QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
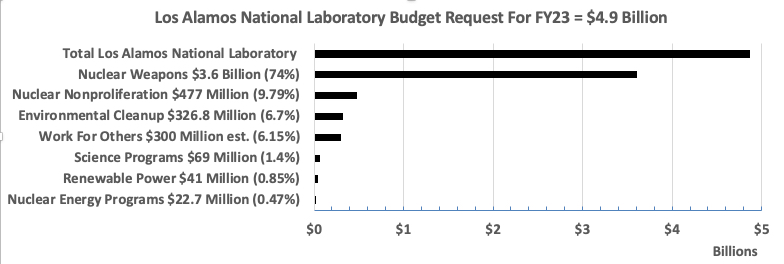
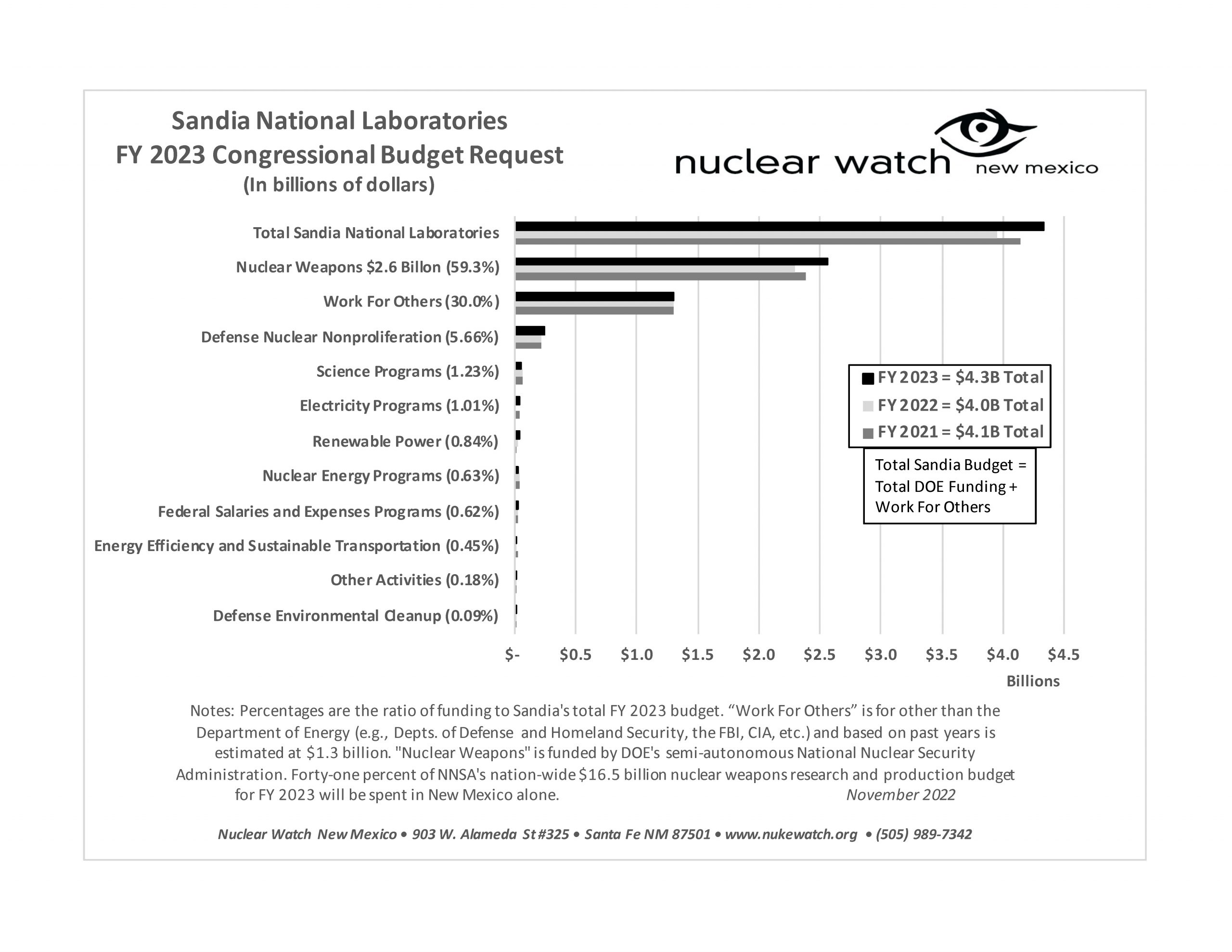
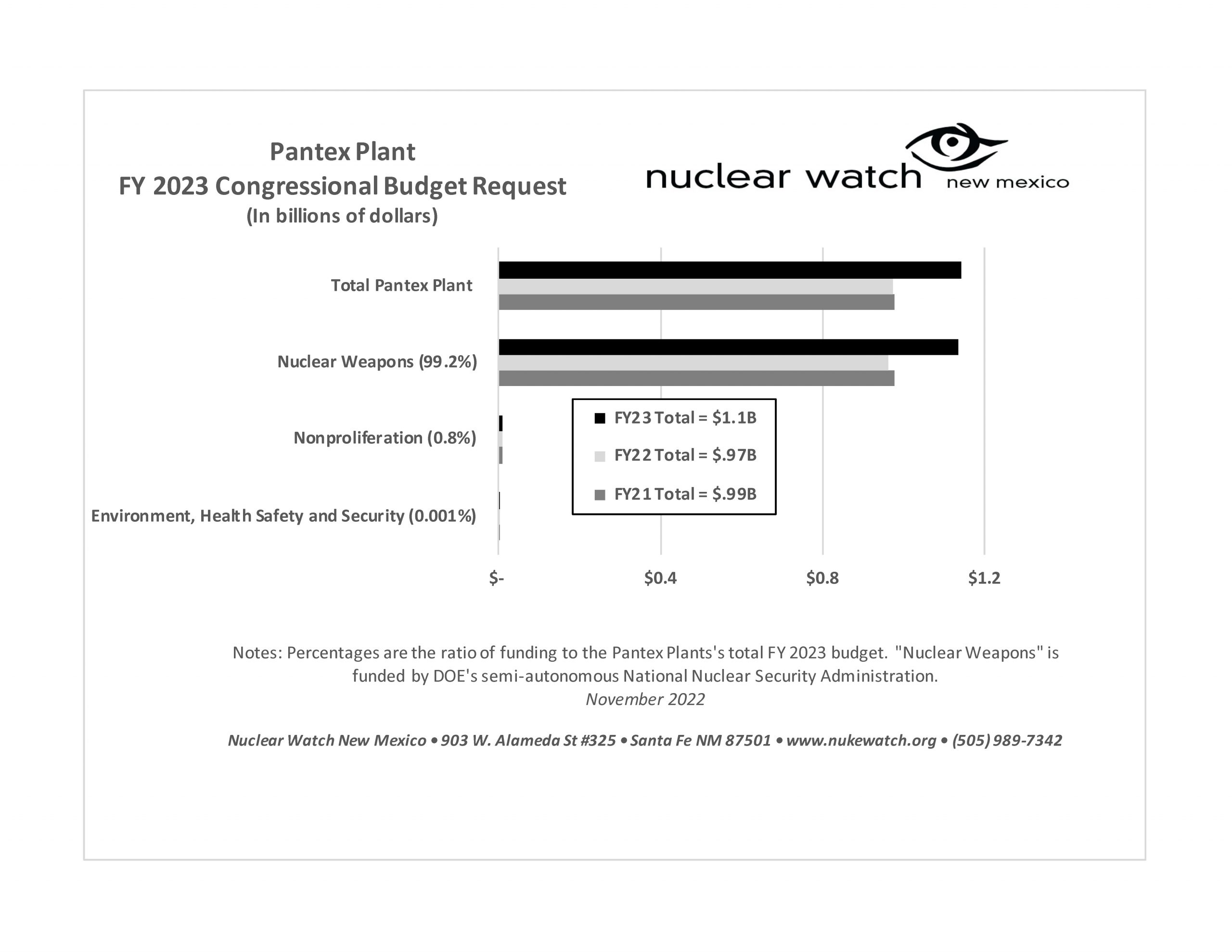
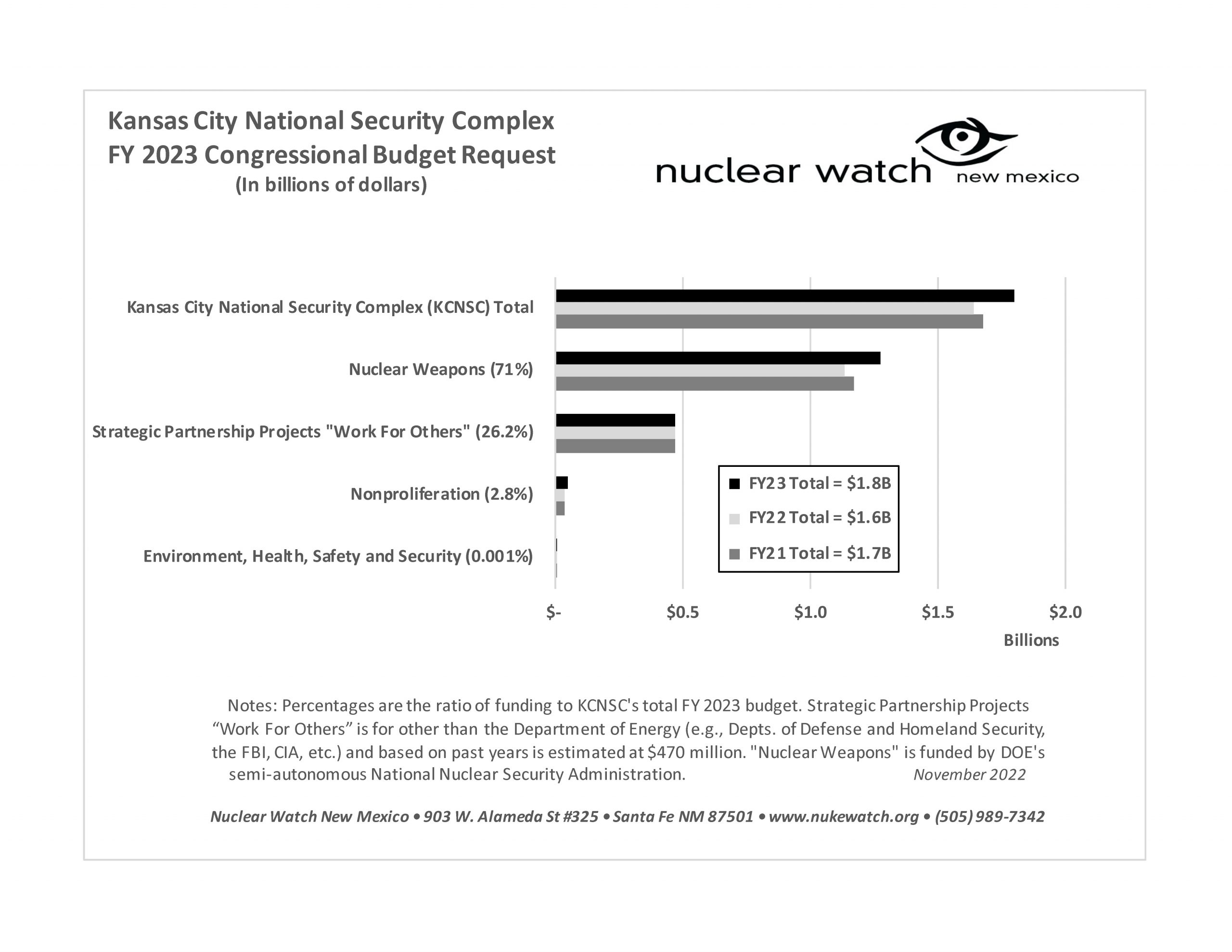
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
Nuclear Watch Interactive Map – U.S. Nuclear Weapons Complex
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
2022 BLOG POSTS
President Biden Should Let His Faith Guide Him Toward Nuclear Disarmament
Did you see what the Santa Fe Archbishop wrote in the very heart of the U.S. nuclear weapons complex?
“With this pending Nuclear Posture Review, President Biden has the opportunity to show his moral leadership. I know he is capable. After all, much of what is needed is only to turn his own past words into new policy—and to reject today’s fearful status quo, embracing a new path that we can all live with.”
Read the entire article here and see the picture.
Happy Are Peacemakers Who Wake Up the Rest of Us
“The difference is that [Santa Fe Archbishop] Wester is alone and standing in what came to be the center of the “American Nuclear Soul” in Santa Fe calling us again to examine our American consciences. As Pope Francis said at the Peace Memorial in Hiroshima on Nov. 24, 2019, “The use of atomic energy for purposes of war is immoral, just as the possessing of nuclear weapons is immoral. … How can we speak of peace even as we build terrifying new weapons of war?”
Current U.S. Nuclear Weapons Issues: New Year’s Update — January 15, 2022
U.S. nuclear weapons issues:
- In anticipation of the NonProliferation Treaty Review Conference that was to start January 4 the P-5 (original nuclear weapons powers U.S., Russia, China, France and U.K.) came out with an unbelievable collective statement on how they are in compliance with the NPT Article VI mandate to disarm. Then the Review Conference was indefinitely postponed because of omicron.
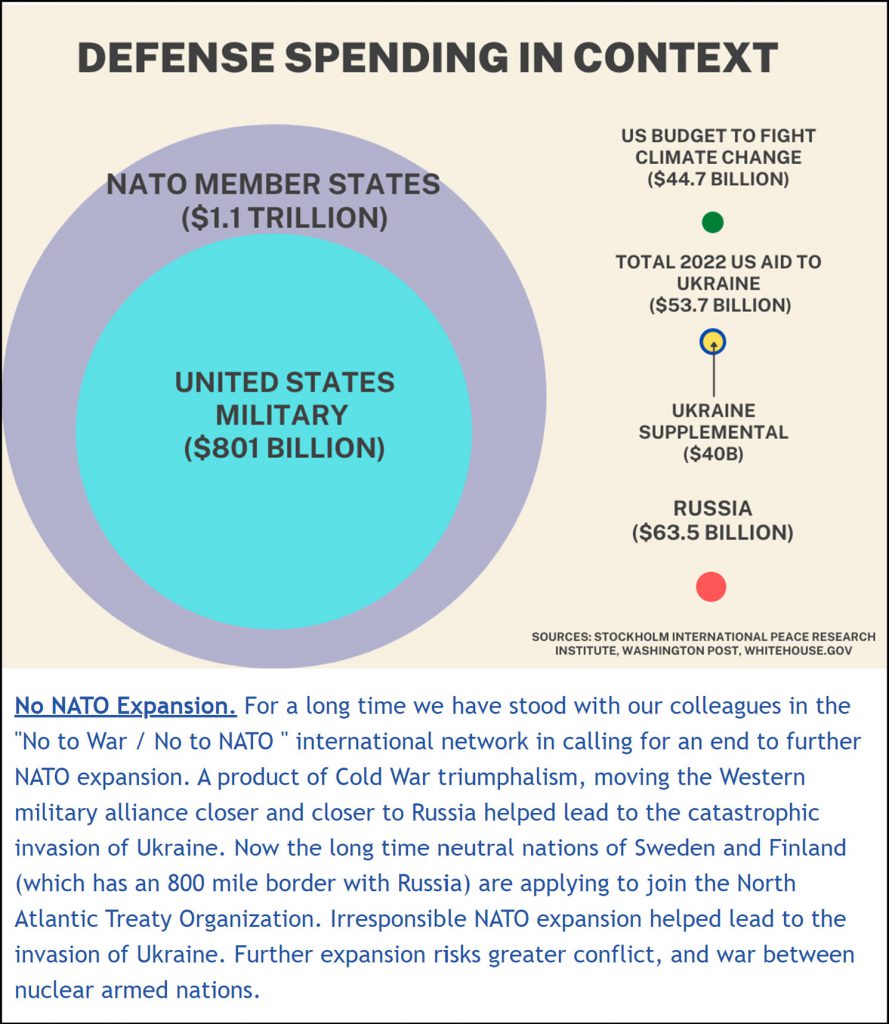
- Biden signed the FY 2022 Defense Authorization Act (DAA). Congress gave the Pentagon $24 billion more than Biden asked for. So much for ending endless wars. The DAA fully authorizes what the Biden Administration asked for National Nuclear Security Administration nuclear weapons programs, which increased Trump’s FY 2021 budget which saw a 25% from his FY 2002 budget. LANL is to get a cool billion in FY 2022 for expanded plutonium pit production alone.
- Still no appropriations. Second Continuing Resolution (CR) runs out in February.
- First anniversary of Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons January 22
New & Updated
Brief Analysis of Today’s U.S. Supreme Court Oral Arguments on the Illegality of Licensing Radwaste Dumps in TX and NM
Today the United States Supreme Court heard arguments in the case of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission vs. Texas. At issue is whether the NRC exceeded its authority when it approved licenses for proposed “consolidated interim storage facilities” for high-level radioactive waste, and this includes highly irradiated “spent” fuel from nuclear power plants.
Two consolidated interim storage facilities are planned for western Texas and southeastern New Mexico. The Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982, as Amended specifically prohibits private “interim” storage of federal spent nuclear fuel, and disallows the Department of Energy from taking title to the waste unless a permanent geologic repository is licensed, built and opened. The law intended to prevent private “interim” storage of federal radioactive waste because interim storage is much less robust than permanent storage, and would double the risk of accident or attack during transport, since consolidated “interim” storage means the waste has to be moved twice, once to the CISF and again to a permanent repository.
Broken arrows: The hidden secret behind America’s missing nuclear weapons
“Dedicated Navy divers, demolition teams, and high-powered sonar spent weeks searching the ocean floor and came up empty.”
By Kaif Shaikh, Interesting Engineering | March 3, 2025 interestingengineering.com
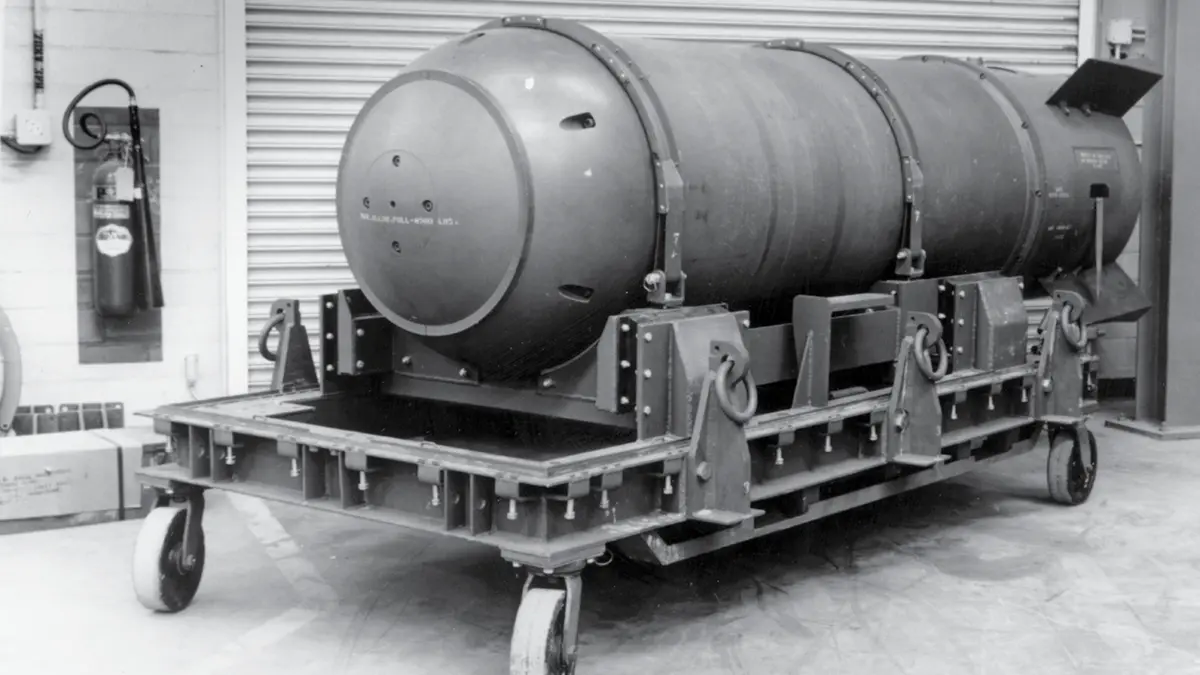

Throughout history, the idea of misplacing a nuclear weapon may sound like a plot twist in an espionage novel. The United States has experienced more than a handful of such incidents. Known as “Broken Arrows,” these events typically refer to any accidents involving nuclear weapons that do not pose an immediate risk of triggering a nuclear war.
For decades, details remained hidden behind top-secret clearances. However, unclassified records reveal that the U.S. military has had a surprising number of mishaps, with some bombs still unaccounted for to this day.
What are broken arrows?
The Department of Defense defines a “Broken Arrow” as any incident involving a U.S. nuclear weapon or warhead that results in accidental launching, firing, detonating, theft, or loss of the weapon. From 1950 to 1980, official sources cite 32 Broken Arrow incidents, but there may have been more, given the secrecy surrounding nuclear matters.
Christie Brinkley: Don’t let the US resume nuclear weapon tests that ended decades ago
“The United States and other nuclear powers are now moving closer to resuming nuclear weapons tests, decades after testing ended. This highly disturbing trend must be halted.”
By Christie Brinkley Special to The Kansas City Star Miami Herald | March 3, 2025 miamiherald.com
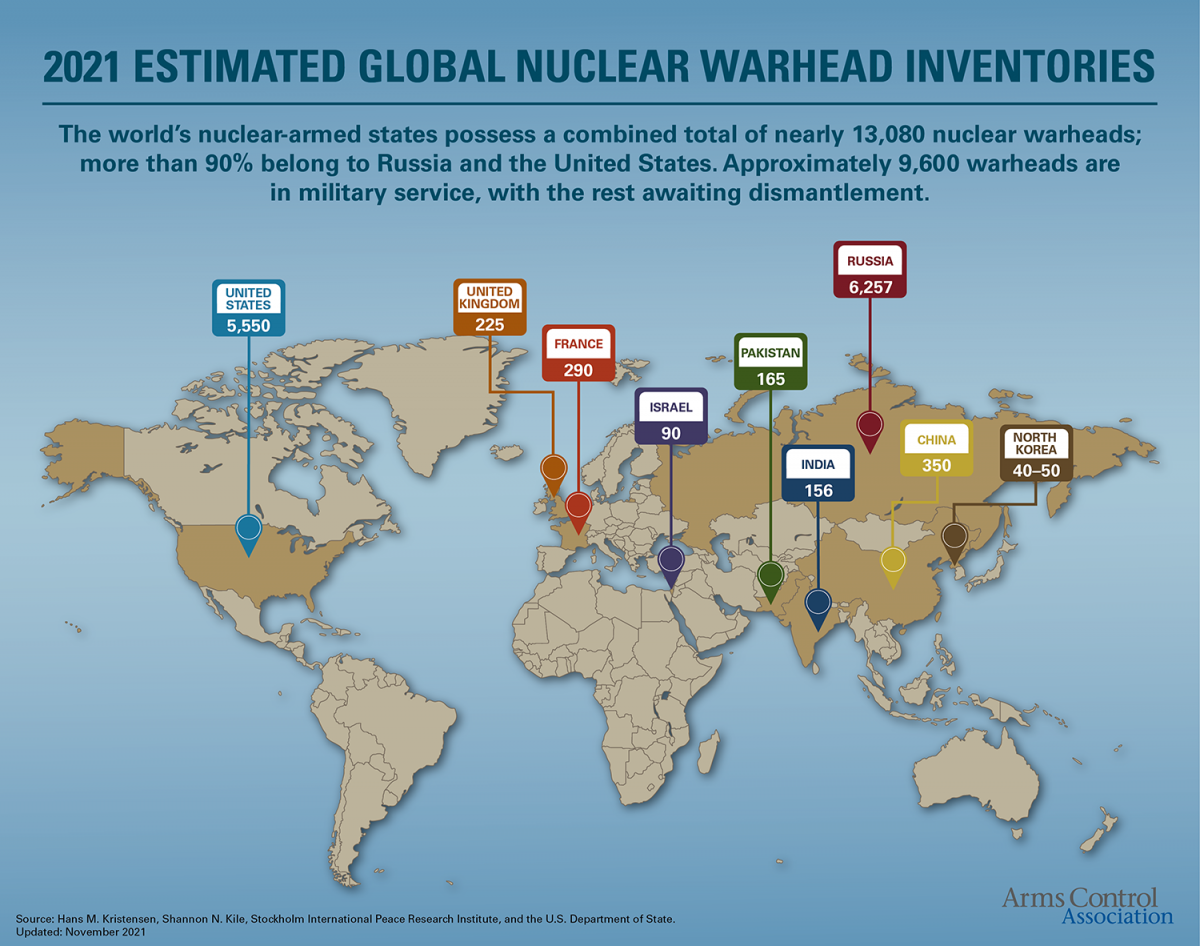
Since the atomic age, 2,056 nuclear weapons have been detonated, 528 of them above the ground. The United States and Soviet Union accounted for about 85% of these tests. The explosive power of atmospheric tests equaled 29,000 Hiroshima bombs. Airborne radioactive fallout circled the globe, re-entered the environment through precipitation, and entered human bodies through food and water.
Cold War bomb testing was part of a massive increase in the number of nuclear weapons, which peaked at more than 60,000. After nuclear war was barely avoided during the Cuban missile crisis, public pressure convinced leaders to ban all above-ground tests in 1963 — a treaty that has never been violated.
The test ban treaty was a huge achievement for peace, beginning eased tensions between nuclear nations. It also was a landmark for public health. A study by St. Louis residents and scientists found an enormous buildup of radioactive strontium-90 levels in baby teeth — 63 times higher in children born in 1963 compared to those born in 1950.
LISTEN LIVE TO U.S. SUPREME COURT ORAL ARGUMENTS ON THE ILLEGALITY OF LICENSING RADWASTE DUMPS IN TX AND NM
“The case pits the nuclear industry’s push for CISFs against the interests of fossil fuel companies which object to high-level radioactive waste dumped in their drilling/fracking areas, the state governments of Texas and New Mexico, which have passed laws prohibiting importation of nuclear waste to their states, and cities along the transport routes which object to it being shipped through their jurisdictions. Their amicus briefs in the case are posted here.”
For immediate release
MEDIA ALERT for Wednesday, March 5, 2025
WASHINGTON, D.C.,
 WHAT? Wednesday morning, March 5, the United States Supreme Court will hear oral arguments in Nuclear Regulatory Commission vs. Texas. At issue in the SCOTUS (Supreme Court of the U.S.) proceeding is whether the NRC exceeded its authority when it approved licenses for proposed “consolidated interim storage facilities” for high-level radioactive waste including highly irradiated “spent” fuel from nuclear power plants. Two CISFs are planned for western Texas and southeastern New Mexico. The Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982, as Amended specifically prohibits private “interim” storage of federal spent nuclear fuel, and disallows the Department of Energy from taking title to the waste (which would be necessary for DOE to transport it to CISFs), unless and until a permanent geologic repository is licensed, built and opened to receive the waste. The law intended to prevent private “interim” storage of federal radwaste, which is much less robust than permanent storage, and would double the risk of accident or attack during transport, since consolidated “interim” storage necessitates moving the waste twice, once to the CISF and again to a permanent repository. The NRC approved recent CISF license applications despite the law, saying it anticipated Congress would change it in the future. But the federal Fifth Circuit court ruled that the NRC didn’t have that authority. If the Supreme Court strikes that ruling down, it could open the floodgates for thousands of shipments of spent fuel from nuclear power plants across the US, through many states, to CISFs in Texas and New Mexico.
WHAT? Wednesday morning, March 5, the United States Supreme Court will hear oral arguments in Nuclear Regulatory Commission vs. Texas. At issue in the SCOTUS (Supreme Court of the U.S.) proceeding is whether the NRC exceeded its authority when it approved licenses for proposed “consolidated interim storage facilities” for high-level radioactive waste including highly irradiated “spent” fuel from nuclear power plants. Two CISFs are planned for western Texas and southeastern New Mexico. The Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982, as Amended specifically prohibits private “interim” storage of federal spent nuclear fuel, and disallows the Department of Energy from taking title to the waste (which would be necessary for DOE to transport it to CISFs), unless and until a permanent geologic repository is licensed, built and opened to receive the waste. The law intended to prevent private “interim” storage of federal radwaste, which is much less robust than permanent storage, and would double the risk of accident or attack during transport, since consolidated “interim” storage necessitates moving the waste twice, once to the CISF and again to a permanent repository. The NRC approved recent CISF license applications despite the law, saying it anticipated Congress would change it in the future. But the federal Fifth Circuit court ruled that the NRC didn’t have that authority. If the Supreme Court strikes that ruling down, it could open the floodgates for thousands of shipments of spent fuel from nuclear power plants across the US, through many states, to CISFs in Texas and New Mexico.
Expanded Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Production is Immoral – Spend Nuclear Weapons “Modernization” Money Ethically ELSEWHERE
Why the nation’s nuclear waste may eventually be headed to northwest Colorado
Nuclear waste is piling up at power plants around the country, and we have no idea where to put it. Many states are aggressively fighting plans for new storage facilities.
But northwest Colorado is quietly opening the door.
By In The NoCo, Scott Franz, Erin O’Toole, Brad Turner | February 22, 2025 kunc.org
KUNC’s investigative reporter Scott Franz recently traveled around rural Colorado talking with people about what nuclear waste storage could do for the local economy – and also interviewing folks who are dead set against that idea.
On this special edition of In The NoCo, we’ve combined all of Scott’s reporting from the past few months into a single episode. You can also see photos and check out more on this investigation.

Arms Control Association – Trump Regains Control Over Nuclear Policy: What’s Next?
It has been barely a month since Inauguration day, but it is apparent that Donald Trump is determined to reshape U.S. foreign policy, radically alter alliance relationships, and upend Washington’s approach toward key adversaries, like Russia, in ways that are not yet clear.
Arms Control Association | February 21, 2025 armscontrol.org
And here at home, Trump’s brash assertion of executive power is putting our nation’s democratic institutions and the rule of domestic law at risk, in part by altering or dismantling key government departments,agencies and functions, all without congressional approval.
All of this makes our mission to provide reliable information and sound policy solutions even more important and difficult.
The Arms Control Association has a clear and focused strategy to reduce the dangers posed by nuclear weapons and other WMD. Many of these priorities are outlined in this ACA-organized January 28 communication to all members of Congress that was endorsed by 16 of our partner organizations and leaders.
Like many others, however, we are still sorting out how to adjust to and contend with the post-Inauguration political dynamics.
But we must and we will, because critical, weapons-related security decisions lie ahead:
- So long as Russia’s assault on Ukraine continues, there is still a heightened risk of nuclear weapons use, and there are narrowing prospects for a deal to maintain limits on the U.S. and Russian nuclear arsenals after New START expires in one year.
- Although Trump has decried exorbitant military expenditures, the authors of Project 2025, the 920-page manifesto crafted by the Heritage Foundation and others, want the United States to spend even more than the current $756 billion ten-year price tag for nuclear modernization in order to increase the size and diversity of the U.S. arsenal. China and Russia are watching and will surely respond to any U.S. nuclear buildup.
- Project 2025 also calls for preparing to resume U.S. nuclear explosive testing for the first time since 1992. Should the United States do so, it would open the door to nuclear testing by other states, unravel the CTBT, and blow apart the global nonproliferation system at a time of increasing nuclear danger.
- Since Trump withdrew from the 2015 Iran nuclear deal, Tehran has expanded its capacity to produce weapons-grade nuclear material and reduced international inspectors’ access. Trump says he wants a nuclear deal; Iran’s president says he wants a nuclear deal. But time is short. Without a deal to scale back tensions and Iran’s nuclear capacity, we could see renewed international sanctions by October, Iranian withdrawal from the NPT, and/or an attempt by Israel to bomb Iran’s nuclear sites.
How exactly the second Trump administration and the new Congress will try to navigate all these nuclear-related challenges ahead is not yet clear — but if Project 2025 becomes the blueprint for U.S. nuclear weapons policy, we are in big trouble.
But, it may also be possible to steer us toward a safer course.
Trump wants to initiate denuclearization talks with Russia and China
On Thursday, President Donald Trump signaled that he wants to engage with Russia and China on denuclearization efforts.
By Erik English, BULLETIN OF ATOMIC SCIENTISTS | February 14, 2025 thebulletin.org
“There’s no reason for us to be building brand new nuclear weapons. We already have so many,” Trump said from the White House.
“You could destroy the world 50 times over, 100 times over. And here we are building new nuclear weapons, and they’re building nuclear weapons, and China’s building nuclear weapons.” The number of nuclear weapons the United States and Russia can have is established by New START, which expires in 2026. Without a new agreement, nuclear states could begin to build up their arsenals for the first time since the Cold War. “Hopefully, there’ll never be a time when we need those weapons,” Trump said. “That’s going to be a very sad day, that’s going to be probably oblivion.”
Share Your Experiences at Los Alamos National Laboratory
The New York Times would like to hear from you about workplace protocols and safety measures at LANL.
By Alicia Inez Guzmán | Alicia Inez Guzmán is reporting on the nuclear industry in New Mexico as part of The Times’s Local Investigations Fellowship – THE NEW YORK TIMES February 11, 2025 nytimes.com
More voices, better journalism. The questionnaire you are reading is just one tool we use to help ensure our work reflects the world we cover. By inviting readers to share their experiences, we get a wide range of views that often lead to a more deeply reported article. We make every effort to contact you before publishing any part of your submission, and your information is secure. Here’s more on how it works and why it’s good for us and you.
The Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) has recently embarked on the “new Manhattan Project” — a hiring spree and multibillion dollar expansion to build plutonium bomb cores for nuclear weapons.
The Times is writing about this new mission and how the lab is keeping workers safe, reporting accidents and environmental contamination and making needed upgrades to key facilities, including in Technical Area 55, the heart of bomb core production.
Have you or someone you know worked at TA-55 or another “hot site” and experienced a workplace accident or been exposed to plutonium, beryllium or another radioactive or toxic substance on the job? What safety measures were in place? Were there follow-up health assessments?
Please answer the questions using the form:
LANL Site-Wide EIS Hearings in Santa Fe and Los Alamos Filled with Loud Protest and Vehement Dissent: Nuclear Weapons are IMMORAL
In this Site-Wide EIS we’re given three options: Expanded nuclear weapons programs (hypocritically called the no action alternative), then we’re presented with yet more expanded nuclear weapons programs, and the third alternative is even more expanded nuclear weapons programs. What we really need is a genuine alternative in this Site-Wide, and I hope that citizens will repeatedly bring this up. We need a TRUE ALTERNATIVE in which the US begins to show global leadership towards nuclear disarmament that it promised to in the Non-Proliferation Treaty, and that should be reflected in the sitewide which shows just passive maintenance of the stockpile. We don’t need Pit Production because it’s for NEW designs – NOT to ensure the safety and reliability of the existing stockpile. The US, for our own national security and global security, we need to lead the world towards global nuclear disarmament – and this Site-Wide EIS does the opposite.
The hearings in Santa Fe and Los Alamos on February 11 and February 13, 2025, respectively, both had virtual participation options. The attendees online and in person were equally vehement in protesting the “rigged game” we’re given with this SWEIS and decrying the fact that there is no alternative besides increased nuclear weapons production.
And read an exceprt from the Archbishop of Santa Fe, John Wester’s comments:
“As we all know, we’re in an accelerating new nuclear arms race that’s made even more dangerous because of artificial intelligence, multiple nuclear actors and hypersonic delivery systems. It’s an already scary situation that has become even scarier, and what concerns me is that Los Alamos and Santa Fe play a key role in naturally fostering and promoting this new nuclear arms race – a race which I believe is an affront to all that is good and holy, all from our perspective that God has placed in us to live in harmony with one another. Nuclear weapons pose one of the greatest threats to that harmony. I think it’s important to know what I’m learning more and more about is that expanded plutonium pit production is not simply to maintain the safety and reliability of our existing so-called deterrence. I think it’s important that people are aware that it’s really for new design nuclear weapons for this new particular armed race. I think it’s important that that people recognize that deterrence is not the way to go. In that light, I would say obviously for me is a Catholic Bishop, Pope Francis I think has really changed the whole moral landscape of looking at nuclear weapons. On the 70th anniversary of the Hiroshima atomic bombing, Pope Francis declared that the very possession of nuclear weapons is immoral. As Catholics this was an extremely important shift there. The 1983 United states conference of Catholic Bishops did allow for deterrence – it was promoting disarmament but made caveats for deterrence. But Pope Francis has taken that off the table in saying that even possessing nuclear weapons is immoral, it’s unethical. One of the main reasons for this church’s shift on this was that the nuclear weapons powers really have failed in their pledge in 1970 when they joined the Non-Proliferation Treaty. The TPNW came about because of that failure, and so it seems to me then based on what Pope Francis said, that if possessing nuclear weapons is immoral, then expanding plutonium pit cores and modernizing our weapons systems in order to be more involved in the new nuclear arms race is also immoral. This policy is unethical. Now I want to be careful here, I am not saying that anyone working at Los Alamos or Sandia or Lawrence Livermore in California, I’m not judging them or saying there are immoral – that’s a different matter in one’s conscience. I’m saying that the policy is involved and the Pope said that nuclear weapons themselves are intrinsically immoral. I think that’s an important thing to keep in mind, that that we need to be moving toward disarmament and that if we’re not, if that’s not our trajectory, rather if it’s just to build up our defenses, then that’s an immoral buildup.”
Gearing Up for the Public Hearings on the LANL Draft Sitewide Environmental Impact Statement: Pit Production at LANL
“Nuclear Watch New Mexico hosted a workshop on February 6 on the newly released Draft Sitewide Environmental Impact Statement (SWEIS) for Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) to present information and elicit discussion on this NEPA process that Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuke Watch, referred to as a “rigged game” at the beginning of the workshop. What that means will become evident as I review the part of the workshop I attended.”
By Kay Matthews, La Jicarita | February 7, 2025 lajicarita.wordpress.com
Archbishop John Wester, an outspoken critic of nuclear weapons proliferation under the guise of nuclear deterrence instead of disarmament spoke briefly to open the discussion. Quoting Pope Francis, he said, “possessing nuclear weapons is immoral.” He then said, “Pit production is immoral.” His only qualification is that it’s the policy that’s immoral, not the people who promote it. We’ve failed to uphold already existing treaties and failed to implement new ones. He’ll be going to the United Nations in March for a meeting, Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, and to Japan in August to meet with his partners in the World Without Nuclear Weapons.
Coghlan explained that next week the Department of Energy (DOE) and the semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) will hold public hearings, as required by NEPA, on the LANL SWEIS, in Santa Fe, Española, and Los Alamos. He cautioned that while we should all be “cynical” about the process, we need to go ahead and protest the fact that all three alternatives provided in the SWEIS expand pit production, just at different amounts. The process is rigged because the DOE and NNSA failed to update a 2008 Environmental Impact Statement before pit production began at LANL (the other nuclear facility, the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, is slated to produce 50 pits a year but is completely unprepared for pit production).
The guest speaker was Dylan Spaulding, Senior Scientist for the Union of Concerned Scientists…
NukeWatch Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop – February 6, 2025
Full Video Recording: NukeWatch Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop |
NukeWatch Presentation: Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop |
|---|---|
|
NukeWatch Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop |
 |
In Memoriam: Ken Mayers
 We here at NukeWatch will dearly miss Ken’s weekly presence at the corner vigil to protest Nuclear Weapons in Santa Fe.
We here at NukeWatch will dearly miss Ken’s weekly presence at the corner vigil to protest Nuclear Weapons in Santa Fe.
Locally, Ken was co-founder of the Santa Fe Chapter of Veterans for Peace and an active member of Santa Feans for Justice in Palestine. Ken worked with the local chapter of US Combatants for Peace and the Justice Council of the Unitarian Universalist Congregation in Santa Fe where he was also an enthusiastic baritone and co-founder of the NM Peace Choir.
A Celebration of Ken’s life will be held Friday, April 4 beginning at 12 noon at the corner of Sandoval and West Alameda, (Santa Fe’s weekly vigil to protest Nuclear Weapons), followed by lunch and a hybrid service at the UU Congregation, 107 West Barcelona Street, Santa Fe, NM.
For those wanting to pay tribute to Ken, please consider planting a tree through A Living Tribute (https://shop.alivingtribute.org/) or make a donation in his memory to the Santa Fe Joan Duffy Chapter of Veterans for Peace https://www.vfp-santafe.org/
Ken was a lifelong, passionate defender of peace. Read more:
ACTION ALERTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Interfaith Panel Discussion on Nuclear Disarmament - August 9
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media
Tactical Nukes: One Little Nuclear Weapon Can Ruin Your Whole Day
Some people believe smaller nuclear weapons can be used to fight battles. But nuclear weapons are nuclear weapons, and contemplating their use on the battlefield opens the door for full-scale nuclear war.