2023 News Articles – All Posts
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
2022 Select Highlighted Press Items
Nuclear Modernization is the ’Absolute Minimum,’ STRATCOM Commander Says | March 8, 2022
US tested hypersonic missile in mid-March but kept it quiet to avoid escalating tensions with Russia | April 4, 2022
Putin’s Nuclear Threats Are a Wake-Up Call for the World | March 15, 2022
Intelligence report determines that Russia's WMD threats will grow as losses mount in Ukraine | March 19, 2022
China and the United States: It’s a Cold War, but don’t panic | March 10, 2022
Russian military doctrine calls a limited nuclear strike “de-escalation.” Here’s why. | March 8, 2022
North Korea says it will strike with nuclear weapons if South attacks | April 4, 2022
Flying Under The Radar: A Missile Accident in South Asia | April 4, 2022
2022 News Articles
Lockheed Martin-Funded Experts Agree: South Korea Needs More Lockheed Martin Missiles
Adam Johnson writes: “As tensions between the United States and North Korea continue to rise, one think tank, the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), has become a ubiquitous voice on the topic of missile defense, providing Official-Sounding Quotes to dozens of reporters in Western media outlets. All of these quotes speak to the urgent threat of North Korea and how important the United States’s deployment of the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) missile system is to South Korea…
“In the past year, FAIR has noted 30 media mentions of CSIS pushing the THAAD missile system or its underlying value proposition in US media, most of them in the past two months. Business Insider was the most eager venue for the think tank’s analysts, routinely copying and pasting CSIS talking points in stories warning of the North Korean menace.
Last August (8/8/16), the New York Times revealed internal documents of CSIS (and the Brookings Institution) showing how the think tanks acted as undisclosed lobbyists for weapons manufacturers…
**Note that the top 10 corporate donors to CSIS include 5 top defense contractors: Lockheed, Northrup-Grumman, Boeing, General Dynamics and Leonardo-Finmeccanica. see CSIS
WIPP, LANL Settlement Projects In Progress
“With nuclear waste again on the road to Carlsbad’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, work is underway to improve WIPP transportation routes around the state….” From Carlsbad Current Argus.
WIPP Seals Off Nuclear Waste For 10,000 Years. Should It Be A Model For Storage?
“Shut down after two 2014 incidents, New Mexico’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant accepted its first new shipments of nuclear waste last week ….” From The Christian Science Monitor.
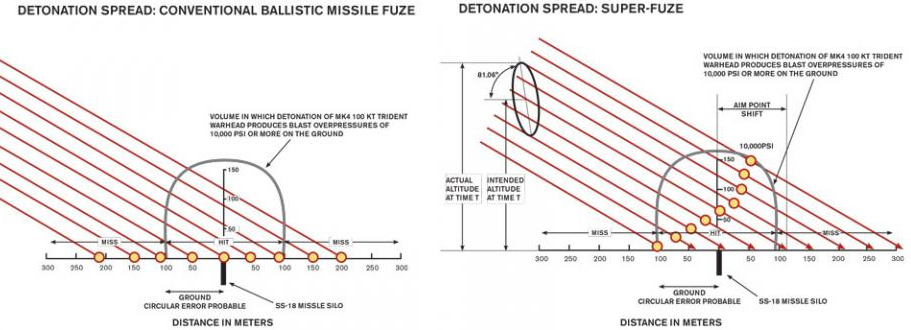
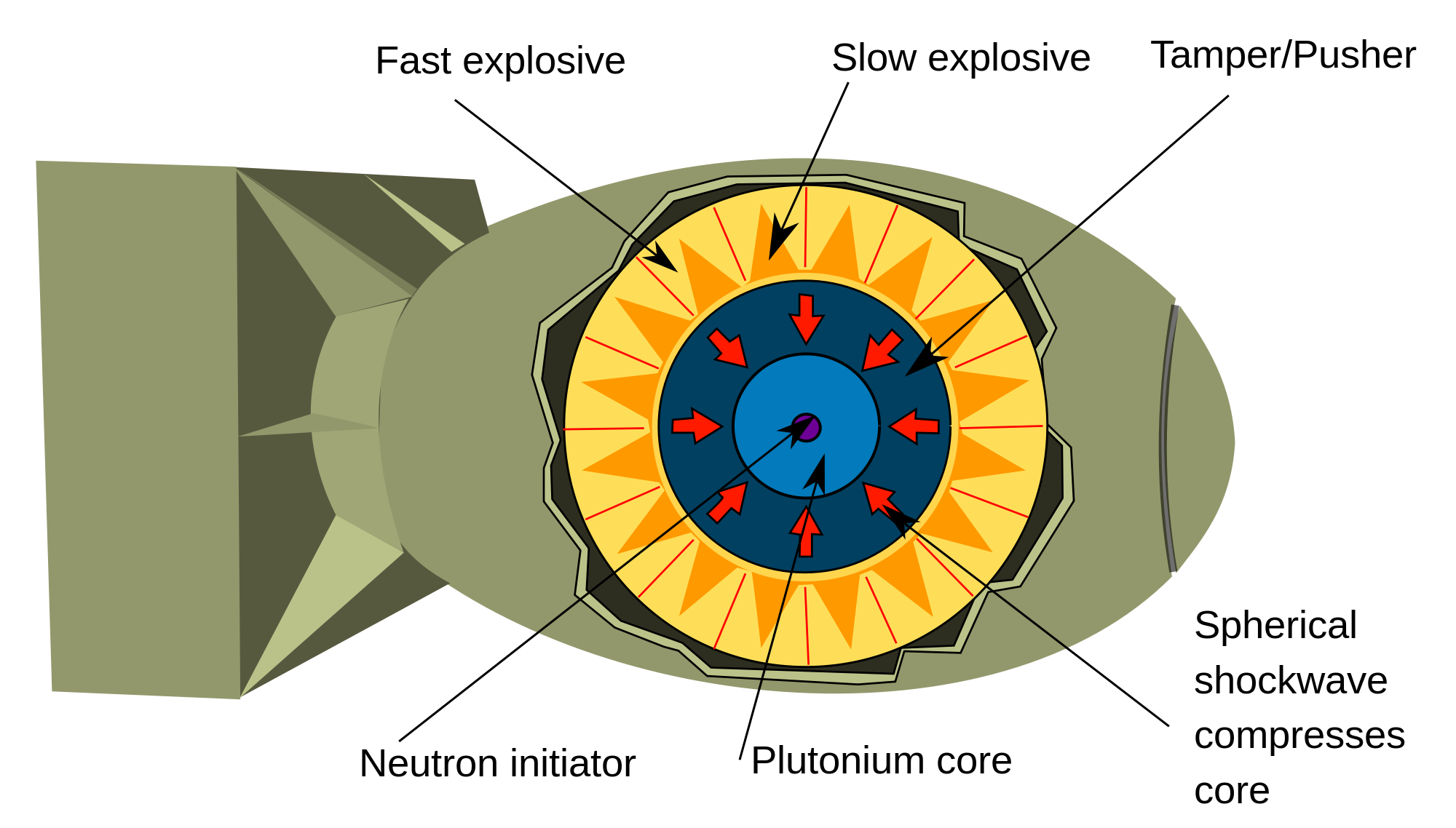
How US Nuclear Force Modernization is Undermining Strategic Stability: The Burst-Height Compensating Super-Fuze
The US nuclear forces modernization program has been portrayed to the public as an effort to ensure the reliability and safety of warheads in the US nuclear arsenal, rather than to enhance their military capabilities. In reality, however, that program has implemented revolutionary new technologies that will vastly increase the targeting capability of the US ballistic missile arsenal. This increase in capability is astonishing- boosting the overall killing power of existing US ballistic missile forces by a factor of roughly three- and it creates exactly what one would expect to see, if a nuclear-armed state were planning to have the capacity to fight and win a nuclear war by disarming enemies with a surprise first strike.
The revolutionary increase in the lethality of submarine-borne US nuclear forces comes from a ‘super-fuze’ device that since 2009 has been incorporated into the Navy’s W76-1/Mk4A warhead as part of a decade-long life-extension program. We estimate that all warheads deployed on US ballistic missile submarines now have this fuzing capability. Because the innovations in the super-fuze appear, to the non-technical eye, to be minor, policymakers outside of the US government (and probably inside the government as well) have completely missed its revolutionary impact on military capabilities and its important implications for global security…
The W76 upgrade reflects a 25-year shift of the focus of US hard-target kill capability from land-based to sea-based ballistic missiles. Moreover, by shifting the capability to submarines that can move to missile launch positions much closer to their targets than land-based missiles, the US military has achieved a significantly greater capacity to conduct a surprise first strike against Russian ICBM silos…
In spite of its severe limitations, this growing defense system could appear to both Russia and China as a US attempt to reduce the consequences of a ragged Russian or Chinese retaliation to a US first strike against them.
We cannot foresee a situation in which a competent and properly informed US president would order a surprise first strike against Russia or China. But our conclusion makes the increased sea-based offensive and defensive capabilities we have described seem all the more bizarre as a strategy for reducing the chances of nuclear war with either Russia or China…”
-Hans M. Kristensen, Matthew McKinzie, Theodore A. Postol from The Bulliten of Atomic Scientists
Defense Science Board Recommends “A More Flexible Nuclear Enterprise”
Sometimes, maybe, the status quo is something we need to safeguard, not disrupt. That may be the case when it comes to a new push to abandon the US-Russian mutual prohibition on the deployment of low-yield nuclear weapon systems as part of theater warfighting doctrine.
Since the late 1980s both US and Soviet, now Russian, policy has been to not develop and deploy ‘tactical’ nuclear weapons, including theater-range missiles, because it was agreed that it would be very difficult to prevent a ‘tactical’ exchange in a regional conflict from progressing rapidly to a civilization-ending ‘strategic’ exchange.
But new doubts are arising about the credibility of a strategic deterrent in the case of a local or regional conflict: one which, for example, the US could be involved in, even though the stakes may not put essential US security at risk. In such cases, some US warfighters would like to have the option of threatening counterforce and intermediate range strikes using low-yield nukes. Or, they argue, what if an adversary uses a tactical nuke to “escalate to de-escalate”? Some want to be able to respond in kind. These doubts about classical deterrence, along with a ‘multipolar’ landscape of nuclear-armed states, are the basis for the nuclear boosters’ meme of “The Second Nuclear Age”).
See Pentagon Panel Urges Trump Team to Expand Nuclear Options
“Astoundingly High” Radiation Levels Detected at Fukushima Unit 2
The radiation level in the containment vessel of reactor two has reached as high as 530 sieverts per hour, Tokyo Electric Power Co, or Tepco as it’s known, said last week.
Are levels rising?
Azby Brown reporting on Safecast’s website, February 4th:
No, radiation levels at Fukushima Daiichi are not rising
“It must be stressed that radiation in this area has not been measured before, and it was expected to be extremely high. While 530 Sv/hr is the highest measured so far at Fukushima Daiichi, it does not mean that levels there are rising, but that a previously unmeasurable high-radiation area has finally been measured. Similar remote investigations are being planned for Daiichi Units 1 and 3. We should not be surprised if even higher radiation levels are found there, but only actual measurements will tell.” (see more at Safecast)
Feb. 8, Denver Post: Could the radiation level be even higher? Possibly. The 530 sievert reading was recorded some distance from the melted fuel, so in reality it could be 10 times higher than recorded, said Hideyuki Ban, co-director of Citizens’ Nuclear Information Center.
García-Robles’ Nobel Medal Sold at Auction
Alfonso García Robles drafted the 1967 Treaty for the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons in Latin America and the Caribbean. He was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1982. He died in 1991. The Treaty of Tlatelolco, as it became known, was the first of its kind and is credited with keeping Latin America and the Caribbean free of nuclear weapons.
Obama Administration Announces Unilateral Nuclear Weapon Cuts
Vice President Joe Biden announced that the Obama administration had cut 553 warheads from the US nuclear weapons stockpile since September 2015. The cuts bring the total number of reductions during the last 8 years to 1,255; the current number of nuclear warheads in the stockpile is now at 4,018. These were not, however, “deployed” nuclear weapons.
FAS stated, “We estimate that the warheads were taken from the inactive reserve of non-deployed warheads that are stored to provide a ‘hedge’ against the technical failure of a warhead type or to respond to geopolitical surprises.”
Hans Kristensen noted, “The cut adds significantly to the large inventory of retired (but still intact) warheads that are awaiting dismantlement.” That number was estimated by VP Biden to be now 2,800. Most, if not all, of these weapons awaiting dismantlement, are stored at the Kirtland AFB storage site in Albuquerque. (Also stored there are some number of “hedge” weapons, so it is possible that these 553 warheads just received a modified designation, but otherwise have not even been moved.) The warheads are meant to be dismantled at the Pantex Plant; however, at the current average rate of 278 per year, it will take to 2026 to dismantle the current backlog.
Kristensen notes, “Even so, the Obama administration still holds the position of being the administration that has cut the least warheads from the stockpile compared with other post-Cold War presidencies.”
From the Federation of American Scientists
Another nuclear weapons contractor pays millions to settle charges of illegally diverting federal funds
Allegations of illegally spending federal funds to lobby for new funds now encompass contractors working at six of the eight U.S. nuclear weapons sites.
By Patrick Malone, Center for Public Integrity
This time it’s Bechtel and URS Corp
The latest settlement involves work by Bechtel National Inc. and its parent Bechtel Corp., and URS Corp. and its subsidiary URS Energy and Construction Inc., which together have been trying to clean up the Hanford Nuclear Reservation, in Washington state, the most toxic site in the country. The settlement is part of an emerging pattern.
Lockheed Martin Corp., which operates one of three U.S. nuclear weapons laboratories – Sandia, agreed in August 2015 to pay $4.7 million to settle a complaint by the Justice Department that it used federal funds to lobby for a no-bid contract extension. In December of 2016, Department of Energy selected a different contractor team, led by Honeywell International, to run Sandia for up to a decade, beginning next year.)
Meanwhile, Fluor Corp. paid $1.1 million in April 2013 to settle accusations that it used federal funds to lobby government agencies for more business at its Hanford training facility.
George Shultz: The Power of Ought
A salute to former Secretary of State George Shultz on his 95th birthday from the organization he co-founded, Nuclear Threat Initiative
Area G – Brief Backgrounder
For more than 70 years, Los Alamos National Laboratory dug thousands of deep and shallow graves across mesas and filled them with the radioactive waste, chemicals, and solvents used to make nuclear weapons.
Workers disposed of the waste in these unlined pits before the widespread contamination that would follow was fully understood or governed by environmental laws. Radioactive particles that live longer than some civilizations mixed freely with the red soil.
WIPP plans will go on even if Russia quits plutonium deal
The Albuquerque Journal reports:
“At Los Alamos and Sandia National Laboratories, the breakdown in the bilateral agreement may deal a decisive blow to already deteriorated relationships between scientists at New Mexico’s national laboratories and their Russian counterparts, who had been working together to iron out the technical aspects of plutonium disposition under the deal, according to Don Hancock with the Southwest Research and Information Center in Albuquerque.”
Ed Lyman of Union of Concerned Scientists said “Even until last week, the U.S. was optimistic that this was one area that Russia and the U.S. could cooperate.”
Security Council Urges All to Ratify Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
“Reaffirming that proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, and their means of delivery, threatens international peace and security, the United Nations Security Council today adopted a resolution urging all States who haven’t done so to sign the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty”
-From UN News
“A world free of nuclear of weapons goes by stopping testing too, and then taking steps that will reinforce the agreements that are already here, and then leading us towards what we all want: a world free of nuclear weapons; a world free of any attempt of modernization that some are talking about today.”
-Lassina Zerbo, Executive Secretary of CTBTO:
The Virtues of Nuclear Ignorance
Zero-knowledge proof and nuclear disarmament verification: how do you prove a bomb is real without revealing what’s inside?
More at the New Yorker
NTI Launches the William J. Perry Project
Former Secretary of Defense William Perry has just published a new book, a memoir titled “My Journey at the Nuclear Brink”. At the same time, NTI has launched the online William J. Perry Project, to “educate and engage the public on the dangers of nuclear weapons in the 21st century”.
“I hope to encourage young people to take the baton I am trying to pass to them. My generation created this existential problem- their generation must find a way to solve it.”
– William Perry.
70th Anniversary of the Trinity Test
The first atomic detonation. Oppenheimer recalls his impressions of the moment for an interview on NBC in 1965.
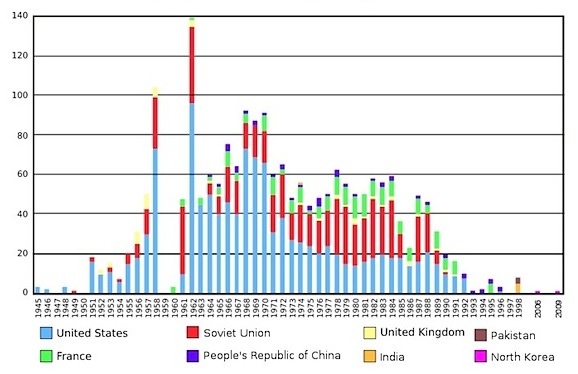
The first nuclear weapon test was carried out by the United States at the Trinity site on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately equivalent to 20 kilotons. The first hydrogen bomb, codenamed “Ivy Mike”, was tested at the Enewetak atoll in the Marshall Islands in November 1952, also by the United States. The largest nuclear weapon ever tested was the “Tsar Bomba” of the Soviet Union at Novaya Zemlya on October 30, 1961, with an estimated yield of around 50 megatons.
In 1963, many (but not all) nuclear and many non-nuclear states signed the Limited Test Ban Treaty, pledging to refrain from testing nuclear weapons in the atmosphere, underwater, or in outer space. The treaty permitted underground nuclear testing. France continued atmospheric testing until 1974, China continued up until 1980. Neither has ever signed the treaty.[1]
The United States conducted its last underground test in 1992, the Soviet Union in 1990, the U.K. in 1991, and both China and France in 1996. After signing the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty in 1996 (which has as of 2012 not yet entered into force), all these states have pledged to discontinue all nuclear testing. Non-signatories India and Pakistan last tested nuclear weapons in 1998. The most recent nuclear test was by North Korea on Feb. 12, 2013.
For a more detailed resource on the history of Nuclear testing, see this United Nations guide,released August 29, 2012, the official ‘International Day Against Nuclear Tests’.
Cooperation of US and Russian scientists helped avoid nuclear catastrophe at Cold War’s end
Former Los Alamos National Laboratory director Siegfried Hecker recounts the epic story of how American and Russian scientists joined forces to avert some of the greatest post-Cold War nuclear dangers.
Hecker is currently a senior fellow at Stanford University’s Center for International Security and Cooperation, and a research professor of Management Science and Engineering.
Flawed Pentagon Nuclear Cruise Missile Advocacy
Hans Kristensen, Federation of American Scientists, writes:
“The Pentagon’s arguments for why the LRSO is needed and why the amendments [to strip funding] are unacceptable are amazingly shallow – some of them even plain wrong.”
Here is a particularly disturbing argument:
“The Kendall letter from March also defends the LRSO because it gives the Pentagon the ability to rapidly increase the number of deployed warheads significantly on its strategic launchers. He does so by bluntly describing it as a means to exploit the fake bomber weapon counting rule (one bomber one bomb no matter what they can actually carry) of the New START Treaty to essentially break out from the treaty limit without formally violating it:
Additionally, cruise missiles provide added leverage to the U.S. nuclear deterrent under the New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty. The accounting rules for nuclear weapons carried on aircraft are such that the aircraft only counts as one weapon, even if the aircraft carries multiple cruise missiles.
It is disappointing to see a DOD official justifying the LRSO as a means to take advantage of a loophole in the treaty to increase the number of deployed strategic nuclear weapons above 1,550 warheads. Not least because the 2013 Nuclear Employment Strategy determined that the Pentagon, even when the New START Treaty is implemented in 2018, will still have up to one-third more nuclear weapons deployed than are needed to meet US national and international security commitments. (more at FAS)
See the DOD letter circulated to Congress in May.
Transcripts Kept Secret for 60 Years Bolster Defense of Oppenheimer’s Loyalty
“…the declassified material, released Oct. 3 by the Energy Department, suggests that Oppenheimer opposed the hydrogen bomb project on technical and military grounds, not out of Soviet sympathies…”
U.S. Had Plans for “Full Nuclear Response” In Event President Killed or Disappeared during an Attack on the United States.
From the Nukevault
Newly declassified document expands limited public record on nuclear “pre-delegation”.
Both USSR and China were to be targeted simultaneously, even if attack were conventional or accidental, and regardless of who was responsible.
LBJ ordered a change in instructions in 1968 to permit more limited response, avert “dangerous” situation.
How A War Game Brought The World To The Brink Of Nuclear Disaster
1983: Once-classified documents show how close Soviet Union came to launching nuclear war
“Chilling new evidence that Britain and America came close to provoking the Soviet Union into launching a nuclear attack has emerged in former classified documents written at the height of the cold war… Cabinet memos and briefing papers released under the Freedom of Information Act reveal that a major war games exercise, Operation Able Archer, conducted in November 1983 by the US and its Nato allies was so realistic it made the Russians believe that a nuclear strike on its territory was a real possibility…”
Russia Has Pulled Out Of The Troubled MOX Project
Russia has given many expliantions for their recent exit from the MOX pact. Overall it is clear that MOX is a “good idea gone bad”. For more see the links below.
Citing “the threat to strategic stability posed by US hostile actions against Russia”. ref
Russia’s Lavrov: Russia’s MOX pact exit is a signal to Washington that: “speaking in the language of sanctions & ultimatums won’t work”
The Russian Non-Proliferation Department’s official reason: The US did not officially inform on planned change of PU disposal method (from MOX plant to WIPP disposal) as required in 2000 pact.
Join the Conversation- PSR Nukebusters Short Film Contest 1st Prize
Physicians for Social Responsibility: This film by Jonathan Deaton won the top award in the Student category. (more award winners)
Studies by Once Top Secret Government Entity Portrayed Terrible Costs of Nuclear War
NESC reports included both Soviet and US first strike scenarios
National Security Archive Electronic Briefing Book No. 480. Posted July 22, 2014.
“The NESC reports on nuclear war were multi-volume, highly classified studies and none has ever been declassified in their entirety. The summaries published here today- for the annual reports from 1957 to 1963- provide a glimpse of the full reports, although important elements remain classified. Besides the summaries and fuller reports for 1962 and 1963, today’s posting includes a number of special studies prepared by the NESC, including an especially secret report requested by President Eisenhower that led to the production of the comprehensive U.S. nuclear war plan in 1960, the Single Integrated Operational Plan (SIOP)…”
Playing Pass the Parcel With Fukushima
“The defilement of Fukushima wasn’t just the result of a natural catastrophe. It was also the aftermath of a manmade disaster caused by a slapdash approach to nuclear safety. Five years on, the Japanese government isn’t handling these issues any more responsibly.”
Read more at Peter Wynn Kirby, NYTimes OpEd
New Push For Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
Since the Senate failure to ratify the CTBT in 1999, significant improvements in monitoring and verification have changed the picture.
High Radiation Forcing a Rethink of Robot Strategy
TEPCO and its network of partner companies at Fukushima Daiichi have yet to identify the location and condition of melted fuel in the three most seriously damaged reactors. Removing it safely represents a challenge unprecedented in the history of nuclear power. Quantities of melted fuel are believed to have accumulated at the bottom of the damaged reactors’ containment vessels, but dangerously high radiation has prevented engineers from accurately gauging the state of the fuel deposits.
TEPCO is now worried that the scorpion robot will not be able to reach the space beneath the pressure vessel, and like its predecessor, will not be able to work for very long in the damaged plant (the scorpion is designed to handle 1,000 total sieverts). The high level of radiation may force TEPCO, a nationally-owned company, to rethink its robot-based strategy for locating the molten fuel. The firm is currently in the early stages of a cleanup that’s expected to last decades. Until TEPCO knows the precise location of the melted fuel, and until it’s able to ascertain the structural damage in each of the three reactors affected, the company won’t be able to decommission the plant and remove the fuel.
New Cruise Missile Capability Debated
By Kingston Reif, Arms Control Association, January/February 2016
“The United States is planning to purchase a new fleet of nuclear-capable air-launched cruise missiles (ALCMs) that will be far more advanced than the ones they are slated to replace, according to members of Congress and other sources, raising questions about the plan’s consistency with a pledge made by the Obama administration not to provide nuclear weapons with new capabilities.
“The development of the new missile also has sparked a debate about whether it could be more ‘usable’ than the existing ALCM, thereby lowering the threshold for when the United States might consider using nuclear weapons.In a Dec. 15 letter to President Barack Obama urging him to cancel the new cruise missile, also known as the long-range standoff weapon, Sen. Ed Markey (D-Mass.) and seven other senators wrote that the ‘proposed missile is a significantly altered version’ of the existing ALCM. The letter did not say what specific capabilities the new missile would provide, but claimed the proposal contradicts the policy statement from the 2010 ‘Nuclear Posture Review [NPR] Report’ that efforts to sustain U.S. nuclear weapons ‘will not support new military missions or provide for new military capabilities.’
Advocates of the new missile argue that it provides a continuing ability to quickly add missiles to bombers. They note that the New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty does not cap the number of weapons that can be carried on each bomber.
The source said the technical characteristics of the new missile are still being defined because the program is still in the early development stage but that the goal is to increase the range and accuracy of the missile. The source said another goal is to incorporate the latest stealth features, making the missile much more difficult for adversary air defense systems to detect.
Regarding the proposed life extension program for the ALCM warhead, known as the W80-4, the source who has been briefed said a goal of that program is to permit ‘greater flexibility in actually picking’ the desired yield. The ALCM warhead is believed have a built-in option to allow detonation at lower or higher yields.
According to the source, increasing the accuracy of the missile allows for more flexibility in the warhead yield, thus enhancing the overall capability of the weapons system.
The source said the briefings made it clear that the Pentagon is envisioning potential uses for the new cruise missile that go beyond ‘the original mission space’ of the ALCM.
For example, the source said that, in the event of a major conflict with China, the Pentagon has talked about using the new missile to destroy Chinese air defenses as a warning to Beijing against escalating the conflict further.”
Cruise Control
“Franklin Miller, a veteran nuclear strategist now at the Scowcroft Group, points out that Mr Obama would never have persuaded the Senate to ratify the New START treaty in 2010 had he not pledged to renew America’s nuclear weapons on land, sea and in the air. That agreement allows for what is known as the ‘bomber discount’, which counts an aircraft carrying several bombs as a single warhead. The LRS-B (the upcoming Long-Range Strike Bomber) will be able to carry internally a payload of cruise missiles, the new B61-12 bombs or a smaller stand-off missile with a conventional warhead. It is improbable that any president would forgo that option while Russia retains it.”
The Case of Lockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin manages the Nevada National Security Site, Sandia National Laboratories, together with Bechtel The Y-12 National Security Site, and the Pantex Plant in Texas.
Last fall, Washington Business Journal reported that
“if anyone is benefitting from the unease between Russia and the rest of the world, it would have to be Bethesda-based Lockheed Martin Corp. (NYSE: LMT). The company is positioned to make large profits off what could very well be an international military spending spree by Russia’s neighbors.”
DOE: IG Sheds More Light on Lobbying for Sandia Contract
“Yesterday, the department’s inspector general released a revised special inquiry report with fewer redactions in response to an appeal under the Freedom of Information Act. The new document is still heavy with white out but does show more of who was helping Sandia as well as who they were trying to influence on Capitol Hill and the Obama administration…”
Mr. President, Kill the New Cruise Missile
The open letter that kick-started the debate:
Former Secretary of Defense Perry and Former Ass’t Secretary of Defense Weber to Obama:
“Because they can be launched without warning and come in both nuclear and conventional variants, cruise missiles are a uniquely destabilizing type of weapon.
Two years ago, when Britain decided not to pursue a sea-launched nuclear cruise missile, Philip Hammond, then-British defense secretary and now-foreign secretary, explained the problem well: ‘A cruise-based deterrent would carry significant risk of miscalculation and unintended escalation. At the point of firing, other states could have no way of knowing whether we had launched a conventional cruise missile or one with a nuclear warhead. Such uncertainty could risk triggering a nuclear war at a time of tension.
One of us (William J. Perry) led the Defense Department’s development and procurement of the current air-launched cruise missile and the B-2 stealth bomber in the late 1970s and early 1980s. At that time, the United States needed the cruise missile to keep the aging B-52, which is quite vulnerable to enemy air defense systems, in the nuclear mission until the more effective B-2 replaced it. The B-52 could safely launch the long-range cruise missile far from Soviet air defenses. We needed large numbers of air-launched nuclear cruise missiles to be able to overwhelm Soviet air defenses and thus help offset NATO’s conventional-force inferiority in Europe, but such a posture no longer reflects the reality of today’s U.S. conventional military dominance.
With the updated B-2 and B61 expected to remain in service for many decades, and the planned deployment of new B-3 penetrating bombers with B61 bombs starting in 2025, there is scant justification for spending tens of billions of dollars on a new nuclear air-launched cruise missile and related warhead life-extension program.
We therefore urge President Obama to cancel the current plan to develop and buy 1,000 to 1,100 new nuclear-capable air-launched cruise missiles. Such strong U.S. leadership, coupled with a challenge to the other major nuclear powers to eliminate or, in the cases of China and India, forgo deployment of this extremely destabilizing class of weapons, would reduce the risk of nuclear weapons use and be a historic practical step in the direction of a world without nuclear weapons.”
– William J. Perry and Andy Weber from Mr. President, Kill the New Cruise Missile
William J. Perry was U.S. secretary of defense from 1994 to 1997. Andy Weber was assistant secretary of defense for nuclear, chemical and biological defense programs from 2009 to 2014.
The Pope and the Bomb: Bishop Oscar Cantú Remarks
Bishop Oscar Cantú, Chairman, Committee on International Justice & Peace, U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops, at “The Pope and the Bomb: New Nuclear Dangers and Moral Dilemmas” event on September 17, 2015, with moderator E.J. Dionne Jr., Washington Post columnist, former Sen. Sam Nunn, NTI Co-Chairman and CEO, and Prof. Maryann Cusimano Love, Associate Professor of International Relations, The Catholic University of America.
The 10 Worst Things About Lockheed Martin’s Alleged Lobbying Fraud
Note that five of the ten “Worst Things” directly involve New Mexico’s ex-Congresswoman Heather Wilson. (read more)
Nukewatch’s Jay Coghlan adds these remarks in regard to Heather Wilson:
Ex-Congresswoman Heather Wilson was appointed by John Boehner to be on the Congressional Advisory Panel on the Governance of the Nuclear Security Enterprise. In December 2014 the Panel came out with its long awaited report, “A New Foundation for the Nuclear Enterprise”, which benefited the contractors. For example, it argued for diminished federal oversight over contractors, which flies in the face of reality (e.g., constant cost overruns, WIPP, Y-12 security incident, etc., etc.)
Perhaps most alarmingly, the Panel recommended that congressional oversight be strengthened by having the DOE Secretary report to the Senate Energy and Natural Resources and Armed Services Committees, and to the House Energy and Commerce and Armed Services Committees. This would likely have the opposite effect, as it seems to preclude the traditional jurisdiction of the House and Senate Energy and Water Development Appropriations Subcommittees, which have provided key oversight in the past, and have often cut certain nuclear weapons programs.
I publicly called on Heather Wilson to resign from that Panel because of her conflict-of-interests. She did not. To add insult to injury, the co-chair of the Panel is Norm Augustine, ex-CEO of Lockheed Martin. LM’s tentacles are very widespread.
- Lockheed Martin had $32 billion in federal contracts in 2014 (classified projects unknown). (ref) and (API)
- This included $28 million for IRS data management. (ref)
- In the nuclear weapons complex, in addition to Sandia Labs it runs the combined Y12-Pantex nuclear weapons production contract ($2 billion requested in FY 2016) with Bechtel, as Consolidated Nuclear Security, LLC.
- Between 2008 and 2015 Lockheed Martin had 169,345 contracts with the US government, worth $293 billion. (ref)
See more at Charles Tiefer’s outstanding article at Forbes
Sandia Corporation Agrees To Pay $4.7 Million To Resolve Allegations Related To Lobbying Activities
Lockheed Martin gets slap on the wrist for lobbying violations in Sandia Labs contract extensions.
Watchdogs Denounce Slap on Wrist for Illegal Lobbying Activities By the World’s Biggest Defense Contractor- and Demand Real Accountability by Barring Lockheed Martin From Future Sandia Labs Contract
Nuclear Watch New Mexico denounces the $4.7 million settlement agreement as a slap on the wrist for the world’s biggest defense contractor. Lockheed Martin clearly broke the law by engaging in illegal lobbying activities to extend its Sandia contract without competition, and engaged in deep and systemic corruption, including paying Congresswoman Heather Wilson $10,000 a month starting the day after she left office for so-called consulting services that had no written work requirements. There should be criminal prosecutions for clear violations of federal anti-lobbying laws, and Lockheed Marin should be barred from future competition for the Sandia Labs contract, expected next year.
View full press release (PDF)
View Department of Justice’s settlement agreement (PDF)
View Rep. Heather Wilson’s contract and invoices pursuant to our FOIA request (PDF)
More on the New Nuclear Cruise Missile
Russia is Proving Why Nuclear-Tipped Cruise Missiles Are a Very Bad Idea
“Those four cruise missiles that crashed in Iran could’ve been carrying nuclear warheads- which is why the US should ban them, not renew them.”
…inherently ambiguous… can add major risks to a crisis… In 2007, six nuclear-armed cruise missiles were mistakenly loaded onto a B-52 bomber and flown across the United States. Because nuclear-armed cruise missiles are virtually indistinguishable from conventional ones, the error went undetected for 36 hours..”
-Tom Collina and William Saetren, Ploughshares Fund.
Jan. 13: Just How New is the New, Nuclear-armed Cruise Missile?
“Deploying the planned new nuclear-armed cruise missile will actually make the United States less secure. Known as the Long-Range Standoff Weapon, or LRSO, it will be significantly more capable than the existing nuclear-armed air-launched cruise missile (ALCM). And for just that reason, by demonstrating that the United States sees this weapon as a valuable military tool, it will undermine higher priority U.S. security goals. Specifically, pursuing the LRSO ignores the reality that nuclear weapons are no longer a security asset for the United States, but a liability that should be constrained.” –Stephen Young, Sr. Analyst, Union of Concerned Scientists
Dec. 15: Eight Senate Democrats, including three members of the Senate Appropriations Committee, sent a letter to President Obama urging him to terminate the Air Force’s plans for its next-generation air-launched cruise missile. Read More
LRSO: The Nuclear Cruise Missile Mission
“It seems clear from many of these statements that the LRSO is not merely a retaliatory capability but very much seen as an offensive nuclear strike weapon that is intended for use in the early phases of a conflict even before long-range ballistic missiles are used.” – Analysis by FAS/Hans Kristensen
- Who Needs a New Nuclear Air-Launched Cruise Missile Anyway?- Steven Pifer, Brookings
- Overkill: The Case Against a New Nuclear Air-Launched Cruise Missile- Kingston Reif/ACA
- You’re NUTS: New Nuclear Cruise Missiles are Inherently Destabilizing
- New Nuclear Cruise Missile Won’t Control Escalation, Will Erode Stability
New York City, 1982: One Million Rally for Nuclear Freeze
On June 12, 1982, one-million concerned citizens gathered in Central Park in New York in an unprecedented call for “the United States and the Soviet Union . . . to adopt a mutual freeze on the testing, production, and deployment of nuclear weapons.” A few months later, Freeze referenda were on the ballots in 9 states and dozens of major cities. Across the nation some 18 million Americans voted on the Freeze in the fall of 1982, with some 10.7 million, or 60 percent, voting in favor.
As Congressman Ed Markey (D-Mass.) said years later:
“It was the closest our country has ever come to a national plebiscite on nuclear arms control. Within a very brief time the freeze had taken education at the grassroots and translated it into political muscle at the ballot box, delivering to the White House a resounding vote of no confidence in its nuclear buildup.”
The Nuclear Bomb Industry is Booming
The Center for Investigative Reporting and PRX hit hard at the fishy collusions in the military-industrial-congressional complex, and the results in the nuclear arsenal, like the new B61-12 nuclear bomb.
To listen to the podcast click here
See also: A Revolving Door in the Nuclear Weapons Industry
Infographic- Back and forth through the nuclear revolving door: Augustine, Wilson, Tauscher, Cook, Mies, Lyons.
Busted: Lockheed’s Sandia Corp Illegally Lobbied Key Congress Members With Federal Funds to Block Competition For Lucrative Contract
The complete DOE IG November 2014 investigation report has now been released to The Center for Public Integrity following their FOIA request.
CPI has come out with a hard-hitting article about illegal lobbying by the world’s biggest defense contractor, Lockheed Martin, to extend its management contract of the Sandia Labs.
This report peels back part of the veil surrounding a defense corporation’s “capture strategy” for the Obama administration.
Last November Inspector General Gregory Friedman issued his report on the Special Inquiry into “Alleged Attempts by Sandia National Laboratories to Influence Congress and Federal Officials on a Contract Extension”. The full report was designated “For Official Use Only” and given exclusively to the contractor; but a summary was released which outlined the case against Lockheed and Sandia Corp, including the payments made from public funds to then just-retired Congresswoman Heather Wilson for ‘consulting services’.
Now, The Center for Public Integrity has obtained the full report through a FOIA request. In it, Inspector General Friedman writes:
“We recognize that Lockheed Martin Corporation, as a for-profit entity, has a corporate interest in the future of the Sandia Corporation contract. However, the use of Federal funds to advance that interest through actions designed to result in a noncompetitive contract extension was, in our view, prohibited by Sandia Corporation’s contract and Federal law and regulations.”
“Given the specific prohibitions against such activity, we could not comprehend the logic of using Federal funds for the development of a plan to influence members of Congress and federal officials to, in essence, prevent competition.”
And in a phrase that did not appear in the November public summary:
“Perhaps [Sandia National Laboratories] felt empowered because it had improperly directed Federal funds to similar activities in the past.”
Nuclear News Archives – 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nuclear News Archives – 2020
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nuclear News Archives – 2019
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nuclear News Archives – 2018
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.