Source/Reference Documents
Map Spreadsheet Examples 2021-2023
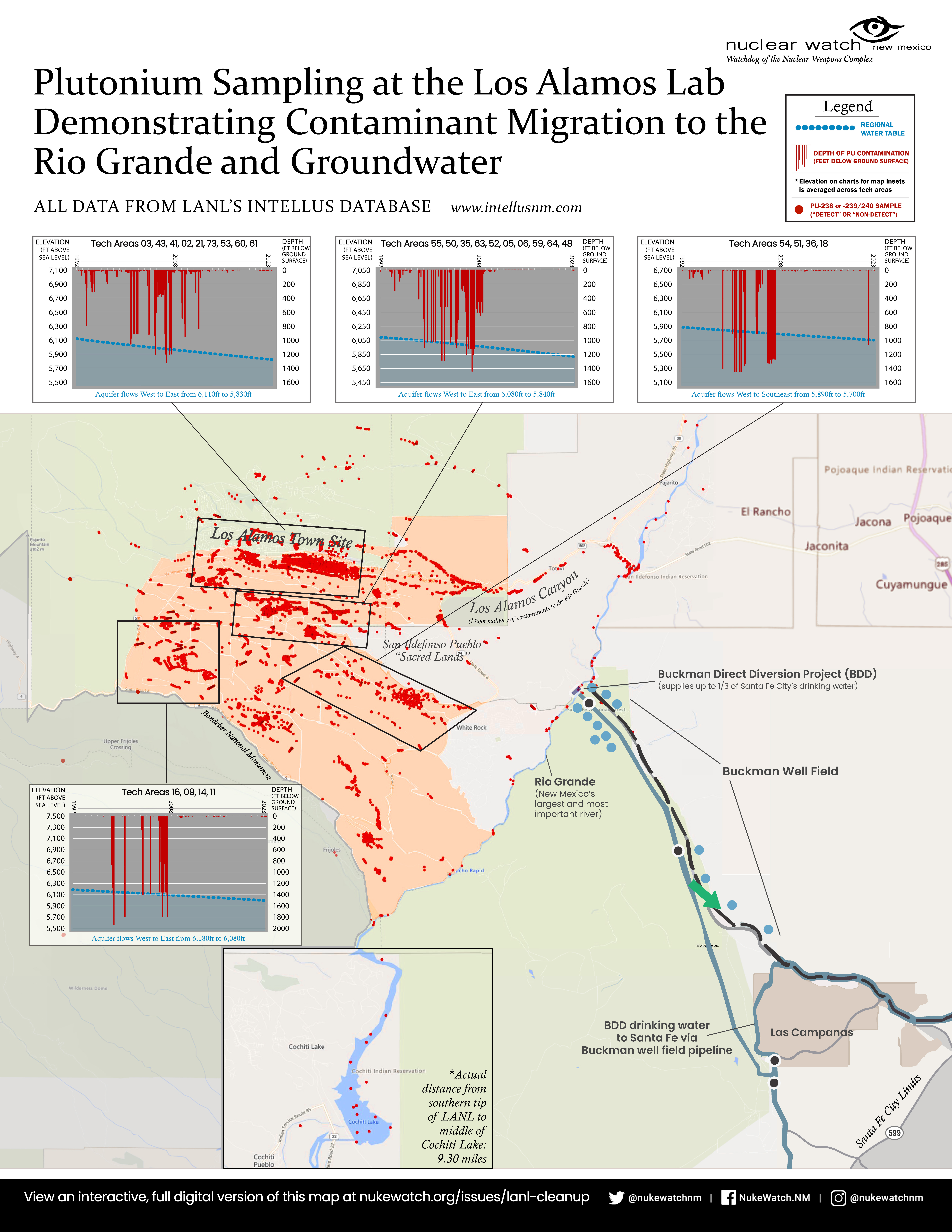
Below are examples of a spreadsheets created in Intellus, which is the environmental database at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The requests were for all soil and groundwater samples taken in, under, and around the Lab in 2021, 2022, and 2023. The spreadsheets were then sorted by “Report Result” (Column ‘F’), which lists the plutonium found in samples in descending order. It shows the highest sample for each year at top of the column.
Looking at the 2021 spreadsheet, there were 2043 samples analyzed for plutonium taken in 2021. There are approximately 100 detects including the high sample of 10100 pCi/g. Please read Dr. Ketterer’s report for a discussion of the ‘detects’ and ‘non-detects.’
Notice the latitude and longitude for each sample (columns ‘O’ and ‘P’). We used these coordinates to create the maps.
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New & Updated
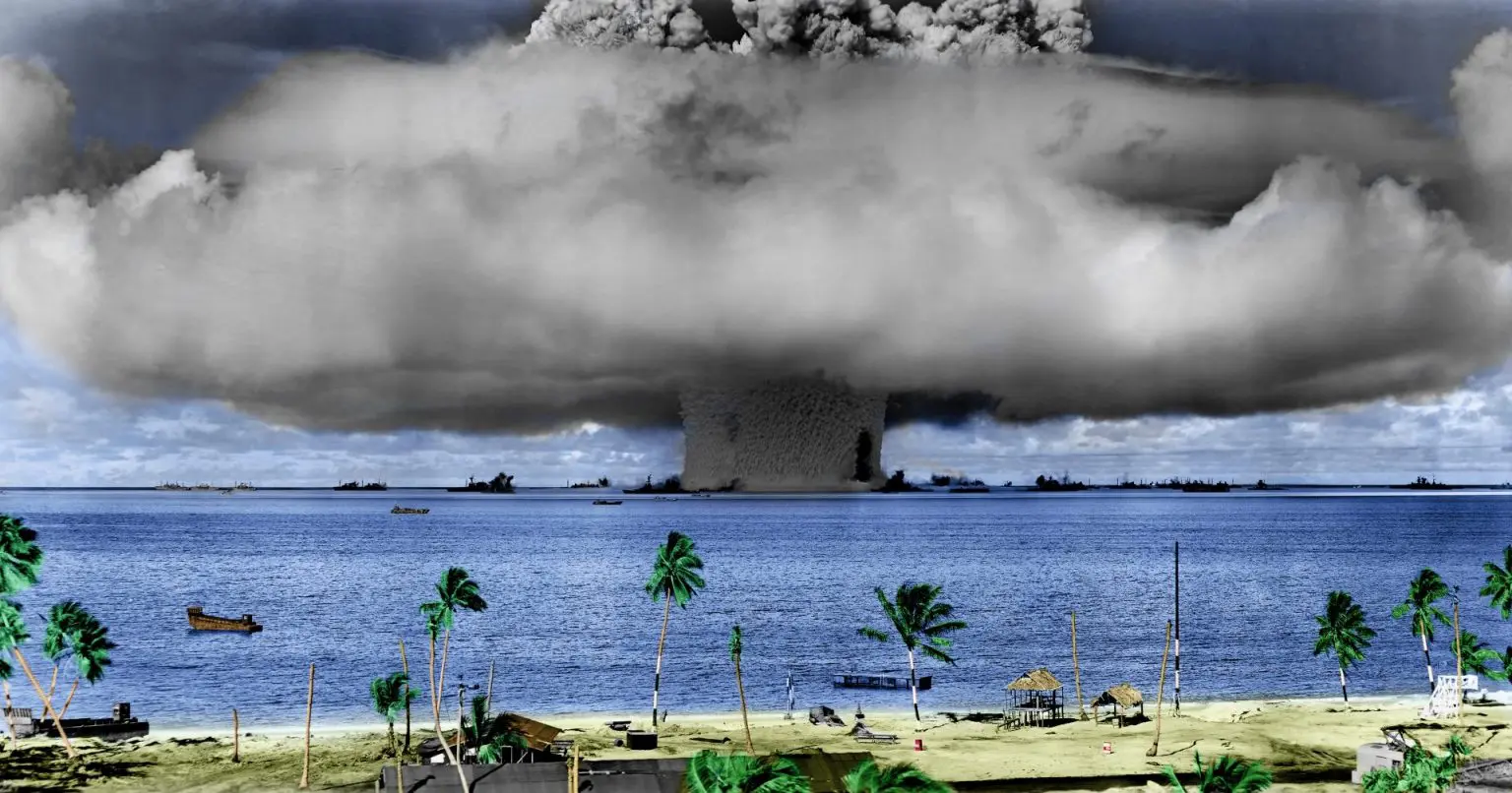
After 75 years, it’s time to clean Bikini
“It is time, finally, to recognize and right the wrongs perpetrated by the US government in the Marshall Islands. The US forced a new and dangerous technology on the native lands and peoples, without fully comprehending the short- and long-term consequences.”

BY: Hart Rapaport, Ivana Nikolić Hughes | thebulletin.org March 9, 2021
Due to their remote location in the Northern Marshall Islands, the people of Bikini Atoll were spared the worst of the mid-Pacific fighting between the American and Japanese armies in the final years of World War II. Their millennia-old culture and sustainable way of life ended abruptly when, in early 1946, Commodore Ben Wyatt, a representative of the occupying United States Navy, informed King Juda and other Bikini residents that the US would begin to test nuclear weapons near their homes. Wyatt asked the Bikinians to move elsewhere, stating that the temporary move was for “the good of mankind and to end all wars.” Though Wyatt may have believed his words to be true, the show of might by the US that followed neither ended all conflict, nor was the exodus short-lived. Seventy-five years later, Bikinians have yet to return.
Continue reading
Can the Energy Department store 50 tons of weapons-grade plutonium for 10,000 years?
Safely ridding the nation of one of the world’s largest excess stockpiles of weapons-grade plutonium will be no minor feat. At issue is the US Energy Department’s 2016 decision to dilute and dispose of, all told, about 48.2 metric tons of plutonium, including 26.2 tons of components, known as “pits,” from several thousand dismantled thermonuclear warheads and 22 metric tons in other forms…If one gram of soil contains as little as 1.587 micrograms of plutonium, the Energy Department is required by federal standards to geologically isolate it from the environment for at least 10,000 years at WIPP.
By: Robert Alvarez | March 8, 2021 | thebulletin.com

The nuclear age is undergoing a paradigm shift. During much of the latter half of the past century, the nuclear enterprise was ascendant; now, it has entered a period of decline and uncertain long-term custodianship. This reversal of fortune is especially apparent in the United States’ efforts to rid itself of its unwanted reserves of plutonium. It’s been more than 75 years since a blinding flash lit up the pre-dawn sky at Alamogordo in the Chihuahua Desert of New Mexico. On July 16, 1945, a single gram of the grapefruit-size sphere of plutonium at the center of the world’s first nuclear explosion released three times the destructive force of the largest conventional bomb used during World War II. [1]
Thereafter, the United States government built a grossly oversized nuclear arsenal and never envisioned having to stop building it. Between 1944 and 1994, the Energy Department and its predecessors produced 99.5 metric tons of plutonium for use in an estimated 70,000 nuclear weapons. (An additional 11 tons were produced or acquired for research and development purposes.)
This Is How the Biggest Arms Manufacturers Steer Millions to Influence US Policy
Five of the nation’s biggest defense contractors — Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies and General Dynamics — spent a combined $60 million in 2020 to influence policy, according to a new report from the Center for Responsive Politics.
By: Stephen Losey | military.com 7 Mar 2021
The paper, “Capitalizing on conflict: How defense contractors and foreign nations lobby for arms sales,” details how a network of lobbyists and donors steered $285 million in campaign contributions and $2.5 billion in lobbying spending over the last two decades, as well as hiring more than 200 lobbyists who previously worked in government.
The amount of money at stake is immense, both at home and abroad, the center states on its website, OpenSecrets.org. Not only is a significant portion of the Pentagon’s $740 billion annual budget spent on weapons, the report explains, but American defense firms agreed to sell $175 billion in weapons to other countries over the last year. That includes deals to sell $23 billion in F-35 Joint Strike Fighters and drones to the United Arab Emirates, and billions more in sales to Taiwan and Saudi Arabia, it adds.
The practice appears unlikely to change significantly under the Biden administration.
Celebrating International Women’s Day 2021 #ChooseToChallenge

Today, as thousands of nuclear weapons remain in unchecked control by only a few men in power, Ploughshares Fund continues to #ChooseToChallenge – the false assumptions, unfair gender biases, as well as the systematic racism that legitimize and normalize dangerously outdated nuclear weapons policies.
A Decade Later: Human Suffering and Failures of Fukushima
Fukushima Daiichi 2011-2021
By: beyondnuclearinternational March 7, 2021

The decontamination myth and a decade of human rights violations
The following is the Executive Summary from the new Greenpeace report. Download the full report.
As a result of a catastrophic triple reactor meltdown at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant on 11 March 2011, several tens of thousands of square kilometres in Fukushima Prefecture and wider Japan were contaminated with significant amounts of radioactive caesium and other radionuclides. The first Greenpeace radiation expert team arrived in Fukushima on 26 March 2011, and Greenpeace experts have since conducted 32 investigations into the radiological consequences of the disaster, the most recent in November 2020.
This report, the latest in a series, chronicles some of our principal findings over recent years, and shows how the government of Japan, largely under prime minister Shinzo Abe, has attempted to deceive the Japanese people by misrepresenting the effectiveness of the decontamination programme as well as the overall radiological risks in Fukushima Prefecture. As the latest Greenpeace surveys demonstrate, the contamination remains and is widespread, and is still a very real threat to long term human health and the environment.
Department of Energy, nuclear oversight agency on ‘high-risk’ list
“This is more than just chronic behavior — it’s like institutionalized bad management,” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
By: Scott Wyland [email protected] | santafenewmexican.com March 3, 2021
The U.S. Department of Energy and its agency overseeing the nation’s nuclear weapons program have serious enough problems with managing contractors and projects — including for nuclear waste cleanup — that they made a government watchdog’s “high-risk” list again this year.
Both the Energy Department and its branch known as the National Nuclear Security Administration have made some progress in how they manage personnel, facilities and waste disposal, but they still are deficient in key areas, the Government Accountability Office said in its biannual high-risk report.
The report lists programs and operations that are high-risk due to their vulnerabilities to fraud, waste, abuse and mismanagement — and some require an overhaul.
The GAO issues the reports at the start of each new session of Congress. They have led to more than $575 billion in cost benefits to the federal government in the past 15 years, the GAO said.
Santa Fe councilors question LANL coalition membership
BY: Kyle Land /
What’s the actual benefit to the city?
That was the question Santa Fe city councilors debated Monday as they considered the city’s membership in the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities.
At the center of it all was a revised Joint Powers Agreement for the coalition, which officials hope will solve some of the group’s long-standing organizational issues.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.