QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
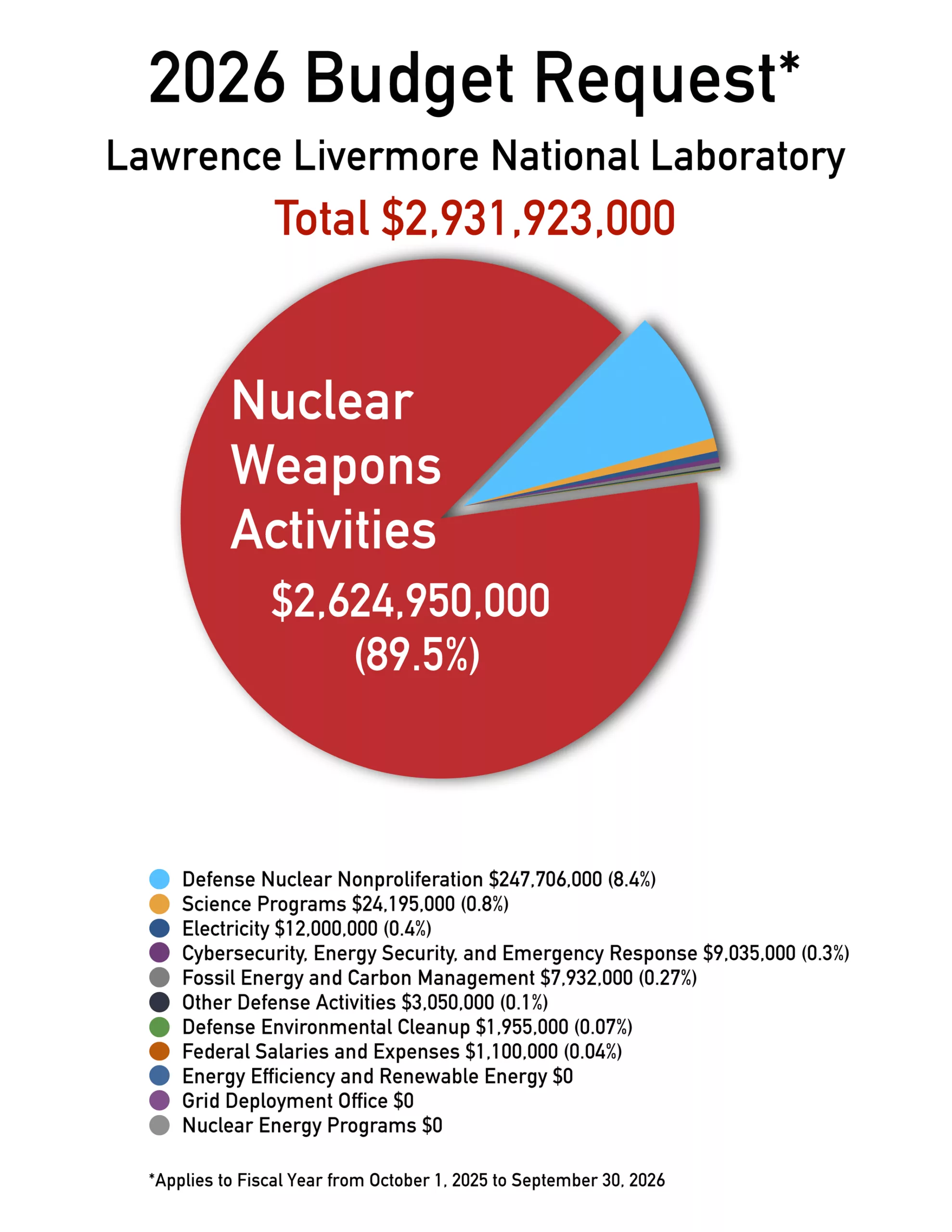
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
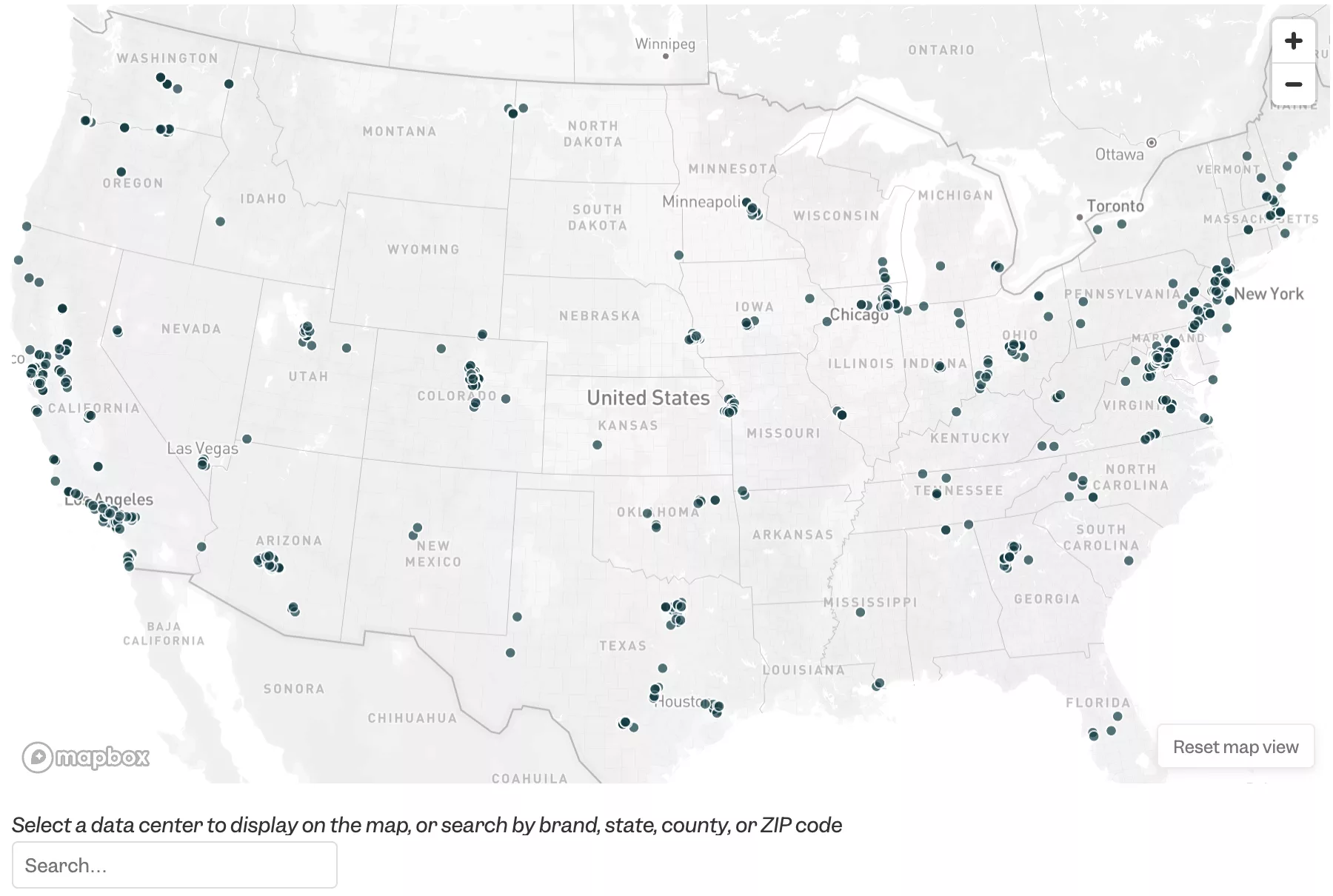
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
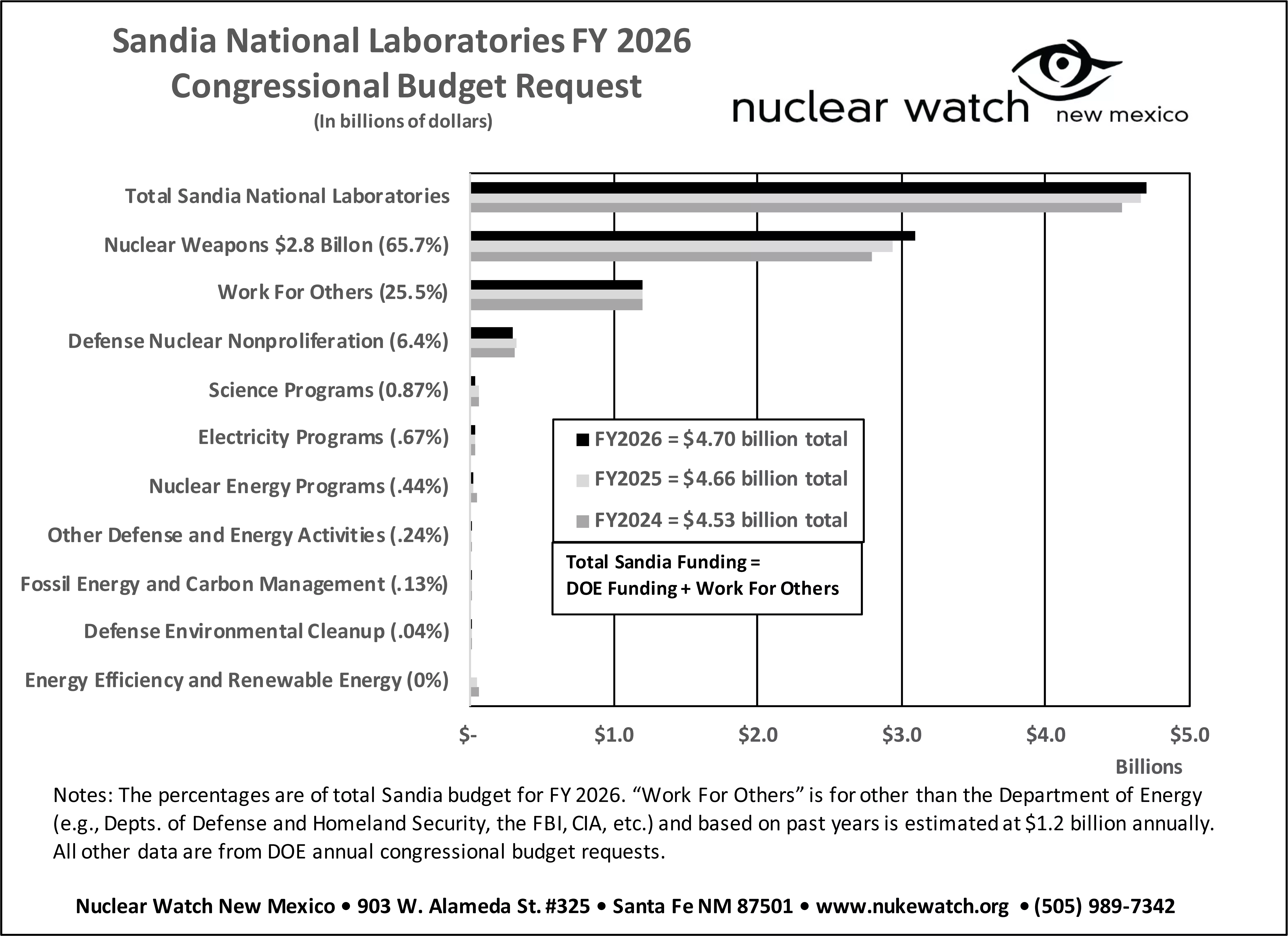
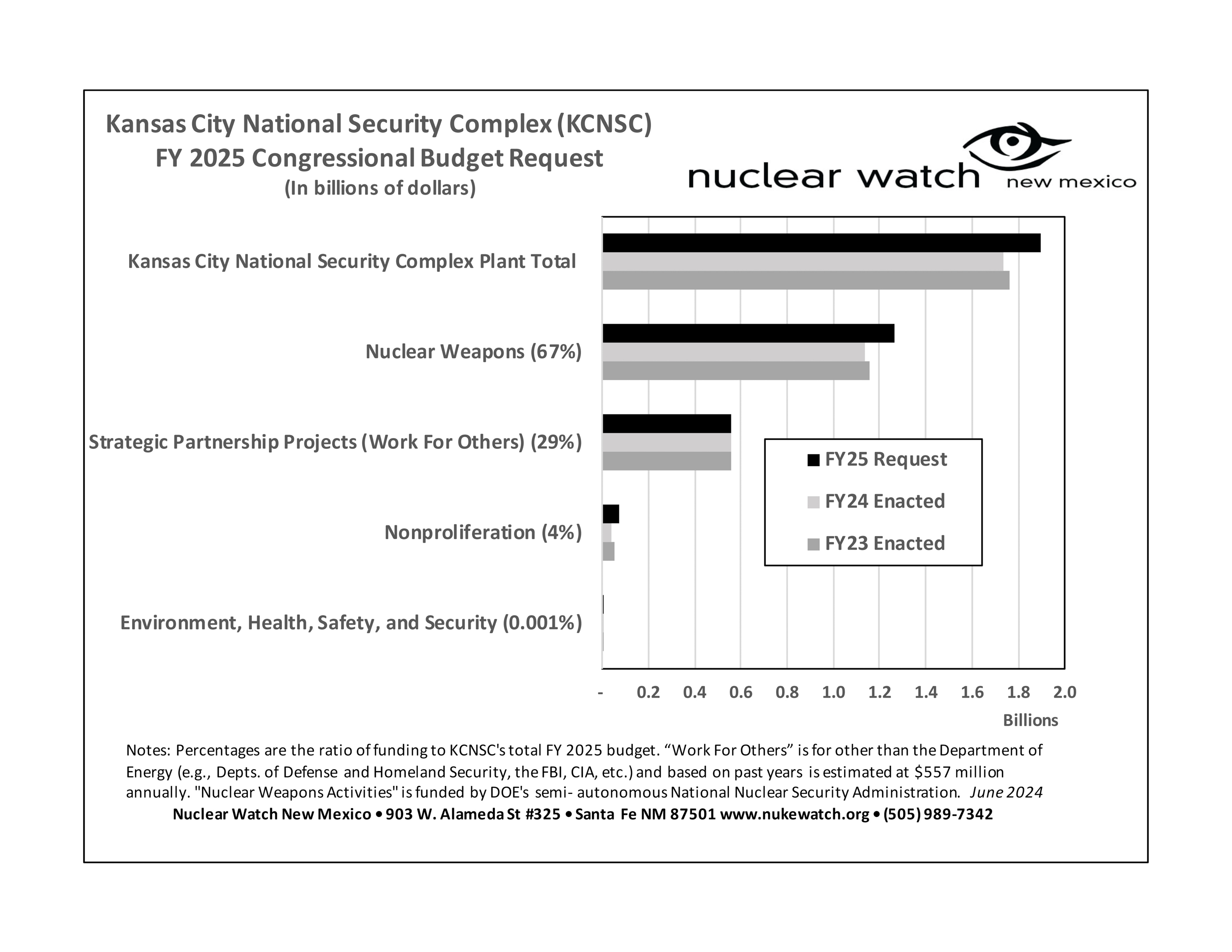
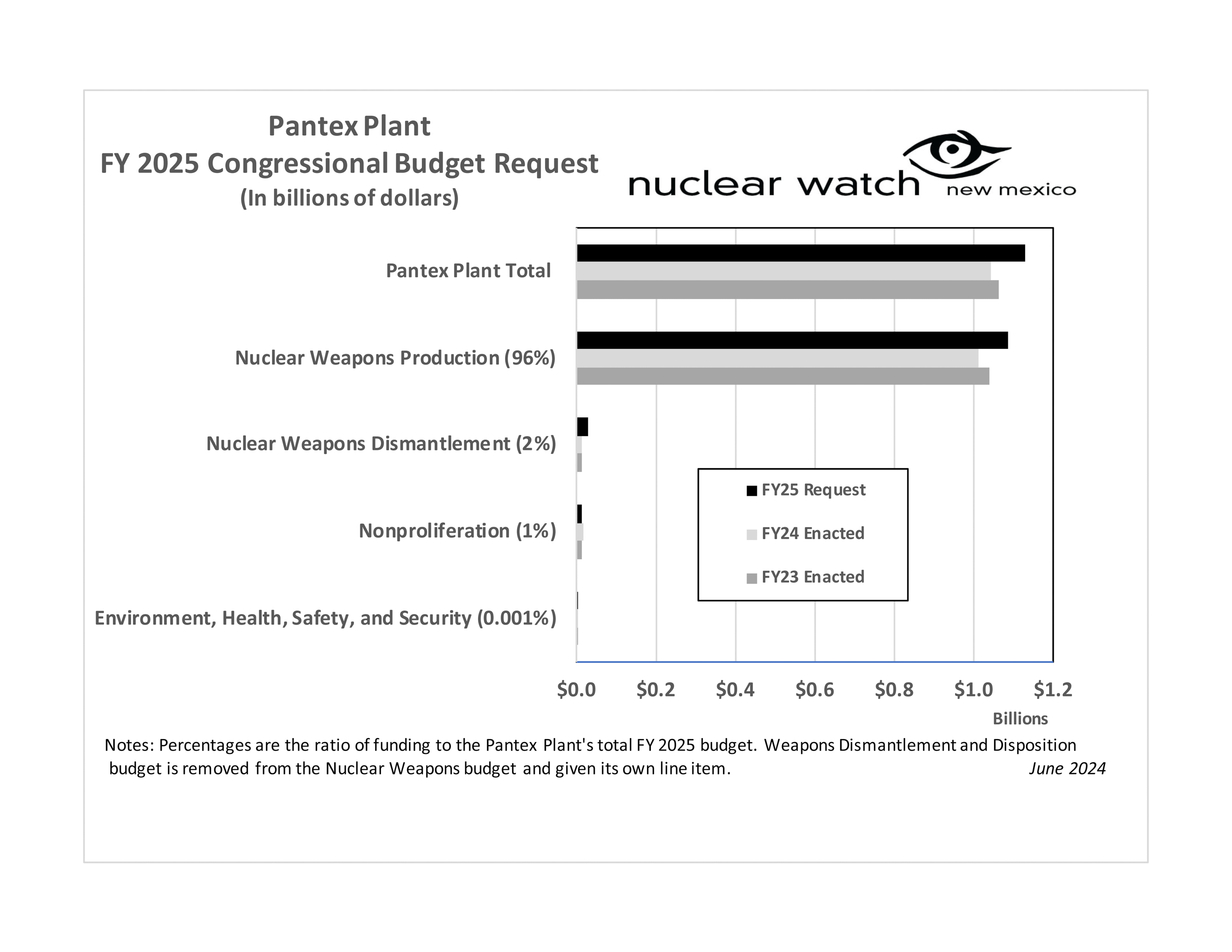
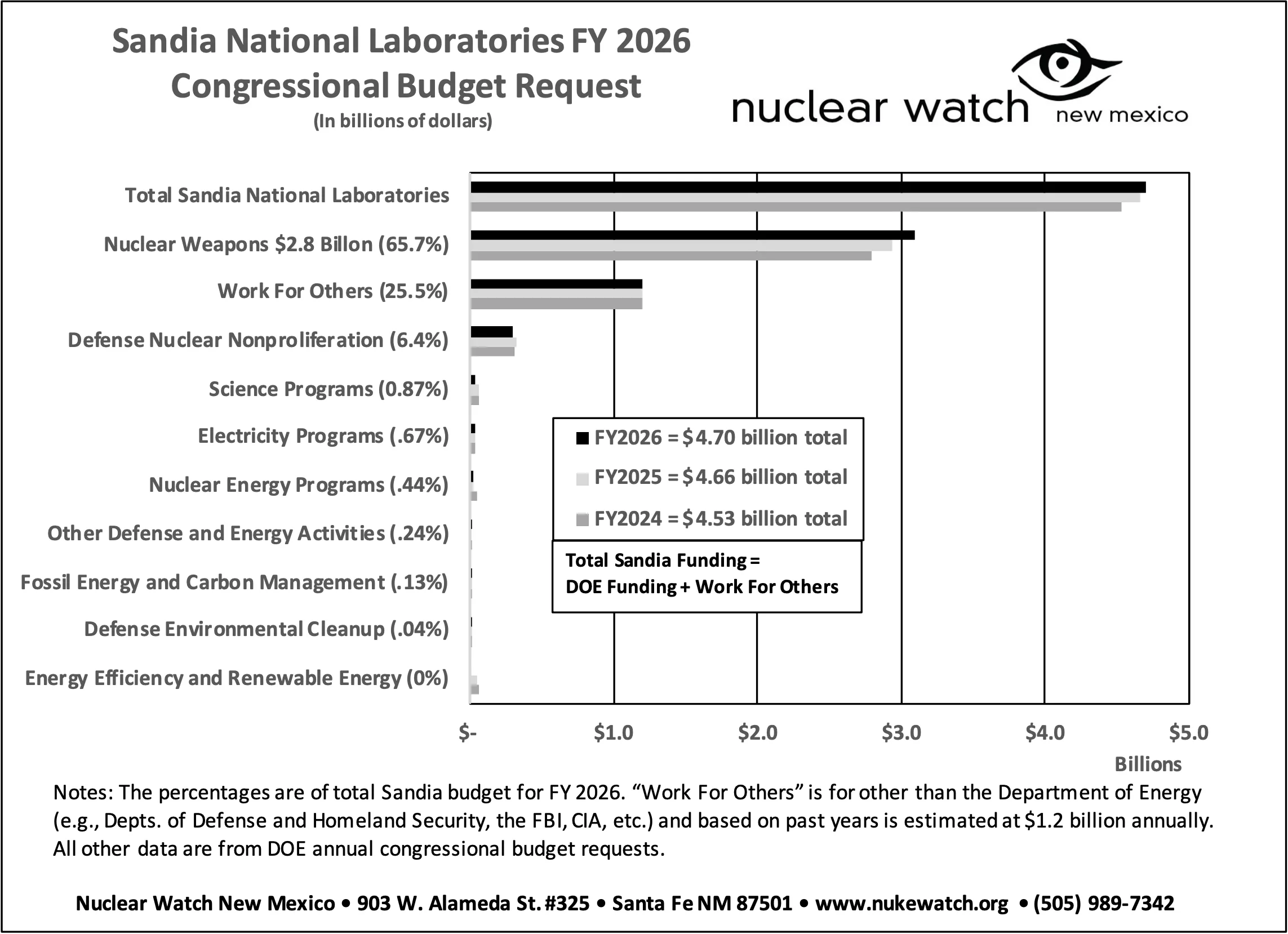
Planned Nuclear Weapons Activities Increase to 84% of Lab’s Budget; All Other Programs Cut
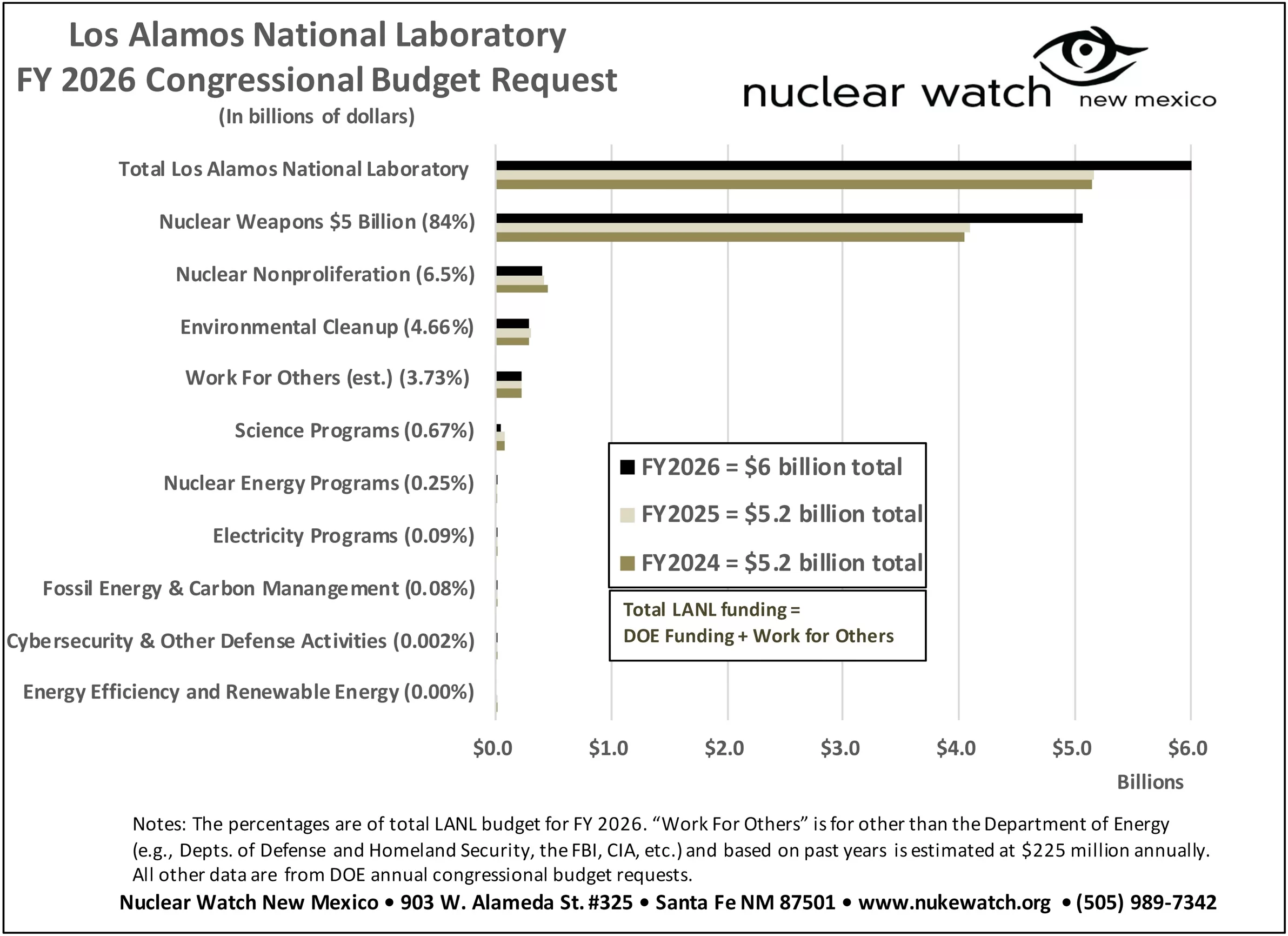
The Department of Energy and Los Alamos National Laboratory have released the LANL congressional budget request for the upcoming fiscal year, 2026, which begins on October 1, 2025. The request shows a continued major increase and expansion of the plutonium pit production program (plutonium pits are the triggers of nuclear weapons). LANL is frantically trying to increase its capabilities to begin making 30 pits per year by 2028.
NukeWatch created the attached chart to give a visual of how taxpayer dollars are annually spent at the Lab. LANL’s FY 2026 total budget request is $6 billion, which is a 17% increase over the FY 2025 $5.2 billion total budget. This includes a 24% increase in the nuclear weapons budget over FY 2025.
Continue reading
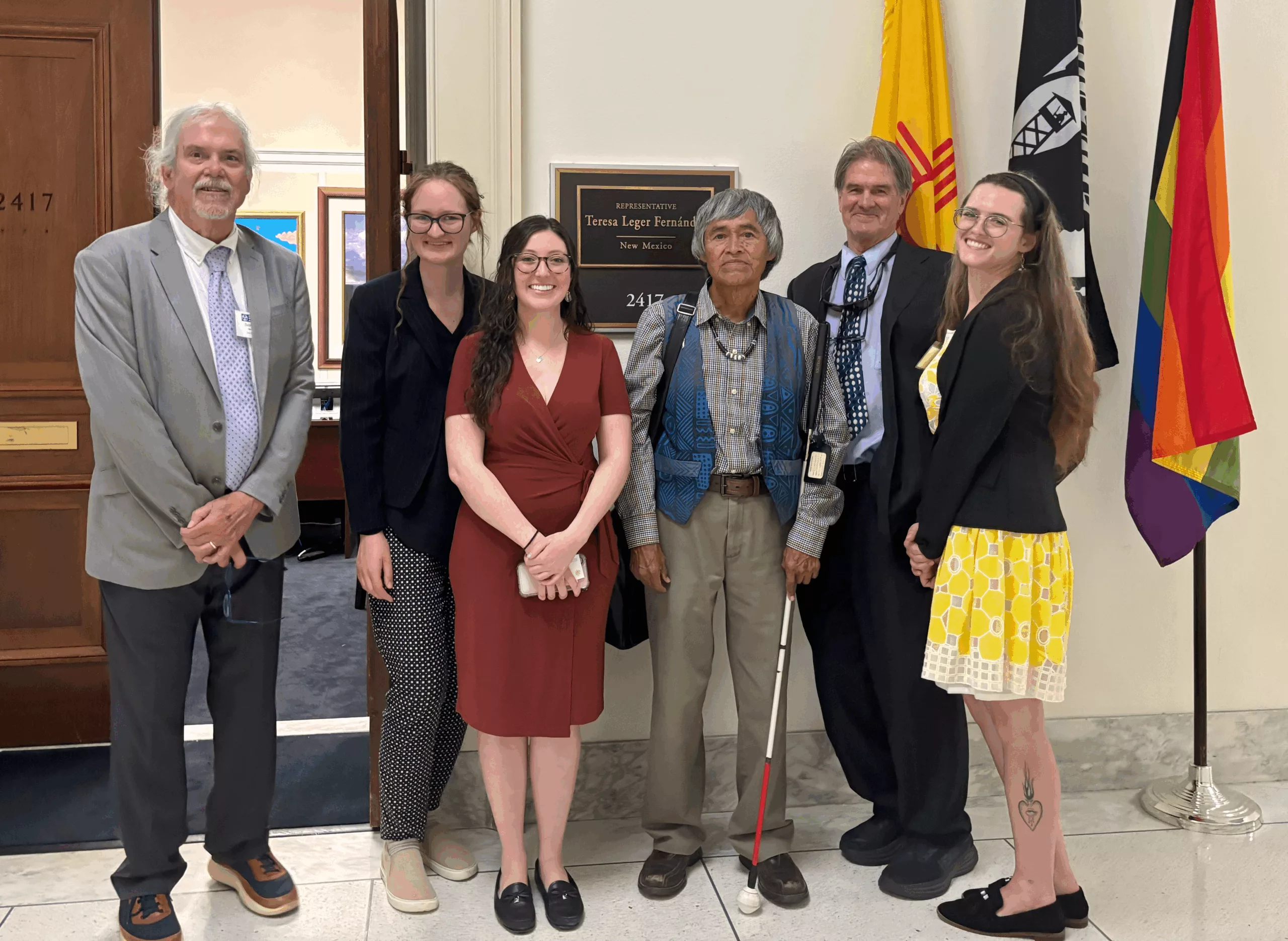
NukeWatch in DC Advocating for Nuclear Disarmament and Non-Proliferation
Your Nuclear Watch New Mexico team has just returned from a weeklong trip to Washington D.C. (we went so you don’t have to!). The Alliance for Nuclear Accountability (ANA) hosts an annual “DC Days” conference and following Spring Meeting, and we proudly joined as part of a record number of groups this year. Over 60 individuals from 30+ organizations journeyed to DC to advocate for nuclear weapons disarmament, nuclear energy, and waste policy on behalf of the frontline nuclear communities we represent. Members were present from groups representing the entire U.S. nuclear complex, including sites in Georgia, New Mexico, Tennessee, California, Missouri, Colorado, Idaho, Nevada and beyond. NukeWatch NM brought all three staff members—Jay Coghlan, Scott Kovac, and Sophia Stroud (whose participation was made possible by a youth scholarship from ANA)—to participate in DC Days and the subsequent two-day spring meeting. The ANA DC Days schedule included over 70 meetings with senators, representatives, and other relevant agencies, such as the Department of Energy, the Government Accountability Office, and the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board. Our NukeWatch team attended nearly 30 of these meetings. The Alliance for Nuclear Accountability put together a new report to present our “asks” to congress as a coalition, including analysis and recommendations for nuclear weapons, nuclear waste, and nuclear energy policy and funding. Please click HERE for the full report, and HERE for a short summary.
I was glad to see increased representation from Nevada this year, and especially Indigenous representation. In light of the current administration’s attacks on Environmental Justice, it is more important than ever that ANA as a whole, as well as individual member groups, continue to prioritize uplifting Native American voices, not only because of their deep cultural, spiritual, and social connections to the land, including sacred sites and traditional knowledge essential to religious freedom and access, but also because of the violent legacy and ongoing reality of nuclear colonialism, in which Indigenous lands and peoples have been deliberately and disproportionately targeted in the nuclear industry with uranium mining, nuclear weapons testing and production, and the disposal of radioactive waste. To learn more about Nuclear Colonialism, see: www.networkadvocates.org/downwinders and read Nuclear Nuevo México: Colonialism and the Effects of the Nuclear Industrial Complex on Nuevomexicanos by Myrriah Gómez.
THE ATOMIC BOWL: Football at Ground Zero —and Nuclear Peril Today
First prize, Best Documentary Feature, International Uranium Film Festival, Rio de Janiero
Coming to PBS in July 2025. (53-minute and 27-minute versions).
There have been numerous films on The Bomb, even one or two about Nagasaki, but “The Atomic Bowl: Football at Ground Zero — and Nuclear Peril Today” is unique, and with many lessons and warnings for today–as nuclear dangers proliferate and civilian casualties in wars climb even higher.
This football showdown featured college and pro stars, on January 1, 1946, and in (of all places) Nagasaki, near ground zero for the second atomic bomb, which killed over 80,000 just a few weeks earlier. The film, narrated by Peter Coyote, is not only the first full first-hand account of the game, but a provocative and disturbing story of the decision to drop a second atomic bomb just three days after Hiroshima–and the dangerous message to today’s leaders. Nearly all of the victims of the “forgotten bomb” were women and children and other civilians.
This important film, which includes rare footage and dozens of never published photographs, then offers a convincing argument about the relevance of Nagasaki today as mass civilian casualties in wars surge and nuclear dangers by all estimates grow every year.
Its writer and director Greg Mitchell has been one of the world’s leading authorities on the atomic bombings for several decades, and his recent film, “Atomic Cover-up,” won several awards, including the top prize from the Organization of American Historians and was aired via PBS. His two other recent films, “The First Attack Ads” and the award-winning “Memorial Day Massacre,” also earned PBS distribution (as well as Emmy nods), and like “The Atomic Bowl” were produced by Academy Award nominee Lyn Goldfarb.
Victory! Proposed Tritium Venting by LANL Halted for Now Due to Community Pressure
Proposed Tritium Venting by Los Alamos National Lab Postponed Indefinitely after Community Pressure
THANK YOU to the over 2,500 of you who signed our Petition to Deny LANL’s Request to Release Radioactive Tritium into the Air!
A massive thank you as well to our fellow campaigners we worked alongside on this issue, Tewa Women United and Concerned Citizens for Nuclear Safety, and of course thank you as well to NMED Secretary Kenney for listening to our community.

From Tewa Women United:
Beloved Community, we have some really good news!
Our Environmental Justice team has finally received the response from the New Mexico Environmental Department regarding the LANL/DOE/NNSA request for temporary authorization to begin venting tritium this summer. The short story: **Secretary Kenney (NMED) says that NMED will not act on the temporary authorization request** until the following criteria is met:
1. independent technical review
2. public meeting
3. tribal consultation (in addition to NMED tribal consultation)
4. compliance audit
These criteria must be met and LANL/DOE/NNSA must submit an updated request before NMED will revisit and make a decision.
The Workers, the Waste, and the Warnings from Bomb Country
“From South Carolina to California, locals in nuclear weapons towns raise health, safety, and environmental concerns over renewed plutonium pit manufacturing.”
By: Taylor Barnes | June 12, 2025 inkstickmedia.com
The United States’ plans to restock its entire nuclear weapons arsenal, known in military parlance as nuclear “modernization,” hit a bump in the road in January. A scrappy coalition of grassroots watchdog groups and impacted communities from places like the Gullah/Geechee sea islands off the Georgia and South Carolina coasts and San Francisco Bay Area neighborhoods near a weapons laboratory sued the government agency that oversees the security of the US nuclear weapons complex.
The plaintiffs argued that the government was moving ahead with plans to produce new plutonium pits for warheads at plants in rural South Carolina and the Los Alamos laboratory in New Mexico without properly evaluating alternatives under the National Environmental Policy Act. A federal judge agreed, and the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) settled with the grassroots groups, agreeing to perform a multi-year environmental analysis.
The extensive environmental impact study is a rare speed bump that everyday Americans have been able to place in the way of the 21st century’s new nuclear arms race — and one that forces the government to hear from locals in the specific communities across the country that produce parts for the weapons.
“A nuclear arms race can feel abstract and distant, but it very much isn’t,” Ravi Garla, a consultant for the Nuclear Threat Initiative, told Inkstick. Garla recently worked on a campaign that led to a unanimous vote in the Nevada state legislature to oppose any resumption of explosive nuclear tests at a desert site outside Las Vegas where the government carried out more than 900 tests during and after the Cold War.
Top photo: A billboard by an advocacy group opposed to nuclear weapons testing in Nevada (Courtesy of Nevadans Against Nuclear Weapons Testing)
NNSA’s Nuclear Weapons Programs Slated for 53% Increase
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, June 3, 2025
Contact: Jay Coghlan – 505.989.7342 | Email
Santa Fe, NM – Topline budget figures for the Department of Energy (DOE) have been released under the headline of “Unleashing a Golden Era of Energy Dominance and Energy Innovation and Protecting the Nation.” But as a baseline, 65% of the Department’s proposed $46 billion budget is earmarked for its semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). In turn, more than 80% of NNSA’s proposed FY 2026 funding is for its nuclear weapons research and production programs, with a 25% funding increase over FY 2025.
But that is not all. The Trump Administration is adding another $4.8 billion from so-called “reconciliation” funding, bringing NNSA’s “Total Weapons Activities” to just under $30 billion. Taken together, this is a 53% increase above FY 2025 for NNSA’s nuclear weapons research and production programs. To help pay for this, nonproliferation and cleanup programs are being cut by 5%, science by 14%, cybersecurity and emergency response by 25%, and energy efficiency and renewable energy programs by 74%.
TELEVISION EVENT Trailer
Television Event is a documentary that follows the dramatic (and sometimes humorous) making and impact of the film The Day After. The 1983 film played a pivotal role in shifting public consciousness around nuclear weapons and, ultimately, President Reagan’s policies. It’s a reminder on the power of art and storytelling to create meaningful change.
The documentary was also reviewed in The New York Times: https://www.nytimes.com/2025/05/30/movies/the-day-after-documentary-television-event.html
More:
In 2023 a book was publishedd about the making of “The Day After”, read the review in Arms Control Today: https://www.armscontrol.org/act/2024-03/book-reviews/apocalypse-television-how-day-after-helped-end-cold-war
As well as: “‘The Day After’: The Arms Control Association’s Forgotten Role.” <https://www.armscontrol.org/act/2019-03/features/day-after-arms-control-associations-forgotten-role> It is a reminder that a few people can, with some luck and good timing, put big things into motion.
Full Recording: Second Scoping Hearing for NNSA’s Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement on Plutonium Pit Production
Operation Crossroads: “The World’s First Nuclear Disaster”
“With Trump back in office, the recurring question of the need for nuclear weapons testing has resurfaced in the national security debate. Project 2025’s directive that the US return to ‘immediate test readiness’ raises further alarm, given the primacy of that document in Trump’s circle. The general uncertainty around current U.S. nuclear posture gives added weight to the historical importance of the atmospheric and underwater nuclear weapons tests conducted on the Bikini Atoll, recounted here by one of the leading advocates for public safety in the nuclear age. —Ed.”
By Robert Alvarez | Washington Spectator, National Security | May 29, 2025, washingtonspectator.com
Beginning in the late 1970’s, I was working for the Environmental Policy Institute around the time when atomic veterans started to descend on the nation’s capital. I would arrange meetings with Congressional offices, and the offices of both the Defense Nuclear Agency and Veterans Affairs, to enable the veterans to share their experiences and seek justice for being sent in harm’s way. About 250,000 soldiers, sailors, Marines, Coast Guard men, and airmen took part in atmospheric nuclear weapons tests from 1945 to 1963.
John Smitherman and Anthony Guarisco were 17- and 18-year-old sailors, respectively, in July of 1946, when they took part in “Operation Crossroads”—the first two nuclear weapons tests following World War II. These tests were conducted on the Bikini Atoll of the Marshall Islands and codenamed “Able” and “Baker.”
As a result of this extraordinary indifference to lethal danger, some 200 U.S. Navy ships were contaminated, and ships carrying radioactive fallout subsequently sailed to home ports in California. These ports are still being cleaned up today, nearly 80 years later. Glenn Seaborg, the chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission from 1961 to 1971, described the Baker test as “the world’s first nuclear disaster.”
Anthony and John were part of the U.S. Navy’s Pacific fleet involving 40,000 service men and 2,000 civilians. They along with others swam in the heavily contaminated Bikini Lagoon. When I met them in 1980, John was suffering from lymphatic cancer and Anthony from a severe form of spinal arthritis.
In March 1983, Anthony and his wife Mary showed up at my cluttered office and ceremoniously handed me a large stack of documents. They had just visited the UCLA library in Los Angeles and found boxes of forgotten, declassified documents belonging to Dr. Stafford Warren, the chief safety officer during both the Manhattan Project and the 1946 Crossroads tests.
Full Recording: First Scoping Hearing for NNSA’s Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement on Plutonium Pit Production
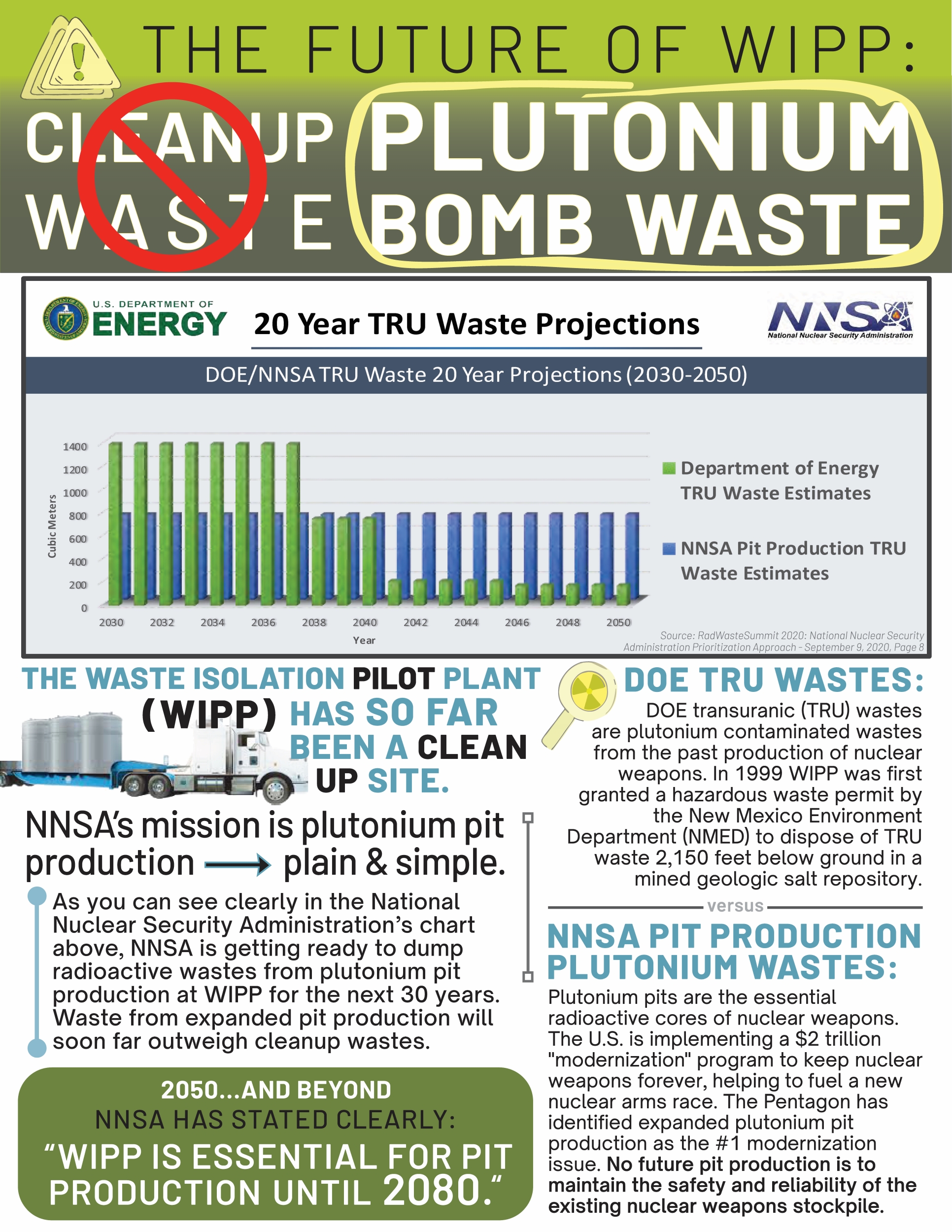
NEW Report on Plutonium Pit Production from the Union of Concerned Scientists
Today, UCS is releasing a comprehensive report on plutonium pit production. It includes a technical assessment of plutonium aging, a critical look at the weapons programs that new pits are slated for, and suggestions for alternatives, including pit re-use.
The final chapter of the study is on the human and environmental impacts of pit production and is intended as a tool for local advocacy groups to deepen their own work around issues such as the programmatic environmental impact survey that has just kicked off.
Links to the report:
https://www.ucs.org/resources/plutonium-pit-production
Spanish language executive summary:
https://es.ucs.org/recursos/la-produccion-de-nucleos-de-plutonio
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com