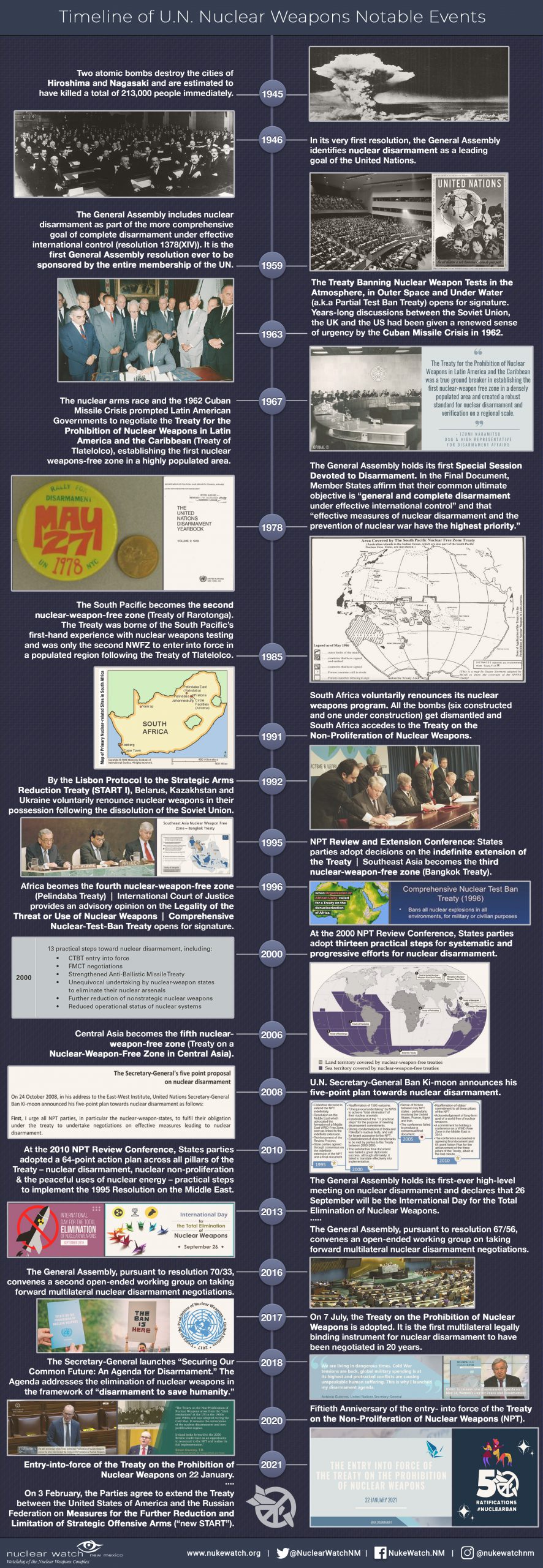
Overview
The U.N. Treaty
on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
On 7 July 2017 – following a decade of advocacy by ICAN and its partners – an overwhelming majority of the world’s nations adopted a landmark global agreement to ban nuclear weapons, known officially as the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons. It will enter into legal force once 50 nations have signed and ratified it.
Prior to the treaty’s adoption, nuclear weapons were the only weapons of mass destruction not subject to a comprehensive ban, despite their catastrophic, widespread and persistent humanitarian and environmental consequences. The new agreement fills a significant gap in international law.
It prohibits nations from developing, testing, producing, manufacturing, transferring, possessing, stockpiling, using or threatening to use nuclear weapons, or allowing nuclear weapons to be stationed on their territory. It also prohibits them from assisting, encouraging or inducing anyone to engage in any of these activities.
A nation that possesses nuclear weapons may join the treaty, so long as it agrees to destroy them in accordance with a legally binding, time-bound plan. Similarly, a nation that hosts another nation’s nuclear weapons on its territory may join, so long as it agrees to remove them by a specified deadline.
Nations are obliged to provide assistance to all victims of the use and testing of nuclear weapons and to take measures for the remediation of contaminated environments. The preamble acknowledges the harm suffered as a result of nuclear weapons, including the disproportionate impact on women and girls, and on indigenous peoples around the world.
The treaty was negotiated at the United Nations headquarters in New York in March, June and July 2017, with the participation of more than 135 nations, as well as members of civil society. It opened for signature on 20 September 2017. It is permanent in nature and will be legally binding on those nations that join it.
Why a ban?
Nuclear weapons are the most inhumane and indiscriminate weapons ever created. That is why it is time to end them, before they end us.
Nuclear weapons are the most inhumane and indiscriminate weapons ever created. They have catastrophic humanitarian and environmental consequences that span decades and cross generations; they breed fear and mistrust among nations, as some governments can threaten to wipe out entire cities in a heartbeat; the high cost of their production, maintenance and modernisation diverts public funds from health care, education, disaster relief and other vital services. Banning these immoral, inhumane weapons under international law was a critical step along the path to ending them.
With the adoption of the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) on July 7th, 2017, the world's majority took a critical step towards making that nuclear-weapon-free future a reality.
Photos from Celebrations of the 1st Anniversary of the Nuclear Ban Treaty – January 22, 2022
Seeking a world without nuclear weapons
Jan. 22 is the one-year anniversary of the U.N. Treaty on the Abolition of Nuclear Weapons entering into force as international law. Today, 59 countries have ratified the Treaty on the Abolition of Nuclear Weapons, with several more countries on the verge of doing the same. The importance of this cannot be overstated. With more and more countries outlawing everything to do with nuclear weapons, it becomes increasingly harder for the nine countries possessing these weapons to defend their continued existence.
recorder.com | BY SUSAN LANTZ January 22, 2022
For instance, Germany, Norway, Sweden, Belgium, Netherlands, Italy are all likely to sign onto the Treaty on the Abolition of Nuclear Weapons eventually, with strong support already in their populations and parliaments. The United States currently has nuclear weapons in Belgium, Germany and Italy. After these countries ratify the treaty, the United States will be required to remove its weapons.
International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons at Ghedi Base in Italy
View photos below of the initiative near the Italian base of Ghedi, which hosts US nuclear warheads, on the occasion of the International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons.



International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons 2021
Today, Sunday, September 26, 2021, marks the United Nations International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons. The United Nations has been working toward achieving global nuclear disarmament since the organization’s inception; it was the subject of the General Assembly’s first resolution in 1946, with a mandate to make specific proposals for the elimination of atomic weapons and all other major weapons adaptable to mass destruction. The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons has been observed annually since 2014, serving as a tool to enhance public awareness and education about the threat posed to humanity by nuclear weapons and the necessity for their total elimination. In 2013, the year the International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons was introduced, the President of the General Assembly noted that a “renewed international focus on the catastrophic consequences of nuclear weapons has led to a reinvigoration of international nuclear disarmament efforts.”
ILHAN OMAR SIGNS ICAN PLEDGE

April 30, 2021: Representative Ilhan Omar today submitted her signed ICAN Pledge to ICAN, becoming the eleventh member of the US Congress to sign the Pledge. Rep. Omar represents Minnesota’s 5th Congressional District in the US House of Representatives. Rep Omar also co-sponsor the H.R.2850 Nuclear Abolition and Economic Conversion Act of 2021 that Representative Eleanor Holmes Norton reintroduced on April 26, 2021.
Nuclear Weapons — They’re Illegal
“Remember that when your congressional members pitch expanding nuclear weapons production as jobs programs; you can respond that they are illegal. Tell them they should show visionary leadership and moral courage by helping to create cleanup and green energy jobs instead.”
By: Jay Coghlan / Santa Fe New Mexican

Jan. 22 will go down in history as the day when the tide turned against nuclear weapons. That was the day when the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons went into effect, signed by 122 countries.
It specifically prohibits nations from developing, testing, using or threatening to use nuclear weapons and assisting others in doing so. It reinforces existing international law obligating all states not to test, use or threaten to use nuclear weapons.
What immediate impact will it have here, given that the Los Alamos National Laboratory is the birthplace of nuclear weapons and now sole producer of plutonium pit triggers for the expanding U.S. stockpile? The brutally honest answer is no impact, not immediately.
But think about it. Nuclear weapons are now internationally illegal, just as horrendous chemical and biological weapons of mass destruction have long been. But nuclear weapons are the worst WMDs, potentially killing millions more while causing radioactive fallout and famine-inducing nuclear winter. Ask your New Mexican congressional members to explain why nuclear weapons shouldn’t be internationally banned just like chemical and biological WMDs, all of which cause agonizing, indiscriminate suffering and death.
How I Came to Support the Treaty Prohibiting Nuclear Weapons
“During my time serving in the Reagan administration, I came to realize that the only nuclear strategy we had was massive retaliation, which would have made the attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki seem almost trivial.”
BY: Lawrence Korb | justsecurity.org

About three years ago, in November 2017, I was honored to be one of about a 100 people invited by the Vatican to an international symposium, “Prospects for a World Free of Nuclear Weapons and for Integral Disarmament.” It was the first global gathering conducted after 120 nations at the United Nations approved the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW).
This treaty, which is the first legally binding international agreement to comprehensively prohibit nuclear weapons, was adopted by the U.N. on July 7, 2017, and needed 50 countries to ratify it in order for it to come into force. The purpose for the treaty was to get world leaders and citizens to consider nuclear weapons as immoral and illegal as chemical and biological weapons, whose use the U.N had previously prohibited.
Pope Francis himself was very invested in the issue. He gave the keynote address in which he condemned not only the threat of their use, but also the possession of nuclear weapons and warned that nuclear deterrence policies offered a false sense of security. He also personally thanked each of the attendees individually.
The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons: A brief explanation by Rick Wayman
Nuclear Weapons Have Always Been Immoral. Now They’re Illegal.
On 7 July 2017, the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) was adopted by the UN General Assembly. Just over three years later, the TPNW reached the 50 national ratifications needed to become international law. The treaty will enter into force on January 22, 2012, and nuclear weapons will become officially illegal under international law. This day will represent a culmination of years of campaigning for nuclear weapons to be reframed as a collective humanitarian problem, one which requires prohibition and elimination, rather than a national military defense asset that needs to be managed and even upgraded.
ICAN IGTV
The international campaign to abolish nuclear weapons on instagram (@nuclearban) tackling some of the more technical legal questions of the treaty: what does entry into force mean, what happens now? Joined with experts, they dive into international law and the TPNW (without getting too technical!) through instagram chats to help break it all down.
View this post on InstagramTim Wright in conversation with Associate Professor Treasa Dunworth of the University of Auckland
A post shared by ICAN (@nuclearban) on
View this post on InstagramA post shared by ICAN (@nuclearban) on
View this post on InstagramA post shared by ICAN (@nuclearban) on
Resources
Final Negotiations Begin on Nuclear Weapons Ban Treaty
Draft Nuclear Weapons Ban Treaty View/download PDF
An Open Letter from Scientists in Support of the UN Nuclear Weapons Negotiations
Selected Elements of a Treaty Prohibiting Nuclear Weapons
Statements and working papers to the conference
The International Association Of Lawyers Against Nuclear Arms is calling for a a prohibition on “threat of use”. (ref)
Unfold Zero, the World Future Council, Parliamentarians for Nuclear Non-Proliferation and Disarmament and the Basel Peace Office are calling for a prohibition on the financing of nuclear weapons production. (ref)
We have a dossier on the background and trajectory of this initiative, and we’ll keep it up to date with news and developments: Ban Treaty dossier.
For further in-depth coverage of these negotiations, see the Reaching Critical Will and ICANwebsites. Also note the ban treaty blog at ICAN for daily news and developments.
Draft Nuclear Weapons Ban Treaty Released Today
(l.) Conference President Elayne Whyte of Costa Rica, and (r.) Tim Wright of ICAN
Pope Francis Calls for the Complete Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
“There is urgent need to work for a world free of nuclear weapons, in full application of the Non-Proliferation Treaty, in letter and spirit, with the goal of a complete prohibition of these weapons.”
– Pope Francis at the UN Sept 25, 2015.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Quotes
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.