QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
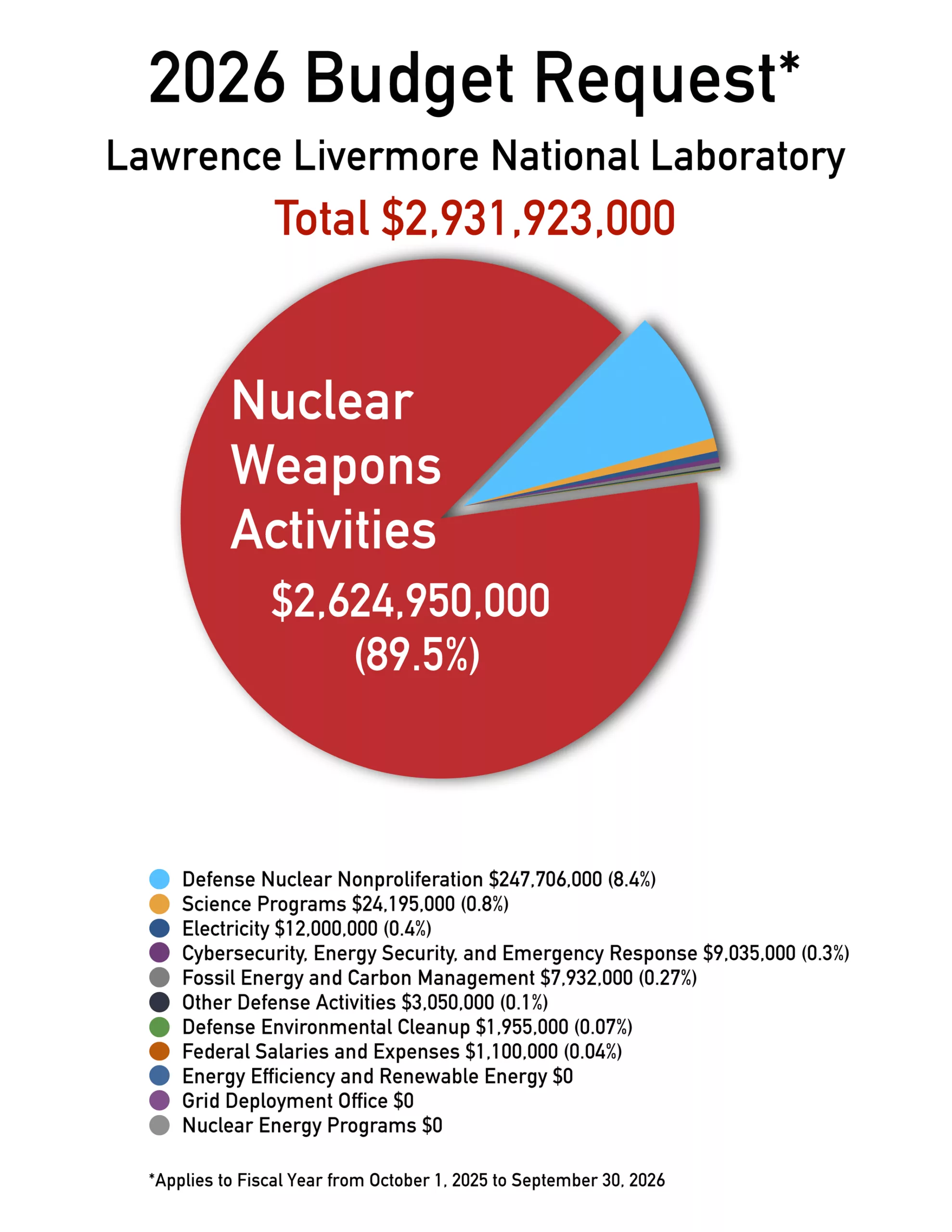
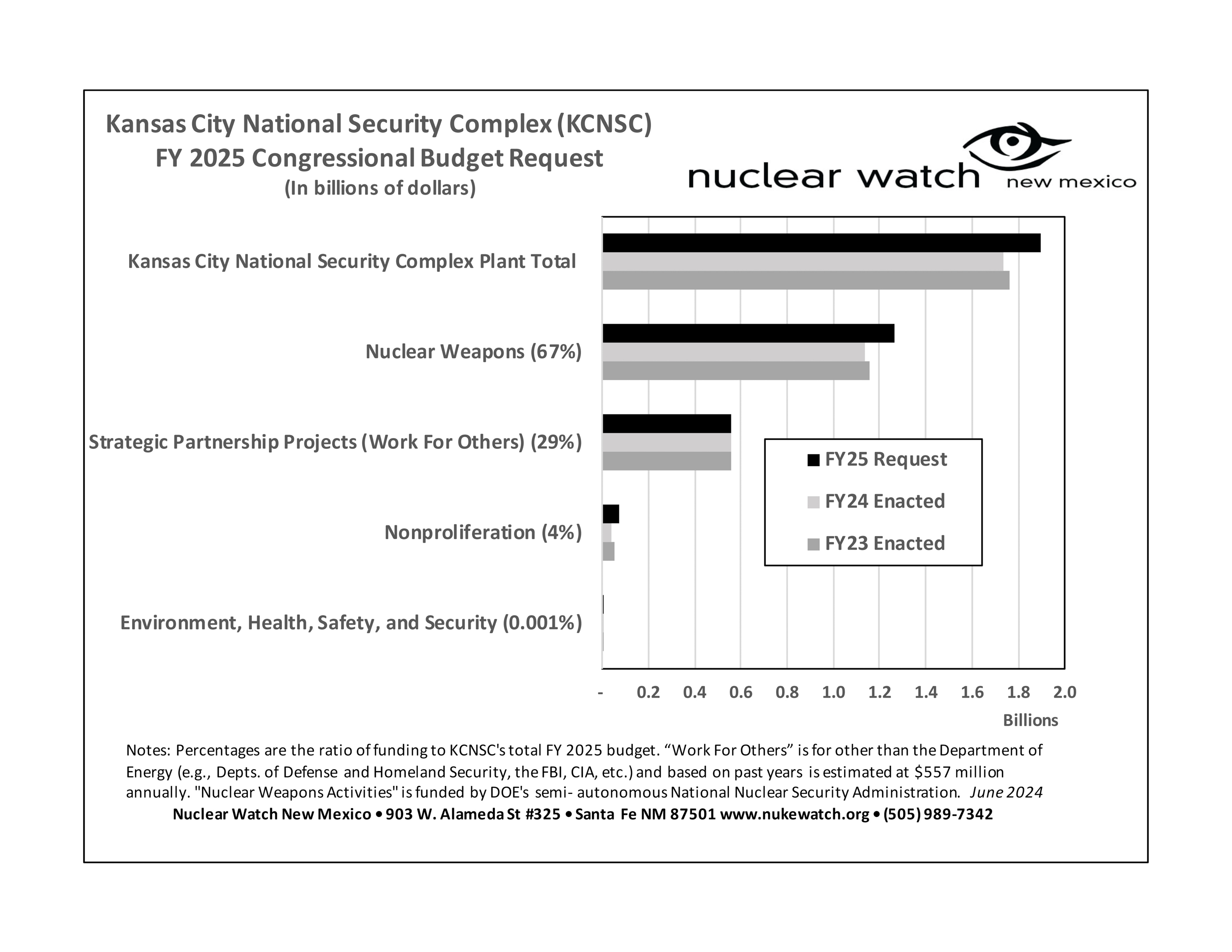
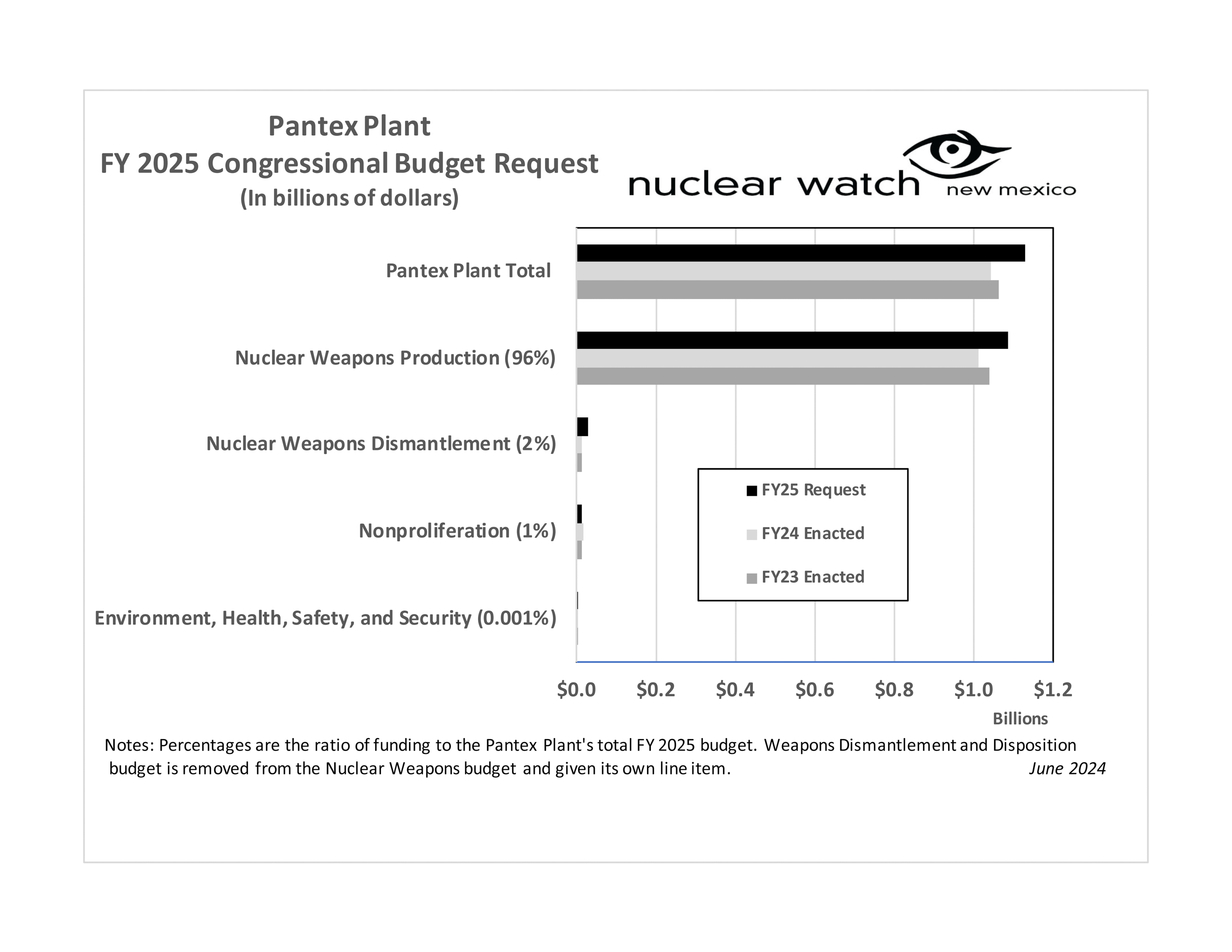
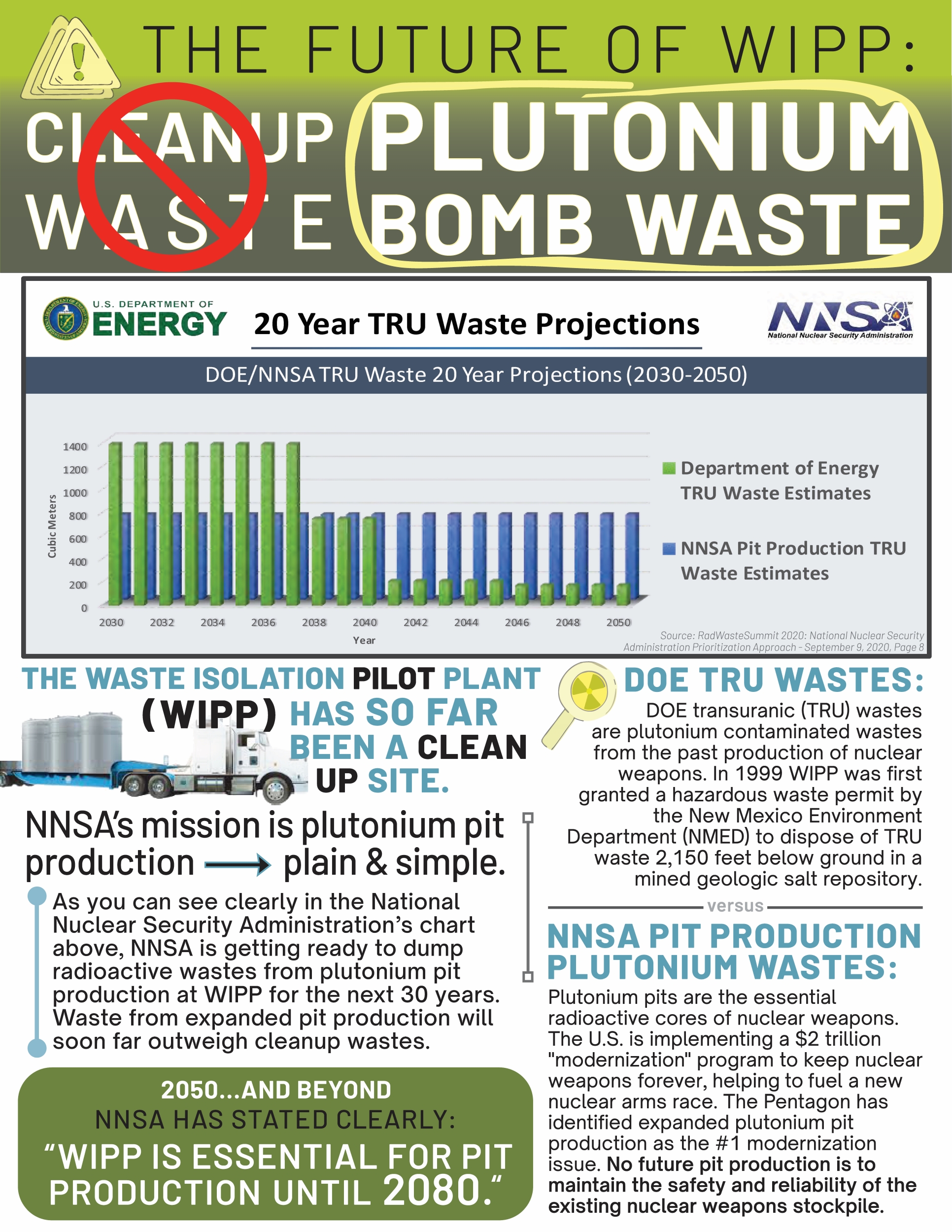
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
Los Alamos’ plutonium facility safety systems need improvement, oversight board says
Nuclear Watch New Mexico executive direcor Jay Coghlan sees PF-4 as being a bigger scale — and having bigger risks — than the other aging buildings.
“PF-4 is not unique in being old,” Coghlan said. “However, PF-4 is totally unique in currently being the only facility that can process large amounts of plutonium … particularly including plutonium pit production. I think, in part, that’s why the Safety Board focuses more on PF-4 than, to my knowledge, than any other single individual facility.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | November 7, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
An independent oversight agency wants to see improved safety systems at the facility at the heart of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s plutonium pit mission: PF-4.
The Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board reported what it believes to be gaps in a safety analysis drafted for PF-4 and delays in upgrades to safety systems in a letter last month to Energy Secretary Chris Wright.
“Maintaining momentum for these safety infrastructure projects is more important in light of the issues with the safety analysis,” the board wrote in the letter dated Oct. 10. It was signed by former acting chairman Thomas Summers.
LANL Prioritizes Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Core Production Over Safety
The independent Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board recently released its Review of the Los Alamos Plutonium Facility Documented Safety Analysis. It concluded that:
“While LANL facility personnel continue to make important upgrades to the Plutonium Facility’s safety systems, many of those projects have encountered delays due to inconsistent funding and other reasons. DOE and LANL should consider prioritizing safety-related infrastructure projects to ensure that the Plutonium Facility safety strategy adequately protects the public, as the facility takes on new and expansive national security missions.” (Page 24)
In early October 2024, the Department of Energy’s semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) announced with great fanfare that the Los Alamos Lab had produced its first “diamond stamped” plutonium pit for the nuclear weapons stockpile. Tens of billions of taxpayers’ dollars have been sunk into LANL’s long delayed and over budget pit production program. Given no further announcements, it is not currently known whether or not the Lab is meeting its congressionally required production goals. Endemic nuclear safety problems have long been an intractable issue, at one point even forcing a three-year halt to plutonium operations at LANL’s Plutonium Facility-4 (“PF-4”).
In its recent Review, the Safety Board reported:
“The [2009] Plutonium Facility safety basis described very large potential [radioactive] dose consequences to the public following seismic events…. DOE committed to upgrade and seismically qualify the ventilation system, with a particular focus on a specific ventilation subsystem…”
“As the only facility in the DOE complex that can process large quantities of plutonium in many forms, [PF-4] represents a unique capability for the nation’s nuclear deterrent. The Board has long advocated for the use of safety-related active confinement systems in nuclear facilities for the purposes of confining radioactive materials…Passive confinement systems are not necessarily capable of containing hazardous materials with confidence because they allow a quantity of unfiltered air contaminated with radioactive material to be released from an operating nuclear facility following certain accident scenarios. Safety related active confinement ventilation systems will continue to function during an accident, thereby ensuring that radioactive material is captured by filters before it can be released into the environment… (Page 2, bolded emphases added)
Trump Orders Nuclear Weapons Testing for New Nuclear Arms Race
New Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Cores at Los Alamos Lab Could Make It Real
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, October 30, 2025
Contact: Jay Coghlan, 505.989.7342, c. 505.470.3154 | Email
Santa Fe, NM – Just minutes before meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping, Trump posted on his Truth Social media platform that “Because of other countries testing programs, I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis. That process will begin immediately.” House Speaker Mike Johnson soon followed on CNN saying, “I think it is an obvious and logical thing to ensure that our weapons systems work.”
No other countries are currently testing nuclear weapons (the last was by North Korea in 2017). Further, any nuclear weapons tests by the U.S. would be performed by the Department of Energy (whose last test was in 1992), not the Department of War (until recently the Department of Defense). Trump was likely referring to Vladimir Putin’s recent claims of a new nuclear powered cruise missile and a tsunami-causing nuclear-armed torpedo that could threaten America’s coastal cities. In addition, China is dramatically expanding its own fleet of intercontinental ballistic missiles.
But central to all this is the U.S.’ own $2 trillion “modernization” program that will rebuild every nuclear warhead in the planned stockpile with new military capabilities and produce new-design nuclear weapons as well. This so-called modernization program will also build new nuclear weapons production facilities expected to be operational until ~2080, and buy new missiles, subs, and bombers from the usual rich defense contractors, all to keep nuclear weapons forever.
AP: Trump appears to suggest the US will resume testing nuclear weapons for first time in 30 years
“For Trump, who has cast Russia as a “paper tiger” for failing to swiftly subdue Ukraine, the message is that Russia remains a global military competitor, especially on nuclear weapons, and that Moscow’s overtures on nuclear arms control should be acted on.”
By MICHELLE L. PRICE and CHRIS MEGERIAN | October 30, 2025 apnews.com
BUSAN, South Korea (AP) — President Donald Trump appeared to suggest the U.S. will resume testing nuclear weapons for the first time in three decades, saying it would be on an “equal basis” with Russia and China.
The Kremlin pointed out that a global ban on nuclear tests has remained in place, but warned that if any country resumes nuclear testing Russia would follow suit.
There was no indication the U.S. would start detonating warheads, but Trump offered few details about what seemed to be a significant shift in U.S. policy.
He made the announcement on social media minutes before he met with Chinese leader Xi Jinping on Thursday in South Korea. He offered little clarity when he spoke to reporters later aboard Air Force One as he flew back to Washington.
The U.S. military already regularly tests its missiles that are capable of delivering a nuclear warhead, but it has not detonated the weapons since 1992. The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, which the U.S. signed but did not ratify, has been observed since its adoption by all countries possessing nuclear weapons, North Korea being the only exception.
REUTERS: Trump tells Pentagon to immediately resume testing US nuclear weapons
“Russia – which tested a new nuclear-powered cruise missile on October 21, held nuclear readiness drills on October 22 and tested a new nuclear-powered autonomous torpedo on October 28 – said it hoped Trump had been properly informed that Moscow had not tested a nuclear weapon itself.”
By Trevor Hunnicutt, Ismail Shakil and Kanishka Singh | October 30, 2025 reuters.com
VIEW THE RECORDING: Santa Fe Ecumenical Conversations Towards Nuclear Disarmament at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Community – Monday, October 27
Archbishop John C. Wester and NukeWatch New Mexico presented a special evening at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Community on Monday, October 27, from 6:00 to 8:00 p.m. MT. Following a presentation from NukeWatch executive director Jay Coghlan on U.S. nuclear weapons “modernization,” the Archbishop shared reflections from his pastoral letter, Living in the Light of Christ’s Peace, and speak about the importance of dialogue and hope in working toward nuclear disarmament.
View the recording at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9LFmQzMoJds&t=1s
Trump Orders Nuclear Weapons Testing for New Nuclear Arms Race
New Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Cores at Los Alamos Lab Could Make It Real
Just minutes before meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping, Trump posted on his Truth Social media platform that “Because of other countries testing programs, I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis. That process will begin immediately.” House Speaker Mike Johnson soon followed on CNN saying, “I think it is an obvious and logical thing to ensure that our weapons systems work.”
No other countries are currently testing nuclear weapons (the last was by North Korea in 2017). Further, any nuclear weapons tests by the U.S. would be performed by the Department of Energy (whose last test was in 1992), not the Department of War (until recently the Department of Defense). Trump was likely referring to Vladimir Putin’s recent claims of a new nuclear powered cruise missile and a tsunami-causing nuclear-armed torpedo that could threaten America’s coastal cities. In addition, China is dramatically expanding its own fleet of intercontinental ballistic missiles.
But central to all this is the U.S.’ own $2 trillion “modernization” program that will rebuild every nuclear warhead in the planned stockpile with new military capabilities and produce new-design nuclear weapons as well. This so-called modernization program will also build new nuclear weapons production facilities expected to be operational until ~2080, and buy new missiles, subs, and bombers from the usual rich defense contractors, all to keep nuclear weapons forever.
‘Nuclear weapons are blasphemous’: Archbishop Wester continues disarmament push with talk
This event was organized by the “Santa Fe Ecumenical Conversations Towards Nuclear Disarmament” group at the Santa Maria de la Paz parish near the Santa Fe Community College. They kindly invited NukeWatch to speak before Archbishop Wester for what turned out to be a wonderful event. The full recording can be viewed at https://www.youtube.com/@SMDLP/streams
By Cormac Dodd cdodd@sfnewmexican.com | October 28, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
Despite saying he has received a somewhat muted response from the local faithful, Santa Fe’s Catholic archbishop is still pushing nuclear disarmament as vital to humanity’s spiritual well-being and continued existence.
“I think nuclear weapons are blasphemous, because I think nuclear weapons are humanity’s attempt to build a Tower of Babel, an attempt to eat from the apple of the tree of the Garden of Eden, to become like God, to become gods,” Archbishop John C. Wester said in a roughly 30-minute address at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Church south of Santa Fe.
“In humility, we must avoid inventing anything that, in a matter of hours, can destroy what God has created,” the leader of the Archdiocese of Santa Fe continued. “The story of Adam and Eve is archetypal, I think: When human beings try to become as God, they lose the Garden of Eden and they must endure the cruel reality of paradise lost.”
The archbishop’s comments followed a journey he undertook to Japan on the 80th anniversary of the U.S. military’s decision to drop atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki toward the end of World War II. He spoke in front of an audience of about 50 people — who gave Wester a standing ovation — at Monday’s event
In a Looming Nuclear Arms Race, Aging Los Alamos Faces a Major Test
The lab where Oppenheimer developed the atomic bomb is the linchpin in the United States’ effort to modernize its nuclear weapons. Yet the site has contended with contamination incidents, work disruptions and old infrastructure.
By Alicia Inez Guzmán | October 28, 2025 The New York Times nytimes.com
In a sprawling building atop a mesa in New Mexico, workers labor around the clock to fulfill a vital mission: producing America’s nuclear bomb cores.
The effort is uniquely challenging. Technicians at Los Alamos National Laboratory must handle hazardous plutonium to create the grapefruit-size cores, known as pits. They do so in a nearly 50-year-old building under renovation to address aging infrastructure and equipment breakdowns that have at times disrupted operations or spread radioactive contamination, The New York Times found.
Now, the laboratory is under increasing pressure to meet the federal government’s ambitions to upgrade the nation’s nuclear arsenal. The $1.7 trillion project includes everything from revitalizing missile silos burrowed deep in five states, to producing new warheads that contain the pits, to arming new land-based missiles, bomber jets and submarines.
But the overall modernization effort is years behind schedule, with costs ballooning by the billions, according to the Congressional Budget Office. In 2018, Congress charged Los Alamos with making an annual quota of 30 pits by 2026, but by last year it had produced just one approved for the nuclear stockpile. (Officials have not disclosed whether more have been made since then.)
*The featured image differs from the article photo due to usage rights.
Why Putin’s ‘invincible’ nuclear-powered missile is more likely to become a disastrous ‘flying Chernobyl’ for Russia
The US abandoned efforts to build nuclear-powered missile weapons during the 1950s arms race with the Soviet Union as a nuclear-powered missile would effectively be a huge radiation risk.
Jeffrey Lewis, a nuclear nonproliferation expert at Middlebury College, described it as a “tiny flying Chernobyl,” referencing the Soviet power plant that melted down and covered a 1,600-mile area with toxic radiation…While Lewis believes the Burevestnik is only capable of subsonic speed and easy to intercept, he warned that Russia’s ambition poses a return to the Cold War era.
“NATO aircraft could intercept it. The problem is that Burevestnik is yet another step in an arms race that offers no victory for either side,” he wrote on X.
By Ronny Reyes | October 28, 2025 nypost.com
Russian strongman Vladimir Putin’s latest threats that Moscow is preparing to deploy its new “invincible” nuclear-powered cruise missile has drawn a rebuke from President Trump and a reminder of America’s own nuclear might.
But experts say the Burevestnik missile could end up being more like a disastrous “flying Chernobyl” for Russia — and proves Putin is actually nervous about the possibility of the US giving Tomahawk cruise missiles to Ukraine.
George Barros, of the Washington-based Institute for the Study of War, described Putin’s ominous Sunday announcement as a form of fear mongering from a Kremlin afraid that the US could give Kyiv a much more conventional weapon — the tried and true Tomahawk.
Russia tested new nuclear-powered Burevestnik cruise missile
“For Trump, who has cast Russia as a “paper tiger” for failing to swiftly subdue Ukraine, the message is that Russia remains a global military competitor, especially on nuclear weapons, and that Moscow’s overtures on nuclear arms control should be acted on.”
By Guy Faulconbridge and Lidia Kelly Tim Balk | October 26, 2025 reuters.com
- Russia tests nuclear-capable Burevestnik missile
- Missile flew for 14,000 km, 15 hours
- Putin says it can pierce any missile defences
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
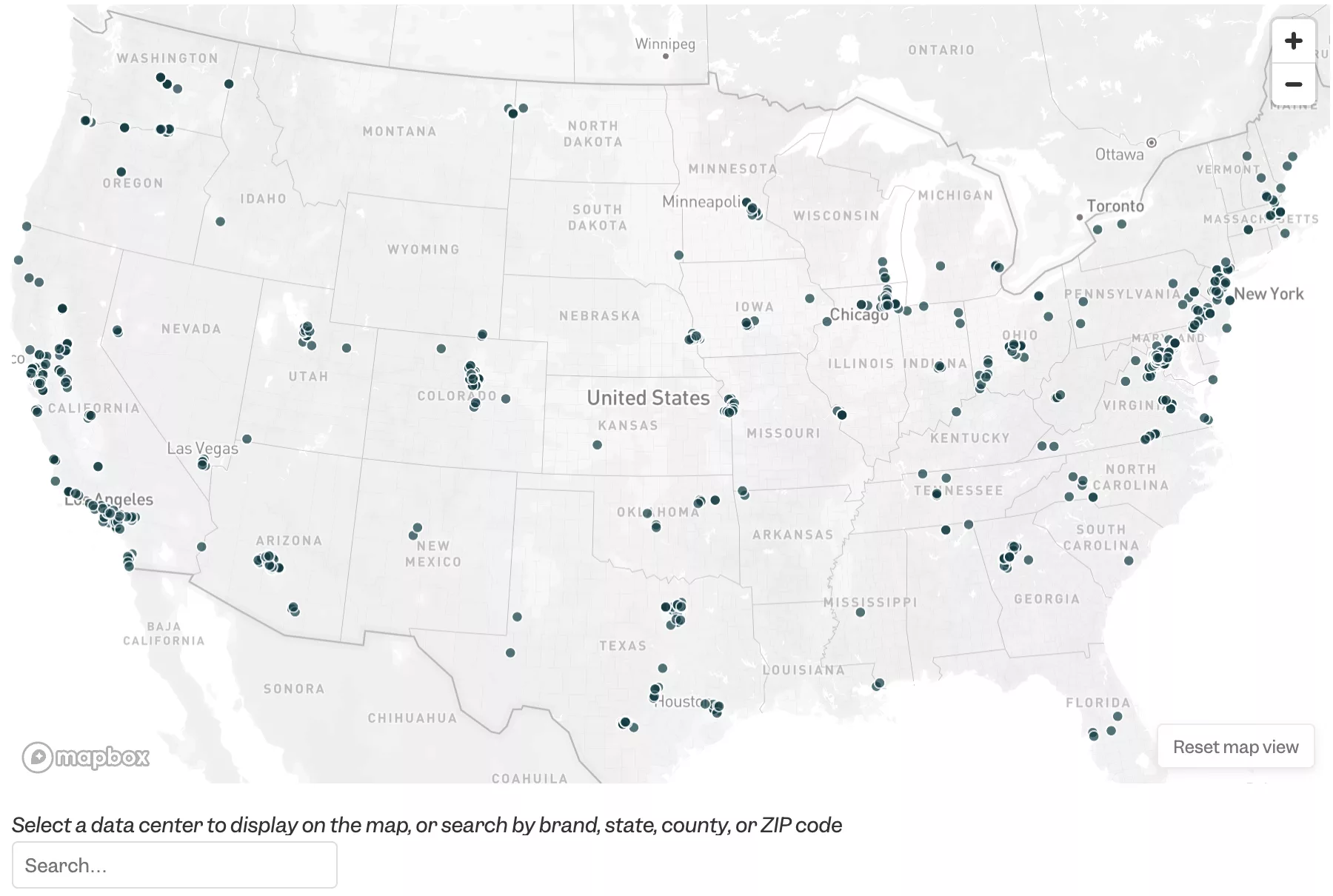
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
The New Mexico Missile that nearly bombed Albuquerque
Tactical Nukes: One Little Nuclear Weapon Can Ruin Your Whole Day
Some people believe smaller nuclear weapons can be used to fight battles. But nuclear weapons are nuclear weapons, and contemplating their use on the battlefield opens the door for full-scale nuclear war.