The first nuclear weapon test was carried out by the United States at the Trinity site on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately equivalent to 20 kilotons. The first hydrogen bomb, codenamed "Ivy Mike", was tested at the Enewetak atoll in the Marshall Islands in November 1952, also by the United States. The largest nuclear weapon ever tested was the "Tsar Bomba" of the Soviet Union at Novaya Zemlya on October 30, 1961, with an estimated yield of around 50 megatons.
In 1963, many (but not all) nuclear and many non-nuclear states signed the Limited Test Ban Treaty, pledging to refrain from testing nuclear weapons in the atmosphere, underwater, or in outer space. The treaty permitted underground nuclear testing. France continued atmospheric testing until 1974, China continued up until 1980. Neither has ever signed the treaty.
The United States conducted its last underground test in 1992, the Soviet Union in 1990, the U.K. in 1991, and both China and France in 1996. After signing the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty in 1996 (which has as of 2012 not yet entered into force), all these states have pledged to discontinue all nuclear testing. Non-signatories India and Pakistan last tested nuclear weapons in 1998. The most recent nuclear test was by North Korea on Feb. 12, 2013.
For a more detailed resource on the history of Nuclear testing, see this United Nations guide on the official 'International Day Against Nuclear Tests'.
JULY 16TH, 2020:
75TH ANNIVERSARY OF THE TRINITY TEST — THE FIRST ATOMIC DETONATION.
OPPENHEIMER RECALLS HIS IMPRESSIONS OF THE MOMENT FOR AN INTERVIEW ON NBC IN 1965.
J. Robert Oppenheimer: "I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds."
A time-lapse map of every nuclear explosion since 1945
Video by Isao Hashimoto
The United States is responsible for 1,032 detonations since 1945 — more than the rest of the countries put together.
News
Trump talk on nuke testing turns focus to New Mexico’s role in decades of blasts
Jay Coghlan, executive director of the nuclear watchdog group Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said Wright’s comments “somewhat” quelled his initial concerns about a renewed explosive nuclear testing program.
But he said claims Russia and China may be conducting small-scale tests known as hydronuclear tests — banned by the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, of which the United States, Russia and China are all signatories — continue to give him pause. He fears rumors about the low-yield tests in other nations could be used to justify a domestic return to testing.
“That, in effect, would give permission to the U.S. [to resume testing],” Coghlan said. “But that would be in violation of the norm of the CTBT.”
Three decades removed from the United States’ last nuclear test, a testing regimen would likely be expensive and time-consuming to start up, Coghlan argued, and could prompt other nuclear powers to follow suit.
It seems likely Russia, at least, would: Following Trump’s post, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced if the United States resumed explosive nuclear testing, the Eastern European nation would follow.
“Then everybody else is going to do it, or virtually everybody else will do it, every other nuclear weapons power,” Coghlan said. “I could just see India and Pakistan champing at the bit to test. And then, of course, there’s North Korea and China.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | November 30, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
It might not have as reverent a name as the Trinity Test or a litany of films made about it. But Project Gnome, a 1961 explosive nuclear test conducted near Carlsbad, is a relic of a bygone era in New Mexico and beyond.
In the 47 years between the Trinity Test and the end of the United States’ explosive nuclear testing in 1992, the nation would perform more than 1,000 such tests — more than any other nuclear nation — with most conducted in Nevada.
New Mexico might not have been the center of the nation’s testing efforts post-Trinity, which marked its 80th anniversary this year, but the state still played a role: Researchers from Sandia National Laboratories and Los Alamos National Laboratory helped design and conduct testing elsewhere, including at the Nevada Test Site and in the Marshall Islands.
US Stands Alone Defying UN Vote on Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
Could the LDS Church end an ongoing nuclear weapons project? These veteran activists think so.
By Thalif Deen, Inter Press Sevice | November 12, 2025 ipsnews.net
UNITED NATIONS, Nov 12 2025 (IPS) – The US took another step backward –to break ranks with the United Nations– when it voted against a draft resolution calling for the entry into force of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT).
The negative vote followed an announcement by President Trump last month that the US plans to resume nuclear testing after a 33-year hiatus. The US stood alone on the UN vote, which was supported by almost all member States in the General Assembly’s First Committee.
The resolution was adopted by an overwhelming majority: with 168 votes in favor, with one against (United States) and 3 abstentions (India, Mauritius, Syria).
During Trump’s first term, the US abstained on the vote. And in other years they had been voting in favour.
Jackie Cabasso, Executive Director, Western States Legal Foundation, which monitors and analyzes U.S. nuclear weapons programs and policies, told IPS the chaos and uncertainty arose from Trump’s factually-challenged social media post that “because of other countries testing programs, I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis.”
The U.S. government’s first ever “No” vote, on the annual UN resolution in support of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT), raises further troubling questions about U.S. intentions.
AP: Trump appears to suggest the US will resume testing nuclear weapons for first time in 30 years
“For Trump, who has cast Russia as a “paper tiger” for failing to swiftly subdue Ukraine, the message is that Russia remains a global military competitor, especially on nuclear weapons, and that Moscow’s overtures on nuclear arms control should be acted on.”
By MICHELLE L. PRICE and CHRIS MEGERIAN | October 30, 2025 apnews.com
BUSAN, South Korea (AP) — President Donald Trump appeared to suggest the U.S. will resume testing nuclear weapons for the first time in three decades, saying it would be on an “equal basis” with Russia and China.
The Kremlin pointed out that a global ban on nuclear tests has remained in place, but warned that if any country resumes nuclear testing Russia would follow suit.
There was no indication the U.S. would start detonating warheads, but Trump offered few details about what seemed to be a significant shift in U.S. policy.
He made the announcement on social media minutes before he met with Chinese leader Xi Jinping on Thursday in South Korea. He offered little clarity when he spoke to reporters later aboard Air Force One as he flew back to Washington.
The U.S. military already regularly tests its missiles that are capable of delivering a nuclear warhead, but it has not detonated the weapons since 1992. The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, which the U.S. signed but did not ratify, has been observed since its adoption by all countries possessing nuclear weapons, North Korea being the only exception.
REUTERS: Trump tells Pentagon to immediately resume testing US nuclear weapons
“Russia – which tested a new nuclear-powered cruise missile on October 21, held nuclear readiness drills on October 22 and tested a new nuclear-powered autonomous torpedo on October 28 – said it hoped Trump had been properly informed that Moscow had not tested a nuclear weapon itself.”
By Trevor Hunnicutt, Ismail Shakil and Kanishka Singh | October 30, 2025 reuters.com
Russia tested new nuclear-powered Burevestnik cruise missile
“For Trump, who has cast Russia as a “paper tiger” for failing to swiftly subdue Ukraine, the message is that Russia remains a global military competitor, especially on nuclear weapons, and that Moscow’s overtures on nuclear arms control should be acted on.”
By Guy Faulconbridge and Lidia Kelly Tim Balk | October 26, 2025 reuters.com
- Russia tests nuclear-capable Burevestnik missile
- Missile flew for 14,000 km, 15 hours
- Putin says it can pierce any missile defences
80 years after nuclear bomb tested in N.M., victims will get reparations
NBC News NOW, July 16, 2025, nbcnewsnow.com
Trinity “downwinders” of New Mexico exposed to the first ever nuclear explosion are receiving recognition and compensation 80 years after the bomb was tested. NBC News’ Aaron Gilchrest spoke with several people who shared their sacrifice and suffering over the years.
The Workers, the Waste, and the Warnings from Bomb Country
“From South Carolina to California, locals in nuclear weapons towns raise health, safety, and environmental concerns over renewed plutonium pit manufacturing.”
By: Taylor Barnes | June 12, 2025 inkstickmedia.com
The United States’ plans to restock its entire nuclear weapons arsenal, known in military parlance as nuclear “modernization,” hit a bump in the road in January. A scrappy coalition of grassroots watchdog groups and impacted communities from places like the Gullah/Geechee sea islands off the Georgia and South Carolina coasts and San Francisco Bay Area neighborhoods near a weapons laboratory sued the government agency that oversees the security of the US nuclear weapons complex.
The plaintiffs argued that the government was moving ahead with plans to produce new plutonium pits for warheads at plants in rural South Carolina and the Los Alamos laboratory in New Mexico without properly evaluating alternatives under the National Environmental Policy Act. A federal judge agreed, and the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) settled with the grassroots groups, agreeing to perform a multi-year environmental analysis.
The extensive environmental impact study is a rare speed bump that everyday Americans have been able to place in the way of the 21st century’s new nuclear arms race — and one that forces the government to hear from locals in the specific communities across the country that produce parts for the weapons.
“A nuclear arms race can feel abstract and distant, but it very much isn’t,” Ravi Garla, a consultant for the Nuclear Threat Initiative, told Inkstick. Garla recently worked on a campaign that led to a unanimous vote in the Nevada state legislature to oppose any resumption of explosive nuclear tests at a desert site outside Las Vegas where the government carried out more than 900 tests during and after the Cold War.
Top photo: A billboard by an advocacy group opposed to nuclear weapons testing in Nevada (Courtesy of Nevadans Against Nuclear Weapons Testing)
Calls to restart nuclear weapons tests stir dismay and debate among scientists
By Emily Conover, Science News | March 27, 2025 sciencenews.org
When the countdown hit zero on September 23, 1992, the desert surface puffed up into the air, as if a giant balloon had inflated it from below.
It wasn’t a balloon. Scientists had exploded a nuclear device hundreds of meters below the Nevada desert, equivalent to thousands of tons of TNT. The ensuing fireball reached pressures and temperatures well beyond those in Earth’s core. Within milliseconds of the detonation, shock waves rammed outward. The rock melted, vaporized and fractured, leaving behind a cavity oozing with liquid radioactive rock that puddled on the cavity’s floor.
As the temperature and pressure abated, rocks collapsed into the cavity. The desert surface slumped, forming a subsidence crater about 3 meters deep and wider than the length of a football field. Unknown to the scientists working on this test, named Divider, it would be the end of the line. Soon after, the United States halted nuclear testing.
Beginning with the first explosive test, known as Trinity, in 1945, more than 2,000 atomic blasts have rattled the globe. Today, that nuclear din has been largely silenced, thanks to the norms set by the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty, or CTBT, negotiated in the mid-1990s.
Only one nation — North Korea — has conducted a nuclear test this century. But researchers and policy makers are increasingly grappling with the possibility that the fragile quiet will soon be shattered.
Some in the United States have called for resuming testing, including a former national security adviser to President Donald Trump. Officials in the previous Trump administration considered testing, according to a 2020 Washington Post article. And there may be temptation in coming years. The United States is in the midst of a sweeping, decades-long overhaul of its aging nuclear arsenal…
Christie Brinkley: Don’t let the US resume nuclear weapon tests that ended decades ago
“The United States and other nuclear powers are now moving closer to resuming nuclear weapons tests, decades after testing ended. This highly disturbing trend must be halted.”
By Christie Brinkley Special to The Kansas City Star Miami Herald | March 3, 2025 miamiherald.com
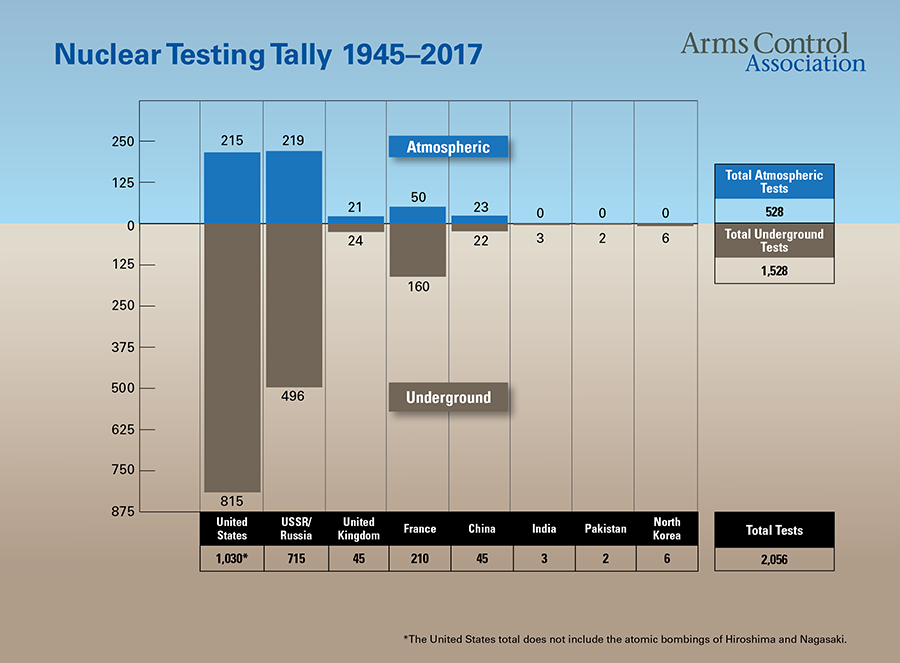
Since the atomic age, 2,056 nuclear weapons have been detonated, 528 of them above the ground. The United States and Soviet Union accounted for about 85% of these tests. The explosive power of atmospheric tests equaled 29,000 Hiroshima bombs. Airborne radioactive fallout circled the globe, re-entered the environment through precipitation, and entered human bodies through food and water.
Cold War bomb testing was part of a massive increase in the number of nuclear weapons, which peaked at more than 60,000. After nuclear war was barely avoided during the Cuban missile crisis, public pressure convinced leaders to ban all above-ground tests in 1963 — a treaty that has never been violated.
The test ban treaty was a huge achievement for peace, beginning eased tensions between nuclear nations. It also was a landmark for public health. A study by St. Louis residents and scientists found an enormous buildup of radioactive strontium-90 levels in baby teeth — 63 times higher in children born in 1963 compared to those born in 1950.
Step inside the secret lab where America tests its nukes
“”The risk is significant,” says Hans Kristensen, director of the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists. The talk of testing comes at a time when nuclear weapons are resurgent: Russia is designing nuclear weapons to attack satellites and obliterate seaports; China is dramatically expanding its nuclear arsenal; and the U.S. is undergoing a major modernization of its nuclear warheads. After years of declining nuclear stockpiles, the world looks poised to begin increasing the number and types of nuclear weapons being deployed.”
By Geoff Brumfiel, NPR | January 29, 2025 npr.org

A half-mile from here, on the morning of May 8, 1953, an Air Force bomber dropped a Mk-6D nuclear bomb from a height of 19,000 feet above the desert floor. It exploded with a yield of 27 kilotons of TNT — creating a shockwave that warped the bridge. The test, code-named “Encore,” was one of several conducted here to see what, if anything, in the civilian world could survive a nuclear blast (the answer is, apparently, not much).
Continue reading
MORUROA FILES: Investigation into French nuclear tests in the Pacific
Poisoned legacy
Leukemia, lymphoma, cancer of the thyroid, lung, breast, stomach … In Polynesia, the experience of French nuclear tests is written in the flesh and blood of the inhabitants. Strontium has eaten into bones, cesium has eaten away at muscles and genitals, iodine has seeped into the thyroid.
The story of this largely unknown health disaster began on July 2, 1966. On that day, the army carried out the Aldebaran fire, the first of the 193 tests fired from the nuclear atolls of Moruroa and Fangataufa until 1996. The first , also, of a series of tests among the most contaminating in the history of the French nuclear program: the tests in the open air. Between 1966 and 1974, the military carried out 46 such explosions.
Disclose and Interprt, in collaboration with the Science & Global Security program at Princeton University (USA), investigated the consequences of atmospheric testing in French Polynesia for two years. With the help of thousands of declassified military documents, hundreds of hours of calculations and dozens of unpublished testimonies, this investigation demonstrates for the first time the extent of the radioactive fallout that struck the inhabitants of this vast territory as the ‘Europe.
According to our calculations, based on a scientific reassessment of the doses received, approximately 110,000 people were infected, almost the entire Polynesian population at the time. Modelling toxic clouds to support, we also unveil how the French authorities have concealed the true impact of nuclear testing on the health of Polynesians for more than fifty years.
On February 18, 2020, the National Institute for Health and Medical Research (Inserm) published, at the request of the Ministry of Defense, a report on “the health consequences of nuclear tests” in French Polynesia. According to this expertise, its authors felt that they could not “make a solid conclusion” to the existence of “links between the fallout from atmospheric nuclear tests and the occurrence of radiation-induced pathologies”. And the college of experts stressed the need to “refine the estimates of doses received by the local population and by civilian and military personnel”. This is precisely what we have endeavored to do in this investigation.
Opinion: Too many ‘downwinders’ are still suffering
“We are sponsoring a bill that would make sure the government’s responsibility to those who were harmed by nuclear testing does not get swept under the rug.”
By Burgess Owens and Chris Stewart deseret.com

Any objective study of American history brings us to the realization that there are many Americans who quietly made, and continue to make, great sacrifices for our national security. Many of these women and men willingly give of themselves to ensure that our country remains free.
Tragically, under the banner of national security the United States government exposed Americans to radioactive uranium ore and radioactive dust — subjecting them to lung cancer and other respiratory illnesses.
On July 16, we marked the 76th anniversary of the detonation of the first nuclear weapon — code-named Trinity — in the desert of New Mexico’s Tularosa Basin. Three weeks after the Trinity detonation, the United States exploded the Little Boy bomb over Hiroshima and, three days later, the Fat Man bomb over Nagasaki. Six days later, Japan surrendered. In the aftermath of World War II, a nuclear arms race began that reached its zenith with over 60,000 nuclear weapons worldwide in 1986.
Many lives were lost or severely altered by the nuclear weapons program. Thankfully, the world stockpile of nuclear weapons has steadily declined since 1986 and will, hopefully, continue to do so in the future. Yet, the effects of detonating over 1,100 nuclear weapons since the Trinity test in 1945 continue to mar the lives of Americans to this day.
Through atmospheric weapons tests, as well as mining, transporting and milling of uranium ore, many Americans have been slowly killed by radiation exposure. Thousands of Utahns were infected by radiation exposure simply by living “downwind” of the federal government’s nuclear weapons testing sites. Additional Utahn miners were affected as they worked the uranium necessary for these weapons. These “downwinders” and miners and their families friends, and communities often suffered excruciating illness, loss and devastation.
In response to this malfeasance, Congress rightly enacted (and later amended in 2000) the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) in 1990. This legislation was a good first step in making recompense to those who mined and hauled uranium ore and those who processed the ore at a mill. The RECA legislation also addresses those exposed to radiation downwind from nuclear test sites.
It has been more than 20 years since any meaningful reform to RECA has been made for those whose lives have been taken or irreversibly altered by our foray into the arms race. Several classifications of workers such as core drillers and ground workers have been denied justice by being excluded completely from the process.
Some diseases that should have been compensable have been excluded. Numerous geographical locations exposed to downwind radiation have been left out. Uranium miners continued to mine after the United States stopped buying uranium for its nuclear weapons programs in 1971. These so-called post-1971 workers were excluded from accessing benefits since the original RECA legislation had an arbitrary cutoff date of Dec. 31, 1971 — even though the federal government continued to regulate uranium mines long after 1971. To make matters worse, RECA is scheduled to sunset in July 2022 — potentially leaving all classifications of exposure victims without redress.
We are honored to represent some of these “downwinders” and their family members and want them to know their suffering — and the sacrifices they made for our nation — are not forgotten.
That is why we are pleased to be the lead Republican members of the House of Representatives on the “RECA Amendments Act of 2021,” legislation that will reauthorize RECA for those still suffering the consequences of nuclear testing.
The tragic consequences of the nuclear arms race cannot be swept under the rug of history. We urge our colleagues in Congress to support the “RECA Amendments Act of 2021.” Our country must act now to address the injustices of those who have been forgotten by their own government.
Rep. Burgess Owens represents Utah’s 4th Congressional District. Rep. Chris Stewart represents Utah’s 2nd Congressional District.
Global Zero Mourns the Loss of Dr. Bruce Blair
June 20, 2020
Source: Global Zero
“We are saddened to announce that Dr. Bruce G. Blair, Co-Founder of Global Zero and President of its Board of Directors, died unexpectedly on Sunday, July 19, following a sudden illness.
Derek Johnson, Executive Director of Global Zero, released the following statement on behalf of the organization regarding the recent passing of Dr. Blair:
“I am heartbroken at the sudden loss of my colleague, mentor, and dear friend, Bruce Blair.
“15 years ago, Bruce brought together an unprecedented international community of leaders and visionaries to build a new kind of movement to persuade governments to come to their senses and set aside the most catastrophic weapons on the planet. A veteran nuclear launch officer and unrivaled expert in command and control, Bruce understood — perhaps better than any single person alive — the urgency, enormity, and complexity of the nuclear threat. He built the Global Zero movement from the ground up and devoted all of his energy to making the world safer and better for all people.
Escalation by Tweet: Managing the new nuclear diplomacy
Can a tweet start a nuclear war? New Report examines impact of Twitter on crisis escalation and recommends a “no tweeting policy” during crises.
[embeddoc url=”https://www.kcl.ac.uk/csss/assets/10957•twitterconflictreport-15july.pdf” download=”all” viewer=”google”]
Maintain the Moratorium
June, 11, 2020
Source: The Independent
By Mary Perner
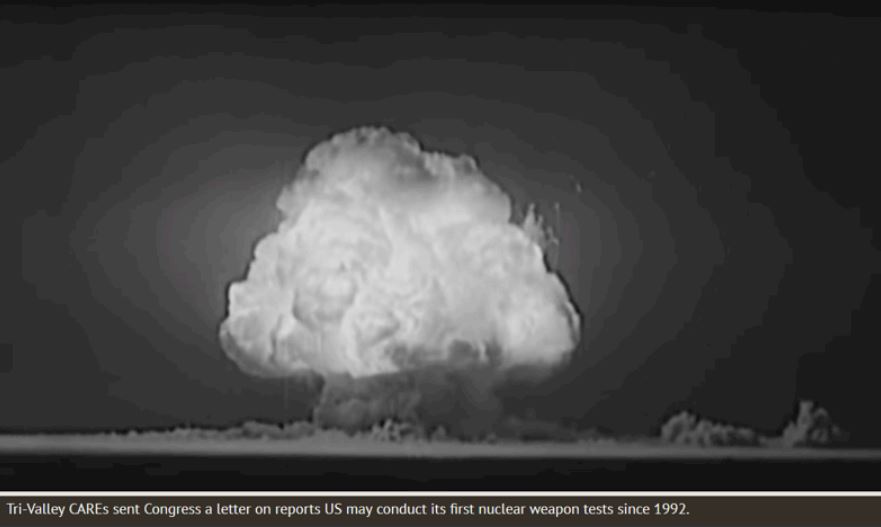
On May 28, 24 non-governmental organizations, including Livermore’s Tri-Valley CAREs, signed onto a letter that was delivered to Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi and Senate Minority Leader Charles Schumer. The letter was in response to recent reports that senior White House officials had discussed conducting the first U.S. nuclear weapon test explosion since 1992.
Why a US nuclear test in Nevada would be bad for the world—and Trump’s reelection
A whole slew of 2020 candidates have either pleaded ignorance on certain nuclear policies or given answers that were borderline incomprehensible.
ARTICLE BY JOHN KRZYANIAK | thebulletin.org
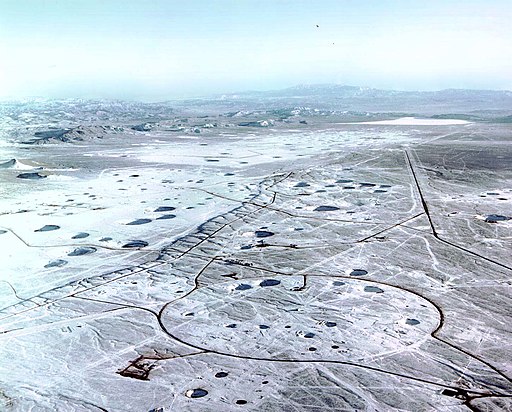

On May 15, according to reporting in the Washington Post and the Guardian, the Trump administration held serious discussions about whether to conduct a nuclear test explosion, and those conversations are continuing.
Though the administration has not made any public remarks on the matter, many experts and policy makers have already chimed in to voice dissent. Lassina Zerbo, the head of the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty Organization, said a nuclear test would “pose a grave challenge to global peace and security.”
Hans Kristensen, who directs the nuclear information project at the Federation of American Scientists, said it was “completely nuts.” Joe Biden, former vice president and presumptive Democratic presidential nominee, said a resumption of testing would be “as reckless as it is dangerous.”
Congress Introduces Legislation to Expand Compensation for Radiation Exposure
Luján, Members of Congress Introduce Legislation to Expand Compensation for Individuals Impacted by Radiation Exposure
Washington, D.C. – Today, Congressman Ben Ray Luján (D-N.M.), the U.S. House Assistant Speaker, introduced legislation to expand compensation for individuals exposed to radiation while working in and living near uranium mines or downwind from nuclear weapon test sites.
Tens of thousands of individuals, including miners, transporters, and other employees who worked directly in uranium mines, along with communities located near test sites for nuclear weapons, were exposed during the mid-1900s to dangerous radiation that has left communities struggling from cancer, birth defects, and other illnesses.
The West’s atomic past, in opera halls
The West’s atomic past, in opera halls
On stage and in Congress, Trinity test downwinders fight for recognition.
Elena Saavedra Buckley, High Country News, Aug. 30, 2018
Outside the Santa Fe Opera, a 62-year-old venue nestled in juniper-covered hills, retirees reclined by cloth-covered tables in the parking lot. As the August heat reflected off the asphalt, they tailgated with flutes of champagne. Soon, they would file in to see Doctor Atomic, an opera about physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer and the 24 hours before the first atomic bomb, which he helped create, detonated over New Mexico’s Tularosa Basin in the Trinity test.
Doctor Atomic has been performed in New York and San Francisco, but never before in New Mexico, where Manhattan Project scientists from Los Alamos Laboratory created the bomb. John Adams composed the opera in 2005, and Peter Sellars’s libretto uses declassified Los Alamos documents, focusing on the scientists’ perspective. This was the first time that downwinders — people whose families lived in the Tularosa Basin, in the path of the bomb’s radiation — appeared on stage during a performance. This summer, 73 years after Trinity, New Mexico’s downwinders are finally receiving some attention — onstage and in Congress.
The Trinity test occurred at 5:30 a.m. on July 16, 1945, about 150 miles south of Santa Fe and the laboratory and only weeks before the bombings in Japan. It bathed the basin in light, creating a half-mile-wide crater. The Tularosa Basin Downwinders believe that blast’s radiation gave their families cancer, either from the air or through milk and produce, and that the diseases are being passed down genetically.
Trinity site cancer study expected to finish in 2019
- By Russell Contreras | Associated Press
- Updated
ALBUQUERQUE — A long-anticipated study into the cancer risks of New Mexico residents living near the site of the world’s first atomic bomb test likely will be published in 2019, the National Cancer Institute announced.
Institute spokesman Michael Levin told the Associated Press that researchers are examining data on diet and radiation exposure on residents who lived near the World War II-era Trinity test site, and scientists expect to finish the study by early next year.
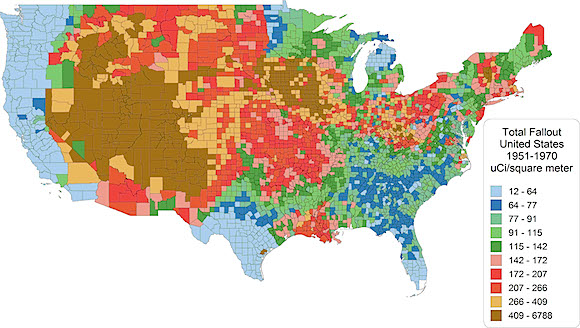
Nuclear Fallout In US from Testing
USA Today reported on an unreleased federal study blaming fallout from worldwide nuclear bomb testing for at least 15,000 cancer-related deaths and more than 20,000 non-fatal cancers in U.S. residents born since 1951.
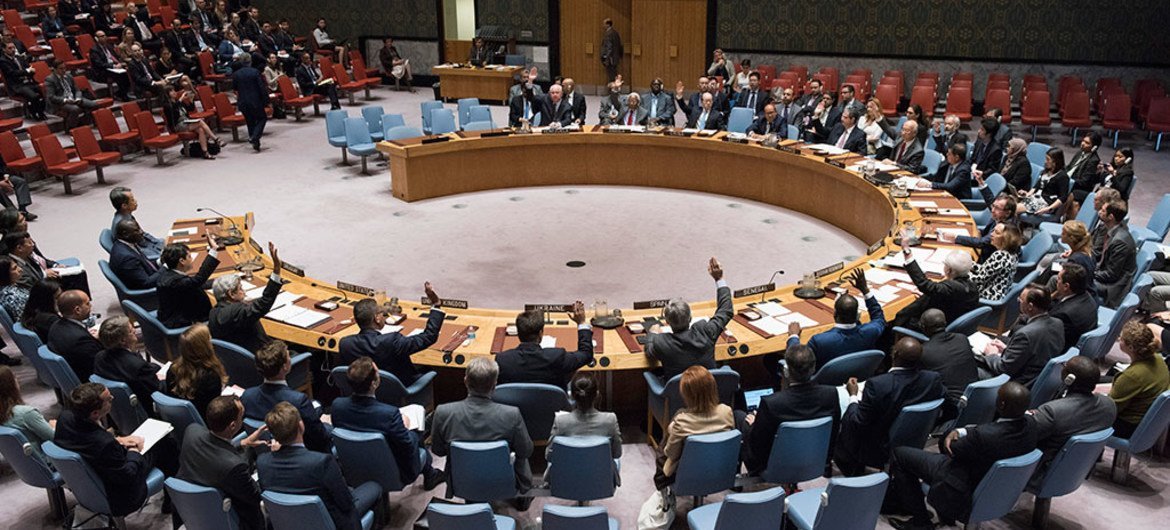
Security Council Urges All to Ratify Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
“Reaffirming that proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, and their means of delivery, threatens international peace and security, the United Nations Security Council today adopted a resolution urging all States who haven’t done so to sign the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty”
-From UN News
“A world free of nuclear of weapons goes by stopping testing too, and then taking steps that will reinforce the agreements that are already here, and then leading us towards what we all want: a world free of nuclear weapons; a world free of any attempt of modernization that some are talking about today.”
-Lassina Zerbo, Executive Secretary of CTBTO:
Resources
Videos
Quotes
Trump’s Talk of Nuclear Tests Recalls Fears of the Cold War
“Yes, we can learn things by nuclear testing. But when you look at the big picture, we have much more to lose by going back to testing than we have to gain.”
– SIEGFRIED S. HECKER, a former director of the Los Alamos weapons lab in New Mexico, where the first atomic bomb was created, after President Trump’s call to resume nuclear testing revived a Cold War debate. The New York Times nytimes.com
Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon,
“Together, let us demand an end to all nuclear tests and get on with the unfinished business of achieving a world free of nuclear weapons.”
–Message on the International Day against Nuclear Tests, July 2014
Dossiers:
Trump's Nuclear Posture Review
Flashpoint: North Korea
Flashpoint: NATO-Russia
UN Treaty to Prohibit Nuclear Weapons
Plutonium Pit Production at LANL
B61-12 Enhanced Nuclear Bomb
LRSO: New Nuclear Cruise Missile
Kirtland AFB Nuclear Weapons Complex
MOX / Plutonium Disposition
Fukushima Disaster and Updates
Nuke Lab Contractors Illegal Lobbying
Nuclear Testing Since 1945
Atomic Histories

Nuclear Watch Interactive Map of the
Nuclear Weapons Complex View full size
Facilities:
Kansas City Plant
Lawrence Livermore National Labs
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Nevada National Security Site
Pantex Plant
Sandia National Laboratories
Savannah River Site
Washington DC
Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP)
Y-12 National Security Complex

Click the image to download this large printable map of DOE sites, commercial reactors, nuclear waste dumps, nuclear transportation routes, surface waters near sites and transport routes, and underlying aquifers. This map was prepared by Deborah Reade for the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability.