QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
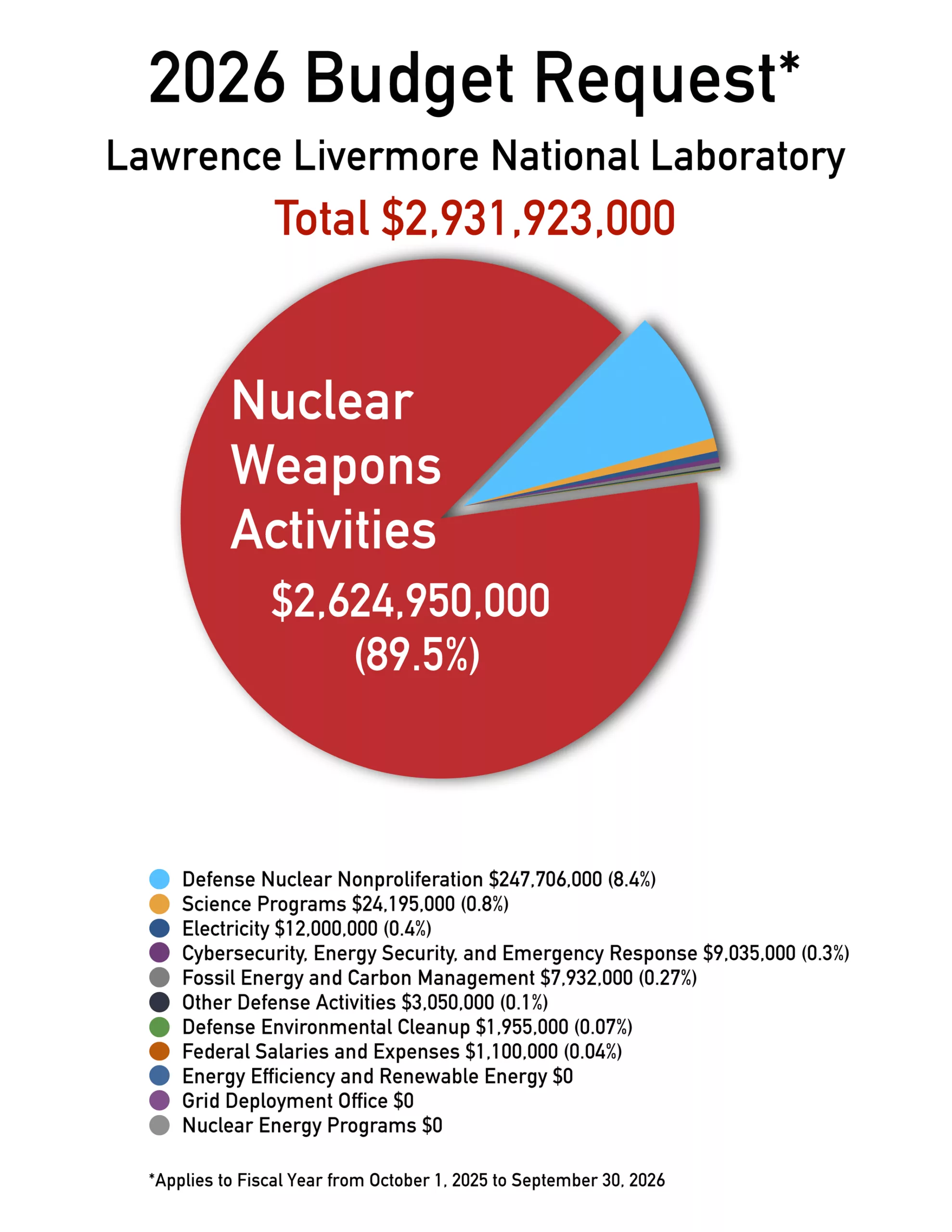
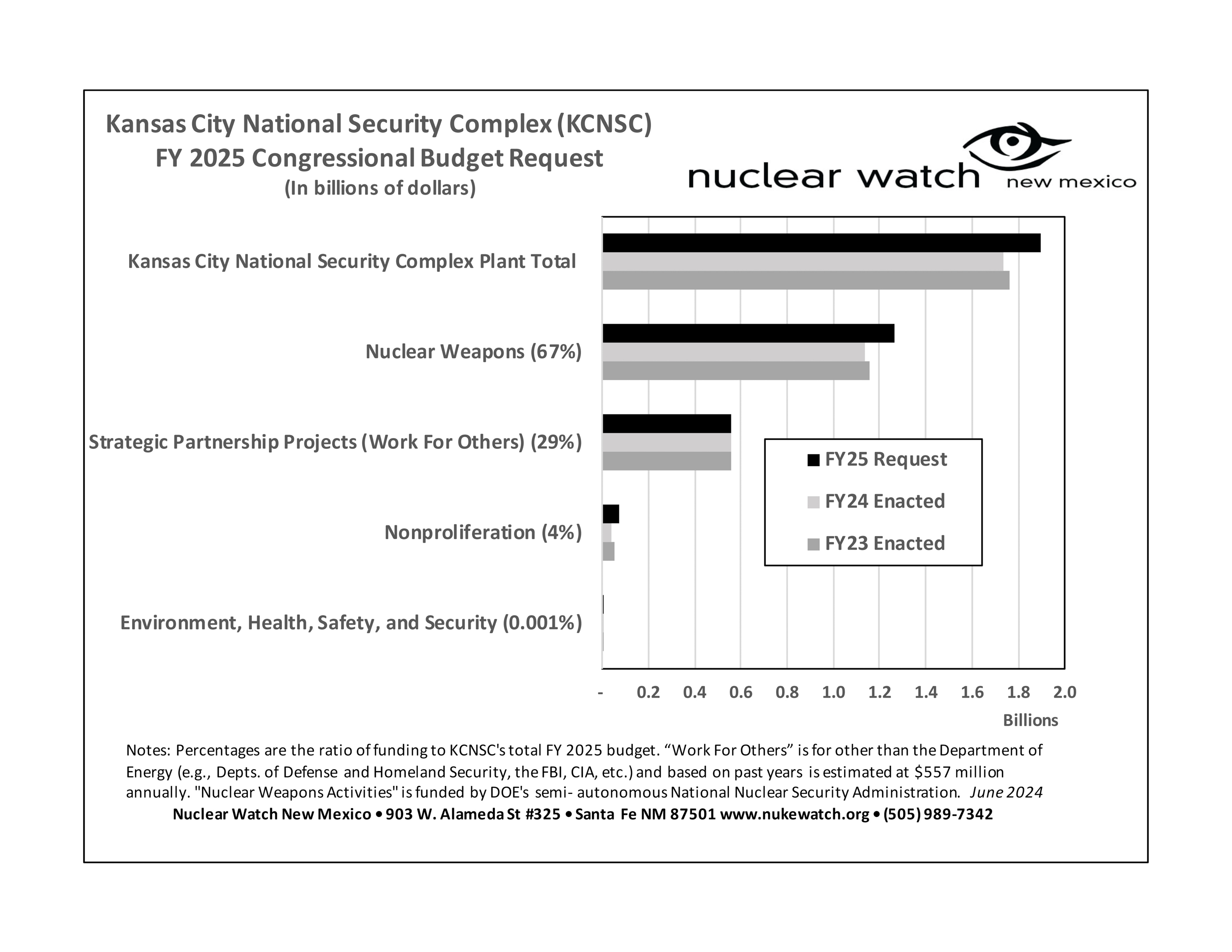
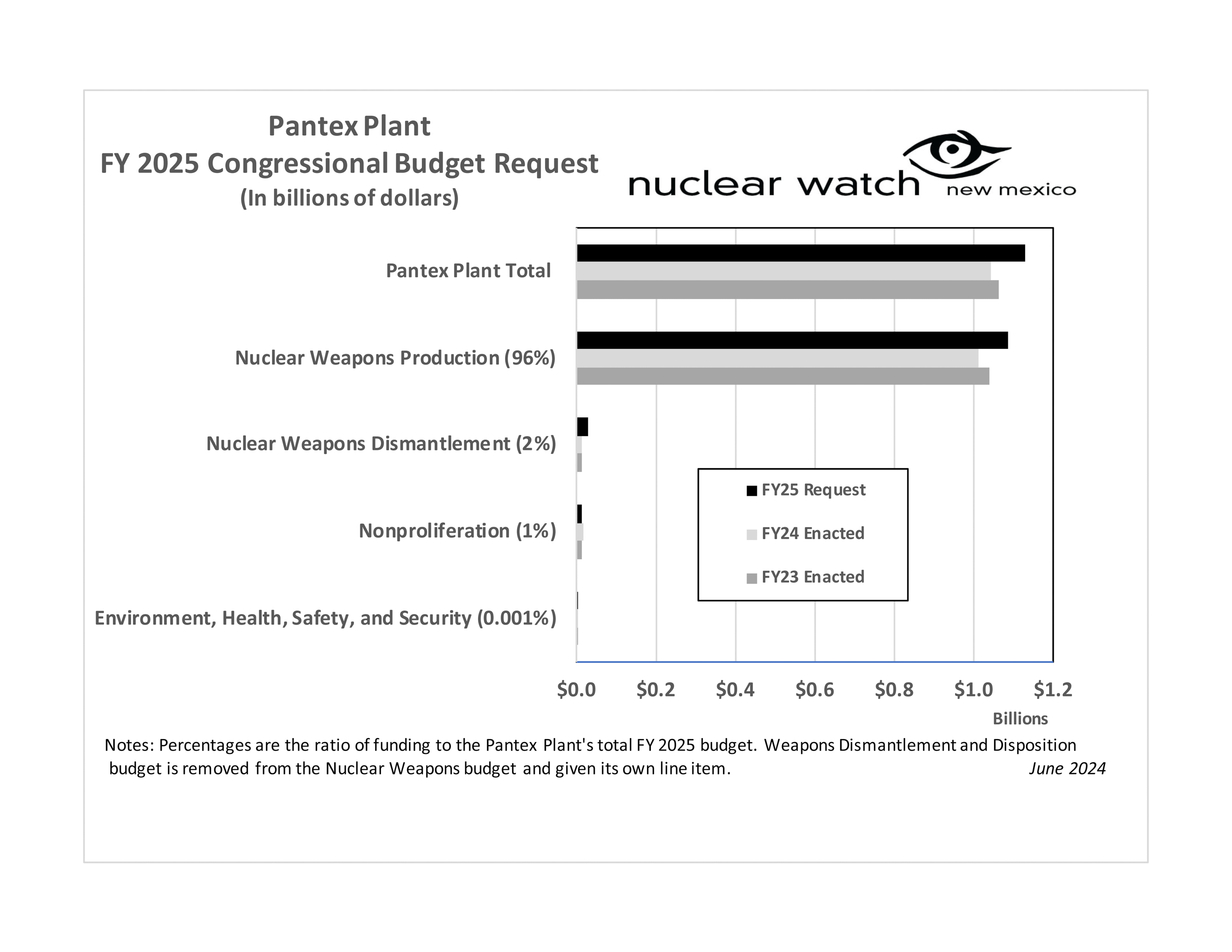
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
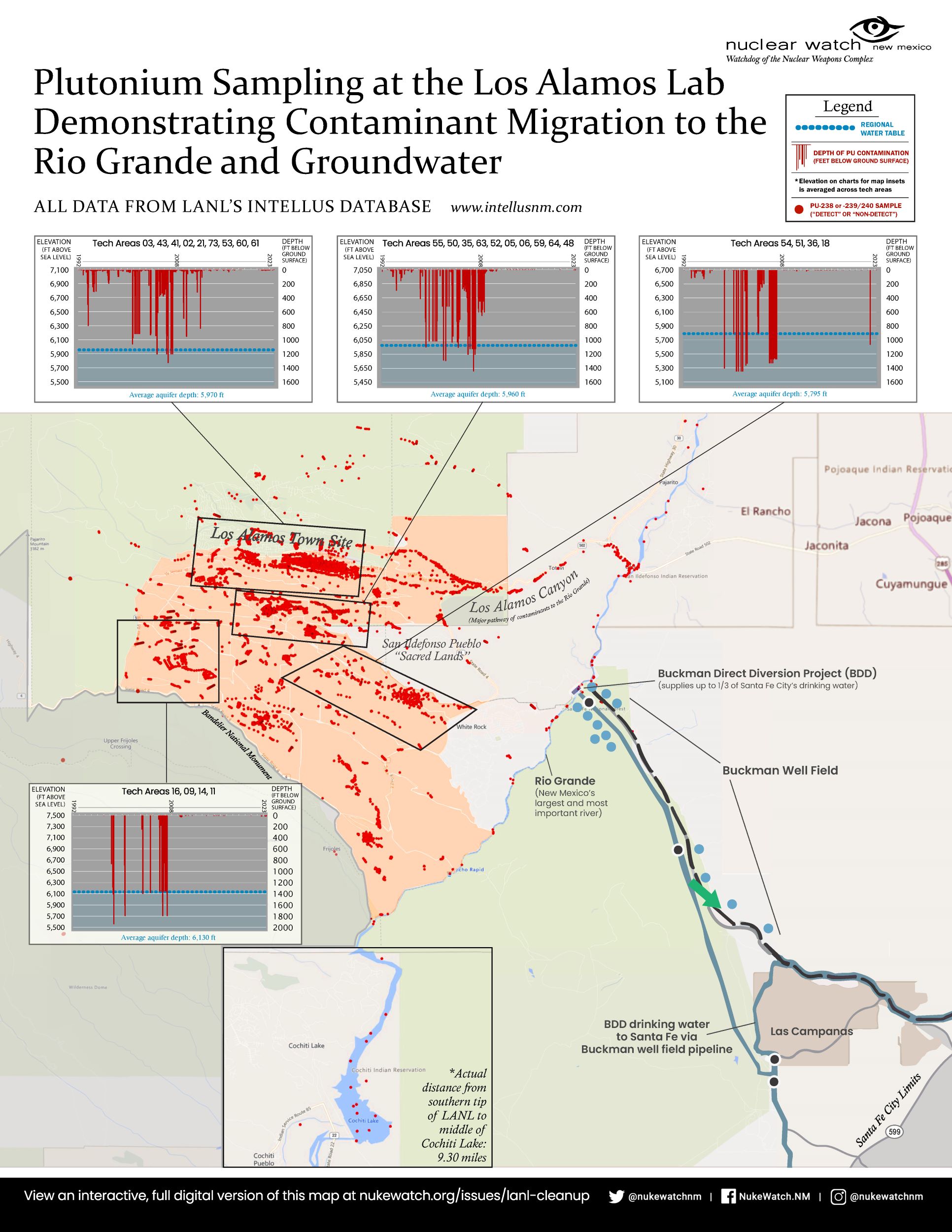
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN – OUR VIEW – Getting rid of plutonium pits — so many questions
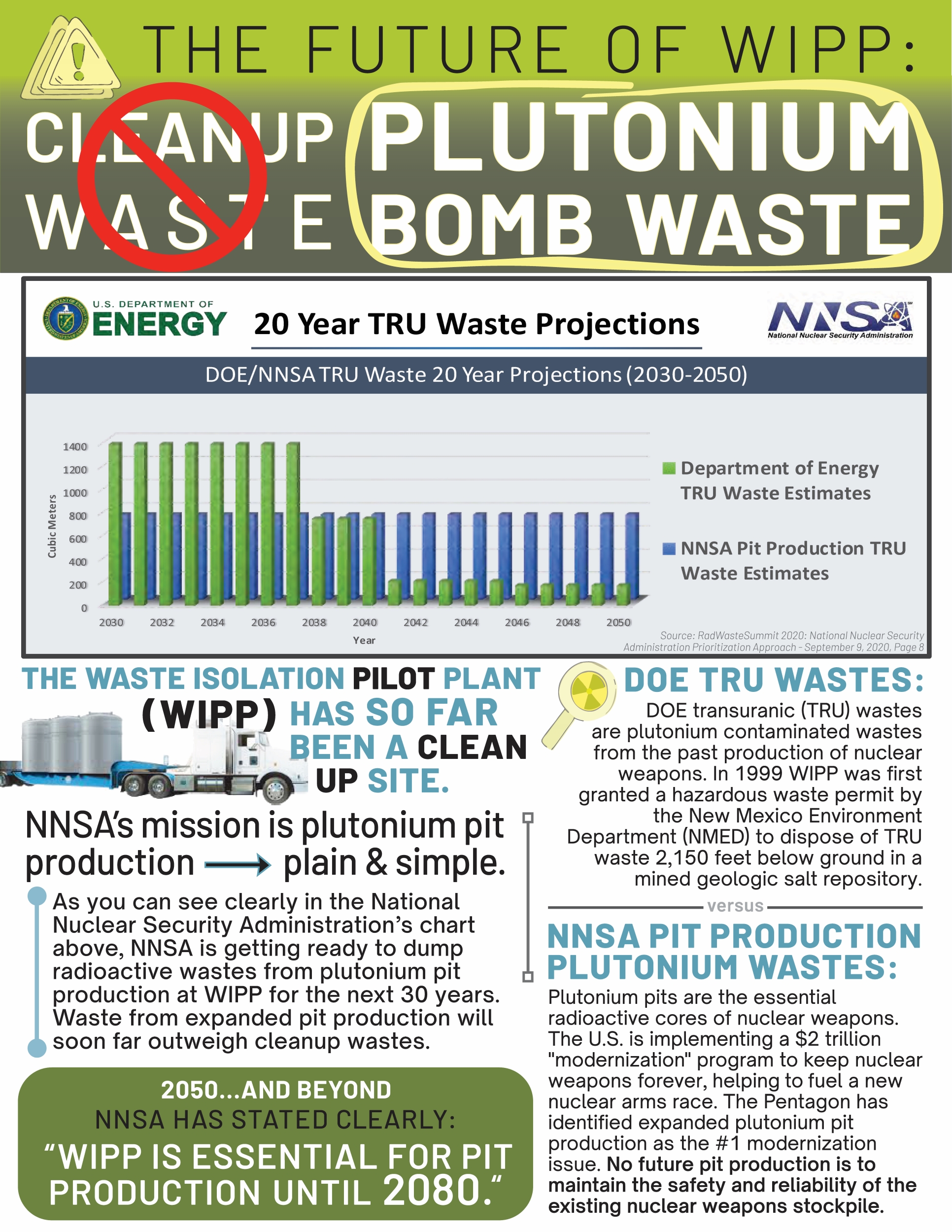
A Department of Energy proposal to dilute and dispose of plutonium waste at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in Carlsbad is ready for public comment — the draft environmental impact statement, all 412 pages of it, has been released.
“Stay alert for notices of meetings and time for public comment. There’s no guarantee informed opposition will change plans by agencies intent on certain action, but speaking up beats staying quiet. Oh, and think about this: before rushing full speed ahead to produce even more plutonium pits, it’s time to at least try to find a way to dispose of the waste we’ve already created.”
[NukeWatch will provide sample comments and make it as easy as possible to participate in the public comment process for the WIPP Permit and Plutonium Waste Disposal plans]
SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN | OUR VIEW December 24, 2022 santafenewmexican.com
The public can weigh in, whether in writing or by showing up for public hearings that will take place early next year.
Buckle up. This is going to be a contentious discussion.
The U.S. wants to be rid of 34 metric tons of plutonium bomb cores, or pits, stored at the Pantex Plant in Amarillo. The pits are Cold War legacies; because WIPP is restricted in the type of waste it can take, before disposing of it, the material must be diluted. Thus, the term, dilute and dispose. The Department of Energy’s decision about the waste was announced two years ago, but with no details.
At one point the Energy Department wanted to turn Cold War plutonium into a mixed oxide fuel for use in commercial nuclear plants. That would have happened at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, but billions in cost overruns and delays hamstrung the effort, and the Trump administration killed the project in 2018.
It chose the dilute-and-disposal plan.
The draft statement fleshes out just what would happen to prepare the pits for disposal — in a facility, we might point out, that currently is seeking a renewal of its hazardous waste permit from the state of New Mexico. WIPP is open, but state Environment Department Secretary James Kenney and Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham want more oversight of waste disposal at the plant.
That back and forth is separate from the Energy Department dilute-and-disposal proposal, but the permit discussion provides context for the coming fierce debate.Continue reading
Exposed: The Most Polluted Place in the United States
A new book investigates the toxic legacy of Hanford, the Washington state facility that produced plutonium for nuclear weapons.
“Bechtel is a privately owned corporation and we’re spending billions of dollars paying this company to not get the job done. It’s a big mess.”
By Tara Lohan, The Revelator | December 21, 2022 ecowatch.com
A container of waste is excavated from an underground storage trench at the Hanford Site. Department of Energy / Public DomainThe most polluted place in the United States — perhaps the world — is one most people don’t even know. Hanford Nuclear Site sits in the flat lands of eastern Washington. The facility — one of three sites that made up the government’s covert Manhattan Project — produced plutonium for Fat Man, the atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki during World War II. And it continued producing plutonium for weapons for decades after the war, helping to fuel the Cold War nuclear arms race.
Today Hanford — home to 56 million gallons of nuclear waste, leaking storage tanks, and contaminated soil — is an environmental disaster and a catastrophe-in-waiting.
It’s “the costliest environmental remediation project the world has ever seen and, arguably, the most contaminated place on the entire planet,” writes journalist Joshua Frank in the new book, Atomic Days: The Untold Story of the Most Toxic Place in America.
It’s also shrouded in secrecy.
Frank has worked to change that, beginning with a series of blockbuster investigations published in Seattle Weekly a decade ago. Atomic Days offers an even fuller picture of the ecological threats posed by Hanford and its failed remediation.
The Revelator spoke with him about the environmental consequences, the botched cleanup operation, and what comes next.
Why is the most polluted place in the country so little known?
We have to understand what it was born out of, which was the Manhattan Project. There were three locations picked — Los Alamos [N.M.], Oak Ridge [Tenn.] and Hanford — to build the nuclear program.
New Mexico Presses US to Develop Other Nuclear Waste Sites
State wants full waste inventory, limits to disposal
WIPP, open since 1999, mining new panels
BLOOMBERG NEWS | December 20, 2022 news.bloomberglaw.com
New Mexico will be “unwavering” in sticking to proposed new conditions on a federal underground nuclear waste repository, a state official said, including one that revokes the facility’s permit should Congress expand its disposal limit.
The state is demanding the Energy Department and its site contractor, Nuclear Waste Partnership LLC, furnish an accurate inventory of all remaining wastes awaiting clean-up and emplacement at the site and an annual report detailing the agency’s progress toward siting another repository in another state.
Clean Energy or Weapons? What the ‘Breakthrough’ in Nuclear Fusion Really Means
 From Tri-Valley CAREs: On NIF, Nuclear Weapons and Fusion Hype
From Tri-Valley CAREs: On NIF, Nuclear Weapons and Fusion Hype

“On December 13, the Department of Energy (DOE) and Livermore Lab held a press conference and, with maximum hoopla, announced that an experiment at the National Ignition Facility earlier that month had achieved fusion “ignition”.
Physicist MV Ramana, who is currently with the University of British Columbia and was previously at Princeton’s Nuclear Futures Laboratory and its Program on Science and Global Security, wrote this article for a science and tech magazine. For more information on what did and did not happen at NIF, we highly recommend it:”
Clean Energy or Weapons? What the ‘Breakthrough’ in Nuclear Fusion Really Means
SCIENCE – THE WIRE | December 19, 2022 science.thewire.in
- On December 13, the US Department of Energy announced that the National Ignition Facility had reached a “milestone”: the achievement of “ignition” in nuclear fusion earlier in the month.
- While the step has been described as a milestone in clean energy, generating electricity commercially or at an industrial scale through fusion is likely unattainable in any realistic sense – at least within the lifetimes of most readers of this article.
- The main utility that the facility offers nuclear weapons designers and planners is by providing a greater understanding of the underlying science and modernizing these weapons.
The Guardian [Letters]: Nuclear fusion ‘holy grail’ is not the answer to our energy prayers
Dr Mark Diesendorf questions the claim that nuclear fusion is safe and clean, while Dr Chris Cragg suspects true fusion power is a long way off. Plus letters from Dick Willis and Martin O’Donovan
“It is great news that scientists have succeeded in getting more energy out of fusion than they put in. It brings to mind a quote from a past director of the Central Electricity Generating Board: ‘One day you may get more energy out of nuclear fusion than you put in, but you will never get more money out than you put in.’” – Martin O’Donovan (Ashtead, Surrey)
THE GUARDIAN: LETTERS | December 19, 2022 theguardian.com
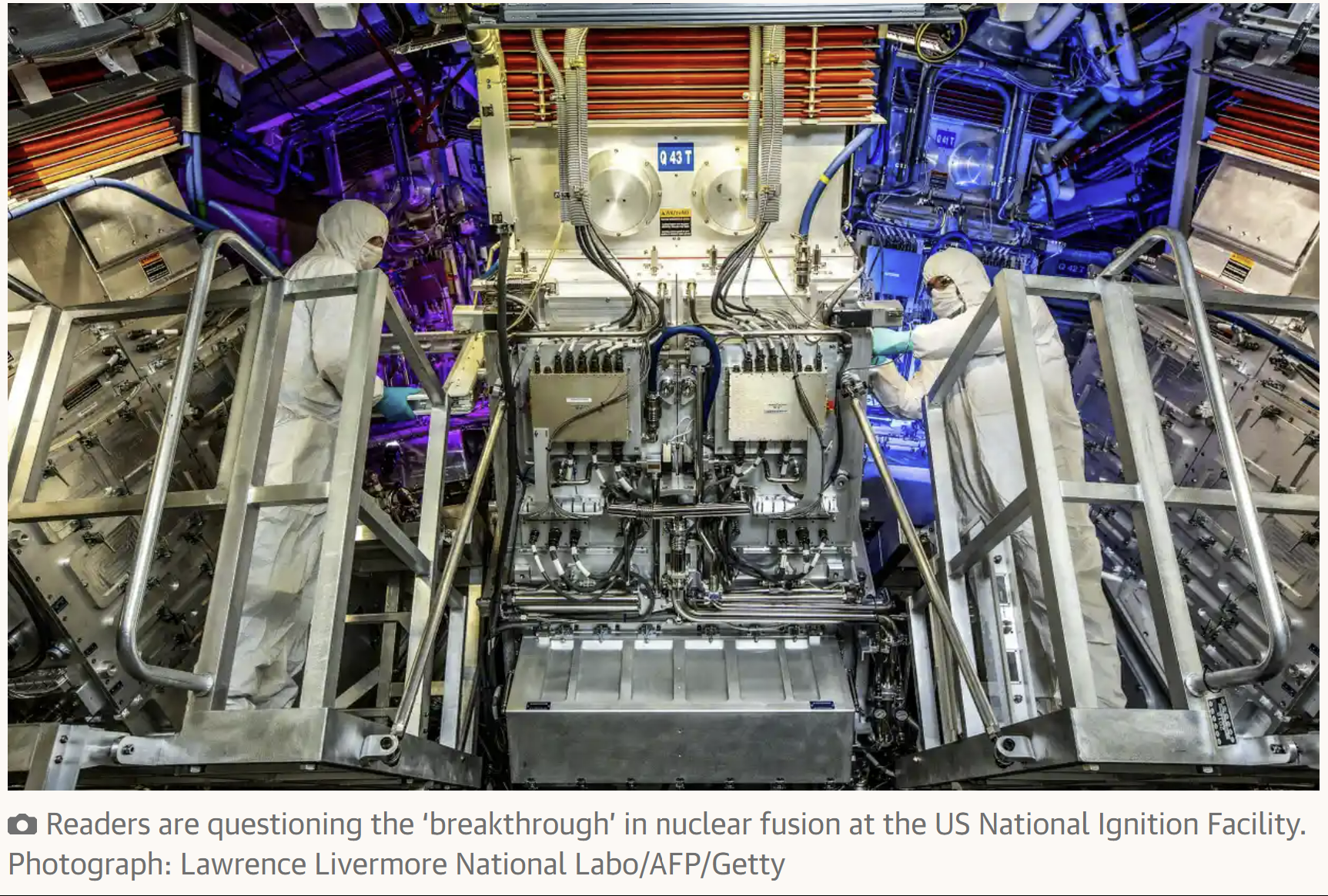
You report on the alleged “breakthrough” on nuclear fusion, in which US researchers claim that break-even has been achieved (Breakthrough in nuclear fusion could mean ‘near-limitless energy’, 12 December). To go from break-even, where energy output is greater than total energy input, to a commercial nuclear fusion reactor could take at least 25 years. By then, the whole world could be powered by safe and clean renewable energy, primarily solar and wind.
The claim by the researchers that nuclear fusion is safe and clean is incorrect. Laser fusion, particularly as a component of a fission-fusion hybrid reactor, can produce neutrons that can be used to produce the nuclear explosives plutonium-239, uranium-235 and uranium-233. It could also produce tritium, a form of heavy hydrogen, which is used to boost the explosive power of a fission explosion, making fission bombs smaller and hence more suitable for use in missile warheads. This information is available in open research literature.
The US National Ignition Facility, which did the research, is part of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, which has a history of involvement with nuclear weaponry.
Dr Mark Diesendorf
University of New South Wales
The Energy Department’s fusion breakthrough: It’s not really about generating electricity
“Because of how the Energy Department presented the breakthrough in a news conference headlined by Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm, news coverage has largely glossed over its implications for monitoring the country’s nuclear weapons stockpile. Instead, even many serious news outlets focused on the possibility of carbon-free, fusion-powered electricity generation—even though the NIF achievement has, at best, a distant and tangential connection to power production.”
By John Mecklin, THE BULLETIN OF ATOMIC SCIENTISTS | December 16, 2022 thebulletin.org
This week’s headlines have been full of reports about a “major breakthrough” in nuclear fusion technology that, many of those reports misleadingly suggested, augurs a future of abundant clean energy produced by fusion nuclear power plants. To be sure, many of those reports lightly hedged their enthusiasm by noting that (as The Guardian put it) “major hurdles” to a fusion-powered world remain.
Indeed, they do.
The fusion achievement that the US Energy Department announced this week is scientifically significant, but the significance does not relate primarily to electricity generation. Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility, or NIF, focused the facility’s 192 lasers on a target containing a small capsule of deuterium–tritium fuel, compressing it and inducing what is known as ignition.
New trend: long-term investments in the nuclear weapons industry are dropping
The report “Risky Returns” provides an overview of investments in 24 companies heavily involved in the production of nuclear weapons for the arsenals of China, France, India, the Russian Federation, the United Kingdom and the United States in 2022. Overall, the report finds that 306 financial institutions made over $746 billion available to these companies, in loans, underwriting, shares or bonds. US-based Vanguard remains the largest single investor, with $68,180 million invested in the nuclear weapon industry.
By ICAN | December 15, 2022 icanw.org
While the total value of investments in the 24 nuclear weapon producers was higher than previous years, this is also attributed to share price variances through a turbulent year in the defence sector. Some nuclear weapon producers also produce conventional weapons and saw their stock values rise, likely resulting from the announcements by NATO states that they would significantly increase defence spending. Yet the report found no increase in the number of investors in the nuclear weapon producers.
Atomic Days: The Untold Story of the Most Toxic Place in America

A new book is out about Hanford, by Joshua Frank, co-editor of Counterpunch, Atomic Days: The Untold Story of the Most Toxic Place in America.
Once home to the United States’s largest plutonium production site, the Hanford Nuclear Reservation in Washington state is laced with 56 million gallons of radioactive waste. The threat of an explosive accident at Hanford is all too real—an event that could be more catastrophic than Chernobyl.
Continue reading
Fallout from a nuclear past: A new book explores the human toll of “nuclear colonization” in New Mexico
Of the three waves of colonization New Mexico has undergone — Spanish, American and nuclear — the latter is the least explored. And for author Myrriah Gómez, there were personal reasons to reveal the truth about how “nuclear colonization” has altered the state’s past and continues to shape its future.
By Alicia Inez Guzmán Searchlight New Mexico | December 2022 searchlightnm.org
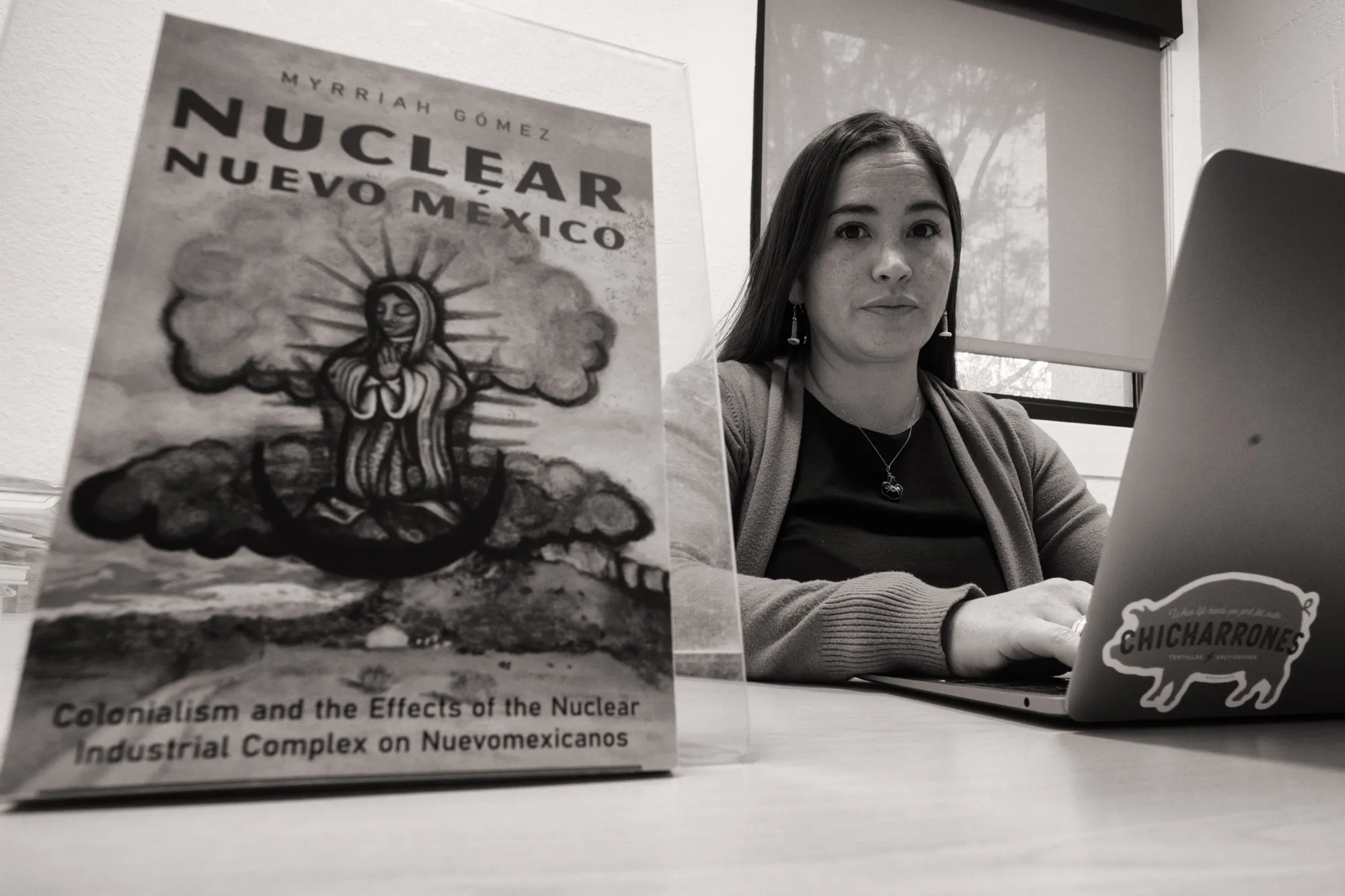 Gómez, an assistant professor at the University of New Mexico, is the author of “Nuclear Nuevo México,” a book that explores the history of the Los Alamos National Laboratory and the fundamental tension of living in its shadow. Its publication this month by the University of Arizona Press couldn’t be timelier: Los Alamos is currently preparing to build plutonium “pits” that act as triggers in nuclear weapons, putting the lab front and center in an ongoing national debate about nuclear impacts.
Gómez, an assistant professor at the University of New Mexico, is the author of “Nuclear Nuevo México,” a book that explores the history of the Los Alamos National Laboratory and the fundamental tension of living in its shadow. Its publication this month by the University of Arizona Press couldn’t be timelier: Los Alamos is currently preparing to build plutonium “pits” that act as triggers in nuclear weapons, putting the lab front and center in an ongoing national debate about nuclear impacts.
“If Spanish colonialism brought Spanish colonizers and U.S. colonialism brought American colonizers,” as Gómez writes in her book, “then nuclear colonialism brought nuclear colonizers, scientists, military personnel, atomic bomb testing, and nuclear waste among them.”
Ukraine still fears another Chernobyl-size disaster at Europe’s largest nuclear plant
“Why did they say it was safe to go outdoors? Why did they build it so close to Kyiv?…Why was it all such a secret?” – Yuriy Samoilenko, chief environmental inspector at Kyiv’s city hall at the time of the Chernobyl meltdown.
By JULIAN HAYDA, NPR | December 11, 2022 npr.org
CHERNOBYL, Ukraine — Sophia Arkadiyivna remembers when the Soviet Union built the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in 1977, just 20 miles from the village where she served as mayor.
After years of atomic energy powering big Russian cities like Moscow, Leningrad and Voronezh, the USSR was finally ready to expand the technology to other Soviet republics like Ukraine. Soviet propaganda promised easier jobs and cleaner air.
“We didn’t have a reason to distrust the government. They showed us how good things could be,” she says.
Or so she thought at the time. It didn’t take long for Arkadiyivna to turn skeptical.
Nuclear waste permit ‘more stringent’ New Mexico says as feds look to renew for 10 years
NMED Cabinet Secretary James Kenney said the State wanted a permit with stronger regulations moving forward, to better protect people and the environment from the impacts of nuclear waste disposal.
“It will be more stringent, full stop,” Kenney said. “The conditions were adding to it are designed to add more accountability to the whole complex that are sending waste to WIPP.”
By Adrian Hedden, Carlsbad Current-Argus | December 10, 2022 currentargus.com
 Tougher rules for a nuclear waste repository near Carlsbad could be on the way as New Mexico officials sought “more stringent” regulations as the federal government sought to renew its permit with the state for the facility.
Tougher rules for a nuclear waste repository near Carlsbad could be on the way as New Mexico officials sought “more stringent” regulations as the federal government sought to renew its permit with the state for the facility.
The State sought new requirements to prioritize nuclear waste from within New Mexico for disposal, called for an accounting of all of the waste planned for disposal in the next decade and regular updates on federal efforts to find the location for a new repository as conditions of the permit.
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant is owned by the U.S. Department of Energy which holds a permit with the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) that must be updated every 10 years.
The facility sees transuranic (TRU) nuclear waste from DOE facilities around the country disposed of via burial in an underground salt formation about 2,000 feet beneath the surface.
The Bizarre Mystery of the Only Armed Nuke America Ever Lost
The lost nuke has never been found—only the pilot’s helmet was recovered, and the government kept it secret for years.
By Matthew Gault, Vice News | 2022 vice.com
In the early days of the Cold War, the United States wanted to make sure it could launch a retaliatory strike against the Soviet Union as quickly as possible if it launched a nuclear strike. The goal was 15 minutes. This was before the advent of submarines that launch ballistic missiles and intercontinental ballistic missile silos. From 1960 until 1968, America maintained that 15-minute ability to pepper the globe with nukes by putting pilots on 24-hour alert. For more than a decade, hundreds of U.S. pilots criss-crossed the planet in planes loaded with nuclear bombs. To keep up with brutal hours, many of the pilots and crew took amphetamine.
As noted in Task & Purpose, the U.S. military had 32 nuclear accidents during the Cold War, and six of the weapons are still unaccounted for. Every story of a Broken Arrow—the military term for a missing nuke—is harrowing, but what happened off the coast of Japan in 1965 was especially frightening.
On December 5, 1965, U.S. Navy Lt. Douglas Webster was supposed take an A-4E Skyhawk loaded with a nuclear bomb into the sky. On the USS Ticonderoga aircraft carrier, stationed in the Philippine Sea about 70 miles from Okinawa, Japan, the crew loaded the weapon onto the vehicle and Webster got into the cockpit. The crew then pushed the plane to an elevator that would bring it up to the flight deck.
Watch a brief YouTube Clip about this event:
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
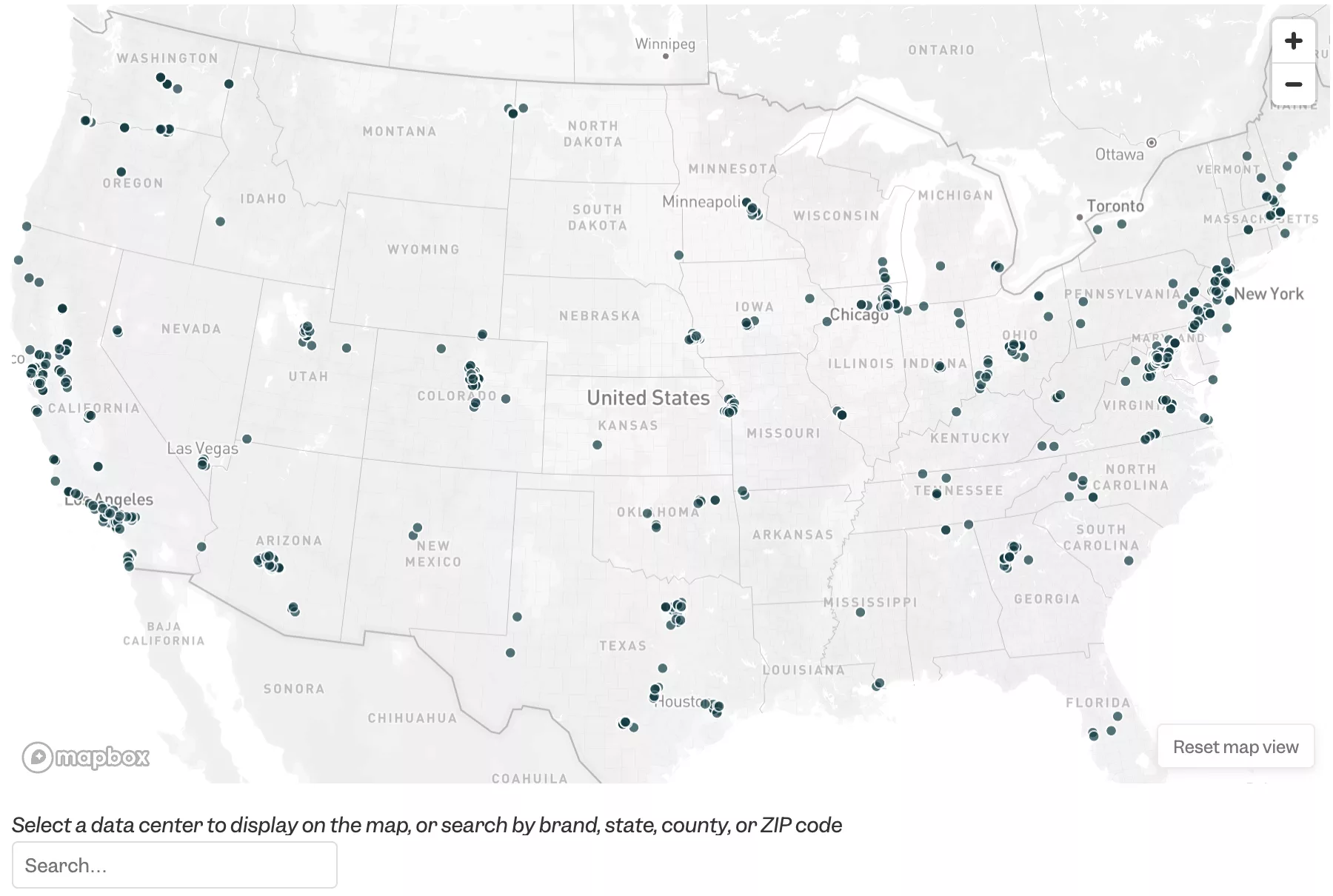
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.