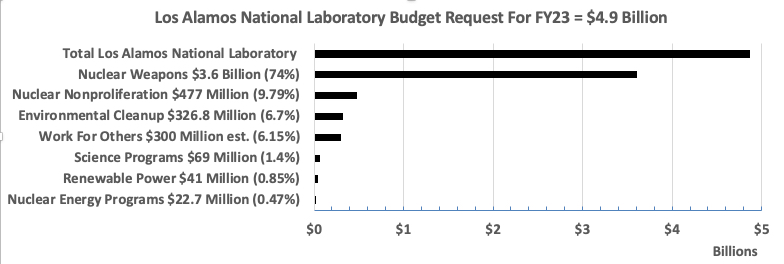
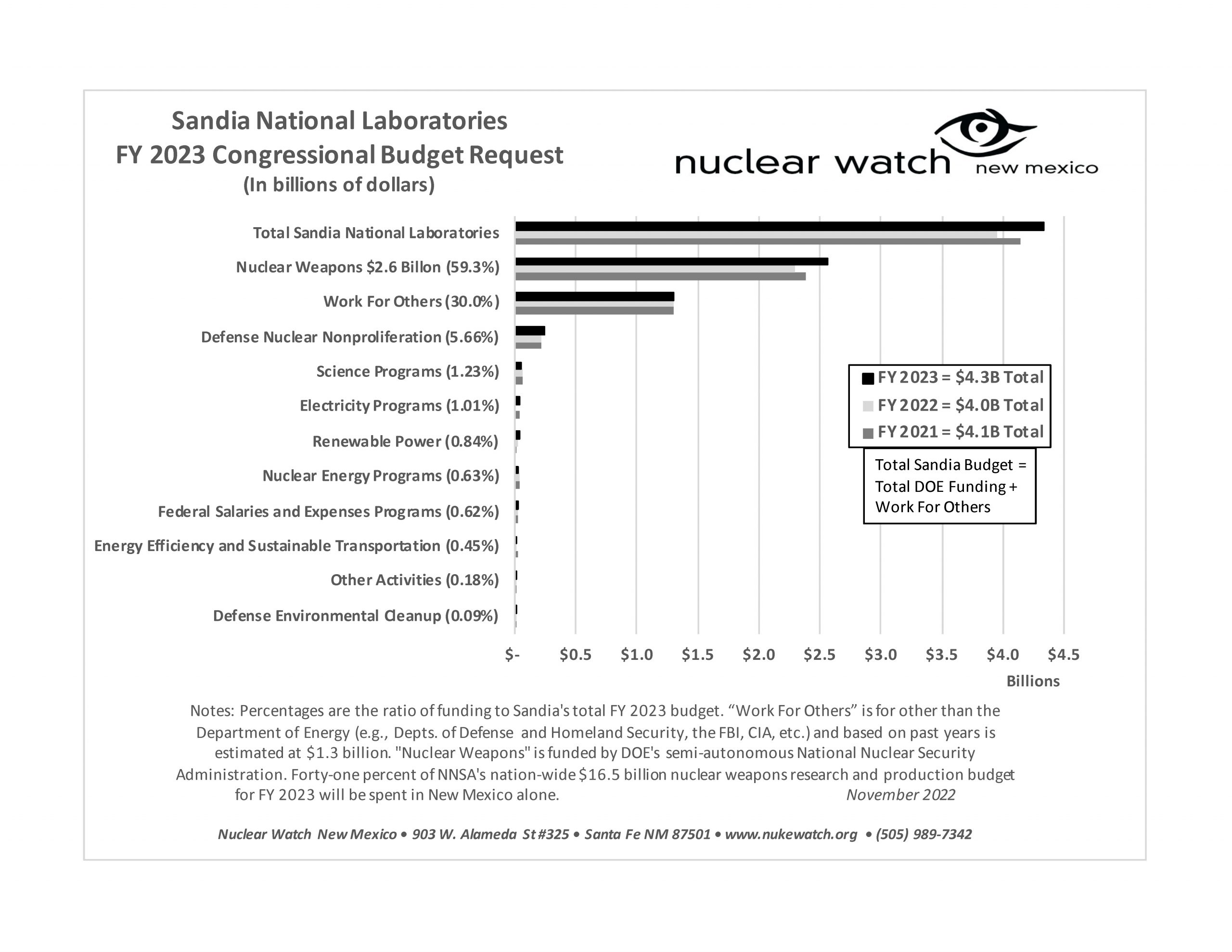
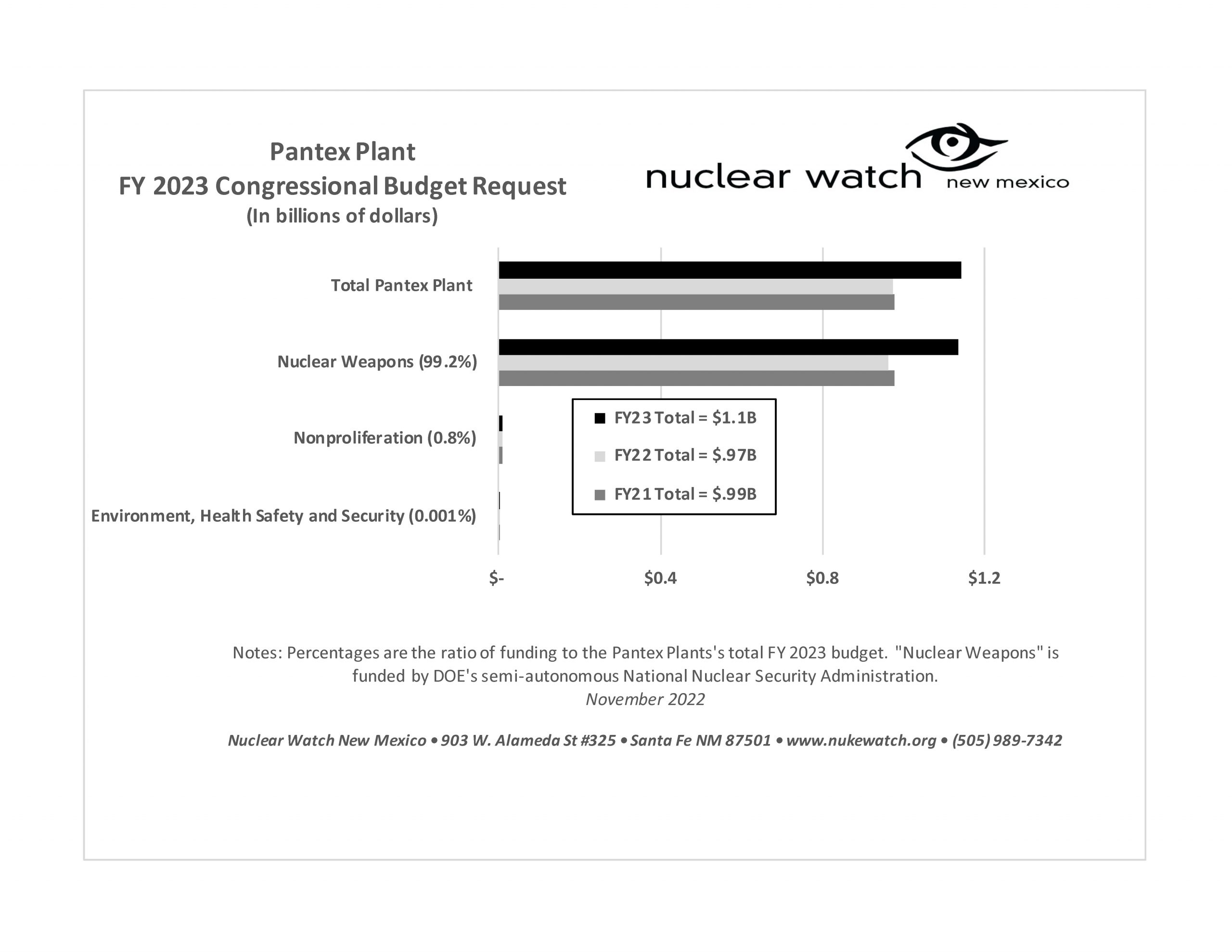
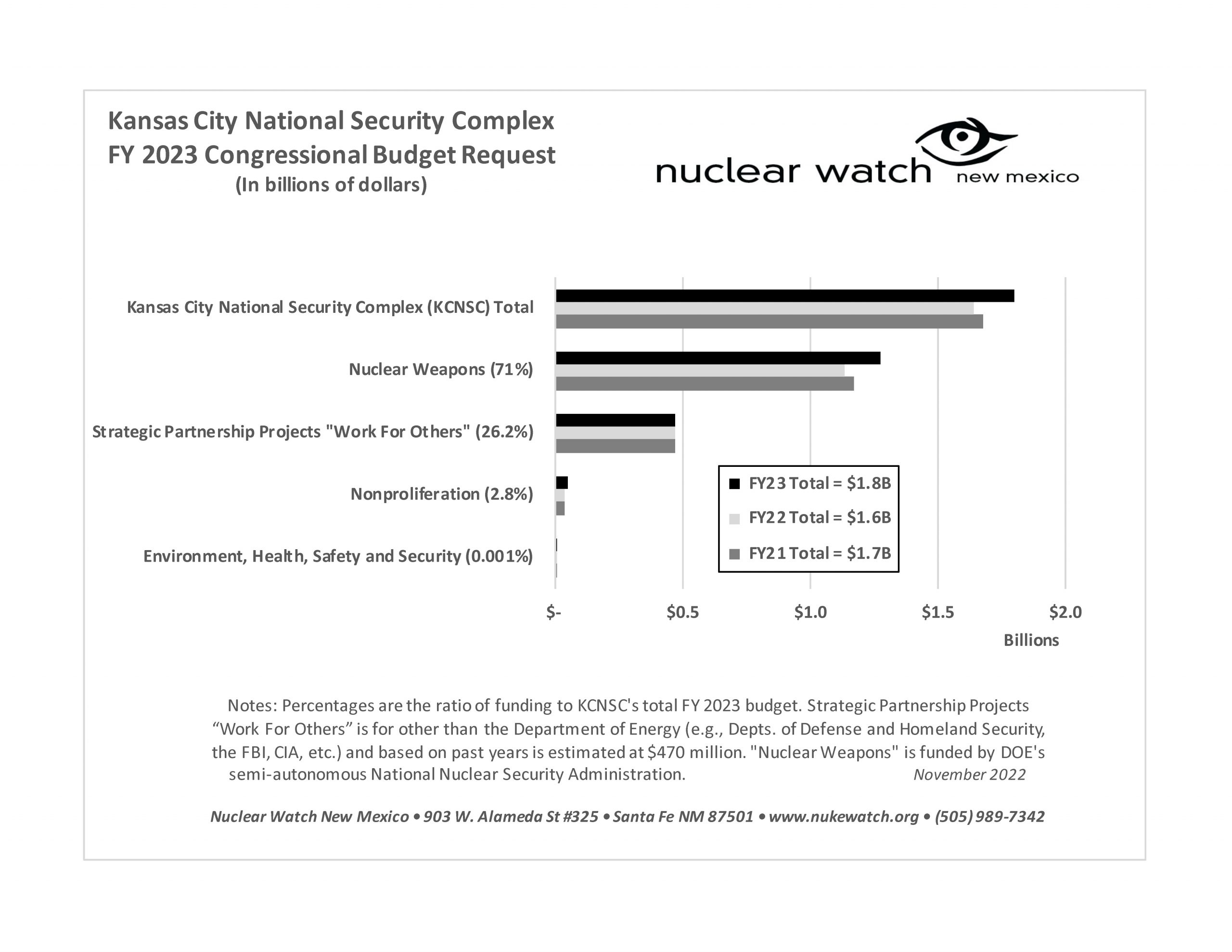
QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
Nuclear Watch Interactive Map – U.S. Nuclear Weapons Complex
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
2022 BLOG POSTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New & Updated
ANA Press Release
Alliance for Nuclear Accountability
immediate release: Tuesday, November 27, 2018
Watchdog groups call for Congress to protect nuclear weapons communities—stop DOE limitations on Safety Board
Watchdog groups from across the country are insisting the Department of Energy withdraw DOE Order 140.1, a controversial order that would compromise safety at dozens of facilities in the US nuclear weapons complex, and are asking key Congressional committees to annul the revised order and preserve the critically important prerogatives of the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB).
 DOE MUST RESTORE DEFENSE NUCLEAR FACILITIES SAFETY BOARD ACCESS TO INFORMATION, NUCLEAR SECURITY FACILITIES, AND PERSONNEL
DOE MUST RESTORE DEFENSE NUCLEAR FACILITIES SAFETY BOARD ACCESS TO INFORMATION, NUCLEAR SECURITY FACILITIES, AND PERSONNEL
What’s HappenedOn May 14, 2018, the Department of Energy (DOE) Deputy Secretary approved DOE Order 140.1 Interface with the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board, which limits release of information, limits the DNFSB’s access to nuclear security sites, and personnel. The impacts are already being felt by Congress, the Board, DOE contractors and workers, and in communities located near some of the most dangerous nuclear facilities across the nation. |
ANA’s MessageThe Alliance for Nuclear Accountability has reviewed DOE Order 140.1 and believes it imposes a level of constraint on DNFSB that jeopardizes the important mission of the Safety Board. In fact, it may well violate the legislation that established the Board. ANA groups and the public at major DOE sites have come to rely on the Safety Board’s expertise to identify and hold accountable the DOE and National Nuclear Security Administration for worker and public safety related issues. |
ANA Letter to Congress
November 27, 2018
RE: DOE Order 140.1 should be annulled by Congress
Dear House/Senate Armed Services Committee Members:
We are writing to ask that you annul the May 2018 DOE Order 140.1, Interface with the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board and reinstate the previous DOE Order 140.1.
The Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (“DNFSB” or “Safety Board”) was established by Congress in September 1988 (Public Law 100-456) in response to growing concerns about health and safety protection that the Department of Energy (“DOE”) was providing the public and workers at defense nuclear facilities. In so doing, Congress sought to provide the general public with an independent source of critical oversight to add assurance that DOE’s defense nuclear facilities are safely designed, constructed, operated, and decommissioned. Over the past 30 years, the Safety Board’s authority and funding has been supported by Congress on a bi-partisan basis.
NNSA Plans to Replace the W78 Warhead

NUCLEAR WEAPONS:
NNSA Has Taken Steps to Prepare to Restart a Program to Replace the W78 Warhead Capability
GAO-19-84: Published: Nov 30, 2018. Publicly Released: Nov 30, 2018.
The National Nuclear Security Administration is preparing to restart a program to replace the W78 nuclear warhead, which is used in Air Force intercontinental ballistic missiles. The goal is to produce the first W78 replacement warhead in fiscal year 2030. Pending further study, this replacement warhead may also be used in Navy submarine launched ballistic missiles.
Please Help Support NukeWatch
![]()
Dear Friends of Nuclear Watch New Mexico:
The Los Alamos and Sandia Labs are the tip of the spear for a one-trillion dollar “modernization” program that will completely rebuild every type of warhead in the nuclear stockpile while giving them new military capabilities. This so-called modernization program will also rebuild the production side of the Department of Energy’s nuclear weapons complex, including the proposal to quadruple production of plutonium pit bomb cores at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). This so-called modernization will be at enormous cost to the taxpayer and our disappearing middle class, robbing citizens of better schools, highways, hospitals, etc.
Join In Giving Tuesday
 Join In Giving Tuesday
Join In Giving Tuesday
We have two days for getting deals – Black Friday and Cyber Monday. On #GivingTuesday, we have a day for giving back. Together, people are creating a new ritual for our annual calendar. #GivingTuesday is the opening day of the giving season.
Founded by the team in the Belfer Center for Innovation & Social Impact at 92nd Street Y, #GivingTuesday is a global giving movement that has been built by individuals, families, organizations, businesses and communities in all 50 states and in countries around the world. This year, #GivingTuesday falls on November 27. #GivingTuesday harnesses the collective power of a unique blend of partners to transform how people think about, talk about, and participate in the giving season. It can inspire people to take collective action to improve their communities, give back in better, smarter ways to the charities and causes they believe in, and help create a better world. #GivingTuesday demonstrates how every act of generosity counts, and that they mean even more when we give together.
Belen passes resolution opposing nuclear waste transportation

Belen passes resolution opposing nuclear waste transportation
NISG (Nuclear Issues Study Group) worked to get a resolution opposing the transportation of High Level Radioactive Waste in front of the City of Belen. The Belen City Council passed the resolution on Nov. 19th! It was 3 votes yes and 1 abstention. Belen is the 18th City or county or chapter house to pass it in New Mexico and Texas.
Read more about it here
Santa Fe County passed a similar resolution – A Resolution in the Interest of Protecting Our Lives, Land and Water From Radioactive Waste Risks.
Read more about it here
European diplomats mount last-ditch effort to stop US scrapping INF treaty
BY JULIAN BORGER in Washington |
theguardian.com
Sun 18 Nov 2018 03.00 EST Last modified on Sun 18 Nov 2018 10.52 EST
– 1987 treaty has kept nuclear weapons out of Europe
– Trump announced withdrawal from deal with Russia in October
European officials are seeking to act as intermediaries between Russia and the US in the hope of salvaging a cold war-era arms control treaty that Donald Trump has threatened to scrap.
However, the diplomats involved are not confident of success in the effort to save the 1987 Intermediate-range Nuclear Forces (INF) treaty. Although they have the support of senior officials in the US defence and state departments, they face opposition from the White House, particularly from the national security adviser, John Bolton.
Incoming HASC Chair: Scale Back Plans for New Nukes
BY MARCUS WEISGERBER defenseone.com
NOVEMBER 14, 2018
Rep. Adam Smith laid out new terms for a debate over the Pentagon’s plans to expand the military’s nuclear arsenal.
The incoming chairman of the House Armed Services Committee is taking aim at the Trump administration’s plans to expand America’s nuclear arsenal.
While Democrats will only control one chamber of Congress for the next two years, Rep. Adam Smith, D-Wash., called for lawmakers to “totally redo the Nuclear Posture Review,” the administration’s blueprint for replacing Cold War-era nuclear weapons with newer ones envisioned to be aroundContinue reading
Trump’s Defense Spending Is Out of Control, and Poised to Get Worse
BY MATT TAIBBI rollingstone.com
Using a time-honored trick, a bipartisan congressional panel argues we should boost the president’s record defense bill even more
A bipartisan commission has determined that President Trump’s recent record defense bill is insufficiently massive to keep America safe, and we should spend more, while cutting “entitlements.”
The National Defense Strategy Commission concluded the Department of Defense was too focused on “efficiency” and needed to accept “greater cost and risk” to search for “leap-ahead technologies” to help the U.S. maintain superiority.
Expanded Plutonium Pit Production for U.S. Nuclear Weapons
Plutonium pits are the radioactive cores or “triggers” of nuclear weapons. Their production has always been a chokepoint of resumed industrial-scale U.S. nuclear weapons production ever since a 1989 FBI raid investigating environmental crimes shut down the Rocky Flats Plant near Denver.Continue reading
LANL Ships Waste Offsite Illegally, Again and Again
LANL Ships Waste Offsite Illegally, Again and Again
Posted by Scott Kovac Nov 14, 2018
New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) issued a Notice of Violation (NOV) to LANL for several problems. The first problem was that the Lab sent a drum to a disposal company offsite that was improperly labeled. It should have been labeled “flammable liquid, corrosive.” The Lab also mislabeled two containers by failing to note that they had lead inside. LANL also sent a container with flammable and toxic liquids with the incorrect container number and label on it. These violations occurred in 2015. The NOV reports several other shipping manifest discrepancies in 2016 and 2017. NMED is happy with the Lab just correcting the manifests. These were mistakes by the old contractor, Los Alamos National Security (LANS).
Possibly more serious violations occurred under DOE’s watch in 2017 and 2018 when LANS failed to characterize waste before shipping it to local landfills, including the Santa Fe landfill.
Nuclear fallout: $15.5 billion in compensation and counting
BY JAMIE GREY & LEE ZURIK mysuncoast.com
November 12, 2018 at 1:00 PM EST – Updated November 12 at 10:54 AM
LOS ALAMOS, NEW MEXICO (InvestigateTV) – Clear, plastic water bottles, with the caps all slightly twisted open, fill a small refrigerator under Gilbert Mondragon’s kitchen counter. The lids all loosened by his 4- and 6-year old daughters because, at just 38, Mondragon suffers from limited mobility and strength. He blames his conditions on years of exposure to chemicals and radiation at the facility that produced the world’s first atomic bomb: Los Alamos National Laboratory. Mondragon is hardly alone in his thinking…
Continue reading
LANL Groundwater Discharge Permit Hearing Underway
BY TRIS DEROMA – lamonitor.com |
In opening testimony at a groundwater discharge permit hearing Wednesday, attorneys for a Los Alamos National Laboratory contractor said spraying the ground with water with remediated levels of chromium and RDX is environmentally safe. Chromium and RDX are known carcinogens. The chemicals are from contamination plumes found on the grounds of the laboratory in the 2000s.
Continue reading
ACTION ALERTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Interfaith Panel Discussion on Nuclear Disarmament - August 9
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
New Nuclear Media
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.