Atomic Histories & Nuclear Testing
NukeWatch Compilation of the DOE/NNSA FY 2020 Budget Request – VIEW
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
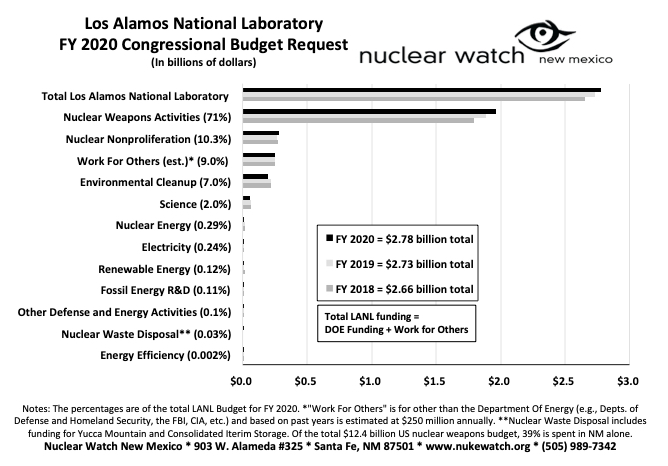
LANL FY 2020 Budget Request – VIEW
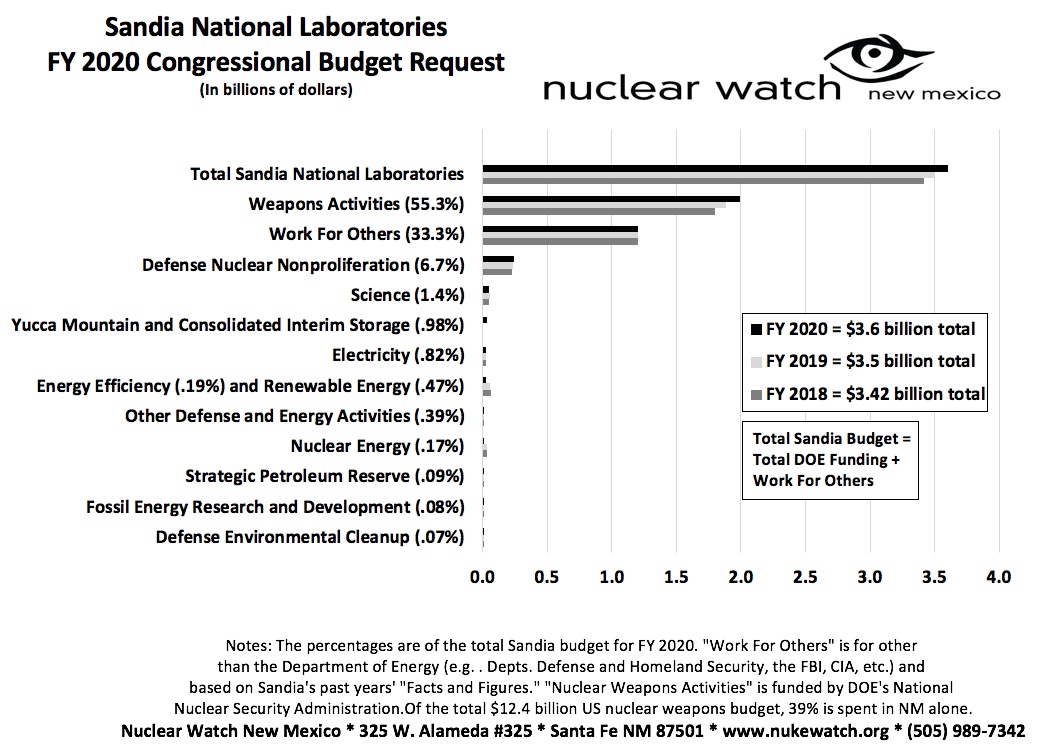
Sandia FY 2020 Budget Request – VIEW
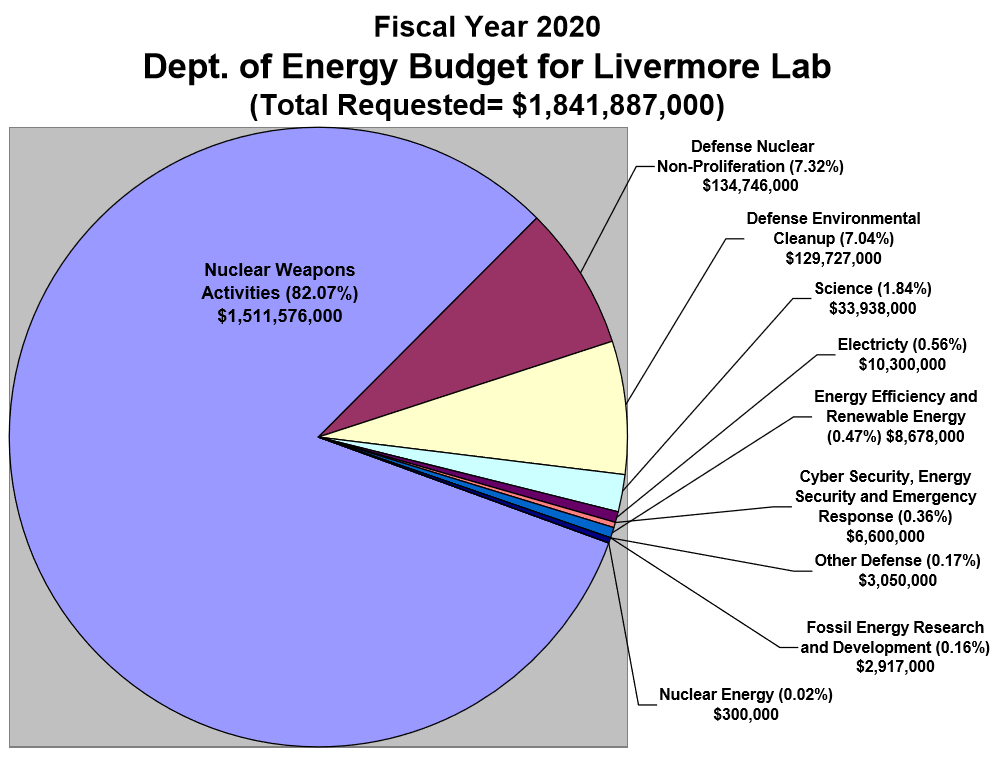
Livermore Lab FY 2020 Budget Chart – Courtesy TriValley CAREs – VIEW
Important Documents & Articles Related to Nuclear Energy Production
Most Recent
The Bomb and Us: Why Gen Z Should Care About Nuclear Disarmament
“Some scholars, including Kenneth Waltz, have gone so far as arguing that we should allow nuclear weapons proliferation as a method of promoting peace. However, this deterrence-based approach does not take into account the possibility of accidental and unauthorized nuclear explosions, or of nuclear terrorism, two very real menaces.”
Anna Bartoux February 10, 2022 cpreview.com

You cannot go around saying to people that there is a 100% chance that they’re gonna die. You know? It’s just nuts. —President Orlean, “Don’t Look Up,” 20:40
This line is from the new Netflix sensation, “Don’t Look Up,” a movie starring Leonardo Dicaprio and Jennifer Lawrence in the role of two astronomers trying to raise awareness about a comet on a collision course with Earth. “Don’t Look Up” has prompted the interest of many because of its not-so-hidden political commentary on the apathy surrounding climate change, however, few seem to realize the relevance of the movie’s message for another, even less recognized issue: nuclear disarmament.
Indeed, the extent to which nuclear weapons still threaten our lives today is little understood. Despite being one of the most socially engaged and politically minded generations across a range of topics, few Gen Zers really consider the nuclear issue with the urgency it demands.
Protesters Denounce French Push to Label Nuclear as Sustainable Energy
“By taking the lead of the toxic alliance between fossil gas and nuclear (energy) at a European level, Emmanuel Macron clearly sides with the polluters’ camp. Nuclear is not a green energy: it produces radioactive waste that piles up across the country”
By Reuters | December 14, 2021
PARIS (Reuters) – Demonstrators unfurled a banner declaring “Gas & nuclear are not green” outside France’s foreign ministry on Tuesday in protest at a government drive to label nuclear energy and fossil gas as sectors for climate-friendly investment.
One of the about 20 protesters, wearing a mask of President Emmanuel Macron, chained himself to a gas bottle and a nuclear barrel outside the ministry’s headquarters in Paris. Another held a banner that read “Macron shame on you.”
The European Union is preparing a rulebook on climate friendly investments, which from next year will define which activities can be labelled as green in sectors including transport and buildings.
The EU’s aim is to restrict the green investment label to climate-friendly activities, steer cash into low-carbon projects and stop companies or investors making unsubstantiated environmental claims.
Pilgrim Nuclear Plant Will Not Release Contaminated Water In 2022
By CBSBoston.com Staff December 7, 2021
PLYMOUTH (CBS) – The company managing the shutdown of the Pilgrim Nuclear Plant now says it will not release contaminated water into Cape Cod Bay in 2022 as planned.
Holtec International planned to discharge the water sometime early next year.
But in a statement on Monday, they promised to store the water on site through 2022 and search for other options to get rid of it.
“We appreciate and understand the public’s questions and concerns and remain committed to an open, transparent process on the decommissioning of Pilgrim Station focused on the health and safety of the public, the environment, and on-site personnel,” Holtec said in a statement.
Pilgrim went offline in 2019.
Nuclear power is never safe or economical
“I hope Sen. Durbin changes his mind about promoting nuclear energy. The real carbon-free sources of electricity are wind and solar.”
Letters to the Editor Chicago Sun Times

I cannot disagree more with the assertion by Sen. Dick Durbin in a recent Sun-Times op-ed that nuclear power is a necessary and viable way to combat climate change.
Electricity production by nuclear power is not, and can never be made, safe and economical.
When nuclear power plants were first touted in the 1950s as a new and safe method for producing electricity, it was said the electricity would be “too cheap to meter.” This is pure nonsense! If it was so safe, why weren’t any power plants built and put on line until passage of the Price-Anderson Act? The law has been amended a number of times and greatly limits the liability of operators of nuclear power plants.
Anything paid out beyond the limits set in Price-Anderson would take years of lawsuits.
Sen. Durbin wrote “It is past time for Congress to step up and develop a comprehensive, consent-based plan to store nuclear waste.” That’s an understatement. Nuclear waste is stored within a half-mile of Lake Michigan at the now-closed Zion nuclear power plant. Why is it close to the source of our drinking water? Because there is nowhere to ship it! Plans to ship such waste to a depository in Yucca Mountain in the southwest fell through when some improperly stored barrels burst into flames, releasing large amounts of high-level radioactive material.
Who does the senator think will agree to a “consent-based plan” when there is no known method of safely storing these dangerous materials for thousands of years, the time it takes for radioactive decay to make it safe for the environment?
Sen. Durbin argued that “we must ensure the nuclear fleet remains safe and economical,” but nuclear power has never been economical. As far as I know, the last time a permit was approved for a new nuclear plant was during the Obama administration. That plant in Georgia is only about half complete, although it was to be finished by now and the cost is already double the initial estimate.
The current “fleet,” as Sen. Durbin called them, of nuclear power plants were designed and engineered to last about 30 to 40 years. Most of our country’s plants are near that age. Their internal systems are constantly bombarded by radioactive particles, making the metal in the systems more brittle and prone to failure every year. Subsidizing them is a waste of taxpayer money and a dangerous gamble with our lives.
I hope Sen. Durbin changes his mind. The real carbon-free sources of electricity are renewables: wind and solar.
George Milkowski, West Ridge
Pilgrim nuclear plant may release 1M gallons of radioactive water into bay. What we know
“Diane Turco, of Harwich, the director of Cape Downwinders, a citizen group that was at the forefront of the effort to close Pilgrim, called any option that included sending radioactive water into the bay “outrageous” and “criminal.” Turco said she has no confidence in the decommissioning process.
“The process has been to allow radioactivity into the environment,” she said. “The answer should be no you can’t do that.””
PLYMOUTH — One of the options being considered by the company that is decommissioning the closed Pilgrim Nuclear Power Station is to release around one million gallons of potentially radioactive water into Cape Cod Bay.
The option had been discussed briefly with state regulatory officials as one possible way to get rid of water from the spent fuel pool, the reactor vessel and other components of the facility, Holtec International spokesman Patrick O’Brien said in an interview Wednesday. It was highlighted in a report by state Department of Environmental Protection Deputy Regional Director Seth Pickering at Monday’s meeting of the Nuclear Decommissioning Citizens Advisory Panel in Plymouth.
“We had broached that with the state, but we’ve made no decision on that,” O’Brien said.
As of mid-December, Holtec will complete the process of moving all the spent fuel rods into casks that are being stored on a concrete pad on the Pilgrim plant site in Plymouth. After that, O’Brien told the panel, the removal and disposal of other components in those areas of the facility will take place and be completed sometime in February.
U.S. ‘very bullish’ on new nuclear technology, Granholm says
“These advanced nuclear reactors, and the existing fleet, are safe,” Granholm says. “We have the gold standard of regulation in the United States.”
Actually…According to a UCS report, if federal regulators require the necessary safety demonstrations, it could take at least 20 years—and billions of dollars in additional costs—to commercialize such reactors, their associated fuel-cycle facilities, and other related infrastructure.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) may have to adapt some regulations when licensing reactor technologies that differ significantly in design from the current fleet. Lyman says that should not mean weakening public health and safety standards, finding no justification for the claim that “advanced” reactors will be so much safer and more secure that the NRC can exempt them from fundamental safeguards. On the contrary, because there are so many open questions about these reactors, he says they may need to meet even more stringent requirements.
By Ben Adler • Yahoo News news.yahoo.com
GLASGOW, Scotland — In an interview at the U.N. Climate Change Conference, Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm told Yahoo News on Friday that the Biden administration is “very bullish” on building new nuclear reactors in the United States.
“We are very bullish on these advanced nuclear reactors,” she said. “We have, in fact, invested a lot of money in the research and development of those. We are very supportive of that.”
Nuclear energy is controversial among environmental activists and experts because while it does not create the greenhouse gas emissions that cause climate change, it has the potential to trigger dangerous nuclear meltdowns and creates radioactive nuclear waste [not a small issue].
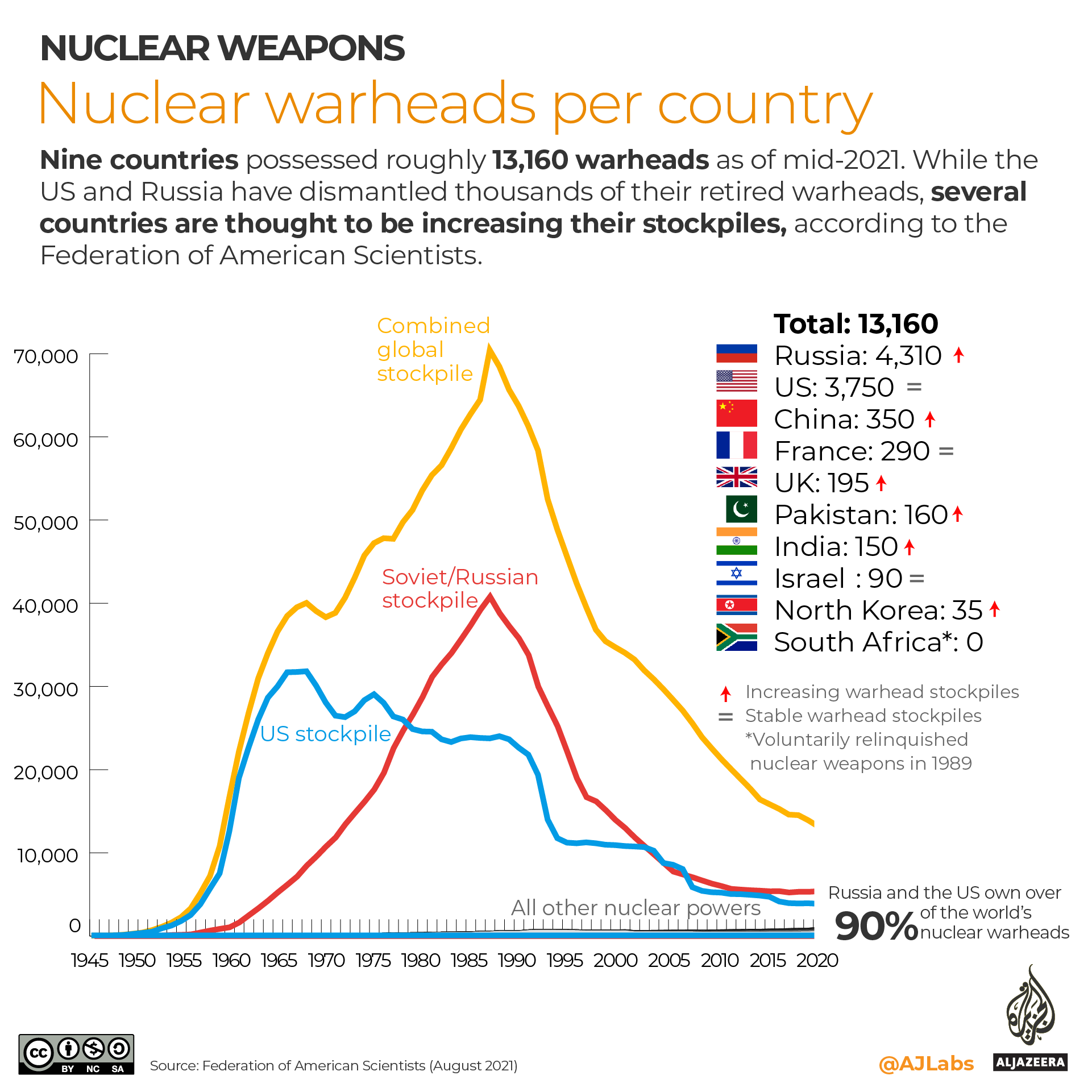
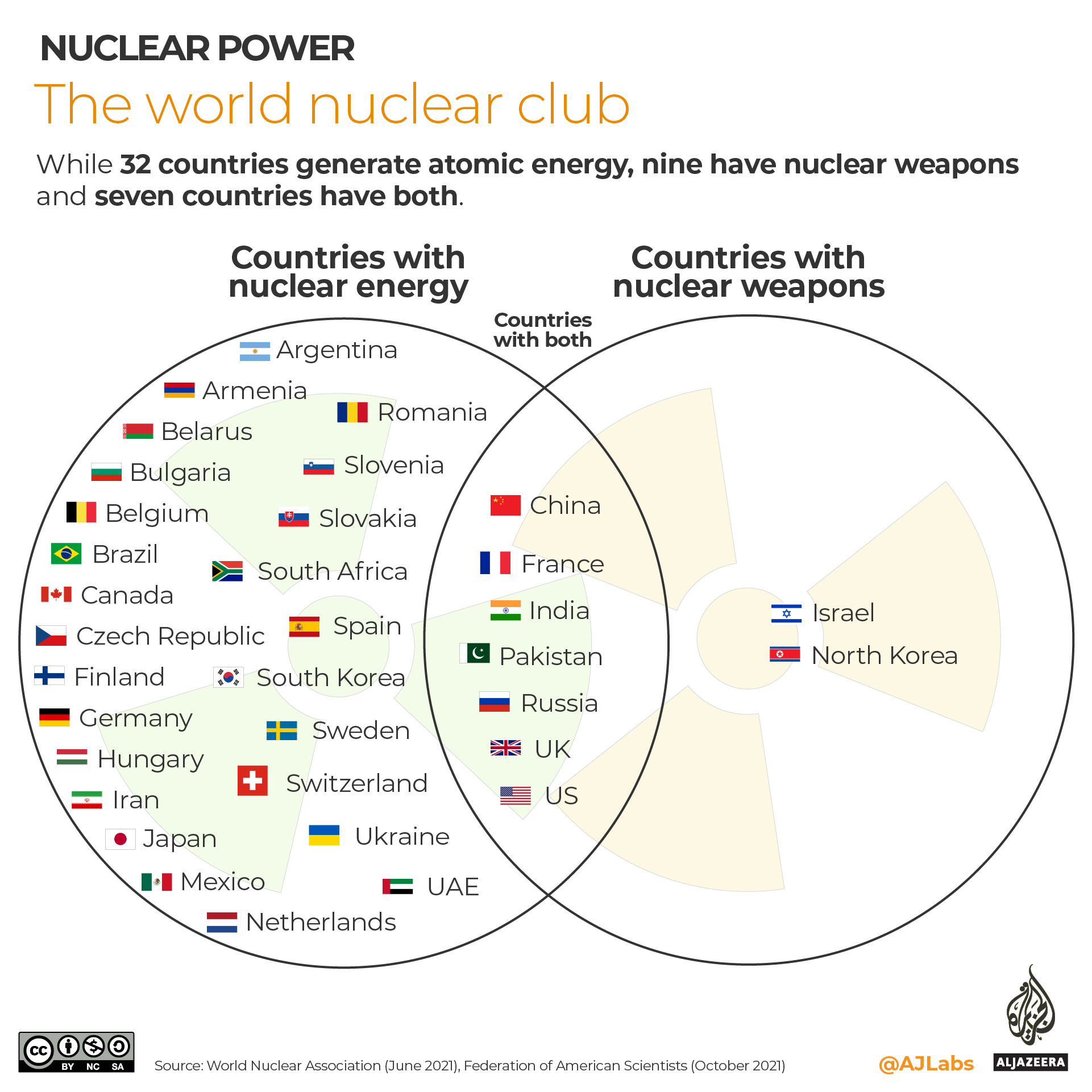
Al Jazeera Infographic: The World Nuclear Club
While 32 countries generate atomic energy, nine have nuclear weapons and seven countries have both.
By Mohammed Haddad and Hanna Duggal Al Jazeera aljazeera.com
Nuclear warheads per country
Nine countries possessed roughly 13,150 warheads as of August 2021, according to the Federation of American Scientists. More than 90 percent are owned by Russia and the US.
At the peak in 1986, the two rivals had nearly 65,000 nuclear warheads between them, making the nuclear arms race one of the most threatening events of the Cold War. While Russia and the US have dismantled thousands of warheads, several countries are thought to be increasing their stockpiles, most notably China.
According to the Pentagon’s 2021 annual report (pdf), China’s nuclear warhead stockpile is expected to more than triple and reach at least 1,000 by 2030.
The only country to voluntarily relinquish nuclear weapons is South Africa. In 1989, the government halted its nuclear weapons programme and in 1990 began dismantling its six nuclear weapons. Two years later, South Africa joined the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) as a non-nuclear country.
With the 26th UN Climate Change Conference over, nations are making plans to move to green energy in a bid to tackle global warming.
But nuclear energy is a particular sticking point. While it is the largest source of low-carbon electricity in OECD countries, some nations have spoken out against the categorisation of nuclear energy as climate-friendly.
Across the globe, 34 countries harness the power of splitting atoms for generating electricity or for nuclear weapons. (Al Jazeera)
Global nuclear energy
Nuclear energy provides roughly 10 percent of the world’s electricity. Of the 32 countries with nuclear power reactors, more than half (18) are in Europe. France has the world’s highest proportion of its electricity – at 71 percent – coming from atomic power.
Up until 2011, Japan was generating some 30 percent of its electricity from nuclear reactors; however, following the Fukushima disaster, all nuclear power plants were suspended for safety inspections. As of 2020, just 5 percent of Japan’s electricity came from nuclear power, according to the World Nuclear Association.
Nuclear power constitutes some 20 percent of the United States’ electricity. About 60 percent of the country’s energy comes from fossil fuels, including coal, natural gas and petroleum, with the remaining 20 percent coming from renewable sources – wind, hydro and solar.
Nuclear Power Is COP26’s Quiet Controversy
“We have to get everything done in the next 25 years…The idea that you’re going to scale up a technology you don’t even have yet, and it’s going to be commercially viable [in that time], just seems to me like la la land.” — Tom Burke, co-founder of climate think tank E3G.
BY ALEJANDRO DE LA GARZA time.com

In the midst of the COP26 climate talks yesterday, U.S. and Romanian officials stepped aside for a session in the conference’s Blue Zone, establishing an agreement for U.S. company NuScale to build a new kind of modular nuclear power plant in the southeastern European country. The company’s plants—designed to be quickly scaled up or down based on need—are intended to be quicker and cheaper to build than the traditional kind, with some considering them to be a promising alternative for countries seeking to wean themselves off fossil fuels.
NuScale CEO John Hopkins sees the agreement as part of a broader recognition that nuclear power has a big role to play as the world decarbonizes. “I’ve seen a significant shift here,” Hopkins said, speaking to TIME from Glasgow yesterday. “It used to be the only thing really discussed was renewables, but I think people are starting to be a little more pragmatic and understand that nuclear needs to be in the mix.”
But others at COP26 aren’t convinced that NuScale’s small reactors can help avoid climate catastrophe. Some point to the fact that NuScale has yet to build a single commercial plant as evidence that the company is already too late to the party.
Jellyfish Keep Attacking Nuclear Power Plants
Jellyfish are continuing to clog the cooling pipes of nuclear power plants around the world.
By Gabriel Geiger • vice.com
Jellyfish are continuing to clog the cooling intake pipes of a nuclear power plant in Scotland, which has previously prompted a temporary shutdowns of the plant.
The Torness nuclear power plant has reported concerns regarding jellyfish as far back as 2011, when it was forced to shut down for nearly a week—at an estimated cost of $1.5 million a day—because of the free-swimming marine animals.
In a short comment to Motherboard, EDF energy, which runs the Torness plant, said that “jellyfish blooms are an occasional issue for our power stations,” but also said that media reports claiming the plant had recently been taken offline because of jellyfish are “inaccurate.” “[There were] no emergency procedures this or last week related to jellyfish or otherwise,” a spokesperson said.
Like many other seaside power plants, the Torness plant uses seawater to prevent overheating. While there are measures in place to prevent aquatic life from entering the intake pipes, according to the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, they are no match for the sheer number of jellyfish that come during so-called “jellyfish blooms.”
HIDDEN AGENDA: The unspoken argument for more nuclear power
Nuclear power is so slow and expensive that it doesn’t even matter whether or not it is ‘low-carbon’ (let alone ‘zero-carbon’). As the scientist, Amory Lovins, says, “Being carbon-free does not establish climate-effectiveness.” If an energy source is too slow and too costly, it will “reduce and retard achievable climate protection,” no matter how ‘low-carbon’ it is.
By Linda Pentz Gunter beyondnuclearinternational.org
 So here we are again at another COP (Conference of the Parties). Well, some of us are in Glasgow, Scotland at the COP itself, and some of us, this writer included, are sitting at a distance, trying to feel hopeful.
So here we are again at another COP (Conference of the Parties). Well, some of us are in Glasgow, Scotland at the COP itself, and some of us, this writer included, are sitting at a distance, trying to feel hopeful.
But this is COP 26. That means there have already been 25 tries at dealing with the once impending and now upon us climate crisis. Twenty five rounds of “blah, blah, blah” as youth climate activist, Greta Thunberg, so aptly put it.
So if some of us do not feel the blush of optimism on our cheeks, we can be forgiven. I mean, even the Queen of England has had enough of the all-talk-and-no-action of our world leaders, who have been, by and large, thoroughly useless. Even, this time, absent. Some of them have been worse than that.
Not doing anything radical on climate at this stage is fundamentally a crime against humanity. And everything else living on Earth. It should be grounds for an appearance at the International Criminal Court. In the dock.
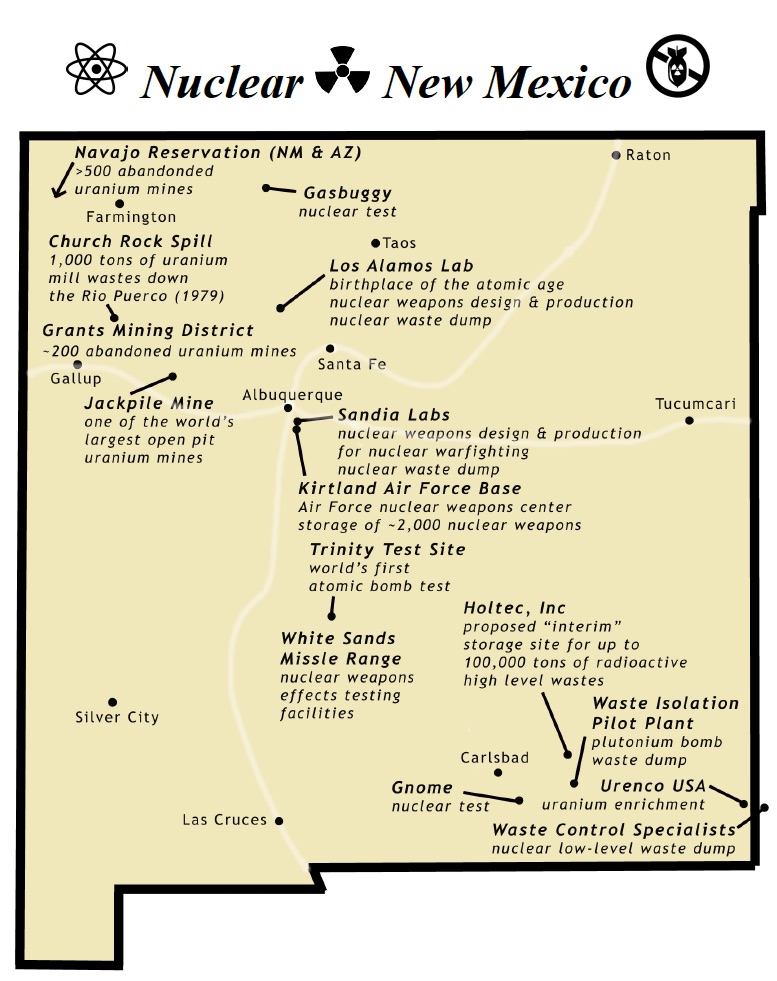
Nuclear Watch Interactive Map – U.S. Nuclear Weapons Complex
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
The Bomb and Us: Why Gen Z Should Care About Nuclear Disarmament
“Some scholars, including Kenneth Waltz, have gone so far as arguing that we should allow nuclear weapons proliferation as a method of promoting peace. However, this deterrence-based approach does not take into account the possibility of accidental and unauthorized nuclear explosions, or of nuclear terrorism, two very real menaces.”
Anna Bartoux February 10, 2022 cpreview.com

You cannot go around saying to people that there is a 100% chance that they’re gonna die. You know? It’s just nuts. —President Orlean, “Don’t Look Up,” 20:40
This line is from the new Netflix sensation, “Don’t Look Up,” a movie starring Leonardo Dicaprio and Jennifer Lawrence in the role of two astronomers trying to raise awareness about a comet on a collision course with Earth. “Don’t Look Up” has prompted the interest of many because of its not-so-hidden political commentary on the apathy surrounding climate change, however, few seem to realize the relevance of the movie’s message for another, even less recognized issue: nuclear disarmament.
Indeed, the extent to which nuclear weapons still threaten our lives today is little understood. Despite being one of the most socially engaged and politically minded generations across a range of topics, few Gen Zers really consider the nuclear issue with the urgency it demands.
Protesters Denounce French Push to Label Nuclear as Sustainable Energy
“By taking the lead of the toxic alliance between fossil gas and nuclear (energy) at a European level, Emmanuel Macron clearly sides with the polluters’ camp. Nuclear is not a green energy: it produces radioactive waste that piles up across the country”
By Reuters | December 14, 2021
PARIS (Reuters) – Demonstrators unfurled a banner declaring “Gas & nuclear are not green” outside France’s foreign ministry on Tuesday in protest at a government drive to label nuclear energy and fossil gas as sectors for climate-friendly investment.
One of the about 20 protesters, wearing a mask of President Emmanuel Macron, chained himself to a gas bottle and a nuclear barrel outside the ministry’s headquarters in Paris. Another held a banner that read “Macron shame on you.”
The European Union is preparing a rulebook on climate friendly investments, which from next year will define which activities can be labelled as green in sectors including transport and buildings.
The EU’s aim is to restrict the green investment label to climate-friendly activities, steer cash into low-carbon projects and stop companies or investors making unsubstantiated environmental claims.
Pilgrim Nuclear Plant Will Not Release Contaminated Water In 2022
By CBSBoston.com Staff December 7, 2021
PLYMOUTH (CBS) – The company managing the shutdown of the Pilgrim Nuclear Plant now says it will not release contaminated water into Cape Cod Bay in 2022 as planned.
Holtec International planned to discharge the water sometime early next year.
But in a statement on Monday, they promised to store the water on site through 2022 and search for other options to get rid of it.
“We appreciate and understand the public’s questions and concerns and remain committed to an open, transparent process on the decommissioning of Pilgrim Station focused on the health and safety of the public, the environment, and on-site personnel,” Holtec said in a statement.
Pilgrim went offline in 2019.
Nuclear power is never safe or economical
“I hope Sen. Durbin changes his mind about promoting nuclear energy. The real carbon-free sources of electricity are wind and solar.”
Letters to the Editor Chicago Sun Times

I cannot disagree more with the assertion by Sen. Dick Durbin in a recent Sun-Times op-ed that nuclear power is a necessary and viable way to combat climate change.
Electricity production by nuclear power is not, and can never be made, safe and economical.
When nuclear power plants were first touted in the 1950s as a new and safe method for producing electricity, it was said the electricity would be “too cheap to meter.” This is pure nonsense! If it was so safe, why weren’t any power plants built and put on line until passage of the Price-Anderson Act? The law has been amended a number of times and greatly limits the liability of operators of nuclear power plants.
Anything paid out beyond the limits set in Price-Anderson would take years of lawsuits.
Sen. Durbin wrote “It is past time for Congress to step up and develop a comprehensive, consent-based plan to store nuclear waste.” That’s an understatement. Nuclear waste is stored within a half-mile of Lake Michigan at the now-closed Zion nuclear power plant. Why is it close to the source of our drinking water? Because there is nowhere to ship it! Plans to ship such waste to a depository in Yucca Mountain in the southwest fell through when some improperly stored barrels burst into flames, releasing large amounts of high-level radioactive material.
Who does the senator think will agree to a “consent-based plan” when there is no known method of safely storing these dangerous materials for thousands of years, the time it takes for radioactive decay to make it safe for the environment?
Sen. Durbin argued that “we must ensure the nuclear fleet remains safe and economical,” but nuclear power has never been economical. As far as I know, the last time a permit was approved for a new nuclear plant was during the Obama administration. That plant in Georgia is only about half complete, although it was to be finished by now and the cost is already double the initial estimate.
The current “fleet,” as Sen. Durbin called them, of nuclear power plants were designed and engineered to last about 30 to 40 years. Most of our country’s plants are near that age. Their internal systems are constantly bombarded by radioactive particles, making the metal in the systems more brittle and prone to failure every year. Subsidizing them is a waste of taxpayer money and a dangerous gamble with our lives.
I hope Sen. Durbin changes his mind. The real carbon-free sources of electricity are renewables: wind and solar.
George Milkowski, West Ridge
Pilgrim nuclear plant may release 1M gallons of radioactive water into bay. What we know
“Diane Turco, of Harwich, the director of Cape Downwinders, a citizen group that was at the forefront of the effort to close Pilgrim, called any option that included sending radioactive water into the bay “outrageous” and “criminal.” Turco said she has no confidence in the decommissioning process.
“The process has been to allow radioactivity into the environment,” she said. “The answer should be no you can’t do that.””
PLYMOUTH — One of the options being considered by the company that is decommissioning the closed Pilgrim Nuclear Power Station is to release around one million gallons of potentially radioactive water into Cape Cod Bay.
The option had been discussed briefly with state regulatory officials as one possible way to get rid of water from the spent fuel pool, the reactor vessel and other components of the facility, Holtec International spokesman Patrick O’Brien said in an interview Wednesday. It was highlighted in a report by state Department of Environmental Protection Deputy Regional Director Seth Pickering at Monday’s meeting of the Nuclear Decommissioning Citizens Advisory Panel in Plymouth.
“We had broached that with the state, but we’ve made no decision on that,” O’Brien said.
As of mid-December, Holtec will complete the process of moving all the spent fuel rods into casks that are being stored on a concrete pad on the Pilgrim plant site in Plymouth. After that, O’Brien told the panel, the removal and disposal of other components in those areas of the facility will take place and be completed sometime in February.
U.S. ‘very bullish’ on new nuclear technology, Granholm says
“These advanced nuclear reactors, and the existing fleet, are safe,” Granholm says. “We have the gold standard of regulation in the United States.”
Actually…According to a UCS report, if federal regulators require the necessary safety demonstrations, it could take at least 20 years—and billions of dollars in additional costs—to commercialize such reactors, their associated fuel-cycle facilities, and other related infrastructure.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) may have to adapt some regulations when licensing reactor technologies that differ significantly in design from the current fleet. Lyman says that should not mean weakening public health and safety standards, finding no justification for the claim that “advanced” reactors will be so much safer and more secure that the NRC can exempt them from fundamental safeguards. On the contrary, because there are so many open questions about these reactors, he says they may need to meet even more stringent requirements.
By Ben Adler • Yahoo News news.yahoo.com
GLASGOW, Scotland — In an interview at the U.N. Climate Change Conference, Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm told Yahoo News on Friday that the Biden administration is “very bullish” on building new nuclear reactors in the United States.
“We are very bullish on these advanced nuclear reactors,” she said. “We have, in fact, invested a lot of money in the research and development of those. We are very supportive of that.”
Nuclear energy is controversial among environmental activists and experts because while it does not create the greenhouse gas emissions that cause climate change, it has the potential to trigger dangerous nuclear meltdowns and creates radioactive nuclear waste [not a small issue].
Al Jazeera Infographic: The World Nuclear Club
While 32 countries generate atomic energy, nine have nuclear weapons and seven countries have both.
By Mohammed Haddad and Hanna Duggal Al Jazeera aljazeera.com
Nuclear warheads per country
Nine countries possessed roughly 13,150 warheads as of August 2021, according to the Federation of American Scientists. More than 90 percent are owned by Russia and the US.
At the peak in 1986, the two rivals had nearly 65,000 nuclear warheads between them, making the nuclear arms race one of the most threatening events of the Cold War. While Russia and the US have dismantled thousands of warheads, several countries are thought to be increasing their stockpiles, most notably China.
According to the Pentagon’s 2021 annual report (pdf), China’s nuclear warhead stockpile is expected to more than triple and reach at least 1,000 by 2030.
The only country to voluntarily relinquish nuclear weapons is South Africa. In 1989, the government halted its nuclear weapons programme and in 1990 began dismantling its six nuclear weapons. Two years later, South Africa joined the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) as a non-nuclear country.
With the 26th UN Climate Change Conference over, nations are making plans to move to green energy in a bid to tackle global warming.
But nuclear energy is a particular sticking point. While it is the largest source of low-carbon electricity in OECD countries, some nations have spoken out against the categorisation of nuclear energy as climate-friendly.
Across the globe, 34 countries harness the power of splitting atoms for generating electricity or for nuclear weapons. (Al Jazeera)

Global nuclear energy
Nuclear energy provides roughly 10 percent of the world’s electricity. Of the 32 countries with nuclear power reactors, more than half (18) are in Europe. France has the world’s highest proportion of its electricity – at 71 percent – coming from atomic power.
Up until 2011, Japan was generating some 30 percent of its electricity from nuclear reactors; however, following the Fukushima disaster, all nuclear power plants were suspended for safety inspections. As of 2020, just 5 percent of Japan’s electricity came from nuclear power, according to the World Nuclear Association.
Nuclear power constitutes some 20 percent of the United States’ electricity. About 60 percent of the country’s energy comes from fossil fuels, including coal, natural gas and petroleum, with the remaining 20 percent coming from renewable sources – wind, hydro and solar.
Nuclear Power Is COP26’s Quiet Controversy
“We have to get everything done in the next 25 years…The idea that you’re going to scale up a technology you don’t even have yet, and it’s going to be commercially viable [in that time], just seems to me like la la land.” — Tom Burke, co-founder of climate think tank E3G.
BY ALEJANDRO DE LA GARZA time.com

In the midst of the COP26 climate talks yesterday, U.S. and Romanian officials stepped aside for a session in the conference’s Blue Zone, establishing an agreement for U.S. company NuScale to build a new kind of modular nuclear power plant in the southeastern European country. The company’s plants—designed to be quickly scaled up or down based on need—are intended to be quicker and cheaper to build than the traditional kind, with some considering them to be a promising alternative for countries seeking to wean themselves off fossil fuels.
NuScale CEO John Hopkins sees the agreement as part of a broader recognition that nuclear power has a big role to play as the world decarbonizes. “I’ve seen a significant shift here,” Hopkins said, speaking to TIME from Glasgow yesterday. “It used to be the only thing really discussed was renewables, but I think people are starting to be a little more pragmatic and understand that nuclear needs to be in the mix.”
But others at COP26 aren’t convinced that NuScale’s small reactors can help avoid climate catastrophe. Some point to the fact that NuScale has yet to build a single commercial plant as evidence that the company is already too late to the party.
Jellyfish Keep Attacking Nuclear Power Plants
Jellyfish are continuing to clog the cooling pipes of nuclear power plants around the world.
By Gabriel Geiger • vice.com
Jellyfish are continuing to clog the cooling intake pipes of a nuclear power plant in Scotland, which has previously prompted a temporary shutdowns of the plant.
The Torness nuclear power plant has reported concerns regarding jellyfish as far back as 2011, when it was forced to shut down for nearly a week—at an estimated cost of $1.5 million a day—because of the free-swimming marine animals.
In a short comment to Motherboard, EDF energy, which runs the Torness plant, said that “jellyfish blooms are an occasional issue for our power stations,” but also said that media reports claiming the plant had recently been taken offline because of jellyfish are “inaccurate.” “[There were] no emergency procedures this or last week related to jellyfish or otherwise,” a spokesperson said.
Like many other seaside power plants, the Torness plant uses seawater to prevent overheating. While there are measures in place to prevent aquatic life from entering the intake pipes, according to the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, they are no match for the sheer number of jellyfish that come during so-called “jellyfish blooms.”
HIDDEN AGENDA: The unspoken argument for more nuclear power
Nuclear power is so slow and expensive that it doesn’t even matter whether or not it is ‘low-carbon’ (let alone ‘zero-carbon’). As the scientist, Amory Lovins, says, “Being carbon-free does not establish climate-effectiveness.” If an energy source is too slow and too costly, it will “reduce and retard achievable climate protection,” no matter how ‘low-carbon’ it is.
By Linda Pentz Gunter beyondnuclearinternational.org
 So here we are again at another COP (Conference of the Parties). Well, some of us are in Glasgow, Scotland at the COP itself, and some of us, this writer included, are sitting at a distance, trying to feel hopeful.
So here we are again at another COP (Conference of the Parties). Well, some of us are in Glasgow, Scotland at the COP itself, and some of us, this writer included, are sitting at a distance, trying to feel hopeful.
But this is COP 26. That means there have already been 25 tries at dealing with the once impending and now upon us climate crisis. Twenty five rounds of “blah, blah, blah” as youth climate activist, Greta Thunberg, so aptly put it.
So if some of us do not feel the blush of optimism on our cheeks, we can be forgiven. I mean, even the Queen of England has had enough of the all-talk-and-no-action of our world leaders, who have been, by and large, thoroughly useless. Even, this time, absent. Some of them have been worse than that.
Not doing anything radical on climate at this stage is fundamentally a crime against humanity. And everything else living on Earth. It should be grounds for an appearance at the International Criminal Court. In the dock.