2023 News Articles – All Posts
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
2022 Select Highlighted Press Items
Nuclear Modernization is the ’Absolute Minimum,’ STRATCOM Commander Says | March 8, 2022
US tested hypersonic missile in mid-March but kept it quiet to avoid escalating tensions with Russia | April 4, 2022
Putin’s Nuclear Threats Are a Wake-Up Call for the World | March 15, 2022
Intelligence report determines that Russia's WMD threats will grow as losses mount in Ukraine | March 19, 2022
China and the United States: It’s a Cold War, but don’t panic | March 10, 2022
Russian military doctrine calls a limited nuclear strike “de-escalation.” Here’s why. | March 8, 2022
North Korea says it will strike with nuclear weapons if South attacks | April 4, 2022
Flying Under The Radar: A Missile Accident in South Asia | April 4, 2022
2022 News Articles
People downwind of atomic blasts renew push for US payout
“Officials say the team at Sandia is working with researchers from Australia as well as particle-technology researchers who are building a second concentrating solar power facility in Saudi Arabia to test variants of key components.”
By: The Associated Press / March 24, 2021 | apnews.com
The first atomic bomb test was conducted at Alamogordo, New Mexico, July 16, 1945. (AP / US Army)ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. (AP) — In the desert northeast of Las Vegas, residents living along the Nevada-Arizona border would gather on their front porches for bomb parties or ride horses into the fields to watch as the U.S. government conducted atomic tests during a Cold War-era race to build up the nation’s nuclear arsenal.
About 100 of those tests were aboveground, and U.S. Rep. Greg Stanton of Arizona testified during a congressional subcommittee hearing Wednesday that residents at the time marveled at the massive orange mushroom clouds billowing in the distance.
“They had no idea. They were never told that they were being exposed to dangerous cancer-causing radiation,” Stanton said. “As a direct result of the radiation exposure from these tests, thousands of Arizonans have suffered from cancer, entire families have suffered from cancer and far too many have died.”
He and others testified as part of a renewed push for compensation from the U.S. government following uranium mining and nuclear testing carried out during the Cold War.
Sandia Labs to build solar power testing center in New Mexico
“Officials say the team at Sandia is working with researchers from Australia as well as particle-technology researchers who are building a second concentrating solar power facility in Saudi Arabia to test variants of key components.”
By: The Associated Press / March 26, 2021 | kob.com

ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. (AP) — Sandia National Laboratories has been awarded a $25 million contract to build, test and operate a new solar power test facility on its campus in New Mexico.
Using a concentrated beam of sunlight to heat up sand-like particles, lab officials say the system will be able to produce thermal energy for thousands of hours and will have the capacity to store six hours of energy. This heat can be used to spin a turbine or power an engine to generate electricity.
The contract was announced Thursday by the lab and the U.S. Energy Department. The goal of the federal agency is to develop technology that can make concentrating solar power plants more reliable and easier to build using fewer high-cost materials so that they can be more widely commercialized.
Critique of the RCLC Amended Joint Powers Agreement
The Santa Fe City Council will vote on March 31 to adopt or not the Amended Joint Powers Agreement (JPA) among seven local governments and two Pueblos to continue the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities (RCLC). Separately, at a date yet to be determined, the City Council may consider whether or not to continue participation in the Coalition.
The City of Santa Fe should reject the Amended Joint Powers Agreement because the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities has wholly failed to live up to the stated goals of the original JPA.
- The RCLC was first formed in 2011. Local governments bought into it on the premise that the Coalition would successfully lobby for mission diversification and accelerated cleanup. After spending two million taxpayer dollars on itself the Coalition has been a spectacular failure in both.
- The Amended JPA states: “the Parties share a common interest in assuring that LANL’s missions remain sustainable and diversified…” The Department of Energy (DOE) and Los Alamos County have provided 80% of RCLC’s funding. The County specifically cites the “interdependent needs of LANL and Los Alamos County.” DOE and Los Alamos County explicitly seek expanded production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores, in which the City of Santa Fe does not share a common interest. Expanded pit production is LANL’s overwhelming growth area (270% increase from $308 million in FY 2020 to $847 million in FY 2021). Concerning “common interests,” DOE completely ignores City resolutions calling for resolution of nuclear safety problems before pit production expansion, comprehensive cleanup and a new site-wide environmental impact statement (particularly important for wildfire protection).
Newly Released Documentary Film on Santa Susana Field Lab Airing Nationwide Nov. 14 at 10 pm ET

In the Dark of the Valley is the first feature film to focus on the Santa Susana Field Laboratory, a former nuclear and rocket-engine testing site near Los Angeles. The film is an in-depth exploration into the site’s long history of cover-ups and negligence by site owners Boeing, NASA, and the Department of Energy. It also tells the harrowing story of how a community of mothers, led by Melissa Bumstead, have dealt with the struggles of childhood cancer and their new found life of environmental advocacy.
ICBM Information Project – View the Interactive ICBM Timeline

The Pentagon is currently planning to replace its current arsenal of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) with a brand-new missile force, known as the Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent, or GBSD.
The GBSD program consists of a like-for-like replacement of all 400 Minuteman III missiles that are currently deployed across Colorado, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, and Wyoming, and will also include a full set of test-launch missiles, as well as upgrades to the launch facilities, launch control centers, and other supporting infrastructure. The GBSD program will keep ICBMs in the United States’ nuclear arsenal until 2075, and is estimated to cost approximately $100 billion (in Then Year dollars) in acquisition fees and $264 billion (in Then Year dollars) throughout its life-cycle.
Examining the Need to Expand Eligibility Under the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) before the U.S. House Judiciary Committee, Subcommittee on the Constitution, Civil Rights, and Civil Liberties
When: Wednesday, March 24, 2021, at 2 pm EDT, noon MDT
Where: https://judiciary.house.gov/calendar/eventsingle.aspx?EventID=4479
At the invitation of Chairman Jerrold Nadler, Tina Cordova, Co-founder of the Tularosa Basin Downwinders Consortium (TBDC), will provide written and oral testimony to the U.S. House Judiciary Committee, Subcommittee on the Constitution, Civil Rights, and Civil Liberties this week to urge the members to expand the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) to include the Trinity Downwinders.
Transcript of interview with US Secretary of State Antony Blinken
Washington’s top diplomat holds roundtable with Japanese media in Tokyo
By: ERI SUGIURA| asia.nikkei.com

TOKYO — U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken held a virtual roundtable with Nikkei Asia and other Japanese media in Tokyo on Wednesday, a day after he and Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin met for “two-plus-two” talks with Japanese counterparts Toshimitsu Motegi and Nobuo Kishi.
Here is an edited transcript of the group interview with Blinken:
— Opening remarks
The partnership between the United States and Japan is absolutely vital. I think it’s vital to our country’s respective citizens to the region, and in so many ways to the world. It really starts with our common commitment to democracy. And I think that’s especially significant today because democracy is under challenge and under threat in ways that it hasn’t been before, certainly not in recent years, particularly from autocratic countries were on the rise around the world.
Explosively Entertaining: Nuclear Weapons on TV
Books, Films & Art of Note | Beyond the Bomb: Maria Diaz-Islas, March
1. Jericho (2006-2008)
This show’s passionate fanbase fought tooth and nail to keep it running before CBS canceled it after only two seasons (sounds a lot like some nuclear weapons manufacturers I’ve heard of…). It follows the story of the fictional Kansas town, Jericho, after a nuclear attack on nearby Denver turns the characters’ worlds upside down. The citizens of Jericho struggle as they avoid nuclear fallout, determine how to communicate with the outside world, and try to restore life back to the way it was before the explosion. The post-apocalyptic plot is also riddled with drama, as the characters’ near-death experiences and the loss of loved ones force them to question whether they were truly happy with their former ways of life, reminiscent of living through the COVID-19 pandemic today.
Continue reading
BACK FROM THE BRINK: ENDING NUCLEAR WEAPONS BEFORE THEY END US
Opportunities Under the Biden Administration to Take Action
EVENT VIDEOS AND RESOURCES: Click below to view video recordings, learning resources and actions you can take to eliminate nuclear weapons and the threat of nuclear war.
preventnuclearwar.org/enw-resources
Former Nuclear Watch New Mexico Intern Alicia Sanders-Zakre Presentation on What the Entry into Force of the TPNW Mean in the United States:
The US Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Force: A Post-Cold War INTERACTIVE Timeline
The Pentagon is currently planning to replace its current arsenal of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) with a brand-new missile force, known as the Ground Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD); it is estimated to cost approximately $100 billion in acquisition fees and $264 billion throughout its lifecycle until 2075 (in Then-Year dollars).
Click the link below to find a comprehensive timeline of all relevant actions taken relating to the ICBM force since the end of the Cold War, including force posture alterations, international treaties, congressional efforts, government studies, and milestones in the GBSD acquisition process.
https://web.archive.org/web/20230216030034/https://fas.org/issues/icbm-information-project/timeline-master/
Links between Box Elder landfill, California business charged in radioactive waste scandal emerge
“[Bradley] Angel, with Green Action, says his organization is relieved that Tetra Tech EC has been taken off the Hunter’s Point cleanup but still worries about all projects Tetra Tech is involved in.
“Promontory Point Resource’s application in Utah stresses the convenient value of superfund cleanup sites in the San Francisco Bay Area. Tetra Tech, which designed the Promontory landfill, has also been deeply invested in other northern California superfund projects. Besides Hunter’s Point, documents from the Environmental Protection Agency and news accounts show the company is actively involved in cleanups at other Bay Area superfunds like the Alameda Naval Air Station and McLellan Air Force Base. All these sites contain radioactive contaminants.”
By: Eric Peterson / Special to the Standard-Examiner | standard.net March 19, 2021

After sitting empty for years on the north shore of the Great Salt Lake in Box Elder County, Promontory Point Resources is trying once again to receive out-of-state waste for its landfill after abandoning a previous attempt in 2018.
In its new Class V landfill application with the state Department of Environmental Quality, the company talks about the lucrative market in contaminated soils from superfund cleanup sites in northern California.
“The full market demand for excavated soil disposal from just counties around the San Francisco Bay appears to have an average in the range of 250,000 to 350,000 tons per year,” the document states.
The report does not mention many sites by name, although they are very well known in California.
Cap on Trident nuclear warhead stockpile to rise by more than 40%
Boris Johnson announcement on Tuesday will end 30 years of gradual disarmament
By: Tricia Ennis | 13abc.com
The increased limit, from 180 to 260 warheads, is contained in a leaked copy of the integrated review of defence and foreign policy. Photograph: Tam McDonald/MoD/EPABritain is lifting the cap on the number of Trident nuclear warheads it can stockpile by more than 40%, Boris Johnson will announce on Tuesday, ending 30 years of gradual disarmament since the collapse of the Soviet Union.
The increased limit, from 180 to 260 warheads, is contained in a leaked copy of the integrated review of defence and foreign policy, seen by the Guardian. It paves the way for a controversial £10bn rearmament in response to perceived threats from Russia and China.
The review also warns of the “realistic possibility” that a terrorist group will “launch a successful CBRN [chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear] attack by 2030”, although there is little extra detail to back up this assessment.
Santa Fe’s benefit from LANL coalition questioned
“We have RCLC, which is funded primarily by the Department of Energy funds, yet DOE doesn’t necessarily listen to the resolutions that we put forward about reducing plutonium pit production. They don’t ask us what we think as city of Santa Fe residents.”
By: Sean P. Thomas, The Santa Fe New Mexican | sfnewmexican.com March 18th, 2021
Mar. 18—Concerns from City Councilor Renee Villarreal over how the city of Santa Fe would benefit by remaining in an amended joint power agreement with the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities continued during Wednesday night’s Quality of Life Committee meeting.
Santa Fe is one of nine cities, counties, towns and tribal governments that make up the regional coalition, which was established in 2011 to give communities in Northern New Mexico more say in decision-making related to job development and cleanup at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Villarreal, however, questioned how the coalition advocates for city policy stances on requests for expanded cleanup at the site and the reduction of plutonium pit production.
THE UK TO INCREASE NUCLEAR CAPABILITY BY 40%: British Defense Review Ends Nuclear Reductions Era
By: Hans M. Kristensen fas.org March 17th, 2021
The United Kingdom announced yesterday that it has decided to abandon a previous plan to reduce its nuclear weapons stockpile to 180 by the mid-2020s and instead “move to an overall nuclear weapon stockpile of no more than 260 warheads.”
The decision makes Britain the first Western nuclear-armed state to increase its nuclear weapons stockpile since the end of the end of the Cold War. In terms of numbers, it takes Britain back to a stockpile size it had in the early-2000s. The change is part of “a shift to a more robust position on security and deterrence.”
NNSA Says No Injuries, Contamination During February 26 Incident At LANL Plutonium Facility
February 26 at the Los Alamos National Laboratory’s Plutonium Facility (PF-4) waste generator site at Technical Area 55 involving sparking in a where a metal waste item in a transuranic waste drum has resulted in a potential noncompliance notification to the New Mexico Environment Department.
By: MAIRE O’NEILL maire@losalamosreporter.com | Los Alamos Reporter March 17, 2021
A spokesperson for the Department of Energy National Nuclear Security Administration Los Alamos Field Office confirmed that there were no injuries, no fire, contamination or release of material to the environment.
“During normal waste packaging operations, small sparks were observed in a plastic waste bag containing a High Efficiency Particular Air (HEPA) from a titanium welding area inside a glovebox,” she said. “The staff at TA-55 responded quickly and effectively, appropriately following safety protocol to evacuate the area and notify the Los Alamos Fire Department.”
A March 12 letter from NNSA to NMED noting the potential for noncompliance under the Hazardous Waste Facility permit says preliminary calculations indicate that there is no imminent or potential threat to human health or the environment and that NNSA is providing this report as a precautionary measure to keep NMED informed of the fact-finding extent of condition and the planned recovery path.
Ongoing ‘review’ forces Pentagon official to pull out of SC pit production briefing
A Pentagon official backed out of a plutonium pit production briefing in Columbia this week because the Biden administration is “engaged in a full review of the program,” according to Rick Lee, the chairman of the S.C. Governor’s Nuclear Advisory Council.
By: Colin Demarest cdemarest@aikenstandard.com | postandcourier.com

Local Governments Should Leave the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities
Summary: Local governments get little in return for being members of the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities (RCLC). That is because the Coalition is ineffective, dysfunctional, wastes taxpayers’ money and stands in the way of genuine, comprehensive cleanup at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. The RCLC was created to serve the interests of the Department of Energy and Los Alamos County, both of whom strongly support expanded plutonium pit production for new nuclear weapons and supply 80% of the Coalition’s funding. The Regional Coalition brings no discernible economic benefit to local governments other than already rich Los Alamos County because the Lab’s presence is an economic net loss to them. Local governments should not put their time and money into the Coalition. Instead, their constituents would be better served if local governments left the coalition and advocated for comprehensive cleanup that would permanently protect the environment while providing hundreds of high paying jobs.
Background
In 2011 the Department of Energy pulled promised funding from the Community Involvement Fund administered by the New Mexico Community Foundation that supported independent, often critical citizen and tribal analyses of DOE cleanup programs. At the same time DOE began funding the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities modeled on earlier alliances with local governments around the Rocky Flats Plant near Denver, CO and the Mound Plant, near Mound, OH.
The Nuclear Weapons Dimensions of the 2021 Integrated Review: A First Look
ACROSS THE POND AND OVER TO THE SAVANNAH RIVER AND NEW MEXICO MOUNTAINS: The UK will rearm itself with new American-made W93 warheads, and the plutonium pits for these weapons will be manufactured here at LANL and at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
BY: SEBASTIAN BRIXEY-WILLIAMS basicint.org March 16th, 2021
Today’s Integrated Review of Security, Defence, Development and Foreign Policy (IR), Global Britain in a Competitive Age, is said to contain the most comprehensive review of UK nuclear weapons policy since the end of the Cold War (pp.76-78). Although there is certainly some continuity with the 2015 Strategic Defence and Security Review, it sets a decisive course away from the United Kingdom’s long-term trend towards nuclear arms reductions and greater transparency.
Warhead Numbers and Transparency
The most headline-grabbing change to UK nuclear weapons policy is the increase to the cap on its overall nuclear warhead stockpile from 180 to 260, which was leaked last week and is now confirmed. This 44.4% increase decisively moves the Johnson Government away from the pledge made by the Coalition Government in 2010 to limit numbers to not more than 180 by the mid-2020s. While neither confirming that numbers will actually rise nor stating the precise reasons for this change, the IR claims vaguely that the previous target cap must be abandoned due to ‘recognition of the evolving security environment, including the developing range of technological and doctrinal threats’ (p.76).
New United Kingdom Defense Strategy a Troubling Step Back on Nuclear Policy
“We have RCLC, which is funded primarily by the Department of Energy funds, yet DOE doesn’t necessarily listen to the resolutions that we put forward about reducing plutonium pit production. They don’t ask us what we think as city of Santa Fe residents.”
For Immediate Release: March 15, 2021
Media Contacts: Daryl G. Kimball, executive director, (202) 463-8270 ext 107; Kingston Reif, director for disarmament policy, (202) 463-8270 ext 104
|
New Mexico demands more of US when addressing nuclear waste
“Some elected officials and watchdog groups say the list is another indication that New Mexico is on the back burner when it comes to cleaning up legacy waste. They’re also raising concerns that new waste generated by Los Alamos when it ramps up production of key nuclear warhead components will need to be cleaned up and could further sideline decontamination efforts.”
BY: SUSAN MONTOYA BRYAN/Associated Press krqe.com March 15th, 2021

ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. (AP) – The U.S. Energy Department has rolled out its 2021 priorities for cleaning up tons of toxic waste left behind by decades of bomb-making and nuclear research at scientific installations and defense sites around the country.
The list includes a goal of sending 30 shipments from the birthplace of the atomic bomb — Los Alamos National Laboratory — to the federal government’s underground waste repository in southern New Mexico.
For the NPT to work, plutonium has to go
Dealing with uranium enrichment is complicated because nuclear power plants use enriched uranium fuel, but that should not hold us back from eliminating the danger we can eliminate—plutonium.
By Victor Gilinsky, Henry Sokolski thebulletin.org | March 15, 2021
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT), whose tenth review conference is coming up in August, is in trouble, and not only because of the crescendo of complaints about the failure of the nuclear-armed states to implement nuclear disarmament. The treaty is threatened with irrelevancy because its controls have not kept up with the times. It was drafted over 50 years ago, when it was widely believed that nuclear energy represented the future and would soon take over the generation of electricity. Not surprisingly, countries put few treaty restrictions on access to technology or materials other than to impose international inspection, and even that was circumscribed. We now have a more realistic view of the dangers of access to fuels that are also nuclear explosives (plutonium and highly enriched uranium) and also of the limited economic utility of these fuels for powering reactors. If we want an effective NPT, we have to eliminate these dangerous materials from civilian nuclear power programs.
Checking in: WIPP maintenance work ‘on schedule’ during 2-month operations pause
At WIPP, the waste is delivered from facilities operated by the U.S. Department of Energy around the country and buried in an underground salt deposit which gradually collapses and encases the waste permanently.
By: Adrian Hedden | currentargus.com March 15, 2021
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant halted waste emplacement and handling operations for the last month at the nuclear waste repository near Carlsbad while an array of maintenance projects was completed.
The facility, which permanently disposes of low-level transuranic (TRU) nuclear waste about 2,000 feet underground, planned the outage for about two months until April 14 to allow workers to complete routine upgrades to its infrastructure and other needed work.
During the two-month pause, WIPP planned on 97 activities from six departments including mine operations, waste handling, hoisting, work control, safety and engineering.
Japan Hasn’t Recovered 10 Years After Fukushima Meltdown
“There is an old laboratory adage that says, “The best way to clean up a spill is not to have a spill,” and this applies on a much larger scale to the entirety of northern Japan, where cleanup will remain economically unfeasible.”
BY: Arnie Gundersen Truthout March 11th, 2021
On March 11, 2011, a devastating offshore earthquake and ensuing tsunami rocked Japan and resulted in nuclear meltdowns in three nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear site. Until the 2020 Tokyo Olympics were placed on a one-year hiatus because of concerns over COVID-19, the Japanese government had portrayed these events as the “Recovery Olympics.” It had hoped to use the Olympics to showcase a claimed restoration of Japan since it was devastated in 2011. But has Japan really “recovered?”
Recently, corresponding author Marco Kaltofen (Worcester Polytechnic Institute), co-author Maggie Gundersen (Fairewinds Energy Education) and I published our second peer-reviewed journal article analyzing hundreds of radioactive samples from northern Japan that we collected with assistance from Japanese citizens and scientists. Our sampling on five occasions over almost a decade totaled 70 days on the ground.
Report: Cancer death rates rising near Fermi nuclear plant
A new study is looking to test baby teeth from children living near the plant.
By: Tricia Ennis | 13abc.com
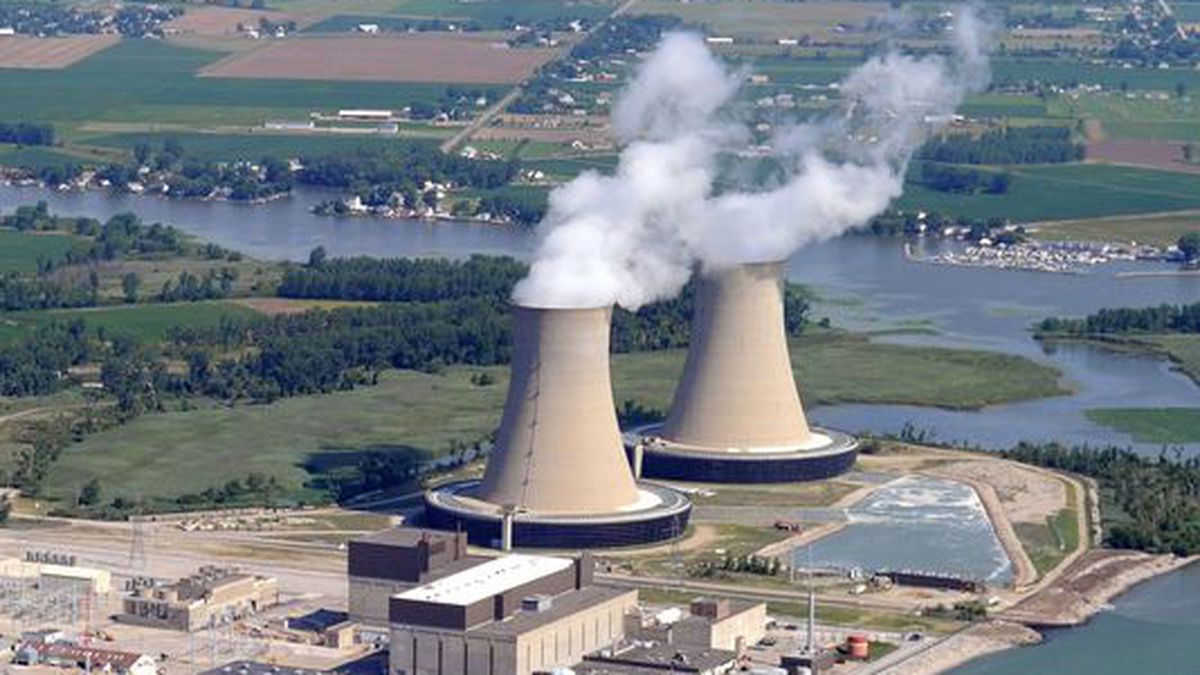

NEWPORT, Mich. (WTVG) – A new report from the Radiation and Public Health Project claims that the cancer death rate in Monroe County, Michigan is on the rise and it’s tying that growth to the Fermi 2 nuclear plant in Newport.
According to the report, which uses public health data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the rate of death due to cancer in Monroe County was roughly equal to that of the rest of the United States. Since 1988, that rate has risen steadily, reaching 11.3% higher than the national average in the most recent 10 years (2009-2018). From 2014-2018, that rate was 14.3% higher than the national average, amounting to 1,794 deaths. In the period between 1969 and 1978, outlines the report, that rate was 4.5% lower than the national average.
LANL W-87-1 Nuclear Warhead and Proposed Expansion into Santa Fe
“CCNS asks that we look more closely at LANL’s claim to boost the local economy – an extra cup of coffee in the morning, a bagel for lunch, a tank of gasoline, a trip to the bank to deposit the salaries of some of the highest paid employees in New Mexico? LANL’s taxes are already contributing to Santa Fe’s economy. Such claims depend on redefining what is meant by “economic support” because there is no commercial product, nothing that is a benefit to the community.”
nucleractive.org March 11th, 2021
The W-87-1, a new plutonium pit for a proposed nuclear warhead for fighting a full-scale nuclear war, would be fabricated at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). A plutonium pit is a grapefruit sized radioactive core of a nuclear warhead. The plutonium pit would fit on a proposed Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent intercontinental ballistic missile. Many people question the need for a new estimated one billion dollar weapon, which they say is “outdated and unnecessary.” https://fas.org/issues/icbm-information-project/ (Federation of American Scientists); https://www.internationalpolicy.org/program/Arms-%26-Security-Program (Issue Brief: Inside the ICBM Lobby: Special Interests or The National Interest, Center for International Policy’s Arms & Security Program); and https://www.opensecrets.org/news/reports/capitalizing-on-conflict (Capitalizing on conflict: How defense contractors and foreign nations lobby for arm sales, Center for Responsive Politics).
The total congressional budget request for LANL in Fiscal Year 2021 is approximately $3.7 billion. Approximately 80 percent is for nuclear weapons activities, or $3 billion.
Recently LANL signed two 10-year leases for nearly 96,000 square feet of space in three vacant office buildings in Santa Fe. LANL plans for 75 employees to be based in one building on the corner of West Alameda and Guadalupe, and 500 more in two buildings on the hill above the intersection of St. Michael’s and Pacheco. It is calculated that of those employees, 460 will work on nuclear weapons.
Staffing, scheduling problems imperil projects at Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, report says
Within the report, the GAO pointed to “significant” staffing shortages at WIPP that could prevent WIPP from completing construction projects needed to increase the facility’s space for waste disposal and allow for more workers in the underground to mine and emplace waste simultaneously.
By: Adrian Hedden | currentargus.com March 11, 2021
Staffing and other problems at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant continued to be voiced by the federal government’s watchdog agency in a two-year report seeking to identify struggling areas in the government and ways to improve operations.
The Government Accountability Office (GAO) identified the U.S. Department of Energy’s contract and project management at both the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and the Office of Environmental Management (EM) as one of six areas in its 2021 “High Risk List” that had showed some improvement since the last such report in 2019.
The EM manages WIPP on a federal level as low-level nuclear waste is permanently disposed of in an underground salt bed at the facility near Carlsbad.
63 Years Ago – March 11, 1958: The Atomic Bomb that Faded into South Carolina History
Two women recall the bizarre day in 1958 when an atomic bomb fell out of the sky and landed on a Mars Bluff farm outside Florence.
Thankfully, the nuclear warhead, which at 30 kilotons was twice as powerful as the Hiroshima bomb, didn’t go off. But its TNT trigger did, leveling the farmhouse and leaving a massive crater. Such “broken arrow”incidents took place an extremely troubling number of times during the Cold War.
House nears vote to repeal nuclear plant bailout
“We need to hit the reset button and start from scratch here,” state Rep. Jeffrey Crossman (D., Parma) said. “We can’t continue this nonsense of pretending that the corruption didn’t happen.”
By: JIM PROVANCE | The Blade, Toledo (TNS)
COLUMBUS — A House committee Tuesday set the stage for a full chamber vote to partly repeal provisions of a state law at the heart of a $61 million Ohio Statehouse bribery scandal.
The full Ohio House of Representatives was expected to vote Wednesday.
This would mark the House’s first action to undo a $1 billion, consumer-financed bailout of the Davis-Besse nuclear power plant near Oak Harbor and the Perry plant east of Cleveland. That law has come to epitomize shady, backroom dealing hidden even to those lawmakers ultimately manipulated to get it passed.
Two players and a nonprofit, dark-money corporation have already pleaded guilty to federal racketeering charges carrying up 20 years in prison for the individuals. Three others — including former House Speaker Larry Householder (R., Glenford) — face similar charges.
Nuclear Power Looks to Regain Its Footing 10 Years after Fukushima
Economics may play a stronger role than fear in steering nuclear power toward a slow decline.
“The pace of nuclear technologies’ progress could also be a factor in clean-energy strategies turning away from such power generation. Small modular reactors, along with other experimental designs, are not expected to begin commercial operations (or even testing) until the 2030s at the earliest, according to the DOE. This suggests that small reactors are unlikely to make a meaningful difference in reducing carbon emissions within the next 20 years. And at that point, they will have to compete in a future energy landscape that has been transformed even further by cheaper renewables and energy-storage technologies.”
“One imagines that solar will be more ingrained and cheaper, wind may be more ingrained and cheaper, the offshore wind will be developed, maybe batteries will be better developed, and storage will be better developed,” says Allison Macfarlane, who was chair of the NRC in 2012–2014. “That’s the market nuclear will have to compete in.”
By: Jeremy Hsu| scientificamerican.com March 9, 2021
Nuclear power faces a wobbly future 10 years after an earthquake and tsunami triggered a triple reactor meltdown at the Fukushima Daiichi plant in Japan. But the industry’s unstable footing has less to do with the Fukushima accident—and more to do with how a natural gas glut and the rise of renewable power have transformed the global energy landscape.
Fukushima has certainly left its mark on the nuclear industry. When the Tohoku earthquake and tsunami occurred on March 11, 2011, there were 54 nuclear reactors in Japan. Since then about a third of them have been permanently shut down, and only nine have resumed operation.
“In Japan, [the accident is] still an outsize event,” says Edwin Lyman, director of nuclear power safety at the Union of Concerned Scientists. “It not only had direct and indirect environmental consequences that they’re still dealing with—and a price tag of hundreds of billions of dollars to clean it up—but also it shattered the confidence of the Japanese people in nuclear power, which the authorities had always assured them was totally safe.”
Additionally, the accident spurred regulatory reviews of nuclear power worldwide and accelerated a preexisting plan in Germany to completely phase out nuclear power by the end of 2022. Other countries, including Spain, Belgium and Switzerland, are in the process of doing so within the next 14 years.
After 75 years, it’s time to clean Bikini
“It is time, finally, to recognize and right the wrongs perpetrated by the US government in the Marshall Islands. The US forced a new and dangerous technology on the native lands and peoples, without fully comprehending the short- and long-term consequences.”
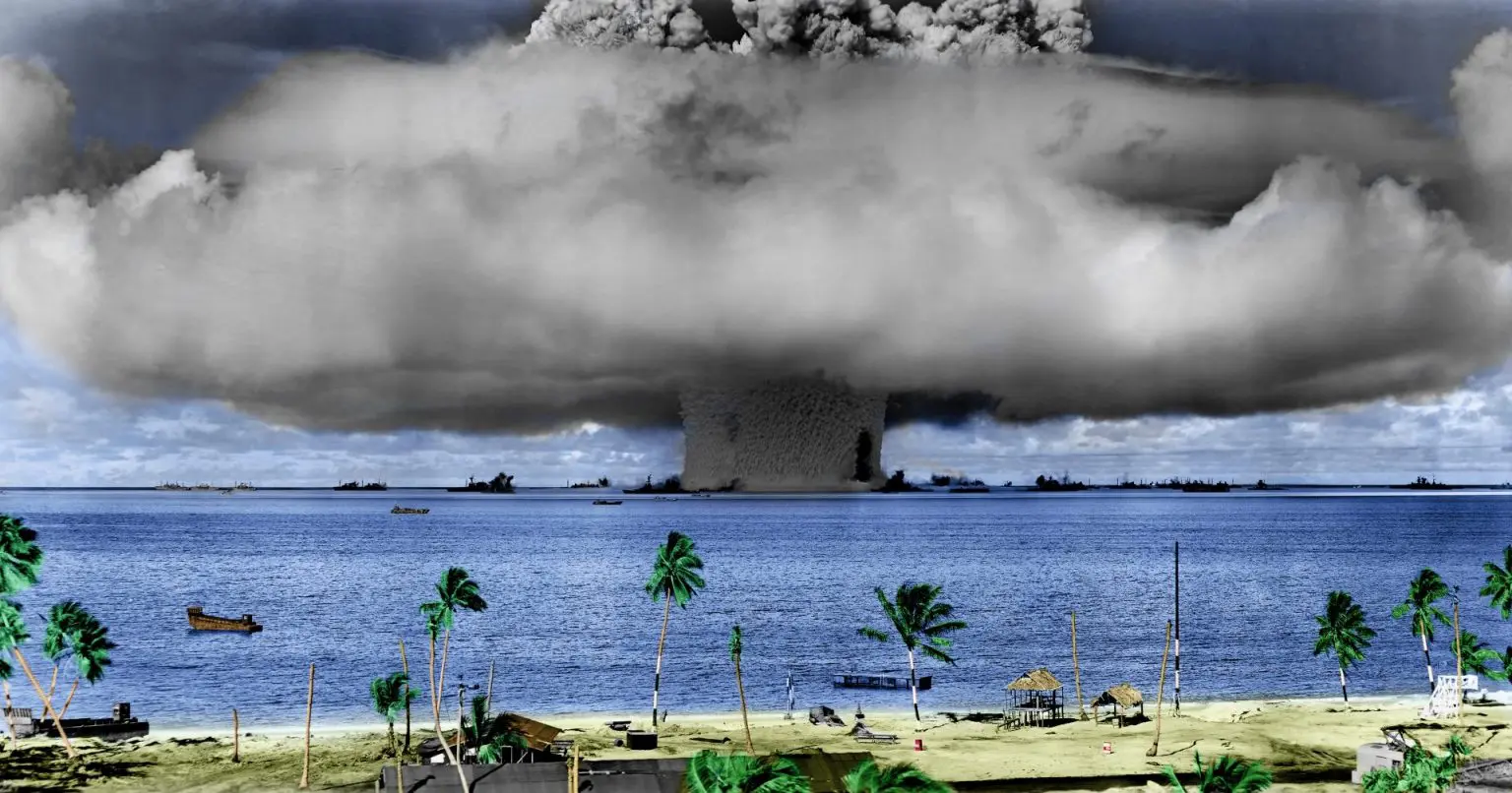

BY: Hart Rapaport, Ivana Nikolić Hughes | thebulletin.org March 9, 2021
Due to their remote location in the Northern Marshall Islands, the people of Bikini Atoll were spared the worst of the mid-Pacific fighting between the American and Japanese armies in the final years of World War II. Their millennia-old culture and sustainable way of life ended abruptly when, in early 1946, Commodore Ben Wyatt, a representative of the occupying United States Navy, informed King Juda and other Bikini residents that the US would begin to test nuclear weapons near their homes. Wyatt asked the Bikinians to move elsewhere, stating that the temporary move was for “the good of mankind and to end all wars.” Though Wyatt may have believed his words to be true, the show of might by the US that followed neither ended all conflict, nor was the exodus short-lived. Seventy-five years later, Bikinians have yet to return.
Continue reading
By: William D. Hartung | Arms & Security Program
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) have been called “some of the most dangerous weapons in the world” by former Defense Secretary William Perry, because under current policies the president would have only a matter of minutes to decide whether to launch them in a crisis, increasing the risks of an accidental nuclear war.1 Despite this reality, proposals for reducing this risk have routinely been blocked, in significant part due to a group of Senators from states that host ICBM bases or ICBM maintenance and development activities, often referred to as the ICBM Coalition. The Coalition includes Senators from Montana, North Dakota, Utah, and Wyoming.
The polices promoted by the ICBM Coalition and its allies do not have wide public support. A recent poll conducted by ReThink Media and the Federation of American Scientists found that 60% of Americans supported either forgoing the development of a new ICBM, eliminating ICBMs altogether, or eliminating all nuclear weapons, an indication that a change in current ICBM policies would have significant public support.
Can the Energy Department store 50 tons of weapons-grade plutonium for 10,000 years?
Safely ridding the nation of one of the world’s largest excess stockpiles of weapons-grade plutonium will be no minor feat. At issue is the US Energy Department’s 2016 decision to dilute and dispose of, all told, about 48.2 metric tons of plutonium, including 26.2 tons of components, known as “pits,” from several thousand dismantled thermonuclear warheads and 22 metric tons in other forms…If one gram of soil contains as little as 1.587 micrograms of plutonium, the Energy Department is required by federal standards to geologically isolate it from the environment for at least 10,000 years at WIPP.
By: Robert Alvarez | March 8, 2021 | thebulletin.com
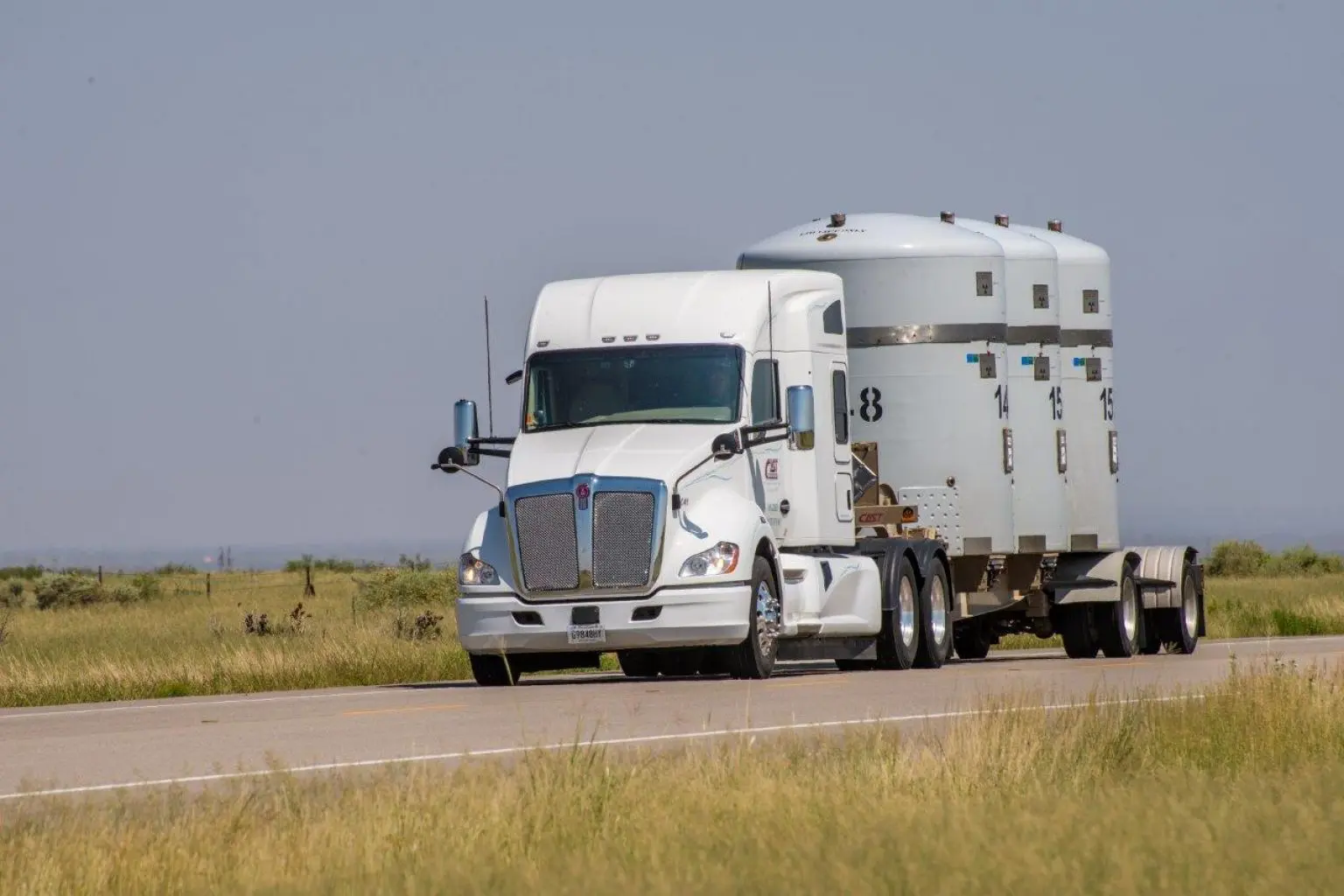

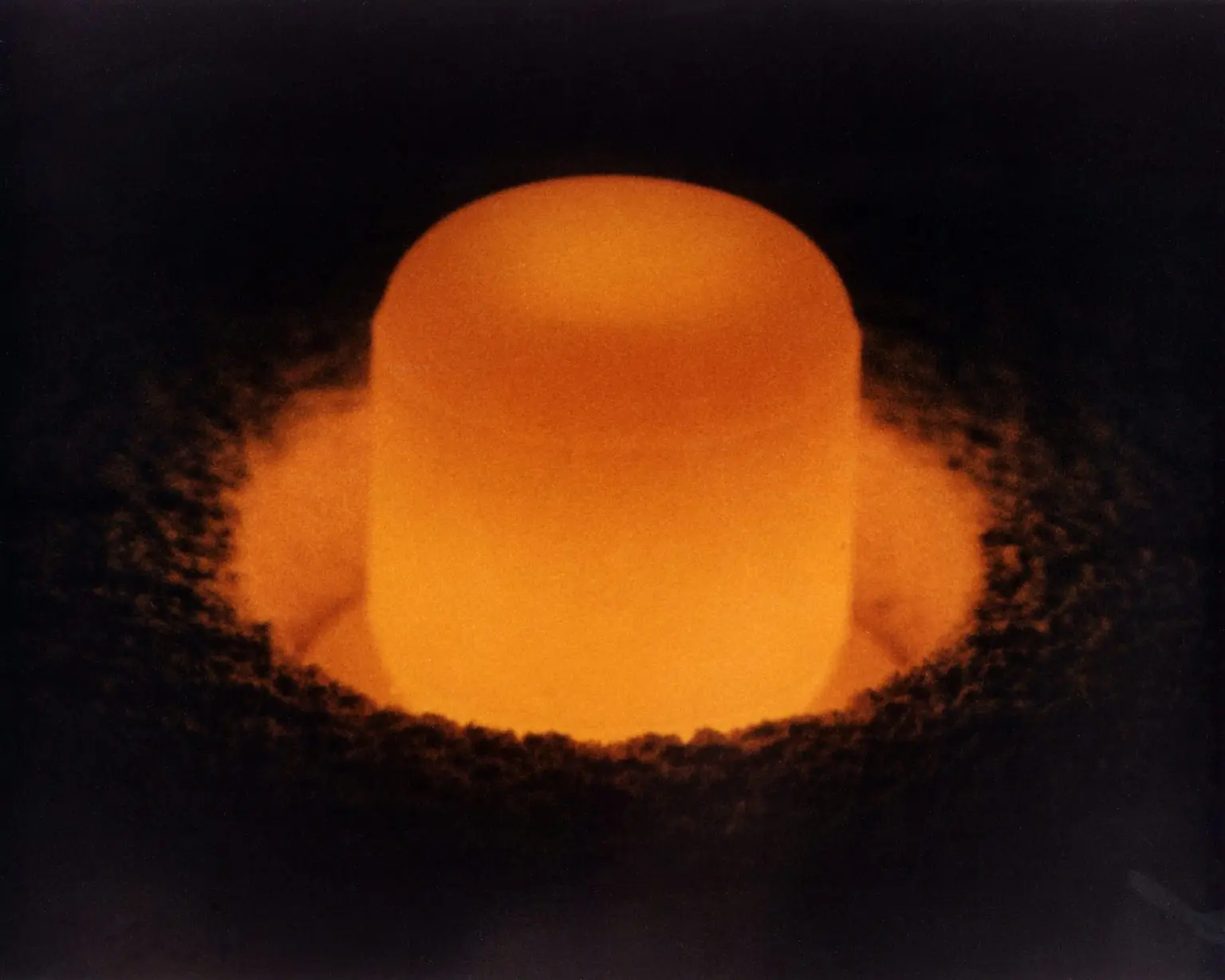
The nuclear age is undergoing a paradigm shift. During much of the latter half of the past century, the nuclear enterprise was ascendant; now, it has entered a period of decline and uncertain long-term custodianship. This reversal of fortune is especially apparent in the United States’ efforts to rid itself of its unwanted reserves of plutonium. It’s been more than 75 years since a blinding flash lit up the pre-dawn sky at Alamogordo in the Chihuahua Desert of New Mexico. On July 16, 1945, a single gram of the grapefruit-size sphere of plutonium at the center of the world’s first nuclear explosion released three times the destructive force of the largest conventional bomb used during World War II. [1]
Thereafter, the United States government built a grossly oversized nuclear arsenal and never envisioned having to stop building it. Between 1944 and 1994, the Energy Department and its predecessors produced 99.5 metric tons of plutonium for use in an estimated 70,000 nuclear weapons. (An additional 11 tons were produced or acquired for research and development purposes.)
This Is How the Biggest Arms Manufacturers Steer Millions to Influence US Policy
Five of the nation’s biggest defense contractors — Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies and General Dynamics — spent a combined $60 million in 2020 to influence policy, according to a new report from the Center for Responsive Politics.
By: Stephen Losey | military.com 7 Mar 2021
The paper, “Capitalizing on conflict: How defense contractors and foreign nations lobby for arms sales,” details how a network of lobbyists and donors steered $285 million in campaign contributions and $2.5 billion in lobbying spending over the last two decades, as well as hiring more than 200 lobbyists who previously worked in government.
The amount of money at stake is immense, both at home and abroad, the center states on its website, OpenSecrets.org. Not only is a significant portion of the Pentagon’s $740 billion annual budget spent on weapons, the report explains, but American defense firms agreed to sell $175 billion in weapons to other countries over the last year. That includes deals to sell $23 billion in F-35 Joint Strike Fighters and drones to the United Arab Emirates, and billions more in sales to Taiwan and Saudi Arabia, it adds.
The practice appears unlikely to change significantly under the Biden administration.
Putin, Biden Should Aim For More Arms Curbs: Gorbachev
Gorbachev told the Interfax news agency that the two leaders – who spoke by phone after Biden’s inauguration last month – should meet and discuss further arms curbs.
By: AFP NEWS – Agence France Presse /
Former Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev on Saturday urged Russian President Vladimir Putin and new US President Joe Biden to push for deeper restrictions on nuclear weapons.
Tensions soared between the two nations under previous US leader Donald Trump, fuelled by allegations of sweeping cyberattacks and a litany of other disagreements.
But soon after Biden took office, the two powers extended a pact that limits each side to 1,550 nuclear warheads, which Putin hailed as a positive development.
Continue reading
Celebrating International Women’s Day 2021 #ChooseToChallenge

Today, as thousands of nuclear weapons remain in unchecked control by only a few men in power, Ploughshares Fund continues to #ChooseToChallenge – the false assumptions, unfair gender biases, as well as the systematic racism that legitimize and normalize dangerously outdated nuclear weapons policies.
A Decade Later: Human Suffering and Failures of Fukushima
Fukushima Daiichi 2011-2021
By: beyondnuclearinternational March 7, 2021

The decontamination myth and a decade of human rights violations
The following is the Executive Summary from the new Greenpeace report. Download the full report.
As a result of a catastrophic triple reactor meltdown at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant on 11 March 2011, several tens of thousands of square kilometres in Fukushima Prefecture and wider Japan were contaminated with significant amounts of radioactive caesium and other radionuclides. The first Greenpeace radiation expert team arrived in Fukushima on 26 March 2011, and Greenpeace experts have since conducted 32 investigations into the radiological consequences of the disaster, the most recent in November 2020.
This report, the latest in a series, chronicles some of our principal findings over recent years, and shows how the government of Japan, largely under prime minister Shinzo Abe, has attempted to deceive the Japanese people by misrepresenting the effectiveness of the decontamination programme as well as the overall radiological risks in Fukushima Prefecture. As the latest Greenpeace surveys demonstrate, the contamination remains and is widespread, and is still a very real threat to long term human health and the environment.
Department of Energy, nuclear oversight agency on ‘high-risk’ list
“This is more than just chronic behavior — it’s like institutionalized bad management,” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
By: Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com | santafenewmexican.com March 3, 2021
The U.S. Department of Energy and its agency overseeing the nation’s nuclear weapons program have serious enough problems with managing contractors and projects — including for nuclear waste cleanup — that they made a government watchdog’s “high-risk” list again this year.
Both the Energy Department and its branch known as the National Nuclear Security Administration have made some progress in how they manage personnel, facilities and waste disposal, but they still are deficient in key areas, the Government Accountability Office said in its biannual high-risk report.
The report lists programs and operations that are high-risk due to their vulnerabilities to fraud, waste, abuse and mismanagement — and some require an overhaul.
The GAO issues the reports at the start of each new session of Congress. They have led to more than $575 billion in cost benefits to the federal government in the past 15 years, the GAO said.
Nuclear News Archives – 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.