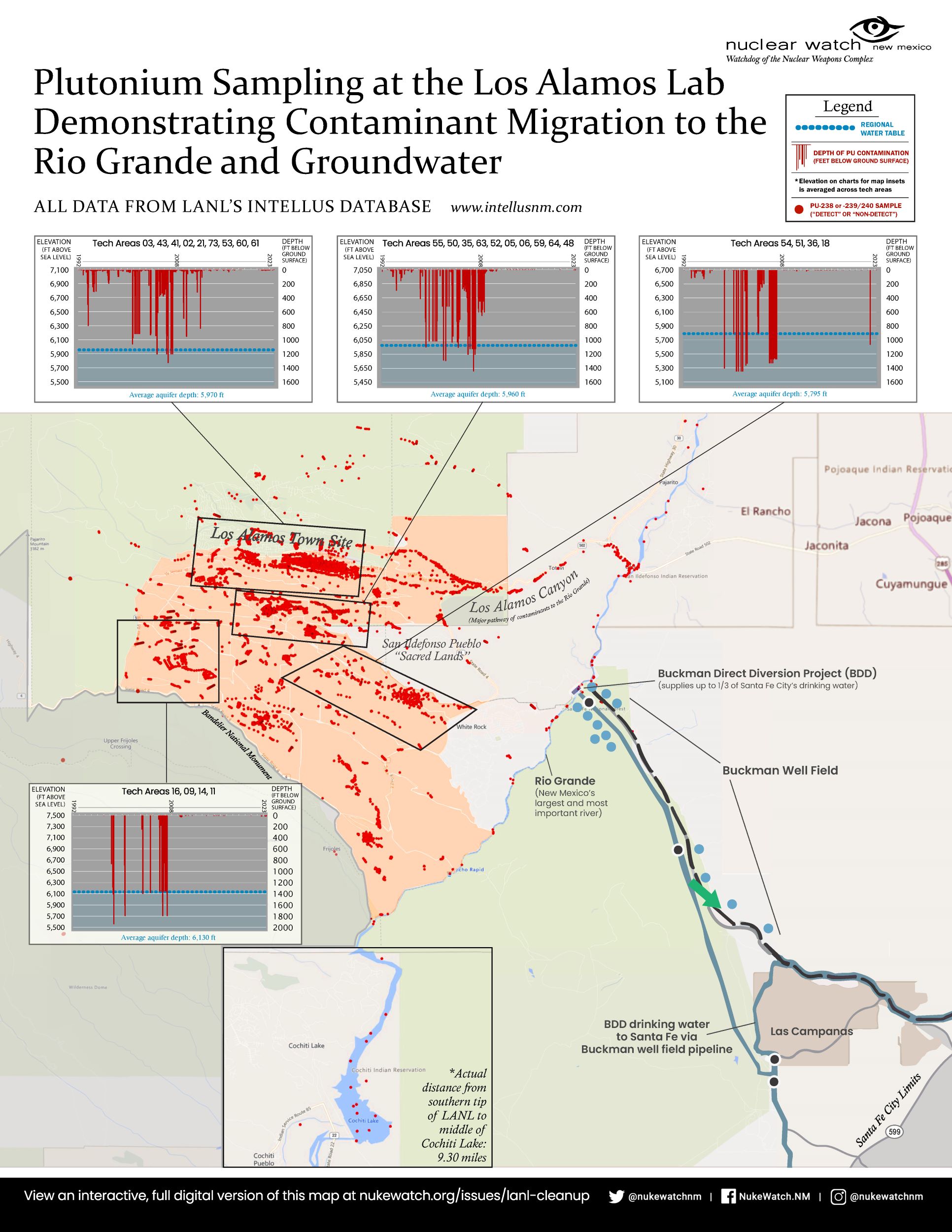
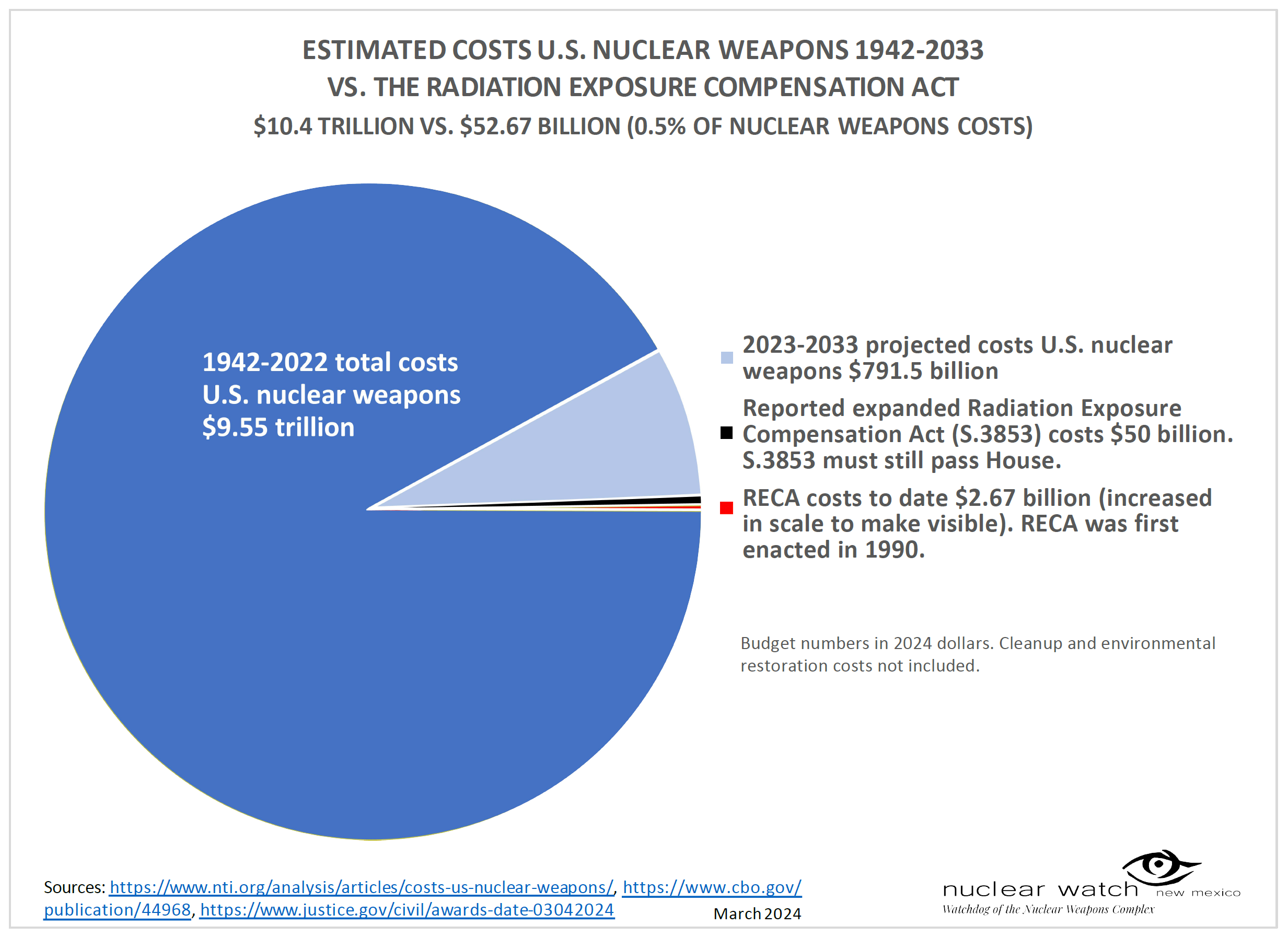
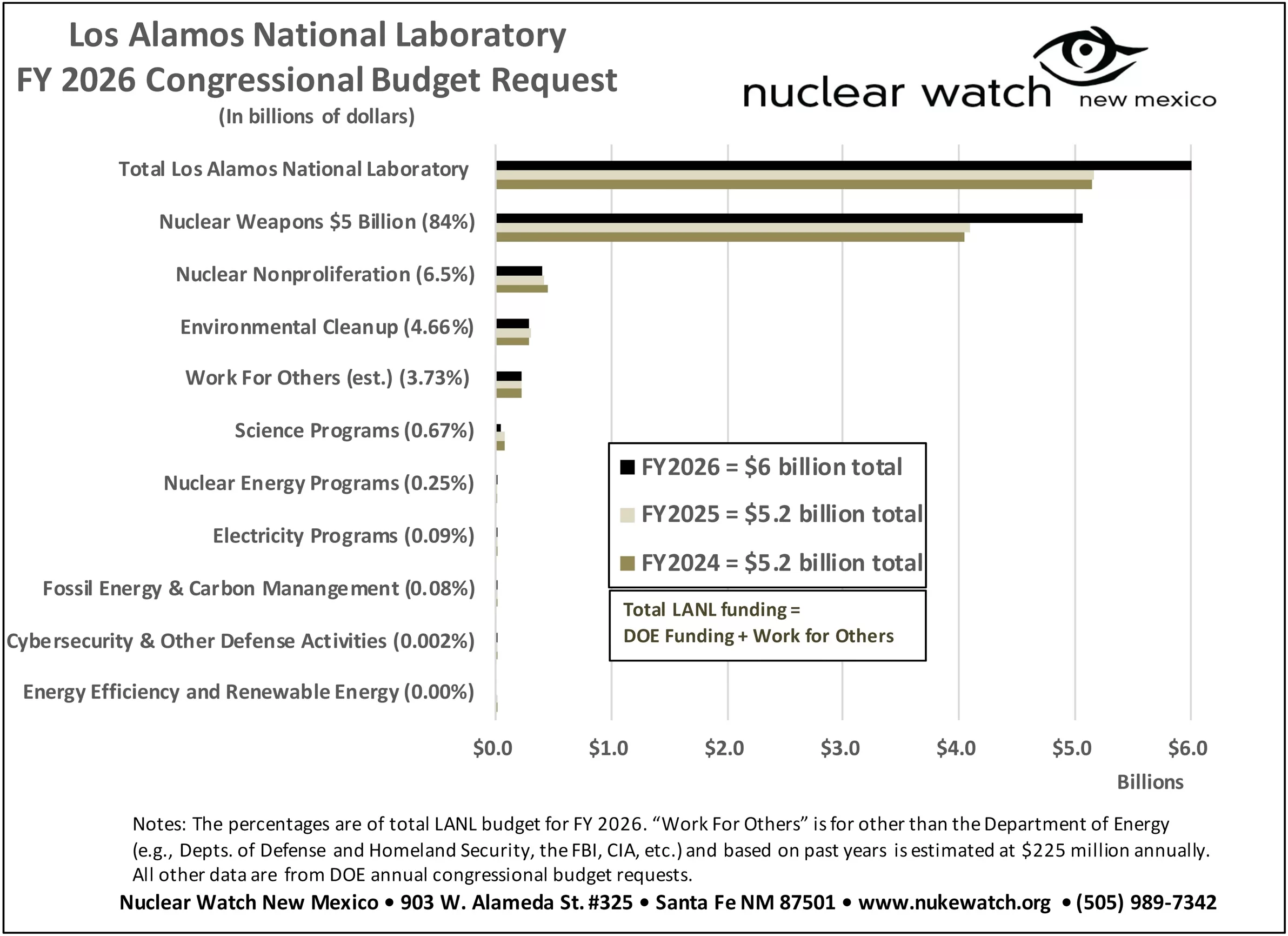
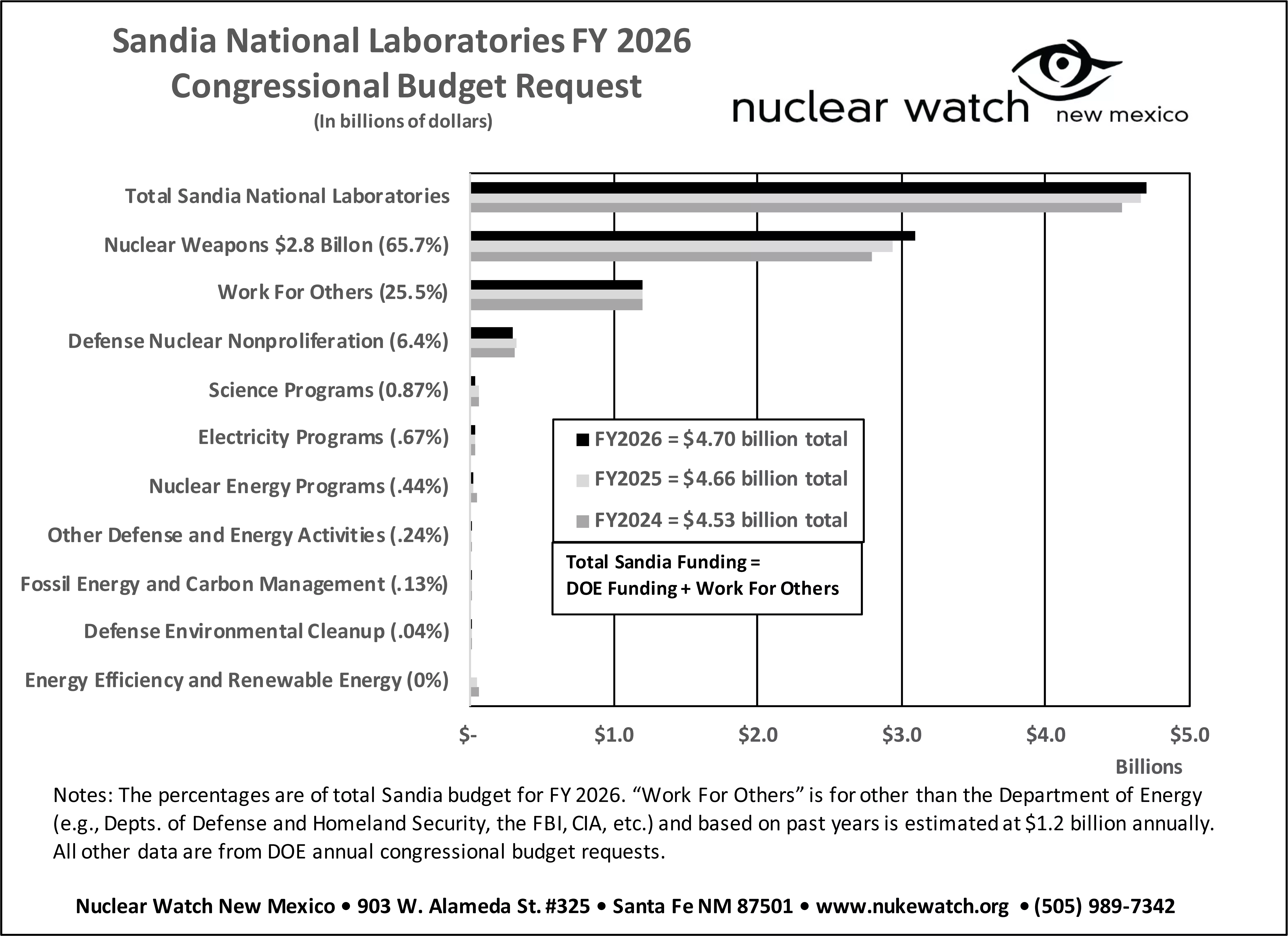
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
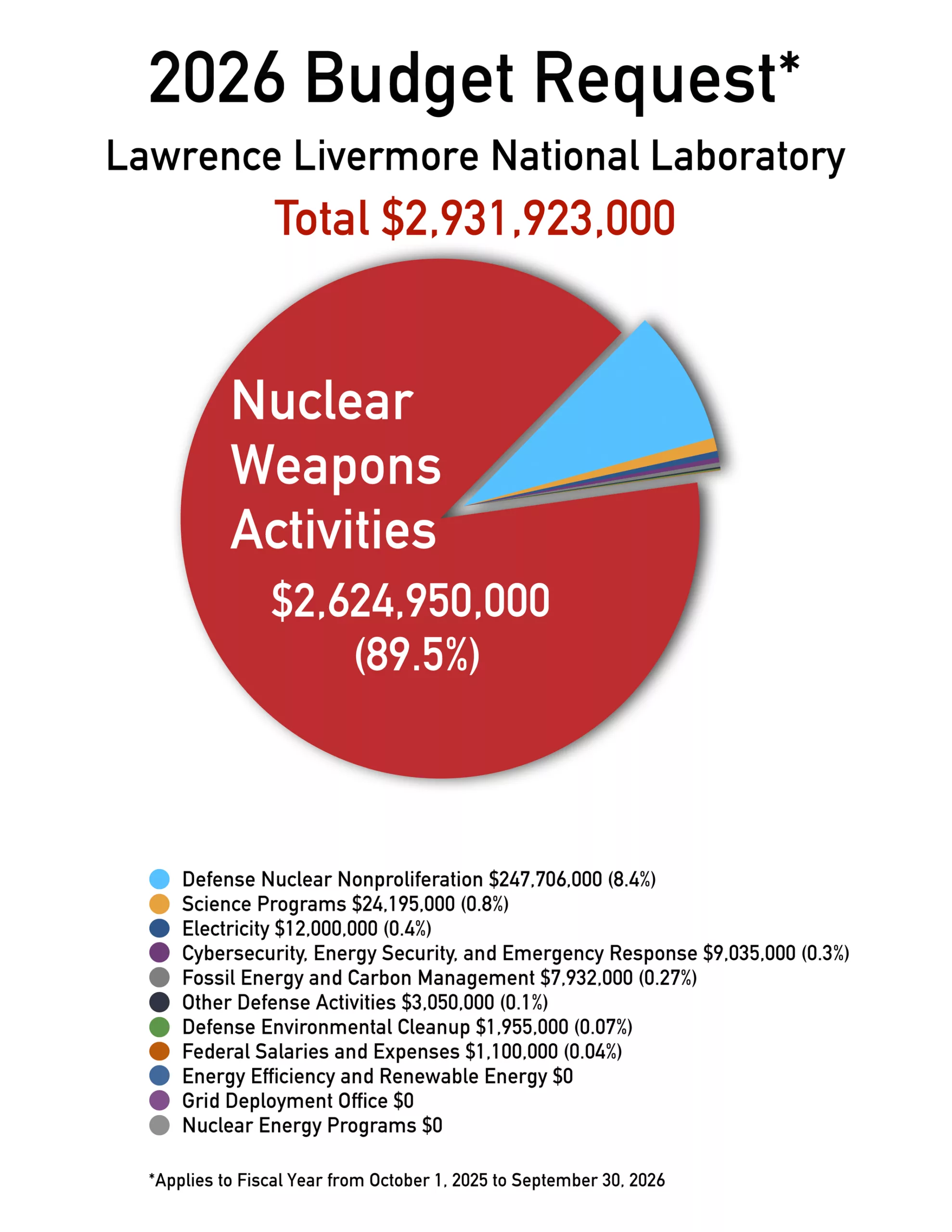
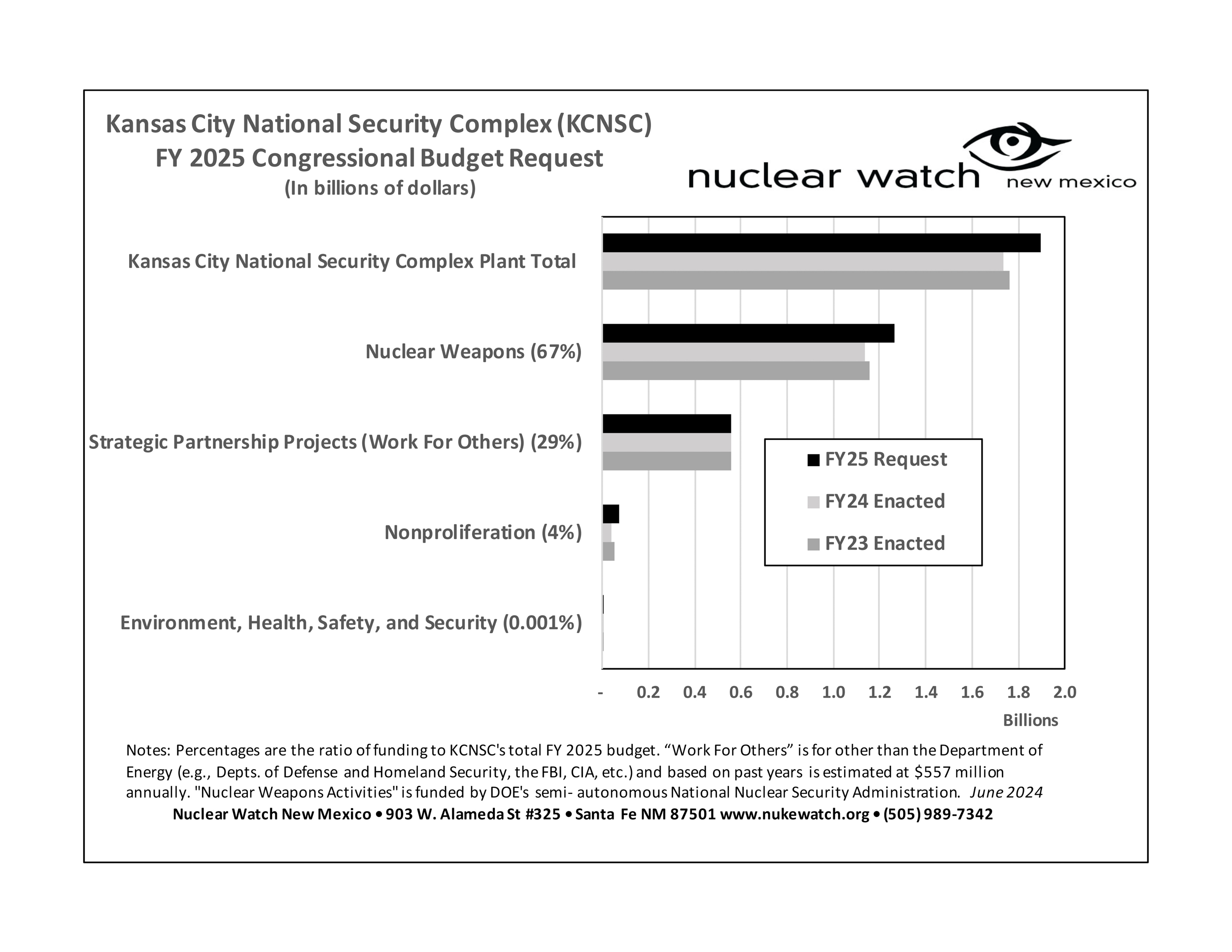
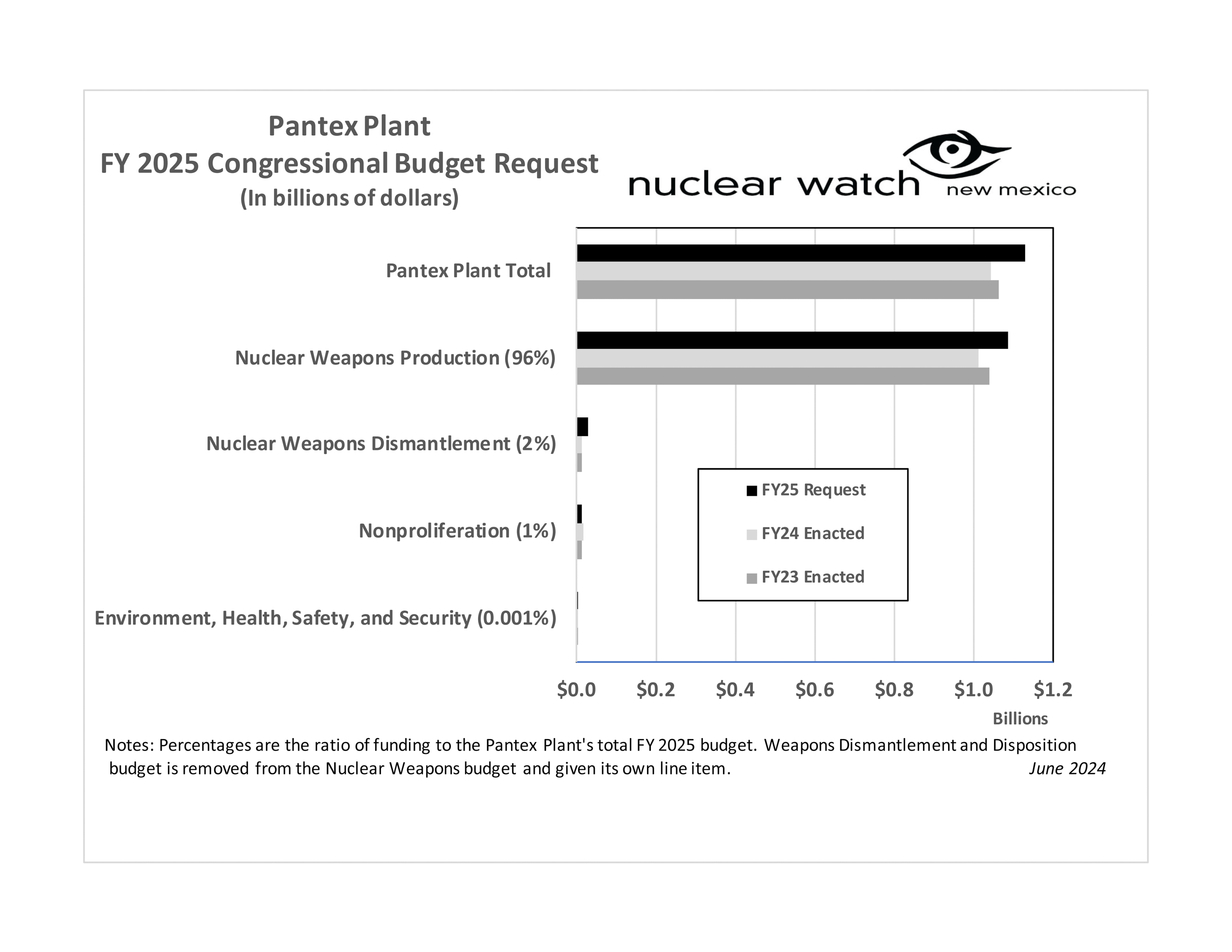
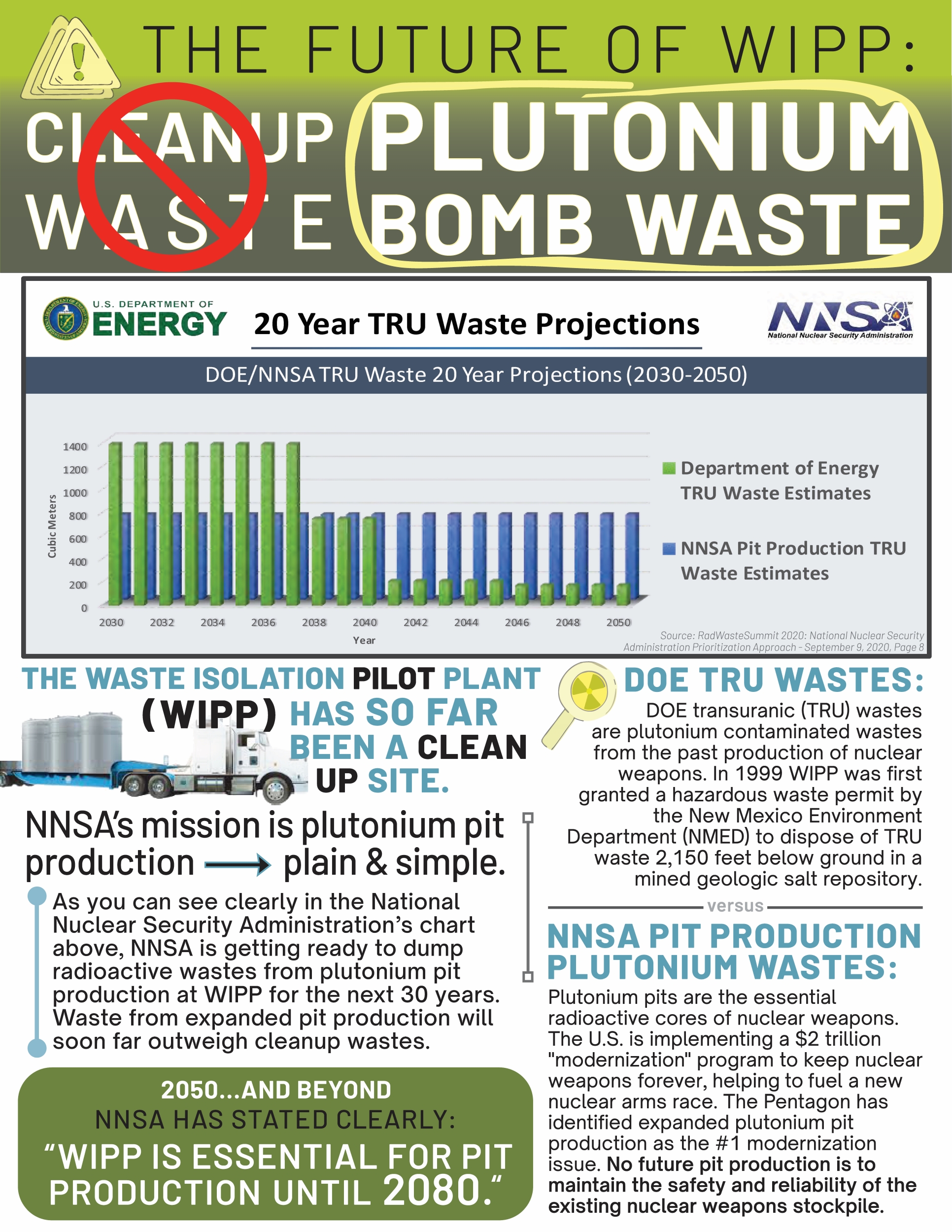
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
Boeing’s Weak Santa Susana Cleanup Triggers Lawsuit
Sweetheart Deal Negotiated Behind Closed Doors Violates CEQA Mandates
PRESS RELEASE
Thursday, October 6, 2022
Contact
Jeff Ruch, PEER, jruch@peer.org (510) 213-7028
Melissa Bumstead, Parents Against Santa Susana Field Lab Santasusanacampaign@gmail.com (818) 233-0642
Denise Duffield, Physicians for Social Responsibility, dduffield@psr-la.org (310) 339-9766
Lawrence Yee lhyee306@gmail.com
Oakland — The Newsom administration’s backroom deal with the Boeing Co. to dramatically weaken cleanup standards at the profoundly polluted Santa Susana Field Laboratory violates the public involvement and transparency requirements of the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA), charges a lawsuit filed today by community and public health groups. The suit would open the cleanup agreement to public scrutiny and force the state agencies and the Boeing Co. to justify a cleanup methodology that leaves 90% of the contamination onsite.
Filed today in Ventura County Superior Court by Parents Against Santa Susana Field Lab, Physicians for Social Responsibility (LA Chapter), and Public Employees for Environmental Responsibility (PEER), the suit would, if successful, vacate both the cleanup agreement and an accompanying promise to free Boeing from toxic stormwater discharge requirements.
“This suit does not prevent cleanup from beginning immediately but instead aims to ensure it continues until it is fully completed,” stated Pacific PEER Director Jeff Ruch, noting that under a prior Consent Order, the cleanup was supposed to have been completed back in 2017. “This lawsuit is about having this cleanup done right and well beyond the outrageous ‘rip and skip’ deal that Boeing wrangled behind closed doors.”
After repeatedly promising to enforce a 2007 legally binding cleanup agreement with Boeing, the Newsom administration secretly negotiated an 800-page agreement that “supersedes” the prior order by substantially relaxing key cleanup requirements, allowing hundreds of times higher levels of toxic chemicals than previously permitted, and leaving much of the contamination onsite.
‘Nuclear accident’ warnings amid Russia missile strikes
By Paraic O’Brien | October 6, 2022 channel4news.com
Russia has faced weeks of military defeats in Ukraine, but today brought a reminder its military is still able to cause substantial destruction.
Overnight, and again this morning, the city of Zaporizhzhia suffered a series of missile attacks, including a direct strike on a residential apartment building.
The strikes raised concerns for the nearby nuclear power plant, leading to a warning from the International Atomic Energy Agency that an accident there is “a very clear possibility”.
NY TIMES: I’ve Studied 13 Days of the Cuban Missile Crisis. This Is What I See When I Look at Putin.
By Michael Dobbs, The New York Times | October 5, 2022 nytimes.com
Two nuclear-armed states on a collision course with no obvious exit ramp. An erratic Russian leader using apocalyptic language — “if you want us to all meet in hell, it’s up to you.” Showdowns at the United Nations, with each side accusing the other of essentially gambling with Armageddon. For six …
Los Alamos National Laboratory’s pit production a year behind schedule
“Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said the lab has a history of delays and cost overruns that predates the pandemic.
“I suspect LANL and [the federal government] are using COVID as a convenient excuse for what’s going to happen anyway,” Coghlan said. “I’m certainly not saying there was no delay for COVID, but I doubt this much.”
Coghlan said the revelation is significant because it’s the first official confirmation the Los Alamos lab is running behind schedule with its planned pit production.”
BY SCOTT WYLAND, THE SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN | October 5, 2022 santafenewmexican.com
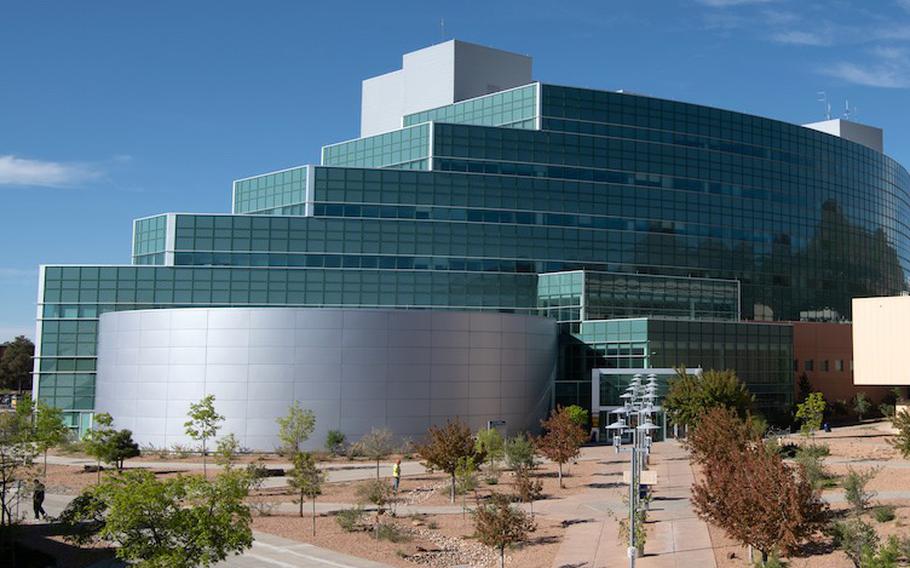

(Tribune News Service) — Los Alamos National Laboratory’s effort to produce 30 nuclear bomb cores a year by 2026 was stalled for 13 months because of the coronavirus pandemic, calling into question whether it can make the much-touted target.
An anti-nuclear activist obtained a redacted management plan for the lab’s plutonium operations through a Freedom of Information Act Request, which describes how the production deadline is more likely to be missed because of preparatory work being delayed during a hard-hitting stretch of the pandemic.
STATEMENT: Archbishop Wester on Feast Day of St. Francis, Pray for Peace in Ukraine, Abolition of Nuclear Weapons
Today, October 4 is the feast day of St. Francis, the tireless promoter of peace and patron saint of the Archdiocese of Santa Fe.
Pope Francis chose his name in honor of St. Francis of Assisi, and three days ago, he declared:
“The course of the war in Ukraine has become so serious, devastating, and threatening as to cause great concern… [W]hat about the fact that humanity is once again faced with the atomic threat? It is absurd… It increases the risk of nuclear escalation, giving rise to fears of uncontrollable and catastrophic consequences worldwide.”
This October is the 60th anniversary of the Cuban Missile Crisis, about which then-Defense Secretary Robert McNamara said humanity survived only by luck. Sixty years later, we are facing the most serious nuclear threats since then.
Pope Francis has called for the abolition of nuclear weapons, declaring they can no longer be justified even by the deterrence strategy of Mutually Assured Destruction.
Biden Thinks Non-Nuclear Threats Will Stop Putin. His Military Doesn’t
“We’re in uncharted territory,” says a senior intelligence officer. “Threatening to respond forcefully and creating catastrophic consequences for Russia [without] suggesting nuclear war: Is that strong enough to deter Putin? And is it really clear? I’m not so sure.”
BY WILLIAM M. ARKIN, NEWSWEEK | September 30, 2022 newsweek.com
The United States would “respond forcefully” to any Russian nuclear strike, President Biden said—but there’s a divide between his administration and some of his military advisers over the role of American nuclear weapons and the most effective way to deter Vladimir Putin, knowledgeable sources tell Newsweek.
“It’s the closest we’ve been to the use of nuclear weapons in over 50 years,” says one civilian working at the Omaha, Nebraska-based Strategic Command. “But I’m not so sure that we are communicating the right thing to deter Putin.”
The Age of Predatory Nuclear-Weapon States Has Arrived
Putin’s nuclear threat marks the start of a new era.
POLITICO | Opinion by Stephen Young, Union of Concerned Scientists | September 30, 2022 politico.com
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine makes at least one thing clear: It’s time for us to update how we think about nuclear weapons. For the first time in the nuclear era, one country used loudly issued nuclear threats — repeated just last week — to deter other countries from intervening in a large-scale conventional war of aggression. We have entered the age of “predatory nuclear-weapon states.”
For political analysts and military officials, this is not an unexpected phenomenon. On the contrary, the concept falls under the so-called stability-instability paradox. Because the threat of nuclear war is so terrifying and the risk of annihilation so real, lower-level conflict actually becomes more feasible. One nuclear-armed country can undertake major conventional military action, expecting that its nuclear capability will prevent outside intervention. That is what’s happening in Ukraine.
BREAKING: Putin illegally annexes 4 occupied regions, escalating war as Ukraine applies to join NATO
“Kyiv has vowed to keep fighting to retake its occupied land, and on Friday appeared on the verge of handing Russia’s military another significant setback.”
NBC NEWS | September 30, 2022 nbcnews.com
The Russian leader repeated his threats of nuclear war to defend his fragile hold over the annexed territory, a dramatic escalation of the seven-month conflict that has seen Moscow respond to heavy losses by calling up hundreds of thousands of reservists and intensifying its confrontation with the West.
The speech was met with an immediate response by Kyiv and its allies.
As well as announcing the annexation, Putin has partially mobilized his military — prompting domestic blowback and an exodus of Russians fleeing the draft — and ramped up his nuclear threats against Ukraine and the West. The moves are seen as a wider escalation after a series of punishing battlefield defeats at the hands of a lightning counteroffensive by Kyiv.
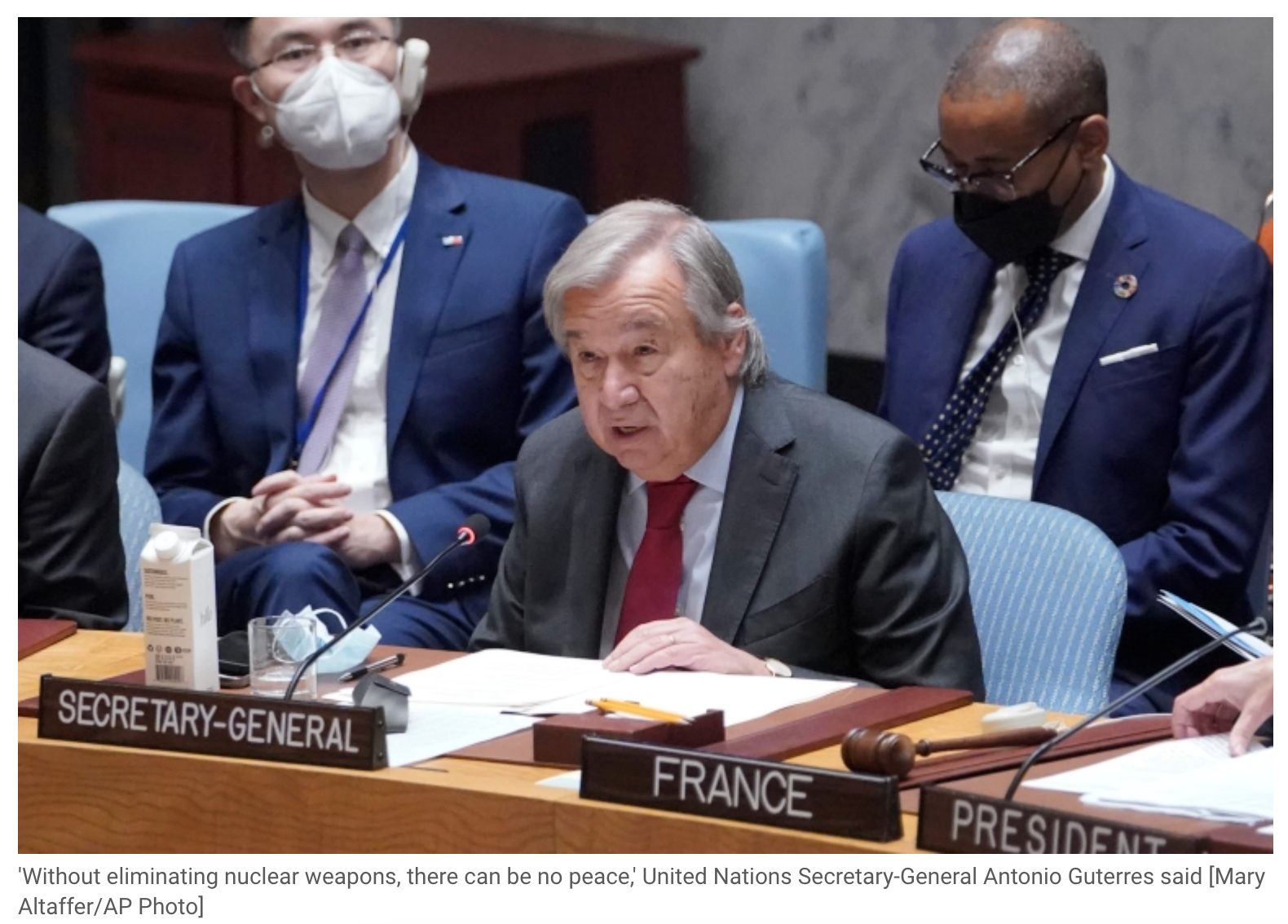
UN chief calls for end to ‘era of nuclear blackmail’
Guterres renews call for the abolition of nuclear weapons as concerns grow over Russia’s threat to use them in Ukraine.
ALJAZEERA | September 26, 2022 aljazeera.com
United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has renewed his call for the global abolition of nuclear weapons as concerns grow over Russia’s threat to use them in the Ukraine war.
“Decades after the fall of the Berlin Wall, we can hear once again the rattling of nuclear sabres,” Guterres told a special UN General Assembly session on nuclear disarmament on Monday.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
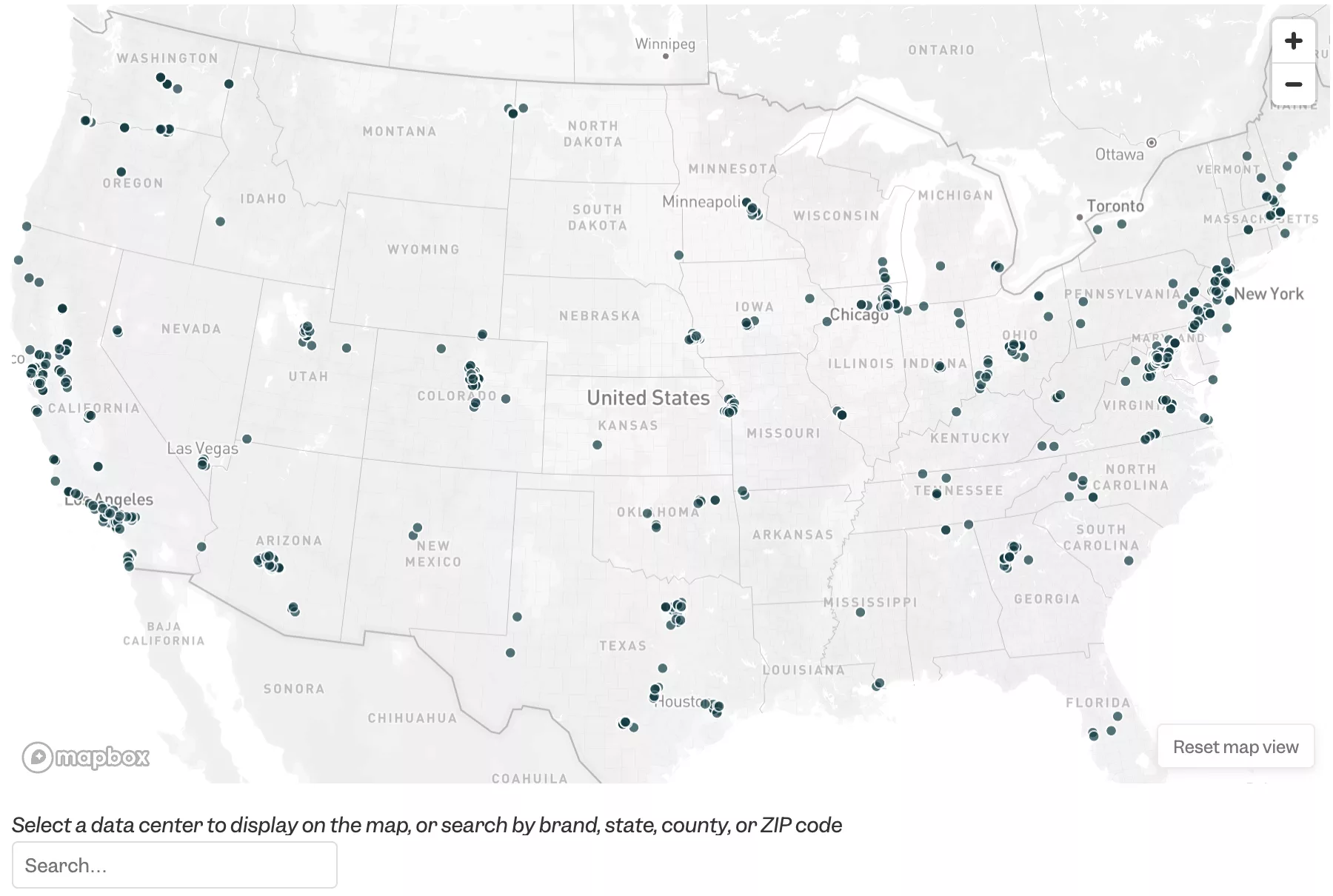
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.