Source/Reference Documents
Map Spreadsheet Examples 2021-2023
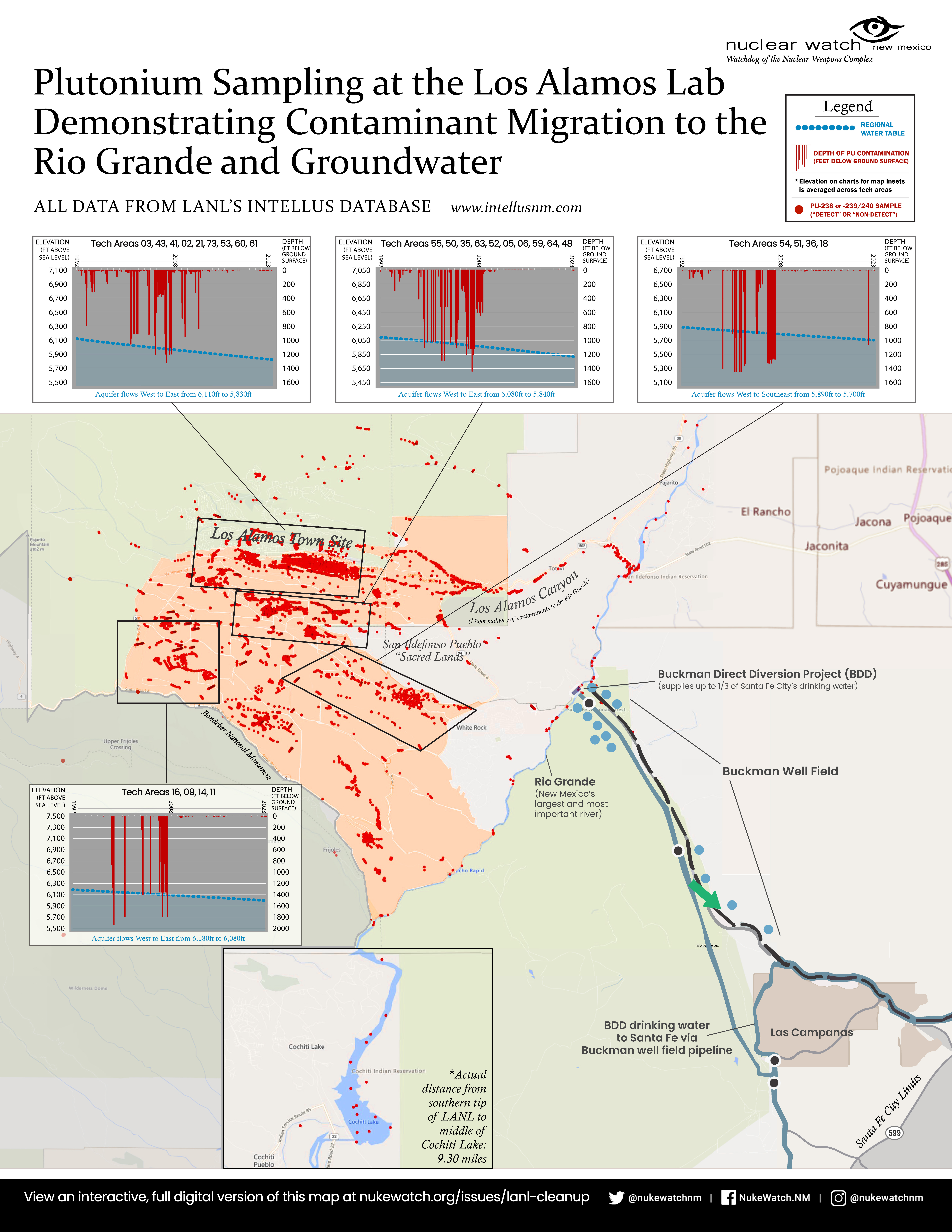
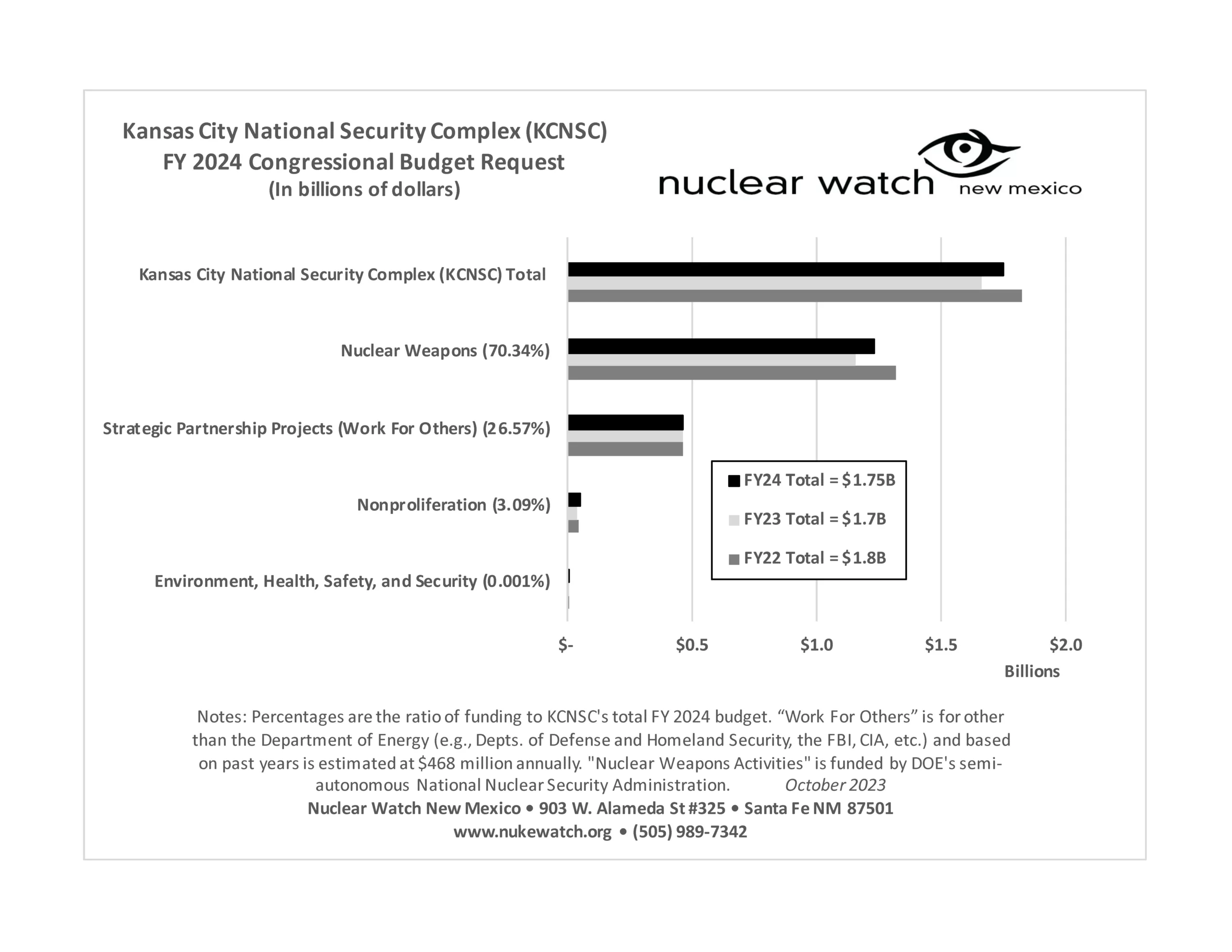
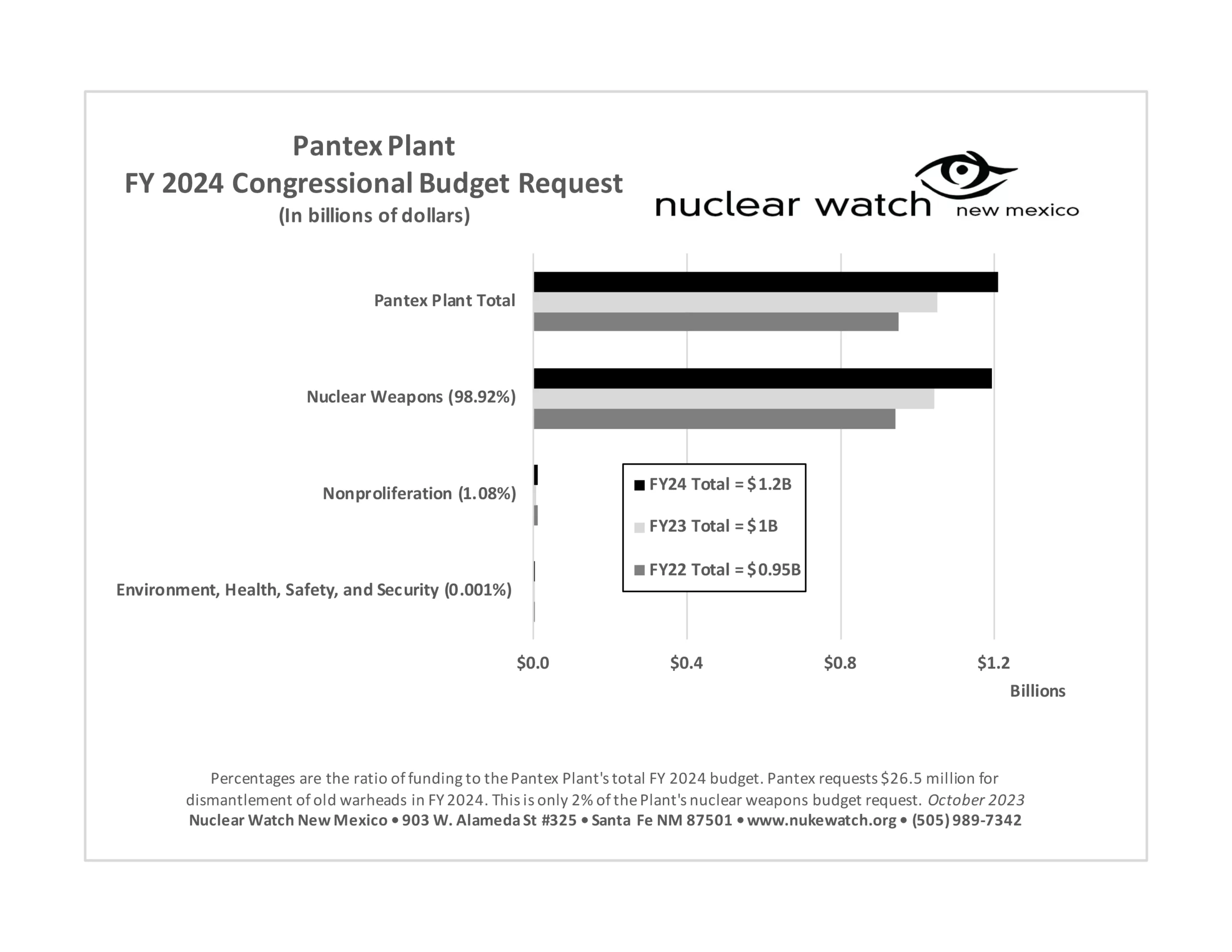
Below are examples of a spreadsheets created in Intellus, which is the environmental database at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The requests were for all soil and groundwater samples taken in, under, and around the Lab in 2021, 2022, and 2023. The spreadsheets were then sorted by “Report Result” (Column ‘F’), which lists the plutonium found in samples in descending order. It shows the highest sample for each year at top of the column.
Looking at the 2021 spreadsheet, there were 2043 samples analyzed for plutonium taken in 2021. There are approximately 100 detects including the high sample of 10100 pCi/g. Please read Dr. Ketterer’s report for a discussion of the ‘detects’ and ‘non-detects.’
Notice the latitude and longitude for each sample (columns ‘O’ and ‘P’). We used these coordinates to create the maps.
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New & Updated
Chromium Groundwater Contamination at Los Alamos Lab Far Greater Than Previously Expected; LANL’s Treatment Plan Must Be Drastically Changed
The Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) has detected far more hexavalent chromium (Cr) contamination than previously estimated in the “sole source” regional groundwater aquifer that serves Los Alamos, Santa Fe and the Española Basin. Sampling in July from a new well meant to inject treated groundwater back into the aquifer detected chromium contamination five times greater than the New Mexico groundwater standard of 50 micrograms per liter (ug/L).
Hexavalent chromium is a known carcinogen, and is the culprit in many illnesses as depicted in the well-known film Erin Brockovich. A “sole source aquifer” is a designation given by the Environmental Protection Agency when an aquifer supplies at least 50 percent of the drinking water for its service area and there are no reasonably available alternative drinking water sources should the aquifer become contaminated. Nuclear Watch discovered the alarming data in obscure entries in the Lab’s contamination database IntellusNM (http://intellusnm.com).
The location of the particular well, Chromium Injection Well 6 (CrIN-6), was chosen because LANL thought that it would be on the edge of the chromium groundwater plume where detection samples would be below the New Mexico standard of 50 ug/L, or in other words on the boundary of what legally requires treatment. Given this new information, if this new well is used to inject treated water, it will help push the contamination beyond Lab boundaries instead of blocking it. The thickness of the chromium plume at this location is not exactly known, but elsewhere it contaminates approximately the top 80 feet of the groundwater aquifer.
LANL’s “Chromium Plume Interim Measures Plan”, approved by the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED), is designed to remove chromium contaminated water from the center of the plume through extraction wells, treat it so it meets the state’s ground water standard, and inject the treated water into the leading edge of the plume in an attempt to slow or halt the plume migration.
CrIN-6 is currently the last proposed injection well, while injection wells 1 through 5 are already active. The new data indicates that the leading edge of the plume passed CrIN-6’s location some time ago. Injecting treated water into it now will only serve to push the plume farther east toward San Ildefonso Pueblo and the Buckman Wells that the City of Santa Fe relies on for a third of its drinking water.
The new data suggest there will have to be will have to be a complete re-thinking of chromium groundwater treatment by LANL and NMED, with more wells needed to both accurately find the true boundary of the chromium plume and eventual treatment. This inevitably means that remediation will take longer and cost more, when at the same time NMED weakened its own regulatory authority through a revised Consent Order governing cleanup that it agreed to with the Department of Energy last year (for more, see background below).
Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch Director, commented, “Timely budgets for additional urgently needed cleanup work at Los Alamos are far from being a given. The 2016 Consent Order that NMED and DOE negotiated both weakened and delayed cleanup at LANL, and allows DOE to get out of cleanup by simply claiming that it is too expensive or difficult. But we demand that DOE find additional funding to immediately address this threat to New Mexico’s precious water resources, without robbing other badly needed cleanup projects.” In contrast, funding for the Lab’s nuclear weapons that caused the contamination to begin with continues to grow.
NukeWatch Operations Director, Scott Kovac stated, “It is easy for data to get buried and never see the light of day in the Lab’s contamination database. LANL should proactively keep the public continuously informed of important new developments. NMED and LANL must modify and expand the chromium groundwater treatment plan to meet this growing threat. The new well must not be used for injection, and instead treated water should be injected in front of the contaminant source to help permanently flush it out, instead of behind it which will push the contamination offsite.”
# # #
Background
Chart of samples data from Intellus NM compiled by Nuclear Watch. To locate data, go to http://intellusnm.com and search by Location ID.
| Field Sample ID | Location ID | Sample Date | Parameter Name | Report Result | Report Units | Sample Time |
| CrIN6-17-142149 | CrIN-6 | 07-16-2017 | Chromium | 247.24 | ug/L | 19:00 |
| CrIN6-17-142150 | CrIN-6 | 07-16-2017 | Chromium | 249.69 | ug/L | 23:00 |
| CrIN6-17-142148 | CrIN-6 | 07-17-2017 | Chromium | 262.07 | ug/L | 15:00 |
| CrIN6-17-142151 | CrIN-6 | 07-17-2017 | Chromium | 252.07 | ug/L | 03:00 |
| CrIN6-17-142152 | CrIN-6 | 07-17-2017 | Chromium | 260.22 | ug/L | 11:00 |
| CrIN6-17-142154 | CrIN-6 | 07-17-2017 | Chromium | 257.65 | ug/L | 07:00 |
| CrIN6-17-142163 | CrIN-6 | 07-17-2017 | Chromium | 259 | ug/L | 15:00 |
Chromium was released into the head of Sandia Canyon until 1972.
- Potassium dichromate was used in cooling towers as a corrosion inhibitor at a Laboratory power plant
- Up to 72,000 kg was released from 1956-72 in hexavalent form [Cr(VI)]
Discovered in 2004
- A Cr plume is in the regional aquifer at 900–1,000 feet below the canyon bottom at deepest, which places the Cr into the top of the aquifer
- Size was estimated at approximately 1 mile x 1/2 mile x <50 feet thick
- Plume edge is approximately 1?2 mile from the closest drinking water well
For how the 2016 Consent Order has weakened NMED’s regulatory authority, see https://nukewatch.org/facts/nwd/Consent-Order-should-be-rescinded-9-10-17.pdf
Expanded Plutonium Pit Production at LANL Will Not Result in Significant Positive Effect On Job Creation and the Regional Economy
Abstract: Expanded production of plutonium pits, the fissile cores of modern thermonuclear weapons, is cynically being justified as a source of job creation. Precise data on employment in plutonium pit production at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) and the number of additional jobs if expanded is not publicly available to our knowledge. However, the National Nuclear Security Administration’s own documents quoted below explicitly state that expanded pit production would not have any significant positive effect on job creation and the regional economy of northern New Mexico. Further, Nuclear Watch argues that expanded plutonium pit production could actually have negative effect if expanded pit production blocks other economic alternatives such as comprehensive cleanup, which could be the real job producer. Moreover, given LANL’s poor safety and environmental record, expanded plutonium pit production could have a seriously negative economic effect on northern New Mexico in the event of any major accidents or additional contamination.
Final Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement for the Nuclear Facility Portion of the Chemistry and Metallurgy Research Building Replacement Project at Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico
https://energy.gov/nepa/eis-0350-s1-supplemental-environmental-impact-statement-nuclear-facility-portion-chemistry-and
Bolded emphasis added
Note: The CMRR-Nuclear Facility was the up to $6.5 billion dollar plutonium facility NNSA proposed to build at LANL in direct support of expanded plutonium pit production. The Obama Administration cancelled it in 2012 after costs rose so high. Nevertheless, the 2011 CMRR-Nuclear Facility supplemental environmental impact statement remains the most relevant source of publically available socioeconomic information concerning expanded plutonium pit production that we know of.
Volume 1, p. 2-43, Socioeconomics
…
Under the Modified CMRR-NF Alternative, an increase in construction-related jobs and businesses in the region surrounding LANL is also expected. Construction employment would be needed over the course of a 9-year construction period under either the Deep or Shallow Excavation Option. Construction employment under either option is projected to peak at about 790 workers, which is expected to generate about 450 indirect jobs in the region. Operation of the Modified CMRR-NF and RLUOB would involve about 550 workers at LANL, with additional workers using the facility on a part-time basis. The personnel working in the Modified CMRR-NF and RLUOB, when fully operational, would relocate from other buildings at LANL, including the existing CMR Building, so an increase in the overall number of workers at LANL is not expected.
Note: The first phase of the Chemistry and Metallurgy Research Replacement Project, the Radiological Laboratory Utility and Office Building (RLUOB), is already built. It is now being retrofitted to handle up to 400 grams of plutonium-239 equivalent instead of the original 8.4 grams. This will greatly increase its special nuclear materials analytical chemistry and materials characterization capabilities in direct support of expanded plutonium pit production.
Under the Continued Use of CMR Building Alternative, about 210 employees would continue to work in the CMR Building until safety concerns force additional reductions in facility operations. In addition, about 140 employees would be employed at RLUOB. A total of about 350 personnel would have their offices relocated to RLUOB. The personnel working in the CMR Building and RLUOB, when fully operational, would not result in an increase in the overall number of workers at LANL.
Pg. 4-12
4.2.9 Socioeconomics
Construction Impacts—Construction of new buildings at TA-55 to house CMR activities would require a peak construction employment level of 300 workers. This level of employment would generate about 852 indirect jobs in the region around LANL. The potential total employment increase of 1,152 direct and indirect jobs represents an approximate 1.3 percent increase in the workforce and would occur over the proposed construction period. This small increase would have little or no noticeable impact on the socioeconomic conditions of the region of influence (ROI).
Operations Impacts—CMRR Facility operations would require a workforce of approximately 550 workers. As evaluated in the CMRR EIS, this would be an increase of about 340 workers over currently restricted CMR Building operational requirements. Nevertheless, the increase in the number of workers in support of expanded CMRR Facility operations would have little or no noticeable impact on socioeconomic conditions in the LANL ROI (region of influence). New LANL employees hired to support the CMRR Facility would compose a small fraction of the LANL workforce and an even smaller fraction of the regional workforce.
4.3.9 Socioeconomics
Construction Impacts – Deep Excavation Option—Construction of the Modified CMRR-NF under the Deep Excavation Option would require a peak construction employment level of about 790 workers (LANL 2011a:Data Call Tables, 002). This level of employment would generate about 450 indirect jobs in the region around LANL. The potential total peak employment of 1,240 direct and indirect jobs represents an increase in the ROI workforce of approximately 0.8 percent. Direct construction employment would average 420 workers annually over this time, approximately half of the estimated peak employment. The average direct construction employment would result in about 240 indirect jobs in the region around LANL. This total of 660 direct and indirect jobs represents an approximate 0.4 percent increase in the ROI workforce. These small increases would have little or no noticeable impact on the socioeconomic conditions of the ROI.
Pg. 4-54
Chapter 4 – Environmental Consequences
Construction Impacts – Shallow Excavation Option—The impacts under the Shallow Excavation Option from construction of the Modified CMRR-NF would be similar to the Deep Excavation Option. The peak employment number of about 790 construction workers would be the same as under the Deep Excavation Option, and the annual average would be 410 workers over the life of the project. The average direct construction employment would result in about 240 indirect jobs in the region around LANL. This total of 650 direct and indirect jobs represents an approximate 0.4 percent increase in the ROI workforce. Therefore, there would be little or no noticeable impact on the socioeconomic conditions of the ROI.
Operations Impacts—Operations at the Modified CMRR-NF and RLUOB would require a workforce of approximately 550 workers, including workers that would come from other locations at LANL to use the Modified CMRR-NF laboratory capabilities. The number of workers in support of Modified CMRR-NF operations would cause no change to socioeconomic conditions in the LANL four-county ROI (region of influence). Workers assigned to the Modified CMRR-NF and RLUOB would be drawn from existing LANL facilities, including the CMR Building. The number of LANL employees supporting the Modified CMRR-NF and RLUOB operations would represent only a small fraction of the LANL workforce (approximately 13,500 in 2010) and an even smaller fraction of the regional workforce (approximately 165,000 in 2010).
Volume 2, p. 2-13: As discussed in this CMRR-NF SEIS, operation of the new CMRR-NF, if built, is not expected to result in any increase in LANL employment. The people expected to work in the new facility would be transferred from other facilities at LANL where CMR-related activities are currently being accomplished (such as the CMR Building).
– End of NNSA quotes –
Note: The CMRR-Nuclear Facility was expected to cost up to $6.5 billion. It’s pathetic that the largest construction project ever in New Mexico (with the exception of the interstate highways) was going to create no new Lab jobs.
Comprehensive cleanup at LANL would be a win-win for northern New Mexicans, permanently protecting the environment while providing hundreds of high paying jobs.
- When DOE wants to do something, it lowballs the cost. When DOE doesn’t want to do something, it highballs the cost. LANL has estimated that comprehensive cleanup of Area G would cost $29 billion. Using actual costs of cleaning up smaller dumps, Nuclear Watch has extrapolated that cleanup of Area G would cost $7 to 8 billion. See https://nukewatch.org/facts/nwd/Area_G_Comparison_Costs-11-14-12.pdf
- But of that $29 billion, DOE estimated that labor costs would be $13 billion. Applying that 45% proportion to Nuclear Watch’s estimate, that would be around $3.5 billion in jobs, jobs that northern New Mexico sorely needs.
- Comprehensive cleanup could be the real job producer. It has the additional advantage of being more conducive to regional economic development in that more locally based contractors could possibly do the cleanup work, instead nuclear weapons work such as expanded plutonium pit production conducted by huge out-of-state defense contractors such as Bechtel and Lockheed Martin.
Chromium Groundwater Contamination at Los Alamos Lab Far Greater Than Previously Expected; LANL’s Treatment Plan Must Be Drastically Changed
Santa Fe, NM.
The Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) has detected far more hexavalent chromium (Cr) contamination than previously estimated in the “sole source” regional groundwater aquifer that serves Los Alamos, Santa Fe and the Española Basin. Sampling in July from a new well meant to inject treated groundwater back into the aquifer detected chromium contamination five times greater than the New Mexico groundwater standard of 50 micrograms per liter (ug/L).
Talking Points: The 2016 LANL Cleanup Consent Order Should Be Rescinded
The 2005 LANL Cleanup Consent Order was all about the enforceable schedules. It required DOE and LANL to investigate, characterize, and clean up hazardous and mixed radioactive contaminants from 70 years of nuclear weapons research and production. It stipulated a detailed compliance schedule that the Lab was required to meet…Continue reading
Talking Points: The 2016 LANL Cleanup Consent Order Should Be Rescinded
Why rescind the 2016 Consent Order?
- In June 2016 the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED), the Department of Energy (DOE) and Los Alamos National Security, LLC (LANS) signed a revised Consent Order governing cleanup at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). The new Consent Order is a big step backward in achieving comprehensive, genuine cleanup at the Lab.
- NMED should have kept the original, enforceable 2005 Consent Order that it fought so hard for under the Richardson Administration, modified as needed for the cleanup schedule and final compliance date.
Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board to advocate for nuclear weaponeers?
From our colleague Don Hancock at the Southwest Research and Information Center:
Two members (Roberson and Santos) of the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB) have gone public over an internal dispute about a Memorandum of Agreement between DNFSB and the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) in which DNFSB staff would be detailed to NNSA so that, among other things, they would be “advocating for and defending NNSA’s FY 2018 budget request.” The internal memo is posted at: https://www.dnfsb.gov/sites/default/files/document/12526/Memo%20from%20Roberson%20and%20Santos%2C%20Objection%20to%20Memorandum%20of%20Agreement%20with%20DOE.NNSA%20.pdf
The memo is dated last Friday (August 11) and the detail would start August 21. Not a good sign that DNFSB is, in part, going from overseeing DOE weapons sites to advocating for NNSA’s budget. – End –
Our comment:
“Nuclear Watch New Mexico strongly objects to this attempt by the National Nuclear Security Administration to compromise the Safety Board. DNFSB has played a vital role in protecting the public from dangerous nuclear weapons activities that have been riddled with safety lapses, incompetence, cost overruns and mismanagement. The Safety Board is commissioned by Congress, not NNSA, and we fully expect the New Mexican congressional delegation to protect the Safety Board’s independence and objectivity.”
Nuclear war can be avoided – let’s get it right!
Despite the hyperbole from both Trump and Kim Jong Un, nuclear war can be avoided. This not an argument for complacency, but rather to get it right.
Perhaps the silver lining in the crisis with North Korea can be that that the focused attention of the peoples of the world will rise to demand brakes on nuclear weapons, as it did to great effect in the 1980’s. But now we finally have an international treaty banning nuclear weapons, just like chemical and biological weapons. It won’t be easy, but let’s roll up our sleeves and get the job done!
North Korea’s “not quite” ICBM can’t hit the lower 48 states
Theodore A. Postol, Markus Schiller, Robert Schmucker
From the point of view of North Korean political leadership, the general reaction to the July 4 and July 28 launches could not have been better. The world suddenly believed that the North Koreans had an ICBM that could reach the West Coast of the United States and beyond. But calculations we have made—based on detailed study of the type and size of the rocket motors used, the flight times of the stages of the rockets, the propellant likely used, and other technical factors—indicate that these rockets actually carried very small payloads that were nowhere near the weight of a nuclear warhead of the type North Korea could have, or could eventually have. These small payloads allowed the rockets to be lofted to far higher altitudes than they would have if loaded with a much-heavier warhead, creating the impression that North Korea was on the cusp of achieving ICBM capability.
In reality, the North Korean rocket fired twice last month—the Hwasong-14—is a “sub-level” ICBM that will not be able to deliver nuclear warheads to the continental United States. Our analysis shows that the current variant of the Hwasong-14 may not even be capable of delivering a first-generation nuclear warhead to Anchorage, Alaska, although such a possibility cannot be categorically ruled out. But even if North Korea is now capable of fabricating a relatively light-weight, “miniaturized” atomic bomb that can survive the extreme reentry environments of long-range rocket delivery, it will, with certainty, not be able to deliver such an atomic bomb to the lower 48 states of the United States with the rocket tested on July 3 and July 28.
….
We emphasize at this point that advances in rocketry demonstrated by North Korea in the Hwasong-14 are significant, and although the Hwasong-14 is not an immediate threat to the continental United States, variants that are almost certainly now under development, but probably years away from completion, will eventually become missiles with sufficient payloads to deliver atomic bombs to the continental United States.
…
General conclusions—for now. Our general conclusions from intensive study of a wide variety of data relating to the two rockets that North Korea launched in July:
- The Hwasong-14 does not currently constitute a nuclear threat to the lower 48 states of the United States.
- The flight tests on July 4 and 28 were a carefully choreographed deception by North Korea to create a false impression that the Hwasong-14 is a near-ICBM that poses a nuclear threat to the continental US.
- The Hwasong-14 tested on July 4 and 28 may not even be able to deliver a North Korean atomic bomb to Anchorage, Alaska.
- Although it is clear that North Korea is not capable of manufacturing sophisticated rocket components, their skill and ingenuity in using Soviet rocket motor components has grown very substantially. This is not good news for the long run.
It is time for the United States to get serious about diplomacy and appropriate defensive preparations (see sidebar, “Comments on the developing situation with North Korea”) to constructively support those diplomatic efforts.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.