QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
Nuclear Watch Interactive Map – U.S. Nuclear Weapons Complex
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
2022 BLOG POSTS
What’s the Current Status of U.S. and Russian Nuclear Weapons? How Many Exist and Just How Powerful Are They?
The interest in this question has gone up immensely over the past 50 days, since Russia first invaded Ukraine on February 24, and since Russian President Vladimir Putin announced that his country’s nuclear forces had been placed on “high alert” just a few days later on the 27th.
In 1986, there were 70,000 nuclear weapons on the planet—an entirely terrifying number. Nuclear weapons analysts estimate that the world’s nine nuclear states—China, France, India, Israel, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States—have around 13,000 nuclear warheads in total today (Arms Control Association). That build-down started when U.S. President Ronald Reagan and Mikhail Gorbachev, former president of the Soviet Union, agreed under the INF Treaty on the Soviet Union destroying 889 of its intermediate-range missiles and 957 shorter-range missiles, and the U.S. destroying 677 and 169 respectively (Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists).
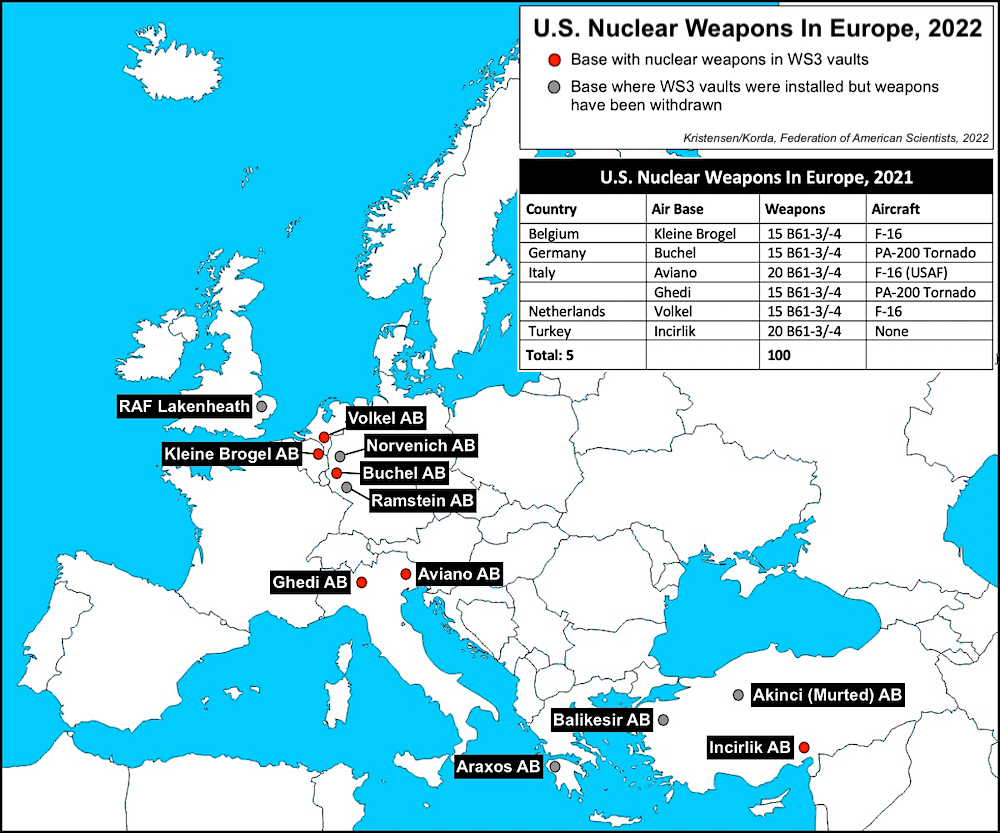
What are the specifics of where the remaining nuclear weapons possessed by the U.S. and Russia are located? How powerful are they, and, most relevantly, what is the readiness levels of these weapons to launch?
HOW MANY WEAPONS IN THE UNITED STATES?
- WHAT ARE THE LIMITS? On April 8, 2010, the United States and Russia signed New START, a legally binding, verifiable agreement that limits each side to 1,550 strategic nuclear warheads deployed on 700 strategic delivery systems (ICBMs, SLBMs and heavy bombers) and limits deployed and nondeployed launchers to 800 (Arms Control Association).
- WHAT ARE THE ACTUAL NUMBERS? At the beginning of 2021, the U.S. maintained an estimated stockpile of approximately 3,800 nuclear warheads for delivery by 800 ballistic missiles and aircraft (Arms Control Association).
Millennials Memeing Nuclear War
 It seems like my generation has never before experienced this much nuclear fear. And what do we do with it? Laugh any way we can, for one. Putin has threatened the use of nuclear weapons by increasing Russia’s nuclear forces alertness levels and stating in a national address, “…For those who may be tempted to interfere in these developments from the outside, No matter who tries to stand in our way or all the more so create threats for our country and our people, they must know that Russia will respond immediately, and the consequences will be such as you have never seen in your entire history.”
It seems like my generation has never before experienced this much nuclear fear. And what do we do with it? Laugh any way we can, for one. Putin has threatened the use of nuclear weapons by increasing Russia’s nuclear forces alertness levels and stating in a national address, “…For those who may be tempted to interfere in these developments from the outside, No matter who tries to stand in our way or all the more so create threats for our country and our people, they must know that Russia will respond immediately, and the consequences will be such as you have never seen in your entire history.”
Nuclear simulations have come close to capturing the extra-short attention spans of millennials and gen-z, but there’s never been anything like the current real time situation that has ever put this much attention on the reality of the threat of nuclear weapons. And of course the only recourse for a heavy dose of reality is a flood of relevant comedy.
How are we Back Here…? Reflecting on the History of Nuclear Close Calls as Putin’s Threat Reignites Cold War Fears of Nuclear War
“Sadly, we are treading back through old historical patterns that we said that we would never permit to happen again,”
– Fiona Hill, Former Senior Director for Europe and Russia at the United States National Security Council, in an interview with POLITICO, today, February 28, 2022: ‘Yes, He Would’: Fiona Hill on Putin and Nukes
New & Updated
Plutonium Pit Production Programmatic EIS “Scoping” Comments
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: May 2025
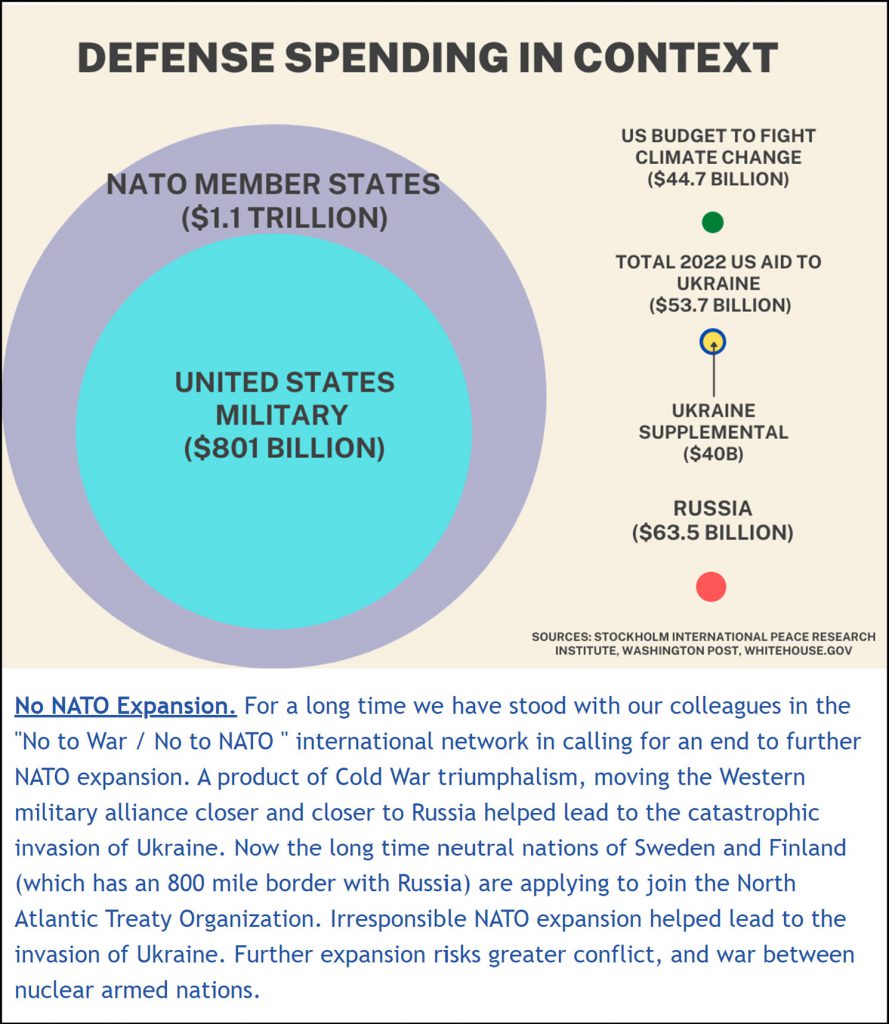
Nuclear Weapons Budget:
• Republicans are pushing for $1 trillion per year for military spending. The fiscal 2026 budget request calls for $892.6 billion in discretionary defense funding — same as FY 2025 (and a cut given inflation). But they are also seeking $119.3 billion through budget “reconciliation.”
• Congressional Budget Office “Projected Costs of U.S. Nuclear Forces, 2025 to 2034,” April 2025:
“Costs of Current Plans: If carried out, DoD’s and DOE’s plans to operate, sustain, and modernize current nuclear forces and purchase new forces would cost a total of $946 billion over the 2025–2034 period, or an average of about $95 billion a year, CBO estimates… CBO’s current estimate of costs for the 2025–2034 period is 25 percent (or $190 billion) larger than its 2023 estimate of $756 billion, which covered the 2023–2032 period.” https://www.cbo.gov/system/files/2025-04/61224-NuclearForces.pdf
Separately it was reported that the twelve new Columbia class submarines will cost $12 billion each, three times more than their projected cost in 2010 and is years behind schedule.
Nuclear Weapons Update:
Nuclear weapons and delivery systems would get an added $12.9 billion in the new reconciliation proposal. This includes $2 billion for sea-launched nuclear cruise missiles and $400 million for their warhead.
Accelerating Arms Race
• The current conflict between India and Pakistan is dangerous.
• 4-4-25 ExchangeMonitor: https://www.exchangemonitor.com/wrap-up-russias-modern-arsenal-and-nukes-in-ukraine-deputy-secretary-of-energy-hearing-rubio-japan-and-rok-in-brussels-more/
“Russia’s top commander in Ukraine Gen. Sergei Surovikin discussed using nuclear weapons to prevent Ukraine from advancing into Crimea in the fall of 2022, the New York Times said March 29. The Times cited U.S. intelligence reports…”
Lawsuit Compels Nationwide Public Review of Plutonium Bomb Core Production
AIKEN, S.C. — Today the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency within the Department of Energy, published a formal Notice of Intent in the Federal Register to complete a nationwide “programmatic environmental impact statement” on the expanded production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores. Pits are the essential radioactive triggers of modern nuclear weapons. The NNSA is aggressively seeking their expanded production for new-design nuclear weapons for the new nuclear arms race.
The South Carolina Environmental Law Project (SCELP) successfully represented the Gullah/Geechee Sea Island Coalition and Nuclear Watch New Mexico, Savannah River Site Watch and Tri-Valley Communities Against a Radioactive Environment in a legal challenge to NNSA’s attempt to improperly jump start dual site pit production. On September 30, 2024, United States District Court Judge Mary Geiger Lewis ruled that the NNSA had violated the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) by failing to properly consider alternatives before proceeding with its plan to produce at least 30 pits per year at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in New Mexico and at least 50 pits per year at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina.
Lawsuit Compels Nationwide Public Review of Plutonium Bomb Core Production
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, May 9, 2025
Media Contacts:
Ben Cunningham, Esquire, SCELP, 843-527-0078, ben@scelp.org
Queen Quet, Gullah/Geechee Sea Island Coalition, 843-838-1171, GullGeeCo@aol.com
Tom Clements, Savannah River Site Watch, 803-834-3084, tomclements329@cs.com
Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch New Mexico, 505-989-7342, jay@nukewatch.org
Scott Yundt, Tri-Valley CAREs, 925-443-7148, scott@trivalleycares.org
AIKEN, S.C. — Today the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency within the Department of Energy, published a formal Notice of Intent in the Federal Register to complete a nationwide “programmatic environmental impact statement” on the expanded production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores. Pits are the essential radioactive triggers of modern nuclear weapons. The NNSA is aggressively seeking their expanded production for new-design nuclear weapons for the new nuclear arms race.
The South Carolina Environmental Law Project (SCELP) successfully represented the Gullah/Geechee Sea Island Coalition and Nuclear Watch New Mexico, Savannah River Site Watch and Tri-Valley Communities Against a Radioactive Environment in a legal challenge to NNSA’s attempt to improperly jump start dual site pit production. On September 30, 2024, United States District Court Judge Mary Geiger Lewis ruled that the NNSA had violated the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) by failing to properly consider alternatives before proceeding with its plan to produce at least 30 pits per year at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in New Mexico and at least 50 pits per year at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina.
NNSA issues plans to assess pits environmental impact
“This programmatic environmental impact statement that we fought long and hard for empowers citizens to tell policy makers what they think about decisions being made in their name,” Jay Coghlan, from environmentalist group Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said Thursday in a press release by the plaintiffs of the case. “Let them know what you think about the $2 trillion ‘modernization’ program to keep nuclear weapons forever while domestic programs are gutted to pay for tax cuts for the rich.”
By ExchangeMonitor | May 9, 2025 exchangemonitor.com
On the heels of a federal judge’s ruling last fall, the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration formally announced plans Friday for a detailed review of environmental impacts of planned plutonium pit production.
DOE’s semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) announced in the Federal Register it is kicking off a programmatic environmental impact statement EIS to ensure that large-scale pit production will comply with the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA).
According to the Federal Register notice, NNSA will hold public meetings and public hearings as part of the process.
Two online public scoping meetings are now scheduled for May 27 and May 28. The May 27 session would commence at 5 p.m. Eastern Time while the May 28 one is scheduled to start at 7 p.m. Eastern. Both can be accessed online or by phone. Details can be found in the Federal Register notice.
A federal district judge ruled last September that DOE and NNSA did not adequately analyze the environmental effects of producing the radioactive cores that trigger nuclear weapons in two different states, but declined to put the pit program, including construction of the Savannah River Plutonium Processing Facility at Aiken, S.C.’s Savannah River Site on hold as a result. In January, the federal government and the plaintiffs, consisting of environmentalists, settled the lawsuit and agreed to leave Los Alamos National Laboratory as the sole pit factory until NNSA completes a nationwide, NEPA-compliant programmatic EIS.Continue reading
US nuclear firm ‘utterly crucial’ to national security expands East Tennessee operations
“Which company produces uranium fuel for U.S. Navy nuclear reactors and manages the only plant where the government disassembles atomic warheads? What about the company helping NASA to develop a nuclear rocket, all while building small modular reactors and developing a pilot plant to restart uranium enrichment for the military?”
By Daniel Dassow, Knoxville News Sentinel | May 5, 2025 newsbreak.com
It’s all the same answer: BWX Technologies , the $2.7 billion juggernaut better known as BWXT has embedded itself in every kind of nuclear project imaginable with a strong and growing presence in East Tennessee, where 1,100 employees at its Nuclear Fuel Services plant in Erwin “downblend” bomb-grade uranium. The facility also creates fuel for the nuclear reactors aboard U.S. Navy submarines and aircraft carriers.
The region is even more important to BWXT after it bought a specialized facility in Jonesborough and 97 acres in Oak Ridge for a centrifuge enrichment project the company says will create hundreds of jobs through millions of dollars in investments.
“We have availed ourselves as a key player in just about every interesting nuclear opportunity that you can think of,” BWXT President and CEO Rex Geveden told Knox News. “We’re all over it.”
BWXT is part of the team led by the Tennessee Valley Authority to build the first small modular nuclear reactors in the U.S. at the federal utility’s Clinch River Nuclear Site in Oak Ridge .
It will manufacture the reactor pressure vessel, the largest component of the 300-megawatt reactor designed by GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy , for small modular reactors in the U.S. and Canada.
Curb the Skyrocketing Cost of U.S. Nuclear Modernization
“Since Russia and the United States agreed 15 years ago to modest nuclear reductions under the New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START), they also have embarked on extraordinarily expensive campaigns to replace and modernize every component of their respective nuclear arsenals to maintain force levels and provide the option to build up.”
By Daryl G. Kimball, Arms Control Today | May 1, 2025 newsbreak.com

At the same time, their leaders have failed to resolve disputes about existing treaties or launch new negotiations to limit or further cut their deadly arsenals below the New START ceiling of 1,550 deployed nuclear warheads and 700 strategic missiles and bombers each.
In 2018, shortly after he withdrew the United States from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty, U.S. President Donald Trump foolishly bragged about the nuclear stockpile that “until people come to their senses, we will build it up. It’s a threat to whoever you want, and it includes China, and it includes Russia, and it includes anybody else that wants to play that game.”
China has responded to U.S. nuclear and conventional military plans by pursuing a buildup of its historically “minimal” nuclear force to ensure that it retains an assured “second strike” capability. Russia has continued to develop new types of intermediate range missiles, as well as some new and exotic strategic systems designed to bypass U.S. missile defense capabilities.
Successive presidential administrations and congresses have failed to seriously consider alternatives that would have reduced costs and still maintained a devastating nuclear force.
Now, the cost of the U.S. nuclear modernization program is skyrocketing even further, siphoning resources from other more pressing human needs and national security priorities.
In April, the Congressional Budget Office issued its latest 10-year cost projection of the departments of Defense and Energy plans to operate, sustain, and modernize existing U.S. nuclear forces and purchase new forces: a total of $946 billion in the 2025-2034 period, or about $95 billion per year.
This new estimate is 25 percent, or $190 billion, greater than the last CBO estimate of $756 billion, which covered the 2023-2032 period. Incredibly, the $946 billion estimate does not include all of the likely cost growth of the new Sentinel intercontinental ballistic missile program, which the Pentagon acknowledged in July 2024 would cost 81 percent, or $63 billion, more than the program’s baseline estimate of $78 billion, generated in 2020.
Find Out the Facts & Sign the Petition: Why NMED Should Deny LANL’s Request for Tritium Releases
Why NMED Should Deny LANL’s Request for Tritium Releases
The Los Alamos National Laboratory plans to begin large releases of radioactive tritium gas any time after June 2, 2025. The only roadblock to the Lab’s plans is that it needs a “Temporary Authorization” from the New Mexico Environment Department to do so.
Reasons why NMED should deny LANL’s request are:
- The state Environment Department has a duty to protect the New Mexican As it states, “Our mission is to protect and restore the environment and to foster a healthy and prosperous New Mexico for present and future generations.” 1
- Why the rush? LANL explicitly admits there is no urgency. According to the Lab’s publicly-released “Questions and Answers” in response to “What is the urgency for this project?”
“There is no urgency for this project beyond the broader mission goals to reduce onsite waste liabilities.” 2
-
- In addition, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) admits that the end time frame for action is 2028, not 2025.3 Therefore, there is time for deliberate consideration.
- Contrary to NMED’s Resource Conservation and Recovery Act permit for LANL, the Lab has not fulfilled its duty to inform the public via NMED of possible alternatives to its planned tritium releases.4 According to Tewa Women United, “LANL has told EPA there are 53 alternatives; that list of alternatives, initially requested in 2022, has not yet been Tewa Women United has repeatedly asked LANL to provide the public with that list.” 5
University of New Mexico to host exhibit on nuclear history, technology, weapons
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. (KRQE) — A provocative international exhibit will open soon at the University of New Mexico. “the bomb” is an immersive, multi-media installation exploring the history, technology, and threat of nuclear weapons.
By Nicole Sanders, KRQE | April 22, 2025 krqe.com
The installation includes an hour-long film projected on 45 screens conveying the hidden chaos and danger of the nuclear age. The experience is coming to UNM from April 30 to May 30. The full schedule at Zimmerman Library is available below:
- Wednesday, April 30
- Friday, May 2, 2025
- Friday, May 9, 2025
- Friday, May 16, 2025
- Friday, May 23, 2025
- Friday, May 30, 2025
Formal Comments on the Draft Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement for Continued Operation of the Los Alamos National Laboratory
The National Environmental Policy Act requires the Los Alamos National Laboratory to periodically prepare a new “Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement (SWEIS) for Continued Operations.”
Please use NukeWatch NM’s recent extensive comments on the Lab’s new draft SWEIS as a resource and citizens’ guide to Lab issues.
Did you know, for example, that:
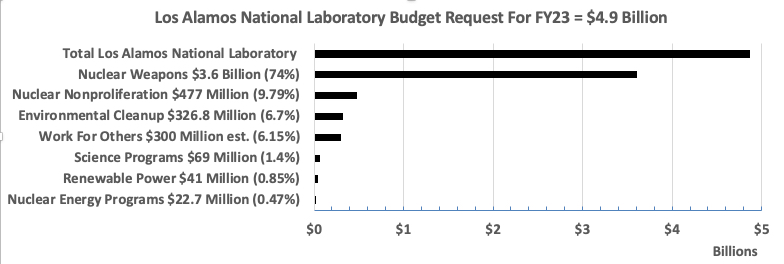
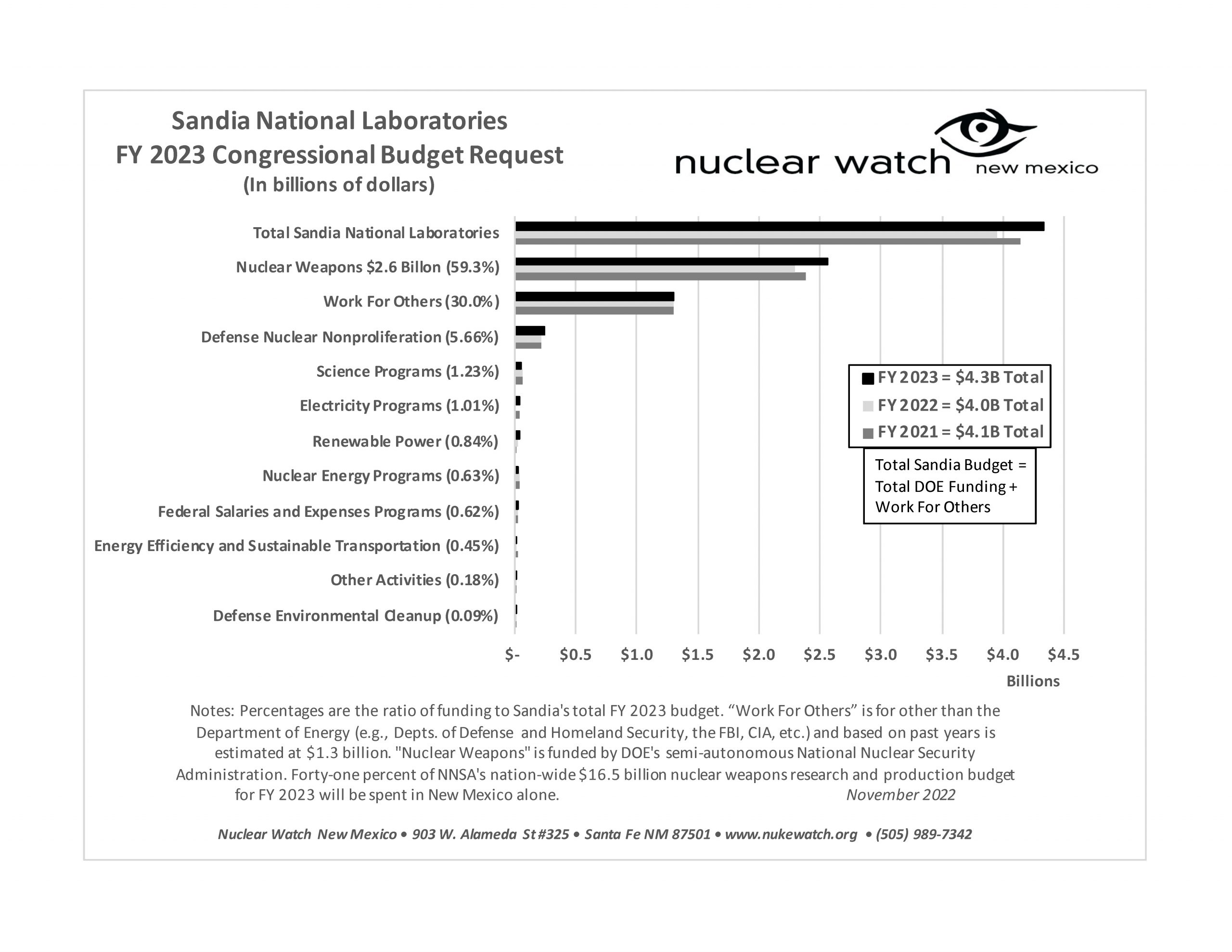
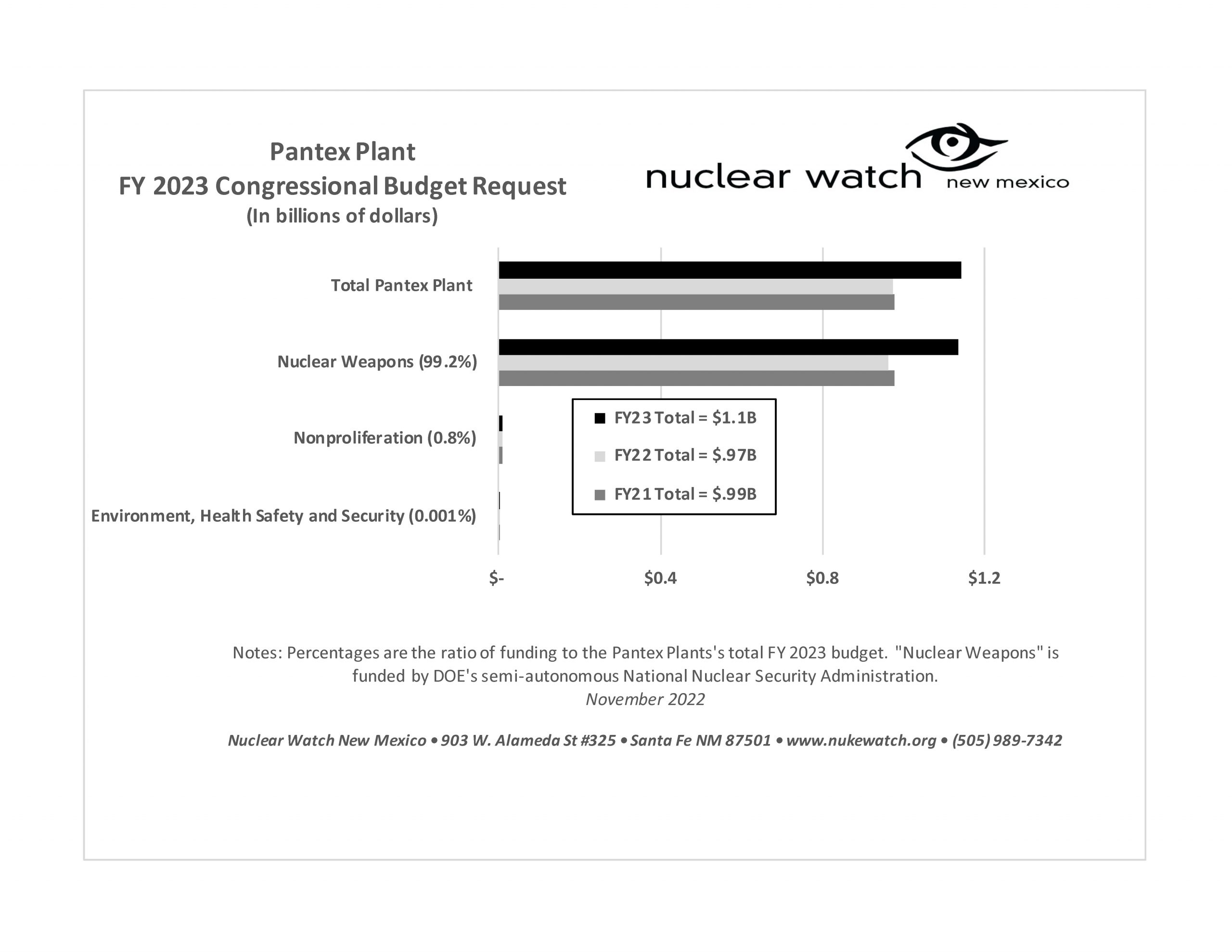
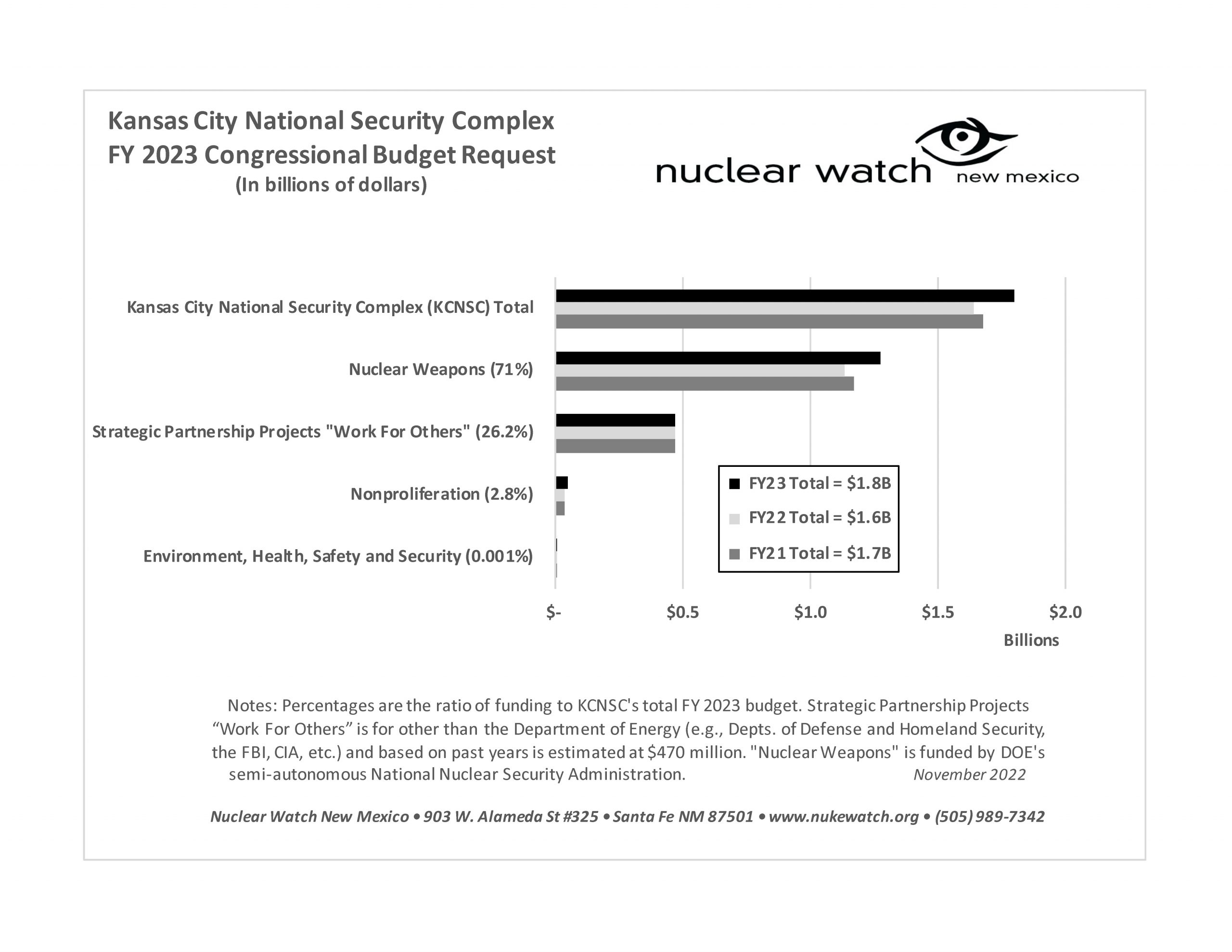
• LANL’s nuclear weapons production budget has doubled over the last decade?
• The Lab’s so-called cleanup plan is to “cap and cover” some 200,000 cubic yards of radioactive and toxic waste, leaving them permanently buried as a perpetual threat to groundwater?
• There is a planned intentional release of up to 30,000 curies of radioactive tritium gas, all without a public hearing?
Use our lengthy formal comments as a starting point, toolkit or resource for dissecting ongoing and future issues at LANL!
We encourage you to use our comments to ask for follow-up info, either from us here at NukeWatch or from the Lab, and to demand better accountability and transparency! Use as background or briefing material for local and congressional advocacy.
For example:
- Cite or excerpt our comments in future public processes under the National Environmental Policy Act. For example, we are expecting that a nationwide programmatic environmental impact statement for plutonium “pit” bomb core production will be announced soon, the result of a lawsuit in which NukeWatch led.
- Share with those organizing around stopping expanded plutonium pit production and advocating for genuine radioactive and toxic wastes cleanup.
- Learn about LANL’s proposed electrical transmission line across the environmentally and culturally sensitive Caja del Rio and alternatives that were not considered.
- The National Environmental Policy Act itself is under assault by the Trump Administration. We expect environmental justice and climate change issues to be stripped from LANL’s final Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement. This needs to be resisted!
NukeWatch NM argued that the draft SWEIS should be withdrawn and a new one issued because:
• The NNSA has rigged the draft LANL Site-Wide EIS with three self-serving scenarios:
– Expanded nuclear weapons programs (contradictorily called the “No Action Alternative”).
– Yet more expanded nuclear weapons programs (“Modernized Operations Alternative”).
– Yet far more expanded nuclear weapons programs (“Expanded Operations Alternative”).
• A Reduced Operations Alternative must be included.
• The SWEIS’ fundamental justification for expanded nuclear weapons programs is “deterrence.” But “deterrence” has always included nuclear warfighting capabilities that could end human civilization overnight.
• The SWEIS purports to align with U.S. obligations under the 1970 NonProliferation Treaty. That is demonstrably false.
• Future plutonium pit production is NOT to maintain the safety and reliability of the existing nuclear weapons stockpile. Instead, it is for new-design nuclear weapons that could lower confidence in stockpile reliability and/or prompt a return to testing.
• The SWEIS’ No-Action Alternative violates the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA).
• The legally required programmatic environmental impact statement on pit production should be completed first, followed by the LANL SWEIS.
• Plutonium pit reuse should be analyzed as a credible alternative to pit production.
• A recent proposal for a data center at LANL is not in the SWEIS. It raises huge issues of future water and electrical use, the appropriateness of commercial interests at a federal lab, and the possible fusion of artificial intelligence and nuclear weapons command and control.
• Recent Executive Orders could strip the final SWEIS of environmental justice and climate change analyses. This must have clarification.
• Planned tritium releases should be fully analyzed.
• The Electrical Power Capacity Upgrade should be analyzed will all credible alternatives.
• The proposed BioSafety Level-3 facility must have its own standalone EIS.
• All Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board concerns should be addressed and resolved.
• Genuine comprehensive cleanup should be a preferred alternative.
• A new SWEIS should follow a new overdue Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis.
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: April 2025
Nuclear weapons
Air Force Weighs Keeping 1970s-Era Missiles Until 2050
The US Air Force is considering contingency plans that would extend the life of 1970s-era intercontinental ballistic missiles by 11 more years to 2050 if delays continue to plague the new Sentinel models intended to replace them. The current plan is to remove all 400 Minuteman III ICBMs made by Boeing Co. from silos by 2039… The Sentinel was projected last year to be deployed starting in May 2029. The first test flight was once projected for December 2023, but fiscal 2025 budget documents indicated a slip to February 2026.
The estimated cost of the new Sentinel intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM), originally at ~$110 billion, is now north of $180 billion. And this is before recognition of the immensity of supplying new command and control communications and recent consideration that its hardened silos may have to be replaced. IMHO it’s a propitious time to argue again for eliminating the land-based ICBM leg of the Triad. After all, one of its stated purposes is to act as a “nuclear sponge” for incoming Russian warheads. The odds of that are not zero and may increase if ICBMs are uploaded with multiple warheads after the New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty expires in February 2026. More temptation for a preemptive first strike.
Deterrence is the Threat: NukeWatch Presentation for Western New Mexico University – April 1, 2025
Calls to restart nuclear weapons tests stir dismay and debate among scientists
By Emily Conover, Science News | March 27, 2025 sciencenews.org
When the countdown hit zero on September 23, 1992, the desert surface puffed up into the air, as if a giant balloon had inflated it from below.
It wasn’t a balloon. Scientists had exploded a nuclear device hundreds of meters below the Nevada desert, equivalent to thousands of tons of TNT. The ensuing fireball reached pressures and temperatures well beyond those in Earth’s core. Within milliseconds of the detonation, shock waves rammed outward. The rock melted, vaporized and fractured, leaving behind a cavity oozing with liquid radioactive rock that puddled on the cavity’s floor.
As the temperature and pressure abated, rocks collapsed into the cavity. The desert surface slumped, forming a subsidence crater about 3 meters deep and wider than the length of a football field. Unknown to the scientists working on this test, named Divider, it would be the end of the line. Soon after, the United States halted nuclear testing.
Beginning with the first explosive test, known as Trinity, in 1945, more than 2,000 atomic blasts have rattled the globe. Today, that nuclear din has been largely silenced, thanks to the norms set by the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty, or CTBT, negotiated in the mid-1990s.
Only one nation — North Korea — has conducted a nuclear test this century. But researchers and policy makers are increasingly grappling with the possibility that the fragile quiet will soon be shattered.
Some in the United States have called for resuming testing, including a former national security adviser to President Donald Trump. Officials in the previous Trump administration considered testing, according to a 2020 Washington Post article. And there may be temptation in coming years. The United States is in the midst of a sweeping, decades-long overhaul of its aging nuclear arsenal…
ACTION ALERTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Interfaith Panel Discussion on Nuclear Disarmament - August 9
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.