Updates
GOP lawmaker accuses administration of ‘playing politics’ with Yucca Mountain reversal
“The Trump Administration again proposes to cut DOE’s budget — by 8 percent overall, and by an astounding 35 percent in non-defense programs. This will limit America’s future by drastically reducing or eliminating programs critical for meeting our future energy needs and assuring our security,” – Rep. Marcy Kaptur (D-Ohio), chairwoman of the Appropriations Committee’s subcommittee on Energy and Water Development
ARTICLE BY: RACHEL FRAZIN | thehill.com

Republican Rep. Dan Newhouse (Wash.) accused the Trump administration of “playing politics” on Thursday with its reversal on funding for a nuclear waste repository in Nevada.
“I can’t tell you how disappointed I was to see this administration playing politics with something as important as completing the permanent solution to our nation’s high-level nuclear waste,” Newhouse said during a hearing on the administration’s proposed Department of Energy (DOE) budget.
“This budget is … a total waste of resources and a distraction from solving this very important issue,” he added.
President Trump announced this month that he no longer supports funding the Yucca Mountain nuclear waste site, reversing his position on a controversial matter in a key state in November’s elections. The change was reflected in his budget proposal for fiscal year 2021.
Energy Secretary Dan Brouillette said during the hearing that the administration would not proceed with either licensing for Yucca Mountain or an interim storage facility.
“My understanding [is] under the Nuclear Waste Policy Act we are prohibited from starting construction on an interim facility, a federal facility,” Brouillette said.
Democrats also criticized the administration over cuts included in the budget proposal.
“The Trump Administration again proposes to cut DOE’s budget — by 8 percent overall, and by an astounding 35 percent in non-defense programs. This will limit America’s future by drastically reducing or eliminating programs critical for meeting our future energy needs and assuring our security,” said Rep. Marcy Kaptur (D-Ohio), chairwoman of the Appropriations Committee’s subcommittee on Energy and Water Development, in her opening statement.
“Your budget proposes deep and arbitrary cuts that threaten progress one one of our most pressing challenges and that is climate change. We can be a leader in exporting clean energy technologies, but not under your budget request,” Kaptur added later in the hearing.
In response, Brouillette said, “Renewable technologies are becoming somewhat mature in the marketplace, so for us to focus again on these technologies that are now commercially widely available seems to us to be inappropriate.”
Trump’s budget request would reduce spending significantly at several energy and environment-related agencies, including the energy department. Trump has consistently proposed cutting funding such agencies, and Congress has routinely ignored those proposals and instead increased funding.
Holes found in protective liner at SC nuclear fuel factory
Inspectors at the Westinghouse nuclear fuel factory near Columbia recently found 13 small leaks in a protective liner that is supposed to keep pollution from dripping into soil and groundwater below the plant.
ARTICLE BY SAMMY FRETWELL | thestate.com

Now, the company plans to check a concrete floor beneath the liner, as well as soil below the plant, for signs of contamination that could have resulted from the tears, which were characterized in a federal inspection report as ‘’pinhole leaks.’’ The pinhole leaks, discovered by Westinghouse late in 2019, may have formed after company employees walked across the liner and weakened it, according to the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission.
Media Advisory: What to Look For in the U.S. Department of Energy’s FY2021 Nuclear Weapons and Cleanup Budget Request
According to media reports, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), the semiautonomous nuclear weapons agency within the Department of Energy (DOE), has persuaded President Trump to increase its weapons budget by more than 20% in one year. NNSA Administrator Lisa Gordon-Hagerty has claimed that a failure to give her agency that huge increase would amount to “unilateral disarmament” despite the U.S. having thousands of nuclear warheads ready to launch on a moment’s notice.
The Alliance for Nuclear Accountability, a 33-year-old network of groups from communities downwind and downstream of U.S. nuclear weapons sites, strongly opposes this unnecessary and dangerous spending that promotes a new global nuclear arms race. In addition, Trump’s FY 2021 budget request is expected to cut or hold flat cleanup, nonproliferation, dismantlement and renewable energy programs that meet real national needs to pay for more unneeded nuclear weapons. To compound all this, DOE’s nuclear weapons and environmental management programs have been on the Government Accountability Office’s “High Risk List” for project mismanagement and waste of taxpayers’ dollars for 27 consecutive years.
US, critics split on whether tech made nuke shipments safer
“There’s enough high-level nuclear waste awaiting disposal in the U.S. to fill a football field 65 feet (20 meters) deep. Few states want to house it within their borders.”
“The public defines ‘safe’ as zero risk…the technical community defines ‘safe’ as complying with regulatory standards.” – Robert Halstead, head of the Agency for Nuclear Projects, is currently fighting plutonium shipments to Nevada and spent nuclear fuel transfers to the proposed Yucca Mountain dump.
BY: SCOTT SONNER | phys.org
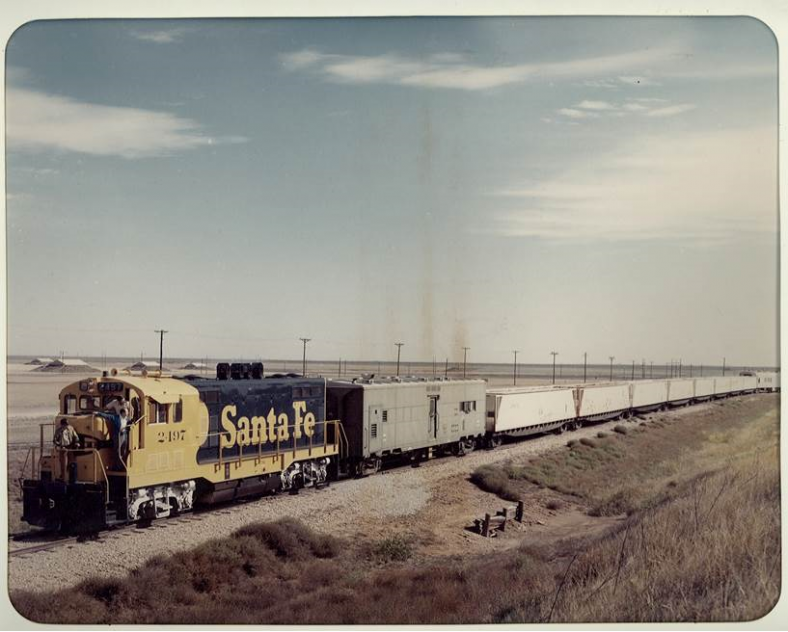

The plutonium core for the first atomic weapon detonated in 1945 was taken from Los Alamos National Laboratory to a test site in the New Mexico desert in the backseat of a U.S. Army sedan.
Officials put other bomb parts inside a metal container, packed it into a wooden crate and secured it in the steel bed of a truck under a tarp, the U.S. Energy Department’s National Nuclear Security Administration says in a historical account.
Grainy black-and-white photos show special agents and armed military police accompanying the shipment nearly 75 years ago.
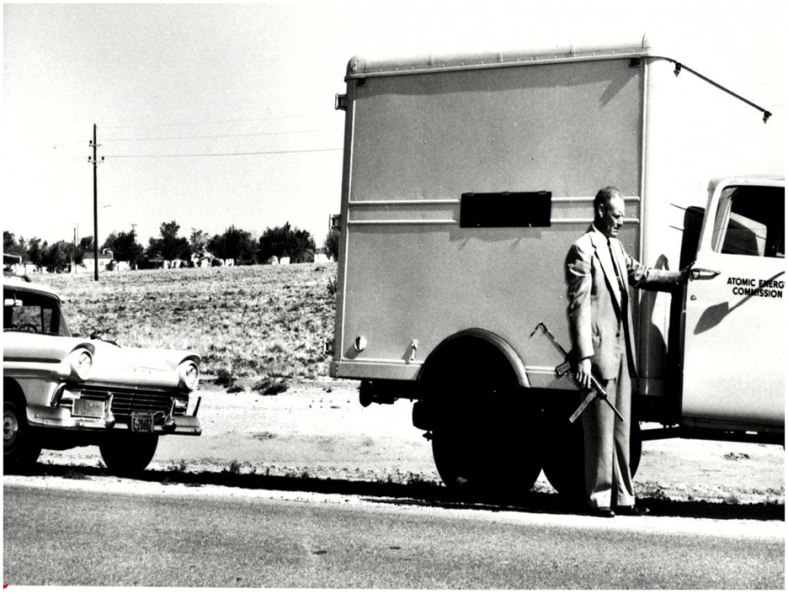

“Nuclear materials transportation has evolved since then,” the department posted online last year.
Today, radioactive shipments are hauled in double-walled steel containers inside specialized trailers that undergo extensive testing and are tracked by GPS and real-time apps.
But whether shipping technology has evolved enough to be deemed safe depends on whom you ask.
New Estimate ($377B) Raises Cost of Cold War Cleanup (Again)
At some point, DOE will have to admit that it has no idea what it will cost to cleanup the Cold War nuclear weapons complex sites. DOE should stop making more wastes until the existing wastes are remediated. The new estimate is more that twice the amount that has been spent in total since cleanup began in 1989, with the most difficult sites still to come.
We’ve said it before and we’ll say it again – Clean Up, Don’t Build Up!
The thing is that the new $377 billion estimate includes leaving much of the waste behind.
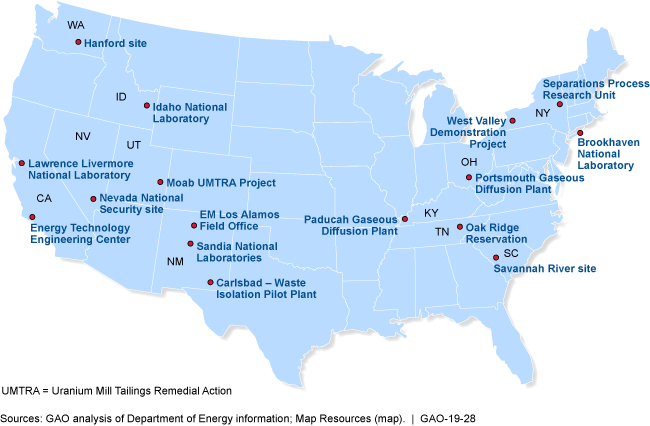
Program-Wide Strategy and Better Reporting Needed to Address Growing Environmental Cleanup Liability GAO-19-28: Published: Jan 29, 2019. Publicly Released: Jan 29, 2019.
The Department of Energy is tasked with cleaning up waste from Cold War nuclear weapons production, much of which is hazardous or radioactive. The department’s Office of Environmental Management estimates that future work could cost at least $377 billion—$109 billion more than last year’s estimate.
Don’t let feds change the rules for cleaning up Hanford nuclear waste
The public can comment on the U.S. Department of Energy’s proposed changes to Hanford nuclear waste cleanup rules until Jan. 9.

By Tom Carpenter
NukeWatch NM and Hanford Challenge are both members of the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability.
seattletimes.com | Originally published January 2, 2019 at 3:11 pm
After almost 30 years of a program to clean up dangerous defense waste at the Hanford nuclear site in southeastern Washington, the Department of Energy now wants to change the rules to make the job easier and save money. If approved, the proposal poses new dangers to the health and safety of people and the environment — not just in southeastern Washington, but at nuclear sites around the country.
In 1943, the U.S. government built the massive complex at Hanford to manufacture plutonium for nuclear weapons. When defense production ceased in 1986, its nine reactors had produced enough material for 60,000 atomic bombs. What remains is North America’s most contaminated site — more than half a billion gallons of nuclear waste and toxic chemicals stored in leaking tanks and dumped into the ground.
Resources
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.

