Statement of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia Concerning the Expiration of the Russia-US New START Treaty
On February 5, 2026, the life cycle of the Russian-US Treaty on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms (New START) finally comes to an end; it was signed by the parties on April 8, 2010, entered into force on February 5, 2011, and was extended for a five-year period in February 2021 on the basis of a relevant one-time option provided for in this agreement.
mid.ru/en/foreign_policy/news/2076815/ February 5, 2026
In February 2023, the Russian Federation suspended the New START Treaty against the backdrop of the unsatisfactory state of affairs with the implementation of certain aspects of the Treaty, as well as due to the absolutely unacceptable steps by the United States running counter to the fundamental principles and understandings of the agreement enshrined in its preamble. It was a compelled measure and an inevitable response of the Russian side to the extremely hostile policy of the Biden administration which resulted in the fundamental change in the security situation, as well as to a number of illegitimate steps taken by Washington in the context of specific provisions of the New START Treaty, which together constituted a material breach incompatible with the Treaty being further implemented in a full-fledged manner.
Among the key negative factors, it is worth to highlight the destabilizing actions of the United States in the field of missile defense, contrary to the inseparable interrelationship between strategic offensive and strategic defensive arms enshrined in the New START Treaty. This contradicted the Treaty’s objectives in terms of maintaining the balance of powers, put significant pressure on its viability, and created grounds for Russia to take compensatory measures outside the scope of the New START Treaty in order to maintain strategic equilibrium.
Despite some obvious problematic moments, basically the New START Treaty used to fulfill its key functions. The conclusion of the Treaty and the years of its initially successful implementation helped to discourage the strategic arms race, allowing for significant reductions in the parties’ arsenals. At the same time, due to the restrictions applied in this area a sufficient level of predictability was ensured on a long-term basis.
4 things to know about the end of the U.S.-Russia nuclear arms treaty
“For the first time in decades, there are no limits on the world’s largest nuclear arsenals. Congress must act now.”
By Austin Headrick, American Friends Service Committee | February 4, 2026 afsc.org
The world changed forever in August 1945, when the United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing an estimated 110,000 to 210,000 people. Scientists, activists, policymakers, and peacebuilders—including organizers at AFSC—have spent the decades since calling for disarmament and an end to all nuclear threats. One crucial result of that work was arms control treaties that limited nuclear arsenals.
But now, that work is being unraveled. On Feb. 5, 2026, the last remaining U.S.-Russia nuclear arms reduction treaty, expired. The New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START) had placed limits on deployed nuclear weapons and created channels for inspections and monitoring.
With the end of the treaty, the guardrails that create transparency and prevent a nuclear arms race end.
Here is what you need to know:
1. The U.S. and Russia hold nearly all the world’s nuclear weapons.
The United States and Russia together possess almost 90% of the world’s nuclear weapons. That is why New START matters even to people far from Washington and Moscow. A world with no limits on the two largest nuclear stockpiles is a more dangerous world.
Without New START, there would be no legally binding guardrails on the two countries’ long-range nuclear weapons for the first time since the first U.S.-Soviet arms control agreements in the early 1970s.
And the risk is not only long-term nuclear development. Without limits, either side could increase the number of nuclear weapons ready to launch relatively quickly by “uploading” additional warheads onto existing missiles, which can fuel pressure for the other side to respond.
2. Arms control makes everyone safer.
New START capped the U.S. and Russia at 1,550 deployed nuclear weapons and limited deployed delivery systems, with an overall limit on launchers and bombers. Those numbers are more than technical details. They limit how many weapons can be used quickly in a crisis.
Continue reading
Los Alamos confirms UMich data center to be used for nuclear weapons research
“A representative of Los Alamos National Laboratory confirmed nuclear weapons research will be a priority for its portion of the data center it intends to construct in collaboration with the University of Michigan in Ypsilanti Township.”
By Glenn Hedin, The Michigan Daily | January 30, 2026 michigandaily.com
Patrick Fitch, deputy laboratory director for science, technology, and engineering at Los Alamos, was present at the University’s open house on the project in Ypsilanti Thursday. When The Michigan Daily asked if Los Alamos intended to use its portion of the data center to support nuclear weapons research, Fitch said yes.
“The short answer is yes, because aspects of a nuclear weapon is key to our simulation expertise,” Fitch said. “We want this loop to include large investments in national security, so that spins back into the basic science, and what we learn here — that list of non-nuclear weapons stuff — spins into nuclear weapons.”
The proposed data center has garnered significant opposition from Ypsilanti residents and U-M community members who worry about its potential to negatively impact the surrounding environment and electrical grid, as well the possibility that the facility could be used in the development of nuclear weapons. The University has maintained the facility will not “manufacture” nuclear weapons.
Some activists consider this statement misleading, as data centers are generally used for computing activities and not manufacturing. However, their computing capabilities could be used to support nuclear research in other ways, including in the production of plutonium pits, which serve as the cores of nuclear weapons. While plutonium pits need not be located at a data center, their development requires intensive computing power. Los Alamos has operated under federal directive to modernize the United State’s nuclear arsenal through the development of these pits since 2018.
*The featured image differs from the article photo due to usage rights. Photo: Google Data Center, Council Bluffs Iowa (49062863796).jpg
chaddavis.photography from United States, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Barring last-minute nuclear deal, US and Russia teeter on brink of new arms race
SUMMARY:
• New START treaty set to expire on February 5
• Trump hasn’t responded to Putin’s offer to extend missile limits
• End in sight to more than 50 years of mutual constraints
• Chinese build-up leaves US facing two big nuclear rivals
By Mark Trevelyan and Jonathan Landay | REUTERS, January 29, 2026 reuters.com
LONDON/WASHINGTON, Jan 30 (Reuters) – The United States and Russia could embark on an unrestrained nuclear arms race for the first time since the Cold War, unless they reach an eleventh-hour deal before their last remaining arms control treaty expires in less than a week.
The New START treaty is set to end on February 5. Without it, there would be no constraints on long-range nuclear arsenals for the first time since Richard Nixon and Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev signed two historic agreements in 1972 on the first-ever trip by a U.S. president to Moscow.
It is now 85 seconds to midnight.
On January 27, 2026, the Doomsday Clock was set at 85 seconds to midnight, the closest the Clock has ever been to midnight in its history.
The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists’ Science and Security Board (SASB), which sets the Clock, called for urgent action to limit nuclear arsenals, create international guidelines on the use of AI, and form multilateral agreements to address global biological threats.
Partnership for a World without Nuclear Weapons: Statement on the Fifth Anniversary of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
ALBUQUERQUE—Wednesday, January 21, 2026—The Partnership for a World without Nuclear Weapons released a statement in recognition of the fifth anniversary of the entry into force of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons:
We hope for its further expansion through additional ratifications, now that a majority of the world’s countries have signed the Treaty. In July 2017, the Vatican was the first nation-state to sign and ratify the Treaty as part of its “unwavering commitment to the total elimination of nuclear weapons.”
We condemn the fact that the nuclear weapons powers have never honored their long-held obligations under the 1970 NonProliferation Treaty to enter serious negotiations leading to global nuclear disarmament.
In contrast, the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons was a great step toward the light of peace. The nuclear-armed states have a moral obligation to hear the voices of the majority of the world, and to listen to those who face the threat of annihilation due to the reckless decisions of any one of their nine leaders. Russia’s nuclear saber-rattling over Ukraine makes this clear, while ongoing crises in the Middle East further escalate the risks. Meanwhile, the nuclear weapons powers are engaged in massive “modernization” programs, designed to keep nuclear weapons forever.
The international legal force of the nuclear weapons ban treaty is limited to those states that have formally ratified it. But its moral power does not recognize boundaries between nations, nor lines on a map. The moral power of this Treaty is global and universal. We hope and pray that it will exert moral pressure on the nuclear weapons states to finally honor their disarmament obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty.
On the fifth anniversary of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, we specifically call upon world leaders to demonstrate measurable progress toward nuclear disarmament. Eight decades of nuclear threats are far too long, as evidenced by the horrors documented by the atomic bombing museums in Japan. It is long past time for the nuclear weapons powers to begin to make tangible progress toward that end.
As our close colleague Robert McElroy, Cardinal of Washington, DC, declared last August in Hiroshima on the 80th anniversary of the atomic bombing:
“We refuse to live in a world of nuclear proliferation and risk-taking. We will resist, we will organize, we will pray, we will not cease, until the world’s nuclear arsenals have been destroyed.”
A Grave Problem with South Carolina’s New Nuclear Warhead
In South Carolina, contractors say new plutonium pit warhead waste will be shipped to New Mexico. Is it true?
“The coming showdown over SRNS’s TRU waste underscores what has long been a truism of the US nuclear weapons complex: that the government’s urgency to produce new weapons outstrips its commitment to plan and fund the cleanup of the sites across the American landscape that are contaminated while doing so.”
By Taylor Barnes | January 22, 2026 inkstickmedia.com
On a crisp evening last October, Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS), a federal contractor that hopes to manufacture thousands of cores for new nuclear warheads at a Cold War-era weapons plant in rural South Carolina, put on a public information session at a library in the town of North Augusta. The purpose of the event was to address any concern from locals that its plan to produce 50 plutonium pits per year for 50 years would leave toxic waste, including radioactive refuse known as TRU waste, in and around the 310-square-mile Savannah River Site (SRS) that people in towns like Allendale and Aiken find themselves neighboring.
The session included about 30 presenters whom SRNS employs. They handed out Halloween candy while standing beside posterboards laying out what they described as a “cradle-to-grave” process for TRU waste generated by producing those pits. They described a plan to store batches of radioactive waste for only one year in both existing and to-be-constructed buildings around an abandoned nuclear fuel plant at the SRS. The waste, according to contractor employees and a map they displayed, would then be transported in trucks along Interstate 20 through Atlanta, Birmingham, and Fort Worth before reaching southern New Mexico, where it would be buried in an 2,150-foot-deep salt mine called the Waste Isolation Pilot Project (WIPP). The 1976 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act requires the company to detail those steps, including, crucially, the final “disposition of such wastes,” in order to apply for a local permit to build and operate what SRNS says will be just temporary waste storage buildings at the plant site. An information sheet from SRNS said the company plans for the permit application to be submitted in January and for the new storage buildings to begin construction a year later.
Trump offers states a deal to take nuclear waste
“Governors would effectively be invited to compete for what the administration believes is a once-in-a-generation economic development prize in exchange for hosting the nation’s most politically and environmentally toxic byproduct.”
By Sophia Cai, E&E News by POLITICO | January 21, 2026 eenews.net
The Trump administration wants to quadruple America’s production of nuclear power over the next 25 years and is hoping to entice states to take the nuclear waste those plants produce by dangling the promise of steering massive investments their way.
President Donald Trump’s big bet on amping up nuclear production is not an easy feat, fraught with NIMBY concerns about safety and waste byproducts. The administration hopes to solve at least one of those issues — what to do with toxic nuclear waste — with a program they plan to roll out this week.
Governors would effectively be invited to compete for what the administration believes is a once-in-a-generation economic development prize in exchange for hosting the nation’s most politically and environmentally toxic byproduct.
Energy Secretary Chris Wright has already begun laying groundwork with governors. Over the last two weeks, Wright has met with at least two governors who have expressed interest, according to two officials familiar with the private meetings granted anonymity to discuss them.
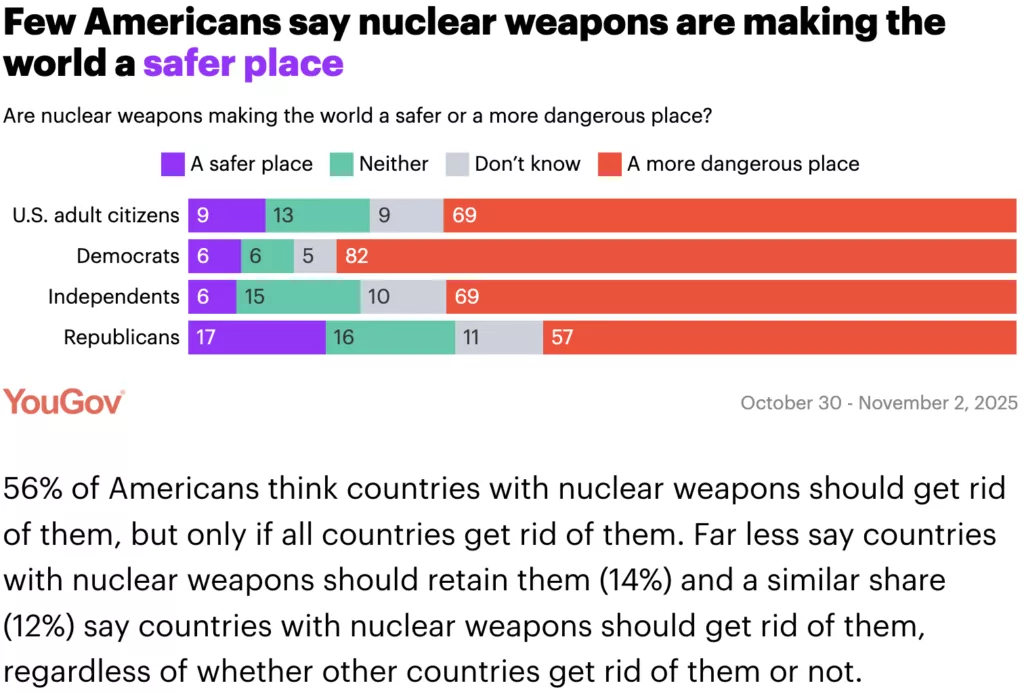
Americans Across Party Lines Want the U.S. to Keep Nuclear Limits with Russia, New Poll Finds
YouGov poll commissioned by ReThink Media and the Nuclear Threat Initiative.
“As the last remaining U.S.-Russia nuclear limitations treaty expires on Feb. 5, an overwhelming majority of Americans (91 percent) say the United States should negotiate a new agreement with Russia to either maintain current limits on nuclear weapons or further reduce both countries’ arsenals.”
Nuclear Threat Initiative | January 21, 2026 nti.org
 The poll of 1,000 registered voters also finds that the vast majority of Americans—including 85 percent of those who voted for President Trump—believe the president should agree to Russia’s proposal to continue abiding by the limits imposed by the New START treaty for at least another year after the treaty expires. In addition, 72 percent of registered voters believe that removing all nuclear limits on U.S. and Russian nuclear arsenals would make the United States less secure.
The poll of 1,000 registered voters also finds that the vast majority of Americans—including 85 percent of those who voted for President Trump—believe the president should agree to Russia’s proposal to continue abiding by the limits imposed by the New START treaty for at least another year after the treaty expires. In addition, 72 percent of registered voters believe that removing all nuclear limits on U.S. and Russian nuclear arsenals would make the United States less secure.
When New START expires, it will be the first time in decades that there are no limits capping the number of nuclear weapons for the world’s two largest arsenals. Together, the U.S. and Russia own almost 90 percent of all nuclear weapons in the world.
President Trump recently said he intends to negotiate a better agreement with Russia after New START expires. Previously, he warned that “when you take off nuclear restrictions – that’s a big problem” and made favorable comments about Russia’s one-year offer to voluntarily maintain the treaty’s limits. He repeatedly has warned of the threat posed by nuclear weapons. However, his administration has not yet taken concrete actions to secure a new nuclear limitations agreement with Russia.
Palomares: Reflections of an American, sixty years later
This past Saturday marked 60 years since the 1966 Palomares mid-air crash that left plutonium contamination scattered around the Spanish village. Dr. Michael E. Ketterer, Professor Emeritus of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Northern Arizona University in Flagstaff, AZ, has authored “Palomares: Reflections of an American, sixty years later.” See his English language version here and below and the Spanish version here.
By Michael Ketterer, elDiario | January 17, 2026 eldiario.es

By U.S. Navy, Courtesy of the Natural Resources Defense Council – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by EH101 using CommonsHelper., The original uploader was Asterion at English Wikipedia., 31 May 2007 (original upload date), Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=2630293
During the early morning hours of January 17, 1966, the six-year-old author was in his bed, asleep in the Buffalo, New York suburb of North Tonawanda. During those very same moments, a crash took place between two US planes: a B-52 bomber and a fully loaded KC-135, which were in the midst of refueling the bomber in-flight. The B-52 was crossing the Iberian Peninsula that morning as part of US Air Force’s Strategic Air Command’s daily routes, performing vigilance on the Soviet Union. Three thermonuclear bombs fell to the land, and a fourth fell into the sea, after the collision in the skies over Palomares, a small village located about two kilometers from the Mediterranean, in the province of Almeria, Andalucía in southeastern Spain.
All of that happened before I got out of bed that day.
Two of the bombs were destroyed upon impact, although neither produced a nuclear explosion. Instead, several kilograms of plutonium (Pu) were dispersed on a windy day, onto several square kilometers of the tomato fields and residential zones of Palomares. An additional bomb was found by a local resident; fortunately, it wasn’t significantly damaged since its parachute had opened. On the other hand, the fourth bomb appeared to have been lost in the Mediterranean, and very soon, that was obviously true. The US Air Force’s top priority quickly became to use whatever resources and heroes that were available, for an urgent mission: find the lost bomb before the Soviets could do so. The search and recovery of the bomb became the success story, and the history that was told. That was the lesson learned from Palomares, among the two governments, their military forces, and in the press. The photos of the military commanders from both countries posing with the recovered bomb aboard the USS Petrel are some of the most famous Internet images of Palomares.
Watch BOMBSHELL on PBS American Experience — streaming across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App!
The wait is over! BOMBSHELL is available NOW on PBS American Experience — and will be streaming simultaneously across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App.
BOMBSHELL examines how the U.S. government manipulated public opinion through propaganda and censorship to justify the use of nuclear weapons and to minimize the human toll. Against this powerful machinery, a small group of journalists—including a Black pool reporter, a Japanese American staffer, a Japanese photographer, and a freelance magazine writer—identified gaps in the official narrative and courageously reported on the human consequences of the atomic bombings.
The Wall Street Journal described BOMBSHELL as offering “lessons for our own age of ascendant AI,” while Foreign Policy called it “provocative history that brings to life the dangers that arise when government secrecy and control overwhelm press freedom.”
New Mexico, Department of Energy at odds over cleanup halt at LANL waste site
In a December public meeting, the field office’s manager indicated approval from the Environment Department likely wasn’t needed to defer the study and cleanup of Area C. According to the compliance decree, “NMED approval is not required” in several cases to change the status of an area to deferred, as long as the Department of Energy complied with other requirements.
Environment Department spokesperson Drew Goretzka wrote in an email to The New Mexican a site can be deferred in one of four cases, including if it is involved in active operations and if the amount of time needed for deferment is assessed.
The department doesn’t agree those requirements have been met, Goretzka wrote, “resulting in a breach of the Consent Order.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | January 9, 2026 santafenewmexican.com
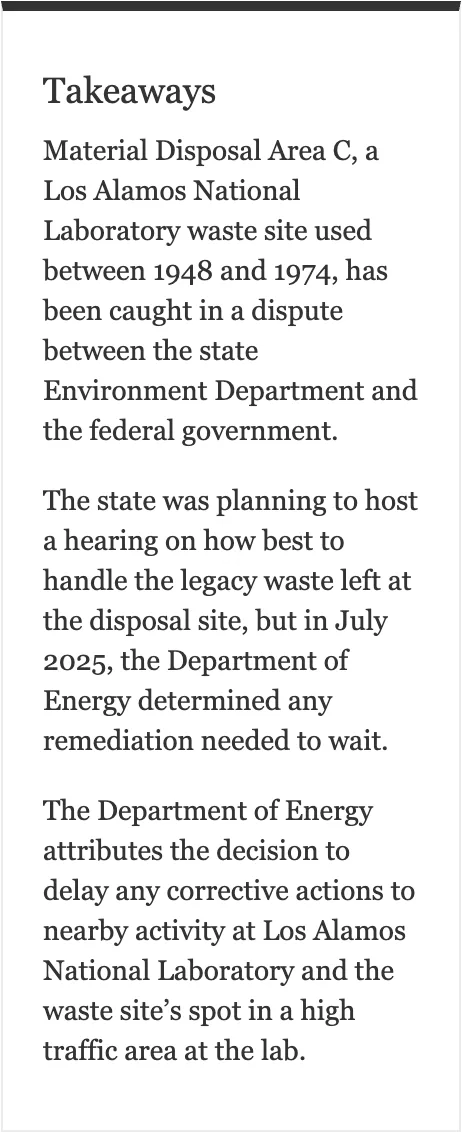 The U.S. Department of Energy has put cleanup of a hazardous waste disposal site at Los Alamos National Laboratory on hold, a decision that seems to have drawn the ire of the New Mexico Environment Department.
The U.S. Department of Energy has put cleanup of a hazardous waste disposal site at Los Alamos National Laboratory on hold, a decision that seems to have drawn the ire of the New Mexico Environment Department.
The state last year was planning to hold a public hearing in early 2026 on how to handle legacy waste left behind at Material Disposal Area C, according to a letter from an official in the Hazardous Waste Bureau.
The Department of Energy, however, had already made up its mind: Any corrective actions at the site would have to wait due to ramped-up operations near Area C. The public hearing is now on hold until the conflict over the deferment of corrective actions is settled, according to an Environment Department spokesperson.
The 11-acre waste site, in use from 1948 to 1974, is located within Technical Area 50 along Pajarito Road. Its six disposal pits were used for various types of waste, including radioactive materials and heavy metals.
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: January 2026
American imperialism:
On the U.S. raid on Venezuela to oust Nicolás Maduro, the Venezuelan president:
Stephen Miller, Donald Trump’s deputy chief of staff for policy and homeland security advisor, told CNN’s Jake Tapper on Monday January 5, 2026:
“We live in a world in which you can talk all you want about international niceties and everything else, but we live in a world—in the real world, Jake—that is governed by strength, that is governed by force, that is governed by power. These are the iron laws of the world that have existed since the beginning of time.”
The “Donroe Doctrine” is a more aggressive Trumpian take on the 1823 Monroe Doctrine, a foreign policy approach focused on unilateral U.S. dominance in the Western Hemisphere. How far does this administration intend to force this new doctrine?
DOE now department of nuclear weapons and Venezuelan oil: The Trump administration engaged the Department of Energy (DOE) and Secretary Chris Wright to oversee the seizure and marketing of Venezuelan oil following the capture of Nicolás Maduro. The U.S. intends to control Venezuelan oil, aiming to sell 30–50 million barrels of accumulated, sanctioned crude to the American people.
Greenland:
Trump describes Greenland as an “absolute necessity” for national security and the defense of the Arctic.
U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent has said that the president believes Greenland is “essential for the Golden Dome missile shield.” https://www.wcvb.com/article/greenland-trump-explainer/70097863
Chicago Tribune Editorial: Tick, tick goes the Doomsday Clock
“It would be madness to resume nuclear testing, let treaties lapse and expand arsenals that already could wipe out the planet. Diplomacy worked for decades, mainly because of an understanding that avoiding nuclear war was essential to humanity’s future. Today’s global leaders need to start acting accordingly.”
By The Editorial Board | Chicago Tribune – January 6, 2026 chicagotribune.com
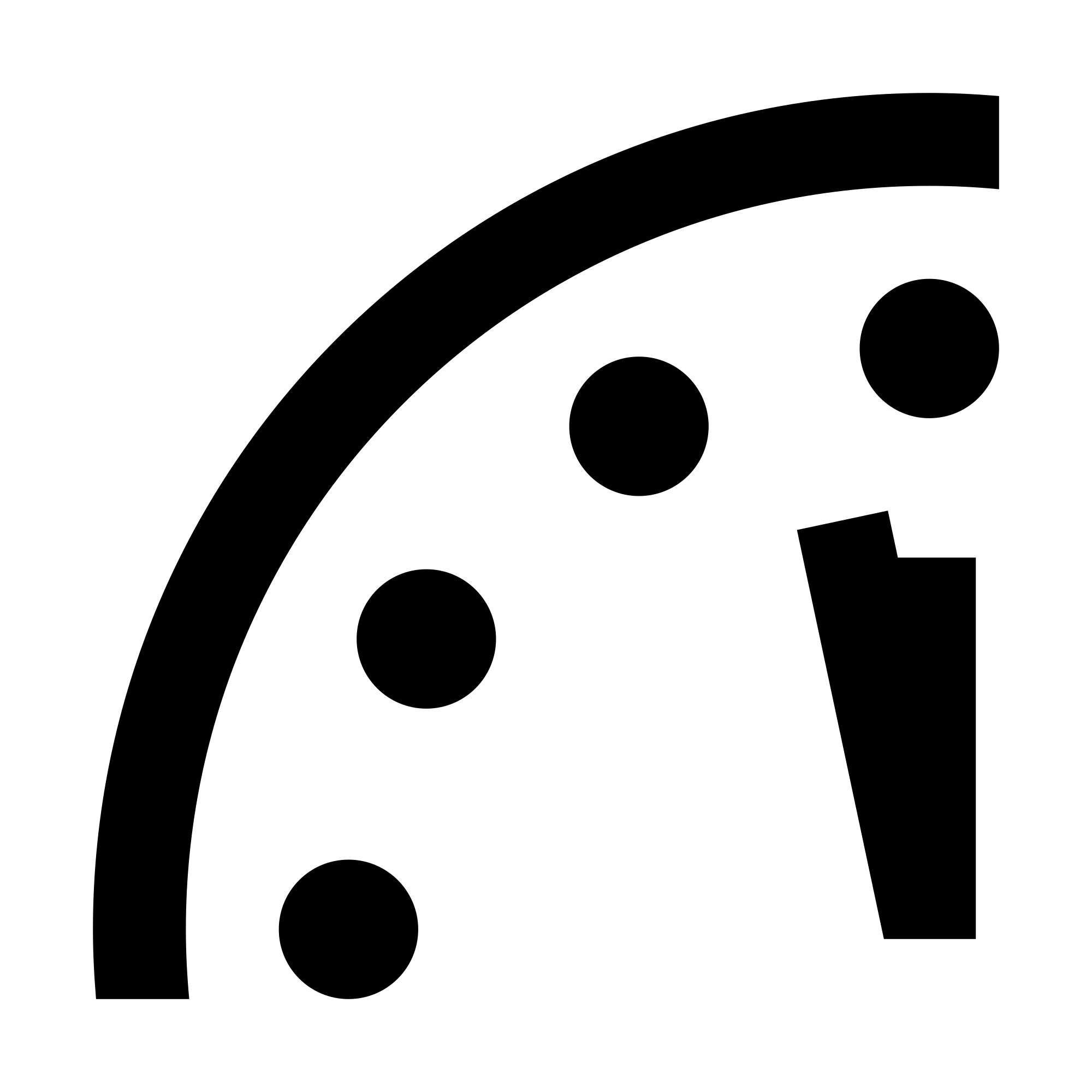 This month, the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists at the University of Chicago is scheduled to announce whether the hands of its famous Doomsday Clock will move closer to midnight. It feels like a safe bet that Armageddon is drawing nearer today than it has in a long, long time.
This month, the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists at the University of Chicago is scheduled to announce whether the hands of its famous Doomsday Clock will move closer to midnight. It feels like a safe bet that Armageddon is drawing nearer today than it has in a long, long time.
The Doomsday Clock started almost 80 years ago, when physicists who developed the Bomb grew alarmed at its use against Japan to end World War II.
Between the late 1940s and the early 1990s, nuclear war wasn’t a remote possibility: It almost happened, repeatedly, as America and the Soviet Union fought the Cold War. Chicago’s atomic scientists moved the hands of their clock from seven minutes to midnight at its start in 1947 to just two minutes to midnight as of 1953, when the U.S. and Soviets started testing enormously powerful hydrogen bombs.
*The image above differs from the article photo due to usage rights.
NEW INTERACTIVE PIECE from USA TODAY: THE NUCLEAR SPONGE — & Much More!
Screenshot from USA Today article January 5, 2026 usatoday.com/graphics/interactives/us-nuclear-weapons-expansion-fallout-map/
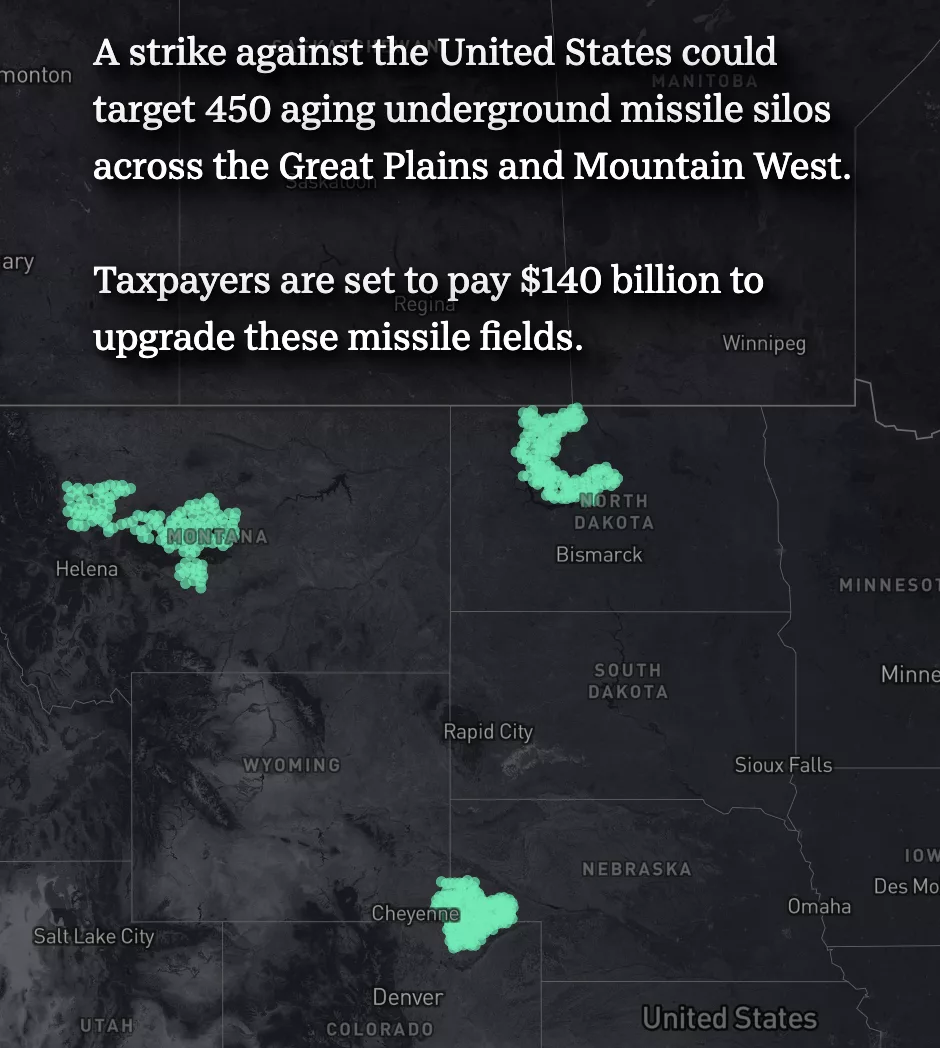
THE NUCLEAR SPONGE
Fallout maps show what could happen if America’s nuclear missile silos were attacked
By Davis Winkie, Ramon Padilla, Stephen Beard, Karina Zaiets and Carlie Procell, USA TODAY | usatoday.com
U.S. nuclear strategy revolves around the idea of the “triad.” Each of the military’s methods for delivering a nuclear strike represents a leg – the air leg (bomber planes), the sea leg (missile submarines) and the land leg (silo-based intercontinental ballistic missiles).
In recent years, arms control advocates have argued that the land leg of the triad is useless compared with its peers and makes the world a more dangerous place. The root of the debate is the vulnerability of the underground silos: An enemy can – and probably would – destroy them in a first strike against the United States.
Those opposed to land-based nuclear missiles, such as Daryl Kimball of the Arms Control Association, say that this vulnerability would push the president into a “use-or-lose logic” if he or she believed the United States were under nuclear attack. If the president launched a nuclear missile counterattack under a false warning, the results would be catastrophic.
The naysayers also highlight the cost of replacing the existing 1970s-vintage fleet of 400 Minuteman III missiles with the under-development Sentinel missiles, which the Air Force estimated will cost $140 billion (an increase from a 2020 estimate of $78 billion).
Warren, Garamendi Press Energy Secretary on Mismanagement and Taxpayer Waste in Plutonium Pit Production Program
Without transparency, accountability, and action around the pit program, the Department of Energy may be enabling the waste of billions of taxpayer dollars.
“In rushing to production, NNSA has developed an excessively risky program structure, with management concerns around fundamental aspects such as the cost and schedule.”
Sen. Elizabeth Warren and Rep. John Garamendi | warren.senate.gov – garamendi.house.gov
Washington, D.C. — In a new letter, U.S. Senator Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) and Representative John Garamendi (D-Calif.), both members of their respective Armed Services Committees and of the Nuclear Weapons and Arms Control Working Group, are urging Department of Energy Secretary Chris Wright to review the scope of and the need for the nuclear weapon plutonium pit production program, and pause the program’s Savannah River site until the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has established guardrails to prevent additional waste of taxpayer funds.
In August, the Department of Energy (DOE) launched a special study into NSSA’s leadership and management of the plutonium pit production mission. The lawmakers believe that, if properly conducted, the study will find that years of mismanagement have put billions of taxpayer dollars at risk with an unrealistic pit production schedule and goals.
“The Trump administration is blindly spending tens of billions of dollars to produce plutonium pits for nuclear weapons without a real budget or plan,” said Senator Warren. “This program is already years behind schedule and over budget, and Congressman Garamendi and I are urging the Secretary of Energy to conduct a vigorous review to rein in years of waste and mismanagement.”
“For years I have called for Congress to take action to fix the failing plutonium modernization effort. Congress has continued to pour billions of dollars into efforts to restart production with arbitrary targets,” said Congressman Garamendi. “This letter cuts to the core of the matter and asks necessary questions of NNSA, including about the questionable management and faulty assumptions underlying the program. I eagerly await their response, along with the results of the Department of Energy’s 120-day special investigation.”
The lawmakers raise concerns about how, years into this program, it is still unclear what the pit production program’s schedule and full cost will be. The Government Accountability Office recommended NNSA create a master schedule to comply with its best practices, but the agency has yet to produce one…
Livermore Lab Uses Trump Executive Order Gutting Environmental Laws to Push Through Enhanced Plutonium Utilization without Public Input
A November notice from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) erases the previously announced public involvement requirement and thereby fast-tracks increased plutonium use at its Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory after decades of limits protected the public from potential risks.
News from our friends at Tri-Valley CAREs | trivalleycares.org
 First announced In January 2025, the NNSA proposal for “Enhanced Plutonium Facility Utilization” at the Livermore Lab was to include a “Draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement” (SEIS) according to its Federal Register Notice. It specifically stated that, “NNSA will prepare a Draft SEIS. NNSA will announce the availability of the Draft SEIS in the Federal Register and local media outlets. NNSA will hold one or more public hearings for the Draft SEIS. Any comments received on the Draft SEIS will be considered and addressed in the Final SEIS.”
First announced In January 2025, the NNSA proposal for “Enhanced Plutonium Facility Utilization” at the Livermore Lab was to include a “Draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement” (SEIS) according to its Federal Register Notice. It specifically stated that, “NNSA will prepare a Draft SEIS. NNSA will announce the availability of the Draft SEIS in the Federal Register and local media outlets. NNSA will hold one or more public hearings for the Draft SEIS. Any comments received on the Draft SEIS will be considered and addressed in the Final SEIS.”
Now the agency has reneged on this promise, instead fast-tracking directly to a Final SEIS and a Record of Decision without any further opportunity for public input!
DOE using its own land to help pair AI centers, nuclear reactors
The Energy Department wants to build nuclear-powered artificial intelligence data centers on federal land using new public-private partnerships.
By Kelly Livingston and Allison Mollenkamp | rollcall.com
Co-locating advanced nuclear reactors with data centers on DOE sites is part of the Trump administration’s bid to accelerate the development of both technologies, sources say, as research efforts tease out their “symbiotic relationship.” But questions remain about how these projects could affect local communities and the actual timeline for bringing more nuclear power online.
DOE first announced its intention to use federal land for data center development and co-location in early April with a request for information to gauge industry interest. According to the RFI, the department intends to begin construction at the selected DOE sites by the end of the year, with operations beginning by the end of 2027.
Lawmakers introduce bill to cancel $100 million University of Michigan data center grant
The University of Michigan has failed to act transparently or coordinate with local officials on data center project, says state Rep. Jimmie Wilson Jr.
“Eighty-four percent of the lab’s 2026 budget request is for nuclear weapons work, according to the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.”
By Brian Allnutt | planetdetroit.org
Michigan State Rep. Jimmie Wilson Jr. (D-Ypsilanti) introduced legislation Thursday to rescind a $100 million state grant for the University of Michigan and Los Alamos National Laboratory’s data center project in Ypsilanti Township.
The university has been unwilling to offer community benefits or consider another site for the data centers, Wilson said.
“The University of Michigan has not been fully transparent with this project and has refused to collaborate with the Ypsilanti Township officials throughout this planning process,” Wilson said in a statement to Planet Detroit.
Ypsilanti Township officials say the university misled state officials about the size of the project when applying for the $100 million grant, and passed a resolution earlier this month seeking to unwind the funding.
…
Petition highlights Los Alamos’ nuclear weapons work
A petition signed by over 700 University of Michigan employees, faculty, and students urges the school to cancel the $1.2 billion project and halt its partnership with Los Alamos, arguing the project will harm the environment, negatively impact low-income communities, and help advance harmful nuclear weapon and artificial intelligence technologies.
Catholic bishops remind political leaders that nuclear weapons are immoral
On August 5, the two American Cardinals present in Japan delivered stirring words from the Hiroshima World Peace Memorial Cathedral, whose bricks contain ashes from the atomic bomb…
“If our gathering here today is to mean anything, it must mean that in fidelity to all those whose lives were destroyed or savagely damaged on August 6, 80 years ago, we refuse to live in such a world of nuclear proliferation and risk-taking,” said Cardinal Robert McElroy of Washington. “We will resist, we will organize, we will pray, we will not cease, until the world’s nuclear arsenals have been destroyed.”
By John Wester | thebulletin.org
In August, a group of American Catholic Church leaders—including Cardinal Blase Cupich of Chicago, Cardinal Robert McElroy of Washington, DC, Archbishop Paul Etienne of Seattle, and me, the Archbishop of Santa Fe—traveled to Japan to mark the 80th anniversary of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. There, we joined our Japanese counterparts—Bishop Mitsuru Shirahama of Hiroshima, Archbishop Emeritus Mitsuaki Takami of Nagasaki, and Archbishop Michiaki Nakamura of Nagasaki—in commemorating the destruction of their cities. Takami is a hibakusha (atomic bomb survivor); he was in his mother’s womb on August 9, 1945, when his city of Nagasaki was bombed. His maternal aunt and grandmother were both killed in the blast.
Eighty years have passed. But the existential threat posed by nuclear weapons is still with us—and it is growing worse every day. In 2019, Pope Francis elevated the Catholic Church beyond conditional acceptance of so-called deterrence. He declared that the mere possession of nuclear weapons is immoral. Nevertheless, the nuclear powers are now spending enormous sums of money on “modernization” that will keep nuclear weapons virtually forever. Meanwhile, in the United States, taxes are being cut to benefit the rich, and economic inequality and homelessness are exploding. This situation is deeply immoral and counter to the Catholic Church’s teachings on social justice.
SEE MORE ON SANTA FE ARCHBISHOP JOHN WESTER’S MONUMENTAL WORK ON NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT HERE:
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: December 2025
Nuclear weapons:
The government is running on a Continuing Resolution (CR) until the end of January. It’s possible to have another shutdown depending on how tough the Dems want to be. The legislative process is starting to move again, with the annual Defense Authorization Act up first and then appropriations. Both give funding increases to nuclear weapons programs, delivery systems and Trump’s “Golden Dome.”
Cost overruns in nearly all things remains the rule. Golden Dome could cost up to $4 trillion, be destabilizing and never be 100% effective. Putin has already taken steps to circumvent it and China may well be doing the same, particularly with hypersonic delivery systems. The arms race continues, likely to be accelerated by artificial intelligence as well.
Nuclear weapons testing: No specific new developments but this article by ex-LANL Director Sig Hecker is good:
| Lessons From Los Alamos |
| Last month, U.S. President Donald Trump rekindled a decades-old debate about nuclear testing. “Because of other countries testing programs,” he wrote on social media, “I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis…” A return to testing at this time would likely benefit U.S. adversaries more than it would the United States. Worse still, it might rekindle an even greater and broader arms race than in the first few decades of the Cold War. |
| Siegfried Hecker | Foreign Affairs |
| Read More |
Article continued:
“My greatest concern about resuming full-scale nuclear testing is that it will fuel another dangerous arms race at a time when global tensions among the great powers are high. Engaging in another arms race is contrary to Trump’s comment that “it would be great if we could all denuclearize, because the power of nuclear weapons is crazy.”
Instead of suggesting an immediate return to nuclear testing, then, Trump should focus on returning to arms control measures to ensure strategic stability with Russia and with China. Hopefully, these measures would lead to a reduction in U.S. and Russian nuclear forces and reduce incentives for China to increase its arsenal. For nuclear testing, he should help erect the highest possible barriers for any country to test by leading an effort to ratify the CTBT. To settle the question of evasion of low-yield tests or hydronuclear experiments, the president and his counterparts in Beijing and Moscow would need to show the political will to agree on a verifiable low-yield limit. That will almost surely require onsite inspections, which were demonstrated to be possible in 1988.
The bottom line is that even though the United States could derive important benefits from resumed nuclear testing, it would lose more than it stands to gain.”
MESSAGE OF HIS HOLINESS POPE LEO XIV FOR THE LIX WORLD DAY OF PEACE
“The idea of the deterrent power of military might, especially nuclear deterrence, is based on the irrationality of relations between nations, built not on law, justice and trust, but on fear and domination by force.”
From the Vatican, 8 December 2025, vatican.va
“In the relations between citizens and rulers, it could even be considered a fault not to be sufficiently prepared for war, not to react to attacks, and not to return violence for violence. Far beyond the principle of legitimate defense, such confrontational logic now dominates global politics, deepening instability and unpredictability day by day. It is no coincidence that repeated calls to increase military spending, and the choices that follow, are presented by many government leaders as a justified response to external threats. The idea of the deterrent power of military might, especially nuclear deterrence, is based on the irrationality of relations between nations, built not on law, justice and trust, but on fear and domination by force. “Consequently,” as Saint John XXIII had already written in his day, “people are living in the grip of constant fear. They are afraid that at any moment the impending storm may break upon them with horrific violence. And they have good reasons for their fear, for there is certainly no lack of such weapons. While it is difficult to believe that anyone would dare to assume responsibility for initiating the appalling slaughter and destruction that war would bring in its wake, there is no denying that the conflagration could be started by some chance and unforeseen circumstance.”
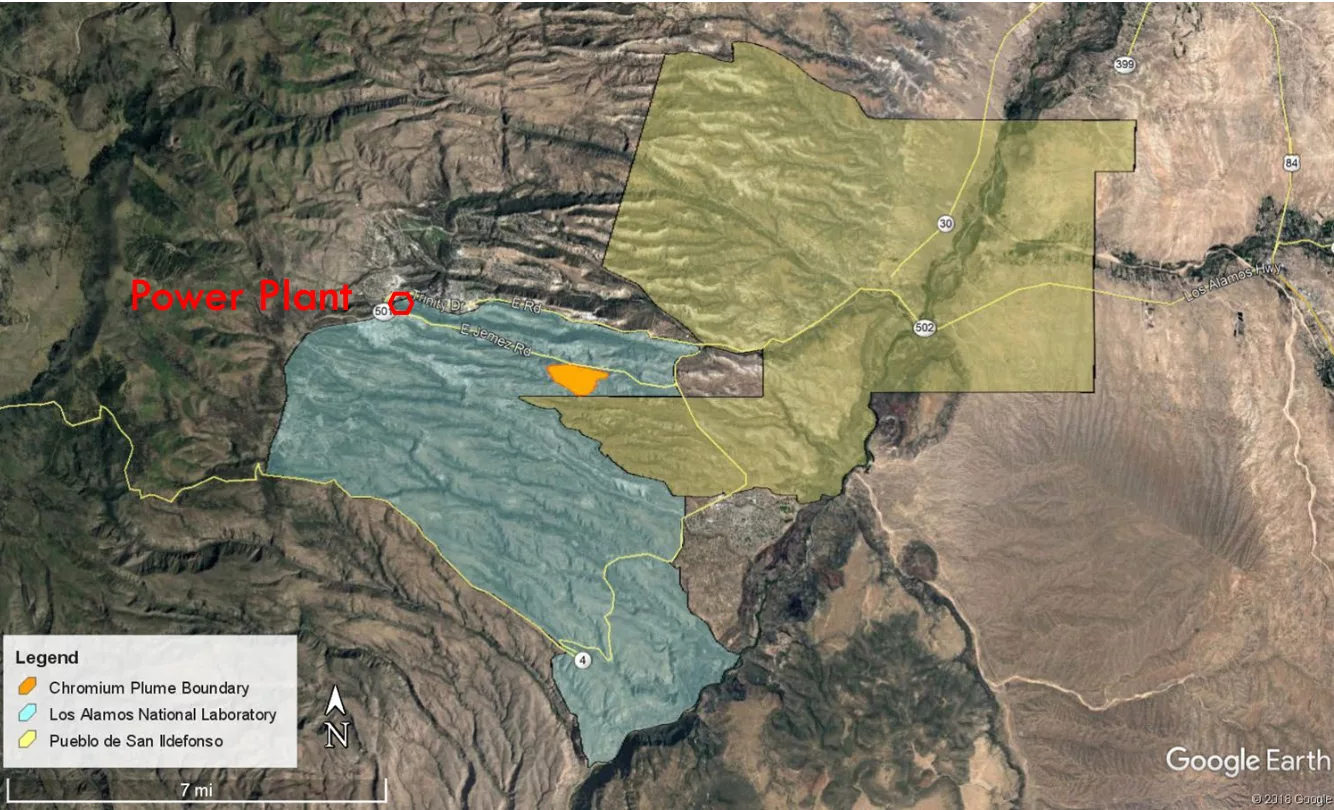
Federal official says further testing needed to determine LANL’s chromium plume migration
“Asked about the difference in opinion between the federal and state agency regarding the sampling, Kunkle said, ‘I can’t answer why we have the disconnect,’ adding that the only sampling done at that monitoring location, called zonal sampling, ‘is really not intended to predict the long term environment or trends in the regional aquifer. That really should be done only with monthly monitoring.’”
By Clara Bates cbates@sfnewmexican.com | santafenewmexican.com
A federal official says more testing is needed to determine whether a toxic chromium plume has seeped into San Ildefonso Pueblo’s groundwater, after the state called groundwater testing “conclusive evidence” the U.S. Department of Energy’s efforts at containment have been “inadequate.”
New Mexico’s Environment Department announced last month hexavalent chromium from Los Alamos National Laboratory had migrated to Pueblo de San Ildefonso land for the first time.
But Jessica Kunkle — the Los Alamos Field Office manager with the U.S. Department of Energy — told state lawmakers on the Radioactive and Hazardous Materials Committee on Monday afternoon the type of groundwater sampling conducted may not have told the whole story. The agency is working with partners to get a monitoring well installed “as quickly as possible,” she said, to get better data.
12/8/25 Los Alamos Legacy Cleanup & Hexavalent Chromium Plume Update
New Air Force Chief Boosts Nuclear Buildup, Moving Away From Deterrence, Experts Warn
“Gen. Ken Wilsbach promotes nuclear “recapitalization” in his first memo to the Air Force — fueling fear of a radical shift away from nukes acting solely as deterrence.”
By: Austin Campbell, The Intercept | theintercept.com

“We will advocate relentlessly for programs like the F-47, Collaborative Combat Aircraft as well as nuclear force recapitalization through the Sentinel program and the B-21,” Wilsbach wrote in a memo dated November 3, referring to planned upgrades to nuclear missiles and stealth bombers.
Experts who spoke to The Intercept said the language signals a doctrinal pivot, prioritizing displays of strength and the buildup of nuclear weaponry over internal repair — an approach that may appeal politically to the Trump administration and Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, but does little to ease the fatigue and distrust spreading among airmen.
…
The Sentinel program Wilsbach referenced is intended to modernize the land-based leg of the nuclear triad, with new missiles, hardened silos, and updated command-and-control infrastructure across missile fields in Wyoming, Montana, and North Dakota. It’s the Air Force’s planned replacement for aging Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile systems. The B-21 Raider is the next-generation stealth bomber designed to replace older strategic bombers like the B-2 and B-1, delivering both conventional and nuclear payloads.
Critics say framing these nuclear modernization efforts as “recapitalization” obscures the ethical and strategic implications of expanding U.S. nuclear capabilities amid declining morale and retention.
“You don’t ‘recapitalize’ genocidal weaponry.”
“The chief of staff’s emphasis on weaponry is disheartening. His description of nuclear weapon ‘recapitalization’ is an abomination of the English language. You don’t ‘recapitalize’ genocidal weaponry. Both the Sentinel missile program and the B-21 bomber are unnecessary systems that could cost as much as $500 billion over the next 20 years,” said William Astore, a retired Air Force lieutenant colonel and military historian.
Los Alamos National Lab (LANL) Town Hall December 3rd, 2025 – Thoughts from Nuclear Watch New Mexico:
The LANL Director mentioned Non-proliferation is a big part of their work. However, the Nuclear Nonproliferation program budget is a mere 6.5% of the total Lab budget (Nuclear Weapons is 84%, with a Billion dollar increase for FY26). https://nukewatch.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/FY26-Lab-Table-spreadsheets-Chart-1.pdf Nuclear Nonproliferation is a valuable program that LANL does well, and its funding should not be cut to provide more money for nuclear weapons production (literally the opposite of nonproliferation). The Nuclear Nonproliferation budget should be increased, especially if the Lab director agrees on its importance. NukeWatch NM is entirely supportive of LANL’s Sealed Sources program, which serves as the nation’s lead for collecting potentially dangerous radioactive materials that are no longer needed, securing them, and ensuring they don’t fall into the wrong hands, protecting communities and enhancing security.
On the discussion of AI missions at the lab:
The lab is partnering with NVIDIA for their hardware and ChatGPT/Open AI for their models. “The goal is to harness the power of the next evolution of high performance computing and apply it to our national security science and technology. Big development on this front is the “genesis” mission…” and in an answer to a question, want to “use artificial intelligence to [for example] help us develop the molecules that could deliver a therapeutic isotope to a cancer cell with high specificity so that when that undergoes radioactive decay the decay products basically kill the cancer cell but no surrounding tissue”
Again, the lab’s nuclear weapons budget ate up almost all else this year – how does the lab propose to work on this kind of work when its’ science budget is less than 1%? How will this advancement of AI be applied to our national security science and technology in terms of nuclear weapons? NukeWatch has serious concerns and questions regarding the tangible risks associated with integrating commercial AI infrastructure to be with active national security and nuclear defense programs. Beyond this, a $1.25 billion advanced computing campus is planned in Michigan to support far-away Los Alamos Lab in high-performance computing and AI research.
Continue reading
Nuclear Watch New Mexico Attends the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability Fall Meeting Nov. 21-23 in Las Vegas, Protesting Nuclear Testing in Nevada & Much More!
Sophie Stroud, Communications and Associate Director, represented NukeWatch at the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability's (ANA) fall meeting Nov. 21-23 in Las Vegas, hosted locally by Ian Zabarte, Principal Man of the Western Shoshone, Secretary of State of the Western Shoshone National Council, and Secretary of the Native Community Action Council (NCAC). The Nevada Test Site, now called the "Nevada National Security Site" and Yucca Mountain are both nuclear sites on Shoshone Land, and nuclear issues continue to threaten the Western Shoshone People. Yucca Mountain is Western Shoshone property with Constitutional protection, and the Department of Energy cannot prove ownership. ANA is a national network made up of 30 organizations whose members live near US nuclear bomb plants and their waste sites. The meeting was scheduled in coordination with the renowned International Uranium Film Festival — uraniumfilmfestival.org. As an organizer of the ANA Meeting as well as the International Uranium Film Festival, NCAC, composed of Shoshone and Paiute peoples, believe these films are a necessary part of the ongoing awareness, witness and resistance to nuclear war, human health and a livable Mother Earth. As 2025 marks the 80th anniversary of the first atomic bombings at the Trinity Site, Hiroshima, and Nagasaki, the world faces a new nuclear arms race that includes nuclear "modernization" of weapons, as well as the fast-tracking of uranium mining for nuclear-powered artificial intelligence data centers.
Friday morning, Nov. 21, the group traveled to the Mercury Exit gate of the Nevada Test Site with banners opposing nuclear weapons and nuclear testing. On October 29, before a meeting in South Korea with Chinese President Xi, President Donald Trump announced on social media that he “instructed the Department of War to start testing [U.S.] Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis” with Russia and China. The post contains various inaccuracies and ambiguity over whether he wants to resume underground nuclear explosive testing — an act the United States, Russia, and China have not undertaken in over 30 years — or continue testing of delivery systems.
Trump Orders Nuclear Weapons Testing for New Nuclear Arms Race
What might Project 2025 mean for N.M.? Non-nuclear cuts at national labs (Updated Dec 1, 2025)
“[The Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025] contemplates pulling funding from any work unrelated to nuclear weapons at Los Alamos National Laboratory, Sandia National Laboratories and sister facility Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California…in New Mexico, some say cutting the labs’ other scientific work would have a devastating economic effect on the state and could ultimately weaken the institutions as a whole.”
“It doesn’t take a nuclear physicist to realize that there could be massive layoffs if this proposal or these ideas were to reach fruition,” said Chandler, who worked in the employment arena for much of her time at the facility. “Now, that might expand the nuclear weapons program to some degree, but it’s not going to absorb the entire workforce.”
“Under the Biden administration, LANL has seen a massive growth in employment as the laboratory ramps up for its production of plutonium pits, the cores of nuclear bombs.”
By Gabrielle Porter and Alaina Mencinger gporter@sfnewmexican.com amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | Updated santafenewmexican.com
Project 2025 — the now-infamous blueprint for a conservative presidency that’s still publicly being held at arm’s length by Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump — proposes all sorts of sweeping policy recommendations, from promoting capital punishment to embracing mass deportations.
But tucked in the 922 pages of its report, “Mandate for Leadership 2025: The Conservative Promise,” is one recommendation that centers squarely on New Mexico.
Trump talk on nuke testing turns focus to New Mexico’s role in decades of blasts
Jay Coghlan, executive director of the nuclear watchdog group Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said Wright’s comments “somewhat” quelled his initial concerns about a renewed explosive nuclear testing program.
But he said claims Russia and China may be conducting small-scale tests known as hydronuclear tests — banned by the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, of which the United States, Russia and China are all signatories — continue to give him pause. He fears rumors about the low-yield tests in other nations could be used to justify a domestic return to testing.
“That, in effect, would give permission to the U.S. [to resume testing],” Coghlan said. “But that would be in violation of the norm of the CTBT.”
Three decades removed from the United States’ last nuclear test, a testing regimen would likely be expensive and time-consuming to start up, Coghlan argued, and could prompt other nuclear powers to follow suit.
It seems likely Russia, at least, would: Following Trump’s post, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced if the United States resumed explosive nuclear testing, the Eastern European nation would follow.
“Then everybody else is going to do it, or virtually everybody else will do it, every other nuclear weapons power,” Coghlan said. “I could just see India and Pakistan champing at the bit to test. And then, of course, there’s North Korea and China.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | November 30, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
It might not have as reverent a name as the Trinity Test or a litany of films made about it. But Project Gnome, a 1961 explosive nuclear test conducted near Carlsbad, is a relic of a bygone era in New Mexico and beyond.
In the 47 years between the Trinity Test and the end of the United States’ explosive nuclear testing in 1992, the nation would perform more than 1,000 such tests — more than any other nuclear nation — with most conducted in Nevada.
New Mexico might not have been the center of the nation’s testing efforts post-Trinity, which marked its 80th anniversary this year, but the state still played a role: Researchers from Sandia National Laboratories and Los Alamos National Laboratory helped design and conduct testing elsewhere, including at the Nevada Test Site and in the Marshall Islands.
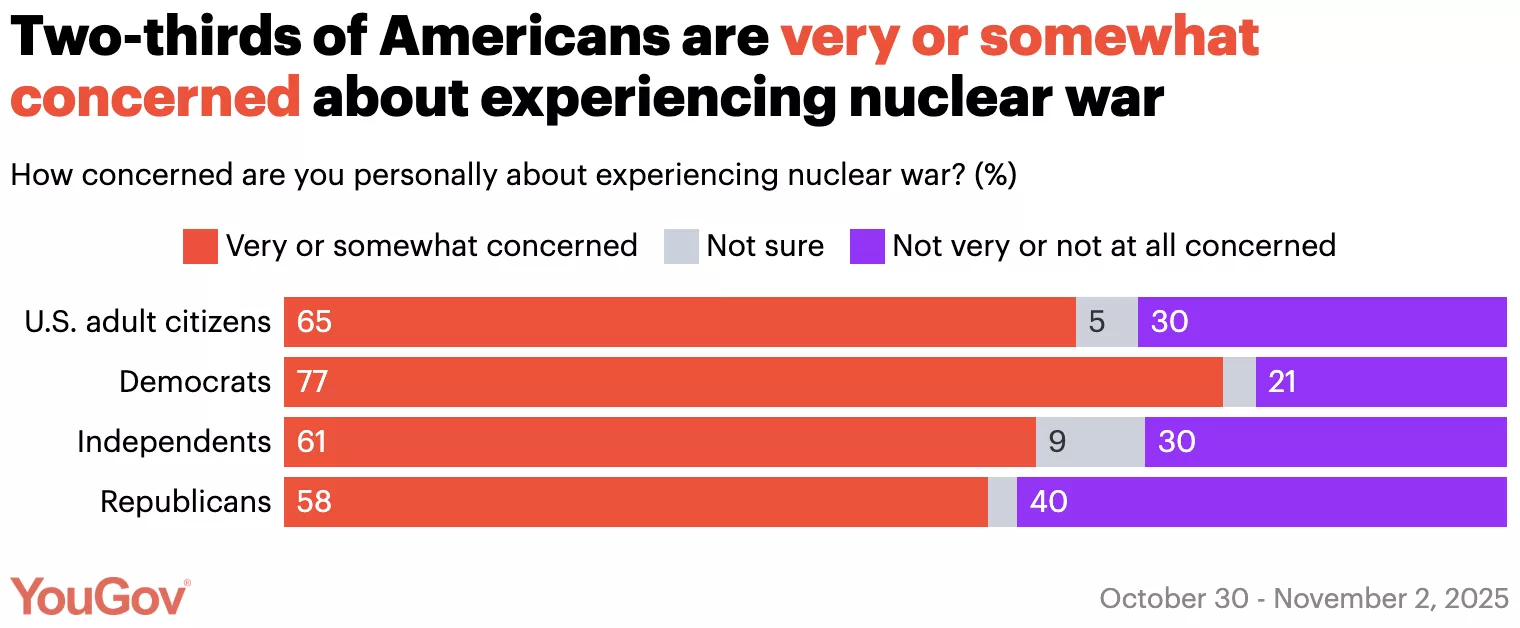
Most Democrats and one-third of Republicans think it’s likely the U.S. will get into a nuclear war in the next decade
A new YouGov poll on nuclear weapons finds that nearly half of Americans believe it’s likely the U.S. will get into a nuclear war in the coming decade, and most are worried about personally experiencing a nuclear war. A majority believe nuclear weapons are making the world less safe, but opinions are mixed on whether the U.S. should dismantle all of its nuclear weapons.
By: Jamie Ballard| November 26, 2025 today.yougov.com
46% of Americans think it’s likely the U.S. will get into a nuclear war within the next 10 years; 37% think this is not very or not at all likely. 57% of Democrats and 37% of Republicans think this is likely.
Department of Energy Seeks to Eliminate Radiation Protections Requiring Controls “As Low As Reasonably Achievable”
An internal Department of Energy (DOE) memorandum eliminates worker and public radiation protection rules known “As Low As Reasonably Achievable” (ALARA). This fundamental departure from decades of accepted health physics practices is being promoted by senior DOE political appointees with little background in health or radiation control. It is marked as “URGENCY: High” under the auspices of the DOE Deputy Secretary, the Under Secretary for Science, and the Administrator of the National Nuclear Security Administration. The memorandum awaits the final signature of DOE Secretary Chris Wright.
The memo’s stated goal is to:
“…remove the ALARA principle from all DOE directives and regulations, including DOE Order 458.1, Radiation Protection of the Public and the Environment, NE [Office of Nuclear Energy] Order 458.1, Radiation Protection of the Public, and, upon completion of the rulemaking process, 10 CFR [Code of Federal Regulations] 835, Occupational Radiation Protection.” [1]
It follows the playbook of the Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025, which called for:
“Set[ting] clear radiation exposure and protection standards by eliminating ALARA (“as low as reasonably achievable”) as a regulatory principle and setting clear standards according to radiological risk and dose rather than arbitrary objectives.” [2]
Lab Chromium Contamination Confirmed on San Ildefonso Pueblo Land
Comprehensive Cleanup Needed Instead of More Nuclear Weapons
The New Mexico Environment Department has announced:
“A toxic chromium plume from Los Alamos National Laboratory has spread beyond Lab boundaries onto Pueblo de San Ildefonso land for the first time, with contamination exceeding state groundwater standards… These new results are conclusive evidence that the U.S. Department of Energy’s efforts to contain the chromium plume have been inadequate.”
In reality, chromium groundwater contamination probably migrated beyond the LANL/San Ildefonso Pueblo boundary long ago, with past Lab maps of the plume “magically’ stopping at the border. In the past, tribal leadership has commented that it was fortunate that the contamination stopped there, but that any future indications of groundwater contamination on Pueblo land could have serious consequences. The San Ildefonso Pueblo is a sovereign Native American tribal government.
As late as the late 1990s the Lab was falsely claiming that groundwater contamination was impossible because underlying volcanic tuff is “impermeable.” [1] This ignored the obvious fact that the Parajito Plateau is heavily seismically fractured, providing ready pathways for contaminant migration to deep groundwater. By 2005 even LANL acknowledged that continuing increasing contamination of the regional aquifer is inevitable.[2] Some 300,000 northern New Mexicans rely upon the aquifer for safe drinking water. The potential serious human health effects (including cancer) caused by chromium contamination was the subject of the popular movie Erin Brockovich.
LANL chromium plume spreads onto San Ildefonso Pueblo land, NMED says
Nuclear Watch New Mexico executive direcor Jay Coghlan sees PF-4 as being a bigger scale — and having bigger risks — than the other aging buildings.
“PF-4 is not unique in being old,” Coghlan said. “However, PF-4 is totally unique in currently being the only facility that can process large amounts of plutonium … particularly including plutonium pit production. I think, in part, that’s why the Safety Board focuses more on PF-4 than, to my knowledge, than any other single individual facility.”
By:Patrick Lohmann | November 13, 2025 sourcenm.com
An underground plume of toxic chromium has spread from Los Alamos National Laboratory to Pueblo de San Ildefonso land, state Environment Department officials announced Thursday.
The discovery marks the first time the plume has been detected within the pueblo boundaries, officials said in a news release, though they added the plume’s spread does not pose imminent threats to drinking water in the pueblo or in Los Alamos County. That’s because the plume is not near any known private or public wells, officials said.
Long-term ingestion of hexavalant chromium can cause serious health problems or increase risk of certain cancers.
US Stands Alone Defying UN Vote on Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
Could the LDS Church end an ongoing nuclear weapons project? These veteran activists think so.
By Thalif Deen, Inter Press Sevice | November 12, 2025 ipsnews.net
UNITED NATIONS, Nov 12 2025 (IPS) – The US took another step backward –to break ranks with the United Nations– when it voted against a draft resolution calling for the entry into force of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT).
The negative vote followed an announcement by President Trump last month that the US plans to resume nuclear testing after a 33-year hiatus. The US stood alone on the UN vote, which was supported by almost all member States in the General Assembly’s First Committee.
The resolution was adopted by an overwhelming majority: with 168 votes in favor, with one against (United States) and 3 abstentions (India, Mauritius, Syria).
During Trump’s first term, the US abstained on the vote. And in other years they had been voting in favour.
Jackie Cabasso, Executive Director, Western States Legal Foundation, which monitors and analyzes U.S. nuclear weapons programs and policies, told IPS the chaos and uncertainty arose from Trump’s factually-challenged social media post that “because of other countries testing programs, I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis.”
The U.S. government’s first ever “No” vote, on the annual UN resolution in support of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT), raises further troubling questions about U.S. intentions.
A Small Town Is Fighting a $1.2 Billion AI Datacenter for America’s Nuclear Weapon Scientists
“Ypsilanti, Michigan resident KJ Pedri doesn’t want her town to be the site of a new $1.2 billion data center, a massive collaborative project between the University of Michigan and America’s nuclear weapons scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratories (LANL) in New Mexico.”
By Matthew Gault | November 10, 2025 404media.co
“My grandfather was a rocket scientist who worked on Trinity,” Pedri said at a recent Ypsilanti city council meeting, referring to the first successful detonation of a nuclear bomb. “He died a violent, lonely, alcoholic. So when I think about the jobs the data center will bring to our area, I think about the impact of introducing nuclear technology to the world and deploying it on civilians. And the impact that that had on my family, the impact on the health and well-being of my family from living next to a nuclear test site and the spiritual impact that it had on my family for generations. This project is furthering inhumanity, this project is furthering destruction, and we don’t need more nuclear weapons built by our citizens.”
At the Ypsilanti city council meeting where Pedri spoke, the town voted to officially fight against the construction of the data center. The University of Michigan says the project is not a data center, but a “high-performance computing facility” and it promises it won’t be used to “manufacture nuclear weapons.” The distinction and assertion are ringing hollow for Ypsilanti residents who oppose construction of the data center, have questions about what it would mean for the environment and the power grid, and want to know why a nuclear weapons lab 24 hours away by car wants to build an AI facility in their small town.
“What I think galls me the most is that this major institution in our community, which has done numerous wonderful things, is making decisions with—as I can tell—no consideration for its host community and no consideration for its neighboring jurisdictions,” Ypsilanti councilman Patrick McLean said during a recent council meeting. “I think the process of siting this facility stinks.”
Harking to the MX, Utahns call on LDS Church President Oaks to speak out against nuclear missile being developed in Utah
Could the LDS Church end an ongoing nuclear weapons project? These veteran activists think so.
THE SALT LAKE TRIBUNE | November 9, 2025 sltrib.com
Decades ago, peace activists helped keep a major nuclear weapons system out of Utah with help from key figures, chiefly Spencer W. Kimball, then the president of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Now some of those same individuals are calling on the church’s newly ascended president, Dallin H. Oaks, to follow in his predecessor’s footsteps and speak out against the federal government’s development of a new generation of nuclear missile, known as Sentinel, partly in the Beehive State.
“The arms race continues,” the group of 12 Utahns and one former resident write in a letter mailed to church headquarters in early October, “and a new moral challenge faces” the leaders of the Utah-based faith.
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: November 2025
Nuclear weapons:
The government shutdown has impact:
National Nuclear Security Agency confirms 152 furloughed at offices in Albuquerque, Los Alamos
Only 14 employees remain at the two sites By: Danielle Prokop-October 22, 2025
The NNSA confirmed 152 New Mexico employees charged with overseeing national laboratories’ nuclear weapons work were furloughed on Oct. 20, 2025. (Courtesy of NNSA)
The federal government this week sent home more than 150 federal New Mexico employees charged with overseeing national laboratories’ nuclear weapons work, with only 14 employees across two sites remaining at work, the National Nuclear Security Agency confirmed to Source NM.
The furloughs include 71 employees at NNSA’s Los Alamos field office and 81 at the Sandia National Laboratories location, NNSA Deputy Director of Communications Laynee Buckels told Source NM in an email. Seven employees remain at each site, working without pay, she said.
The field offices are responsible for “ensuring compliance with federal contracts to manage and operate the national security assets,” according to the NNSA website
To date there doesn’t appear to be furloughs at LANL, whose employees technically work for a contractor rather than the federal government. Congress is not furloughed, but Speaker Mike Johnson has kept the House out of session. As a result, legislation has come to a screeching halt.
Los Alamos’ plutonium facility safety systems need improvement, oversight board says
Nuclear Watch New Mexico executive direcor Jay Coghlan sees PF-4 as being a bigger scale — and having bigger risks — than the other aging buildings.
“PF-4 is not unique in being old,” Coghlan said. “However, PF-4 is totally unique in currently being the only facility that can process large amounts of plutonium … particularly including plutonium pit production. I think, in part, that’s why the Safety Board focuses more on PF-4 than, to my knowledge, than any other single individual facility.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | November 7, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
An independent oversight agency wants to see improved safety systems at the facility at the heart of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s plutonium pit mission: PF-4.
The Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board reported what it believes to be gaps in a safety analysis drafted for PF-4 and delays in upgrades to safety systems in a letter last month to Energy Secretary Chris Wright.
“Maintaining momentum for these safety infrastructure projects is more important in light of the issues with the safety analysis,” the board wrote in the letter dated Oct. 10. It was signed by former acting chairman Thomas Summers.
LANL Prioritizes Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Core Production Over Safety
The independent Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board recently released its Review of the Los Alamos Plutonium Facility Documented Safety Analysis. It concluded that:
“While LANL facility personnel continue to make important upgrades to the Plutonium Facility’s safety systems, many of those projects have encountered delays due to inconsistent funding and other reasons. DOE and LANL should consider prioritizing safety-related infrastructure projects to ensure that the Plutonium Facility safety strategy adequately protects the public, as the facility takes on new and expansive national security missions.” (Page 24)
In early October 2024, the Department of Energy’s semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) announced with great fanfare that the Los Alamos Lab had produced its first “diamond stamped” plutonium pit for the nuclear weapons stockpile. Tens of billions of taxpayers’ dollars have been sunk into LANL’s long delayed and over budget pit production program. Given no further announcements, it is not currently known whether or not the Lab is meeting its congressionally required production goals. Endemic nuclear safety problems have long been an intractable issue, at one point even forcing a three-year halt to plutonium operations at LANL’s Plutonium Facility-4 (“PF-4”).
In its recent Review, the Safety Board reported:
“The [2009] Plutonium Facility safety basis described very large potential [radioactive] dose consequences to the public following seismic events…. DOE committed to upgrade and seismically qualify the ventilation system, with a particular focus on a specific ventilation subsystem…”
“As the only facility in the DOE complex that can process large quantities of plutonium in many forms, [PF-4] represents a unique capability for the nation’s nuclear deterrent. The Board has long advocated for the use of safety-related active confinement systems in nuclear facilities for the purposes of confining radioactive materials…Passive confinement systems are not necessarily capable of containing hazardous materials with confidence because they allow a quantity of unfiltered air contaminated with radioactive material to be released from an operating nuclear facility following certain accident scenarios. Safety related active confinement ventilation systems will continue to function during an accident, thereby ensuring that radioactive material is captured by filters before it can be released into the environment… (Page 2, bolded emphases added)
AP: Trump appears to suggest the US will resume testing nuclear weapons for first time in 30 years
“For Trump, who has cast Russia as a “paper tiger” for failing to swiftly subdue Ukraine, the message is that Russia remains a global military competitor, especially on nuclear weapons, and that Moscow’s overtures on nuclear arms control should be acted on.”
By MICHELLE L. PRICE and CHRIS MEGERIAN | October 30, 2025 apnews.com
BUSAN, South Korea (AP) — President Donald Trump appeared to suggest the U.S. will resume testing nuclear weapons for the first time in three decades, saying it would be on an “equal basis” with Russia and China.
The Kremlin pointed out that a global ban on nuclear tests has remained in place, but warned that if any country resumes nuclear testing Russia would follow suit.
There was no indication the U.S. would start detonating warheads, but Trump offered few details about what seemed to be a significant shift in U.S. policy.
He made the announcement on social media minutes before he met with Chinese leader Xi Jinping on Thursday in South Korea. He offered little clarity when he spoke to reporters later aboard Air Force One as he flew back to Washington.
The U.S. military already regularly tests its missiles that are capable of delivering a nuclear warhead, but it has not detonated the weapons since 1992. The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, which the U.S. signed but did not ratify, has been observed since its adoption by all countries possessing nuclear weapons, North Korea being the only exception.
REUTERS: Trump tells Pentagon to immediately resume testing US nuclear weapons
“Russia – which tested a new nuclear-powered cruise missile on October 21, held nuclear readiness drills on October 22 and tested a new nuclear-powered autonomous torpedo on October 28 – said it hoped Trump had been properly informed that Moscow had not tested a nuclear weapon itself.”
By Trevor Hunnicutt, Ismail Shakil and Kanishka Singh | October 30, 2025 reuters.com
VIEW THE RECORDING: Santa Fe Ecumenical Conversations Towards Nuclear Disarmament at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Community – Monday, October 27
Archbishop John C. Wester and NukeWatch New Mexico presented a special evening at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Community on Monday, October 27, from 6:00 to 8:00 p.m. MT. Following a presentation from NukeWatch executive director Jay Coghlan on U.S. nuclear weapons “modernization,” the Archbishop shared reflections from his pastoral letter, Living in the Light of Christ’s Peace, and speak about the importance of dialogue and hope in working toward nuclear disarmament.
View the recording at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9LFmQzMoJds&t=1s
Nuclear News Archive – 2022
Biden Proposes $1 billion for Nuclear Weapons Work
If Savannah River is delayed in reaching its pit-making goal, Los Alamos lab could be pressured to produce more than 30 pits a year.
“All of this may boomerang on Los Alamos lab, which has been incapable of making a pit for the nuclear weapons stockpile since 2011,” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
Coghlan was referring to a contract in which the lab made 11 pits in one year for Navy missiles a decade ago. That was the lab’s highest pit production, which soon ceased.
BY: Scott Wyland | © Santa Fe New Mexican
Los Alamos National Laboratory would receive about $1 billion for plutonium operations at the heart of its effort to produce 30 nuclear bomb cores by 2026, according to a partial budget the White House released Friday.
The amount would be more than a 20 percent jump from the $837 million being spent this year on the lab’s plutonium work, a clear signal that President Joe Biden will echo his predecessors’ calls to modernize the nuclear stockpile to deter China, Russia, Iran and other adversaries that have growing first-strike abilities.
The lab’s $837 million plutonium budget this year was 2.7 times larger than the prior year’s allocation of $308 million.
The lab’s plutonium funding was part of the draft budget for the National Nuclear Security Administration, the federal agency in charge of the country’s nuclear weapons program.
The budget also requests $603 million — a 37 percent increase — to move the Savannah River Site in South Carolina toward producing 50 pits a year.
Next Steps Following Public Hearing on New Shaft for WIPP Expansion
 Last week the New Mexico Environment Department virtual public hearing on the new shaft to expand the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) took place over four days, from Monday through Thursday. The public comment period ended on Friday.
Last week the New Mexico Environment Department virtual public hearing on the new shaft to expand the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) took place over four days, from Monday through Thursday. The public comment period ended on Friday.
[A special shout out to all those who submitted public comments. THANK YOU!!!]
The hearing process continues until at least October with the filing of post-hearing documents by the Parties supporting the expansion, including the Hazardous Waste Bureau of the Environment Department https://www.env.nm.gov/hazardous-waste/ , the Department of Energy (DOE), and Nuclear Waste Partnership, LLC, the contractors at WIPP. https://wipp.energy.gov/
The Parties opposing the expansion are: Southwest Research and Information Center http://www.sric.org/ ; CCNS http://nuclearactive.org/ ; Nuclear Watch New Mexico https://nukewatch.org/ ; and individuals, including longtime activist Deborah Reade; former Environment Department Regulator for WIPP, Steve Zappe; and a former Environmental Evaluation Group (EEG) scientist, George Anastas. Dr. James Channell, another former EEG scientist, testified in opposition to the new shaft and WIPP’s physical expansion. http://www.sric.org/nuclear/eeg.php
CCNS anticipates the Hearing Officer’s report and the Parties’ comments will end up on the Environment Department Secretary’s desk in mid-September.
Piketon Fears More Radiation Risk from Demolition of Former Uranium Plant
Piketon fears more radiation risk from demolition of former uranium plant. … The demolition in Piketon comes after the federal agency promised the community, which has experienced high cancer rates, independent testing for radiological contaminants. The results are expected to come later this year.
Big Development on the Nuclear Horizon – Huge growth at LANL in plutonium pit production raises ethical issues
ABQJournal – May 26, 2021 —
SANTA FE, N.M. — Huge growth at LANL in plutonium pit production raises ethical issues.
Honeywell the Moneyhell : Metropolis Nuclear Whistleblower Exposé Exclusive
Regional Coalition Of LANL Communities Board Unanimously Passes Resolution To Dissolve
THANK YOU to everyone who contacted city officials opposing the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities!
BY MAIRE O’NEILL maire@losalamosreporter.com| losalamosreporter.com
Members of the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities board voted Friday afternoon to approve a resolution authorizing the direction of the winding down of the RCLC at the point of its termination. The resolution also directs legal counsel Nancy Long, treasurer Los Alamos County Councilor David Izraelevitz and Los Alamos County as the fiscal agent to take all actions necessary and warranted to see that the termination and all matters that need to be attended to upon that termination, are taken care of in an orderly way and ratifies actions that have been taken to this point to accomplish that.
Long said the resolution is the beginning of the process and that the resolution expresses the will of the board that the RCLC be wound down and terminated officially with the actions that are necessary to accomplish that.
“We foresee that there will be matters relating to payment of invoices and completing the audit for the fiscal year and we’re hoping to accomplish all those in short order if the board decides this is the direction it wants to take with the organization,” she said.
Ironically, the motion to proceed with the resolution for the disbandment and dissolution of the Coalition was made by Rio Arriba County Commissioner Christine Bustos who later said it was her first and last meeting. Santa Fe City Councilor Michael Garcia seconded the motion. Garcia had abstained during voting with his own government in decisions regarding the Coalition.
Only five member entities were represented at the meeting and all five voted in favor of the resolution. Absent were Santa Fe County, Taos County, Jemez Pueblo and Ohkay Owingeh Pueblo.
Garcia thanked the community members for their constant engagement in the RCLC process.
“I think its critical that in the RCLC or any other entity community engagement is critical and I believe that as we move forward through this process we still need to continue to keep our community members engaged and make sure we are working towards our best interests,” he said.
Espanola Mayor Javier Sanchez said he learned a lot in terms of what Espanola needs to do in terms of advocacy and what need to be done to champion issues improve the lives of constituents.
NM Archbishop Can’t Stay Silent on LANL’s Arms Work
“I believe strongly that Pope Francis is right. For peace to flourish, we have to lay down weapons,” [Archbishop of Santa Fe John Wester] said, referring to Pope Francis’ statement that even the possession of atomic weapons of war was immoral.
“And any continuing development of nuclear weapons, and refining them, is going in the wrong direction.”
BY: T.S. Last / Journal North
Published: Wednesday, May 26th, 2021
Copyright © 2021 Albuquerque Journal
SANTA FE – Archbishop of Santa Fe John Wester praises much of the work being done at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The lab’s expertise greatly contributes to developments in bioscience, computer science, engineering, medicine and modeling that helped the nation navigate through the COVID-19 pandemic.
But it also builds bombs – the kind capable of killing massive numbers of people. And that’s not an easy thing for him – and some Catholics working for the lab – to reconcile.
Wester says that as the archdiocese within which the lab operates, the Santa Fe Archdiocese has a “moral responsibility” to facilitate discussion about the lab’s national security mission, most of which is dedicated to weapons production.
“I believe strongly that Pope Francis is right. For peace to flourish, we have to lay down weapons,” he said, referring to Pope Francis’ statement that even the possession of atomic weapons of war was immoral. “And any continuing development of nuclear weapons, and refining them, is going in the wrong direction.”
Wester’s remarks come just as Los Alamos National Laboratory is expanding its national security mission through production of plutonium pits, the cores of nuclear warheads that detonate the bombs. As a direct result of the project, the lab has begun expanding into Santa Fe, the city named for St. Francis of Assisi.
The pope’s 2019 statement was the harshest condemnation of weapons of mass destruction to date from the church. He could have been speaking about LANL and its new mission to manufacture plutonium pits when he said, “In a world where millions of children and families live in inhumane conditions, the money that is squandered, and the fortunes made in the manufacture, upgrading, maintenance and sale of ever more destructive weapons, are an affront crying out to heaven.”
Meet the Senate nuke caucus, busting the budget and making the world less safe
These lawmakers represent states with a direct interest in pouring billions into modernizing and building new weapons.
By: Marcy Winograd and Medea Benjamin | responsiblestatecraft.org

Democrats might control the legislative and executive branches of the U.S. government right now, but a small Republican-dominated Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) Coalition exercises outsized influence in a frightening campaign for nuclear rearmament.
The coalition, comprising six senators from states that house, develop, or test underground land-based nuclear weapons, is pushing a wasteful and dangerous $1.7 trillion, decades-long plan to produce new nuclear weapons, some with warheads 20 times more powerful than the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima.
While the 1980s witnessed the nuclear freeze and a mass movement to demand nuclear disarmament between the U.S. and Soviet Union, the 1990s gave birth to the missile caucus, the Congressional engine careening the U.S. into a renewed nuclear arms race.
Santa Fe to exit Regional Coalition of LANL Communities
THANK YOU to everyone who contacted city officials in support of overturning the RCLC for good!
By: Sean P. Thomas sthomas@sfnewmexican.com | Santa Fe New Mexican
The Santa Fe City Council unanimously approved a resolution Wednesday to pull the city from the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities, a consortium of local and tribal governments with economic ties to Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Santa Fe’s resolution requests that the coalition return dues paid by the city and instructs city officials to begin exploring other ways to lobby the laboratory for economic opportunities and environmental cleanup.
The coalition’s board voted Friday to begin winding down the entity and close out debts, before paying back members their 2021 dues.
“I think it’s important to state while this process is going on that we approved this resolution withdrawing the city of Santa Fe from the RCLC,” said Councilor Renee Villarreal.
The coalition was formed in 2011 to advocate for sitewide cleanup and economic opportunities at the laboratory, but critics have said the coalition no longer achieves its original purpose.
Surprise! Upgrading America’s Nuclear Arsenal Will Be Stupefyingly Expensive
The cost jumped $140 billion in just 2 years. Here’s why.
BY: KYLE MIZOKAMI | popularmechanics.com
- The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) now says the cost of updating the U.S.’s nuclear weapons is $140 billion more than it estimated just 2 years ago.
- The increase is largely due to inflation and the inclusion of new, expensive projects the CBO didn’t cover 2 years ago.
- The new estimate comes as a proposal in Congress seeks to trim the nuclear budget.
The nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office’s (CBO) estimate of nuclear weapon expenditures over the next decade has jumped a staggering $140 billion in just 2 years.
The estimate, which the agency provided to Congress to give an idea of how much it will take to build new missiles, ships, and planes, as well as revamp America’s vast nuclear infrastructure, comes as key members of the legislature are pushing to cut nuclear weapons spending over the next 10 years.
Estimated Cost of US Nuclear Modernization Jumps 28 Percent
The Congressional Budget Office’s latest estimate puts the price tag at $634 billion as some lawmakers try to bring it back down.
BY PATRICK TUCKER | defenseone.com May 24, 2021
The estimated cost of replacing America’s nuclear bombers, missile submarines, and ICBMs just jumped again—from $315 billion in 2015 to $494 billion in 2019 and now to $634 billion, a 28 percent increase, according to a Congressional Budget Office report released Monday.
The report identifies a $140 billion increase in the cost of nuclear delivery systems and weapons, such as ICBMs, as the largest contributor to the jump. “Projected costs for command, control, communications, and early-warning systems have also increased substantially,” it says, adding that if full costs of B-52 and B-21 bombers were included, “the total costs of nuclear forces, with cost growth, would be $711 billion.”
It’s the second time CBO has raised their projections for the costs of modernizing U.S. nuclear forces.
Some lawmakers have balked at what they perceive as the steep price tag for modernizing the U.S. nuclear weapons arsenal. Sen. Ed Markey, D-Mass., has called for a debate specifically on the high cost of replacing the intercontinental leg of the triad. On Monday, he unveiled a new bill, dubbed the SANE act, to cut $73 billion from the U.S. nuclear weapons budget.
Department of Energy seeks to modify N.M. plant’s nuclear waste permit
Dragging out WIPP’s operations decades past the original 20-year agreement violates the social contract made with New Mexicans, said Scott Kovac, research and operations director for the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
WIPP is being equipped to take the waste that will be generated from production of plutonium pits for nuclear warheads, Kovac said.
“It [WIPP] was never really suppose to do that,” Kovac said.
Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com | Santa Fe New Mexican May 17, 2021
Federal officials say a new air shaft is needed at the nuclear waste disposal site in Southern New Mexico to keep workers safe and run more efficiently.
Watch this video from the Stop Forever WIPP coalition: “When is a shaft more than a shaft?” dispelling the idea that an expansion of WIPP will mostly impact the South Eastern part of New Mexico; The new waste targeted for WIPP would be re-processed at Los Alamos. It also dispels the idea that targeting NM for waste disposal has nothing to do with our minority majority population.
The U.S. Government Hides Some Of Its Darkest Secrets At The Department Of Energy
The Department of Energy controls many ‘black projects’ that live outside of the limelight that is intrinsic to the DoD and the intel community.
BY BRETT TINGLEY | thedrive.com May 13, 2021
When it comes to discussions of government secrecy, much of the conversation tends to revolve around the Department of Defense (DOD) or the U.S. Intelligence Community (IC). After all, the U.S. military develops many of the United States’ most sensitive weapon systems used to defend America and project its power globally, and the IC gathers and analyzes sensitive information on foreign threats and external national security matters. Each year, the budget requests from the U.S. military are packed with classified and Special Access Programs, or SAPs, sporting vague code names, many of which never see the light of day. When we talk of the “black world,” most often that conversation centers around these programs and technologies suspected to be housed deep within the classified ends of the Pentagon and its various service branches.
Often left out of this conversation is the fact that there is a wholly separate cabinet-level department of the U.S. government that is arguably even more opaque in terms of secrecy and oversight than the Department of Defense. Over the last few years, allegations of secret, exotic technologies have reinvigorated claims that the DOD may be concealing scientific breakthroughs from the American public. However, if the U.S. government, or some faction within it, hypothetically came across a groundbreaking development in energy production or applied physics, a very strong case could be made that such a revolution would likely be housed deep within the Department of Energy (DOE) rather than DOD.
County Commission votes to exit Regional Coalition of LANL Communities
The exodus from the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities continued Tuesday.
“Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, agreed, adding he believed the coalition effectively stood in the way of site cleanup by supporting a 2016 consent order.”
By Sean P. Thomas sthomas@sfnewmexican.com | Santa Fe New Mexican
The Santa Fe County Commission voted unanimously to ditch the coalition after some commissioners voiced concerns that the body was no longer the proper vehicle to advocate for site cleanup and mission diversification at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
“The mission of the RCLC and the attempt of the collaboration is admirable,” said commission Chairman Henry Roybal, who stepped down as chairman of the Regional Coalition of Los Alamos National Laboratory Communities this year. “However with the progress, it does not seem like this vehicle is the best avenue to express this collaborative voice. There are so many things that just aren’t where they need to be.”
The coalition was formed in 2011 and consists of local and tribal governments. It was created to provide local governments an opportunity to advocate for jobs, environmental cleanup and other priorities at the laboratory.
Each member organization pays annual dues to be a member, with Santa Fe County at $10,000.
LANL’s move to Santa Fe means jobs, and controversy
By: Editorials / ABQJournal
Santa Fe’s relationship with Los Alamos National Laboratory has been rocky for years. The City Council, with some regularity, has passed resolutions of concern about the nuclear weapons lab’s environmental impact and radioactive materials safety lapses, the production of weapons parts in Los Alamos and the proliferation of nuclear weapons in general.
ILHAN OMAR SIGNS ICAN PLEDGE

April 30, 2021: Representative Ilhan Omar today submitted her signed ICAN Pledge to ICAN, becoming the eleventh member of the US Congress to sign the Pledge. Rep. Omar represents Minnesota’s 5th Congressional District in the US House of Representatives. Rep Omar also co-sponsor the H.R.2850 Nuclear Abolition and Economic Conversion Act of 2021 that Representative Eleanor Holmes Norton reintroduced on April 26, 2021.
Regional Coalition Of LANL Communities Struggles To Survive
Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico complained that the RCLC main selling point was to lobby for mission diversification and accelerated cleanup and said he would argue that the Coalition has been a spectacular failure on both counts.
“When the Coalition was founded in 2011, LANL’s nuclear weapons budget was $1.9 billion. A decade later that budget is $2.9 billion and the total spending on core nuclear weapons research and production has risen year after year to where now it’s a full 70 percent of all funding and all of the remaining 30 percent either directly or indirectly supports those nuclear weapons,” Coghlan said.
By: MAIRE O’NEILL maire@losalamosreporter.com | losalamosreporter.com May 3, 2021
The next couple of months may determine the demise of the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities. The City of Santa Fe opted last month not to approve the RCLC’s amended and restated joint powers agreement which has been hanging out there waiting for the City’s decision since March 2019. The City is slated to decide whether to withdraw completely from the RCLC later this month.
The Taos County Commission is slated to decide Tuesday whether it wishes to continue as a member and Santa Fe County Commissioners have the same decision to make at their May 11 meeting.
Los Alamos County Council is expected to discuss its RCLC status in June which will be the first time the Council will have had an agenda item on the RCLC since it approved the amended JPA in July of 2020. The discussion is at the request of Council Vice Chair James Robinson. Councilor David Izraelevitz, who serves as RCLC treasurer, has been a strong advocate of the RCLC and has recently addressed several meetings of members of the Santa Fe City Council at the behest of Councilor Michael Garcia to encourage them to approve the amended JPA. City of Espanola Mayor Javier Sanchez also attended a Santa Fe City Council meeting to advocate and answer questions.
NNSA approves Critical Decision 1 for Los Alamos Plutonium Pit Production Project
“Recommended approach to producing 30 plutonium pits per year identified”
CD-1 approval marks the completion of the project definition phase and the conceptual design as part of DOE’s Order 413.3B process for the acquisition of capital assets. NNSA identified its recommended approach to produce at least 30 plutonium pits per year to meet national security needs.
The CD-1 cost estimate for LAP4 is $2.7-$3.9 billion, with an overall project completion range of 2027-2028. Critical equipment is scheduled to be installed in time to achieve the 30 pits per year production capacity in 2026. The CD-1 cost estimate and project completion date ranges are preliminary estimates that will be refined as the project conceptual design is matured to the 90% design level required to achieve CD-2 (approval of the performance baseline). Consistent with industry best practices and DOE policy, NNSA will set the performance cost and schedule baseline at CD-2, which is expected in 2023.
NNSA leadership and LANL will continue to review this project to improve the fidelity of the current price estimate and schedule.
###
Los Alamos lab sees two mishaps in a week
The water spill should be a reminder that the plutonium facility’s work is done by people, and people make mistakes, said Scott Kovac, research and operations director for the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
“Pit production will place a real time-pressure crunch on the workers and lead to more accidents,” Kovac said.
“It should lead us to consider the consequences if someone left a plutonium furnace on or something that could endanger the public…these kinds of missteps are likely to increase as the lab ramps up production of plutonium pits used to trigger nuclear warheads. Current plans call for the lab to make 30 of the nuclear bomb cores a year by 2026,”
By: Scott Wyland | santafenewmexican.com April 26, 2021
Los Alamos National Laboratory had two mishaps in one week: a glove box breach that contaminated workers’ protective equipment and a spill of 1,800 gallons of water into a vault corridor after an employee left a valve open.
The incidents were the latest in a series of accidents in recent months at the lab, as reported by the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board.
In the board’s most recent report, an alarm sounded March 29 when a worker tore a protective glove attached to a sealed compartment known as a glove box while handling a piece of plutonium.
Continue reading
Sleepwalking into Nuclear War?
“People like to think that every nuclear-armed country has only one “button”, with which a president could consciously choose to start a nuclear war, after careful deliberation. But in fact there are thousands of people in the world controlling different parts of different arsenals who could independently initiate a nuclear war.” – Caitlin Johnstone
JONATHAN POWER | indepthnews.net
LUND, Sweden (IDN) — Last week on Tuesday (April 20), US Strategic Command, the part of the military responsible for nuclear weaponry and its use, posted an official Tweet that read, “We must account for the possibility of conflict leading to conditions which could very rapidly drive an adversary to consider nuclear use as their least bad option”.
This came just as Russia was pulling back its large deployment of troops on Ukraine’s border which, in turn, was triggered in part by President Joseph Biden’s decision to ship for the first time sophisticated weapons to Ukraine.
The crisis has now passed but the lesson lingers. Arguably we are closer to war with Russia than at any time since the Cuban missile crisis of 1962 (which I wrote about last week, April 20).
CHERNOBYL: 35 YEAR ANNIVERSARY OF THE WORLD’S WORST NUCLEAR ACCIDENT

ON THIS DAY in 1986, workers ran a safety test at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in northern Ukraine. But the test went awry, starting a fire in a reactor and leading to one of the largest nuclear disasters in history. Smoke from the fire and a second explosion launched radioactive elements into the atmosphere, scattering them over the surrounding fields and towns.
Chernobyl is generally recognized as the worst nuclear accident on record, directly killing 31 people and causing widespread contamination in Eurasia. It’s estimated that thousands of people will eventually die earlier than they would have due to the cancers caused by their exposure.
Today, 35 years later, scientists are still uncovering the extent of the damage and starting to answer questions about the long-term legacy of radiation exposure on power plant workers, the people in the nearby community, and even their family members born years later.
READ: New studies highlight the possible impact of Chernobyl on genes
- Published on Science Daily, the studies—both conducted by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), a branch of the National Institute of Health (NIH)—sought to find what kind of changes the exposure to carcinogenic ionizing radiation had on those who came into contact with the explosion.
WIPP completes maintenance outage, intends to up shipments of nuclear waste post-pandemic
Reinhard Knerr, manager of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Carlsbad Field Office said WIPP will resume accepting shipments of low-level transuranic waste from DOE sites around the country and will continue to emplace the waste for final disposal in WIPP’s underground mine.
By: Adrian Hedden | currentargus.com April 26, 2021
Shipments and disposal of nuclear waste resumed at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant after a two-month pause in the repository’s primary operations to allow personnel to complete several maintenance projects underground and on the surface.
WIPP completed 97 projects during the maintenance outage which ran from Feb. 15 to April 15, upgrading infrastructure throughout the facility.
The work involved mine operations, waste handling, hoisting, ground control, safety and engineering, and the break included a site-wide power outage to allow electrical work to be completed safely.
The Nuclear Bomb Is Ready: In Italy Soon. The B61-12 has a Nuclear Warhead with 4 “Selectable Power Options”
“It has been officially announced that the new nuclear bomb series production will begin in the fiscal year 2022, beginning October 1, 2021. It is unknown the number of B61-12 bombs that the US will deploy in Italy, Germany, Belgium and Holland to replace the B61s, whose actual number is secret. Satellite photos show renovations that have been carried out at Aviano and Ghedi bases in preparation for the new nuclear bombs’ arrival, the US Air Force F-35A, and Italian Air Force F-35A under US command will be armed with these bombs.”
BY: Manlio Dinucci | globalresearch.ca April 24, 2021

First published on December 3, 2020
***
A video was released on November 23 2020 by Sandia National Laboratories that shows a US F-35A fighter flying at supersonic speed 3000 meters above sea level, launching a B61-12 nuclear bomb (non-nuclear warhead equipped). The bomb did not fall vertically but glided until the tail section rocket ignition gave a rotational motion and the B61-12 (satellite-guided system) headed for the target and hit 42 seconds after launch. The test was carried out on August 25 at the Tonopah shooting range in the Nevada desert.
An official statement confirmed its full success: it was a real nuclear attack, proof that the fighter carried out at supersonic speed and in stealth attitude (with nuclear bombs placed in its internal hold) has the capability to penetrate through enemy defenses.
The B61-12 has a nuclear warhead with four selectable power options at launch depending on the target to hit. It has the ability to penetrate underground, exploding deep to destroy command center bunkers and other underground structures. The Pentagon’s program foresees the construction of about five hundred B61-12 with an estimated cost of roughly 10 billion dollars (so each bomb will cost double what it would cost if it were built entirely of gold).
Minorities threatened by atomic weapons plants in S. Carolina and NM, groups say
“As construction problems mounted, costs rose, and schedules slipped, (and) defendants hid the true status of the project,” the indictment said.
“…Delays and cost overruns — hidden by SCANA officials from the public and state regulators — eventually doomed the effort, making it one of the largest business failures in South Carolina history.”
BY SAMMY FRETWELL | April 22, 2021 thestate.com

A coalition of environmental groups from the southern and western United States is threatening to sue the federal government over plans for plutonium pit factories in South Carolina and New Mexico that would produce components for additional atomic weapons.
In a letter Tuesday to U.S. Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm, a non-profit law firm said the government should prepare an extensive environmental study before deciding to establish pit production factories at the Savannah River Site near Aiken and the Los Alamos site near Santa Fe, N.M.
African American and Native American communities have been hurt by past activities at the nuclear sites, and President Joe Biden’s administration should consider how the production factories would add to that burden, according to the South Carolina Environmental Law Project, a non-profit legal service in South Carolina.
Nine environmental groups, including SRS Watch, the Gullah Geechee Sea Island Coalition, Tri-Valley Cares of California and Nuclear Watch New Mexico, are among those seeking more study.
The law project’s letter also was sent to the National Nuclear Security Administration, a division of the energy department.
“The plans of DOE and NNSA to expand this production program will saddle the already-burdened communities represented by these groups with a significant amount of nuclear waste and pollution,’’ the letter from lawyer Leslie Lenhardt said.
Her letter said the pit production efforts are in “complete contravention’’ to an executive order by President Biden that federal agencies weigh the impact their policies and plans have on disadvantaged communities.
Groups Notify Biden Admin of Impending Lawsuit Over Nuclear Bomb Core Plans
Multi-state coalition says DOE’s plans to massively expand plutonium pit production violate a major environmental law and constitutes an environmental injustice.
Jay Coghlan of Nuclear Watch New Mexico commented, “Instead of maintaining the safety and reliability of the existing nuclear weapons stockpile, NNSA may actually undermine it because all future pit production is for speculative new-design nuclear weapons. This is a colossal and unnecessary waste of taxpayers’ money on top of already wasted taxpayers’ money.”
CHARLESTON, S.C. — A coalition of public interest organizations notified (PDF below) the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) urging a comprehensive review of plans to vastly ramp up production of nuclear bomb cores at the Los Alamos National Lab in New Mexico and the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
In Tuesday’s letter to department officials, the groups say this lack of review violates the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and would saddle already-burdened communities nearby the two DOE sites with significant quantities of toxic and radioactive waste, contravening President Biden’s executive order of making environmental justice a part of the mission of every agency.
Sparks flying from nuclear waste barrel prompt investigation
Flawed packing of radioactive waste caused sparks to fly from a container at Los Alamos National Laboratory, prompting evacuation of the work area and later the underground disposal site near Carlsbad where two similarly packed canisters were stored.
By: Scott Wyland | santafenewmexican.com April 15, 2021
The sparking caused no injuries, damage or radiation to be released, according to a letter the lab wrote to the New Mexico Environment Department.
But any combustion involving transuranic nuclear waste is deemed dangerous and calls up memories of the 2014 incident in which a ruptured container from Los Alamos closed the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in Southern New Mexico for three years and cost almost $2 billion to clean up.
Environment, Public Health On The Way To Better Protection As Environment Department Receives Budget Increase
“After a decade of budget cuts, the New Mexico Environment Department’s (NMED) base budget will increase by 21.3% for the upcoming state fiscal year starting July 1, 2021. The additional $2.8 million will be a recurring increase to NMED’s operating budget. NMED’s overall operating budget for the upcoming fiscal year is approximately $93.4 million.”
NMED NEWS | LOS ALAMOS REPORTER April 14, 2021
“Starting in July, the New Mexico Environment Department will expand its efforts to safeguard communities and our environment,” said NMED Cabinet Secretary James Kenney. “Budget is policy and this is a clear investment in the health of New Mexicans and their environment.”
NMED’s budget is a combination of state general fund, federal funding, and revenues collected for various permits and licenses. Starting July 1, 2021, the general fund portion of NMED’s budget will increase from $13.1 million to $15.9 million – an increase of $2.8 million. The remainder of NMED’s budget is $77.5 million (federal funding and revenues collected for permits/licenses).
Offline Iowa Nuclear Plant Eyed as Site of Solar Project
CEDAR RAPIDS, Iowa (AP) — A decommissioned eastern Iowa nuclear plant could become the site of a new massive solar energy project.
NextEra Energy of Florida on Tuesday laid out plans in a meeting with nearby landowners to build a solar farm near the now-idle Duane Arnold Energy Center in Palo, The Gazette of Cedar Rapids reported.
The company said the project could bring in a $700 million capital investment and about 300 construction jobs. The solar farm would stretch across 3,500 acres near the plant and would produce up to 690 megawatts of solar energy — more than the nuclear plant had generated.
“We’re also hoping to accompany that solar project with up to 60 megawatts of AC-coupled batteries,” project manager Kimberly Dickey said in the meeting. Battery storage allows a company to store energy for use during peak energy-use times.
Waste Isolation Pilot Plant aims to expand underground facility to hold nuclear waste
“WIPP is supposed to be limited. The state did not agree to 12 panels.”
By: Adrian Hedden | currentargus.com April 15, 2021
A plan to build two new areas to dispose of nuclear waste began taking shape at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant after the U.S. Department of Energy published a report on the feasibility of adding an 11th and 12th waste panel to the underground nuclear waste repository.
Japan To Dump Wastewater From Wrecked Fukushima Nuclear Plant Into Pacific Ocean
Japan’s government announced a decision to begin dumping more than a million tons of treated but still radioactive wastewater from the crippled Fukushima nuclear plant into the Pacific Ocean in two years.
Anthony Kuhn | npr.org April 13, 2021
The plant was severely damaged in a 2011 magnitude 9.0 quake and tsunami that left about 20,000 people in northeast Japan dead or missing.
Despite Tokyo’s assurances that discharging wastewater will not pose a threat to people or the environment, the decision was roundly criticized by the local fishing community, environmental groups and Japan’s neighbors. Within hours of the announcement, protesters rallied outside government offices in Tokyo and Fukushima.
Fukushima Wastewater Will Be Released Into the Ocean, Japan Says
Beyond Nuclear | beyondnuclear.org April 13, 2021
The government says the plan is the best way to dispose of water used to prevent the ruined nuclear plant’s damaged reactor cores from melting.
As reported by the New York Times.
The New York Times also ran a companion piece, focused on the official international protest of the ocean dumping, as by the neighboring governments of South Korea, China, and Taiwan.
The Washington Post has also reported on this story.
Thom Hartmann interviewed Beyond Nuclear’s Kevin Kamps on his national radio show (“Fukushima Nuclear Fish Coming to Your Plate, Happy?”). Here is the write up:
More nuclear waste is about to be released into the Pacific Ocean from Fukushima. Where it will be absorbed by plants, eaten by small fish, who are eaten by bigger fish, and concentrated through a process called “bioaccumulation.” Pretty soon those fish end up on your plate… Looking forward to a swim off the west coast? Enjoying your fish?
Here is the link to the recording of the interview.
[Corrections: The actual volume of radioactive wastewater to be dumped in the ocean is currently enough to fill around 500 Olympic-sized swimming pools; the dumping is not set to begin until a couple years from now, not before the Tokyo Olympics.]
Environmental Racism, Environmental Justice
“When uranium mining occurred in white communities, the waste it produced was removed from the proximity of the residents. This level of clean-up did not take place when uranium mining occurred close to low-income communities of color”
By: Ruby Stigers| snakeriveralliance.org April 10, 2021
Those living near Nuclear Power Plants (NPP’s) face extreme health risks. Blood, thyroid, breast, and other forms of cancer have the potential to form due to the various types of radioactive emissions that escape the NPP’s through the air, water, and soil.
The World Nuclear Association and The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) claim that exposure to low-level radiation is undetectable and not unsafe, yet countless studies confirm the danger of the radiation that occurs during normal operation at an NPP. According to Dean Kyne and Bob Bolin, Children are especially vulnerable to this exposure.
Toxic incinerators, uranium mines, atomic reactors, and other nuclear dumping sites are generally located on cheap land where there are limited resources and little organized opposition (Jantz, p. 249). Unfortunately, because of this, they are often located in Black, Indigenous, and low-income communities that suffer the devastating consequences of improperly handled nuclear waste and pollution.
DOE Planning to Increase Down-Blended Plutonium Shipments to Waste Isolation Pilot Plant
Savannah River Site is the third largest shipper of waste to WIPP, with 1,679 as of April 3, per the latest records from WIPP.
By: Adrian Hedden | currentargus.com April 7, 2021
Federal nuclear waste managers are planning to ramp up shipments of plutonium from a site in South Carolina for final disposal at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in southeast New Mexico.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Environmental Management (EM) began preparing equipment at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in Aiken, South Carolina used to package and inspect drums of the waste before shipping to WIPP where it will be permanently disposed of in the repository’s underground salt formation.
The plutonium waste will be inspected to verify that it meets the criteria required for emplacement at WIPP, which is used to dispose of low-level transuranic (TRU) nuclear waste – mostly clothing items and equipment radiated during nuclear activities.
Scotland Reaches Green Landmark – Scotland generated 97.4% of its electricity demand from renewables last year
By: Juan Cole | scheerpost.com
In 2011, Scotland’s government, urged on by visionaries like Richard Dixon, set itself the ambitious goal to get 100% of its electricity from renewables by 2020. At that time, it only only got about a fourth from clean energy sources, and a lot of that was hydro.
The report card is in for 2020 and Scotland generated 97.4% of its electricity demand from renewables last year, just a whisker less than the 100% goal.
Scotland will host the COP26 climate summit in Glasgow in a few months, and is well placed to assert climate leadership.
Scotland no longer has a coal plant, and its one natural gas plant is under-utilized and seems likely to close in a few years.
DOE’s NNSA Reveals it’s Out of Money. Flat Broke. Busted. Nothing Left for Beneficial Nuclear Non-Proliferation Program to Convert Reactor from Weapon-Grade Uranium Fuel
By: SRS Watch | srswatch.com
The U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has revealed that it has spent all of our money. Busted flat. Nothing left. Nada. Zilch. Nichts.
Well, that’s what it seems like at the NNSA has notified GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy that there are no funds available to convert a test reactor in Vallecitos, California from weapon-grade uranium (highly enriched uranium, HEU) to low-enriched uranium (LEU), as part of an nuclear non-proliferation effort.
On March 25, 2021, NNSA told GE Hitac hi Nuclear Energy: “you are hereby notified that Department of Energy funding will not be available in fiscal year 2021 to complete the conversion of NTR to LEU fuel.” And GE subsequently told the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission that ” DOE funding is not currently available for conversion of the NTR fuel.”
See: “GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy Americas, LLC – Annual Statement of Non-availability of Federal Government Funding for Conversion from HEU to LEU for VNC Nuclear Test Reactor (NTR) at https://adamswebsearch2.nrc.gov/webSearch2/main.jsp?AccessionNumber=ML21084A808
BUT WAIT! NNSA continues to front for boosters and contractors engaged in project to convert the abandoned plutonium fuel (MOX) plant at the Savannah River Site into the SRS Plutonium Bomb Plant (PBP) at a cost of $4.6 billion (add higher number if you wish) by 2030 (add any date you wish). So, there seems to be money available for projects dangerous to our national security – making plutonium pits for unneeded and provocative new nuclear weapons – but not a penny left to get HEU out of commerce. This confirms that the priorities of NNSA are totally screwed up and that it’s placing contractor enrichment and parochial politics above national security. Congress must make sure that the HEU conversion program is fully funded and that the Ground Based Strategic Deterrent (with W87-1 warhead) and the new SLBM (with W93 warhead) – the first new weapons to get new plutonium pits – are terminated and funded halted. As in nada, zilch, nothing.
The New Shaft Permit Modification Part 3: Your Comments and the May 17th Public Hearing
As demanded by organizations and individuals, the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) has scheduled a public hearing on adding a New Utility Shaft to the WIPP permit. The hearing will start at noon on Monday, May 17, 2021. Hundreds of people commented on the proposed new shaft in 2019 and 2020, 97 percent of whom objected to WIPP expansion and the new shaft.
NMED allowed the Department of Energy (DOE) to bypass the public process and start digging the new shaft with just a Temporary Authorization. But after receiving so many public comments in 2020 against the new shaft and against the Temporary Authorization, NMED stopped the construction of the shaft until after the public hearing. Public comments do make a difference!
You can comment now on the proposed new WIPP shaft, which is part of DOE’s plan to expand WIPP and operate it forever, rather than developing new repositories. The plan violates existing limits set in federal law, state agreements, the WIPP Permit, and DOE’s decades-old social contract with New Mexicans.
Your comments and participation can help stop the new shaft and DOE’s WIPP expansion plan!
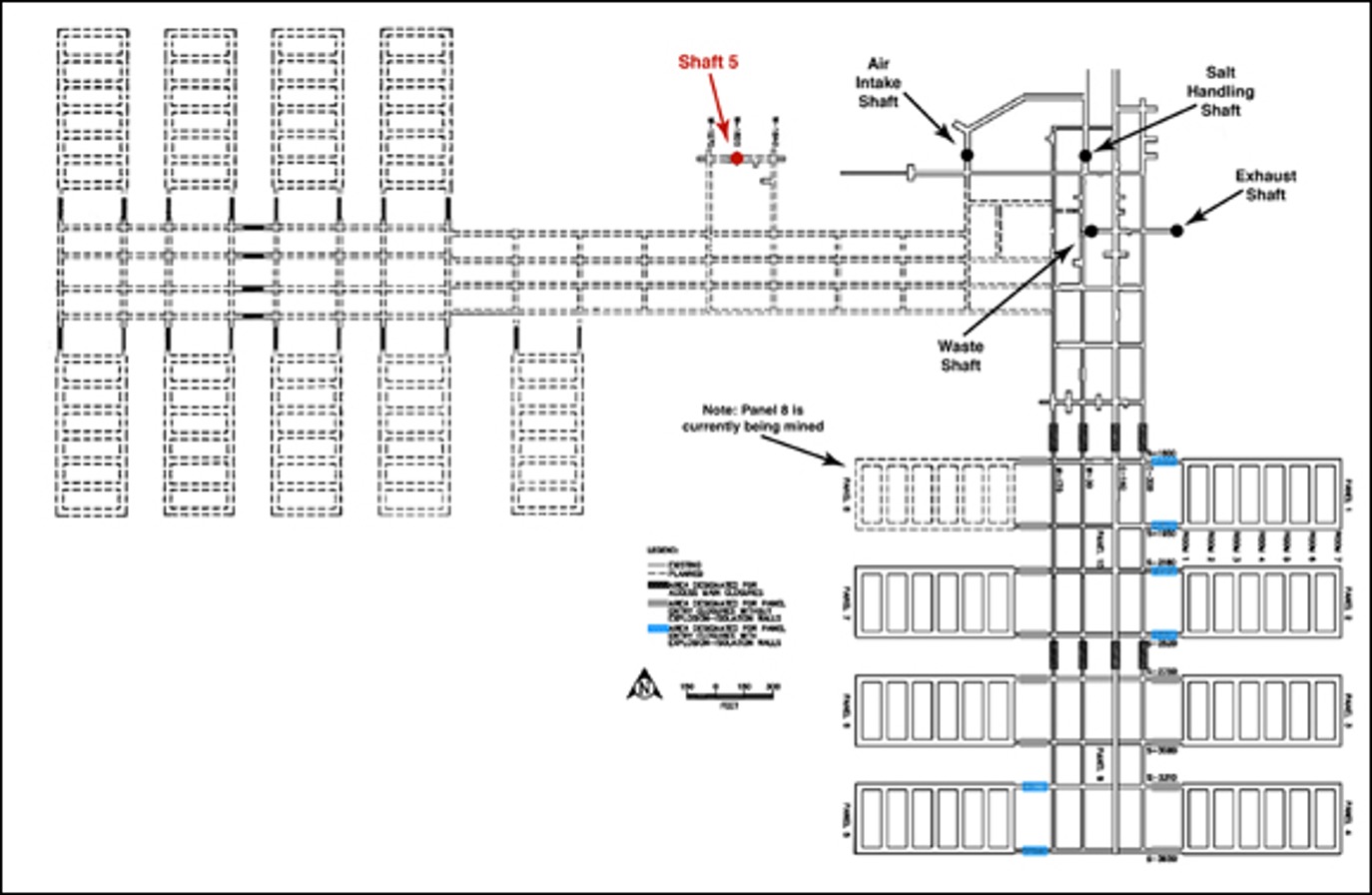
Santa Fe City Council rejects LANL coalition agreement
By: Sean P. Thomas, The Santa Fe New Mexican | sfnewmexican.com March 31, 2021
The Santa Fe City Council has rejected an amended joint powers agreement with the Regional Coalition of LANL Communities over concerns about the organization’s impact and one councilor’s plan to introduce a measure removing the city from the group.
“I don’t think we should just approve an updated JPA because we want to go along to get along,” said City Councilor Renee Villarreal, who noted she intends to propose the city end its affiliation with the coalition. “Some of my colleagues say we should have a seat at the table, but I think we should have it at the right table.”
The council voted 5-3 against the agreement, with Mayor Alan Webber and Councilors Carol Romero-Wirth and Jamie Cassutt-Sanchez voting in favor. City Councilor Michael Garcia, the city’s representative on the coalition, abstained.
Rejecting the agreement does not pull the city out of the organization.
Villarreal has been the loudest critic of the coalition, which was established in 2011 to give communities surrounding Los Alamos National Laboratory more of a voice in its job development and cleanup. She questioned in previous committee meetings how the city stood to benefit.
“Our values have not aligned,” Villarreal said. “I’m trying to understand changing the JPA, what does that change? How does our voice actually get heard since it hasn’t been heard the last 10 years?”
Trinity Downwinders: 75 Years And Waiting
Watch the Hearing with the House Judiciary Committee below, which occurred 3/24/21. Click HERE to visit the website. Click HERE to read the Santa Fe New Mexican article written about the hearing. See Hearing below:
‘Sparking’ nuclear waste drum at Los Alamos National Lab leads to evacuation at WIPP
“A sparking drum of nuclear waste at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) led to a temporary evacuation of a section of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant’s underground repository as officials investigated if any other drums of waste emplaced at WIPP posed a similar threat.”
By: Adrian Hedden, Carlsbad Current-Argus March 31, 2021
Investigators later found no one was hurt and no radiation was released, according to a March 12 letter from the lab to the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) Hazardous Waste Bureau.
The lab reported it happened as workers packed a drum of low-level transuranic (TRU) waste on Feb. 26 for delivery and disposal at WIPP.
TRU waste is equipment, clothing materials and other items radiated during nuclear activities.
During the packing process, two high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters were placed into a drum, followed by a “metal waste item,” read the letter from the lab.
The item tore the bag containing the HEPA filters, and sparks were observed coming out of the container when the item contacted the filters.
Nuclear News Archives – 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.