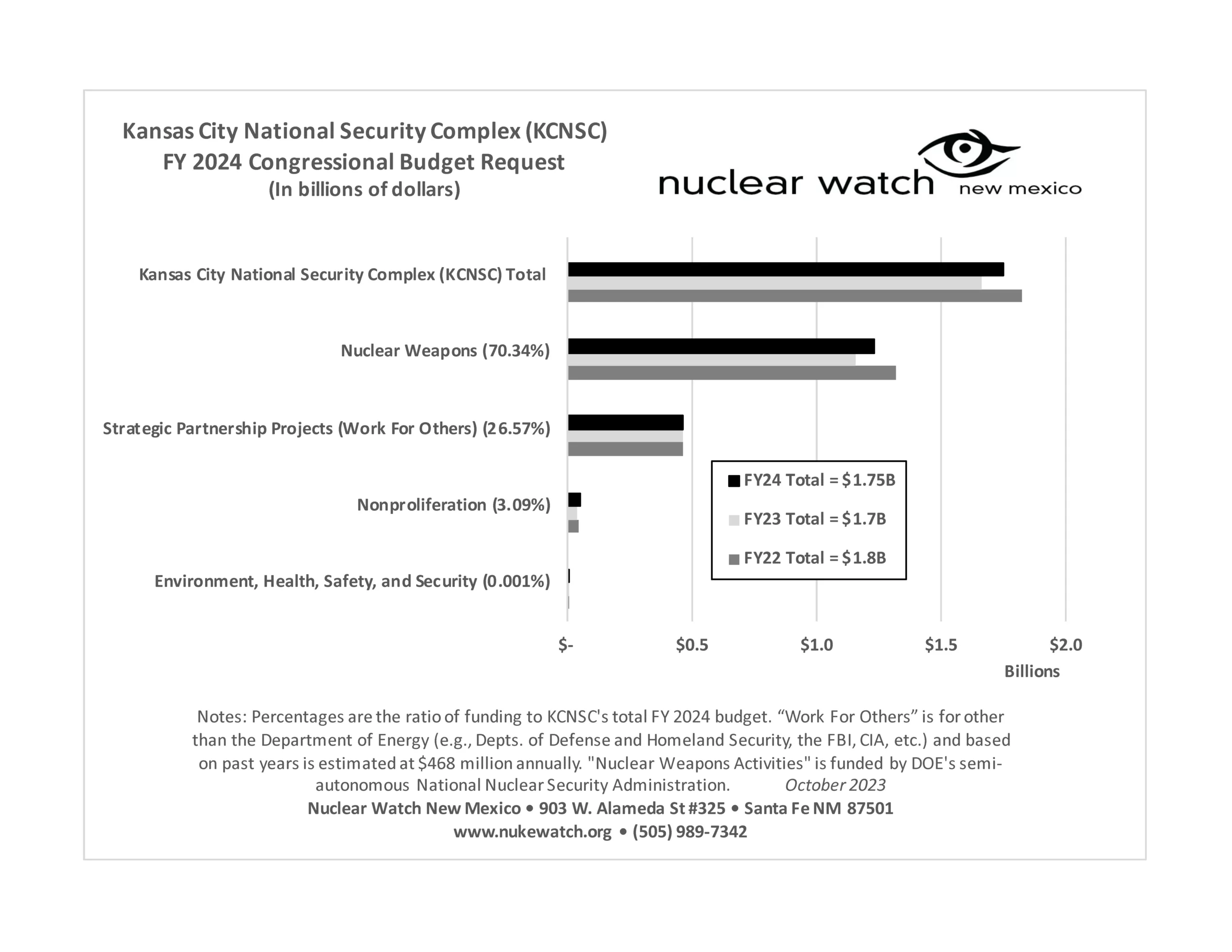
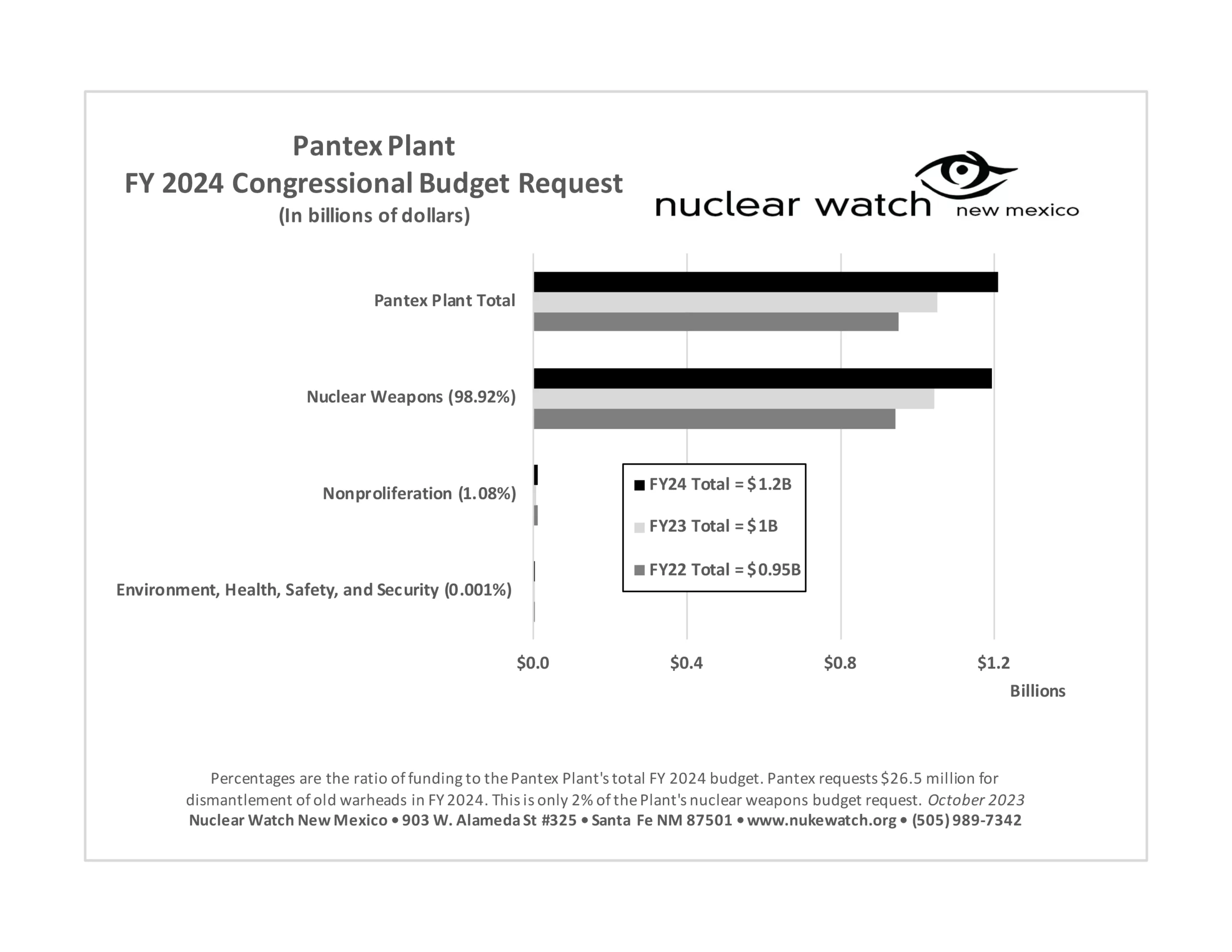
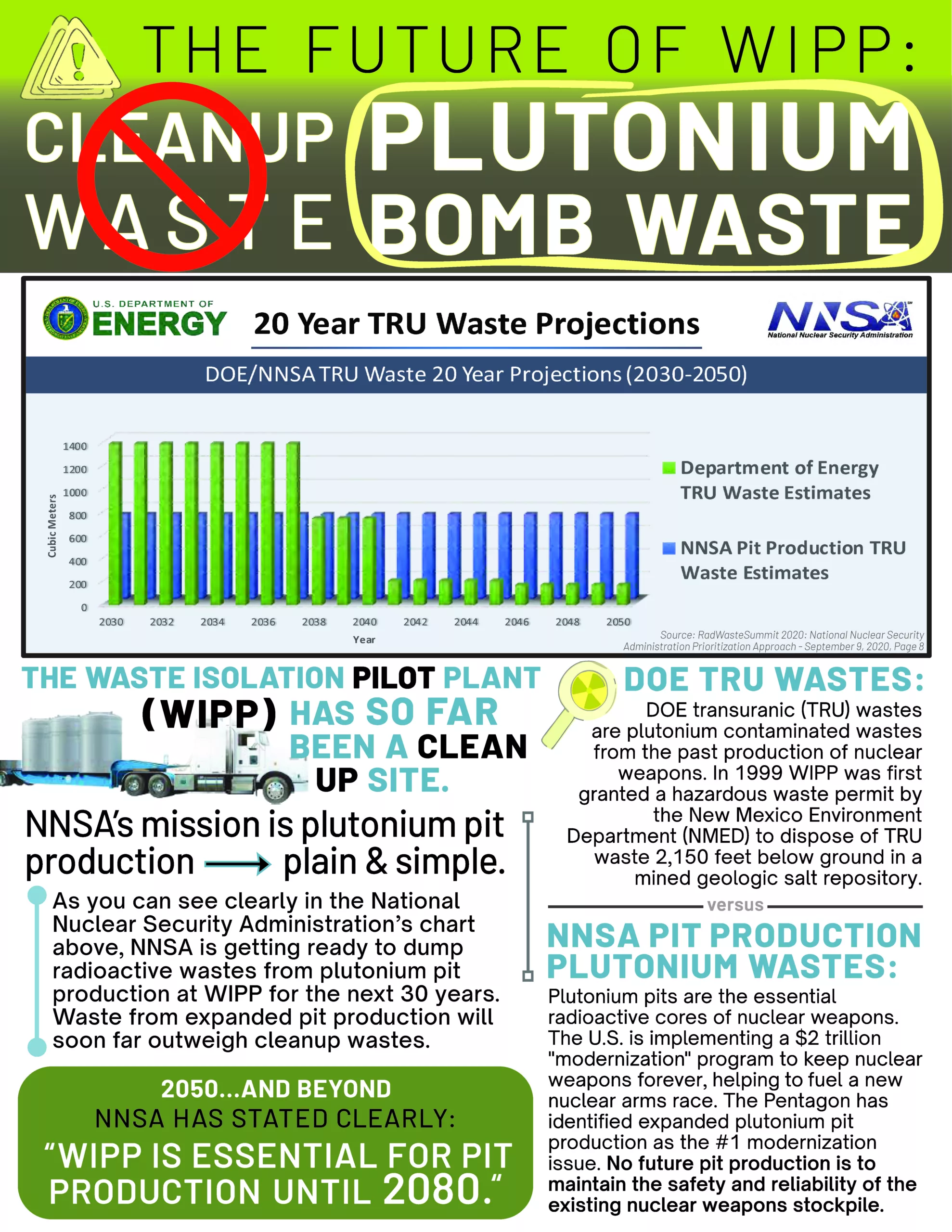
Source/Reference Documents
Map Spreadsheet Examples 2021-2023
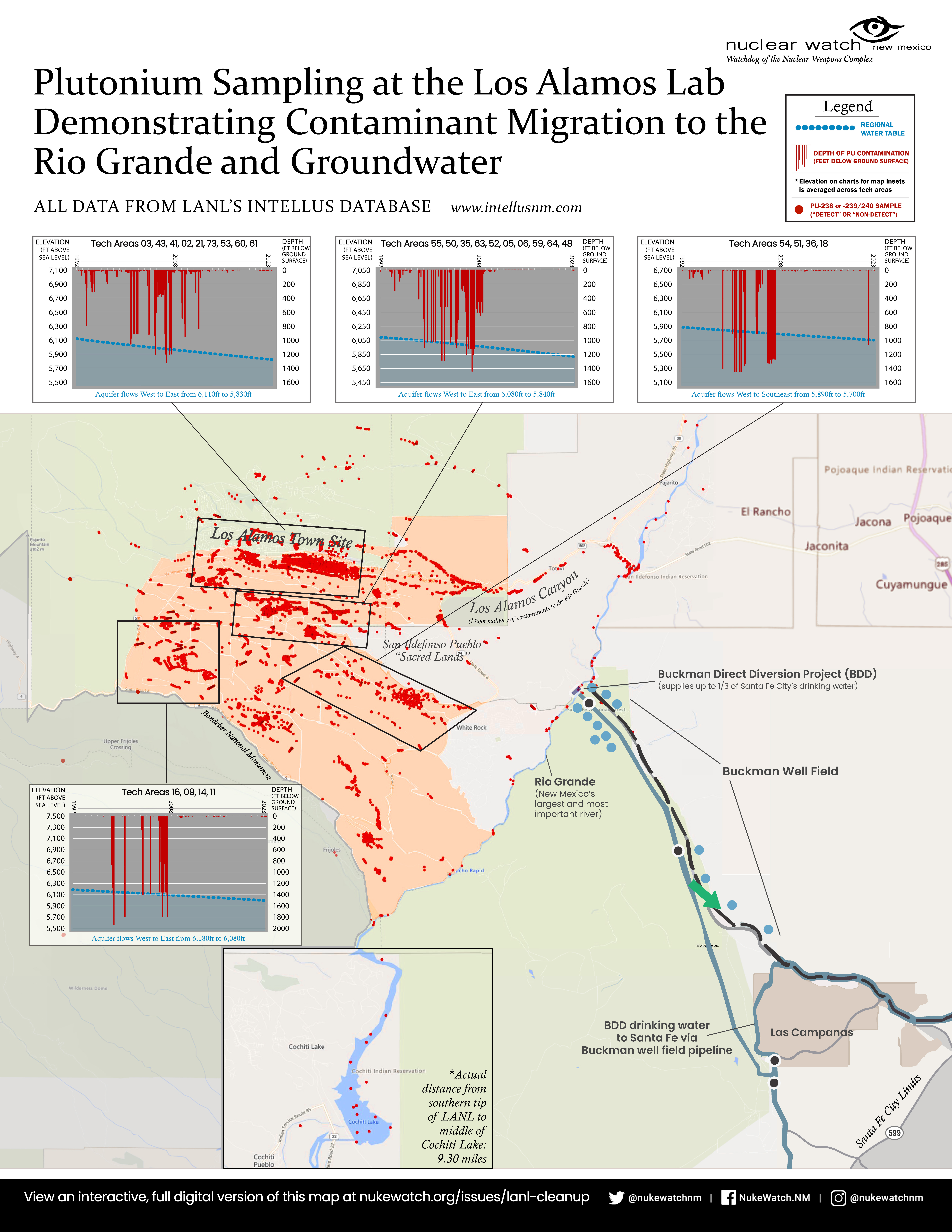
Below are examples of a spreadsheets created in Intellus, which is the environmental database at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The requests were for all soil and groundwater samples taken in, under, and around the Lab in 2021, 2022, and 2023. The spreadsheets were then sorted by “Report Result” (Column ‘F’), which lists the plutonium found in samples in descending order. It shows the highest sample for each year at top of the column.
Looking at the 2021 spreadsheet, there were 2043 samples analyzed for plutonium taken in 2021. There are approximately 100 detects including the high sample of 10100 pCi/g. Please read Dr. Ketterer’s report for a discussion of the ‘detects’ and ‘non-detects.’
Notice the latitude and longitude for each sample (columns ‘O’ and ‘P’). We used these coordinates to create the maps.
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New & Updated
DOE Inspector General report on the B61-12 nuclear smart bomb
The Department of Energy Inspector General has issued its audit report National Nuclear Security Administration’s Management of the B61-12 Life Extension Program. The B61-12 will literally cost twice its weight in gold. It is slated for production beginning 2020 and will blur the line between battlefield and strategic nuclear weapons by combining one strategic and three tactical variants. It will also be the world’s first “smart” nuclear bomb with a steerable tailfin kit giving it vastly improved accuracy. Nevertheless the U.S. government denies that the B61-12 will have any new military capabilities.
In its audit report, the DOE IG notes:
We believe without further improvement to its project management tools, it will be difficult for the program to proactively manage the costs, schedule, and risks of the B61-12 LEP to ensure it can deliver the First Production Unit within cost and meet its critical national security schedule. In addition, there is uncertainty whether the original cost estimate for the B61-12 LEP contains sufficient management reserve to allow the program to respond to the numerous risks identified in the program. Finally, not having documented assurance that unresolved significant finding investigations are a part of weapons design input significantly reduces management’s ability to ensure that redesigned nuclear weapon components have addressed prior safety and reliability concerns.
Regarding the last sentence “… reduces management’s ability to ensure that redesigned nuclear weapon components have addressed prior safety and reliability concerns”:
There was a problem with the new-design arming, firing and fuzing set for the W76-1, which is being produced now in its current Life Extension Program. It wasn’t a showstopper, but nevertheless a problem where new individual AF&F components had to be screened to determine whether their performance was affected.
The graph below from the 1993 Sandia Stockpile Life Study shows how the supermajority of nuclear weapons defects are discovered within the first few years of production. The point I’m reaching for is that as Life Extension Programs become more aggressive and more new-design components are used, design and production defects will be inevitable. It would be far better to maintain the stockpile through a conservative curatorship approach.
Circa 1995 I met with DOE Asst. Sec. for Defense Programs Victor Reis, the so-called father of the Stockpile Stewardship Program. Reis explicitly told me that the exorbitant Stockpile Stewardship Program was all about “the other side of the bathtub curve,” meaning it’s all about accelerated defects showing up at some time due to aging. Guess what? It hasn’t happened, not with ongoing surveillance and maintenance and exchange of limited life components that have been almost routine for decades. As the 1993 Sandia Stockpile Life Study concluded,
“It is clear that, although nuclear weapons ages, they do not wear out; they last as long as the nuclear weapons community (DOE and DOD) desire. In fact, we can find no example of a nuclear weapon retirement where age was ever a major factor in the retirement decision.”
Since then, the 1993 Sandia Stockpile Life Study’s conclusion has been buttressed by the JASON’s 2006 Pit Life Study and 2009 Life Extension Programs Study. In short, Life Extension Programs are not necessary for maintaining the nuclear stockpile, and may in fact undermine reliability by intentionally introducing major changes to an extensively tested stockpile. Life Extension Programs are, however, essential for creating new military capabilities for existing nuclear weapons, which is pretty clearly demonstrated by the B61-12 about to go into production, and arguably the W76-1 as well.

NNSA Set to Approve New Facilities for Expanded Plutonium Pit Production Without Credible Plans and Required Public Review
August 10, 2016
Santa Fe, NM – Yesterday, on the 71st anniversary of the destruction of Nagasaki by a plutonium bomb, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) submitted a report to the Senate Armed Services Committee on the National Nuclear Security Administration’s (NNSA’s) plans to expand plutonium pit production at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. NNSA has scheduled a formal “Critical Decision 2” at the end of this coming September to proceed with preliminary design of the upgraded and new facilities necessary to expand plutonium pit production.
The NNSA is a semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency within the Department of Energy, which has the singular distinction of being the only federal department on the GAO’s High Risk List for wasting taxpayer’s dollars for 25 consecutive years. LANL is NNSA’s so-called “Plutonium Center of Excellence” and the nation’s only site for pit production, but major operations at PF-4, its main plutonium facility, have been stopped since June 2013 because of nuclear criticality safety concerns. In addition, there is no place for LANL to send its radioactive transuranic wastes from plutonium pit production since one of its waste drums ruptured at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in February 2014 and indefinitely closed that multi-billion facility.
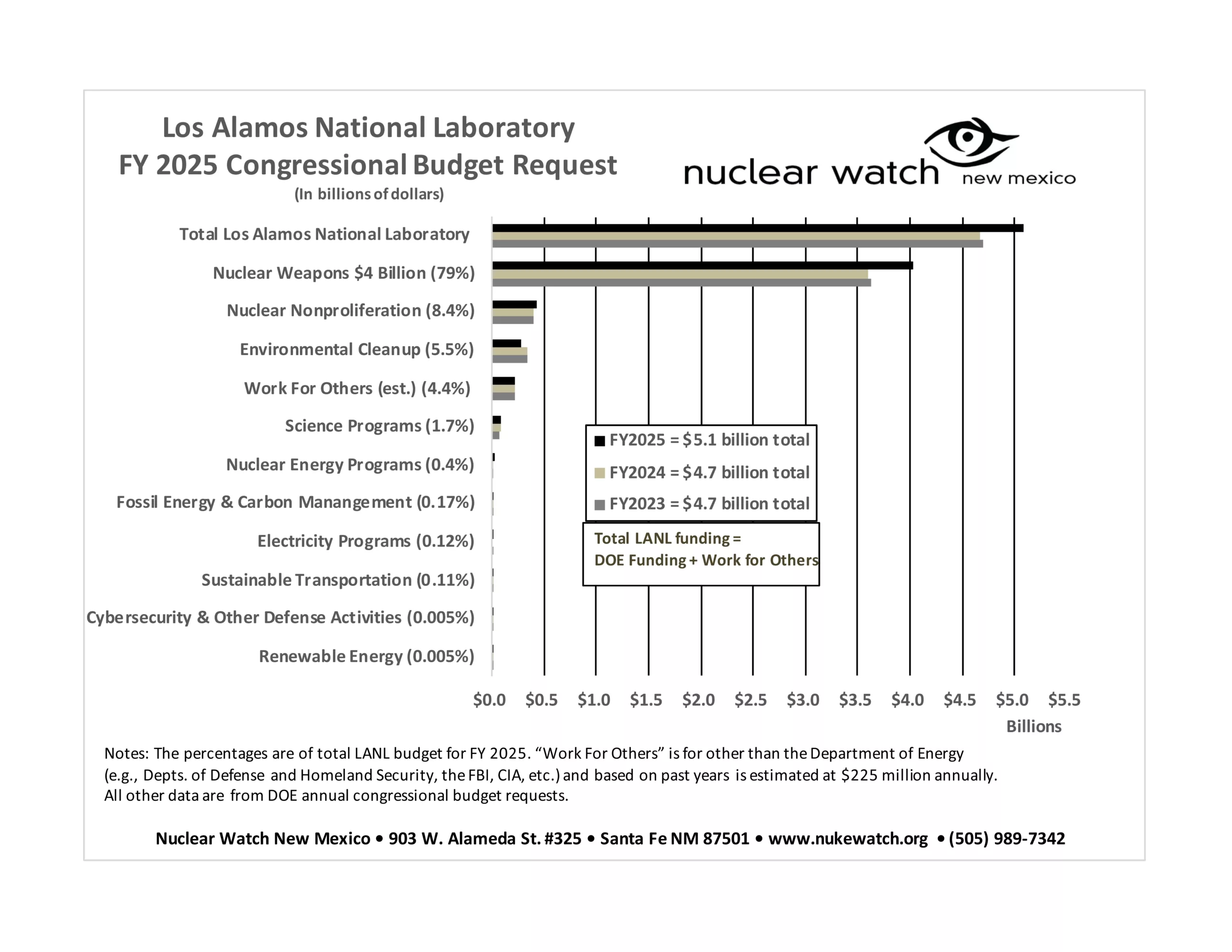
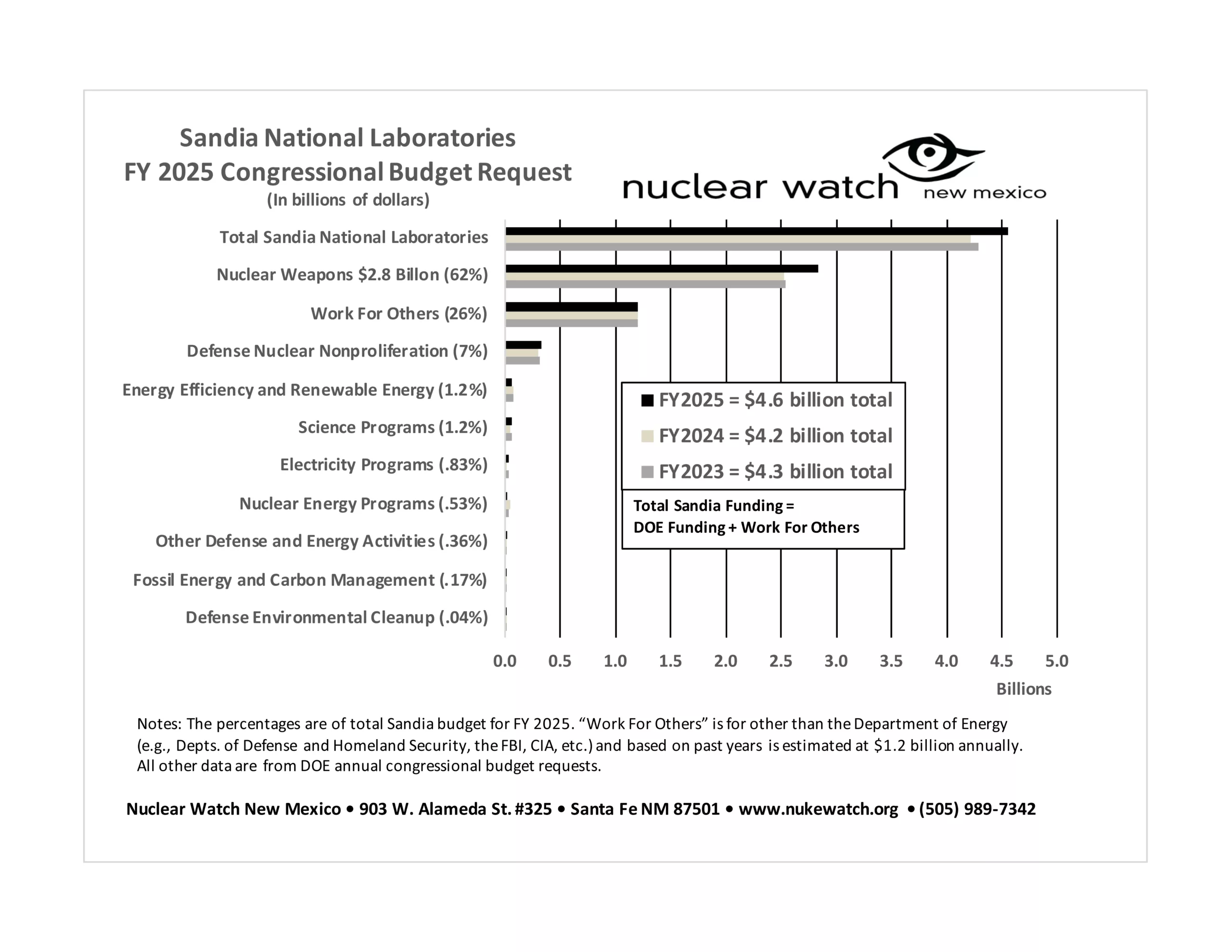
Despite all this, funding for NNSA’s nuclear weapons research and production programs is being increased to nearly double the Cold War’s historic average, while nonproliferation, warhead dismantlement and cleanup programs are being cut or held flat. This is in part due to plans to spend at least a trillion dollars over the next 30 years on completely rebuilding U.S. nuclear weapons and producing new missiles, subs and bombers to deliver them. The “modernized” U.S. nuclear force is expected to be operational until at least until 2080, more than a century after the 1970 NonProliferation Treaty’s mandate for global nuclear disarmament.
The GAO’s report found that NNSA’s plans for upgraded and new facilities to expand plutonium pit production to 50-80 pits per year “did not include key performance parameters” and lacked analysis of a full range of alternatives. LANL’s currently approved production level is up to 20 pits per year, sanctioned in a 1996 Stockpile Stewardship and Management Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement that was required under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). Subsequent NEPA efforts by NNSA to formally approve expanded plutonium pit production at LANL failed, and new efforts to expand plutonium pit production without adequate NEPA coverage could be vulnerable to legal challenge. Additionally, there is no public explanation or justification for the need to expand to 50-80 pits per year other than the nuclear weaponeers saying so. In contrast, independent expert studies have shown that pits have reliable lifetimes of at least a century (the average age of pits in the stockpile is now around 31 years), and up to 20,000 plutonium pits are already stored at the Pantex Plant near Amarillo, TX.
In 2012, in the face of exploding costs and rising citizen opposition, NNSA cancelled an earlier proposal to build a Walmart-sized “Chemistry and Metallurgy Research Replacement (CMRR) Project-Nuclear Facility” for expanded plutonium pit production. Now, as an alternative, NNSA and LANL seek to raise the administrative limit on plutonium in the CMRR Project’s first phase, the newly constructed Radiological Lab, from an original 8.4 grams to 400 grams; upgrade PF-4, the Lab’s main plutonium facility; and proceed with a “Plutonium Modular Approach project.”
Raising the amount of plutonium in the Rad Lab to 400 grams allows for dramatically increased “materials characterization” and “analytical chemistry” in direct support of expanded plutonium pit production. But it also raises the Rad Lab from a “radiological facility” to a “Hazard Category 3” nuclear facility, which has never been done before. Planned gloveboxes and the existing ventilation system may have to change and the facility’s seismic safety rating re-examined. The Rad Lab was originally constructed and equipped for a total cost of $400 million, but now up to another $675 million in equipment is being added. On top of that, re-categorizing the Rad Lab to a Hazard Category 3 facility could cost another $365 million. In all, the Rad Lab can cost up to $1.5 billion, while upgrades to PF-4 will cost another billion.
The Plutonium Modular Approach involves building at least two and perhaps three underground “modules” at one billion dollars each or more. The GAO report notes how since NNSA narrowly defined the program requirement as building the modules themselves instead of examining the need for the modules, “there is effectively no project alternative other than the modular approach,” despite DOE’s own orders to complete an analysis of a full range of alternatives.
In all, according to the GAO report, the full CMRR alternative of upgrading the Rad Lab and PF-4 and building at least two modules would cost at least 4 billion dollars, compared to the CMRR”s previous price tag of $5.8 billion (which was up from $975 million in 2005), and this is before the usual cost overruns. The GAO report also notes how the CMRR alternative appears cheaper because non-nuclear weapons operations, such as preparing plutonium for NASA’s spacecraft battery packs, have been eliminated. NNSA’s pattern when faced with its own cost overruns is to cut out all but nuclear weapons production, as it did with the Uranium Processing Facility (UPF) near Oak Ridge, TN. When a Defense Department estimate put UPF construction at $19 billion (up from $6.5 billion), NNSA eliminated dismantlements and downblending of highly enriched uranium so that it could keep production of thermonuclear components that can kill millions.
Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch Director, commented, “Expanded plutonium pit production at LANL is not needed to maintain stockpile safety and reliability, but instead is a must for nuclear weaponeers who want to give existing weapons new military capabilities through so-called Life Extension Programs. This GAO report is more evidence of how taxpayers’ money could be far better spent than on poorly planned, unnecessary and very expensive expanded plutonium pit production.”
# # #
The GAO report NNSA Needs to Clarify Requirements for Its Plutonium Analysis Project at Los Alamos is available at
http://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-16-585?utm_medium=email&utm_source=govdelivery
DOE’s 25 year status on GAO’s High Risk list is documented at
http://www.gao.gov/highrisk/doe_contract_management/why_did_study
For an extensive history of successful citizen activism against plutonium pit production see
NNSA Set to Approve New Facilities for Expanded Plutonium Pit Production Without Credible Plans and Required Public Review
Santa Fe, NM
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) is a semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency within the Department of Energy, which has the singular distinction of being the only federal department on the GAO’s High Risk List for wasting taxpayer dollars for 25 consecutive years. LANL is NNSA’s so-called “Plutonium Center of Excellence” and the nation’s only site for pit production, but major operations at PF-4, its main plutonium facility, have been stopped since June 2013 because of nuclear criticality safety concerns. In addition, there is no place for LANL to send its radioactive transuranic wastes from plutonium pit production since one of its waste drums ruptured at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in February 2014 and indefinitely closed that multi-billion facility.
Despite all this, funding for NNSA’s nuclear weapons research and production programs is being increased to nearly double the Cold War’s historic average, while nonproliferation, warhead dismantlement and cleanup programs are being cut or held flat…
LANL Estimate of $2.9 Billion for “Remaining” Cleanup Leaves Nuclear & Toxic Wastes Behind and Kills Needed Jobs
For immediate release July 28, 2016
LANL Estimate of $2.9 Billion for “Remaining” Cleanup
Leaves Nuclear & Toxic Wastes Behind and Kills Needed Jobs
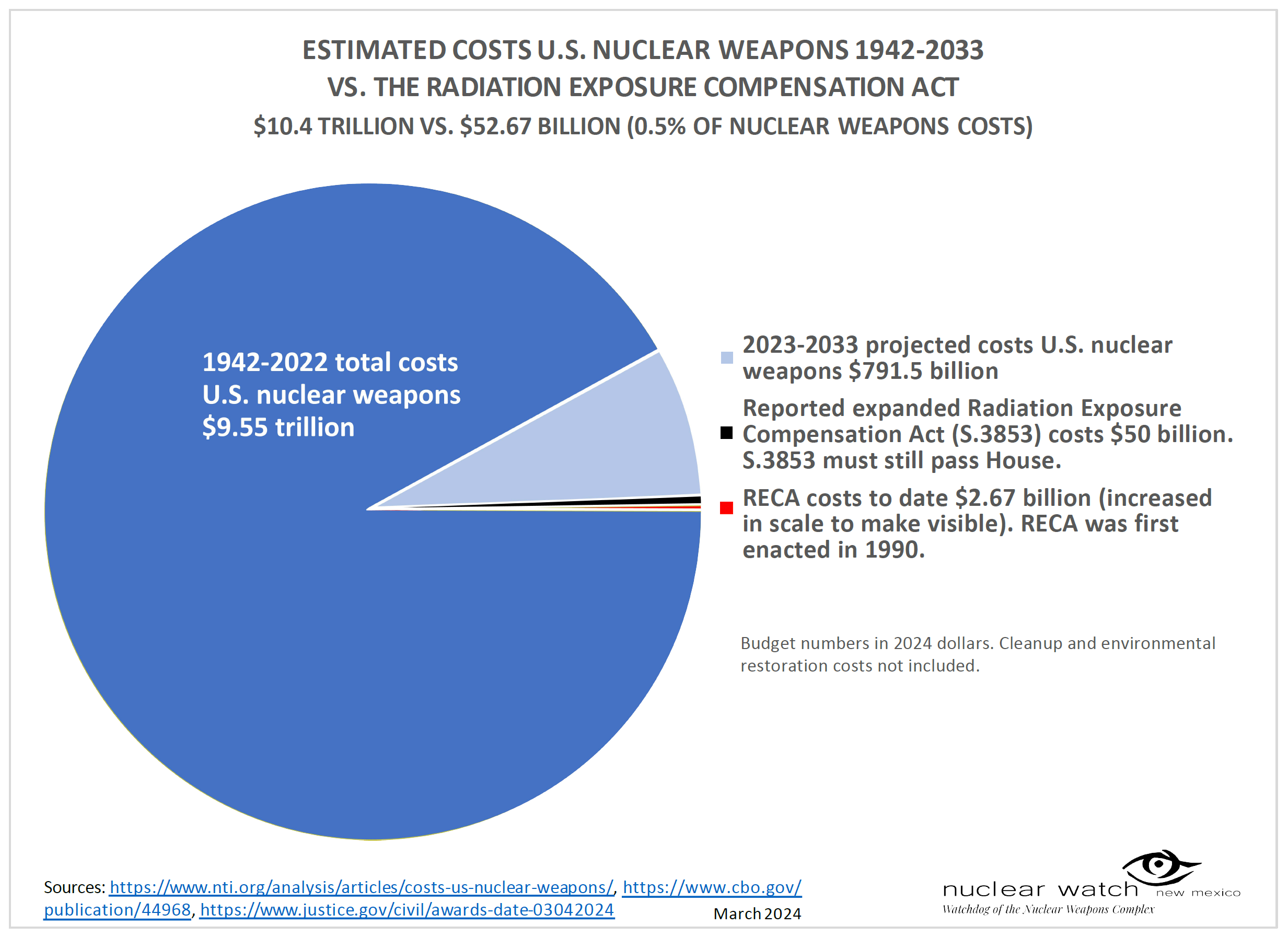
Santa Fe, NM – The Department of Energy (DOE) has announced that the cost of “Remaining Legacy Cleanup” of radioactive and toxic wastes from more than 70 years of nuclear weapons research and production at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) will cost $2.9 billion through fiscal year 2035, averaging $153 million per year.
That cost estimate clearly assumes that the Lab’s major radioactive and toxic wastes dumps will not be cleaned up. Instead they will be “capped and covered,” leaving some 200,000 cubic yards of radioactive and toxic wastes at Area G, its largest waste dump. Those wastes sit in unlined pits and trenches, 800 feet above groundwater and three miles uphill from the Rio Grande (plutonium contaminants have been detected 200 feet below Area G). During this same period of time the Lab’s nuclear weapons programs that caused the mess to begin with will cost ten times as much, even before expected funding increases for expanded production of plutonium bomb core “pits” and increasingly aggressive “Life Extension Programs” that give existing nuclear weapons new military capabilities.
DOE’s announcement also pegs the cost of past cleanup at LANL at $3.2 billion to date, raising the question of what has been and will be accomplished with precious taxpayer dollars. The answer is not much for the money. According to DOE’s own data, for the next couple of years only around a sixth of LANL’s “cleanup” funding will actually go to cleanup. Approximately one-third will be used to catch up on worker pensions and another third to babysit improperly treated radioactive waste barrels, one of which ruptured and closed the multi-billion dollar Waste Isolation Pilot Plant. More than half of the remaining one-third for real cleanup goes to LANL’s notoriously high overhead.
DOE’s cost estimate for future LANL cleanup assumes flat funding out to FY 2035, and notes how that cost is “Aligned to [the] 2016 Consent Order.” Despite repeated requests, DOE refused to estimate cleanup costs at LANL until a new Consent Order was finalized with the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED). Both agencies recently signed it, creating a giant loophole in which the Lab can claim that cleanup is too expensive or impractical to achieve. This is the exact opposite of the original 2005 Consent Order, whose underlying intent was to make DOE and LANL ask Congress for additional cleanup funding. Subsequently, funding for LANL cleanup has fallen from $224 million in FY 2014 to $189 million requested for FY 2017.
Under the Gov. Martinez Administration, NMED Secretary Ryan Flynn granted more than 150 milestone extensions to the 2005 Consent Order at the Lab’s request and then claimed that the old Consent Order did not work. Nuclear Watch New Mexico has filed suit against DOE and LANL for missing compliance milestones under the original Consent Order, with potential fines of more than $300 million. NMED explicitly absolves those violations and fines through the new Consent Order and has intervened in the lawsuit against NukeWatch. This raises the question of whose side the Environment Department is on, the environment or the polluter (in this case, a $2.3 billion per year nuclear weapons facility)?
DOE and NMED kill the chance for serious job creation at the Los Alamos Lab with a deceptive plan for so-called cleanup that leaves tons of radioactive and toxic wastes in the ground that will permanently threaten northern New Mexico’s precious water resources. In addition to the environmental and safety threats and contamination, nuclear weapons programs are not big producers of new jobs. For example, the environmental impact statement for a planned $6.5 billion plutonium facility for expanded nuclear weapons production explicitly stated that not one new Lab job would be created because it would merely relocate existing jobs. In contrast, a LANL study of full cleanup of Area G assumed that around 40% of the total cost would go to labor. Thus, as a rough approximation, for every additional billion dollars put into cleanup, another 3,000 years of cleanup work could be created for one hypothetical worker (in other words, hundreds of high paying jobs for the regional economy).
Jay Coghlan, NukeWatch Director, commented, “The Department of Energy and the New Mexico Environment Department deal New Mexicans a bad hand by pushing a plan that blocks genuine cleanup at the Los Alamos Lab. We need real cleanup that protects our precious water resources for future generations, not more nuclear bombs that cause the mess to begin with.”
# # #
DOE’s presentation on its cost estimate for future LANL cleanup is available at
LANL Estimate of $2.9 Billion for “Remaining” Cleanup Leaves Nuclear and Toxic Wastes Behind and Kills Needed Jobs
Santa Fe, NM.
The Department of Energy (DOE) has announced that the cost of “Remaining Legacy Cleanup” of radioactive and toxic wastes from more than 70 years of nuclear weapons research and production at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) will cost $2.9 billion through fiscal year 2035, averaging $153 million per year.
“That cost estimate clearly assumes that the Lab’s major radioactive and toxic wastes dumps will not be cleaned up. Instead they will be “capped and covered,” leaving some 200,000 cubic yards of radioactive and toxic wastes at Area G, its largest waste dump. Those wastes sit in unlined pits and trenches, 800 feet above groundwater and three miles uphill from the Rio Grande (plutonium contaminants have been detected 200 feet below Area G). During this same period of time the Lab’s nuclear weapons programs that caused the mess to begin with will cost ten times as much, even before expected funding increases for expanded production of plutonium bomb core “pits” and increasingly aggressive “Life Extension Programs” that give existing nuclear weapons new military capabilities…”
Nuclear Watch NM Amends LANL Cleanup Lawsuit – Claims New Consent Order To Be Invalid
 Nuclear Watch NM Amends LANL Cleanup Lawsuit – Claims New Consent Order To Be Invalid
Nuclear Watch NM Amends LANL Cleanup Lawsuit – Claims New Consent Order To Be Invalid
Nuclear Watch New Mexico has amended its federal lawsuit against the Department of Energy (DOE) and Los Alamos National Security, LLC (LANS) that alleges twelve violations of a 2005 Consent Order governing cleanup at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). Those violations could result in potential penalties of more than $300 million dollars that would go to the state, if only the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) were to enforce them.
Nuclear Watch now asks the court to declare the new 2016 Consent Order to be invalid because the requirement for the opportunity of a public hearing was not met.
NMED intervened in the case on June 23, 2016. The next day, NMED and DOE signed the 2016 Consent Order after a 60-day comment period, during which over 40 citizens, nonprofit organizations, public officials, and two Pueblos provided comments. Lack of enforceability and lack of concrete long-term schedules were common major foci of the comments. Despite that, “No change” without any further explanation was NMED’s overwhelming response to specific public comments as the two agencies moved from the draft to final Consent Order.
The finalized new Consent Order surrenders enforceability by creating a giant loophole where DOE and LANL can avoid cleanup by claiming that it is either too expensive or impractical. This is clearly the opposite of what is needed, when nuclear weapons research and production programs that caused the mess to begin with are receiving increased taxpayer funding, while cleanup programs are being cut.
In addition, NMED’s new Consent Order explicitly absolves DOE and LANS of past violations. In response, Nuclear Watch has added to its lawsuit this request for declaratory judgment by the court that DOE and NMED violated the public’s right for the opportunity of a formal hearing, explicitly required by the 2005 Consent Order.
Scott Kovac, NukeWatch Research Director, noted, “We will not let the public’s right for cleanup at the Los Alamos Lab be papered over by DOE and NMED. Both agencies agreed to all parts of the 2005 Consent Order, which included rigorous public participation requirements and a detailed the cleanup schedule, including a final compliance date. We will continue to push for the public to have a true voice in these important matters. ”
The New Mexico Environmental Law Center and Attorney John E. Stroud are representing NukeWatch in this legal action to enforce timely cleanup at LANL.
###
Nuclear Watch New Mexico’s 1st amended complaint is available here
NMED’s Final Consent Order and the “response” to comments matrix are available here
Nuclear Watch New Mexico’s original lawsuit complaint is available here
Our May 5, 2016 second notice of intent to sue (which is a good summary of our complaint) is available here
Our January 20, 2016 notice of intent to sue is available here
Successful Citizen Activism Against Expanded U.S. Plutonium Pit Production
This is the unsung story of successful citizen activism against repeated government attempts to expand the production of plutonium pit cores, which has always been the choke point of resumed U.S. nuclear weapons production. This history is a critical part of the march toward a future world free of nuclear weapons.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.