2023 News Articles – All Posts
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
2022 Select Highlighted Press Items
Nuclear Modernization is the ’Absolute Minimum,’ STRATCOM Commander Says | March 8, 2022
US tested hypersonic missile in mid-March but kept it quiet to avoid escalating tensions with Russia | April 4, 2022
Putin’s Nuclear Threats Are a Wake-Up Call for the World | March 15, 2022
Intelligence report determines that Russia's WMD threats will grow as losses mount in Ukraine | March 19, 2022
China and the United States: It’s a Cold War, but don’t panic | March 10, 2022
Russian military doctrine calls a limited nuclear strike “de-escalation.” Here’s why. | March 8, 2022
North Korea says it will strike with nuclear weapons if South attacks | April 4, 2022
Flying Under The Radar: A Missile Accident in South Asia | April 4, 2022
2022 News Articles
Trump administration talking tough about another government shutdown for border wall funding
On Thursday, the Senate failed a veto override on Donald Trump’s emergency declaration, which is being used to purloin funds appropriated for other programs and use them for his border wall. That sets up yet another budget fight that will simmer along between the House, Senate, and White House for the next month. It also sets up another fight over a Trump government shutdown.
ARTICLE BY JOAN MCCARTER | dailykos.com
Before the August recess, all parties agreed to a continuing resolution to fund the government until the week before Thanksgiving, in anticipation that all the individual spending bills for all the departments would be passed and signed by then. What it really set up was another fight with Trump. “Trump is not interested in signing other domestic spending bills until there is agreement on the border wall,” a senior administration official told The Washington Post.
Feds give Navajo uranium contract to firm with sketchy past
A High Country News investigation finds the EPA awarded Tetra Tech a contract despite knowing its subsidiary had likely engaged in data manipulation, false reporting and profiteering.
ARTICLE BY SUSIE NIELSEN | hcn.org

In September 2017, the Environmental Protection Agency received a troubling message from the Navy: Tetra Tech EC, the firm tasked with cleaning up the radioactive former naval shipyard Hunters Point in San Francisco, might have manipulated its data.
The past performance of Tetra Tech, even beyond its subsidiary at Hunters Point, has been marked by controversy. The parent company has been at the center of other lawsuits, including a consolidated case regarding its involvement in cleaning up after the North Bay Fires, a series of wildfires that devastated regions north of San Francisco in the fall of 2017.
“The Navajo Nation project is a bull’s-eye radioactive project with dangerous radioactivity. For Tetra Tech to get that project at all — to be even allowed to bid on it — is shocking.” – David Anton, attorney for the Tetra Tech EC whistleblowers
In 2008, the EPA and five other federal agencies, in consultation with Navajo Nation, developed the first comprehensive plan to address the legacy of uranium contamination in and around the Navajo Nation. As of 2014, of the 43 highest-priority Navajo Nation mines as designated by the EPA, only one of them — the Skyline Mine — had been mostly cleaned up.
Energy Secretary Rick Perry To Resign
NPR ALL THINGS CONSIDERED JEFF BRADY | npr.org Updated at 6:30 p.m. ET
Secretary of Energy Rick Perry plans to leave his position at the end of the year, President Trump confirmed to reporters Thursday in Fort Worth, Texas. Trump praised Perry and said he already has a replacement in mind.
“Rick has done a fantastic job,” Trump said. ” But it was time.”
Trump said that Perry’s resignation didn’t come as a surprise and that he has considered leaving for six months because “he’s got some very big plans.”
Perry, 69, is one of Trump’s original Cabinet members and recently has emerged as a central figure in the impeachment inquiry of Trump.
Urgent: Move US Nuclear Weapons Out Of Turkey
BLOG BY HANS M. KRISTENSEN | fas.org
A US Navy aircraft flies over Incirlik airbase in Turkey.Should the U.S. Air Force withdraw the roughly 50 B61 nuclear bombs it stores at the Incirlik Air Base in Turkey? The question has come to a head after Turkey’s invasion of Syria, Erdogan’s increasingly authoritarian leadership and deepening discord with NATO, Trump’s inability to manage U.S. security interests in Europe and the Middle East, and war-torn Syria only a few hundred miles from the largest U.S. nuclear weapons storage site in Europe.
The US is rethinking the 50-plus nuclear weapons it keeps in Turkey
“The US is storing perhaps 50 air-dropped thermonuclear bombs at its Incirlik Airbase in southern Turkey, less than 100 miles from the Syrian border where this conflict is taking place.”
BY: TIM FERNHOLZ | qz.com
Turkish forces are pushing into northern Syria, replacing and sometimes even firing on the US troops retreating at Donald Trump’s orders.
The question of whether Turkey, a member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is really a US ally was put to US defense secretary Mark Esper on Fox television this morning. “No, I think Turkey, the arc of their behavior over the past several years has been terrible,” he said.
The nuclear stockpile dates back to the Cold War, when the US sought to keep a sufficient supply of atomic weapons deployed in Europe to deter potential Soviet aggression. Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, and Italy also host similar arsenals, and the US trains the participating nations in the use of the doomsday devices.
Turkey Troubles
October 15 Heather Hurlburt, director of the New Models of Policy Change project at New America’s Political Reform program, joins Michelle Dover for a discussion on US national security and foreign policy under President Donald Trump. She is the co-author of The Consensual Straitjacket: Four Decades of Women in Nuclear Security.
News analysis with Michelle Dover, John Carl Baker and Geoff Wilson of Council for a Livable World focuses on the Trump administration’s decision to withdraw US troops from the Turkey-Syria border. Joe Cirincione answers a question from Johnny from Massachusetts.
Listen, Subscribe and Share on iTunes · Spotify · SoundCloud · YouTube · Google Play · Sticher
Also available on ploughshares.org/pressthebutton
Even a limited nuclear war between India and Pakistan could induce nuclear winter, thereby potentially killing 100’s of millions beyond South Asia.
From study: “Rapidly expanding nuclear arsenals in Pakistan and India portend regional and global catastrophe”
What if We Nuke a City?
“The world has changed in the past few years with world leaders again explicitly and publicly threatening each other with nuclear weapons. Many experts think the danger of a nuclear strike is higher than it has been in decades.
Governments tell their citizens that it’s good that we have nuclear weapons, but bad when others have them; that it’s somehow necessary to threaten others with mass destruction to keep us safe. But does this make you feel you feel safe? It only takes a small group of people in power to go crazy or rouge, a small misstep or simple misunderstanding to release a catastrophe of unimaginable proportions.”
Kurzgesagt – In a Nutshell
Video Description: “Until we did the research. It turned out we were a bit oblivious off the real impact of nuclear weapons in the real world, on a real city. And especially, how helpless even the most developed nations on earth would be if an attack occurred today. So hopefully this video demonstrates how extremely non fun a real world nuclear attack would be, without being too gruesome.”
DOE Order 140.1: DNFSB Response, Oct. 11
Chair Hamilton responds, “Pursuant to our enabling legislation, we have directed our staff to attend all phases of the NES study process. Should you wish to prohibit our access to a particular study, we respectfully request written communication to the Board.”
[NES = the nuclear explosive safety (NES) elements of DOE O 452.1E, Nuclear Explosive and Weapon Surety Program]
Oct. 11, 2019
The Honorable James Richard Perry Secretary of Energy
U.S. Department of Energy
1000 Independence Avenue, SW Washington, DC 20585-1000
Dear Secretary Perry:
We have received NNSA’s response dated August 9, 2019, concerning Board access to all phases of the nuclear explosive safety study process. We respectfully disagree with the justification offered for continued exclusion of our staff from NES study deliberations. NNSA’s response notes deliberations as collaborative efforts where participants consider all sides of identified issues, requiring free and open communication. Our staff’s observation of this interaction provides them with an understanding of the bases of the safety decisions being taken.
Today is Indigenous People’s Day, a holiday to honor and celebrate Native American and Indigenous peoples.
Among the many injustices suffered by native communities in the centuries that have passed since Europeans arrived on North America’s shores and claimed it for their own is the dangerous and deadly exposure to the radioactive materials used to create nuclear weapons. The United States’ nuclear arsenal has taken an especially hard toll on the Navajo, who continue to live with the repercussions of nuclear mining even today.
BACKGROUND
EXCERPT FROM POST BY CASSANDRA VARAKA, POLICY DIRECTOR OF WAND |
The process of building nuclear weapons starts with mining. One of the main elements of a nuclear bomb is enriched uranium. Some of the world’s richest uranium deposits span across Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah — heavily overlapping with the Navajo Nation. These mines provided the uranium used in the Manhattan Project; the United States’ top-secret endeavor to build the first nuclear bombs. Between 1944 and 1986 mining companies blasted 4 million tons of uranium out of Navajo land. Until 1971, uranium from these mines was sold exclusively to the United States government. Many Navajo were employed in the uranium mines and exposed to unsafe conditions by the companies in employing them. The mining companies knew that mine workers were at heightened risk for developing lung cancer and other serious respiratory diseases in 15 or 20 years. Additionally, the mines operated in a way that contaminated the surrounding lands and water by leaving large piles of radioactive materials exposed.
Many Navajo continue to live in close proximity to contaminated uranium mines. Of the 523 abandoned mines, the Environmental Protection Agency has only successfully cleaned up nine. The legacy of these mines and the contamination they leached into the environment on the Navajo Nation has been devastating: the cancer rate on the reservation doubled from the early 1970’s to the late 1990’s, even as the cancer rate declined nationwide. Each and every day, minority populations like the Navajo continue to be unduly affected by the militaristic pursuits of our government. For the Navajo, that means generations of health problems in the name of our nuclear weapons. We owe it to them, and to all the marginalized communities harmed by our pursuit and maintenance of nuclear weapons, to highlight the price they have been forced to pay for our nuclear arsenal.
READ MORE
When Talking About the Climate Crisis, We Can’t Forget About Nuclear Weapons
Both are existential threats, but only one is getting the attention it deserves.
BY: MATT KORDA | thenation.com
The first atomic bomb test was conducted at Alamogordo, New Mexico, July 16, 1945. (AP / US Army)“The current attention gap between the climate crisis and nuclear weapons is bizarre, given their common existential stakes and challenges. Climate change and nuclear weapons have a symbiotic relationship: Each threat exacerbates the other. Climate change is setting the stage for conflict between nuclear-armed states, and a recent study suggests that even a regional nuclear war would cool the planet by 2 to 5 degrees Celsius and cause mass starvation for over a decade. Not to mention the fact that even during peacetime, decades of uranium mining, nuclear testing, and nuclear waste dumping have contaminated some of our planet’s ecosystems beyond repair, displacing entire communities—often communities of color—in the process.
The flip side of this symbiosis, however, means that climate change and nuclear weapons also share a common solution. A progressive nuclear policy should be based upon four core principles of the Green New Deal—international cooperation, reductions, transparency, and justice. Only by challenging the nuclear-industrial complex in its entirety—in a way akin to how the Green New Deal challenges the carbon economy in its entirety—can a progressive nuclear policy pull us back from the brink of atomic and environmental catastrophe. Progressive climate change policies should include demilitarization and disarmament provisions, and progressive nuclear policies should address the climate and humanitarian impacts of nuclear weapons. Similarly, nuclear activists and climate change activists are natural allies in the fight against existential risk, and both causes would benefit from a more robust partnership.
To that end, the significant attention imbalance between climate change and nuclear weapons must be urgently corrected; keeping them siloed reinforces an incomplete narrative about the nature of these existential threats.
US, critics split on whether tech made nuke shipments safer
“There’s enough high-level nuclear waste awaiting disposal in the U.S. to fill a football field 65 feet (20 meters) deep. Few states want to house it within their borders.”
“The public defines ‘safe’ as zero risk…the technical community defines ‘safe’ as complying with regulatory standards.” – Robert Halstead, head of the Agency for Nuclear Projects, is currently fighting plutonium shipments to Nevada and spent nuclear fuel transfers to the proposed Yucca Mountain dump.
BY: SCOTT SONNER | phys.org
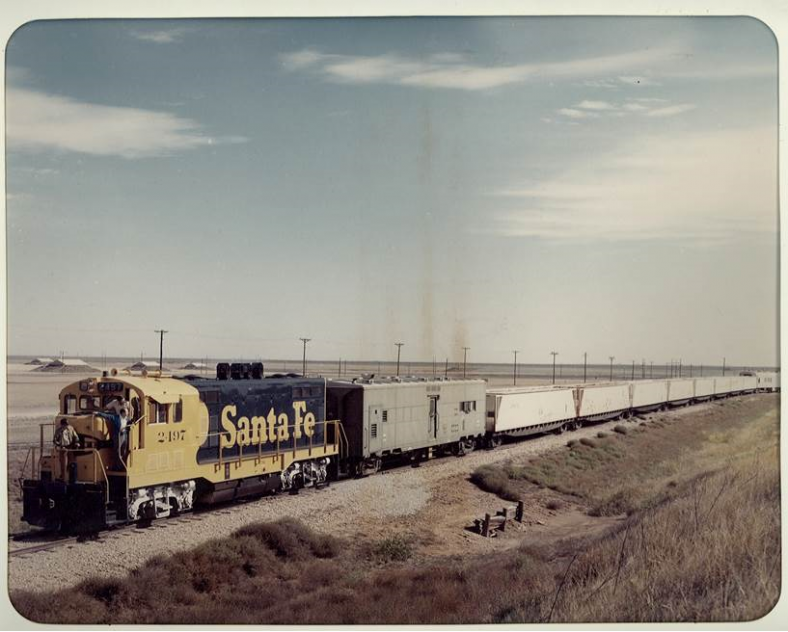

The plutonium core for the first atomic weapon detonated in 1945 was taken from Los Alamos National Laboratory to a test site in the New Mexico desert in the backseat of a U.S. Army sedan.
Officials put other bomb parts inside a metal container, packed it into a wooden crate and secured it in the steel bed of a truck under a tarp, the U.S. Energy Department’s National Nuclear Security Administration says in a historical account.
Grainy black-and-white photos show special agents and armed military police accompanying the shipment nearly 75 years ago.
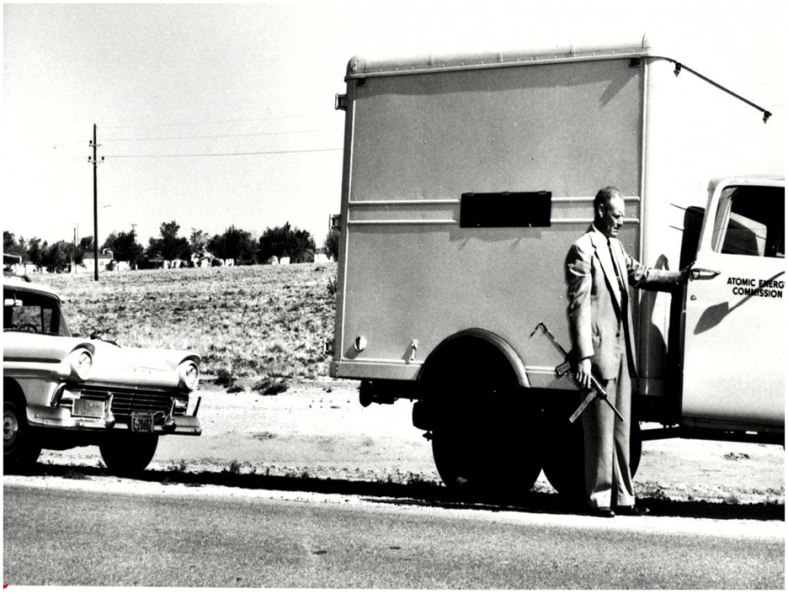

“Nuclear materials transportation has evolved since then,” the department posted online last year.
Today, radioactive shipments are hauled in double-walled steel containers inside specialized trailers that undergo extensive testing and are tracked by GPS and real-time apps.
But whether shipping technology has evolved enough to be deemed safe depends on whom you ask.
New research: Regional nuclear war will cause catastrophic global consequences
Two scientific studies modelling the effects of nuclear war released in the past few weeks have revealed some terrifying figures:
- 91.5 million deaths in a matter of hours, if nuclear conflict breaks out between the United States and Russia,
- 125 million deaths in case of a week-long conflict between India and Pakistan using 100 kilotonne nuclear warheads,
- A 30% reduction in surface sunlight due to the 36 teragrams of black carbon released into the atmosphere after the India-Pakistan conflict,
- Two billion people at risk of famine.
The two studies, Princeton’s Science and Global Security programme “Plan A” [ 1] and Science Advances’ Rapidly expanding nuclear arsenals in Pakistan and India portend regional and global catastrophe [ 2], show that there is no such thing as a contained nuclear conflict.
These are not farfetched scenarios. This new research comes out as tensions are increasing between India and Pakistan, and four of the nine nuclear-armed states have tested nuclear missiles in just the past two weeks. [3, 4] You can read more about this new research here.
The science is clear: we need to eliminate nuclear weapons, before they are used again.
Feds move to demolish 13 structures at toxic Santa Susana site without state oversight
BY: MIKE HARRIS | vcstar.com

The U.S. Department of Energy announced this week it has decided to demolish and remove, without state oversight, 13 of 18 remaining structures from its portion of the contaminated Santa Susana Field Laboratory as part of the much-delayed cleanup of the site.
However, in a so-called record of decision it issued Monday, the federal agency said it recognizes that the demolition and removal of the other five structures must be “compliant” with state permits and state hazardous waste laws.
Expanding nuclear weapon production is reckless
“Placing a novel warhead design in the active nuclear weapons stockpile with a substantially untested pit is irresponsible. Rapidly increasing production at sites with spotty records compounds that error with added safety hazards. Increasing plutonium pit production to a rate of 80 or more annually is both reckless and unnecessary.”
BY: MARYLIA KELLEY & JOSEPH RODGERS | thehill.com
© Getty ImagesBehind closed doors, Congress is in the process of making a decision that will have a profound impact on nuclear risk levels and global security. Hanging in the balance is a decision to recklessly increase production of plutonium bomb cores or “pits.” The NDAA conference committee must not make that mistake.
Pits are the triggers for thermonuclear weapons. Currently, the United States does not manufacture plutonium pits on an industrial scale. In its fiscal 2020 budget request the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) seeks authorization to produce at least 80 plutonium pits per year by 2030 at two facilities separated by some 1,500 miles. The Senate NDAA fully funds the request. The House instead authorizes 30 pits per year, all at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in NM. Los Alamos is presently authorized to produce 20 pits annually.
WIPP: New Mexico nuclear waste site’s five-year plan deemed ‘insufficient’ by state leaders
A group of governors from western states voiced “disappointment” in a recently released five-year strategic plan for ongoing operations at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, contending they weren’t adequately consulted on the future of the nuclear waste repository near Carlsbad.
BY: ADRIAN HEDDEN | carlsbadcurrentargus.com

Don Hancock, director of the Nuclear Waste Program at the Southwest Research and Information Center said the plan was insufficient in that it did not detail plans and costs needed to keep WIPP open until 2050. He said the plan detailed projects intended to keep WIPP open beyond 2025, without adequately explaining the associated costs.
“It’s not a five-year plan,” Hancock said. “The centerpiece of the plan is WIPP being open until 2050. That’s 30-year plan. They’re saying WIPP’s timeline needs to be doubled. This should be saying how WIPP is transitioning from emplacement to closure, but it does the opposite.”
Hancock said the DOE must communicate with the public on either keeping WIPP, known as a pilot project, open indefinitely or developing other repositories to handle the low-level transuranic (TRU) waste disposed of at the site.
He said another alternative would be for the DOE to develop a plan to emplace the waste at the generator sites – multiple nuclear facilities across the country – themselves.
US official: Research finds uranium in Navajo women, babies
About a quarter of Navajo women and some infants who were part of a federally funded study on uranium exposure had high levels of the radioactive metal in their systems, decades after mining for Cold War weaponry ended on their reservation, a U.S. health official said. The early findings from the University of New Mexico study were shared Monday during a congressional field hearing in Albuquerque.
MARY HUDETZ, ASSOCIATED PRESS jhnewsandguide.com
Leslie Begay, left, speaks with U.S. Rep. Deb Haaland, D-New Mexico, Monday outside a congressional field hearing in Albuquerque, N.M., highlighting the atomic age’s impact on Native American communities. Begay, a former uranium miner on the Navajo Nation with lung problems, says there are lingering injustices and health problems on his reservation decades after mines closed. An Indian Health Service official cited federal research at the hearing that she says showed some Navajo women, males and babies who were part of the study had high levels of uranium in their systems.Dr. Loretta Christensen — the chief medical officer on the Navajo Nation for Indian Health Service, a partner in the research — said 781 women were screened during an initial phase of the study that ended last year. Among them, 26% had concentrations of uranium that exceeded levels found in the highest 5% of the U.S. population, and newborns with equally high concentrations continued to be exposed to uranium during their first year, she said. The research is continuing as authorities work to clear uranium mining sites across the Navajo Nation.
“It forces us to own up to the known detriments associated with a nuclear-forward society,” said U.S. Rep. Deb Haaland, who is an enrolled member of Laguna Pueblo, a tribe whose jurisdiction lies west of Albuquerque.
The hearing held in Albuquerque by U.S. Sen. Tom Udall, Haaland and U.S. Rep. Ben Ray Lujan, all Democrats from New Mexico, sought to underscore the atomic age’s impact on Native American communities. The three are pushing for legislation that would expand radiation compensation to residents in their state, including post-1971 uranium workers and residents who lived downwind from the Trinity Test site in southern New Mexico.
An evolving nuclear agenda spurs plutonium pit production at LANL
A ‘dirty, dirty process’
BY: KENDRA CHAMBERLAINE | nmpoliticalreport.com
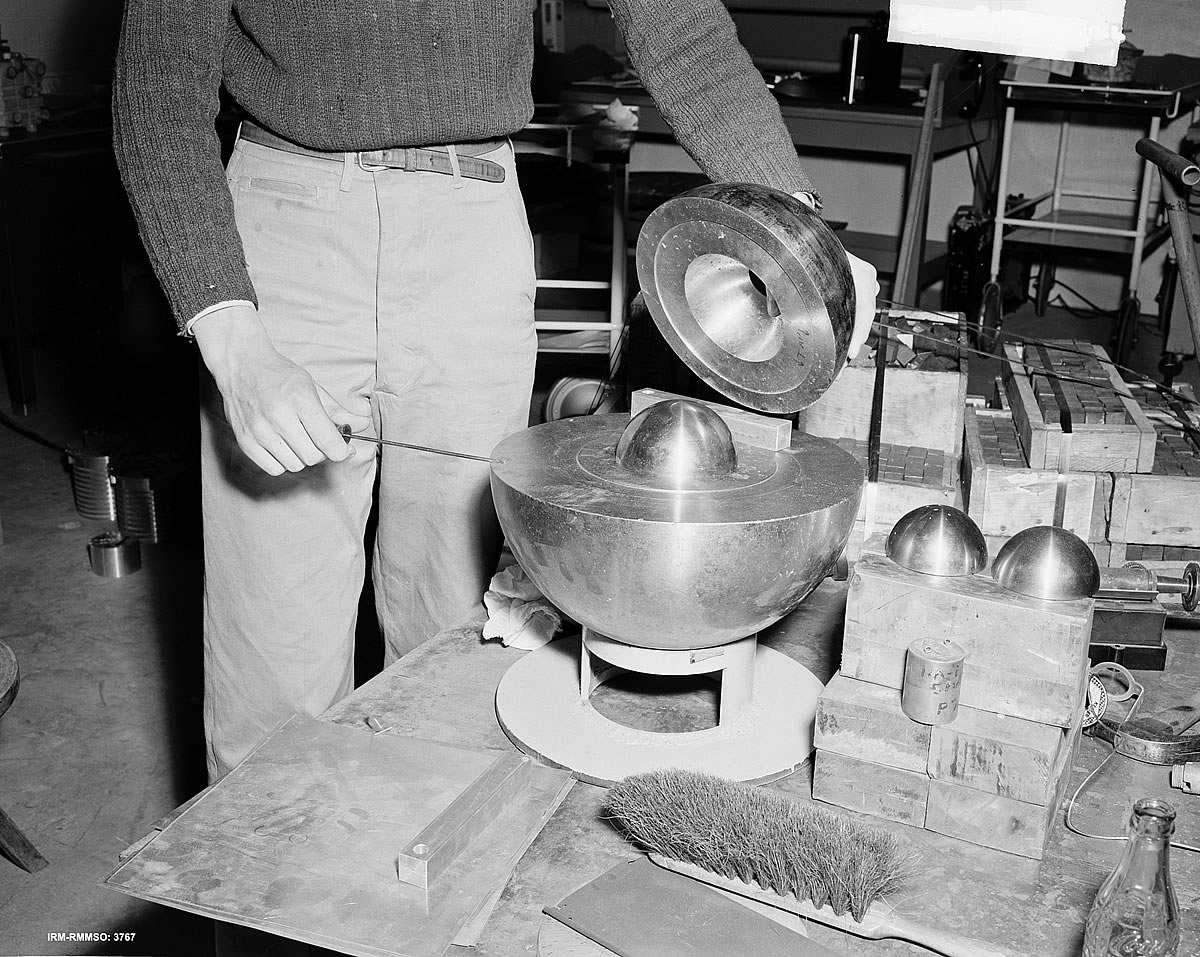

Los Alamos has a starring role in a shift to U.S. nuclear policy that’s two presidential terms in the making. Nuclear watchdog groups in the state are concerned about the United States’ evolving nuclear agenda, which will see a sharp increase in plutonium pit production at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL).
LANL recently released its $13 billion expansion proposal to accommodate increased pit production at the site. The expansion is part of a wider push across the country to ramp up the nuclear warhead manufacturing machine, according to Greg Mello, executive director of the Los Alamos Study Group.
Plutonium pits are central to nuclear weaponry. They are the “radioactive cores of modern nuclear weapons,” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico. He added that the pits themselves are weapons. “It was essentially a plutonium pit that destroyed Nagasaki on August 9, 1945,”
The ramp-up is years in the making, as successive presidential administrations have struggled to address how to modernize the U.S. nuclear stockpile. But nuclear watchdog groups worry an increase in pit production at LANL would have negative repercussions for the region. While LANL has touted the proposed economic benefits of its proposal for the area, activists argue the dangers outweigh the benefits.
Trump’s rumored pullout from Open Skies Treaty would idle Offutt jets
BY: STEVE LIEWER | OMAHA WORLD HERALD omaha.com
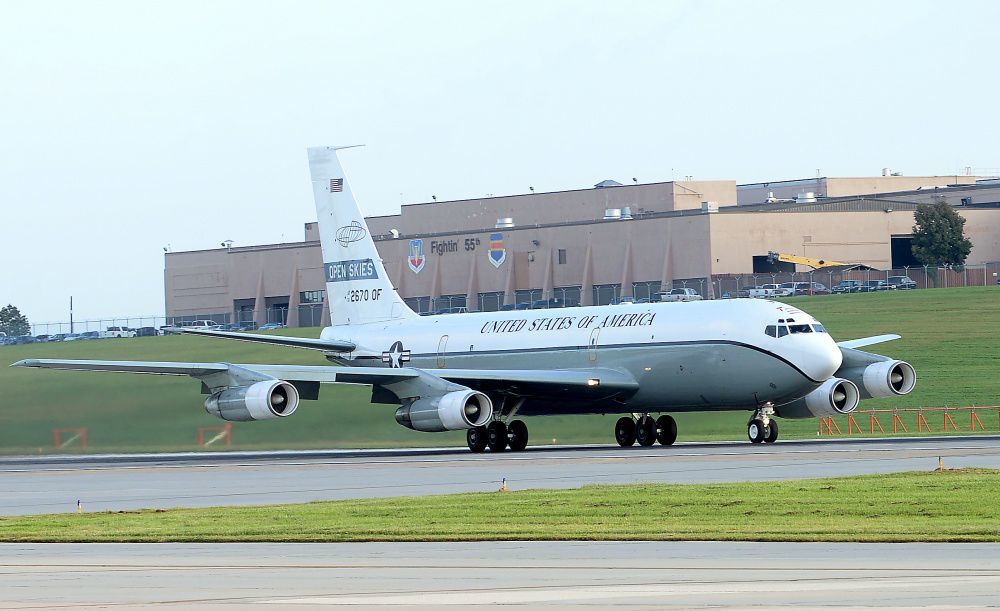

The Trump administration is believed to be preparing to pull out of the 34-nation Open Skies Treaty, a plan that would idle two Offutt-based OC-135B reconnaissance jets and their crews.
The treaty, proposed by President George H.W. Bush following the Cold War, allows member nations to fly supervised photo-reconnaissance flights over one another’s countries. This week, the U.S. and Germany are partnering on an Open Skies mission over Russia.
The planes are crewed and maintained at Offutt by the 45th Reconnaissance Squadron, which is part of the 55th Wing. Several dozen Offutt airmen are involved in the program.
The Nuclear Philanthropist
October 8 The MacArthur Foundation Director of the Nuclear Challenges Program Emma Belcher comes on Press the Button to discuss the role of philanthropy in fighting the two existential threats to humanity – nuclear weapons and climate change. On the Early Warning news segment, Erica Fein from Win Without War joins Tom Collina and Akshai Vikram from Ploughshares Fund to discuss the impeachment inquiry and how it’s affecting the debate over the defense budget.
Also, an answer to the question: Do nuclear weapons work in space?
Listen, Subscribe and Share on iTunes · Spotify · SoundCloud · YouTube · Google Play · Sticher
Also available on ploughshares.org/pressthebutton
There are about 26 nuclear weapons corporations earning nearly $100 billion per year amongst themselves. ‘They have vested financial interests in producing more and more nuclear weapons,’ says Dr Keith Suter (Australia), Economics Futurist and member of the Club of Rome, ‘and they exert intense political power on decision makers to protect these interests.‘
As the United Nations First Committee (Disarmament and International Security) starts its 2019 session in New York today, plans are progressing to publicise the colossal waste of money on nuclear weapons by physically ‘counting out’ the global nuclear weapons budget.
Over the next four weeks, governments meeting at the UN will debate and vote upon a number of nuclear disarmament resolutions. However, the impact of these resolutions is likely to be minimal as long as there continues to be strong financial interests in maintaining the nuclear arms race.
Count the Nuclear Weapons Money
The Count the Nuclear Weapons Money Action, which takes place during UN Disarmament Week (October 24-30), aims to raise media and public attention to this, and to publicise actions that indivduals and organisations can take to cut nuclear weapons budgets, end investments in nuclear weapons corporations, and shift these budgets and investments to better purposes.
The money counting will take place in a number of outside locations around Manhattan (as well as in New Jersey and Long Island) and at an interactive installation in an art gallery in the Chelsea neighborhood of Manhattan. Click here if you would like to join the counting.
Impeachment Slows All Hill Defense Biz; DoD Approps On Life Support
There’s not a lot of confidence out there about the prospects for a 2020 budget agreement. “A stripped down mini-NDAA may be all that could pass this year for defense,” says one long-time budget watcher.
BY COLIN CLARK | breakingdefense.com
WASHINGTON: As the House of Representatives gears up to impeach President Trump, it’s getting harder and harder for anyone involved in defense to get a hearing with leadership, and the chances for a defense appropriations bill appear to be getting smaller every day.
While the chances for a second year of regular order (actually passing spending and major policy bills) already seemed unlikely, impeachment is sucking the oxygen out of the room, leaving regular order gasping for air. President Trump’s decision to take $3.6 billion from military construction accounts to build the so-called wall along the border with Mexico probably killed the chances for a defense spending bill. Add impeachment and the experts say abandon hope, all ye who enter the Capitol.
We’re More at Risk of Nuclear War With Russia Than We Think
U.S. lawmakers on both sides of the aisle need to start addressing the danger.
BY: GEORGE BEEBE | politico.com

In the 1950s and 1960s, Americans genuinely and rightly feared the prospect of nuclear war with the Soviet Union. Schoolchildren regularly participated in air raid drills. Federal, state and local governments prepared for operations in the event of a nuclear emergency. More than a few worried citizens built backyard bomb shelters and stockpiled provisions.
Today, that old dread of disaster has all but disappeared, as have the systems that helped preclude it. But the actual threat of nuclear catastrophe is much greater than we realize. Diplomacy and a desire for global peace have given way to complacency and a false sense of security that nuclear escalation is outside the realm of possibility. That leaves us unprepared for—and highly vulnerable to—a nuclear attack from Russia.
The most recent sign of American complacency was the death, a few weeks ago, of the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty—a pivotal 1987 agreement that introduced intrusive on-site inspection provisions, destroyed an entire class of dangerous weaponry, and convinced both Washington and Moscow that the other wanted strategic stability more than strategic advantage.
Trump Claims Energy Secretary Rick Perry Is Behind Ukraine Call at Heart of Impeachment Inquiry: Report
President Trump told House Republicans that he made his now infamous phone call to Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky at the urging of Energy Secretary Rick Perry — a call Trump claimed he didn’t even want to make.
BY ANNA KAPLAN | thedailybeast.com Oct. 5, 2019
President Trump has reportedly tried to pin the explosive Ukraine call at the center of an impeachment inquiry on Energy Secretary Rick Perry. Axios reports that the president claimed Perry had asked him to make the July phone call to Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky that sparked a whistleblower complaint. Trump reportedly claimed that he did not even want to call Zelensky, but said Perry had wanted him to inquire about a liquified natural gas plant. Trump is currently facing an impeachment inquiry for allegedly using that phone call to pressure Zelensky to pursue an investigation into former vice president Joe Biden and his son’s ties to a major Ukrainian gas company.
Rapidly expanding nuclear arsenals in Pakistan and India portend regional and global catastrophe
The title of a new study by Toon et al, published this week in Science Advances, speaks volumes: “Rapidly Expanding nuclear arsenals in Pakistan and India portend regional and global catastrophe.”
advances.sciencemag.org | PSR’s press statement | usatoday.com | icanw.org
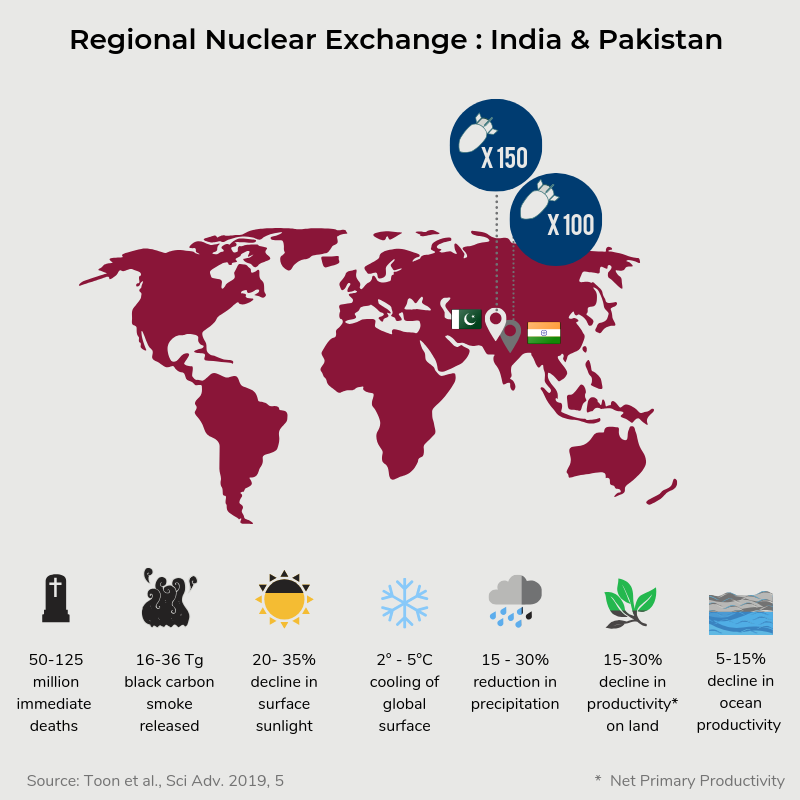
The study models the potential impacts of a regional nuclear conflict and found that, given the increased size and power of their respective nuclear arsenals, the effects of a nuclear conflict between India and Pakistan would have even more catastrophic impacts than previously thought.
Top Health Expert Warns of Drinking Water Risks in Piketon Radiation Case
“The source of the uranium and other poisonous substances found in the air and on school property — the Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant near Piketon, Ohio, which made material for nuclear bombs throughout the Cold War — is owned by the federal government. Simply put, the feds aren’t working very hard to investigate themselves.”
BY STUART H. SMITH | stuarthsmith.com
One thing that I’ve found to be a constant in more than 25 years of working cases around pollution from radiation: A good outside expert will often tell citizens the things that government or big business simply can’t or won’t.
IG: Embattled coalition should return up to $300K to DOE
ARTICLE BY: T.S. LAST | abqjournal.com
SANTA FE – The U.S. Department of Energy’s inspector general is recommending that the department seek reimbursement of up to $300,000 in DOE grant money that a coalition of local governments in northern New Mexico didn’t properly account for.
“The Regional Coalition is not the effective lobbying voice for clean up at Los Alamos that it claims to be because it condones DOE’s plan for cleanup on the cheap that will leave the vast majority of radioactive and toxic wastes permanently buried above our groundwater,” Jay Coghlan of Nuclear Watch New Mexico said in a statement Wednesday.
“The Coalition should pay the American taxpayer back whatever it improperly spent and be terminated. At a minimum, the City of Santa Fe should resign from this discredited Coalition right away.”
October 1 House Democrats launched an impeachment inquiry against President Donald Trump last week. What does this mean for nuclear policy and national security? Ro Khanna, US Representative from California’s 17th congressional district, joins Joe Cirincione for a special interview on the explosive allegations against the US president and the need to prevent a new war of choice during this time. Rep. Khanna, with Rep. Matt Gaetz (R-FL), introduced a bipartisan amendment to the annual National Defense Authorization Act to prevent federal funds from being used for any military force against Iran without congressional authorization. “In the Silo” provides an exclusive look at the August 6 protest in front of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, featuring narration by Ploughshares Fund Development Associate Elissa Karim.
News summary with Mary Kaszynski, Joe Cirincione, and Abigail Stowe-Thurston of the Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation. Joe Cirincione answers a question from Susan in California.
Listen, Subscribe and Share on iTunes · Spotify · SoundCloud · YouTube · Google Play · Sticher
Also available on ploughshares.org/pressthebutton

BY THAD MOORE tmoore@postandcourier.com
About this series
This article is the second part in “Lethal Legacy,” The Post and Courier’s investigation into the nation’s plans for disposing of plutonium, the dangerous metal that triggers nuclear weapons. This installment probes the Department of Energy’s failed MOX project, an ambitious but doomed effort to clean up the legacy of the Cold War.
Part I: Why South Carolina is likely stuck with a stockpile of the nation’s most dangerous nuclear materials
Dogged by faulty assumptions and lacking political will, the federal government squandered billions of dollars and an opportunity to dispose of the nation’s most dangerous nuclear material by chasing a massive construction project in South Carolina that was doomed from the start.
The MOX saga reveals an unsettling reality of the nuclear era after the Cold War. The U.S. and the world’s other nuclear powers have proven they are capable of pulling the explosive potential out of atoms, but they have proven unable to dispose of a creation that will retain immense power and be a danger for eternity.
What is MOX? MOX, short for mixed-oxide, is a type of fuel for commercial nuclear reactors. It gets its name from the combination of two oxidized nuclear metals: plutonium and uranium.The U.S. government and Russia agreed to make MOX fuel with highly enriched plutonium, which they made for nuclear weapons during the Cold War. The idea was to make the plutonium less potent and generate electricity by reacting it in power plants; the project’s supporters described it as a way for the countries to turn their “swords into plowshares.”
Nuclear weapons: Explained in numbers
There are far fewer nuclear weapons now than at the height of the Cold War and the major nuclear powers have all signed up to the principle of disarmament. But there are other countries that possess nuclear weapons which have not signed up to any arms control treaties.
And with fears of a renewed nuclear arms race between the US, Russia and China, the topic is high on the agenda at this year’s UN General Assembly. Reality Check’s Jack Goodman takes a look at the facts and figures behind the world’s nuclear arsenals.
Motion graphics by Jacqueline Galvin. | 26 Sep 2019 © bbc.com
Is it time to ditch the NPT?
“Nuclear weapon states have used this treaty to argue that their nuclear weapons are legal and a sovereign right. As a result, the NPT became the cornerstone of a severely hypocritical nuclear order where a few states regard wielding their nuclear weapons as legitimate while proscribing this sovereign right to other states…nuclear weapon states have no intention to give up their nuclear weapons.”

BY JOELIEN PRETORIU & TOM SAUER | thebulletin.org ![]()
In 2020, the participants in the 1970 Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) will congregate for the treaty’s 10th review conference. Which means that it may be a good time to re-examine the relevance of the NPT, and even consider the idea of dropping this treaty in its entirety, in favor of the new kid on the block: the 2017 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, also know as the Ban Treaty. At the risk of grossly oversimplifying, one treaty seeks to stop the further spread of nuclear weapons, while the other goes further and seeks to get rid of them entirely. This difference is reflected in their formal titles.
New Aerial Photos Released of Trifecta of U.S. Nuclear Construction Debacles
“We are pleased to facilitate distribution of the photos of the three failed nuclear projects in South Carolina and Georgia as close observation of them will reveal the status of the sites and where so much money has been needlessly wasted,” said Tom Clements, Director of Savannah River Site Watch (SRS Watch). “It is stunning to realize that perhaps $40 billion has been spent so far on the three sites, with the cost at all of them going up daily, money that should have been spent on projects of positive benefit to the public,” added Clements. “The photos commemorate the three largest, failed nuclear construction projects in the United States and will be of use when the proper investigations into the failed projects are conducted,” added Clements.
How a $5 part used to modernize nuclear warheads could cost $850 million to fix
World’s first nuclear smart bomb to become even more expensive..
BY AARON MEHTA | defensenews.com
WASHINGTON — Issues with commercial parts on two nuclear warhead modernization projects could cost up to $850 million to fix, but the agency in charge of America’s warheads believes it has a solution.
The issue, first revealed by Verdon during the Sept. 4 Defense News Conference, would put both warhead modernization programs at an 18- to 20-month delay of their first production units, although NNSA is hopeful there won’t be significant delays on the overall program timelines.
The parts in question are commercially available capacitors that, during stress testing, did not give NNSA confidence they could survive the 20-30 years needed for these designs. Verdon stressed that the parts were not at risk of failure under normal circumstances, but that the agency was acting out of an abundance of caution for the long-term life of the weapons.
That caution is pricey: the Original capacitors, Verdon said, ran about $5 per unit. The upgraded ones, built to a higher standard NNSA believes can survive the lifetime of the programs, come in at $75 per unit. All told, the B61-12 will cost an extra $600-700 million, and the W88 will cost about $120-$150 million because of the capacitor issue.
Federal Court Vacates former Y-12 Bomb Plant Ruling
ARTICLE FROM HUNGTINGTON NEWS huntingtonnews.net
“With this ruling,” said Ralph Hutchison, coordinator of the Oak Ridge Environmental Peace Alliance, “the NNSA no longer has any legal authority to continue construction of the Uranium Processing Facility bomb plant.” The decision may have ramifications for NNSA’s efforts to expand nuclear weapons production at other sites, too, including Los Alamos, NM and Savannah River, SC, where environmental scoping is underway for a new plutonium pit manufacturing facility.
Jay Coghlan, director of co-plaintiff Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said, “Uranium and plutonium components manufacturing are two sides of the same coin of expanding nuclear weapons production in an escalating arms race. The Department of Energy should take this court ruling against its Uranium Processing Facility as a warning that it must also comply with National Environmental Policy Act requirements while ill-advisably expanding the production of plutonium pits, the radioactive cores of nuclear weapons.”
The ruling also points out the crucial role the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board plays in monitoring safety issues at Y-12 and across the nuclear weapons complex. Since last year, the Department of Energy has worked to reduce the Safety Board’s access to some nuclear facilities, even issuing a revised Order to limit the information available to the Board and the restricting who the Board can and cannot speak to directly.
12 States join the Nuclear Ban Treaty on International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons 2019
On the International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons, 12 states took another significant step towards achieving this goal by signing or ratifying the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, during a special High-Level Ceremony at the UN Headquarters in New York.
The five nations that ratified during the ceremony are:
- Bangladesh
- Kiribati
- Laos
- Maldives
- Trinidad & Tobago
These states are also joined by Ecuador, which became the 27th state to ratify the Treaty on September 25th, one day before the ceremony.
The following states signed on to the Treaty: Botswana, Dominica, Grenada, Lesotho, St Kitts and Nevis, Tanzania and Zambia, as well as the Maldives and Trinidad and Tobago (as the latter two states both signed and ratified the Treaty during the ceremony).
The treaty now has 79 signatories and 32 States Parties. By signing, a State commits to not take any action that would undermine the treaty’s object and purpose. Upon depositing its instrument of ratification, acceptance, approval or accession, a state becomes legally bound by the terms of the treaty. When the Treaty has 50 states Parties it will enter into force, making nuclear weapons illegal under international law.
The ceremony was hosted by long-time champions of the Treaty: Austria, Brazil, Costa Rica, Indonesia, Ireland, Mexico, New Zealand, Nigeria, South Africa and Thailand and enabled presidents and foreign ministers to take this important step while they were gathered at the UNGA.
Newly-elected President of the UN General Assembly, Mr Tijjani Muhammad-Bande of Nigeria, opened the ceremony, and spoke passionately in support of the Treaty’s importance in ending nuclear weapons. “We commend states that have joined TPNW and urge those who have not done so to do join in this most vital action,“ he said during his address to the UNGA Plenary event earlier in the day.
Beatrice Fihn, Executive Director of ICAN, celebrated the move by these 12 countries and the outspoken support for the Treaty around the world throughout the day. “Away from most cameras, we come together to do the actual work of nuclear disarmament. For the good of your people and the good of the world you propel the Treaty toward entry-into-force […] Today, in this room, I feel the scale tilting toward the Elimination of Nuclear Weapons. This day of action gives us all hope at a bleak time.”
After today, the treaty is almost two-thirds of the way to its entry into force, and this momentum is expected to continue. Several countries have confirmed to ICAN that their ratifications are imminent, and campaigners around the world will not stop until every country is on board.
Join the movement to end nuclear weapons
The full ceremony can be viewed here:
Nuclear power is not the answer in a time of climate change
Wild weather, fires, rising sea levels, earthquakes and warming water temperatures all increase the risk of nuclear accidents, while the lack of safe, long-term storage for radioactive waste remains a persistent danger.
BY HEIDI HUTNER & ERICA CIRINO | aeon.co

Proponents of nuclear power say that the reactors’ relative reliability and capacity make this a much clearer choice than other non-fossil-fuel sources of energy, such as wind and solar, which are sometimes brought offline by fluctuations in natural resource availability. Yet no one denies that older nuclear plants, with an aged infrastructure often surpassing expected lifetimes, are extremely inefficient and run a higher risk of disaster.
‘The primary source of nuclear power going forward will be the current nuclear fleet of old plants,’ said Joseph Lassiter, an energy expert and nuclear proponent who is retired from Harvard University. But ‘even where public support exists for [building new] nuclear plants, it remains to be seen if these new-build nuclear plants will make a significant contribution to fossil-emissions reductions given the cost and schedule overruns that have plagued the industry.’
Nuclear Abolition: The Road from Armageddon to Transformation
Nuclear weapons pose a grave threat to the future of civilization. As long as we allow these weapons to exist, we flirt with the catastrophe that they will be used, whether intentionally or accidentally.
ESSAY BY DAVID KRIEGER
Great Transition Initiative (August 2018), http://www.greattransition.org/publication/nuclear-abolition.
Meanwhile, nuclear weapons skew social priorities, create imbalances of power, and heighten geopolitical tension. Diplomacy has brought some noteworthy steps in curbing risks and proliferation, but progress has been uneven and tenuous. The ultimate aim of abolishing these weapons from the face of the earth—the “zero option”—faces formidable challenges of ignorance, apathy, and fatigue.
Yet, the total abolition of nuclear weapons is essential for a Great Transition to a future rooted in respect for life, global solidarity, and ecological resilience.
Judge voids UPF decision, requires more seismic hazard analysis
BY: JOHN HUOTARI oakridgetoday.com
A federal judge in Knoxville on Tuesday said a critical decision made in 2016 for enriched uranium operations at the Y-12 National Security Complex, including for the $6.5 billion Uranium Processing Facility, violated a national environmental law, and she ordered the decision vacated, or set aside.
The UPF is already under construction, and Wedenesday morning, the National Nuclear Security Administration, which oversees work at Y-12, said construction will continue.
The 104-page opinion and order was filed in U.S. District Court on Tuesday by Chief U.S. District Judge Pamela L. Reeves.
The lawsuit was initially filed in U.S. District Court in the District of Columbia, but it was later moved to the Eastern District of Tennessee. Besides OREPA, the plaintiffs included two other public interest organizations—Nuclear Watch of New Mexico and Natural Resources Defense Council of Washington, D.C.— and several individual plaintiffs.
DOE for First Time Rejects Safety Board Recommendation – SRS Watch
SRS Watch and Nuclear Watch New Mexico have been working hard together on pit production issues. SRS Watch and NukeWatch NM, alongside other groups in ANA, have requested that the DNFSB now get involve in issue related to conversion of the canceled plutonium fuel (MOX) plant at SRS into a Plutonium Bomb Plant (PBP) to produce plutonium “pits” for nuclear weapons.
“The safety board informed ANA that it is monitoring the situation with pit production but we think they should actively be involved as NNSA continues to push this risky new mission on SRS,” said Clements of SRS Watch.
September 23 John F. Tierney, former US Representative and current executive director of the Council for a Livable World and the Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation, joins Joe Cirincione to discuss his work on the National Defense Authorization Act, and challenges the idea that US national security depends on ever-increasing defense spending.
News summary with Mary Kaszynski, Joe Cirincione, and Michelle Dover. Joe Cirincione answers a question from Clair in Massachusetts.
Listen, Subscribe and Share on iTunes · Spotify · SoundCloud · YouTube · Google Play · Sticher
Also available on ploughshares.org/pressthebutton
Nuclear News Archives – 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nuclear News Archives – 2020
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nuclear News Archives – 2019
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nuclear News Archives – 2018
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.





