Over the last decade funding for the Los Alamos National Laboratory’s (LANL’s) nuclear weapons programs has increased 20%. However, funding for needed cleanup has remained flat at one-tenth of the almost $2 billion requested for nuclear weapons programs in FY 2020. Nuclear weapons funding is slated to keep climbing under the $1.7 trillion 30-year nuclear weapons “modernization” program begun under Obama. Trump is adding yet more money, and is accelerating the new arms race with Russia by adding two new types of nuclear weapons. Cleanup funding, on the other hand, is doomed to stay flat for the next two decades because the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) under Gov. Martinez gutted a 2005 “Consent Order” that would have forced the Department of Energy (DOE) and LANL to get more money for cleanup.
Tag: Congress
Editorial: LANL leaders must make safety the lab’s top mission

Falling short of the bare minimum in the eyes of the DOE is a far cry from where the public expects or needs LANL to be.
The Albuquerque Journal Editorial Board has a great editorial except for this part –
Because LANL is home to some of the best and brightest in the nuclear industry. It is the home of the Manhattan Project. And its future is important not only to the prosperity of our state, but also to our national security.
Trump’s 2020 Nuclear Weapons Budget Escalates New Arms Race

Posted By Scott Kovac
Santa Fe, NM – Today the Trump Administration released more budget details for the Department of Energy and its semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration’s nuclear weapons programs for fiscal year 2020. This same fiscal year will also mark the 75th anniversaries of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Global Nuclear Weapons Threats Are Rising
More than 25 years after the end of the Cold War, all eight established nuclear weapons powers are “modernizing” their stockpiles. Talks have broken down with North Korea, the new nuclear weapons power. Nuclear-armed India and Pakistan narrowly averted war last month. Russian President Vladmir Putin made new nuclear threats in response to Trump’s announced withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty. This could lead to hair-trigger missile emplacements in the heart of Europe and block extension of the New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty with Russia. If so, the world will be without any nuclear arms control at all for the first time since 1972.
Continue reading
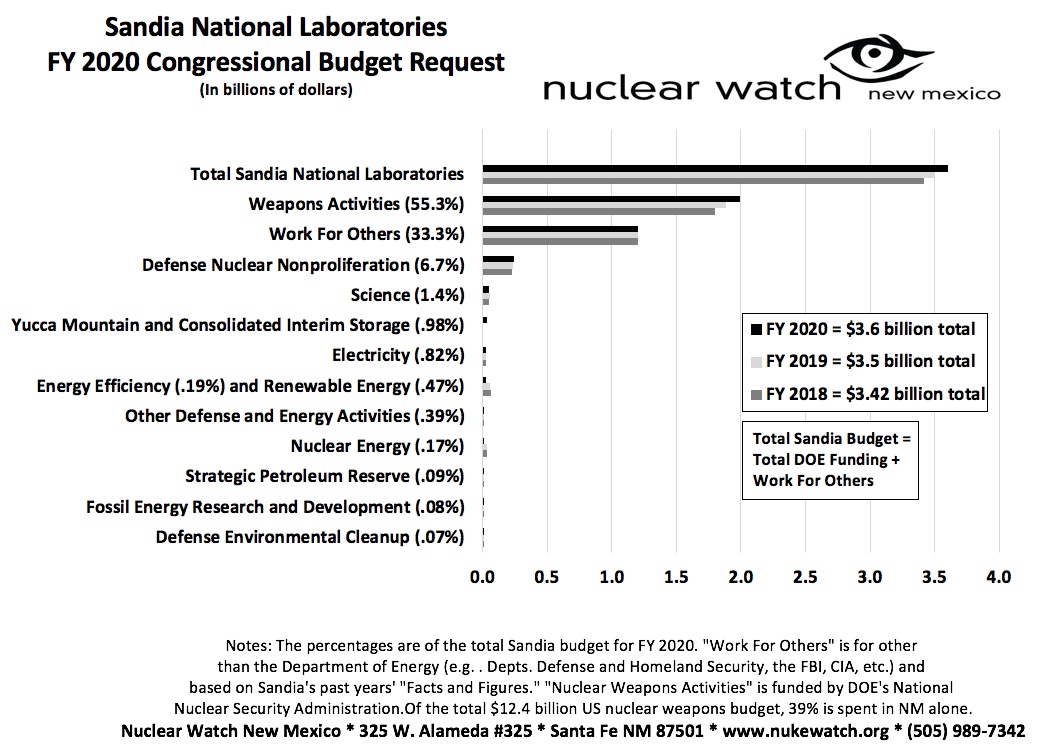
Sandia National Laboratories Annual Budget is 81% Military Work
Posted by Scott Kovac – Sandia National Laboratories, has one of the Department Of Energy’s (DOE’s) largest annual budgets and the fiscal year 2020 (FY20) Congressional Budget Request shows continued military priorities for the Lab. There are two components of Sandia’s annual budget – work for DOE (with a $2.4 billion request for FY20) and ‘Work For Others’ (with an annual request of $1.2 billion). Sandia’s work for DOE centers around nuclear weapons engineering. ‘Work for Others’ (WFO) is work done for federal agencies other than the DOE and for non-federal entities. An annual total budget of $3.6 billion puts Sandia’s budget second only behind Washington Headquarters among DOE sites.
Trump Budget Would Continue Nuclear Weapons Buildup and Bring More Nuclear Waste to NM

By Scott Kovac, Operations and Research Director
The White House released the top line numbers of its fiscal year 2020 Congressional budget request and, although there are some increases heading to New Mexico, they are not the increases that we’d like to see. It’s called – A Budget For a Better America, Promises Kept. Taxpayers First. but only Defense and Department of Energy (DOE) weapons contractors are going to think that anything is better. Meanwhile the rest of us taxpayers will, first and foremost, be looking at cuts to programs that affect us daily.
Testimony Calls Out Continued DOE Cost Estimating Mismanagement
Testimony Calls Out Continued DOE Cost Estimating Mismanagement
Given that DOE has challenges estimating almost all large projects, taxpayers must push to spend on cleanup first. Both nuclear weapons and environmental management estimates keep increasing. We can keep spending on dangerous nuclear weapons that we don’t need, or we can finally focus on cleaning up the Cold War mess.
Government Accountability Office (GAO) officials presented some of their recent work to Congress concerning management problems facing the Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and Office of Environmental Management (EM). NNSA is responsible for managing the nation’s nuclear weapons and supporting the nation’s nuclear nonproliferation efforts. In support of these missions, NNSA’s February 2016 budget justification for the Weapons Activities appropriations account included about $49.4 billion for fiscal years 2017 through 2021 to implement its nuclear weapons complex modernization plans. More recently, in November 2017, NNSA issued its Stockpile Stewardship and Management Plan, which included about $10.2 billion for nuclear weapons activities for fiscal year 2018.
Since the end of the Cold War, it is claimed that much of the nuclear weapons production infrastructure has become outdated, prompting congressional and executive branch decision makers to call on DOE to develop plans to modernize. The Department of Defense’s (DOD) 2010 Nuclear Posture Review identified long-term modernization wishes and alleged requirements. In January 2017, the President directed the Secretary of Defense to initiate a new Nuclear Posture Review to meet the Administration’s vision. This review was released in February 2018.
GAO has found that NNSA’s estimates of funding needed for its modernization plans exceeded the budgetary projections included in the President’s own modernization budgets. And the costs of some major modernization programs—such as for nuclear weapon Life Extension Programs (LEPs) — may also increase and further bust future modernization budgets.
The LEPs facing potential cost increases include:
B61-12 LEP. An independent cost estimate for the program completed in October 2016 exceeded the program’s self-conducted cost estimate from June 2016 by $2.6 billion.
W80-4 LEP. Officials from NNSA’s Office of Cost Policy and Analysis told us that this program may be underfunded by at least $1 billion to meet the program’s existing schedule
W88 Alteration 370. According to officials from NNSA’s Office of Cost Policy and Analysis, this program’s expanded scope of work may result in about $1 billion in additional costs.
EM is responsible for decontaminating and decommissioning nuclear facilities and sites that are contaminated from decades of nuclear weapons production and nuclear energy research. In February 2017, GAO reported that, since its inception in 1989, EM has spent over $164 billion on cleanup efforts, which include retrieving, treating, and disposing of nuclear waste.
GAO found that the federal government’s environmental liability has been growing for the past 20 years—and is likely to continue to increase—and that DOE is responsible for over 80 percent ($372 billion) of the nearly $450 billion reported environmental liability. Notably, this estimate does not reflect all of the future cleanup responsibilities that DOE may face.
Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management’s Annual Spending and Growing Environmental Liability
As NNSA works to modernize the nuclear weapons complex, EM is addressing the legacy of 70 years of nuclear weapons production. These activities generated large amounts of radioactive waste, spent nuclear fuel, excess plutonium and uranium, and contaminated soil and groundwater. They also contaminated thousands of sites and facilities, including land, buildings, and other structures and their systems and equipment. Various federal laws, agreements with states (including New Mexico), and court decisions require the federal government to clean up environmental hazards at federal sites and facilities, such as nuclear weapons production facilities. For years, GAO and others have reported on shortcomings in DOE’s approach to addressing its environmental liabilities, including incomplete data on the extent of cleanup needed.
EM has some budget issues, too.
Examples of costs that DOE cannot yet estimate include the following:
DOE has not yet developed a cleanup plan or cost estimate for the Nevada National Security Site and, as a result, the cost of future cleanup of this site was not included in DOE’s fiscal year 2015 reported environmental liability. The nearly 1,400-square-mile site has been used for hundreds of nuclear weapons tests since 1951. These activities have resulted in more than 45 million cubic feet of radioactive waste at the site. According to DOE’s financial statement, since DOE is not yet required to establish a plan to clean up the site, the costs for this work are excluded from DOE’s annually reported environmental liability.
DOE’s reported environmental liability includes an estimate for the cost of a permanent nuclear waste repository, but these estimates are highly uncertain and likely to increase. In March 2015, in response to the termination of the Yucca Mountain repository program, DOE proposed separate repositories for defense high-level and commercial waste. In January 2017, we reported that the cost estimate for DOE’s new approach excluded the costs and time frames for site selection and site characterization.
“Gateway Drug to Nuclear War” Feeds More Nuke Addiction
“Gateway Drug to Nuclear War” Feeds More Nuke Addiction
The Trump Administration’s high policy document, the Nuclear Posture Review (NPR), released February 2, includes recommendations for the deployment of lower yield, “more usable” nuclear warheads. This will only feed the US addiction to nukes.
An article on the same day in The American Conservative, “Trump’s Nuke Plan Raising Alarms Among Military Brass”, quotes one retired senior Army officer who tracked the NPR as saying that nuclear neocons were providing Donald Trump with “gateway drug for nuclear war.”
So while the [NPR’s] recommendations won’t necessarily be a surprise, what is less public is the bitter battle during its drafting that pitted senior Army and Navy warriors against nuclear wonks inside the Defense Department. That fight—over the exorbitant costs associated with the NPR, and charges that it could make nuclear war more likely—are bound to continue through implementation.
“It’s one thing to write a policy,” a senior Pentagon civilian privy to the NPR fight told The American Conservative, “and it’s another thing to have it implemented. What the NPR is recommending will break the bank, and a lot of people around here are worried that making nuclear weapons more usable isn’t what we should be doing. The conventional military guys have dug in their heels, they’re dead-set against it. This battle isn’t over.”
In effect, the congressionally mandated review calls for the U.S. to deploy two new types of lower yield nuclear warheads, generally defined as nuclear bombs below a five kiloton range (the one dropped on Hiroshima was 20 kilotons), that could be fitted onto a submarine-launched ballistic missile, and one, yet to be developed, that would be fitted onto a submarine-launched cruise missile. Additionally, the NPR calls for “recapitalizing” the complex of nuclear laboratories and plants, which, taken together with the proposed modernization program of the U.S. nuclear arsenal (the “triad”), will almost certainly cost in excess of the estimated price tag of $1.2 trillion over the next 30 years.
The article continues that Army and Navy officers worry that senior administration officials would promote massive new funding initiatives at the expense of badly needed funding for conventional military readiness. They also worry, more urgently, that the administration would put the nation on the slippery slope to nuclear escalation.
NukeWatch’s bottom line: Addiction to nukes is a potentially world-ending problem.
Trump’s Nuclear Posture Review goes in the opposite direction of meeting our long-term need to eliminate the one class of weapons of mass destruction that can truly destroy our country. It will instead set back nonproliferation and arms control efforts across the globe, and further hollow out our country by diverting yet more huge sums of money to the usual fat defense contractors at the expense of public education, environmental protection, natural disaster recovery, etc. Under the Trump Administration, expect Medicare and Social Security to be attacked to help pay for a false sense of military security. Trump’s Nuclear Posture Review is part and parcel of that.
Nuclear Watch New Mexico seeks to promote safety and environmental protection at nuclear facilities; mission diversification away from nuclear weapons programs; greater accountability and cleanup in the nation-wide nuclear weapons complex; and consistent U.S. leadership toward a world free of nuclear weapons. Please help support NukeWatch.
Los Alamos Nuclear Weapons Activities Reaches 70% Of Annual Budget
Make no doubt about it, Los Alamos National Laboratory is a nuclear weapons research, development, and production facility. In this year’s FY18 Congressional Budget Request:
70% of the Lab’s budget is Nuclear Weapons Activities
11% is for Nuclear Nonproliferation
10% for ‘Work For Others’
8% Cleanup
1% Science
.4% Nuclear Energy
.2% Renewables
Los Alamos National LaboratoryFY 2018 Congressional Budget Request
(In billions of dollars)
This chart and the FY18 LANL Lab tables to back it up are here
US Still On Track For $1 Trillion Nuclear Weapons Modernization
Here’s a breakdown of nuclear weapons costs. The average is $34 billion per year.
10-Year Estimates for Sustaining and Modernizing the U.S. Nuclear DeterrentDOD and DOE are undertaking an extensive effort to sustain and modernize U.S. nuclear weapons capabilities. This effort is expected to take decades and cost hundreds of billions of dollars. Congress requires submission of an annual report to congressional committees on DOD’s and DOE’s plans for related matters and includes a provision that GAO review aspects of that joint report. GAO has previously recommended that future joint reports provide more thorough documentation of methodologies and context for significant changes from year to year.
GAO analyzed the departments’ internal plans and budget estimates for sustaining and modernizing the nuclear deterrent and interviewed DOD and DOE officials. The fiscal year 2017 joint report continues to omit explicit information about all assumptions and limitations in DOD’s and DOE’s methodologies and reasons for year-to-year programmatic changes in some estimates—information that could improve transparency for decision makers in Congress.
Read the GAO Report Here
NukeWatch NM Heads to DC To Stop U.S. Nuclear Weapons “Trillion Dollar Trainwreck”
NukeWatch NM Heads to Washington to Press Congress, Obama Officials
To Stop U.S. Nuclear Weapons “Trillion Dollar Trainwreck” —
LANL Whistleblower Chuck Montaño to Be Honored
Three members of Nuclear Watch New Mexico will visit Washington, DC from April 17 to April 20 to oppose U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) nuclear weapons projects, which they say will lead to a “trillion dollar trainwreck” through out-of control spending, more radioactive waste generation, and weapons proliferation. The group will meet with the New Mexican congressional delegation, committee staffers, and administration officials with responsibility for U. S. nuclear policies to press for new funding priorities.
The Nuclear Watch NM delegation will be working with more than 50 colleagues from two dozen other states who are participating in the 28th annual Alliance for Nuclear Accountability “DC Days.” They will distribute copies of the ANA’s new report “Trillion Dollar Trainwreck” a detailed analysis of the Obama Administration’s latest plans to spend more money on nuclear weapons without truly enhancing U.S. security.
Jay Coghlan, NukeWatch director and president of the ANA Board of Directors, said, “Massive spending on nuclear weapons ‘modernization’ creates potential catastrophic risks for U.S. taxpayers, the environment and world peace. We will press policy-makers to cut programs that fund dangerous DOE boondoggles. The money saved should be redirected to dismantling weapons and cleaning up the legacy of nuclear weapons research, testing and production.”
NukeWatch NM Steering Committee member Chuck Montaño will receive recognition during DC Days from the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability (ANA) at a reception on April 19, 2015, at the Hart Senate Office Building. He, along with California’s senior U.S. Senator Diane Feinstein and ranking member of the House Armed Services Committee Rep. Adam Smith (D.-WA), will be among those honored by ANA for their efforts to hold the nuclear weapons military-industrial complex accountable. Montaño is being recognized for his advocacy confronting whistleblower and employee abuse, managerial malfeasance and fraudulent activity, all of which he documents in his recently released book detailing the chain of events that led to him becoming a federally protected whistleblower.
Montaño commented that he wrote Los Alamos: Secret Colony, Hidden Truths, “so people can appreciate the Lab’s full impact and legacy, not just what institutional leaders want the public to remember. There are important events I document for posterity, which may otherwise be hidden or erased from memory, and I didn’t want that to happen.”
Jay Coghlan, NukeWatch director, said, “I am very proud of Chuck Montaño, especially since he’s a Nuke Watch Steering Committee member as well. We depend on people like him with the inside story to help keep the Lab safe for communities and workers alike. It’s gratifying to see that the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability and its many member organizations appreciate his efforts.”
Mr. Montaño, a lifelong Santa Fe area resident, was employed at the Los Alamos National Laboratory for 32 years, until his forced retirement from the lab in 2010. He is also the former Director of Fraud and Special Audits for the Office of the New Mexico State Auditor.
The Alliance for Nuclear Accountability (ANA) is a network of three-dozen local, regional and national organizations representing the concerns of communities downwind and downstream from U.S. nuclear weapons production and radioactive waste disposal sites.
# # #
Chuck Montaño’s book Los Alamos: Secret Colony, Hidden Truths
is available at www.losalamosdiary.com
Governor Udall?
Governor Udall?
Michael Coleman had an interesting article for the Albuquerque Journal – Does New Mexico’s future lie in D.C.?
Coleman relates a conversation with NM Senator Tom Udall that made it clear the Senator isn’t ruling a gubernatorial run out.
It’s not surprising to think that Udall – who has been in Washington as a congressman and U.S. senator since 1998 – might want to come home to beautiful Santa Fe and take up residence in the governor’s mansion as a coda to his long political career.
Just two years into his second six-year term in the Senate, Udall could run for governor without giving up his Senate seat, which doesn’t expire until 2020. If he won the 2018 governor’s race, he would appoint his Senate replacement. That kind of power is alluring to any politician.
But as Coleman says, “it’s all just a parlor game at this point.”
Four Strikes and You’re Out
Four Strikes and You’re Out
In stunning news on December 18, Justin Horwath of the SF New Mexican reported that the management and operating contractor of Los Alamos National Laboratory will not have its contract renewed after it ends Sept. 30, 2017. This is stunning because LANS LLC, the M&O contractor, could have potentially run the Lab until for 20 years until 2026, had it not had so many problems.
The annual contract for FY 2016 was over $2.2 billion. This means that Los Alamos National Security (LANS) left upwards of $20 billion (9 years of lost contract) on the table. It’s not often that a company gets the opportunity to make mistakes that costs them $20 billion worth of contracts.
The management of the Lab was privatized when LANS was awarded the contract in 2005. LANS is a partnership between the University of California, Bechtel Corp., Babcock & Wilcox Co., and AECOM (formerly URS). Before 2005 the University of California exclusively managed LANL as a non-profit. The for-profit experiment for managing the Lab will hopefully be reconsidered.
As a reminder, Nuclear Watch NM, along with our friends at Tri-Valley CARES, submitted a bid to manage the Lab back in 2005. We thought the management should be non-profit and that nuclear weapons research should be phased out.
The overall direction of future missions at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) – We propose to downgrade the Lab’s nuclear weapons programs and subordinate them under a new Associate Directorship of Nuclear Nonproliferation so that it can be better assured that national and international obligations under the NonProliferation Treaty are met.
LANS lost the M&O contract because they failed to earn the “award term” 4 times. The award term is simply another year added to the contract. Section H-13(f) of the current contract states, ‘If the Contractor fails 4 times to earn award term, the operation of this Award Term clause will cease.”
Then, LANS lost award term in 2014 AND had one extra award term that was previously earned taken away because of improperly packing the radioactive waste drum that shut down WIPP.
And LANS lost this award term for 2015. LANL may be negotiating this, but they got a waiver in 2012 that granted them an award term when they didn’t actually earn it. They were told that was their last waiver.
That’s four.
These award terms are based on the Lab’s Performance Evaluation Reports (PERs), which thanks to a successful Freedom of Information Act lawsuit by NukeWatch, are available online. We wonder if having these available to the public could have helped the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) in any way to not give the award terms.
We do thank NNSA and the DOE LA Field Office for sticking to their guns by providing genuine oversight of the Lab this go-around. But the past few years serve as a reminder of the dangerous and difficult side of nuclear weapons work, the continuing health impacts to workers, and the impossibility of isolating the radioactive waste for hundreds of thousands of years. When will the US decide that it’s just not worth it?
The SF New Mexican also tells that NM Congressional delegation has weighed in. We agree with the joint statement issued by U.S. Sens. Tom Udall and Martin Heinrich and U.S. Rep. Ben Ray Luján that, “DOE must hold all of its contractors accountable and be responsible stewards of federal funds.”
But we have some questions about this statement:
“Los Alamos National Laboratory employs some of the best and brightest minds in the country whose contributions are indispensable to our national security. The lab also strengthens our economy by providing quality jobs, and we will always fight to protect its mission. As DOE prepares a new contract proposal, assuring continuity for the employees at LANL and the high-quality scientific, energy, and security contributions they make to our nation will be paramount. We are confident that Los Alamos will continue to have a critical role in national and international security, research and science. We expect to receive further details and regular briefings from NNSA as the process moves forward in the new year.”
The delegation’s joint letter seems to demonstrate how overly concerned they are with LANL’s “mission” of nuclear weapons production and with the institutional benefit of profit-making national security contractors. The Lab’s actual contributions to energy research and basic science are also a small proportion to the taxpayer dollars expended there.
A major rewrite of the Lab’s missions is needed where true national security is not based on nuclear weapons.
NukeWatch Calls for Public Seats at the Table in LANL Cleanup Negotiations
For immediate release December 7, 2015
Contacts: Jay Coghlan, jay[at]nukewatch.org
Deadline for Last Cleanup Milestone of LANL Consent Order Passes
NukeWatch Calls for Public Seats at the Table in Negotiations
Santa Fe, NM – Yesterday, December 6, was the deadline for the last compliance milestone in the Consent Order between the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) and the Department of Energy (DOE) that governs cleanup at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). Ironically, that last milestone required the submittal of a report by the Lab on how it successfully completed cleanup of Area G, its largest waste dump. Real comprehensive cleanup is decades away at current funding levels. One of the purposes of the 2005 Consent Order was to prod Congress to increase funding for cleanup of 70 years of neglected Cold War contamination at the Lab.
NMED has the final decision on what form cleanup of hazardous wastes takes at LANL. But any revised Consent Order is still off in the future, and the degree of public participation in its formulation yet to be determined by NMED. Meanwhile, LANL plans to “cap and cover” Area G, thereby creating a permanent nuclear waste dump in unlined pits and shafts, with an estimated 200,000 cubic yards of toxic and radioactive wastes buried above the regional groundwater aquifer, 4 miles uphill from the Rio Grande.
Following protracted negotiations and threatened litigation by DOE against NMED, the Environment Department succeeded in getting DOE and the LANL contractor to sign the original Consent Order in March 2005. However, beginning in 2012, NMED signed a “Framework Agreement” with DOE that prioritized the transfer of 3,706 cubic meters of aboveground, monitored “transuranic” (TRU) wastes from nuclear bomb production at Area G to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) in southern New Mexico.
The stated rationale of this so-called 3706 Campaign was to minimize the risk from wildfire following the 2010 Las Conchas Fire that burned within 3.5 miles of Area G. However, if those TRU wastes were really at risk from wildfire, they would have burned during the 2000 Cerro Grande Fire that came within a half-mile of Area G. The Framework Agreement allowed LANL to discontinue most legacy cleanup to concentrate on TRU shipments that should have already been completed.
Moreover, the 3706 Campaign itself ended in disaster in February 2014 when an improperly treated radioactive waste drum from LANL ruptured at WIPP, contaminating 21 workers and indefinitely closing down that multi-billion dollar facility. Dealing with the 59 similarly treated “suspect” drums still at LANL will use a substantial amount of scarce cleanup funding for at least the next two years. Combined with the need to address a large chromium groundwater plume discovered after the original Consent Order went into effect, cleanup of buried mixed radioactive wastes will remain on the back burner, if ever addressed.
Further, since 2011 LANL has requested and NMED perfunctorily granted more than 150 milestone extensions, thus effectively eviscerating the Consent Order without public comment and consent. Which brings us to today, after the last compliance milestone deadline has expired, with little cleanup actually accomplished since 2012. A new schedule of cleanup is on hold until a revised Consent Order is negotiated.
Previously NMED Secretary Ryan Flynn has said that a draft revised Consent Order would be released for a 60-day public comment period before the end of 2015. But as of mid-November negotiations had not started. More recently Secretary Flynn has said that a draft renewed Consent Order would be released only after the schedule of payments is finalized for a $73 million settlement over WIPP violations. WhileNuclear Watch New Mexico appreciates NMED’s firmness on the WIPP settlements, we would like to see the same amount of zeal applied to enforcing cleanup at LANL through the Consent Order.
NukeWatch strongly believes that much more vigorous public participation steps, including the opportunity for a public hearing, are legally required by the existing Consent Order. Specifically, the March 2005 Consent Order incorporated the full public participation requirements applicable to hazardous waste permits. Federal environmental regulations, which are incorporated into New Mexico state regulations, establish the public participation procedures for various types of permit modifications, including extending final compliance dates. These are deeper levels of public participation than the 60-day public comment period that NMED is currently contemplating. In our view, a 60-day public comment period on a draft Consent Order is tantamount to commenting on a done deal already negotiated between DOE and NMED.
Scott Kovac, Research and Operations Director for Nuclear Watch New Mexico, stated, “The requirements are clear for deep and meaningful public participation in LANL cleanup decisions, including the opportunity for the interested public to have a seat at the negotiating table and the possibility for a public hearing. NMED must make Cold War legacy cleanup a priority at LANL and should start by prioritizing full public participation while negotiating the revised Consent Order.”
Jay Coghlan, NukeWatch Executive Director, added, “Ultimately this is all about the future of cleanup at LANL, which is receiving less federal funding while the nuclear weapons programs that created the mess to begin with are getting more money. We want nothing short of comprehensive cleanup at the Los Alamos Lab. That would be a real win-win for New Mexicans, permanently protecting our water and the environment while creating hundreds of high-paying jobs.
# # #
Nuclear Watch’s letter to Secretary Flynn – on Consent Order public participation requirements.
The existing Consent Order governing cleanup at LANL
Los Alamos Cleanup Budget Request Slips to 8% for FY 2016
Los Alamos Cleanup Budget Request Slips to 8% for FY 2016
Even as Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) faces more fines from the State for missed environmental cleanup, the cleanup budget request slips to 8% of the Lab’s total budget of $2.2 billion. The request for cleanup for Fiscal Year 2016 is $185.2 million. See the full chart and Lab tables here.
Even this ridiculously small amount is under attack. The ABQ Journal reported that the Department of Energy could be planning to pay for existing LANL fines out of this cleanup budget. In December 2014 the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) issued fines totalling $37 million for improper waste handling that closed the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in SE NM.
But really, the breeched drum that closed WIPP (full operations will not resume until 2018 at the earliest) came from the nuclear weapons activities programs. It’s like the weapons program handed the environmental cleanup program a ticking time bomb and said, “You deal with it.” Then when it blows up, it gets blamed on the environment folks. Reckless historic environmental practices by the nuclear weapons programs at the Lab have left a legacy of radioactive and hazardous wastes in the ground above our aquifer.
The official estimate for the total cleanup at Los Alamos has yet to be released. But it could easily $15 – 20 billion to remove the contamination threatening our future. Doing the math, a $15 billion cleanup estimate at $200 million per year would take 75 years. That is too long.
Ask your Congressional Representatives to fully fund cleanup at Los Alamos National Laboratory and to NOT use cleanup funds to pay any fines!
NM Congressional Representative Ben Ray Lujan
Questions for the DOE FY 2016 Nuclear Weapons and Cleanup Budget Request
The Administration releases its Congressional Budget Request this Monday, February 2, 2015.
Questions for the U.S. Department of Energy FY 2016 Nuclear Weapons and Cleanup Budget Request
From
Alliance for Nuclear Accountability
A national network of organizations working to address issues of nuclear weapons production and waste cleanup
The US nuclear weapons budget continues to spiral out of control. Look for double-digit increases in Department of Energy (DOE) weapons activities. Core nonproliferation programs will be cut because of funding for mixed-oxide fuel. Cleanup of radioactive and toxic pollution from weapons research, testing, production and waste disposal will fall further behind. The DOE budget for FY 2016 will illuminate the Obama Administration’s misplaced nuclear priorities.
The Alliance for Nuclear Accountability (ANA), a 28-year-old network of groups from communities downwind and downstream of U.S. nuclear sites, will be looking at the following issues. For details, contact the ANA leaders listed at the end of this Advisory.
— Does the budget request boost funding for “modernization” programs that indefinitely maintain nuclear warheads? Such funding is contrary to the Obama Administration’s previously declared goal of a future world free of nuclear weapons.
— Does the budget reflect the Administration’s commitment to reduce funding (currently $335 million) on the multi-billion dollar Uranium Processing Facility at Oak Ridge by downsizing it to the capacity needed to support stockpile surveillance, maintenance and limited life extension?
— Does the budget increase funds for nuclear weapons dismantlement capacity? Will cooperative programs with Russia be maintained?
— Is there increased funding for expanded production of plutonium bomb cores? Why is expanded production needed when expert studies find that existing plutonium pits are durable?
— Is more than $300 million provided for the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Livermore Lab that has repeatedly failed to achieve “ignition”? What is the funding level for uncontained plutonium shots although they will taint the NIF target chamber and optics with alpha radiation?
— Does the budget seek an increase for the B61 Life Extension Program (currently $643 million)?
— As DOE affirms that the $30-billion plutonium fuel (MOX) project at the Savannah River Site is financially unsustainable, is the MOX plant construction again proposed for “cold standby” (~$200 million) or a level to barely allow it to survive (~300+ million)? Does the budget include the current validated base-line cost of MOX plant, a validated construction and operation schedule and names of nuclear utilities willing to use experimental MOX fuel?
— Does the budget include $0 for Yucca Mountain? No funding is consistent with past requests that terminate this technically flawed site that is strongly opposed by Nevada state officials and the public.
— Does the budget provide additional Environmental Management (EM) funding (currently $5 billion) to meet all legally mandated cleanup milestones? States say cleanup agreements at a dozen major sites are underfunded by hundreds of million dollars.
– How will DOE and its contractors pay fines for missing milestones? In the past three months, the states of New Mexico, Idaho, and Washington have issued fines of tens of millions of dollars, and fines loom in South Carolina. In which other states does DOE face fines and lawsuits for missing milestones?
— What is the high range for total life-cycle cleanup costs (LCC) for EM sites? Because of funding shortfalls, High Range LCC costs have increased from $308.5 billion in the FY 2013 Budget Request, to $330.9 billion in the FY 2014 Request, and were $328.4 billion in the FY 2015 Request.
— How much does the budget include for the shut down of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP)? How much is for recovery and how much for waste emplacement (previously $220 million a year) even though no waste is being emplaced? How much additional funding is requested for the Idaho National Lab, Los Alamos, Savannah River, and Oak Ridge because of the shutdown?
— Does the budget for Hanford (more than $2 billion) protect workers from toxic chemical exposures, provide an Operational Readiness Review of the nuclear safety of the Waste Treatment Plant, and fund construction of new double-shell tanks to replace the leaking ones?
— Does the budget increase funding (currently $28.5 million) for the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB) to provide independent oversight of DOE projects because of the many cost overruns, schedule delays, safety culture issues and technical problems?
— Is the funding for design and licensing of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) enough to make them viable? As private financing is lacking, will DOE reaffirm that it will not finance SMR construction?
For further information, contact:
Jay Coghlan jay(at)nukewatch.org
Download the pdf and more contact info here.
Comments to DOE Re: Transition of Legacy Clean-up Work at Los Alamos National Laboratory
December 10, 2014
Jack R. Craig, Jr.
DOE EM
Re: Transition of Legacy Clean-up Work at Los Alamos National Laboratory
Mr. Craig,
Please consider these preliminary comments and requests concerning the transition of legacy clean-up work at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Through comprehensive research, public education and effective citizen action, Nuclear Watch New Mexico seeks to promote safety and environmental protection at regional nuclear facilities; mission diversification away from nuclear weapons programs; greater accountability and cleanup in the nation-wide nuclear weapons complex; and consistent U.S. leadership toward a world free of nuclear weapons.
First, we request that alternatives to the current Department of Energy contract process be considered. The privatization of the nuclear weapons complex may be failing the U.S. taxpayer. Cost overruns plague the current system. Different variations of the same contractors still continue to line up for different variations of the same contracts. Yet, with a few exceptions, cleanup only crawls along. Many of the sites are still contaminated decades after the work was completed. And now, WIPP is shut down.
We ask that alternatives such as looking to governmental agencies instead of private contractors be tasked with cleanup at Los Alamos. For instance, could the Army Corp. of Engineers do the job?
We also strongly request that alternatives to “No-Bid” and “Cost-Plus” contracts be considered first. Recently, Senate Armed Services Committee Chairman John McCain spoke to prohibit the Pentagon from awarding cost-plus contracts, arguing such deals encourage nefariousness. (DefenseNews.com, December 5, 2014)
Second, if a conventional contract is used, we request that the following specific items be included in the proposed new EM contract at LANL. We also ask that these items be included in the ‘bridge’ contract:
- Must be tied to LANL Consent Order and LANL RCRA permit.
- Any “campaigns” must be legally binding, and not used as justification to miss Consent Order milestones.
- Should be more incentive based – less fixed.
- Should be more transparent like ARRA, including public availability of Performance Evaluations.
- Should have dramatically lower overhead costs, for example lower security and no LDRD costs. These overhead costs should be made public just as the old Functional Support Costs were available to the public.
- Must include public update meetings semi-annually.
- Should favor local/regional economic development.
- Must have public update meetings at least semi-annually.
Third, for the new bridge contract and any final contract we ask:
- Cleanup must continue at current pace during transition.
- There must be a new lifecycle baseline – with the range with assumptions spelled out. Comprehensive cleanup must be considered, not just cap and cover.
- Corrective Measures Evaluations must be completed on all areas as one of the priorities.
Finally, concerning the new bridge contract, the synopsis doesn’t address the issue of how much LANS will be paid under the to-be-finalized bridge contract in relation to how much it would have been paid under the existing contract. It also doesn’t state which of the tasks mentioned are different than under the existing contract. We request that costs and tasks be fully described in the to-be-finalized bridge contract.
Thank you for your consideration in these matters and please call if you have any questions.
Sincerely,
Jay Coghlan Scott Kovac
Executive Director Research Director
Los Alamos Budget is 65% Nuclear Weapons
Los Alamos Budget is 65% Nuclear Weapons
There are people who don’t realize that there still are nuclear weapons in the world. There are those who don’t realize that Los Alamos is still in the nuclear weapons business. I’ve created a chart that illustrates that nuclear weapons activities are 65% of the Lab’s annual $2.1 billion dollar budget. The actual Laboratory table from the Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) budget is included.
First, please remember to add three zeroes to all the numbers in the table because all “Dollars in Thousands”. And remember that the Fiscal Year (FY) 2015 Request numbers are just the President’s request, which Congress then slices and dices to arrive at the final appropriation during the congressional budget process.
Notice the largest FY 2015 Request budget by far is “Total Weapons Activities” at $1,417,502,(000). That’s $1.4 billion. “Total Defense Environmental Cleanup”, which is the remediation of radioactive and hazardous waste, is $222,262,(000). That’s $222 million.
The full budget categories are described in Volume 1 of the DOE budget here.
This page also has the Laboratory Tables on it. In addition, there is a “FY 2015 State Table” that shows all of New Mexico receives a total of $4.6 billion from DOE annually including $3.4 billion for nuclear weapons. Sandia National Laboratory in Albuquerque has a $1.5 billion request for nuclear weapons for FY 2015.
What is not on the Laboratory Tables is “Work For Others”, which is work that Los Alamos performs for government agencies other than DOE. This number is estimated at $250 million for FY 2015.
Let me know if you have any questions.
WIPP Video Story and Congressional Delegation Statements from KRQE
KRQE TV 13 aired a news story last night that included statements from the five members of the NM Congressional Delegation:
On the recent radiation leak: “From my perspective on the (U.S. Senate Energy and Natural Resources) committee, the first priority is making sure that the personnel who actually work at WIPP are safe and that the community and environment around WIPP is safe.”
On whether high-level waste should be stored at WIPP: “WIPP was never designed as a high level facility, and I don’t think we should retrofit it to be a high level facility. There has been talk of moving other transuranic waste there that was generated in different ways than the transuranic waste that’s coming from Los Alamos, for example. That’s something we can have the conversation about, but it should never be a high level facility.”
On any future change in WIPP’s mission: “We have a very long standing and robust conversation in my office with the community in Carlsbad all the time. The input from the community is always critical.” “There is nothing more important than making sure that that community feels like we are doing everything possible to make sure that WIPP is a success, and that the people who work there in the surrounding community and their well-being is our first priority.”
~ U.S. Sen. Martin Heinrich, D-New Mexico
“It’s too early to say whether the leak factors into my thoughts about the future of WIPP because we don’t know what happened. I’m taking the leak very seriously, and our focus right now is on the immediate safety of the community and WIPP personnel and the recovery work. It would be premature to draw any conclusions. This is a very technical issue, and the science is extremely important. My position on expansion now is the same as it has always been. When it comes to proposals that would significantly change WIPP’s mission, I support the provision in the current law that bans high-level waste at WIPP. WIPP was not fully studied for high-level waste, and it does not meet permit requirements for high-level waste. Additionally, New Mexico’s people and state government are the ones who have the power to decide what waste our state will accept and under what terms. Any attempt to alter WIPP’s mission would take many years of study, permitting, and require the state of New Mexico’s full support.”
~ U.S. Sen. Tom Udall, D-New Mexico
On the radiation leak: “Congressman Pearce has introduced legislation to protect New Mexico jobs at WIPP, which has safely disposed of TRU waste for over a decade. Right now, Congressman Pearce is focused on monitoring the present situation closely, ensuring DOE and WIPP continue to make public safety the top priority. To date, all information shared with our office indicates there is no risk or danger to the community. At the appropriate time, the Congressman fully expects and will insist that the Department of Energy conduct a thorough investigation and answer all the public’s questions.”
On whether high-level waste should be stored at WIPP: “Now is not the time to speculate about proposals that are not even on the table. Taking high level waste at WIPP is not on the table. Congressman Pearce’s number one priority right now is public safety, and there are many questions that need to be answered before any changes in WIPP’s mission are discussed.”
~ Eric Layer, Spokesman for U.S. Rep. Steve Pearce, R-NM 2nd District
“Right now, the number one priority is the health and safety of the WIPP employees who were affected by the leak as well as the residents of the surrounding community. As the response effort continues, there must be nothing short of full transparency and accountability to ensure the public that they are safe. This incident further proves that any expansion of WIPP’s mission warrants close scrutiny that’s rooted in science and that includes extensive outreach to and input from all stakeholders and local communities.”
~ U.S. Rep. Michelle Lujan Grisham, D-NM 1st District
“I am very concerned about the recent detection of radiation near WIPP and the health and safety of those exposed to radiation. It will be important that answers are provided detailing the causes of the elevated levels and how this will be prevented in the future. The safety and security of the community must be the top priority.
As far as the larger discussion about changes at WIPP, one aspect that cannot be forgotten or overlooked – especially given the recent incident – is the reality of exposure and what will happen when workers or members of the community are exposed to harmful levels of radiation. Sadly in New Mexico, we are all too familiar with the story of those who worked in uranium mines and other government facilities and suffered exposure to radiation. They contributed to our national security, yet paid a steep cost as many individuals became sick and some paid with their life. I am still fighting in Congress to see that many of these workers are compensated for the health problems they developed as a result of their work. While we hope we never have to face a similar situation in the future, it is important we have these discussions now rather than when it’s too late, especially given the recent reports that 13 workers tested positive for radiation exposure.”
~ U.S. Rep. Ben Ray Lujan, D-NM 3rd District
QUESTIONS FOR DOE FY 2015 BUDGET
ALLIANCE FOR NUCLEAR ACCOUNTABILITY
A national network of organizations working to address issues of
nuclear weapons production and waste cleanup
Ashish Sinha: (301) 910-9405 asinha@ananuclear.org
Bob Schaeffer: (239) 395-6773 bobschaeffer@earthlink.net
for use with March 4, 2014 Obama Administration Budget Request
QUESTIONS FOR THE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY (DOE)
FY 2015 NUCLEAR WEAPONS, REACTOR AND CLEANUP BUDGET
The U.S. nuclear budget is out of control. Huge cost overruns for unnecessary production facilities are common. At the same time, cleanup of radioactive and toxic pollution from weapons research, testing, production and waste disposal is falling behind. The Department of Energy (DOE) budget for FY 2015 will reveal the Obama Administration’s nuclear priorities.
The Alliance for Nuclear Accountability (ANA), a 25-year-old network of groups from communities downwind and downstream of U.S. nuclear sites, will be looking at the following issues. For details, contact the ANA leaders listed at the end of this Media Advisory.
— Does the budget reflect the Administration’s commitment to curtail unnecessary spending on the $19 billion Uranium Processing Facility at Oak Ridge by downsizing it to the capacity needed to support stockpile surveillance, maintenance and limited life extension?
— Does the budget address the looming deficit in nuclear weapons dismantlement capacity so the United States can meet its international arms reduction commitments?
— Will the Obama Administration articulate its alternative plutonium strategy to the $6 billion “CMRR Nuclear Facility,” which was effectively cancelled in 2012? Is any expanded production needed when expert studies have found that existing plutonium pits are durable?
— Will NNSA reduce funding or impose meaningful milestones at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), which performed less than half of its planned Stockpile Stewardship experiments in FY2013 and still has not achieved ignition.
— Is the budget a de facto cancellation of plans to pursue “interoperable warhead designs” by imposing a delay of five years or more on the program? How much money will taxpayers save?
— Does the FY 2015 budget seek more than the $537 million requested for the B61 Life Extension Program last year? Will the “First Production Unit” from this $10 billion program continue to slip to 2020 or later delaying needed routine replacement of critical components?
— How much of the additional $26 billion in Defense Sec. Chuck Hagel’s “Opportunity, Growth and Security Initiative” will go to DOE nuclear weapons programs?
— Will the Administration support increased funding for the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB) to provide independent oversight of DOE projects given the many cost over-runs, schedule delays, safety issues and technical problems?
— What is the projected life-cycle cost of the plutonium fuel (MOX) program at Savannah River? Is DOE’s internal cost assessment consistent with ANA’s estimate of $27 billion? When will it be released? Have any nuclear reactor operators committed to using MOX fuel?
— Does the Request include continued funding for design and licensing of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), which private investors have been unwilling to finance fully because of concerns about viability and risks? Does DOE have plans to finance SMR construction?
—How much additional Environmental Management (EM) funding would be necessary in FY 2015 to meet all legally mandated cleanup milestones? States say cleanup agreements at a dozen major sites are underfunded by hundreds of million dollars.
— In which states does DOE face fines and lawsuits for missing milestones due to budget shortfalls? Which states are enforcing their binding clean-up agreements by imposing fines and taking further legal action?
— What is the high range for total life-cycle clean-up costs (LCC) for EM sites Because of funding shortfalls, are LCC costs continuing to increase? In the FY 2013 Budget Request High Range LCC was $308.5 billion, and in the FY 2014 Request LCC was $330.9 billion.
— Does the FY 2015 Request include funds to cleanup contamination from the recent radiation release at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP)? How much will this incident delay shipments from the Idaho National Lab, Los Alamos, Savannah River, and Oak Ridge?
— How much money is included for construction of new double-shell tanks to replace those leaking radioactive waste at the Hanford site? Are funds included for emergency pumping of tanks found to be leaking?
— Is DOE allocating sufficient funds to monitor and address ignitable hydrogen gas buildup in Hanford’s nuclear waste tanks as recommended by the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board to protect workers, the public and the environment from possible explosions?
— Is an independent review of the Hanford Waste Treatment Plant included in the budget request to address concerns about the reliability of many of the parts and materials?
–– How much money is DOE allocating for building and development of the Hanford Waste Treatment Plant based on the current, flawed design and how much on redesign?
— For information about specific DOE nuclear weapons sites and programs, contact:
Meredith Crafton – Hanford: (206) 292-2850 x26 meredithc@hanfordchallenge.org
Tom Clements – Savannah River and MOX Plant: (803) 240-7268 tomclements329@cs.com
Jay Coghlan – Los Alamos Lab and Life Extension: (505) 989-7342 jay@nukewatch.org
Don Hancock – Environmental Management Program: (505) 262-1862 sricdon@earthlink.net
Ralph Hutchison – Oak Ridge Site and Dismantlement: (865) 776-5050 orep@earthlink.net
Marylia Kelley – Livermore Lab and Life Extension: (925)-443-7148 marylia@trivalleycares.org
LANL Community Support Is Contract Requirement
LANL Community Support Is Contract Requirement
A recent press release from Los Alamos National Laboratory stated that the LANL “Board of Governors last week approved a $3.1 million extension to the company’s plan supporting education, economic development and charitable giving in Northern New Mexico.”
This, like most LANL statements, could use a little decoding.
1. The Lab’s contract with DOE requires community support. The LANL Conformed Contract (Conformed to Mod 215, 01/25/2013) tells us:
H-24 NNSA AND CONTRACTOR COMMUNITY COMMITMENTS
(a) The Contractor shall perform the activities described in the Contract’s Section J Appendices entitled “Regional Initiatives”, “Regional Purchasing Program” and “Technology Commercialization”, which sets forth the NNSA’s commitments to support the community…
(b) The Contract’s Section J Appendix entitled “Contractor and Parent Organization Commitments, Agreements, and Understandings” sets forth the Contractor’s Community Commitment plan that describes its planned activities as to how the Contractor will be a constructive partner to the communities in northern New Mexico, the eight northern pueblos, and to citizens of the State of New Mexico who should all benefit from the Contractor’s management and operation of Los Alamos National Laboratory…
2. For 2014, the Press release states the Plan will provide “$1 million for economic development such as financial and technical assistance to start and grow regional businesses. ” However, the contract states that the Lab receives a $1.8 million tax credit (per year) from the State of New Mexico for providing technical services assistance to small business. It is unclear to us what the Lab does with the other $.8 million.
4. The Press release continues that the Plan will provide “$1.1 million for educational programs and scholarships for New Mexico students and teachers as well as workforce development programs.” One of the scholarship programs that the Lab provides is the Out-of-State Tuition and Fee Waiver program. The contract explains that this program is for any LANS “full-time active employee and/or dependent who is accepted to any University of California undergraduate or graduate program. Based on the past 3 years of data, approximately 100 students will take advantage of this program annually. Out-of-state tuition and fee waiver represents a savings of $17,000 per student each year” or $1.7 million annually.
5. For meeting its community giving contract requirements, the then Lab receives an award fee on top of the regular payments. LANL’s FY 2012 Performance Evaluation Report does not give the public the exact breakout, but we know that Performance Based Initiative 11 (PBI 11: Excellence in Business and Institutional Management), which includes community giving, earned the Lab an additional $3,656,808 for 2012.
6. Not mentioned in the press release was one of the biggest gives, which is to Los Alamos Public Schools. The contract states, “The primary management and operations contractor shall provide $8.0 million in each fiscal year to the Los Alamos Public School District to support public elementary and secondary education.”
Excellence Unfulfilled at the LANL’s Plutonium Facility
A Los Alamos National Laboratory fact sheet touts the Lab as a plutonium “center of excellence”. However, the Laboratory Director paused operations in the Plutonium Facility on June 27, 2013. (The Plutonium Facility, called PF-4, is located at Technical Area 55 at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). PF-4 is home for the Lab’s plutonium work, including nuclear weapons component production.) The pause was based on issues identified during safety reviews and findings from recent assessments. For one, the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (Board) performed a review of the Criticality Safety Program at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in May 2013. (The Board is an independent organization within the executive branch chartered with the responsibility of providing recommendations and advice to the President and the Secretary of Energy regarding public health and safety issues at Department of Energy (DOE) defense nuclear facilities.) This review identified significant non-compliances with DOE requirements and industry standards in the Lab’s Criticality Safety Program (CSP). In addition, this review identified criticality safety concerns around operations at the Plutonium Facility. The Board noted that some of these deficiencies are long standing and indicated flaws in federal oversight and contractor assurance. Much plutonium work, especially work with a high potential for criticality, will be stopped through the rest of 2013.
Nuclear criticality safety is defined as “protection against the consequences of an inadvertent nuclear chain reaction, preferably by prevention of the reaction.” The most potentially dangerous aspect of a criticality accident is the release of nuclear radiation if it maintains a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction.
To date, the only thing self-sustaining is the Lab’s inability to address its criticality issues and yet still convince Congress to keep funding plutonium work there. To prevent bad things from happening, DOE’s regulations and directives require contractors to evaluate potential accident conditions and put in place appropriate controls and safety measures. History shows that the Los Alamos Laboratory just cannot do this, even though much of the work is performed on plutonium pits, the primaries of nuclear weapons. Even though actual need for this work has not been proven, the Lab has entrenched itself as the only place in the country where plutonium pits can be made, developed, and tested.
For fiscal year 2014, the budget request for nuclear ‘weapons activities’ at LANL was $1.4 billion. The exact amount that is spent on plutonium operations in PF-4 is unknown to us, but the budget request for 2014 for Directed Stockpile Work, which is where major parts of the plutonium operations are located, was $460 million. This is a 23% increase over last year’s budget. The funding pours into the Lab regardless of whether the Lab is actually doing any work, which is frequently stopped.
Here’s history of criticality problems and work stoppages at Los Alamos Laboratory:
In 2005, an assessment determined that LANL’s expert-based Criticality Safety Program (CSP) was not compliant with applicable DOE requirements and industry standards.
In 2006, LANS developed a Nuclear Criticality Safety Program Improvement Plan.
In 2007, in response to concerns raised by the Board’s staff, LANL determined that the authorized loading of vault storage rooms in PF-4 could lead to a critical configuration.
In 2008, the Government Accountability Office reported concerns about nuclear safety at LANL are long-standing. Problems included 19 occasions since 2003 where criticality safety requirements were violated, such as storing materials in quantities higher than safety limits allow, 17 of 19 of the site’s nuclear facilities operating without proper safety documentation, reported inadequacies in safety systems, radiological releases, and four enforcement actions for significant violations of nuclear safety rules.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending April 3, 2009
LANL management placed the facility in stand-by mode until roughly 125 safety evaluations could be re-evaluated.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending October 2, 2009
The Plutonium Facility was placed in standby mode because management declared the fire suppression system inoperable based on recent hydraulic calculations that concluded the system was not able to achieve the water coverage required. LANL had performed a system adequacy analysis in 2008. The hydraulic calculation completed for the system identified that 13 of approximately 100 hydraulic areas did not meet the requirement.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending October 16, 2009
A general evacuation alarm was caused by a Criticality Alarm System signal because of a loss of all facility ventilation and failure of the Facility Control System at the Plutonium Facility. The facility was in standby mode during this event due to previously identified issues with the fire suppression system and, therefore, limited personnel were in the facility.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending September 10, 2010
Operations in Plutonium Facility were suspended because potentially explosive ammonium nitrate was discovered in two filter ducts.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending December 3, 2010
It was revealed that greater than 1000 items, or about 20%, of the total vault holdings are items packaged in potentially vulnerable containers with taped slip-top lids rather than in robust safety-significant containers that include a HEPA-filtered vent. The presence of these slip-top containers requires respirator use whenever operators access the vault. In FY10, LANL made meaningful progress in addressing these legacy materials.
In 2011, an event occurred at PF-4 in which fissile material handlers violated procedural requirements and criticality safety controls while moving and photographing plutonium rods.
Beginning in 2012, LANS experienced an 18-month exodus of criticality safety professionals from its criticality safety group. LANS currently employs 2 full-time and 2 part-time qualified criticality safety analysts, in addition to 3 part-time subcontractors—far fewer than the 17 criticality safety analysts it has determined to be necessary to support operations, meet mission goals, and maintain the CSP.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending April 20, 2012
Plutonium Facility personnel use a software program called MAR Tracker to track plutonium that is used in the facility. A system engineer discovered an error in
MAR Tracker that caused only a small subset of applicable facility containers (roughly 1700 out of 13000 containers) to be checked during the required annual MAR surveillance. The Plutonium Facility was placed in Standby Mode.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending June 15, 2012
LANL identified a number of fuel rods in TA-35 Building 27 that were not consistent with the criticality safety evaluation for the facility. Operations at this building had previously been suspended in late-May due to the discovery of three fuel rods that were not in the facility or institutional tracking systems.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending December 14, 2012
LANL identified that the Criticality Safety Evaluations (CSEs) for two rooms did not adequately address the potential for interaction effects between storage locations. Plutonium Facility management suspended operations in these two vault rooms.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending February 15, 2013
LANL began a focused training program (“boot camp”) to provide an intensive learning environment for new criticality safety staff. The program consisted of nine modules including: nuclear theory; criticality safety calculation methods; ANSI/ANS, DOE and LANL criticality safety standards and requirements; criticality safety evaluations; and criticality alarm and detection systems. This program along with on-the-job training and performance demonstrations was to provide a mechanism for achieving full qualification as a LANL criticality safety analyst. Conduct of the boot camp was part of the LANL corrective action plan for improving the nuclear criticality safety program.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending May 3, 2013
The laboratory completed criticality safety assessments at LANL nuclear facilities. The review teams identified 3, 4, and 6 findings for TA-55, CMR, and Area G, respectively. In all cases, the assessments concluded adequate implementation of the Criticality Safety Program with the exception of identified findings. Notably, one of the findings at Area G identified that supervisors and operations center personnel did not have an adequate understanding of criticality safety requirements. Area G management paused operations based on this finding and conducted appropriate training to resolve this issue.
In May 2013, the staff of the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (Board) performed a review of the Criticality Safety Program at Los Alamos National Laboratory. This review identified significant non-compliances with applicable Department of Energy requirements and industry standards in the implementation of the Criticality Safety Program. The Board’s staff identified the following non-compliances during its review:
• Most criticality safety controls are not incorporated into operating procedures.
• Operators typically do not utilize written procedures when performing work.
• Fissile material labels do not list parameters relevant to criticality safety (e.g., mass).
• Some fissile material operations lack Criticality Safety Evaluations (CSEs).
• Some CSEs do not analyze all credible abnormal conditions.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending June 28, 2013
The Laboratory Director paused programmatic activities at the Plutonium Facility. The pause was directed based on issues identified during procedural and criticality safety reviews and findings from recent assessments. Reviews at PF-4 have identified a number of procedural issues and the need for clarification and improvement of criticality safety controls.
Los Alamos Report for Week Ending July 26, 2013
Plutonium Facility personnel identified several criticality safety issues associated with recent construction activity. Even though plutonium work was paused, the Laboratory Director and the Facility Operations Director (FOD) approved construction activities that had the potential to affect nuclear materials.
For more information, please read the LAMonitor article By John Severance
Safety board visits LANL
Why the appointment of ex-NM Rep. Heather Wilson to security panel is not a good thing
Reportedly House Speaker Boehner has appointed former Rep. Heather Wilson (R-NM) to the Congressional Advisory Panel on the Governance of the Nuclear Security Enterprise. Other appointments have not been yet announced.
That is not good. Wilson (a former protégé of Sen. Pete Domenici) is a self-interested advocate for the Labs. According to an October 16, 2012 Santa Fe Reporter article she has had numerous consulting contracts with defense contractors, including Sandia Labs beginning in 2009 and up to her Senate campaign in 2012 (see .http://www.sfreporter.com/santafe/article-7028-this-is-heather-wils.htm). Moreover, in the past her congressional staff has included Sandia Labs personnel.
She also incorrectly and repeatedly argued in her Senate campaign against Martin Heinrich that the deferral of the CMRR-Nuclear Facility would cost 1,000 jobs at the Los Alamos Lab (my repeated attempts to contact her campaign and correct her had no apparent effect).
The provision in the FY 2013 Defense Authorization Act that enabled the Congressional Advisory Panel on the Governance of the Nuclear Security Enterprise was largely written by a staffer on the House Armed Services Committee who is a former Sandia Labs employee. Its purpose is to create greater autonomy for the nuclear weapons labs with less federal oversight. (See “Governance, Management, and Oversight of the Nuclear Security Enterprise, ” House Report 112–479, National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2013, H.R. 4310, page 329).
Given the long string of chronic cost overruns and security infractions, diminished federal oversight and greater autonomy for privatized corporate nuclear weapons contractors is not the way to go. Don’t expect Heather Wilson to help the American taxpayer correct that wrong direction.
On a final note, this Panel should be subject to the Federal Advisory Committee Act. A 2008 Government Accountability Office report on the Act states “Because advisory committees provide input to federal decision makers on significant national issues, it is essential that their membership be, and be perceived as being, free from conflicts of interest and balanced as a whole.” http://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-08-611T
This should apply to Wilson if she still has consulting jobs with the nuclear weapons labs.