QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
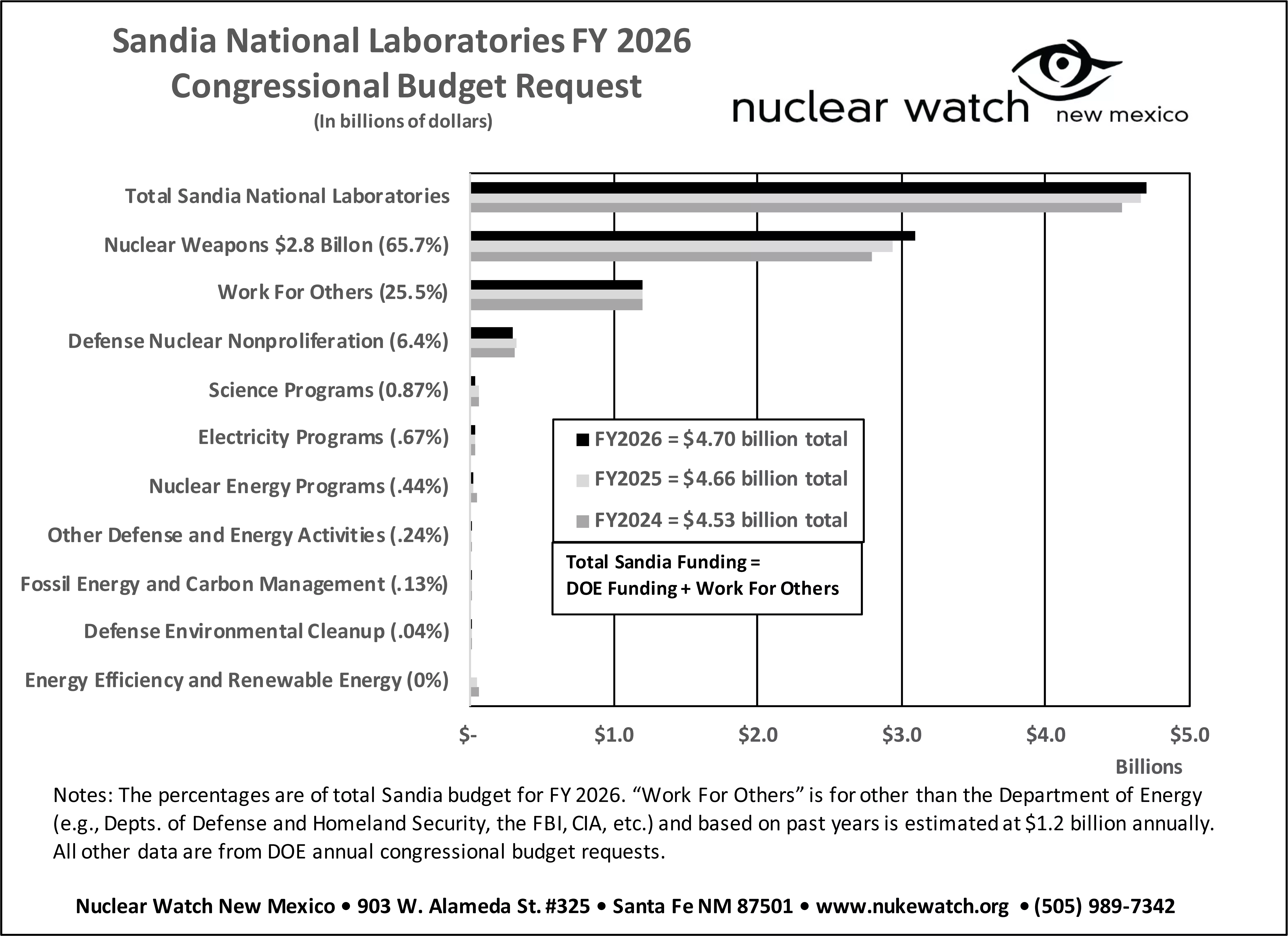
Follow the Money!
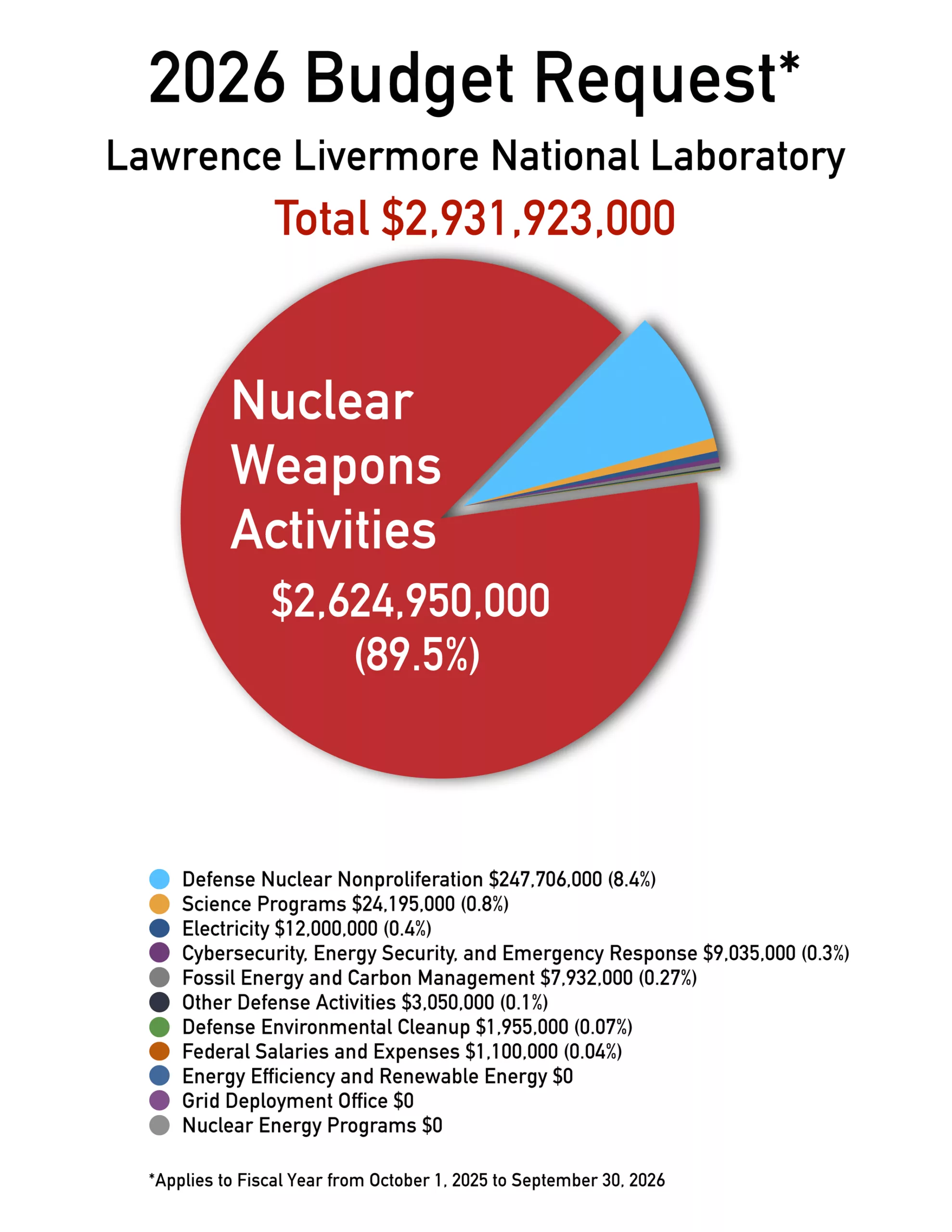
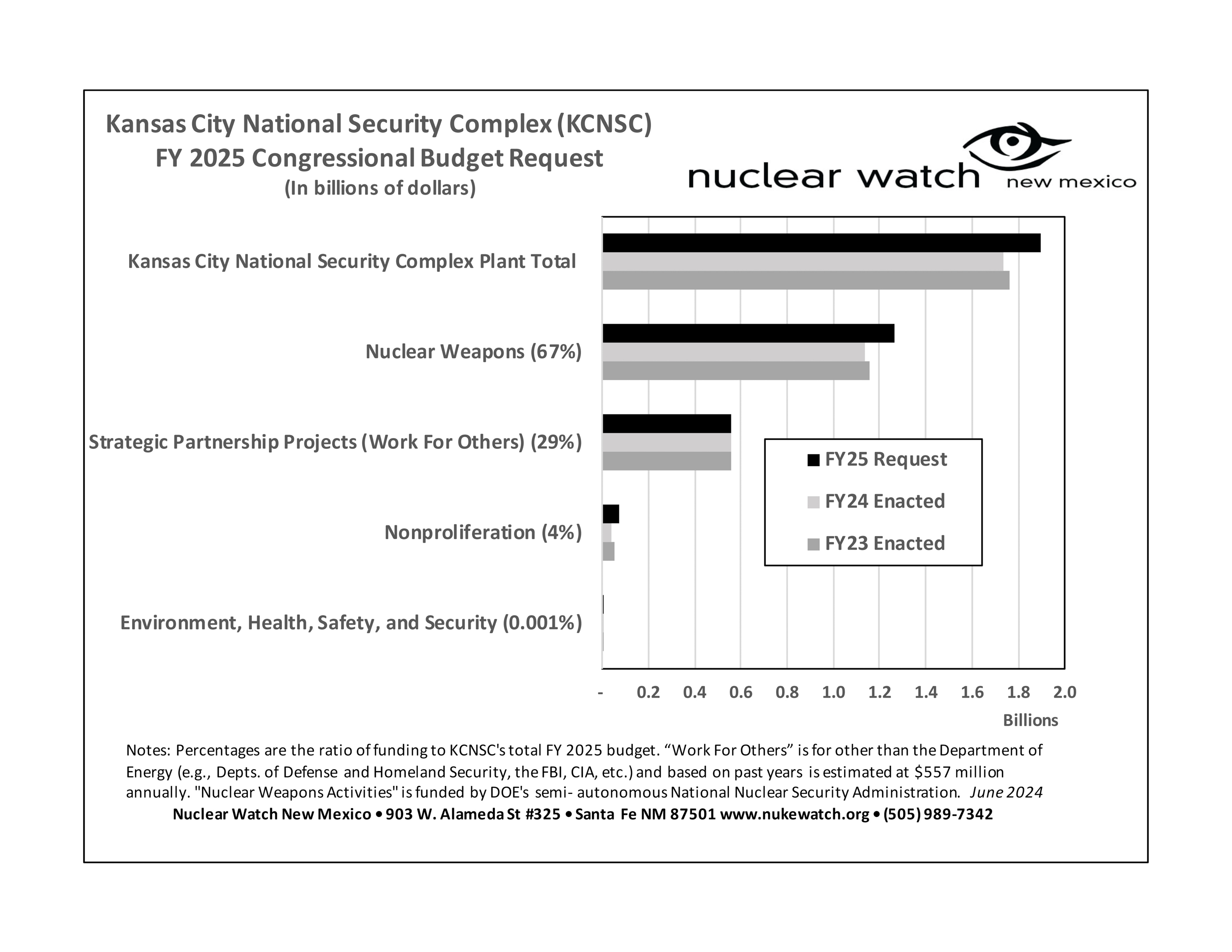
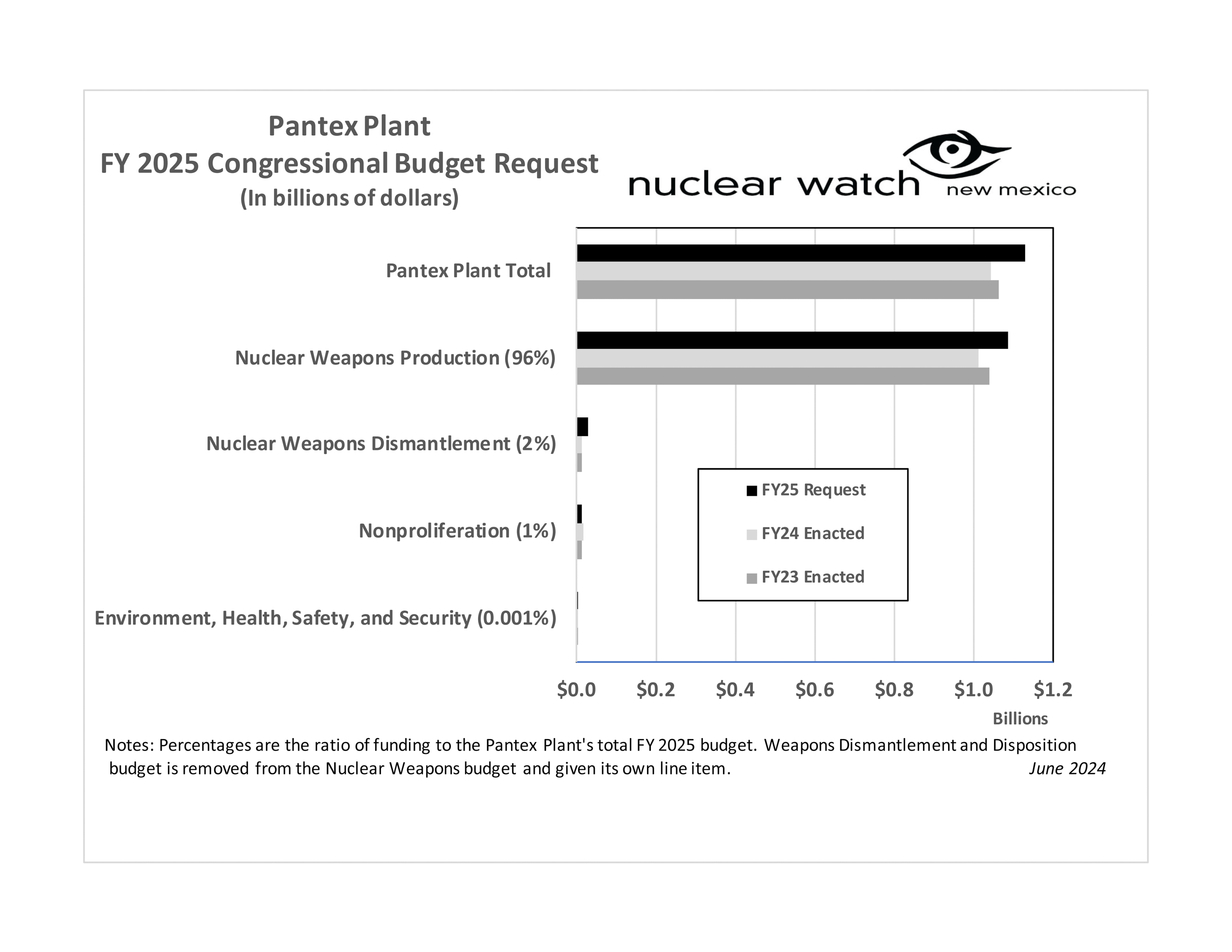
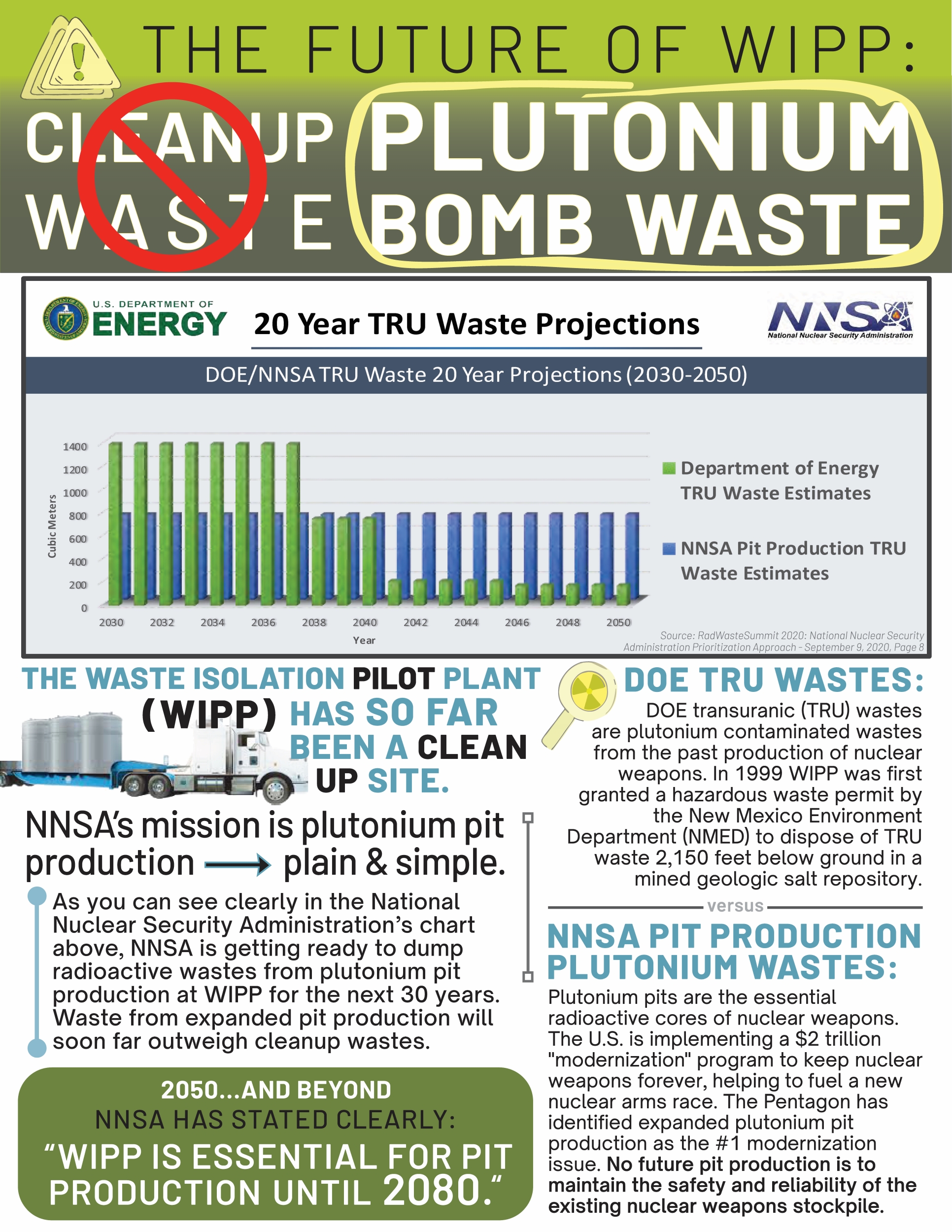
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
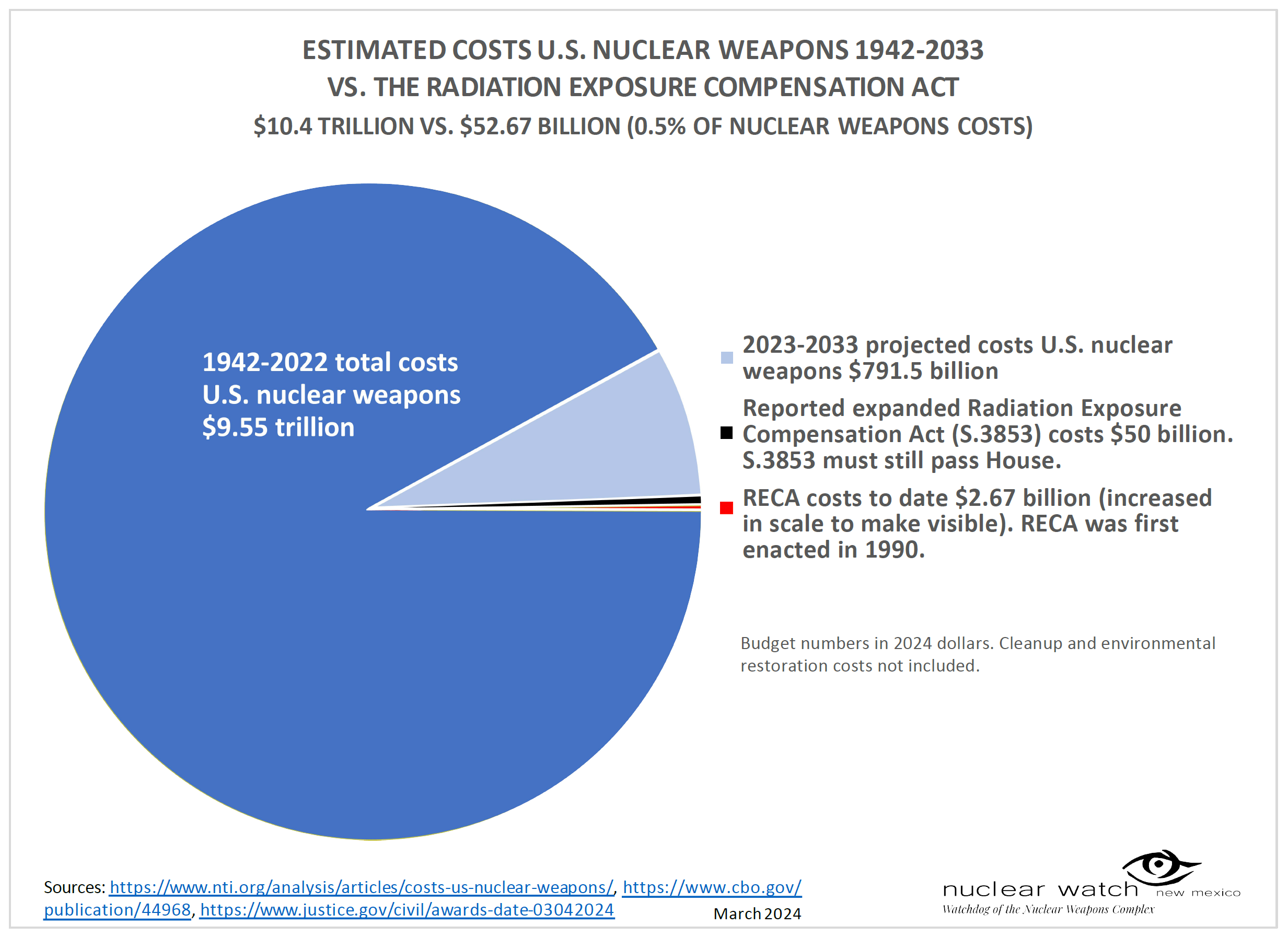
U.S. Senators Luján, Hawley, Heinrich, Schmitt, Reintroduce RECA To Give Nuclear Radiation Victims Compensation

By Carol A. Clark, Los Alamos Daily Post | January 24, 2025 ladailypost.com
Despite the Senate passing this bill, the House of Representatives failed to pass the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) reauthorization before its expiration deadline in the 118th Congress.
“In New Mexico and across the country, thousands sacrificed to contribute to our national security. Today, individuals affected by nuclear weapons testing, downwind radiation exposure, and uranium mining are still waiting to receive the justice they are owed,” Sen. Luján said.
“It is unacceptable that so many who have gotten sick from radiation exposure have been denied compensation by Congress. Despite having passed RECA legislation twice through the Senate with broad bipartisan support, and securing the support of the previous administration, I was disheartened that Speaker Johnson refused a vote on RECA to help victims. This Congress, I am proud to partner with Senator Hawley again to extend and expand RECA. RECA is a bipartisan priority and I am hopeful that we will once again get it through the Senate and hope the Speaker commits to getting victims the compensation they are owed.”
Trump wants nuclear reduction talks with China, Russia
Trump recounted talks with Putin ahead of the 2020 U.S. election about denuclearization talks and how “China would have come along.”
“We want to see if we can denuclearize, and I think that’s very possible,” Trump said.
By Laura Kelly, The Hill | January 23, 2025 thehill.com
President Trump while addressing the World Economic Forum in Davos on Thursday said that he wants to hold talks with Russia and China about reducing nuclear weapon stockpiles.
Trump during his first term failed to bring China into negotiations to extend a nuclear arms treaty with Russia, called New START, which places key limits on deployed nuclear weapons and expires February 2026.
U.S. and Russian participation in the treaty effectively froze during the Biden administration, as Russian President Vladimir Putin sought to impose costs on Washington for supporting Ukraine militarily.
Remember the Downwinders
Today, Jan. 27 is a National Day of Remembrance for Downwinders. Nuclear testing by the U.S. government started in New Mexico with the Trinity Test in July 1945, and the Crossroads Series of three tests followed in the Pacific in 1946. The United States took part in nuclear testing as part of the escalating Cold War arms race, and nuclear weapons proliferated. Americans working and living downwind from nuclear testing sites became sick and killed by the radiation exposure generated from the aboveground atomic tests in Nevada, which began on January 27, 1951 and ended on July 17, 1962. With each nuclear test, radioactive fallout spread globally. Of course, downwinders are not only American. At the so-called “Pacific Proving Grounds” in the Marshall Islands, 67 nuclear weapons were detonated between 1945 and 1962.
From GUAM PACIFIC DAILY NEWS 1/27/25:
“It became a site of unimaginable destruction that did not stop at the blast zones. The radioactive fallout spread across the Pacific, settling on many islands like ours.” — Guam Senator Therese Terlaje
Seven of the top 10 adult cancers on Guam are now recognized as compensable for radiation exposure by the federal government, the senator noted.
Honoring Black Leaders in Disarmament
Russia Nuclear Update a project based at the MIT Security Studies Program that produces fact-based visual content on the threats posed by nuclear weapons, has shared a fantastic set of content that highlights the vital role that Black leaders have played in arms control and nuclear disarmament in celebration of Martin Luther King Jr. Day and Black History Month.
“50 Faces of Black Leaders” honors the many contributions of civil rights and other leaders who opposed nuclear war. This video content is provided in vertical and horizontal formats and is free of charge.
Russia Nuclear Update (MIT) | January 17, 2025 russianuclearupdate.org
The individuals featured in this series include both contemporary figures like Ambassador Bonnie Jenkins, and past generations, including Coretta Scott King, Bayard Rustin, and iconic artists.
Historic Settlement Reached in NEPA Lawsuit Over Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Core Production
Nonprofit public interest groups have reached an historic settlement agreement with the Department of Energy’s semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). This is the successful result of a lawsuit against NNSA over its failure to complete a programmatic environmental impact statement on the expanded production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores, as required by the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). This agreement and a joint motion to dismiss have been submitted to Judge Mary Lewis Geiger of the Federal District of South Carolina. Should the Court enter the dismissal and retain jurisdiction to enforce the settlement, the agreement will go into effect.
This lawsuit was first filed in June 2021 by co-plaintiffs Savannah River Site Watch of Columbia, SC; Nuclear Watch New Mexico of Santa Fe, NM; Tri-Valley Communities Against a Radioactive Environment (CAREs), based in Livermore, CA; and the Gullah/Geechee Sea Island Coalition of coastal Georgia. NNSA promptly moved to have the case dismissed which in February 2023 Judge Lewis rejected, calling her decision “not a close call.”
In September 2024, Judge Lewis ruled that DOE and NNSA had violated NEPA by failing to properly consider alternatives before proceeding with their plan to produce plutonium pits, a critical component of nuclear weapons, at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in New Mexico and, for the first time ever, at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina. The Court found that the plan’s purpose had fundamentally changed from NNSA’s earlier analyses which had not considered simultaneous pit production at two sites. Judge Lewis directed the Defendants and Plaintiffs to prepare a joint proposal for an appropriate remedy which fostered additional negotiations.
Historic Settlement Reached in NEPA Lawsuit Over Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Core Production
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, January 17, 2025
Media Contacts:
Ben Cunningham, Esquire, SCELP, 843-527-0078, ben@scelp.org
Tom Clements, Savannah River Site Watch, 803-834-3084, tomclements329@cs.com
Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch New Mexico, 505-989-7342, jay@nukewatch.org
Scott Yundt, Tri-Valley CAREs, 925-443-7148, scott@trivalleycares.org
Queen Quet, Gullah/Geechee Sea Island Coalition, 843-838-1171, GullGeeCo@aol.com
AIKEN, S.C. — Nonprofit public interest groups have reached an historic settlement agreement with the Department of Energy’s semi-autonomous nuclear weapons agency, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). This is the successful result of a lawsuit against NNSA over its failure to complete a programmatic environmental impact statement on the expanded production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores, as required by the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). This agreement and a joint motion to dismiss have been submitted to Judge Mary Lewis Geiger of the Federal District of South Carolina. Should the Court enter the dismissal and retain jurisdiction to enforce the settlement, the agreement will go into effect.
This lawsuit was first filed in June 2021 by co-plaintiffs Savannah River Site Watch of Columbia, SC; Nuclear Watch New Mexico of Santa Fe, NM; Tri-Valley Communities Against a Radioactive Environment (CAREs), based in Livermore, CA; and the Gullah/Geechee Sea Island Coalition of coastal Georgia. NNSA promptly moved to have the case dismissed which in February 2023 Judge Lewis rejected, calling her decision “not a close call.”
Anti-nuclear advocates, feds, compromise on pit production lawsuit
“We’re generally satisfied [with the terms],” said Nuclear Watch New Mexico executive director Jay Coghlan.
But what about the other half of the two-site plan?
“The fish that got away is Los Alamos,” Coghlan said.
Alaina Mencinger | January 17, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
The National Nuclear Security Administration and anti-nuclear advocates have reached agreement in a lawsuit over the National Environmental Protection Act that could temporarily halt plutonium pit production efforts at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
If approved, the proposed agreement, reached Thursday, would leave Los Alamos National Laboratory as the agency’s only pit production site until a far-reaching environmental impact statement can be completed, which is expected to take at least 2½ years.
Nuclear Watch New Mexico and other groups around the country alleged in a 2021 lawsuit the federal government had violated the National Environmental Protection Act in the course of deciding to produce plutonium pits, the trigger device for nuclear weapons, at both Los Alamos National Laboratory and the Savannah River Site.
DOE Rejects Comprehensive Cleanup at Los Alamos Lab; Designates Expanded Nuclear Weapons Production as Preferred Future
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, January 15, 2025
Contact: Jay Coghlan, 505.989.7342 | Email
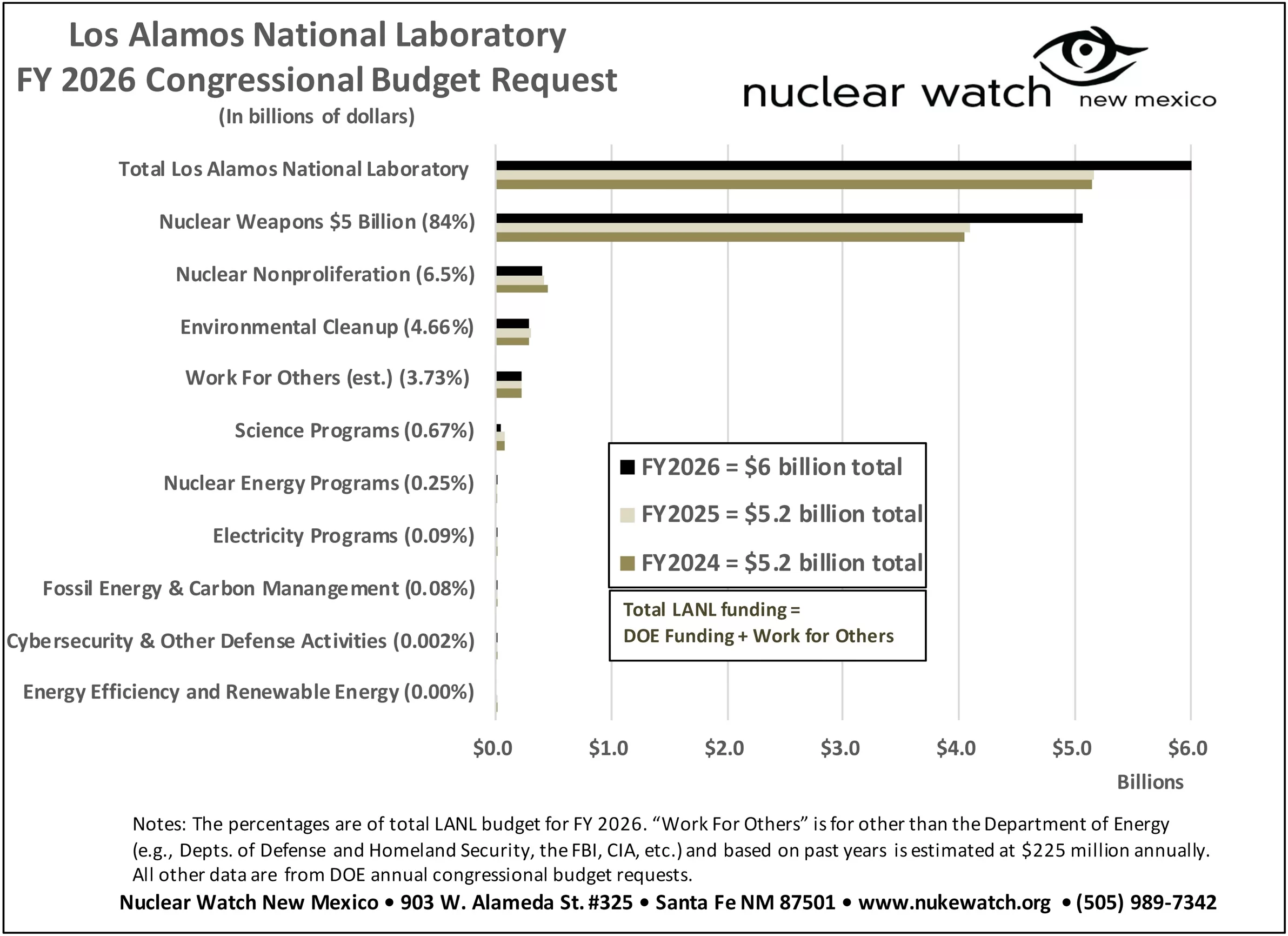
Santa Fe, NM – Today, in an informal conference hosted by the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED), the Department of Energy rejected future excavation, characterization and further treatment of its radioactive and toxic wastes at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. Just five days ago, DOE’s National Nuclear Security Administration formally designated radically expanded nuclear weapons programs as the “preferred alternative” for the Lab’s future.[1] The key issue is the expanded production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores for the accelerating nuclear arms race.
In a draft Order, NMED directed DOE to comprehensively clean up “Area C,” a radioactive and toxic waste dump from the 1950s. Nuclear Watch New Mexico strongly supports NMED’s position. Area C is relatively small and shallow at 11 acres and not more than 25 feet deep. Therefore, it is an excellent model for future comprehensive cleanup at LANL, such as the much larger Area G waste dump. A public hearing is required before NMED can implement a final Order, but DOE seeks to delay that hearing as well.
Feds release statement on LANL expansion possibilities
Despite the name, even the no action plan means growth for LANL — just a smaller amount. Given already-approved projects, the lab’s footprint is estimated to grow 4% under the no action plan and include increased demands for water and energy.
That has Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, feeling like the process is “rigged” — and too late, given that the plan to restart pit production was approved before a site-wide environmental impact statement was drafted to weigh the impacts.
“It’s a choice between expanded nuclear weapons programs, yet more expanded nuclear weapons programs, or far more expanded nuclear weapons programs,” Coghlan said. “And all the while, these are for new designs. None of this is to maintain the safety and reliability of the existing, extensively tested stockpile. It’s this is all about new design nuclear weapons.”
Alaina Mencinger | January 10, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
As Los Alamos National Laboratory takes on a starring role in a plan to update the U.S. nuclear arsenal, the National Nuclear Security Administration is looking at what future operations of the lab might look like for the environment.
On Friday, NNSA released a draft site-wide environmental impact statement about LANL’s ongoing operations, the first since 2008. In the 17 years since, LANL’s budget has more than doubled and hundreds of new employees have been added, according to the statement.
The draft statement includes three visions for LANL’s future: a no action plan, a plan to modernize operations and a plan to expand operations. NNSA’s preferred choice is to grow operations; questions sent to the agency were not immediately returned.
New Draft LANL Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement is Released
NNSA’s Preferred Future for the Lab is Radically Expanded Nuclear Weapons Programs
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, January 10, 2025
Jay Coghlan – 505.989.7342 | Email
Santa Fe, NM – The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has finally released its Draft Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement (SWEIS) for Continued Operation of the Los Alamos National Laboratory. This is more than two years after it was first announced and sixteen years after the last site-wide EIS. During that time the Lab has become more and more a nuclear weapons production site for the new global nuclear arms race. Accordingly, the central point of the new draft LANL SWEIS is “NNSA has identified the Expanded Operations Alternative as the preferred alternative for the continuing operations of LANL.” Draft LANL SWEIS, page S-13.
New Draft LANL Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement is Released
NNSA’s Preferred Future for the Lab is Radically Expanded Nuclear Weapons Programs
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has finally released its Draft Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement (SWEIS) for Continued Operation of the Los Alamos National Laboratory. This is more than two years after it was first announced and sixteen years after the last site-wide EIS. During that time the Lab has become more and more a nuclear weapons production site for the new global nuclear arms race. Accordingly, the central point of the new draft LANL SWEIS is “NNSA has identified the Expanded Operations Alternative as the preferred alternative for the continuing operations of LANL.” Draft LANL SWEIS, page S-13.
As policy background, the draft LANL SWEIS pays lip service to the 1970 NonProliferation Treaty (NPT):
“In Article VI of the NPT, treaty parties “undertake to pursue negotiations in good faith on effective measures relating to cessation of the nuclear arms race at an early date and to nuclear disarmament…” The U.S. takes this commitment seriously and has emphasized dedication to both the long-term goal of eliminating nuclear weapons and the requirement that the U.S. has modern, flexible, and resilient nuclear capabilities that are safe and secure, until such a time as nuclear weapons can prudently be eliminated from the world.” P. 1-7.
Left unsaid is that no nuclear power, including the United States, has ever even tried to enter into good faith negotiations toward nuclear weapons disarmament, pledged to more than a half-century ago. Instead, all nuclear weapons states are now engaged in massive “modernization” programs to keep nuclear weapons forever, leading to today’s accelerating nuclear weapons arms race. Also, very much left unsaid is the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, ratified by 73 countries, nearing its fourth anniversary since it went into effect.
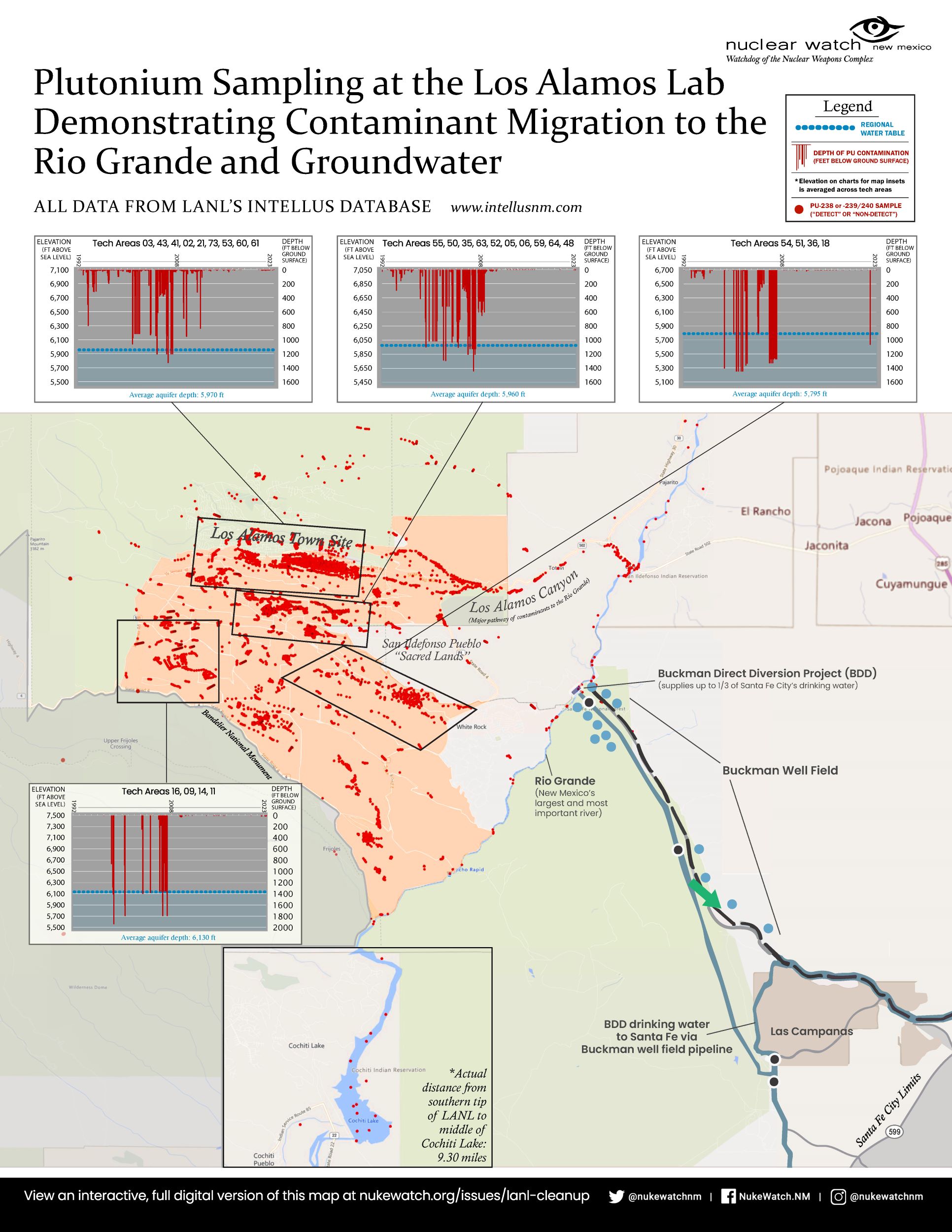
Independent Review of Chromium Groundwater Contamination Fails to Make Final Cleanup Recommendation
After 20 Years Los Alamos Lab Still Doesn’t Know Size of Plume
At Present Rate Cleanup Will Take More Than a Century
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, January 2, 2025
Contact: Jay Coghlan, Nuclear Watch New Mexico, 505-989-7342, jay@nukewatch.org
Santa Fe, NM – On December 30, 2024, in the middle of the holiday season, the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) posted the report Independent Review of the Chromium Interim Measures Remediation System to its largely unknown Legacy Cleanup Electronic Public Reading Room. This report attempts to address the Lab’s extensive contamination of the region’s deep groundwater aquifer by a large plume of hexavalent chromium, whose potentially serious human health effects (including cancer) was the subject of the popular movie Erin Brockovich.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
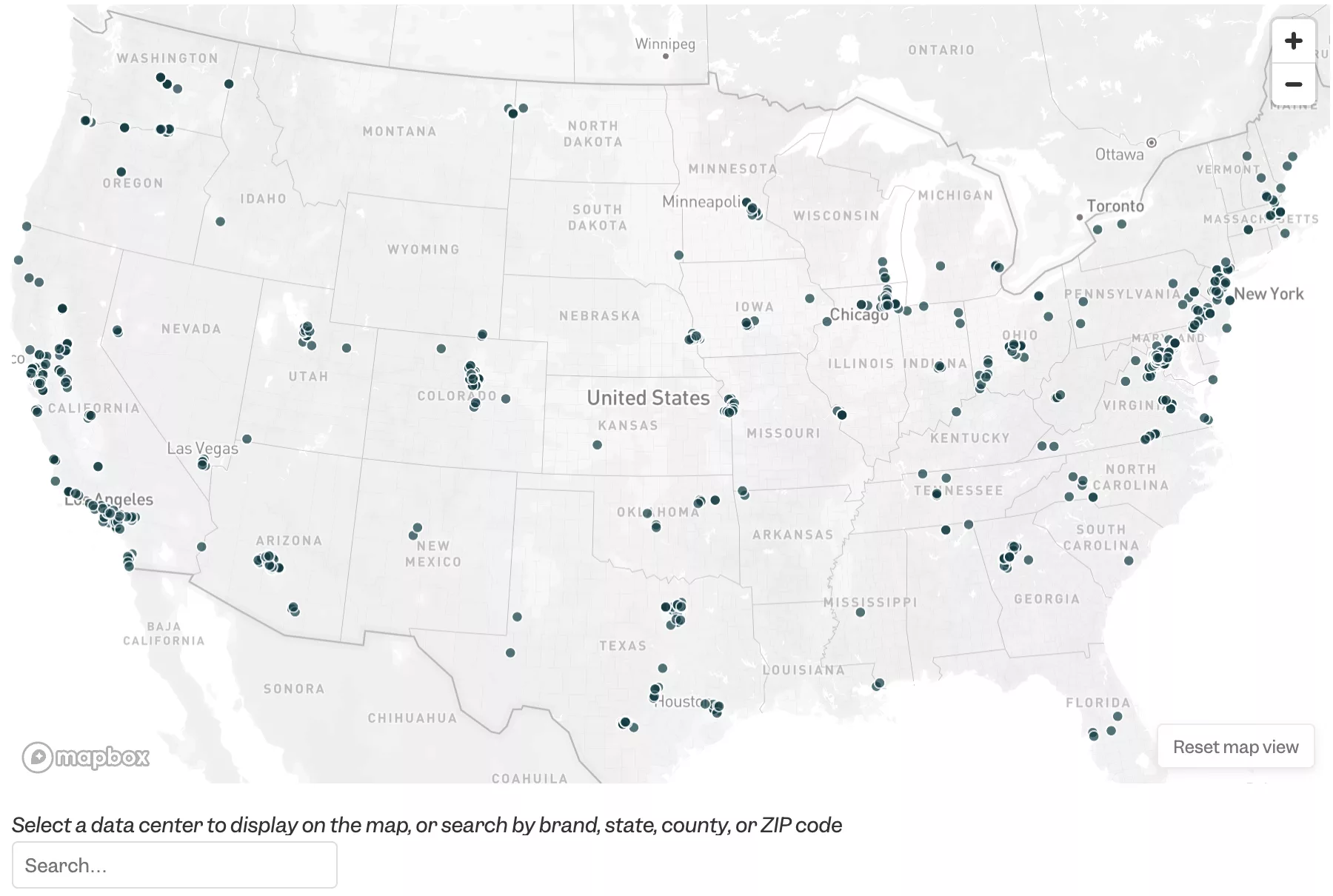
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
DARK CIRCLE: The Sundance Grand Prize-winning classic doc about the dangers of the atomic age – newly restored!
Dark Circle – Official Trailer from First Run Features on Vimeo.
It’s been 75 years this month since the start of the Atomic Age, with the U.S. nuclear bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki killing hundreds of thousands of civilians, but its trail of destruction has never ended.
Jay Coghlan on The Richard Eeds Show August 3, 2020
The Richard Eeds Show. 8/3 – Jay Coghlan of Nuclear Watch New Mexico on The Event Commemorating the 75th Anniversary of the Bombing of Hiroshima.