QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
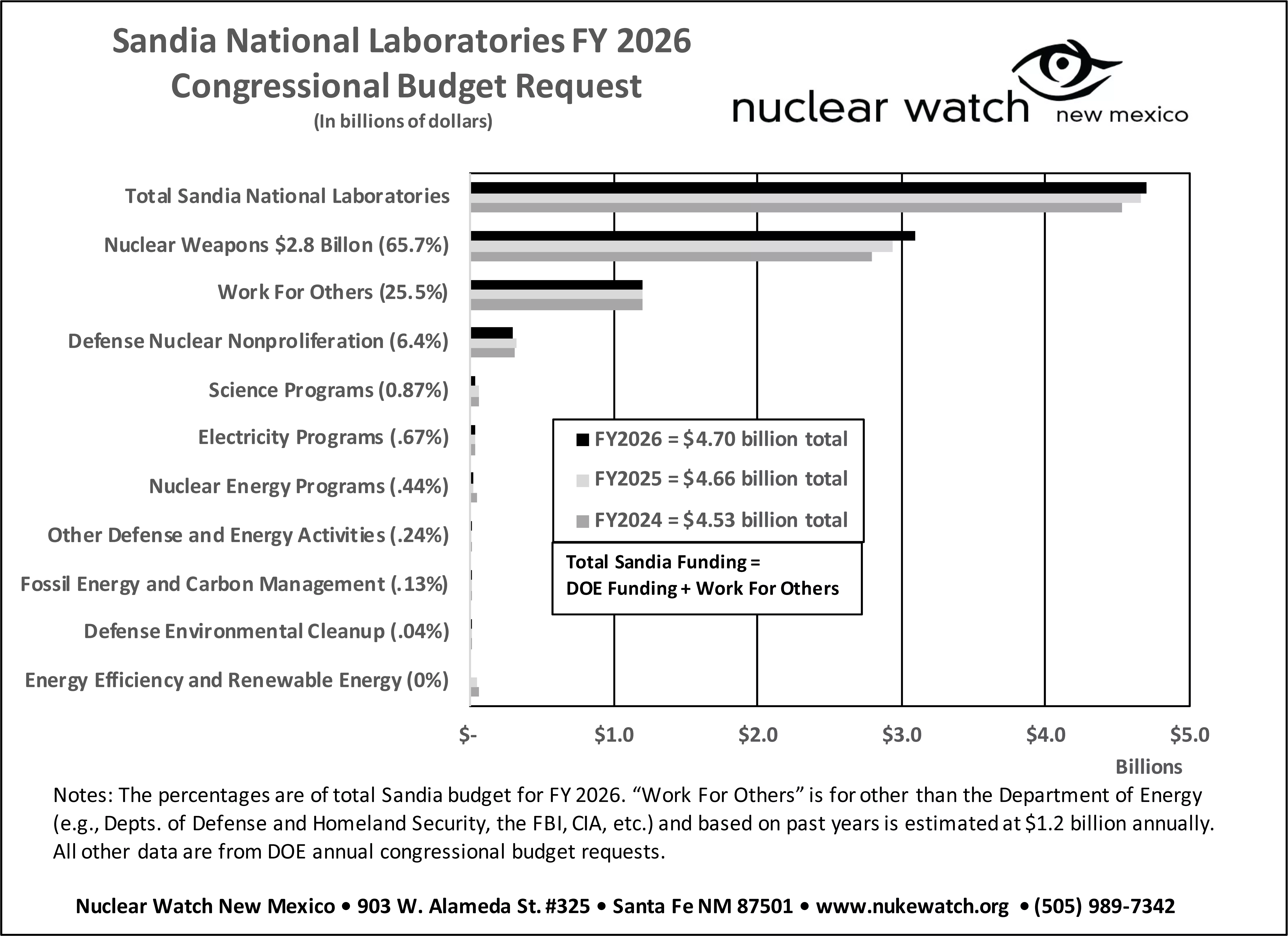
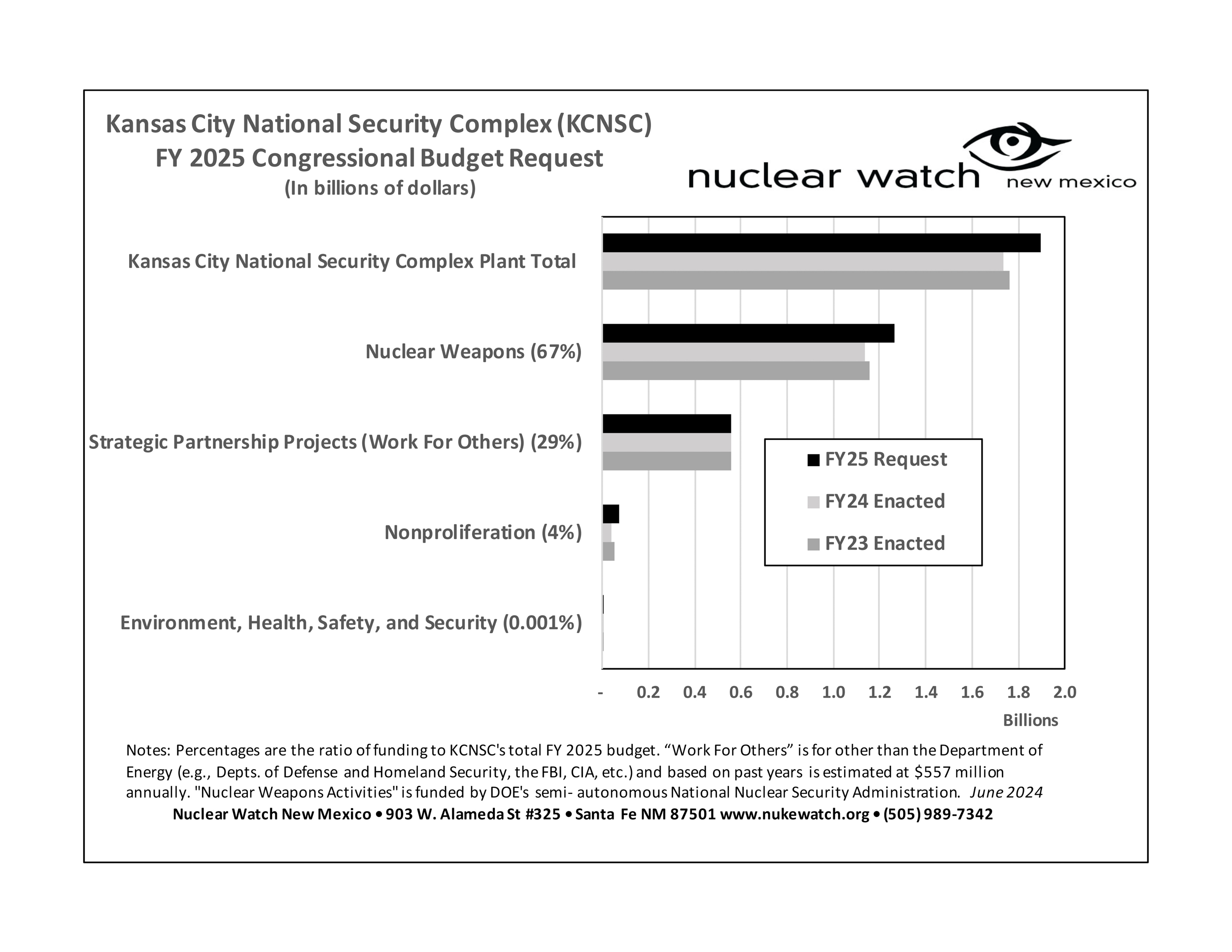
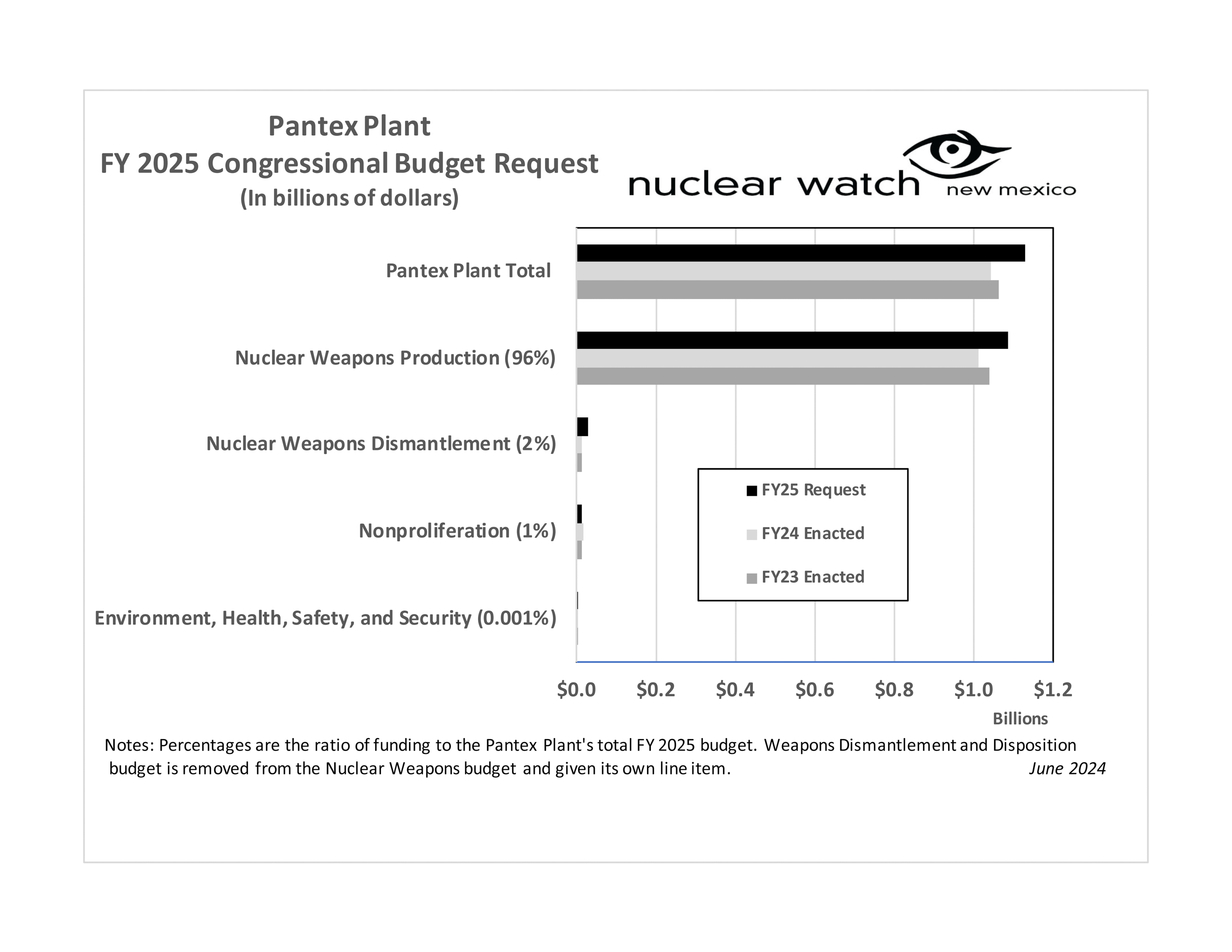
Follow the Money!
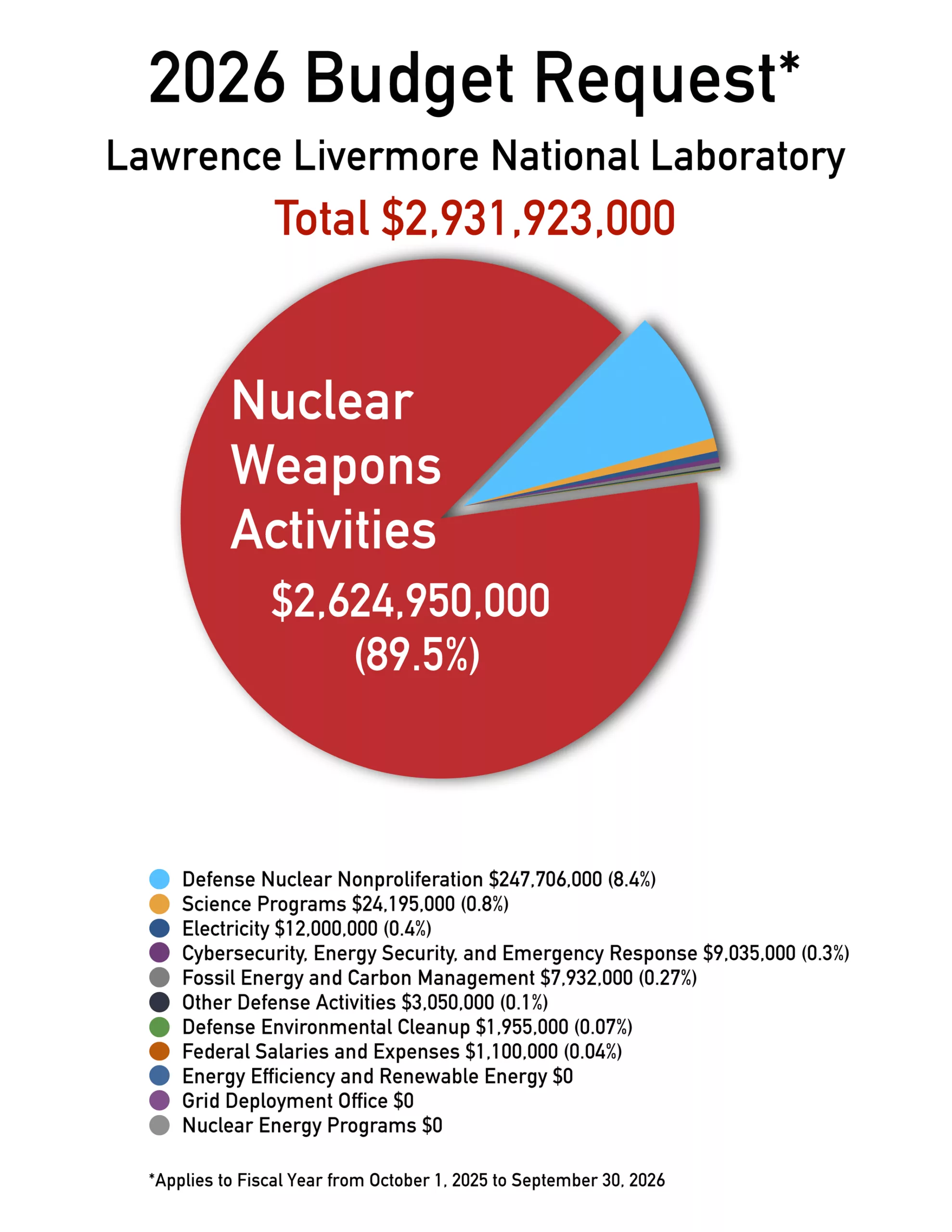
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
NEW INTERACTIVE PIECE from USA TODAY: THE NUCLEAR SPONGE — & Much More!
Screenshot from USA Today article January 5, 2026 usatoday.com/graphics/interactives/us-nuclear-weapons-expansion-fallout-map/
THE NUCLEAR SPONGE
Fallout maps show what could happen if America’s nuclear missile silos were attacked
By Davis Winkie, Ramon Padilla, Stephen Beard, Karina Zaiets and Carlie Procell, USA TODAY | usatoday.com
U.S. nuclear strategy revolves around the idea of the “triad.” Each of the military’s methods for delivering a nuclear strike represents a leg – the air leg (bomber planes), the sea leg (missile submarines) and the land leg (silo-based intercontinental ballistic missiles).
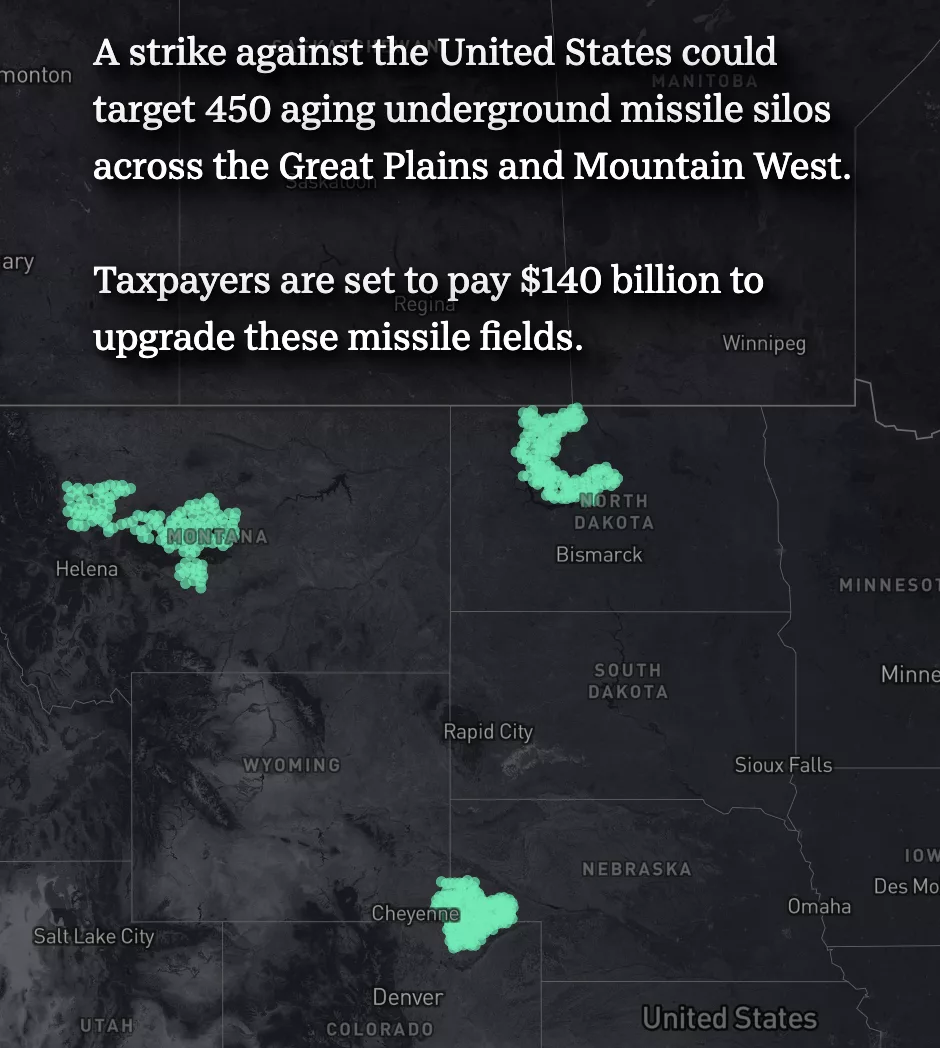
In recent years, arms control advocates have argued that the land leg of the triad is useless compared with its peers and makes the world a more dangerous place. The root of the debate is the vulnerability of the underground silos: An enemy can – and probably would – destroy them in a first strike against the United States.
Those opposed to land-based nuclear missiles, such as Daryl Kimball of the Arms Control Association, say that this vulnerability would push the president into a “use-or-lose logic” if he or she believed the United States were under nuclear attack. If the president launched a nuclear missile counterattack under a false warning, the results would be catastrophic.
The naysayers also highlight the cost of replacing the existing 1970s-vintage fleet of 400 Minuteman III missiles with the under-development Sentinel missiles, which the Air Force estimated will cost $140 billion (an increase from a 2020 estimate of $78 billion).
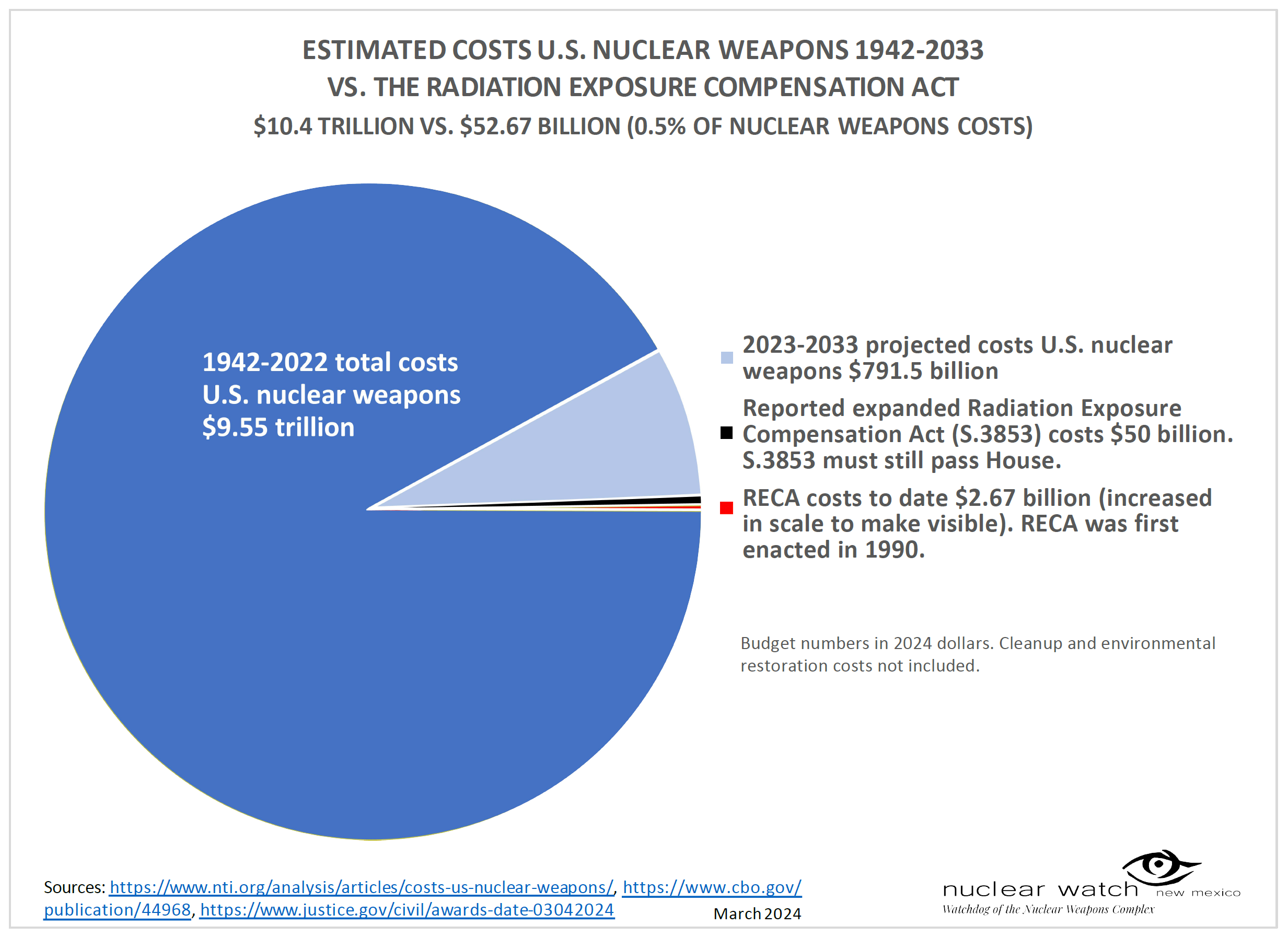
Warren, Garamendi Press Energy Secretary on Mismanagement and Taxpayer Waste in Plutonium Pit Production Program
Without transparency, accountability, and action around the pit program, the Department of Energy may be enabling the waste of billions of taxpayer dollars.
“In rushing to production, NNSA has developed an excessively risky program structure, with management concerns around fundamental aspects such as the cost and schedule.”
Sen. Elizabeth Warren and Rep. John Garamendi | warren.senate.gov – garamendi.house.gov
Washington, D.C. — In a new letter, U.S. Senator Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) and Representative John Garamendi (D-Calif.), both members of their respective Armed Services Committees and of the Nuclear Weapons and Arms Control Working Group, are urging Department of Energy Secretary Chris Wright to review the scope of and the need for the nuclear weapon plutonium pit production program, and pause the program’s Savannah River site until the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has established guardrails to prevent additional waste of taxpayer funds.
In August, the Department of Energy (DOE) launched a special study into NSSA’s leadership and management of the plutonium pit production mission. The lawmakers believe that, if properly conducted, the study will find that years of mismanagement have put billions of taxpayer dollars at risk with an unrealistic pit production schedule and goals.
“The Trump administration is blindly spending tens of billions of dollars to produce plutonium pits for nuclear weapons without a real budget or plan,” said Senator Warren. “This program is already years behind schedule and over budget, and Congressman Garamendi and I are urging the Secretary of Energy to conduct a vigorous review to rein in years of waste and mismanagement.”
“For years I have called for Congress to take action to fix the failing plutonium modernization effort. Congress has continued to pour billions of dollars into efforts to restart production with arbitrary targets,” said Congressman Garamendi. “This letter cuts to the core of the matter and asks necessary questions of NNSA, including about the questionable management and faulty assumptions underlying the program. I eagerly await their response, along with the results of the Department of Energy’s 120-day special investigation.”
The lawmakers raise concerns about how, years into this program, it is still unclear what the pit production program’s schedule and full cost will be. The Government Accountability Office recommended NNSA create a master schedule to comply with its best practices, but the agency has yet to produce one…
Livermore Lab Uses Trump Executive Order Gutting Environmental Laws to Push Through Enhanced Plutonium Utilization without Public Input
A November notice from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) erases the previously announced public involvement requirement and thereby fast-tracks increased plutonium use at its Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory after decades of limits protected the public from potential risks.
News from our friends at Tri-Valley CAREs | trivalleycares.org
 First announced In January 2025, the NNSA proposal for “Enhanced Plutonium Facility Utilization” at the Livermore Lab was to include a “Draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement” (SEIS) according to its Federal Register Notice. It specifically stated that, “NNSA will prepare a Draft SEIS. NNSA will announce the availability of the Draft SEIS in the Federal Register and local media outlets. NNSA will hold one or more public hearings for the Draft SEIS. Any comments received on the Draft SEIS will be considered and addressed in the Final SEIS.”
First announced In January 2025, the NNSA proposal for “Enhanced Plutonium Facility Utilization” at the Livermore Lab was to include a “Draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement” (SEIS) according to its Federal Register Notice. It specifically stated that, “NNSA will prepare a Draft SEIS. NNSA will announce the availability of the Draft SEIS in the Federal Register and local media outlets. NNSA will hold one or more public hearings for the Draft SEIS. Any comments received on the Draft SEIS will be considered and addressed in the Final SEIS.”
Now the agency has reneged on this promise, instead fast-tracking directly to a Final SEIS and a Record of Decision without any further opportunity for public input!
DOE using its own land to help pair AI centers, nuclear reactors
The Energy Department wants to build nuclear-powered artificial intelligence data centers on federal land using new public-private partnerships.
By Kelly Livingston and Allison Mollenkamp | rollcall.com
Co-locating advanced nuclear reactors with data centers on DOE sites is part of the Trump administration’s bid to accelerate the development of both technologies, sources say, as research efforts tease out their “symbiotic relationship.” But questions remain about how these projects could affect local communities and the actual timeline for bringing more nuclear power online.
DOE first announced its intention to use federal land for data center development and co-location in early April with a request for information to gauge industry interest. According to the RFI, the department intends to begin construction at the selected DOE sites by the end of the year, with operations beginning by the end of 2027.
Lawmakers introduce bill to cancel $100 million University of Michigan data center grant
The University of Michigan has failed to act transparently or coordinate with local officials on data center project, says state Rep. Jimmie Wilson Jr.
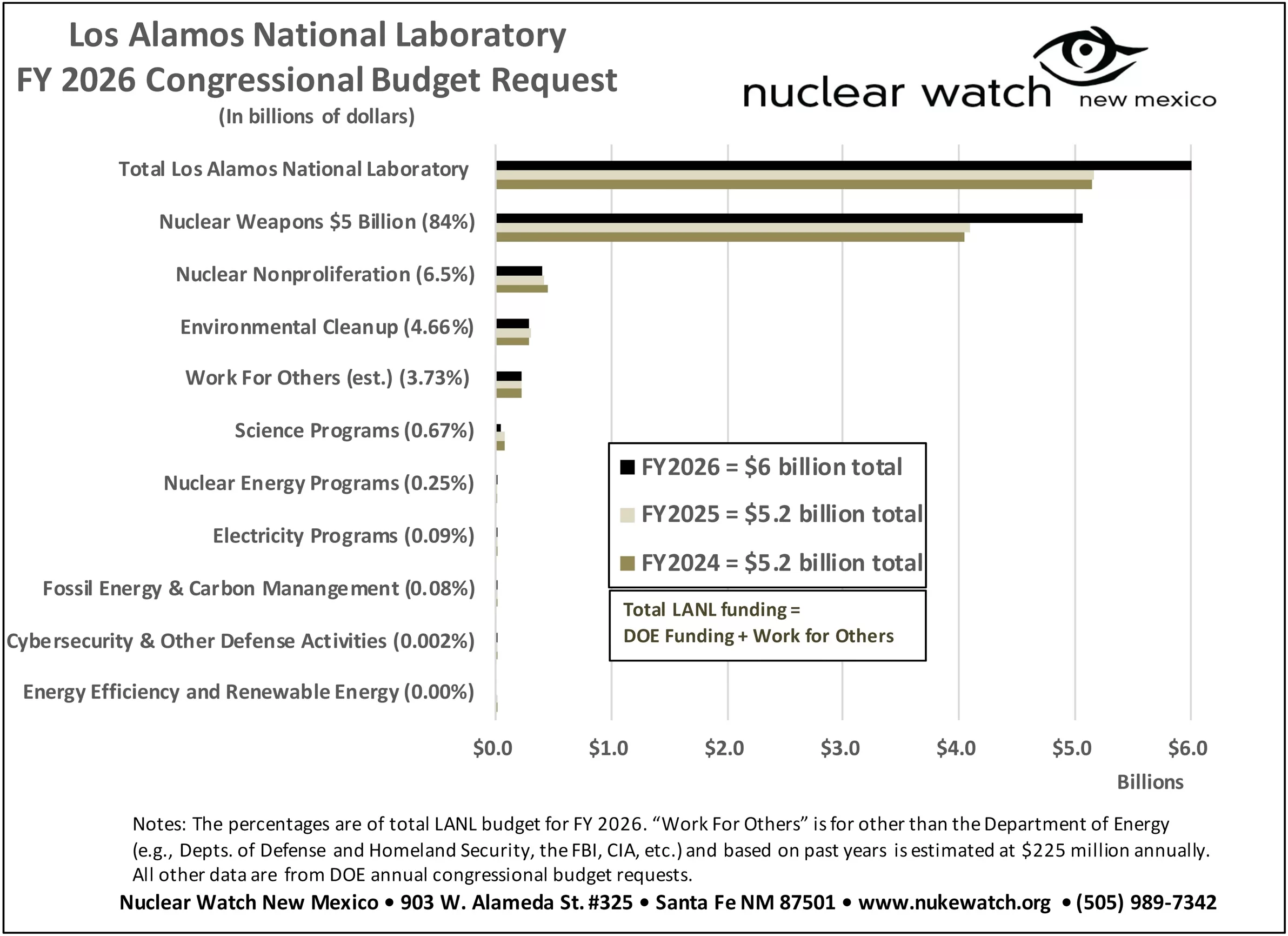
“Eighty-four percent of the lab’s 2026 budget request is for nuclear weapons work, according to the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.”
By Brian Allnutt | planetdetroit.org
Michigan State Rep. Jimmie Wilson Jr. (D-Ypsilanti) introduced legislation Thursday to rescind a $100 million state grant for the University of Michigan and Los Alamos National Laboratory’s data center project in Ypsilanti Township.
The university has been unwilling to offer community benefits or consider another site for the data centers, Wilson said.
“The University of Michigan has not been fully transparent with this project and has refused to collaborate with the Ypsilanti Township officials throughout this planning process,” Wilson said in a statement to Planet Detroit.
Ypsilanti Township officials say the university misled state officials about the size of the project when applying for the $100 million grant, and passed a resolution earlier this month seeking to unwind the funding.
…
Petition highlights Los Alamos’ nuclear weapons work
A petition signed by over 700 University of Michigan employees, faculty, and students urges the school to cancel the $1.2 billion project and halt its partnership with Los Alamos, arguing the project will harm the environment, negatively impact low-income communities, and help advance harmful nuclear weapon and artificial intelligence technologies.
Catholic bishops remind political leaders that nuclear weapons are immoral
On August 5, the two American Cardinals present in Japan delivered stirring words from the Hiroshima World Peace Memorial Cathedral, whose bricks contain ashes from the atomic bomb…
“If our gathering here today is to mean anything, it must mean that in fidelity to all those whose lives were destroyed or savagely damaged on August 6, 80 years ago, we refuse to live in such a world of nuclear proliferation and risk-taking,” said Cardinal Robert McElroy of Washington. “We will resist, we will organize, we will pray, we will not cease, until the world’s nuclear arsenals have been destroyed.”
By John Wester | thebulletin.org
In August, a group of American Catholic Church leaders—including Cardinal Blase Cupich of Chicago, Cardinal Robert McElroy of Washington, DC, Archbishop Paul Etienne of Seattle, and me, the Archbishop of Santa Fe—traveled to Japan to mark the 80th anniversary of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. There, we joined our Japanese counterparts—Bishop Mitsuru Shirahama of Hiroshima, Archbishop Emeritus Mitsuaki Takami of Nagasaki, and Archbishop Michiaki Nakamura of Nagasaki—in commemorating the destruction of their cities. Takami is a hibakusha (atomic bomb survivor); he was in his mother’s womb on August 9, 1945, when his city of Nagasaki was bombed. His maternal aunt and grandmother were both killed in the blast.
Eighty years have passed. But the existential threat posed by nuclear weapons is still with us—and it is growing worse every day. In 2019, Pope Francis elevated the Catholic Church beyond conditional acceptance of so-called deterrence. He declared that the mere possession of nuclear weapons is immoral. Nevertheless, the nuclear powers are now spending enormous sums of money on “modernization” that will keep nuclear weapons virtually forever. Meanwhile, in the United States, taxes are being cut to benefit the rich, and economic inequality and homelessness are exploding. This situation is deeply immoral and counter to the Catholic Church’s teachings on social justice.
SEE MORE ON SANTA FE ARCHBISHOP JOHN WESTER’S MONUMENTAL WORK ON NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT HERE:
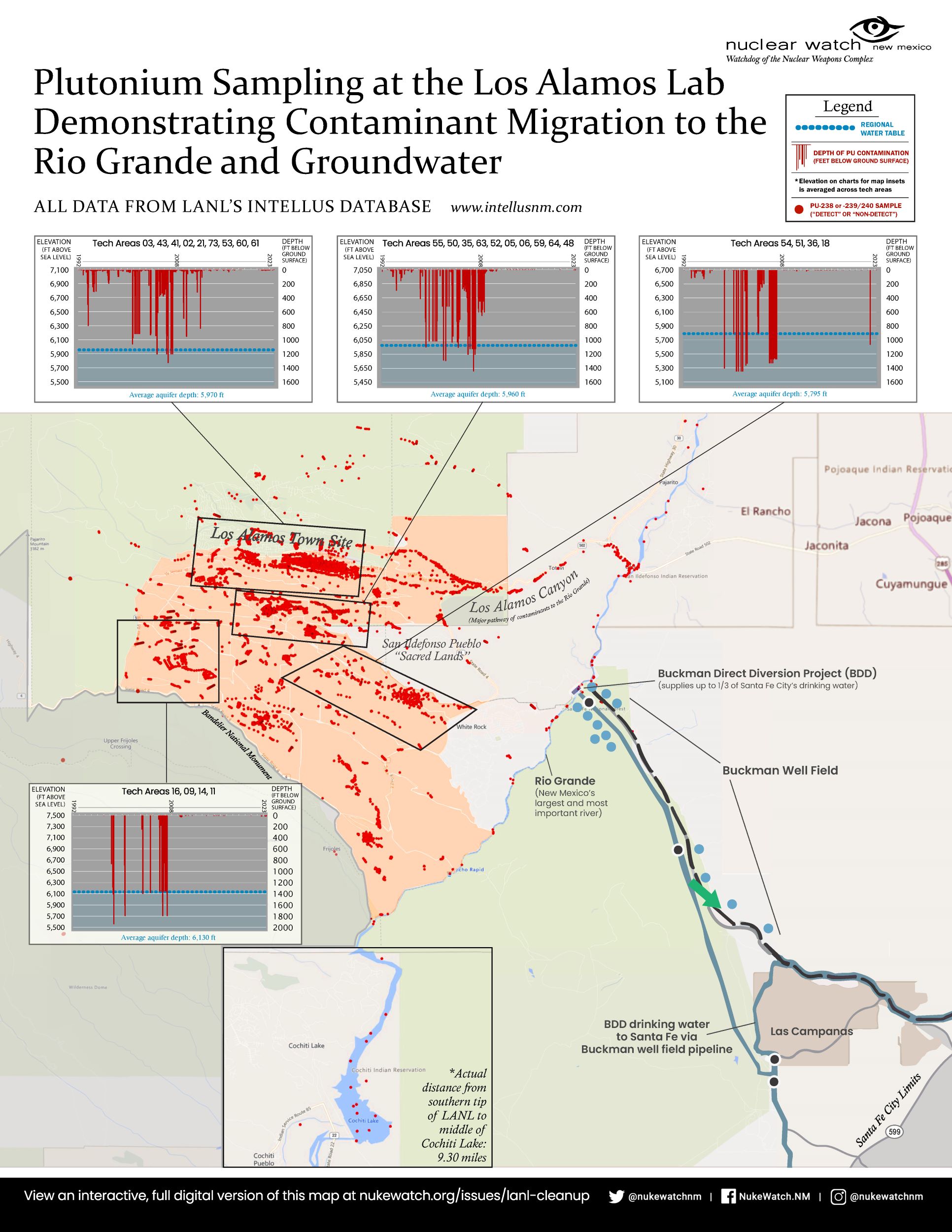
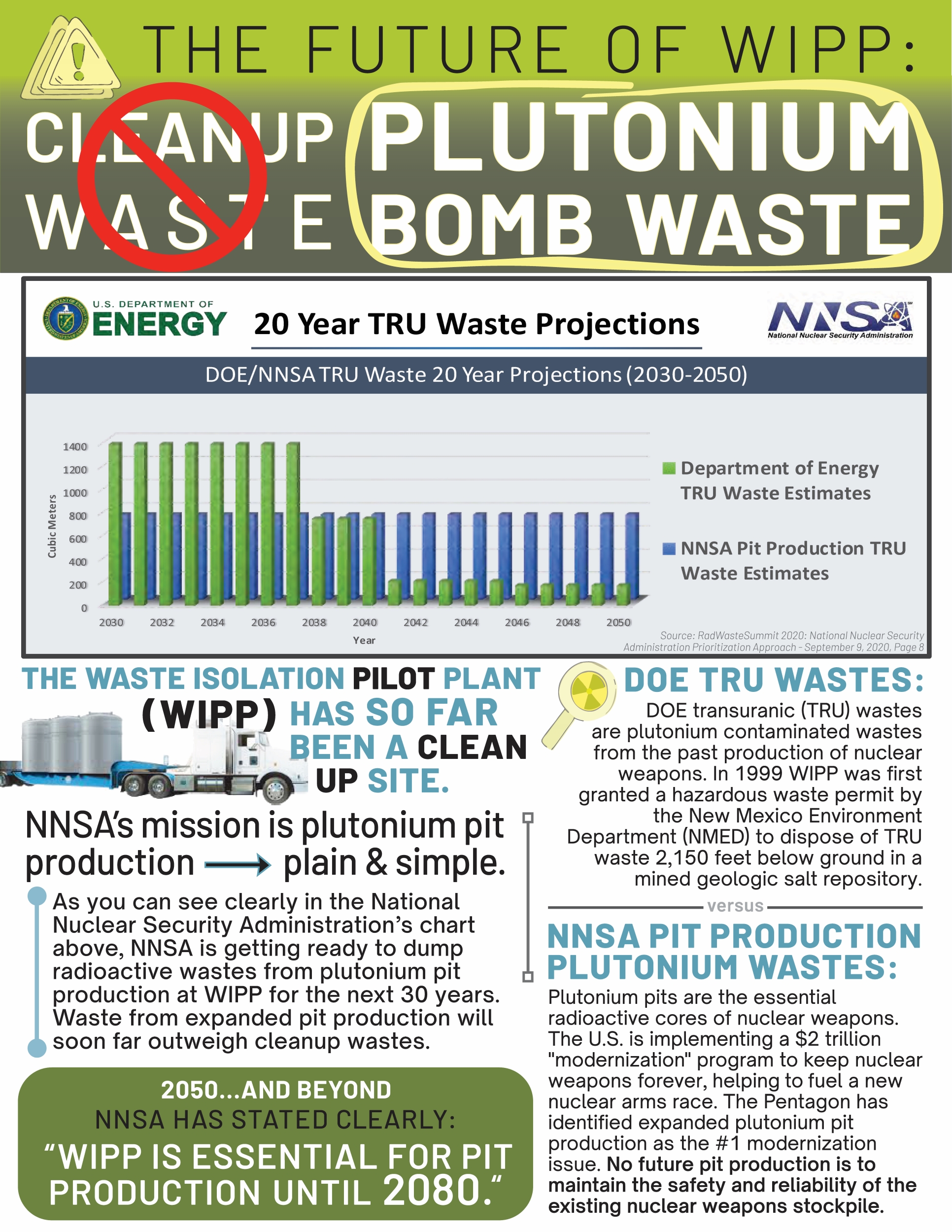
The Future of Los Alamos Lab: More Nuclear Weapons or Cleanup?
The Department of Energy “Defers” Comprehensive Cleanup Until Plutonium Pit Production Is Done
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, December 11, 2025
Contact: Jay Coghlan, 505.989.7342, c. 505.470.3154 | Email
Contact: Scott Kovac, 505.316.4148 | Email
Santa Fe, NM – Nuclear Watch New Mexico has released its new fact sheet The Future of Los Alamos Lab: More Nuclear Weapons or Cleanup? It documents the following:
In September 2023 the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) issued a groundbreaking draft Order to excavate and comprehensively clean up an estimated 198,000 cubic meters of radioactive and toxic wastes at the Los Alamos National Laboratory’s (LANL’s) “Area C” waste dump. The Lab and the Department of Energy (DOE) are adamantly against comprehensive cleanup. In this particular case, their unyielding opposition is amplified by fear of how Area C cleanup could impact LANL’s primary mission of plutonium “pit” bomb core production for new-design nuclear weapons. Instead, they want to “cap and cover” the wastes, leaving them permanently buried in unlined pit and trenches as a perpetual threat to groundwater.
Area C last received radioactive and toxic wastes in 1974. But in a legal maneuver to evade real cleanup, in June 2025 DOE unilaterally declared that the old waste dump:
“is associated with active Facility operations and will be Deferred from further corrective action under [NMED’s] Consent Order until it is no longer associated with active Facility operations.”
Area C is within a few hundred yards of LANL’s plutonium pit production facility. DOE’s unilateral deferral of Area C until it “is no longer associated with active Facility operations” in effect means that it will never be cleaned up. DOE plans to produce new plutonium pit bomb cores for new design nuclear weapons until at least 2050.
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: December 2025
Nuclear weapons:
The government is running on a Continuing Resolution (CR) until the end of January. It’s possible to have another shutdown depending on how tough the Dems want to be. The legislative process is starting to move again, with the annual Defense Authorization Act up first and then appropriations. Both give funding increases to nuclear weapons programs, delivery systems and Trump’s “Golden Dome.”
Cost overruns in nearly all things remains the rule. Golden Dome could cost up to $4 trillion, be destabilizing and never be 100% effective. Putin has already taken steps to circumvent it and China may well be doing the same, particularly with hypersonic delivery systems. The arms race continues, likely to be accelerated by artificial intelligence as well.
Nuclear weapons testing: No specific new developments but this article by ex-LANL Director Sig Hecker is good:
| Lessons From Los Alamos |
| Last month, U.S. President Donald Trump rekindled a decades-old debate about nuclear testing. “Because of other countries testing programs,” he wrote on social media, “I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis…” A return to testing at this time would likely benefit U.S. adversaries more than it would the United States. Worse still, it might rekindle an even greater and broader arms race than in the first few decades of the Cold War. |
| Siegfried Hecker | Foreign Affairs |
| Read More |
Article continued:
“My greatest concern about resuming full-scale nuclear testing is that it will fuel another dangerous arms race at a time when global tensions among the great powers are high. Engaging in another arms race is contrary to Trump’s comment that “it would be great if we could all denuclearize, because the power of nuclear weapons is crazy.”
Instead of suggesting an immediate return to nuclear testing, then, Trump should focus on returning to arms control measures to ensure strategic stability with Russia and with China. Hopefully, these measures would lead to a reduction in U.S. and Russian nuclear forces and reduce incentives for China to increase its arsenal. For nuclear testing, he should help erect the highest possible barriers for any country to test by leading an effort to ratify the CTBT. To settle the question of evasion of low-yield tests or hydronuclear experiments, the president and his counterparts in Beijing and Moscow would need to show the political will to agree on a verifiable low-yield limit. That will almost surely require onsite inspections, which were demonstrated to be possible in 1988.
The bottom line is that even though the United States could derive important benefits from resumed nuclear testing, it would lose more than it stands to gain.”
MESSAGE OF HIS HOLINESS POPE LEO XIV FOR THE LIX WORLD DAY OF PEACE
“The idea of the deterrent power of military might, especially nuclear deterrence, is based on the irrationality of relations between nations, built not on law, justice and trust, but on fear and domination by force.”
From the Vatican, 8 December 2025, vatican.va
“In the relations between citizens and rulers, it could even be considered a fault not to be sufficiently prepared for war, not to react to attacks, and not to return violence for violence. Far beyond the principle of legitimate defense, such confrontational logic now dominates global politics, deepening instability and unpredictability day by day. It is no coincidence that repeated calls to increase military spending, and the choices that follow, are presented by many government leaders as a justified response to external threats. The idea of the deterrent power of military might, especially nuclear deterrence, is based on the irrationality of relations between nations, built not on law, justice and trust, but on fear and domination by force. “Consequently,” as Saint John XXIII had already written in his day, “people are living in the grip of constant fear. They are afraid that at any moment the impending storm may break upon them with horrific violence. And they have good reasons for their fear, for there is certainly no lack of such weapons. While it is difficult to believe that anyone would dare to assume responsibility for initiating the appalling slaughter and destruction that war would bring in its wake, there is no denying that the conflagration could be started by some chance and unforeseen circumstance.”
Federal official says further testing needed to determine LANL’s chromium plume migration
“Asked about the difference in opinion between the federal and state agency regarding the sampling, Kunkle said, ‘I can’t answer why we have the disconnect,’ adding that the only sampling done at that monitoring location, called zonal sampling, ‘is really not intended to predict the long term environment or trends in the regional aquifer. That really should be done only with monthly monitoring.’”
By Clara Bates cbates@sfnewmexican.com | santafenewmexican.com
A federal official says more testing is needed to determine whether a toxic chromium plume has seeped into San Ildefonso Pueblo’s groundwater, after the state called groundwater testing “conclusive evidence” the U.S. Department of Energy’s efforts at containment have been “inadequate.”
New Mexico’s Environment Department announced last month hexavalent chromium from Los Alamos National Laboratory had migrated to Pueblo de San Ildefonso land for the first time.
But Jessica Kunkle — the Los Alamos Field Office manager with the U.S. Department of Energy — told state lawmakers on the Radioactive and Hazardous Materials Committee on Monday afternoon the type of groundwater sampling conducted may not have told the whole story. The agency is working with partners to get a monitoring well installed “as quickly as possible,” she said, to get better data.
12/8/25 Los Alamos Legacy Cleanup & Hexavalent Chromium Plume Update
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
“Turning Point: The Bomb and the Cold War” Explores Impact of US–Soviet Conflict
The nine-part doc examines how two global superpowers have irrevocably altered the course of history.
By Roxanne Fequiere, Netflix | netflix.com
While the the Cold War ended in 1991, even a casual appraisal of current headlines reveals that relations between the United States and Russia — the one-time center of the Soviet Union — remain tense, to say the least. The global repercussions of the Cold War continue to ripple through the current geopolitical landscape to this day, but it can be difficult to understand just how a mid-20th century struggle for ideological dominance continues to ensnare countless nations in ongoing unrest.
In Search of Resolution: Documentary on Nuclear Dangers
“In Search of Resolution,” examines the current state of international nuclear arms control and is the third film of The Nuclear World Project.
Filmed in 2022 after the Russian invasion of Ukraine, this timely documentary examines the continuing dangers posed by the existence of nuclear weapons.