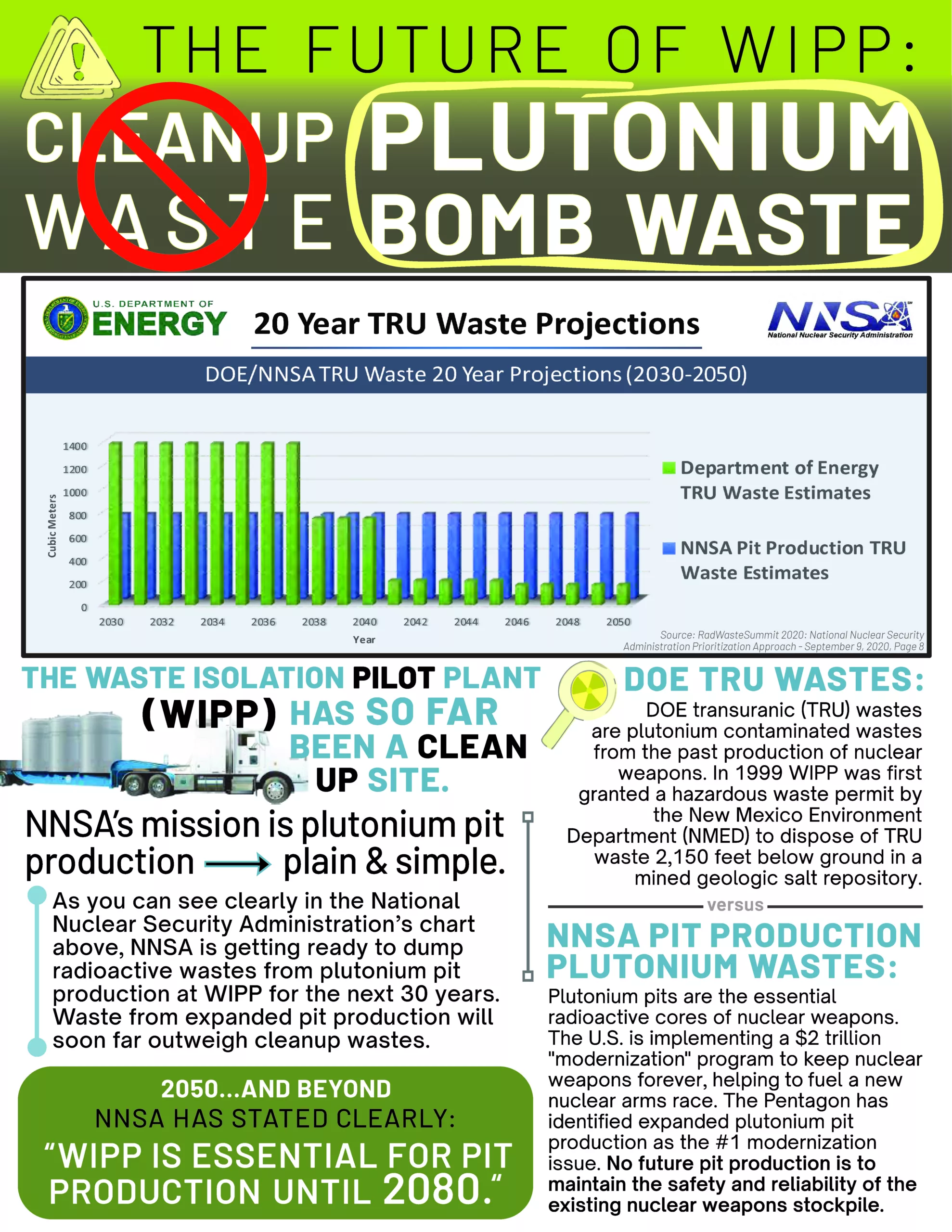
Source/Reference Documents
Map Spreadsheet Examples 2021-2023
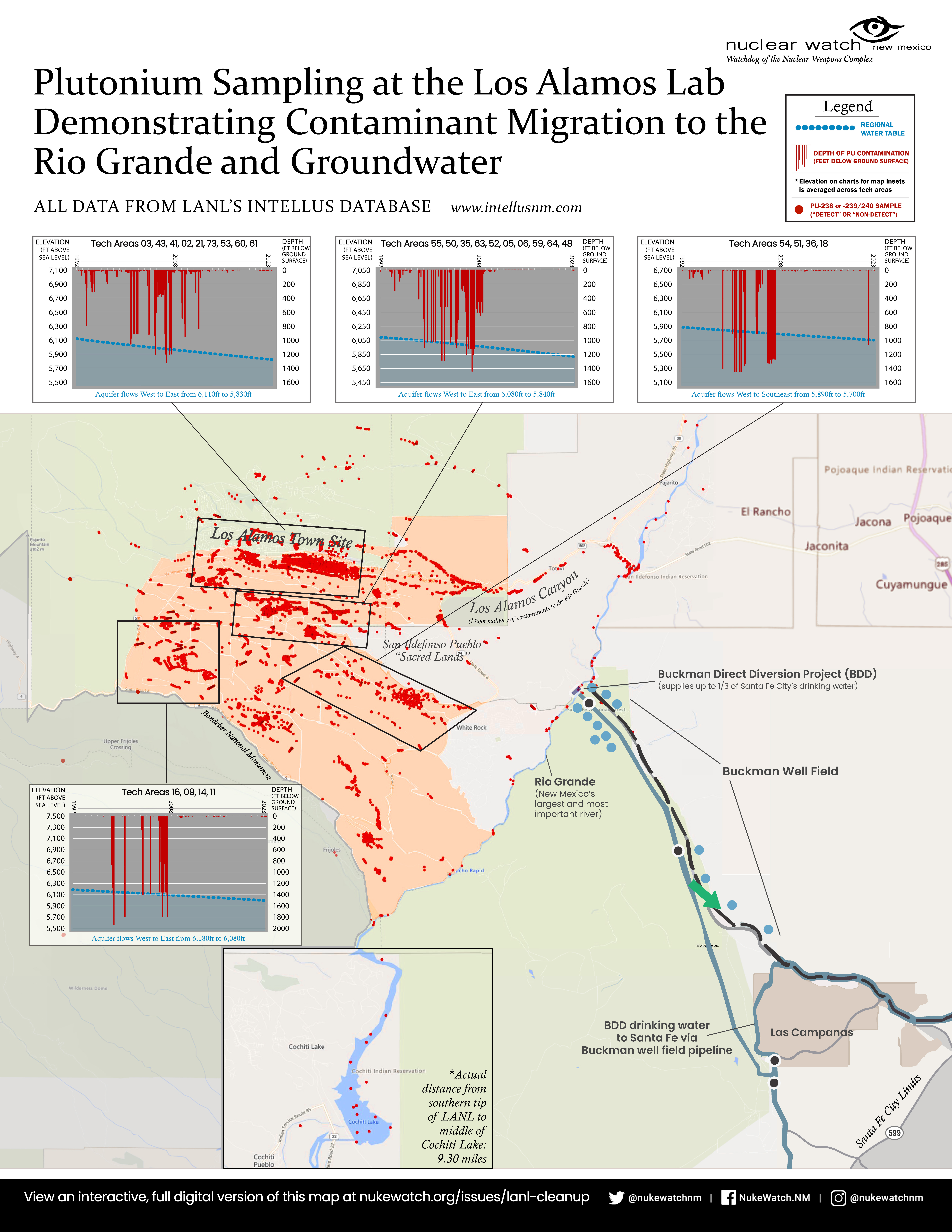
Below are examples of a spreadsheets created in Intellus, which is the environmental database at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The requests were for all soil and groundwater samples taken in, under, and around the Lab in 2021, 2022, and 2023. The spreadsheets were then sorted by “Report Result” (Column ‘F’), which lists the plutonium found in samples in descending order. It shows the highest sample for each year at top of the column.
Looking at the 2021 spreadsheet, there were 2043 samples analyzed for plutonium taken in 2021. There are approximately 100 detects including the high sample of 10100 pCi/g. Please read Dr. Ketterer’s report for a discussion of the ‘detects’ and ‘non-detects.’
Notice the latitude and longitude for each sample (columns ‘O’ and ‘P’). We used these coordinates to create the maps.
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
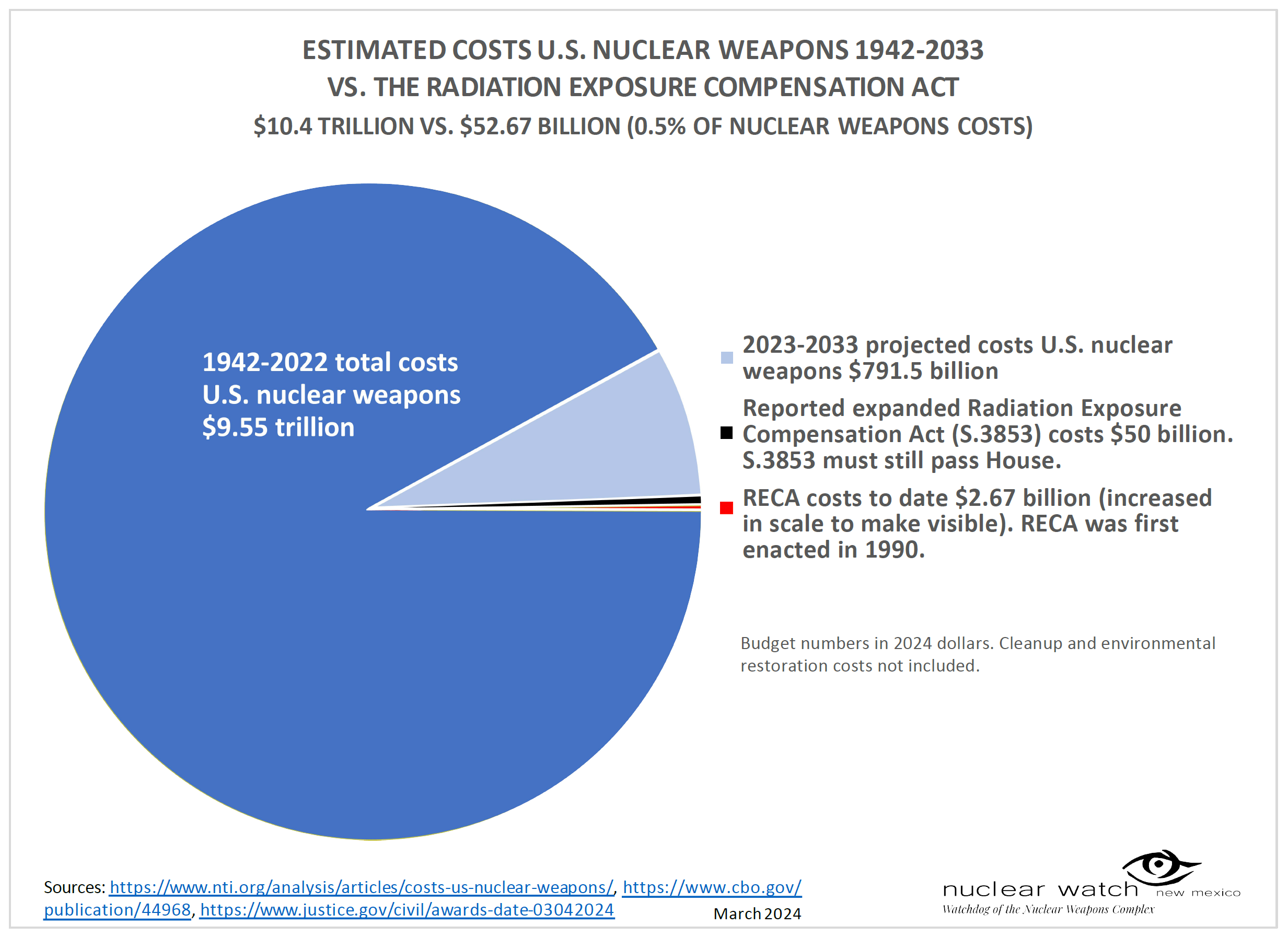
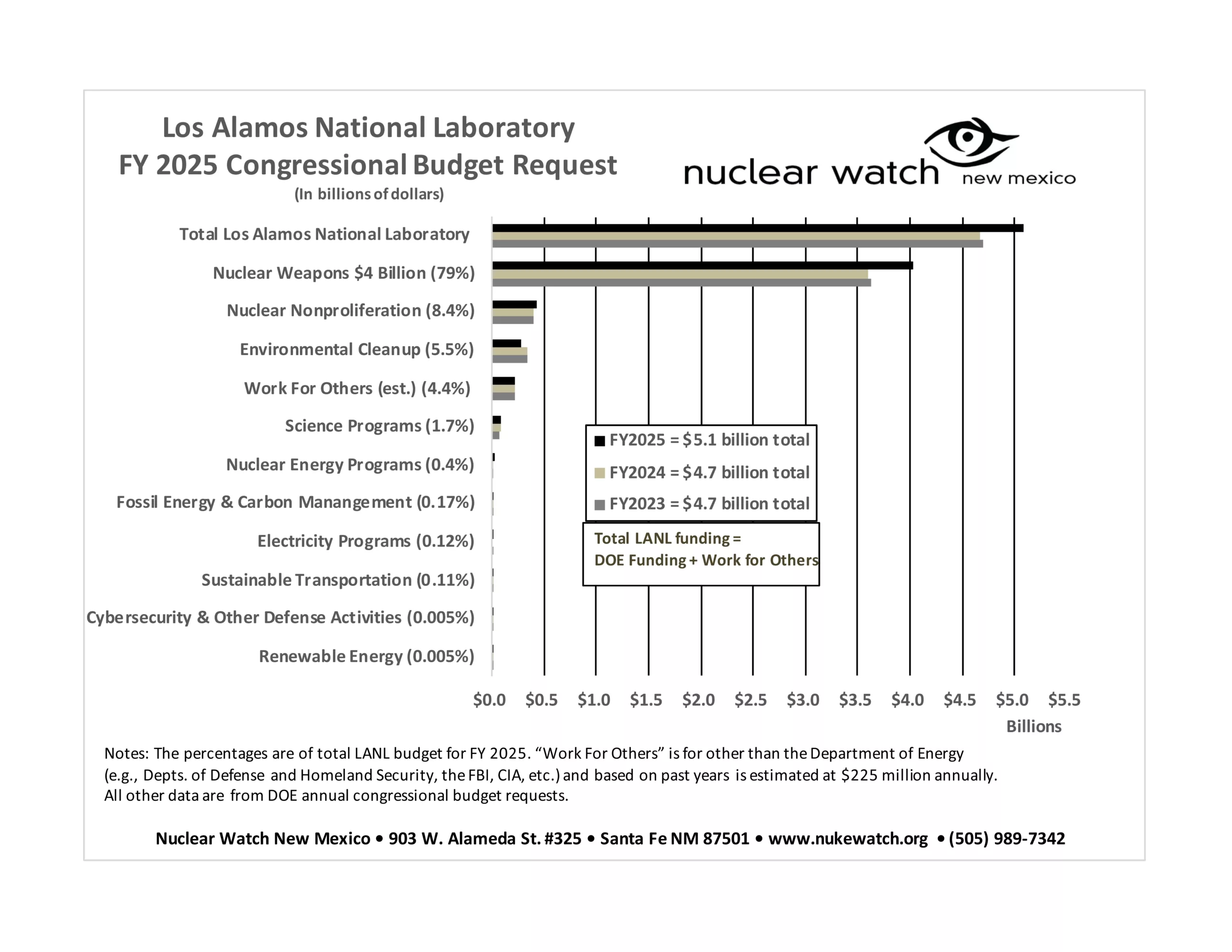
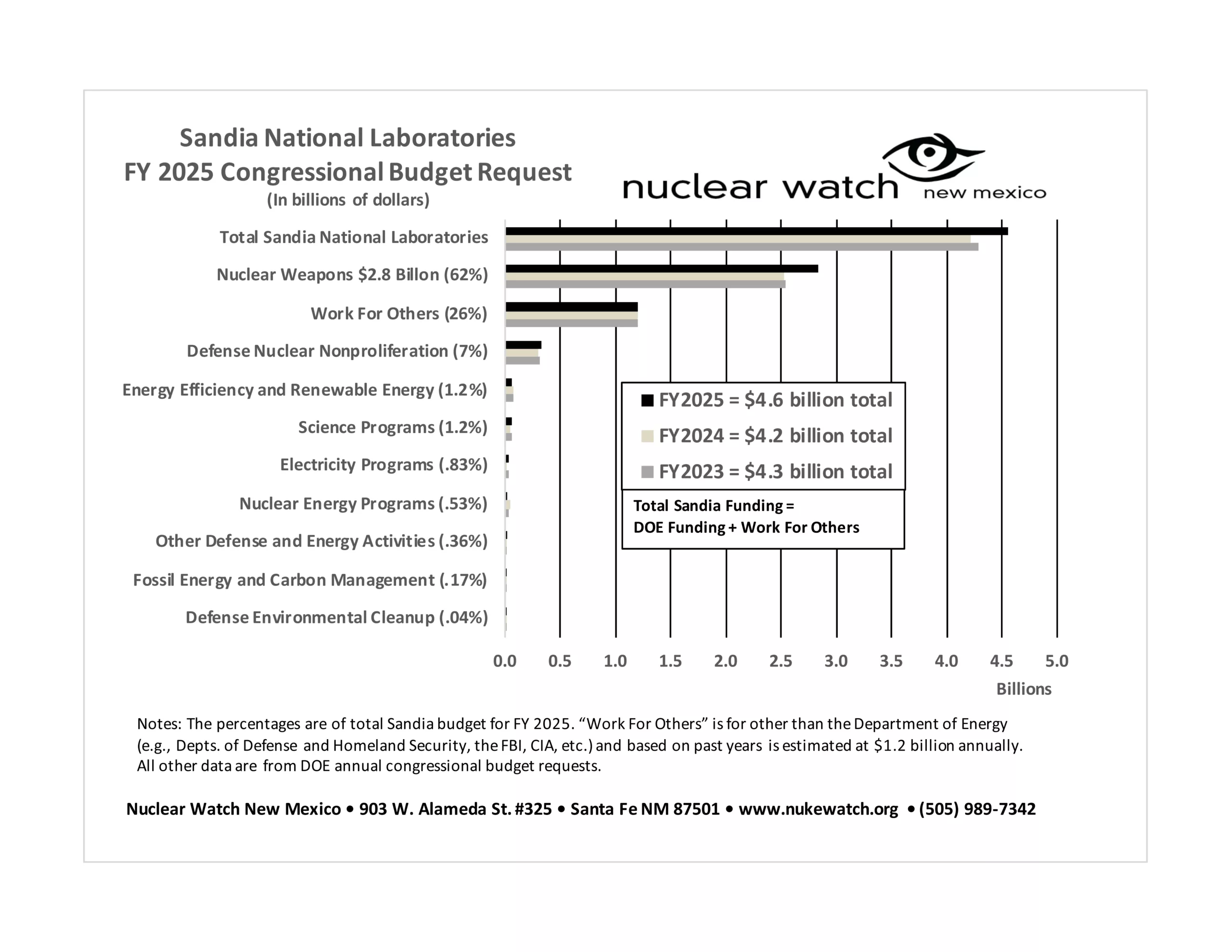
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New & Updated
Rep. Smith presses Biden to audit pit production as Nuclear Posture Review progresses
Smith in his Monday missive warned a bevy of NNSA endeavors, like pit production and the Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility before it, “have seen massive cost increases, schedule delays, and cancellations of billion-dollar programs. This must end.” Two things, Smith wrote, are vital to the successful modernization of U.S. nuclear weapons: affordability and executability.
By Colin Demarest [email protected]
The chairman of the House Armed Services Committee on Monday urged President Joe Biden to include an audit of plutonium pit production plans and costs in his administration’s broader assessment of U.S. nuclear policy and capabilities.
Writing about the Pentagon’s Nuclear Posture Review, Rep. Adam Smith pressed the president to closely examine pit production — the crafting of nuclear weapon cores, namely in South Carolina and New Mexico — and to “ensure it is both necessary and achievable within the announced cost and schedule.”
“As we near the budgetary heights of the ‘nuclear modernization mountain’ we can ill afford further delays and cost overruns,” wrote the Washington Democrat, who time and again has expressed reservations about pit production in the Palmetto State. He continued: “It is simply acknowledging reality that we must make hard choices.”
Federal law mandates production of 80 plutonium pits per year by 2030 — a rate and date motivated by military demand.
But while National Nuclear Security Administration officials believe production benchmarks in 2024, 2025 and 2026 can be met in New Mexico, at Los Alamos National Laboratory, they do not think a 2030 production target in South Carolina, at the Savannah River Site, is achievable.
Hiroshima and Nagasaki Remembered
We must speak out and call for action, to ensure that the horrific events witnessed in Hiroshima and Nagasaki are never repeated
BY: Chris McDonnell | United Kingdom

It was just after breakfast time on August 6, 1945 when a single B29 super fortress bomber plane of the US Air Force appeared in the clear blue sky above the Japanese city of Hiroshima.
It was about to unleash the most destructive weapon of war yet developed by mankind on the unsuspecting population going about their business in the streets below.
Piloted by Paul Tibbets, the B29 bore the name of his mother on its fuselage nosecone — Enola Gay. Its payload bomb known as Little Boy was the result of years of nuclear research in the United States under the code name of the Manhattan Project. It was the start of the Atomic Age.
In the middle of July the first experimental atomic weapon was detonated at the Alamogordo test range in New Mexico. It created a crater 300 metres in width. It was ironically given the code name “Trinity”. The scene was set for the first use of nuclear weapons in the theatre of war.
Preparations went ahead on the Pacific island of Tinian for the first attack, the city of Hiroshima, with a population well over a quarter of a million people, the designated target.
The bomb was released over the city at 8.15 am that Monday morning and exploded at an altitude of just under 2,000 feet.
The blast equivalent was estimated to be the equivalent of 13 kilotons of TNT, destroying an area of just under 5 square miles. It is likely that 90,000 people lost their lives…
Report: Some Los Alamos nuclear waste too hazardous to move
“In the October report, the safety board said lab personnel had failed to analyze chemicals present in hundreds of containers of transuranic nuclear waste, making it possible for incompatible chemicals to cause a container to explode. Crews also never sufficiently estimated how much radiation would be released by such an event.”
BY: Scott Wyland [email protected] August 2, 2021
Los Alamos National Laboratory has identified 45 barrels of radioactive waste so potentially explosive — due to being mixed with incompatible chemicals — that crews have been told not to move them and instead block off the area around the containers, according to a government watchdog’s report.
Crews have worked to ferret out drums containing volatile compounds and move them to a more secure domed area of the lab after the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board issued a scathing report last year saying there were possibly hundreds of barrels of unstable nuclear waste.
The safety board estimated an exploding waste canister could expose workers to 760 rem, far beyond the threshold of a lethal dose. A rem is a unit used to measure radiation exposure. In its latest weekly report, the safety board said crews at Newport News Nuclear BWXT Los Alamos, also known as N3B — the contractor in charge of cleaning up the lab’s legacy waste — have pegged 60 barrels with volatile mixtures and have relocated 15 drums to the domed area.
Energy Department: Cap rather than clean up Los Alamos lab waste site
A watchdog group called the plan an attempt to save money without considering the potential long-term hazards of keeping highly toxic, slow-decaying waste buried in unlined pits roughly 1,000 feet above a vital groundwater source.
“The aquifer — that’s our main concern,” said Scott Kovac, research and operations director for the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico. “If climate change does affect us and things start drying out, then our aquifer is going to be even more important than it already is. We have to do everything to protect our aquifer that we can.”
Scott Wyland [email protected] | Santa Fe New Mexican July 31, 2021

New Mexican file photo
One of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s older nuclear waste disposal sites — a Cold War relic — would be capped and covered rather than cleaned up under a plan put forth by federal officials.
Known as Area C, the 73-year-old dumpsite was shut down in 1974 after taking radioactive waste, caustic chemicals, treatment-plant sludge and a variety of trash, according to records.
U.S. Department of Energy officials propose installing a 2-foot-thick, dirt-and-rock cover they say will safely contain the waste, prevent toxins from leaching into soil and groundwater, and avoid the hazards that excavating the waste would pose to workers and the environment. It also would save hundreds of millions of dollars.
Waste Isolation Pilot Plant needs more space to dispose of nuclear waste, officials say
“..A 10-year renewal of the permit itself was underway after expiring last year and Don Hancock, nuclear waste program manager at watchdog group Southwest Research and Information Center said any modifications to the permit should be included in the full renewal or wait until after its approval.
He said the DOE aimed to “piecemeal” an expansion of WIPP operations and its lifetime to avoid a discussion on broadening the facility’s purpose and keeping it operational indefinitely.
The current permit called for WIPP to be closed by 2024, but officials speculated it could take as long as until 2050 to complete its mission.”
BY: Adrian Hedden Carlsbad Current-Argus
More underground space is needed to complete the mission at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant to dispose of nuclear waste, contend WIPP officials during a Monday public meeting.
The U.S. Department of Energy was underway with a permit modification request (PMR) that would amend the DOE’s permit with the State of New Mexico to allow for the mining of two new panels where waste would be disposed of along with drifts connecting the panels to the rest of the underground repository.
At WIPP, transuranic (TRU) nuclear waste consisting of clothing items and equipment irradiated during nuclear activities at DOE sites across the country is disposed of via burying in an underground salt deposit.
To achieve this, panels consisting of seven rooms each are mined about 2,000 feet underground where drums of the waste are emplaced, and the salt gradually collapses to permanently entomb the waste.
But due maintenance issues and a three-year shutdown of underground operations in 2014 following an accidental radiological release, portions of three of panels were left unusable and the DOE hoped to mine new panels to finishing burying the waste.
America’s Nuclear Waste Has Nowhere to Go and More Is Coming
“Nuclear power isn’t a silver bullet for our climate problems and there’s a host of issues with constructing new plants. The biggest of which is what to do with the waste. One of the most frequently proposed long term solutions is a geologic repository, a specially designed hole in the ground with thick barriers where large amounts of toxic waste can slowly degrade over hundreds of years.
The problem is that no one can ever agree on where to build a giant and expensive hole to dump nuclear waste that will render the site unusable for generations.”
BY Matthew Gault VICE News

Outside the sleepy Maine town of Wiscasset (population 3,700), armed guards patrol a slab of concrete surrounded by a chain link fence. On the slab is 60 cement and steel canisters containing 550 tons of nuclear waste with nowhere to go according to the Bangor Daily News.
It’s a problem across the country. Nuclear power plants produce waste that’s stored on site in what’s billed as a temporary solution. After decades of promising to move the waste, the Department of Energy (DOE) hasn’t found a more permanent solution. And now, the Pentagon is moving forward with plans to increase the production of plutonium pits, a core component of nuclear weapons, which will produce more highly toxic and radioactive waste.
Nuclear power is incredibly efficient and produces little carbon. A move towards a world based on nuclear power would dramatically cut down on emissions that lead to climate change. But nuclear power produces nuclear waste, a variety of highly toxic substances that will take hundreds of years to become inert.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.