QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
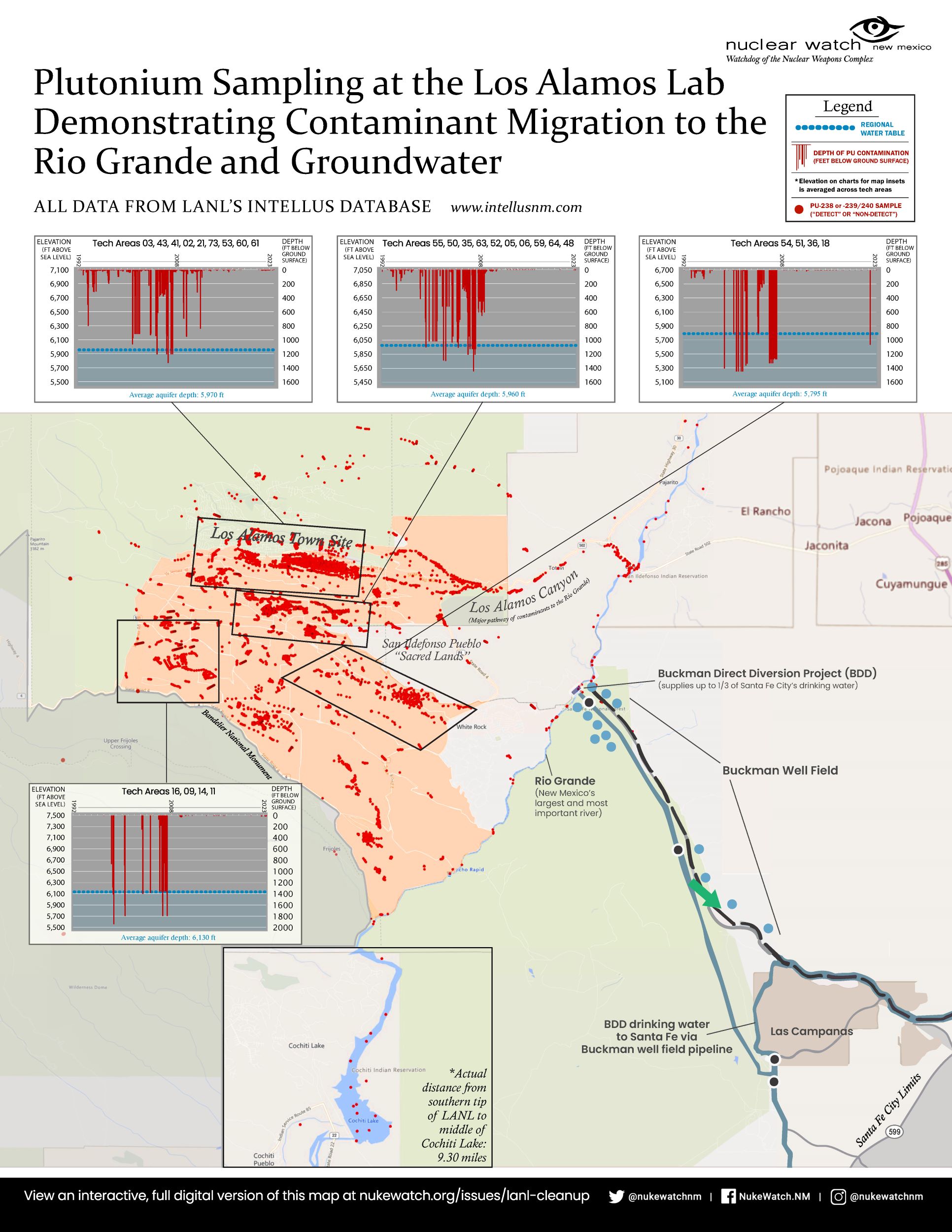
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
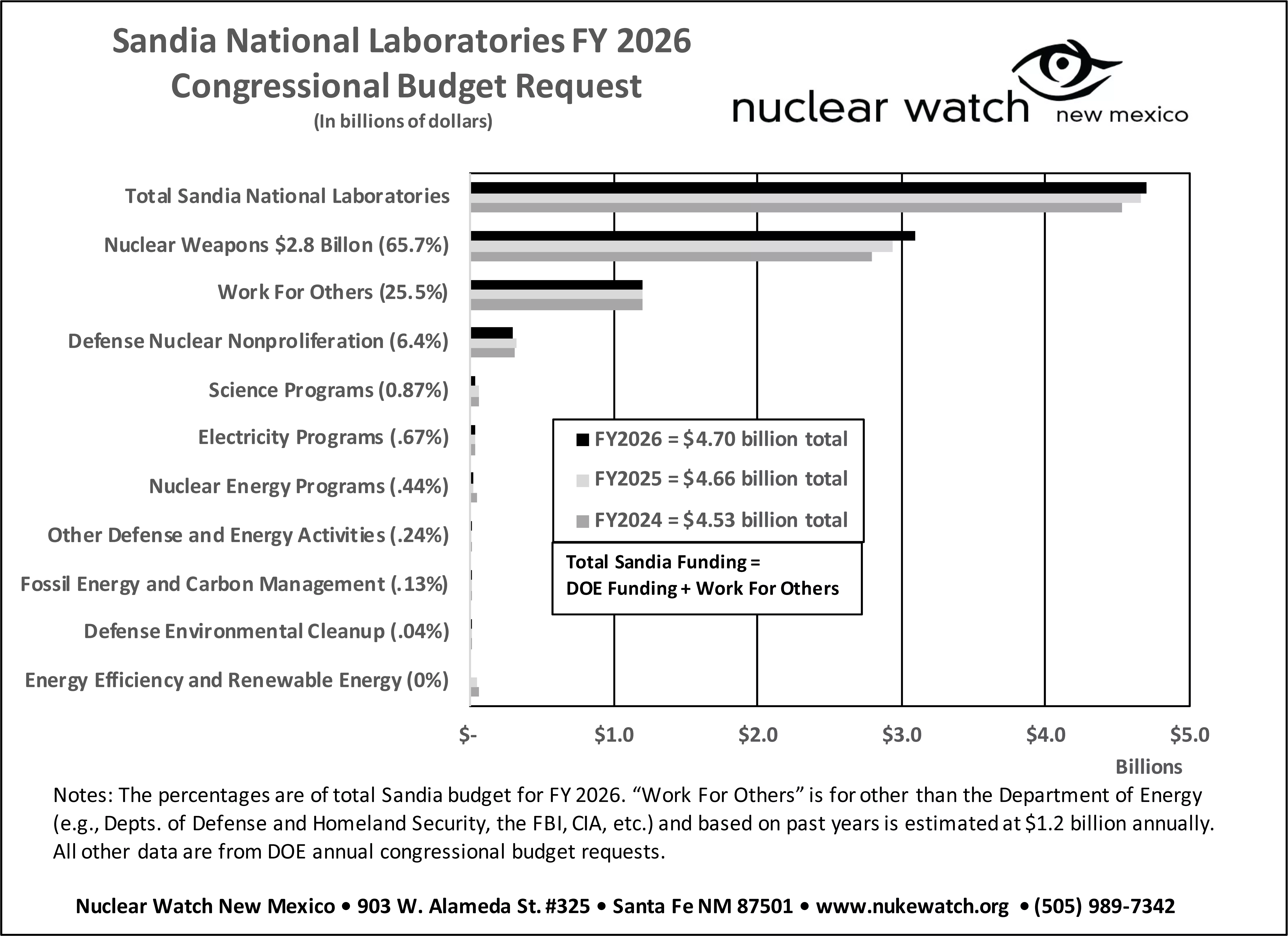
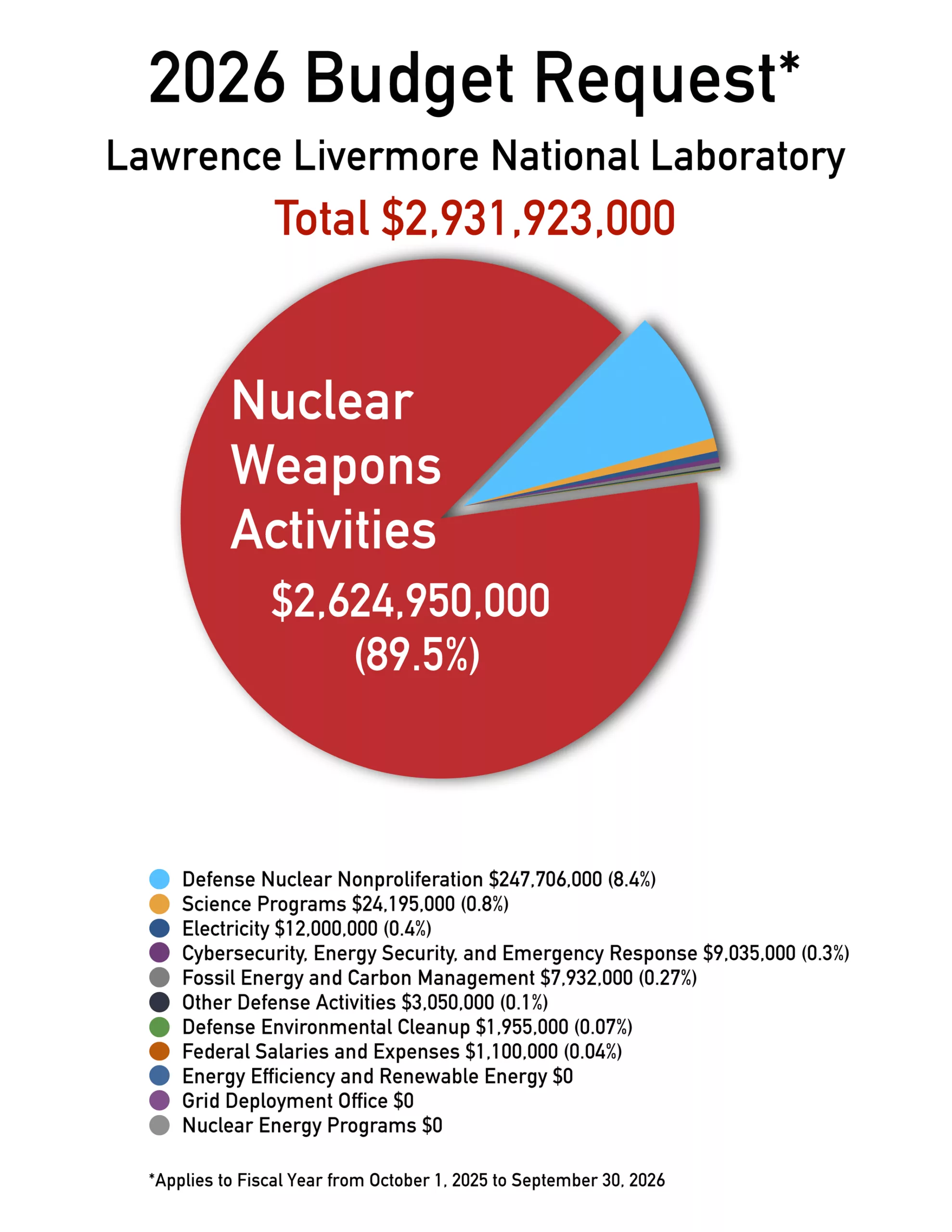
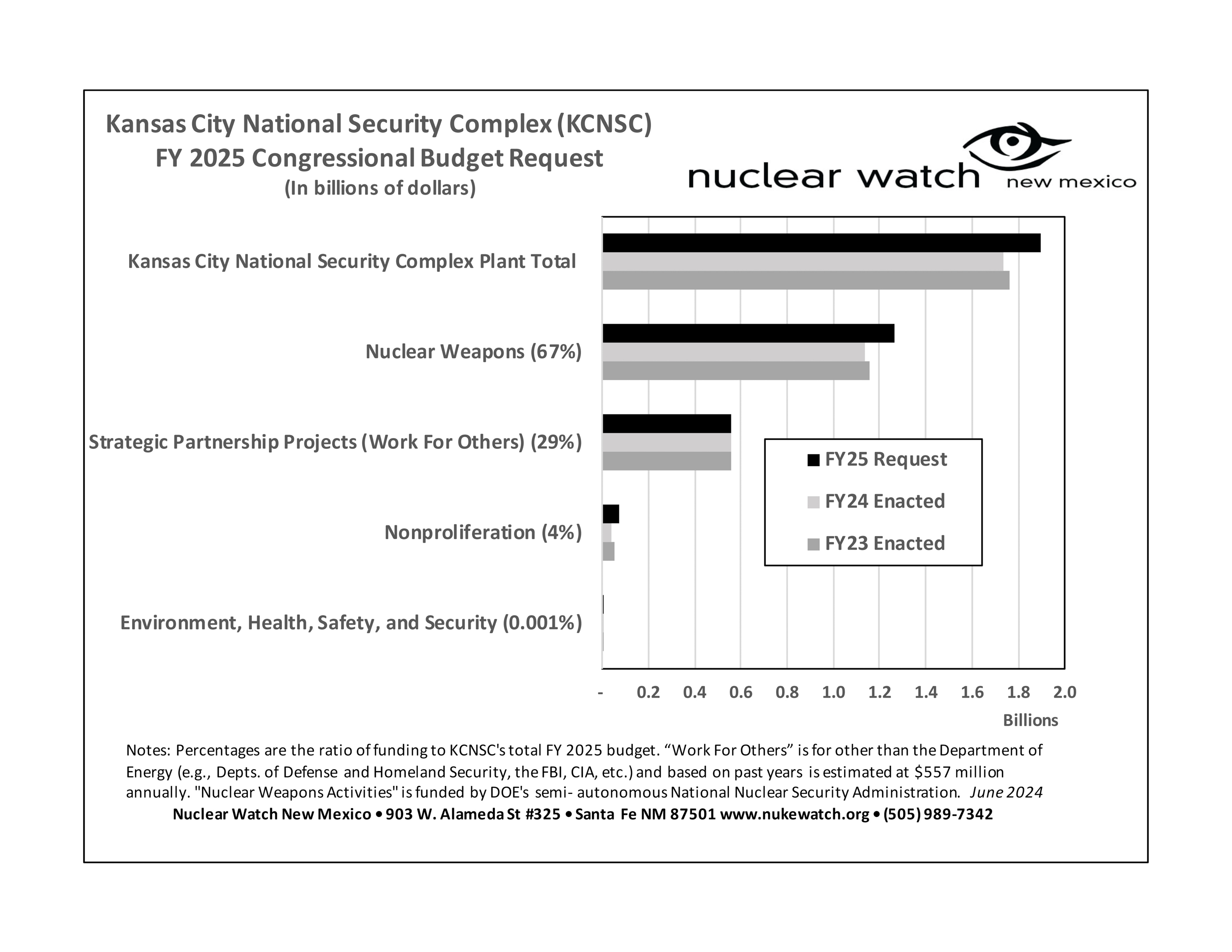
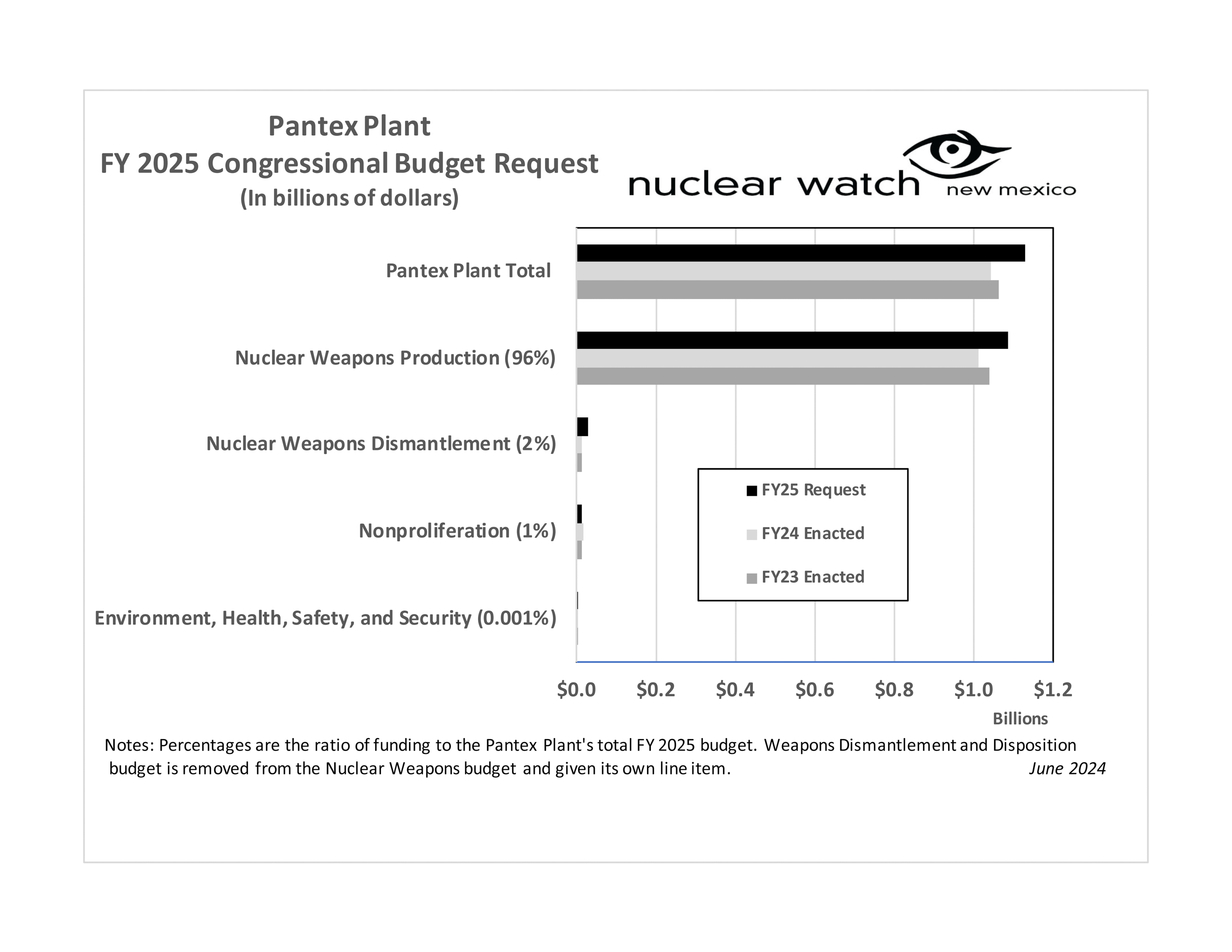
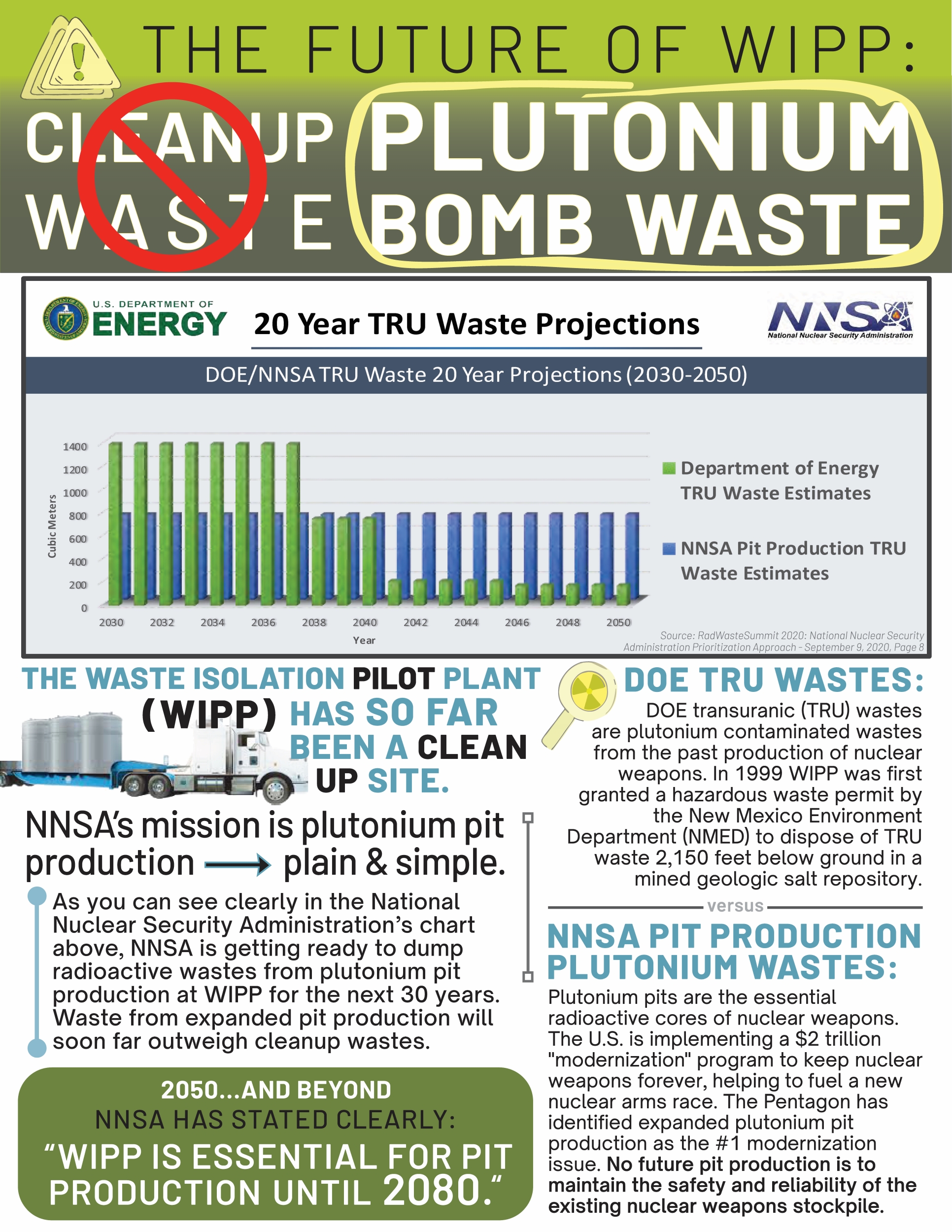
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
LANL Site-Wide EIS Hearings in Santa Fe and Los Alamos Filled with Loud Protest and Vehement Dissent: Nuclear Weapons are IMMORAL
In this Site-Wide EIS we’re given three options: Expanded nuclear weapons programs (hypocritically called the no action alternative), then we’re presented with yet more expanded nuclear weapons programs, and the third alternative is even more expanded nuclear weapons programs. What we really need is a genuine alternative in this Site-Wide, and I hope that citizens will repeatedly bring this up. We need a TRUE ALTERNATIVE in which the US begins to show global leadership towards nuclear disarmament that it promised to in the Non-Proliferation Treaty, and that should be reflected in the sitewide which shows just passive maintenance of the stockpile. We don’t need Pit Production because it’s for NEW designs – NOT to ensure the safety and reliability of the existing stockpile. The US, for our own national security and global security, we need to lead the world towards global nuclear disarmament – and this Site-Wide EIS does the opposite.
The hearings in Santa Fe and Los Alamos on February 11 and February 13, 2025, respectively, both had virtual participation options. The attendees online and in person were equally vehement in protesting the “rigged game” we’re given with this SWEIS and decrying the fact that there is no alternative besides increased nuclear weapons production.
And read an exceprt from the Archbishop of Santa Fe, John Wester’s comments:
“As we all know, we’re in an accelerating new nuclear arms race that’s made even more dangerous because of artificial intelligence, multiple nuclear actors and hypersonic delivery systems. It’s an already scary situation that has become even scarier, and what concerns me is that Los Alamos and Santa Fe play a key role in naturally fostering and promoting this new nuclear arms race – a race which I believe is an affront to all that is good and holy, all from our perspective that God has placed in us to live in harmony with one another. Nuclear weapons pose one of the greatest threats to that harmony. I think it’s important to know what I’m learning more and more about is that expanded plutonium pit production is not simply to maintain the safety and reliability of our existing so-called deterrence. I think it’s important that people are aware that it’s really for new design nuclear weapons for this new particular armed race. I think it’s important that that people recognize that deterrence is not the way to go. In that light, I would say obviously for me is a Catholic Bishop, Pope Francis I think has really changed the whole moral landscape of looking at nuclear weapons. On the 70th anniversary of the Hiroshima atomic bombing, Pope Francis declared that the very possession of nuclear weapons is immoral. As Catholics this was an extremely important shift there. The 1983 United states conference of Catholic Bishops did allow for deterrence – it was promoting disarmament but made caveats for deterrence. But Pope Francis has taken that off the table in saying that even possessing nuclear weapons is immoral, it’s unethical. One of the main reasons for this church’s shift on this was that the nuclear weapons powers really have failed in their pledge in 1970 when they joined the Non-Proliferation Treaty. The TPNW came about because of that failure, and so it seems to me then based on what Pope Francis said, that if possessing nuclear weapons is immoral, then expanding plutonium pit cores and modernizing our weapons systems in order to be more involved in the new nuclear arms race is also immoral. This policy is unethical. Now I want to be careful here, I am not saying that anyone working at Los Alamos or Sandia or Lawrence Livermore in California, I’m not judging them or saying there are immoral – that’s a different matter in one’s conscience. I’m saying that the policy is involved and the Pope said that nuclear weapons themselves are intrinsically immoral. I think that’s an important thing to keep in mind, that that we need to be moving toward disarmament and that if we’re not, if that’s not our trajectory, rather if it’s just to build up our defenses, then that’s an immoral buildup.”
Gearing Up for the Public Hearings on the LANL Draft Sitewide Environmental Impact Statement: Pit Production at LANL
“Nuclear Watch New Mexico hosted a workshop on February 6 on the newly released Draft Sitewide Environmental Impact Statement (SWEIS) for Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) to present information and elicit discussion on this NEPA process that Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuke Watch, referred to as a “rigged game” at the beginning of the workshop. What that means will become evident as I review the part of the workshop I attended.”
By Kay Matthews, La Jicarita | February 7, 2025 lajicarita.wordpress.com
Archbishop John Wester, an outspoken critic of nuclear weapons proliferation under the guise of nuclear deterrence instead of disarmament spoke briefly to open the discussion. Quoting Pope Francis, he said, “possessing nuclear weapons is immoral.” He then said, “Pit production is immoral.” His only qualification is that it’s the policy that’s immoral, not the people who promote it. We’ve failed to uphold already existing treaties and failed to implement new ones. He’ll be going to the United Nations in March for a meeting, Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, and to Japan in August to meet with his partners in the World Without Nuclear Weapons.
Coghlan explained that next week the Department of Energy (DOE) and the semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) will hold public hearings, as required by NEPA, on the LANL SWEIS, in Santa Fe, Española, and Los Alamos. He cautioned that while we should all be “cynical” about the process, we need to go ahead and protest the fact that all three alternatives provided in the SWEIS expand pit production, just at different amounts. The process is rigged because the DOE and NNSA failed to update a 2008 Environmental Impact Statement before pit production began at LANL (the other nuclear facility, the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, is slated to produce 50 pits a year but is completely unprepared for pit production).
The guest speaker was Dylan Spaulding, Senior Scientist for the Union of Concerned Scientists…
NukeWatch Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop – February 6, 2025
Full Video Recording: NukeWatch Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop |
NukeWatch Presentation: Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop |
|---|---|
|
NukeWatch Los Alamos Lab Site-Wide EIS Workshop |
 |
In Memoriam: Ken Mayers
 We here at NukeWatch will dearly miss Ken’s weekly presence at the corner vigil to protest Nuclear Weapons in Santa Fe.
We here at NukeWatch will dearly miss Ken’s weekly presence at the corner vigil to protest Nuclear Weapons in Santa Fe.
Locally, Ken was co-founder of the Santa Fe Chapter of Veterans for Peace and an active member of Santa Feans for Justice in Palestine. Ken worked with the local chapter of US Combatants for Peace and the Justice Council of the Unitarian Universalist Congregation in Santa Fe where he was also an enthusiastic baritone and co-founder of the NM Peace Choir.
A Celebration of Ken’s life will be held Friday, April 4 beginning at 12 noon at the corner of Sandoval and West Alameda, (Santa Fe’s weekly vigil to protest Nuclear Weapons), followed by lunch and a hybrid service at the UU Congregation, 107 West Barcelona Street, Santa Fe, NM.
For those wanting to pay tribute to Ken, please consider planting a tree through A Living Tribute (https://shop.alivingtribute.org/) or make a donation in his memory to the Santa Fe Joan Duffy Chapter of Veterans for Peace https://www.vfp-santafe.org/
Ken was a lifelong, passionate defender of peace. Read more:
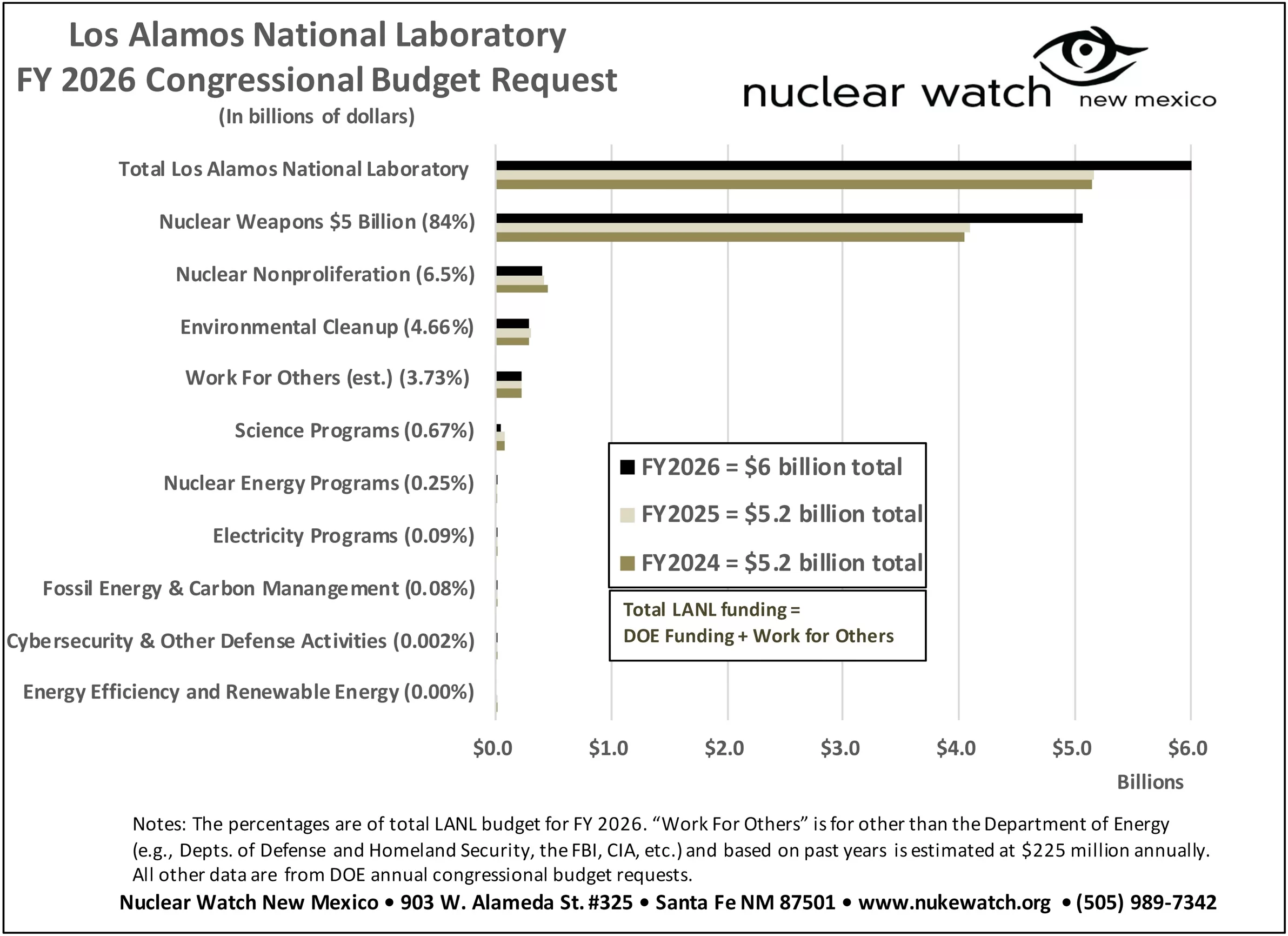
Los Alamos’ plutonium pit production of 30 annually for Sentinel may have to wait beyond 2026
As the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration awaits its marching orders from the President Donald Trump (R) administration, the Los Alamos National Laboratory is now saying it will get to an annual plutonium pit production goal of 30 “ASAP.”
Exchange Monitor | January 31, 2025 counterpunch.com
Such pits are the triggers for thermonuclear weapons…
Step inside the secret lab where America tests its nukes
“”The risk is significant,” says Hans Kristensen, director of the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists. The talk of testing comes at a time when nuclear weapons are resurgent: Russia is designing nuclear weapons to attack satellites and obliterate seaports; China is dramatically expanding its nuclear arsenal; and the U.S. is undergoing a major modernization of its nuclear warheads. After years of declining nuclear stockpiles, the world looks poised to begin increasing the number and types of nuclear weapons being deployed.”
By Geoff Brumfiel, NPR | January 29, 2025 npr.org

A half-mile from here, on the morning of May 8, 1953, an Air Force bomber dropped a Mk-6D nuclear bomb from a height of 19,000 feet above the desert floor. It exploded with a yield of 27 kilotons of TNT — creating a shockwave that warped the bridge. The test, code-named “Encore,” was one of several conducted here to see what, if anything, in the civilian world could survive a nuclear blast (the answer is, apparently, not much).
Continue reading
Exchange Monitor: Compromise reached on pit production suit environmental review
“The National Nuclear Security Administration and environmental plaintiffs settled a lawsuit that could put a pause on plutonium pit production efforts at Savannah River Site if approved.”
By Exchange Monitor | January 29, 2025 exchangemonitor.com
The agreement, made public Jan. 16, would leave Los Alamos National Laboratory as the National Nuclear Security Administration’s (NNSA) sole pit factory until an environmental impact statement is completed as part of the National Environmental Protection Act (NEPA). The process is expected to take at least two-and-a-half years, according to the document.
Until a record of decision is issued from the environmental review, NNSA is enjoined from installing classified equipment or introducing nuclear material at the Savannah River plant, according to a press release from the citizen groups. Actual pit production at Savannah River is not expected before the 2030s, according to NNSA.
The plaintiffs alleged in the lawsuit from 2021 that NNSA and DOE would violate NEPA by producing plutonium pits at Los Alamos and Savannah River Site without conducting a proper environmental review. A federal judge agreed with the plaintiffs in September, but instigated months of back and forth between both parties by forcing them to agree to a solution themselves.
The settlement requires NNSA to produce a new programmatic environmental impact statement within two-and-a-half years. Until that is complete in a process that would include public hearings nationwide and public comment on the draft of the statement, NNSA would not be able to process nuclear material at Savannah River’s plutonium facility.
The plaintiffs in the suit include environmental watch group Savannah River Site Watch of South Carolina; Tom Clements, director of Savannah River Site Watch; The Gullah Geechee Sea Island Coalition, a group representing the interests of some descendants of enslaved Africans dwelling on the lower Atlantic coast; Nuclear Watch New Mexico of Santa Fe, N.M.; and the Tri-Valley Communities Against a Radioactive Environment, of Livermore, Calif.
Hot Plutonium Pit Bomb Redux
“Plaintiffs including Savannah River Site Watch, South Carolina Environmental Law Project Gullah/Geechee Sea Island Coalition, Nuclear Watch New Mexico and Tri-Valley CAREs forced NNSA to halt construction on many phases of its plutonium pit facility near Aiken, SC, to hold public scoping meetings, solicit public comments, and produce a Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement within thirty months.”
By Mark Muhich, Counterpunch | January 31, 2025 counterpunch.com

Last week U.S. District Judge Mary Lewis Geiger, South Carolina, faulted the Department of Energy and the National Nuclear Security Agency for ignoring the National Environmental Protection Act and rushing plans to fabricate plutonium pit bombs at Savannah River Site, near Aiken, South Carolina.
Newly designed plutonium pits will serve as “triggers” for the next generation of nuclear warheads mounted atop Sentinel, the next generation of intercontinental ballistic missile, and for new submarine-launched nuclear weapons. Combined, these projects comprise major components in the trillion-dollar “modernization” of the U.S. strategic deterrence force.
Continue reading
Lawmakers say no to storing nuclear waste in Wyoming
Distrust over the federal government’s ability to build a permanent repository played a critical role in committee’s decision to kill controversial ‘temporary’ storage bill.
In addition to being flooded with emails and phone calls from constituents opposed to warehousing the deadly, radioactive material, several lawmakers on the panel were not convinced that a “temporary” storage facility would, in fact, be temporary. They noted that the federal government has tried and failed for decades to establish a permanent nuclear waste repository that would give some legitimacy to the “temporary” storage concept.
By Dustin Bleizeffer, WyoFile | January 30, 2025 wyofile.com
Despite growing support for nuclear energy nationally and here in Wyoming, there are simply too many concerns to entertain the possibility of opening the state to the country’s growing stockpile of spent nuclear fuel waste, some lawmakers say.
House Bill 16, “Used nuclear fuel storage-amendments,” touted by its backers as a tool to initiate a larger conversation, died Wednesday morning in the House Minerals, Business and Economic Development Committee.
In addition to being flooded with emails and phone calls from constituents opposed to warehousing the deadly, radioactive material, several lawmakers on the panel were not convinced that a “temporary” storage facility would, in fact, be temporary. They noted that the federal government has tried and failed for decades to establish a permanent nuclear waste repository that would give some legitimacy to the “temporary” storage concept.
Related:
Doomsday Clock: It is now 89 seconds to midnight
Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists | January 28, 2025 thebulletin.com
In 2024, humanity edged ever closer to catastrophe. Trends that have deeply concerned the Science and Security Board continued, and despite unmistakable signs of danger, national leaders and their societies have failed to do what is needed to change course. Consequently, we now move the Doomsday Clock from 90 seconds to 89 seconds to midnight—the closest it has ever been to catastrophe. Our fervent hope is that leaders will recognize the world’s existential predicament and take bold action to reduce the threats posed by nuclear weapons, climate change, and the potential misuse of biological science and a variety of emerging technologies.
In setting the Clock one second closer to midnight, we send a stark signal: Because the world is already perilously close to the precipice, a move of even a single second should be taken as an indication of extreme danger and an unmistakable warning that every second of delay in reversing course increases the probability of global disaster.
In regard to nuclear risk, the war in Ukraine, now in its third year, looms over the world; the conflict could become nuclear at any moment because of a rash decision or through accident or miscalculation. Conflict in the Middle East threatens to spiral out of control into a wider war without warning. The countries that possess nuclear weapons are increasing the size and role of their arsenals, investing hundreds of billions of dollars in weapons that can destroy civilization. The nuclear arms control process is collapsing, and high-level contacts among nuclear powers are totally inadequate given the danger at hand. Alarmingly, it is no longer unusual for countries without nuclear weapons to consider developing arsenals of their own—actions that would undermine longstanding nonproliferation efforts and increase the ways in which nuclear war could start.
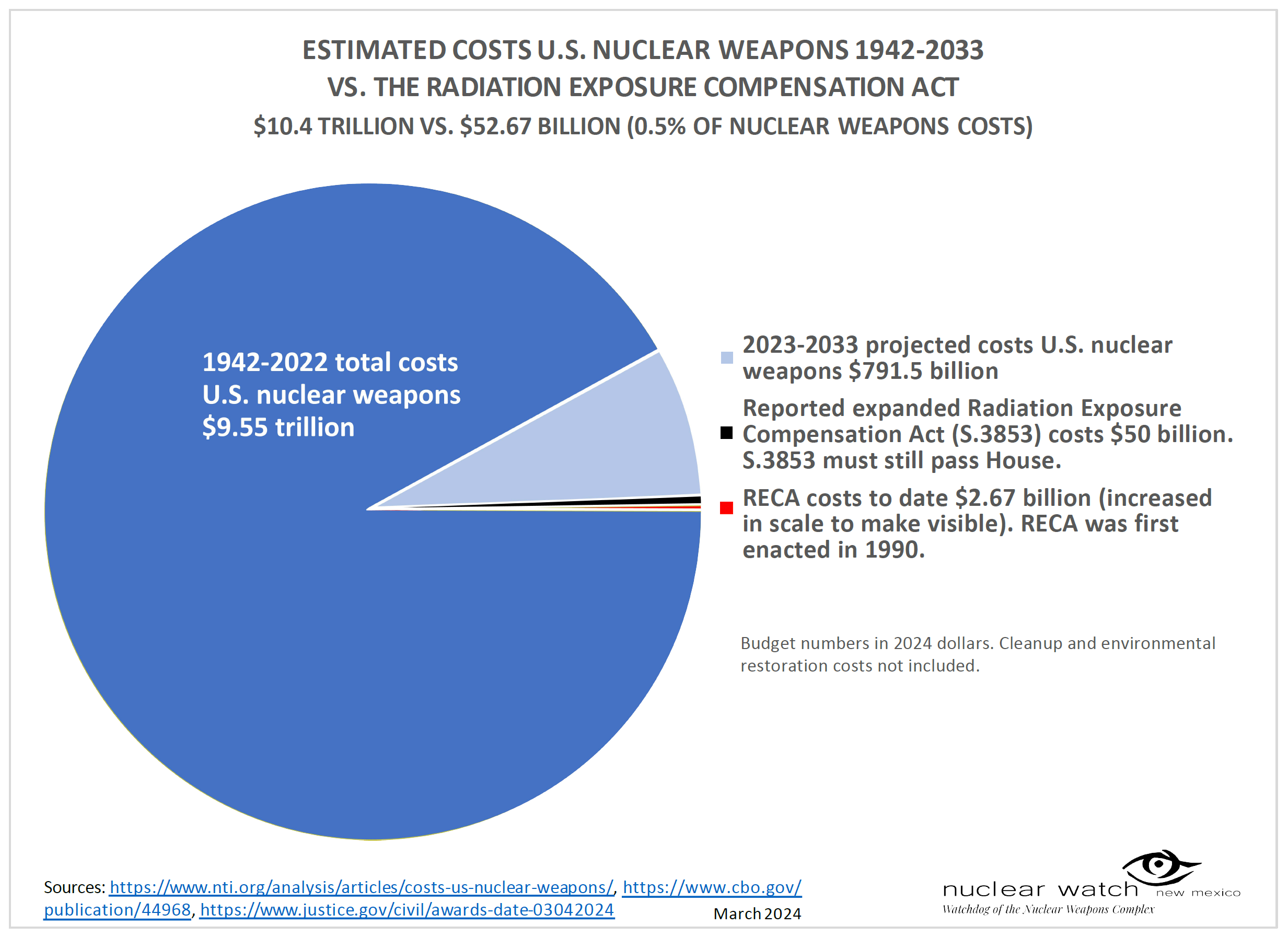
U.S. Senators Luján, Hawley, Heinrich, Schmitt, Reintroduce RECA To Give Nuclear Radiation Victims Compensation

By Carol A. Clark, Los Alamos Daily Post | January 24, 2025 ladailypost.com
Despite the Senate passing this bill, the House of Representatives failed to pass the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) reauthorization before its expiration deadline in the 118th Congress.
“In New Mexico and across the country, thousands sacrificed to contribute to our national security. Today, individuals affected by nuclear weapons testing, downwind radiation exposure, and uranium mining are still waiting to receive the justice they are owed,” Sen. Luján said.
“It is unacceptable that so many who have gotten sick from radiation exposure have been denied compensation by Congress. Despite having passed RECA legislation twice through the Senate with broad bipartisan support, and securing the support of the previous administration, I was disheartened that Speaker Johnson refused a vote on RECA to help victims. This Congress, I am proud to partner with Senator Hawley again to extend and expand RECA. RECA is a bipartisan priority and I am hopeful that we will once again get it through the Senate and hope the Speaker commits to getting victims the compensation they are owed.”
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
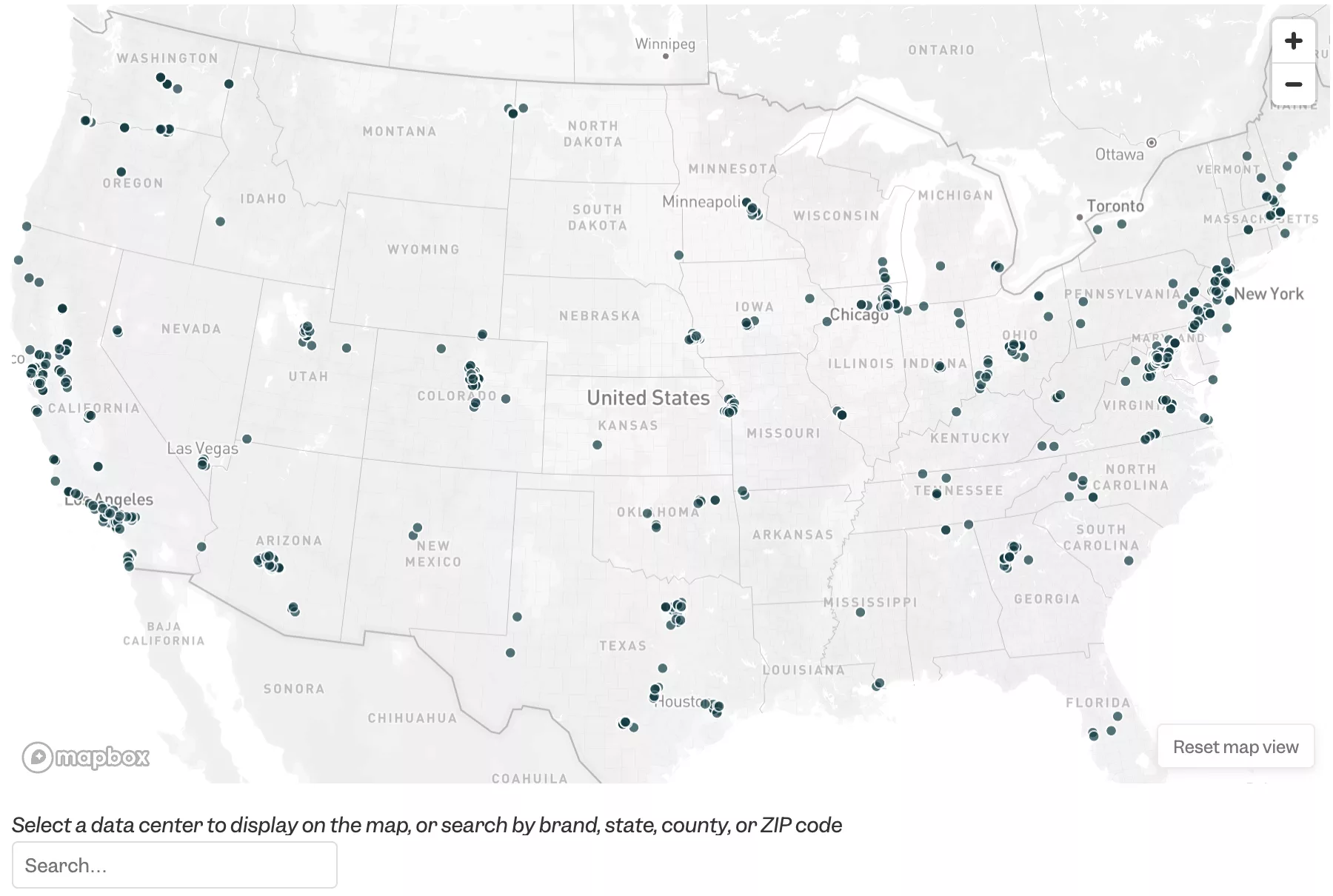
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
REMEMBERING HIROSHIMA: This Hiroshima survivor returned to the site of the atomic bombing 75 years later.
Hiroshima to a Healthy Tomorrow: Embracing Our Common Humanity in a Virtual Rally
|
|