2023 News Articles – All Posts
U.S. sees a new era of nuclear risk dawning in China-Russia cooperation – Japan Times
“To avert miscalculations, nuclear-weapons states must engage on existing and potential threats, from Iran’s atomic ambitions to the use of artificial intelligence for decision-making during crises,” — Pranay Vaddi, the National Security Council’s senior director for arms control.
JAPAN TIMES | May 6, 2023 japantimes.co.jp
An undated image released in July 2021 shows what researchers say are missile silos under construction in the Chinese desert. | 2021 PLANET LABS INC. / VIA AFP-JIJI
The deepening cooperation between China and Russia threatens to overturn decades of international stability in nuclear arms control, according to a top adviser to U.S. President Joe Biden.
“We’re entering a different period,” Vaddi said after talks at the International Atomic Energy Agency. “It requires a little bit of experimentation.”
Assessments that China is expanding its nuclear arsenal, along with Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and its disavowal of arms-control agreements, are adding to concern about an era fraught with new dangers. Unlike the Cold War, when the U.S. and Soviet Union maintained atomic parity and agreed to limit certain types of arms, more nations are developing the technologies and materials needed for weapons of mass destruction.
Never Give Artificial Intelligence the Nuclear Codes – The Atlantic
“AI offers an illusion of cool exactitude, especially in comparison to error-prone, potentially unstable humans. But today’s most advanced AIs are black boxes; we don’t entirely understand how they work. In complex, high-stakes adversarial situations, AI’s notions about what constitutes winning may be impenetrable, if not altogether alien. At the deepest, most important level, an AI may not understand what Ronald Reagan and Mikhail Gorbachev meant when they said, ‘A nuclear war cannot be won.’”
By Ross Andersen – THE ATLANTIC | May 4, 2023 rsn.org
The temptation to automate command and control will be great. The danger is greater.
No technology since the atomic bomb has inspired the apocalyptic imagination like artificial intelligence. Ever since ChatGPT began exhibiting glints of logical reasoning in November, the internet has been awash in doomsday scenarios. Many are self-consciously fanciful—they’re meant to jar us into envisioning how badly things could go wrong if an emerging intelligence comes to understand the world, and its own goals, even a little differently from how its human creators do. One scenario, however, requires less imagination, because the first steps toward it are arguably already being taken—the gradual integration of AI into the most destructive technologies we possess today.
Nuclear Waste Storage in New Mexico Angers State, Cheers Locals – Bloomberg News
America’s Nuclear Waste Capital Wants More of It, Against State Wishes
Burying the country’s nuclear weapons waste brought an economic lifeline to Carlsbad, New Mexico. State leaders worry it’s become a dumping ground.
By Daniel Moore – BLOOMBERG NEWS | May 2, 2023 bloomberg.com
Photographer: Daniel Moore/Bloomberg
A half-mile underground beneath a windswept field in the southeast corner of New Mexico, hundreds of workers haul drums of radioactive waste into a salt mine that will entomb them for at least 10,000 years.
Up on the surface, federal officials overseeing the Energy Department’s Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) are working harder than ever to smooth over tensions with state officials and skeptics in the state capital so the facility can meet its mission: cleaning up the country’s nuclear weapons production sites.
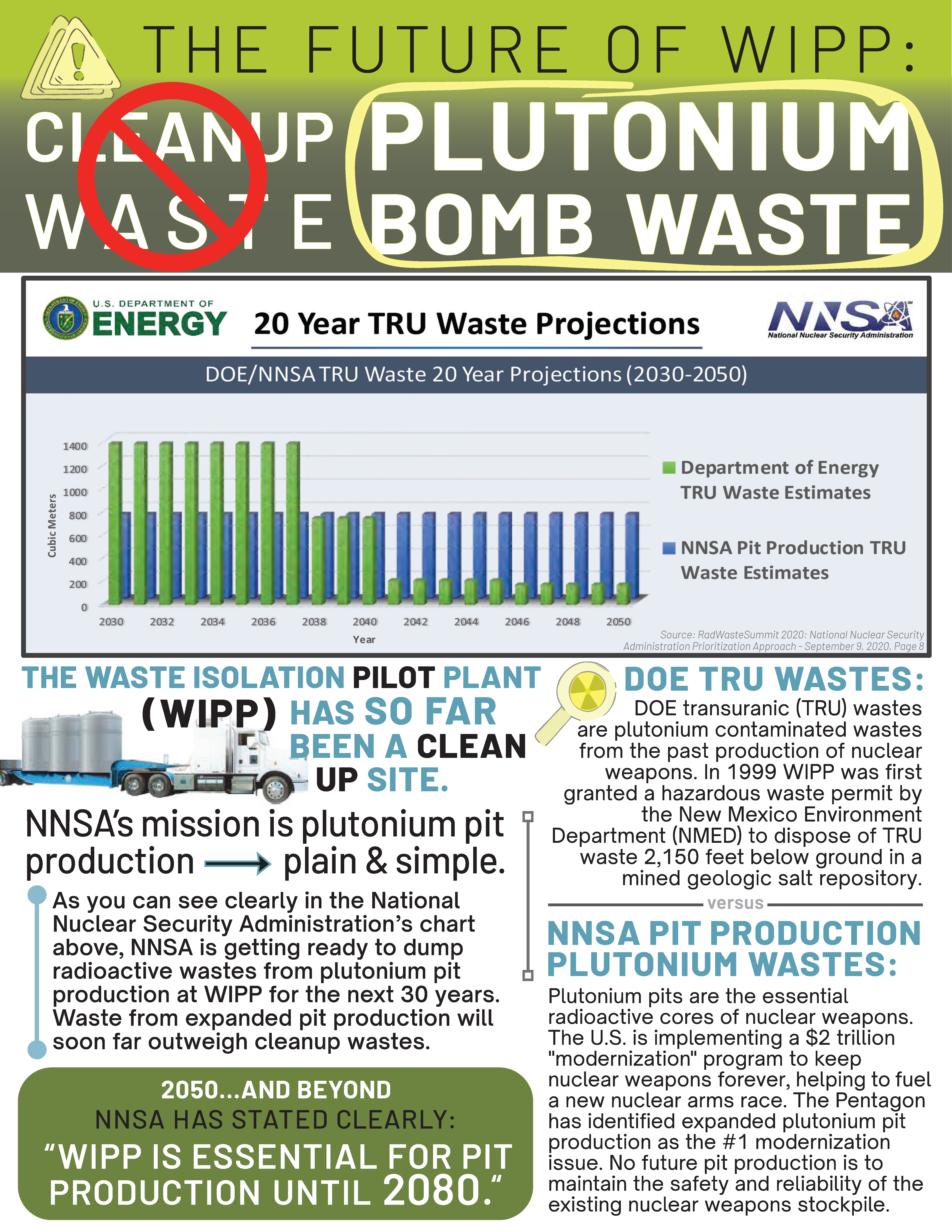
Dealing with a debacle: A better plan for US plutonium pit production
“There is…another concern about the NNSA’s plans: The designs of new warheads in which new plutonium pits would be used may depart from designs that have been previously tested. This could result in demands to resume explosive testing, which would undermine the moratorium on nuclear testing that has been observed by all nuclear-weapon states (other than North Korea) since 1998.”
By Curtis T. Asplund, Frank von Hippel, Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists | April 27, 2023 thebulletin.org
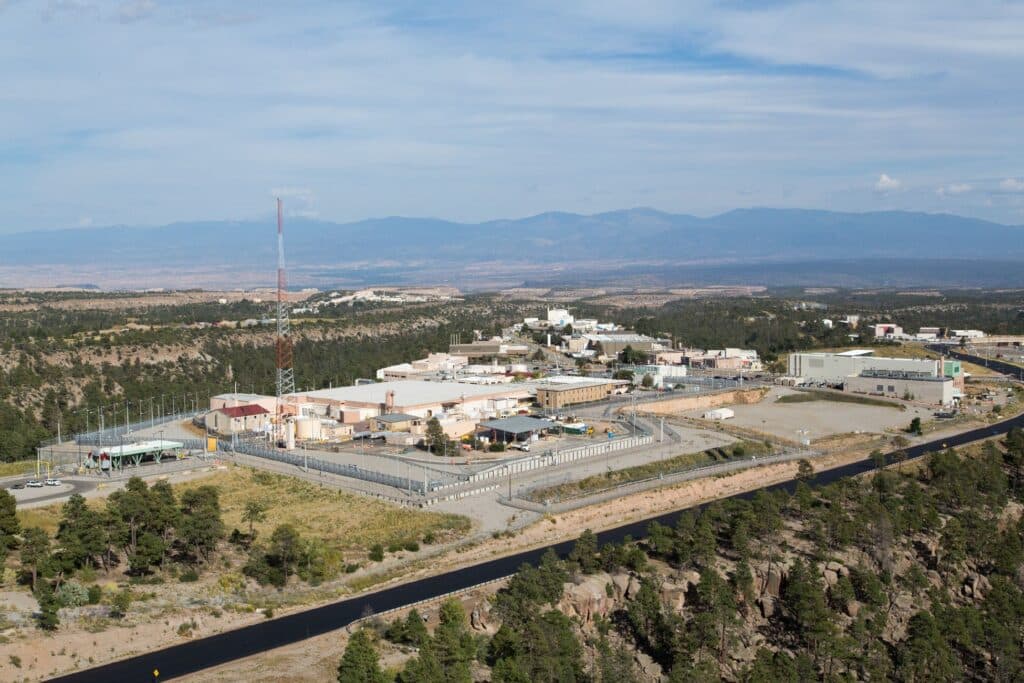

For two decades, the Pentagon and Congress have been increasingly concerned that the United States does not have a reliable capability to produce plutonium “pits,” the cores of US thermonuclear warheads. In 2018, the agency responsible for the production and maintenance of US nuclear warheads, the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), responded with a plan to build, on a crash basis, pit production lines in New Mexico and South Carolina at the same time, with a combined production capacity of 80 pits per year.
Video Indicates that Lida Air Base Might Get Russian “Nuclear Sharing” Mission in Belarus
On 14 April 2023, the Belarusian Ministry of Defence released a short video of a Su-25 pilot explaining his new role in delivering “special [nuclear] munitions” following his training in Russia. The features seen in the video, as well as several other open-source clues, suggest that Lida Air Base––located only 40 kilometers from the Lithuanian border and the only Belarusian Air Force wing equipped with Su-25 aircraft––is the most likely candidate for Belarus’ new “nuclear sharing” mission announced by Russian President Vladimir Putin.
By Matt Korda, Eliana Reynolds and Hans Kristensen – FEDERATION OF AMERICAN SCIENTISTS | April 19, 2023 fas.org
 The Belarusian MoD’s military channel features a Belarusian pilot standing in front of a Su-25 aircraft at an unidentified air base.
The Belarusian MoD’s military channel features a Belarusian pilot standing in front of a Su-25 aircraft at an unidentified air base.
The video shows the pilot standing in a revetment with a Su-25 in the background. The interview takes place at a grassy location with trees in the distance along with several distinct features, including two drop tanks flanking the Su-25 on either side, and objects behind the aircraft. The revetment itself is also somewhat distinct, as the berm wraps around three sides of the hardstand and the size and orientation of the six rectangular tiles across the opening are clearly visible in the video.

Although the pilot is announcing the completion of their training that occured in Russia, the footage was filmed and released by the Belarusian Ministry of Defense. This factor seemed to indicate that the filming location took place in Belarus instead of at the training center in Russia. Additionally, while Su-25s have operated out of other air bases in Belarus throughout the war, including Luninets Air Base, the only Su-25 wing in the Belarusian Air Force is based at Lida.
NNSA Administrator Jill Hruby Offers Frank Answers On LANL Plutonium Pit Production And More During Hybrid Town Hall Meeting In Santa Fe
“We are working around the U.S and we are working with our international partners to develop verification technologies some of which are associated with imagining a world without nuclear and some that are associated with a test treaty with Russia and/or China,” Hruby said, saying to Santa Fe Archbishop John Wester that while she knows his vision is clear, she wanted to make these comments about “where NNSA is today so that it’s understood and not misunderstood”.
Nuke Watch New Mexico Executive Director Jay Coghlan told Hruby it strikes him that NNSA has been avoiding an update pit life study. He mentioned a 2005 Jason Study that concluded that plutonium pits last at least 100 years.
BY MAIRE O’NEILL, LOS ALAMOS REPORTER | April 11, 2023 losalamosreporter.com

DOE-EM Senior Advisor William ‘Ike’ White, DOE NNSA Administrator Jill Hruby, center, and Santa Fe County Commission Chair Anna Hansen following Tuesday’s town hall meeting in Santa Fe. Photo by Maire O’Neill/losalamosreporter.com
It was described by some as a somewhat momentous occasion last Tuesday evening (April 4) when Jill Hruby and William “Ike” White joined Santa Fe County Commission Chair Anna Hansen on the dais for a hybrid town hall meeting at the Santa Fe Convention Center, which was attended by some 250 people in person and another 200 online.
Crowd turns out for town hall on plutonium pits, nuclear waste storage
“…Residents of Santa Fe, Albuquerque, Los Alamos and beyond asked questions and made comments about nuclear production and disposal in New Mexico. The crowd addressed a pair of officials from the National Nuclear Security Administration and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management. There was hardly an empty seat in the auditorium; 150 others attended the town hall virtually. Speakers at the town hall generally focused on three main issues: increased production of plutonium pits, ramped up disposal of transuranic waste at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, and nuclear proliferation.”
By Alaina Mencinger / Journal Staff Writer, ALBUQUERQUE JOURNAL | April 5, 2023 abqjournal.com

Archbishop John Wester, left, and Jay Coghlan, director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, listen as different people speak against plans to start pit production at LANL. (Eddie Moore/Albuquerque Journal)
‘Stop making nuclear weapons’: Activists press federal chief on LANL pit push
“We live in the third-most impoverished state in the nation, and yet we’re throwing away money to build weapons of war rather than take care of our own people…The U.S. must be the one to end the nuclear arms race because only then will other nations follow,” – Rikki Farrell of the ANSWER coalition
Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said new pits will be used to equip two new warheads being developed. He asked whether these new designs could lead to a return to explosive nuclear testing underground.
By Scott Wyland – SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN | April 5, 2023 santafenewmexican.com

Anti-nuclear advocates showed up in force Tuesday to grill the head of the federal nuclear security agency at a town hall about plans to have Los Alamos National Laboratory make 30 plutonium pits for warheads a year, a pursuit that has generated heated controversy in Northern New Mexico since its inception.
Continue reading
Recording of April 4 Santa Fe Town Hall – Overview of NNSA and EM’s National Security and Environmental Cleanup Priorities
Town Hall – Overview of NNSA and EM’s National Security and Environmental Cleanup Priorities
Anna Hansen, Santa Fe County Commission Chair, is moderating a town hall in collaboration with Jill Hruby, Under Secretary for Nuclear Security and Administrator of the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), and Ike White, Senior Advisor for the Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Environmental Management (EM). The town hall style event will feature a brief overview of NNSA and EM’s national security and environmental cleanup priorities and then will move into an expanded public question and answer period.
Posted by Nuclear Watch New Mexico on Monday, April 10, 2023
LANL plume cleanup halted due to water concerns
Milestones to meet in the coming year are to work on three monitoring wells and complete two reports, said Scott Kovac, Nuclear Watch New Mexico’s operations director. He called the effort inadequate for a large contaminated area discovered two decades ago.
“We’re going to have to do better than that,” Kovac said after the meeting. “We should be a lot farther along by now.”
Kovac also questioned why the report on the lab’s site-wide groundwater monitoring should be deemed a milestone. It’s something that must be done every year, so the lab’s parent agency shouldn’t get points for it, he said.
By Scott Wyland – SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN | March 31, 2023 santafenewmexican.com
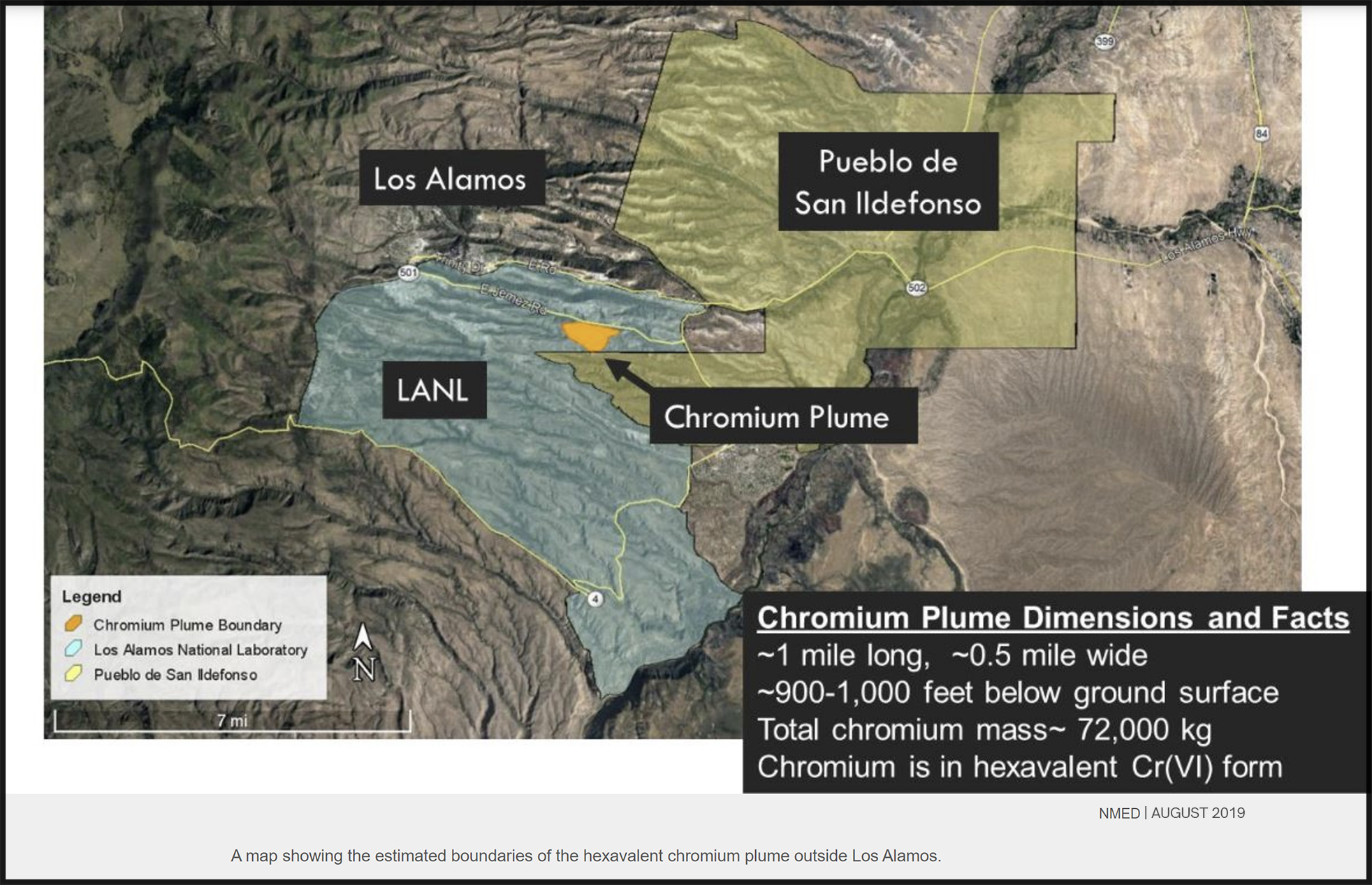
State regulators’ order to halt injections of treated water into the sprawling chromium plume under Los Alamos National Laboratory will go into effect Saturday as scheduled, federal and state officials confirmed this week at an annual meeting to review cleanup of legacy waste.
Regulators say the technique of extracting contaminated water, treating it and pumping it back into the decades-old plume is not fixing or containing the problem but instead is stirring up the hexavalent chromium and pushing it both toward San Ildefonso Pueblo and deeper into the aquifer.
The U.S. Energy Department’s environmental managers at Los Alamos insist the pump-and-treat method is working to dilute the toxic chromium and prevent its spread but said at a Wednesday meeting they would cease injections on Friday.
“Right now, we don’t have another avenue for any of that extracted water, so it will effectively be turning off the system for the interim measure for the chromium plume treatment,” said Troy Thomson, environmental remediation program manager for N3B, the lab’s legacy waste cleanup contractor.
A state Environment Department manager reiterated the agency’s position that the injection wells were placed inside the plume rather than on the borders, causing the injected water to spread the contaminants outward.
START treaty: Russia stops sending nuclear arms info to US
Russia’s Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Ryabkov said: ‘There will be no notifications at all’ with Washington as the US also stops sharing data on its nuclear weapons with Moscow.
By Aljazeera – Aljazeera | March 30, 2023 aljazeera.com
Russia will no longer share detailed information on its nuclear weapons with the United States as outlined in the New START treaty, a senior official in Moscow has said, as Russia’s military began drills with its Yars intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) launchers in Siberia while fighting in Ukraine rages and tension with the US mounts.
Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Ryabkov told Russian news agencies on Wednesday that Moscow had halted all information exchanges with Washington after suspending its participation in the New START nuclear arms treaty last month.
Putin says Russia will station tactical nuclear weapons in Belarus
The U.S. said it would “monitor the implications” of Putin’s announcement.
“We have not seen any reason to adjust our own strategic nuclear posture nor any indications Russia is preparing to use a nuclear weapon,” National Security Council spokesperson Adrienne Watson said. “We remain committed to the collective defense of the NATO alliance.”
By The Associated Press – NPR | March 25, 2023 npr.org
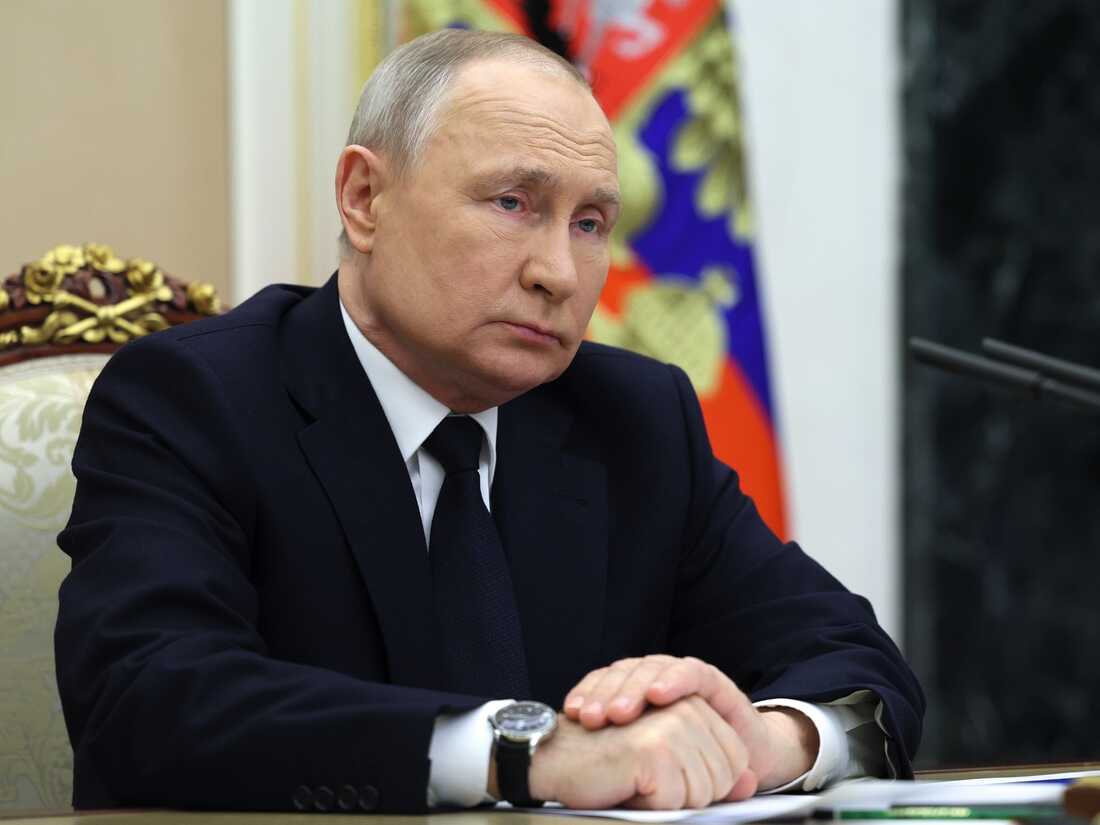

MOSCOW — Russian President Vladimir Putin announced plans on Saturday to station tactical nuclear weapons in neighboring Belarus, a warning to the West as it steps up military support for Ukraine.
Putin said the move was triggered by Britain’s decision this past week to provide Ukraine with armor-piercing rounds containing depleted uranium.
Tactical nuclear weapons are intended for use on the battlefield and have a short range and a low yield compared with much more powerful nuclear warheads fitted to long-range missiles. Russia plans to maintain control over those it sends to Belarus, and construction of storage facilities for them will be completed by July 1, Putin said.
He didn’t say how many nuclear weapons Russia would keep in Belarus. The U.S. government believes Russia has about 2,000 tactical nuclear weapons, which include bombs that can be carried by tactical aircraft, warheads for short-range missiles and artillery rounds.
A nuclear power plant leaked contaminated water in Minnesota. Here’s what we know
Xcel is based in Minneapolis, Minn., and operates in eight states around the U.S. Its two nuclear power plants are both based in Minnesota. Monticello is about 40 miles northwest of Minneapolis and has a population of about 15,000 people.
By Kaitlyn Radde, NPR | March 19, 2023 npr.org
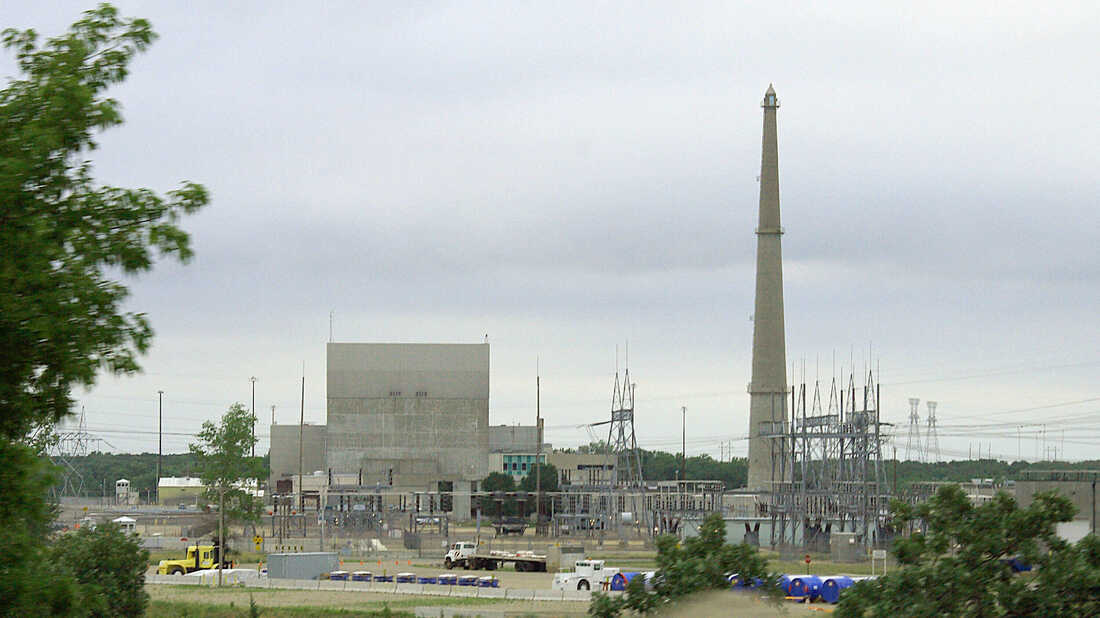

Minnesota officials are monitoring the cleanup of a 400,000 gallon leak of contaminated water from a nuclear power plant in the city of Monticello run by the energy giant Xcel Energy. Officials said there is no danger from the leak.
The leak was detected nearly four months ago and reported to state and federal regulators. The federal Nuclear Regulatory Commission posted a notice publicly at the time, but the company and state agencies did not notify the general public until last week.
“Xcel Energy took swift action to contain the leak to the plant site, which poses no health and safety risk to the local community or the environment,” the company announced in a statement on Thursday. Ongoing monitoring has confirmed that the leak “is fully contained on-site and has not been detected beyond the facility or in any local drinking water,” the company said.
Santa Fe Reporter Letter to the Editor: March 15
Cover, March 15: “The Foilies”
Notorious LANL delays
Concerning the article “presenting the nationwide look at the last year’s most terrible transparency,” the Santa Fe Reporter could have stayed home and reported on its own backyard. The Department of Energy and the Los Alamos National Laboratory are notorious for their lengthy delays in honoring Freedom of Information Act requests. As a federal judge ruled in one of our FOIA lawsuits, “administrative officials invoke every conceivable delaying technique and force citizens requesting information under the FOIA to resort to expensive litigation for vindication of their rights. Information is often useful only if it is timely. Thus, excessive delay by the agency in its response is often tantamount to denial.”
Nuclear Weapons Today – Peril and Promise, with Jay Coghlan and Ralph Hutchison

Nuclear Weapons Today – Peril and Promise, with Jay Coghlan and Ralph Hutchison: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P_0aqUG9hmw&t=15s
Sample Surplus Plutonium Disposition Comments – Copy, Paste, Edit & Submit yours!!
*NNSA will accept comments submitted through this weekend (3/19)* Please use our sample comments below and submit your own! The more you can edit and personalize, the better; however, simply copying our comments is fine if you are short on time!
Submit Via email to SPDP-EIS@nnsa.doe.gov:
Ms. Maxcine Maxted, NEPA Document Manager
National Nuclear Security Administration
Office of Material Management and Minimization
P.O. Box A, Aiken, SC 29802
National Nuclear Security Administration
Office of Material Management and Minimization
P.O. Box A, Aiken, SC 29802
Savannah River Nuclear Solutions receives ‘very good’ rating from National Nuclear Security Administration
“The performance evaluation report was released after Nuclear Watch New Mexico filed a lawsuit asking the court to require the NNSA to release its performance evaluation reports for all eight nuclear weapons research and production sites.”
By Matthew Christian mchristian@aikenstandard.com, Post and Courier | March 13, 2023 postandcourier.com
Savannah River Nuclear Solutions earned a rating of “very good” from the National Nuclear Security Administration and will receive over $39 million of the nearly $44 million available to it during the fiscal year ending Sept. 30, 2022 according to a recently released performance evaluation report.
LANL operator gets good review, but safety, production concerns remain
“One watchdog group, which requested the complete reports, said the lab appears to have consistent struggles in its quest to produce pits.
“’It’s more indication that production is prioritized over safety,’” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico. “’And even then, there’s apparent problems with production.’”
By Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com, Santa Fe New Mexican| March 13, 2023 santafenewmexican.com
Los Alamos National Laboratory’s primary contractor earned an overall good rating on a federal performance review but continued to wrestle with worker safety problems, production inefficiencies and staying on schedule on projects required to make nuclear warhead triggers by the target date.
FOX 13 Investigates: Tons of radioactive waste from Europe arrived in Utah last year
“Certainly, becoming a world destination site for radioactive waste disposal is not something that appeals to the tribe,” – Scott Clow, the environmental programs director for the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe.
By Nate Carlisle, FOX 13 NEWS | March 12, 2023 fox13now.com
SAN JUAN COUNTY, Utah — About 660 metric tons of radioactive material from Estonia traveled to a mill in southeast Utah last year, according to state inspection reports.
The state of Utah had approved the shipments to the mill, sitting on U.S. Highway 191 between Blanding and White Mesa. The latter is a community belonging to the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe.
The tribe worries about the chance for pollution.
NUCLEAR ARMAGEDDON GAMES IN UKRAINE
“’As Russia’s war on Ukraine continues, the last remaining nuclear weapons treaty between Russia and the United States… stands in jeopardy,’ read a January 2023 press release from the Bulletin before Putin backed out of the agreement. ‘Unless the two parties resume negotiations and find a basis for further reductions, the treaty will expire in February 2026. This would eliminate mutual inspections, deepen mistrust, spur a nuclear arms race, and heighten the possibility of a nuclear exchange.’ Of course, they were correct…”
By Joshua Frank, Inkstick Media | March 6, 2023 inkstickmedia.com
In 1946, Albert Einstein shot off a telegram to several hundred American leaders and politicians warning that the “unleashed power of the atom has changed everything save our modes of thinking and we thus drift toward unparalleled catastrophe.” Einstein’s forecast remains prescient. Nuclear calamity still knocks.
Even prior to President Vladimir Putin’s bloody invasion of Ukraine, the threat of a nuclear confrontation between NATO and Russia was intensifying. After all, in August 2019, President Donald Trump formally withdrew the US from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty, long heralded as a pillar of arms control between the two superpowers.
San Ildefonso governor says halt of plume cleanup will lead to spread onto pueblo
“Moquino said communication between the various parties will become vital if the plume continues to spread.”
“If it’s detected on our land, that changes the whole scope and dynamic of this entire issue,” Moquino said.
By Scott Wyland, Santa Fe New Mexican | March 6, 2023 santafenewmexican.com
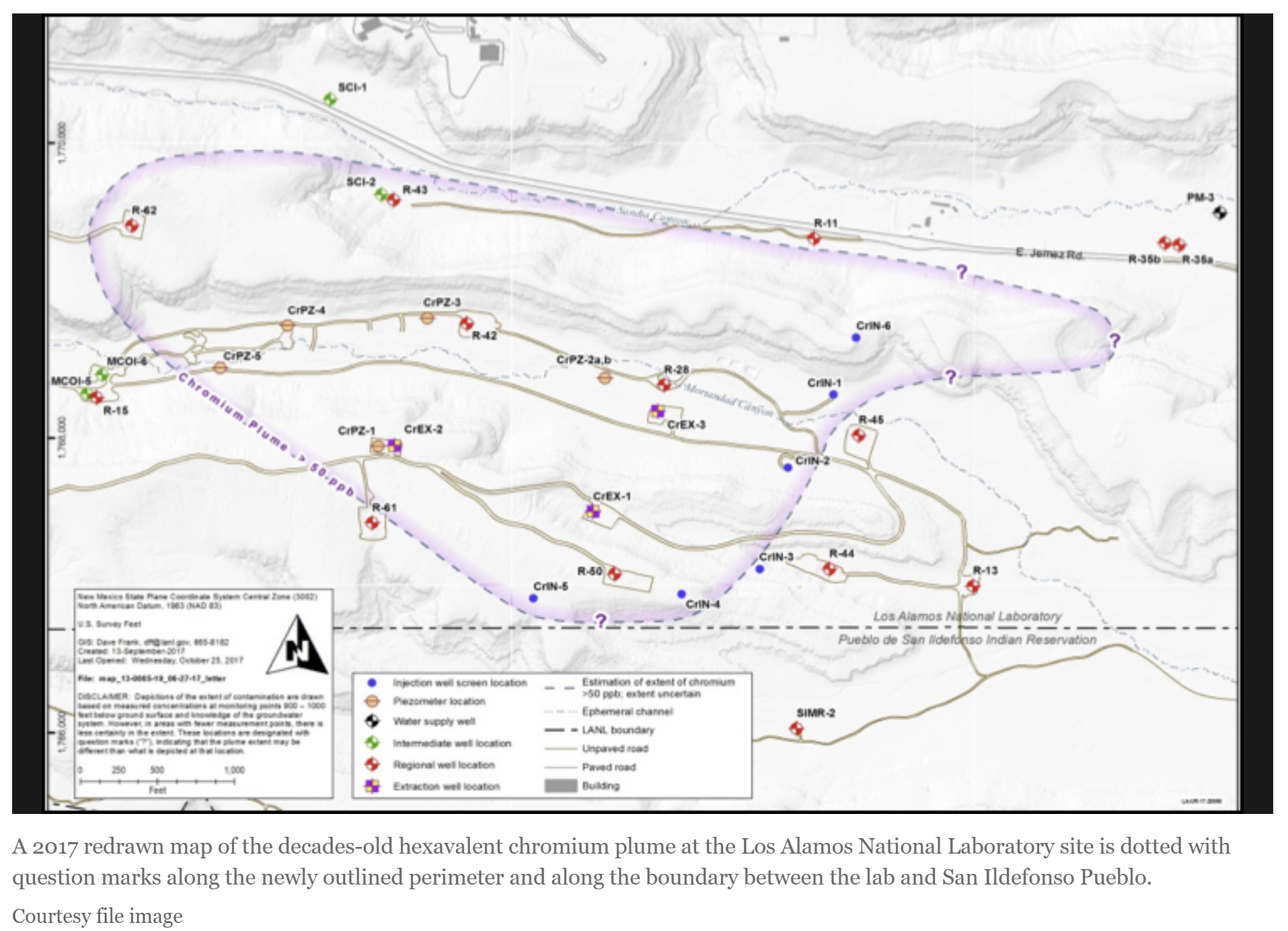 San Ildefonso Pueblo’s governor expressed concerns about the state Environment Department’s order to halt cleanup of a mile-long toxic plume by April 1, saying suspending the measures would cause the contamination to spread to the pueblo.
San Ildefonso Pueblo’s governor expressed concerns about the state Environment Department’s order to halt cleanup of a mile-long toxic plume by April 1, saying suspending the measures would cause the contamination to spread to the pueblo.
Gov. Christopher Moquino said tests and sampling show injecting treated water into the decades-old hexavalent chromium plume at the Los Alamos National Laboratory site has reduced the contaminants and kept them away from the pueblo.
“Halting is a concern,” Moquino said. “We don’t see any positive effect to stop the work. That could have some type of negative effect as far as the plume moving or expanding, but that’s to be determined.”
Moquino’s view contrasts with the state Environment Department, which contends the U.S. Energy Department’s method of extracting contaminated water, treating it and pumping it back into the aquifer is not diluting or containing contaminants but is pushing them toward the pueblo and deeper into the aquifer.
ALLIANCE FOR NUCLEAR ACCOUNTABILITY MEDIA ADVISORY: WHAT TO LOOK FOR IN THE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY’S FY 2024 NUCLEAR WEAPONS AND CLEANUP BUDGET REQUEST
Alliance for Nuclear Accountability | March 8, 2023 ananuclear.org
The Biden Administration is releasing its Fiscal Year 2024 federal budget on Thursday, March 9. It is expected to be a “skinny budget” with just topline financial numbers. If the pattern of the last few years for the Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) budget is continued, there can be three more releases over the next six weeks that grow progressively more detailed (there is initially little if any site-specific budget information). Historically around 60% of DOE’s funding has been earmarked for nuclear weapons production and cleanup of Cold War wastes and contamination.
The release of the presidential budget begins the annual legislative process for funding DOE programs and sites. The two bicameral congressional subcommittees that have jurisdiction over the DOE budget are the Armed Services Committee Strategic Forces Subcommittee which “authorizes” funding, and the Energy and Water Development Appropriations Subcommittee which actually provides funding. Congress has managed to pass the Defense Authorization Act for more than 50 consecutive years, but is increasingly unable to pass appropriations bills, leading to short-term Continuing Resolutions (CRs). Given bipartisan friction and the beginning of election campaigning, Continuing Resolutions are likely for this coming federal fiscal year 2024, which begins October 1, 2023.
The Alliance for Nuclear Accountability strongly opposed the massive 25% FY 2021 increase that the Trump Administration gave to the nuclear weapons programs of DOE’s semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). The Biden Administration not only kept Trump’s increases in subsequent budgets but substantially added to them, particularly for expanded production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores for nuclear weapons. Meanwhile, dismantlements of nuclear warheads have slowed to a crawl and funding for cleanup of Cold War radioactive and hazardous wastes has remained flat.
DOE’s nuclear weapons and environmental management programs have been on the Government Accountability Office’s “High Risk List” for project mismanagement and waste of taxpayers’ dollars for more than 30 consecutive years. Defense Department and DOE costs for so-called “modernization” of U.S. nuclear forces begun under Obama is expected to be around $2 trillion over the next 30 years.
March 1: Nuclear Remembrance Day – Anniversary of the Castle Bravo test in the Marshall Islands
Upcoming Events and More Resources:
- Wed, March 1, Annual Commemoration hosted in the RMI
- Wed March 1: Nuclear Victims Remembrance Day Solidarity March, hosted by Marshall Islands Student Association (MISA) – Fiji
- Saturday, April 4 : Bikini Day 2023, Salem Oregon, hosted by the Oregon Marshallese Community Assocation. More info coming soon.
Marshallese Advocates/Groups
- RMI National Nuclear Commission (Facebook, Twitter)
- Marshall Islands Student Association – FIJI (Facebook, Twitter)
- Marshallese Educational Initiative (Facebook, Twitter)
- COFA Alliance National Network (Facebook)
- Oregon Marshallese Community Assocation (Facebook)
- Selina Leem
- Kathy Jetnil Kijiner
- David Anitok
Resources:
- Interview with Tony de Brum: https://vimeo.com/256801160
- Darlene Keju at the World Council of Churches: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1hxCGlA5oJQ
-
SUMMARY OF HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF U.S. NUCLEAR TESTING IN THE MARSHALL ISLANDS, by Arjun Makhijani
- The Marshall Islands and the NPT, by Robert Alvarez
House panel OKs bill opposing nuclear waste storage plan
Holtec has said the facility would be temporary until a permanent repository could be built, but Rep. Janelle Anyanonu, D-Albuquerque, fears that wouldn’t be the case.
“Once it opens, it’s going to be permanent,” Anyanou said.
Several lawmakers brought up the recent toxic train wreck near East Palestine, Ohio, as evidence hazardous waste could contaminate communities if a similar incident happened in New Mexico. Holtec has said it will transport all the waste by train.
By Robert Nott, THE SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN | February 25, 2023 santafenewmexican.com
A bill that would stymie, if not stop, efforts to build a radioactive waste disposal storage site in the southeastern part of the state is getting closer to the legislative finish line.
The House Government, Elections and Indian Affairs Committee voted 6-3 on Saturday to approve Senate Bill 53, which would prohibit the storage and disposal of radioactive materials or waste in New Mexico unless the state has agreed to the creation of the disposal facility and unless the federal government has already created a permanent nuclear waste repository.
The Senate has passed the bill, which now goes to the House Judiciary Committee. If it clears that committee, it will go the floor of the House of Representatives for a final vote.
The effort, sponsored by four Democratic lawmakers, is aimed at slowing the efforts of Holtec International from building a proposed storage site between Hobbs and Carlsbad that would hold highly radioactive uranium from reactor sites around the country.
“I don’t want to see New Mexico become the nation’s dumping ground [for radioactive waste],” Rep. Matthew McQueen, D-Galisteo, one of the bill’s co-sponsors, told committee members.
Regulators order halt to plume cleanup, say contaminants moving toward pueblo
“It’s been nearly 20 years since the chromium plume was discovered, yet DOE is still struggling with cleanup,”
The current pump-and-treat method is marginally effective at best and a process that actually could take centuries to complete at this pace, said Scott Kovac, Nuclear Watch New Mexico’s operations director.
The contaminated water should be removed, treated and taken to another site instead of injected back into the plume, he said.
By Scott Wyland, The Santa Fe New Mexican | February 22, 2023 santafenewmexican.com
State regulators have ordered the U.S. Energy Department to stop injecting treated water into an underground chromium plume by April 1, saying the method is pushing the contamination at the Los Alamos National Laboratory site toward a nearby pueblo and deeper into the aquifer.
The state Environment Department has called into question a pump-and-treat method the federal agency’s environmental management branch has used for years in an effort to remedy the mile-long toxic plume and keep it from spreading to the adjacent San Ildefonso Pueblo.
Regulators say the technique of extracting contaminated water, treating it and pumping it back into the aquifer is not remediating the decades-old plume or containing it but instead is stirring up the hexavalent chromium and pushing it toward the pueblo.
Hexavalent chromium is a known carcinogen. If ingested in drinking water, it can harm the liver, kidneys and reproductive systems, and some research indicates consuming large amounts over a long period can cause stomach cancer.
“DOE has not demonstrated … that injection of treated water has resulted in hydraulic control of the plume,” Environment Department spokesman Matt Maez wrote in an email. “NMED is concerned about threats to public health and the environment from the plume being pushed towards and onto San Ildefonso, instead of being mitigated by DOE’s current injection strategy.”
Fire ‘involving URANIUM’ breaks out at Tennessee National Security Complex where America’s first atom bomb was developed, forcing evacuation of 200 staffers
The Oak Ridge complex was home to the Manhattan Project for research and development during World War II
An NNSA spokesperson confirmed that the fire started at 9.15am at the federal facility: Authorities confirmed that the material involved in the fire was a metal compound of uranium.
By EMMA JAMES FOR DAILYMAIL.COM | February 22, 2023 dailymail.co.uk

A fire ‘involving uranium’ broke out at a National Security Complex in Tennessee with all staff being evacuated from the site.
The National Nuclear Security Administration said that an emergency response responded to the blaze on Wednesday morning at the Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge.
All of their 200 employees were accounted for, with other buildings next to the site being evacuated as a precaution.
An NNSA spokesperson confirmed that the fire started at 9.15am at the federal facility, and the blaze was limited to the site itself.
They added: ‘Emergency Services responded to the event. The site activated the Y-12 Emergency Response Organization and we’ve been in close contact with local and state officials.
But they confirmed that they would assess employees, if needed, following the incident.
Putin Suspends Nuclear-Arms Treaty Between Russia, U.S.
“‘Putin’s announcement makes it far more likely that after New START expires, there will be no agreement limiting U.S. and Russian strategic nuclear arsenals for the first time since 1972,’ said Daryl Kimball, executive director of the Arms Control Association, a Washington-based organization that supports arms control agreements.”
What does justice, therefore, mean to a community that has lost so much?
By Ann M. Simmons, Sabrina Siddiqui and Austin Ramzy THE WALL STREET JOURNAL | February 21, 2023 wsj.com
MOSCOW—Russian President Vladimir Putin said Moscow would step back from the last remaining major nuclear-arms-control treaty between the U.S. and Russia, and vowed to continue the military campaign in Ukraine as the diplomatic gulf widened between Moscow and the West.
Mr. Putin’s move, announced Tuesday during a wide-ranging state-of-the-nation address in Moscow, came hours before President Biden again sought to rally international support for Ukraine in Poland ahead of the first-year anniversary of the invasion, and a day after traveling to Kyiv to meet with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky.
What justice means to communities affected by nuclear testing
A traditional—and sustainable—way of eating is just one of many things the US government has stolen from the Bikini community and other Marshallese by conducting 67 atmospheric nuclear tests. Marshallese have lost their culture, their land, and their health.
What does justice, therefore, mean to a community that has lost so much?
By Rebecca Davis Gibbons | February 2, 2023 thebulletin.org
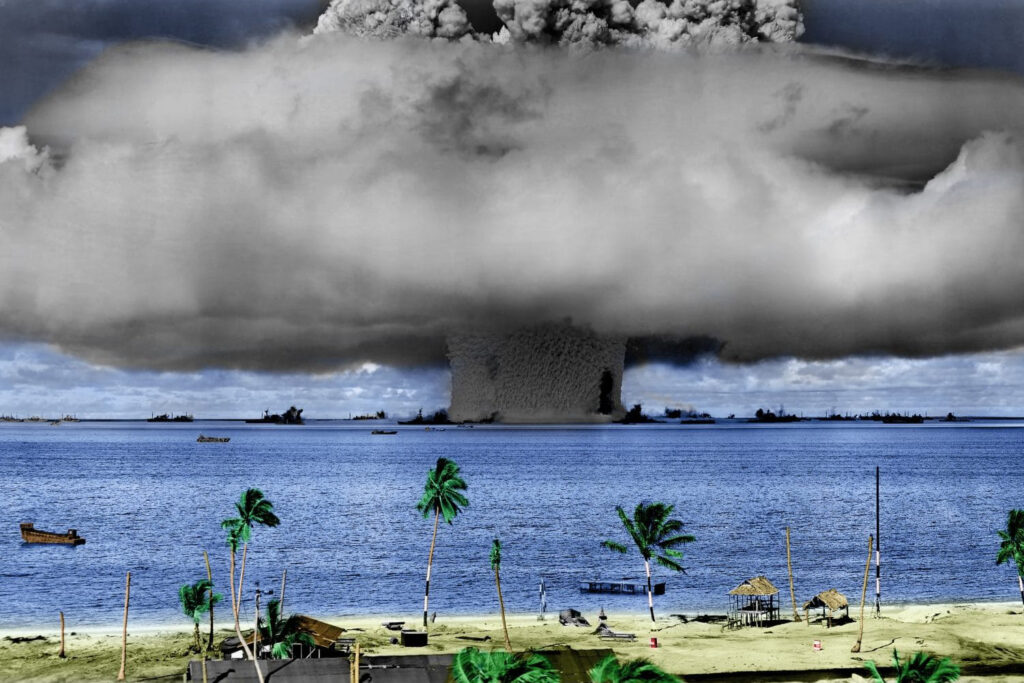

Editor’s note: This commentary is part of a roundtable on nuclear injustice.
I commend Franziska Stärk and Ulrich Kühn on calling attention to the important but underappreciated topic of nuclear injustice in their recent piece in the Bulletin. As their article makes clear, many individuals, communities, and countries have faced nuclear-induced injustices over the course of the nuclear age.
Some readers of Stärk and Kühn’s article may disagree over aspects of their assessment of nuclear deterrence or the effects of nuclear weapons in the ongoing war in Ukraine. But there should be little debate over the injustices faced by communities victimized by past nuclear testing and uranium mining. A prime example of nuclear injustice can be found on Kili Island in the Republic of the Marshall Islands, a place where I have firsthand experience.
On the day I arrived on Kili Island with two other recent college graduates, our hosts walked us down to the beach. A power boat came ashore, making its way through a channel where the coral that makes up and surrounds the island had been blasted away. One of the fishermen held up a large tuna. He pulled out a knife and cut some of the flesh and gave it to us. I enjoyed the freshest sashimi I had ever tasted to this day.
It turned out, however, that fish, a traditional staple of the Marshallese diet, was not going to be part of mine as I lived and taught elementary school on the island in the early 2000s. The community on Kili, a speck of an island at 200 acres, is inhabited by the Bikini people. In February 1946, the US military governor for the Marshall Islands arrived on Bikini Atoll and asked its residents to temporarily move off their atoll, with its 23 islands and a lagoon full of fish, so the United States could test weapons for “the good of mankind and to end all world wars.” They agreed to leave with the promise they would return.
Santa Fe new Mexican “MY VIEW” – Tina Cordova: No more nuclear sacrifice in our state
“No more waste. No more wasteland. No more sacrifice. No more sacrifice zone. No more suffering. We’ve done enough.”
Santa Fe New Mexican, Tina Cordova | January 28, 2023 santafenewmexican.com

Many years ago, Jan. 27 was designated the National Day of Remembrance for Downwinders, a time to recognize the sacrifice and suffering so long experienced by those who were overexposed to radiation as part of our country’s testing of nuclear weapons. The people of New Mexico were, after all, the first “Downwinders” any place in the world.
It would be monumental if our government would do more than set aside a day to remember us and actually take responsibility for the damage that was done to us. Holding the government to account is an ongoing fight that we wage every day with Congress — only to be told it’s going to cost too much. This, while they pass an $857 billion defense budget.
This year, as the people of New Mexico reflect on what happened to us more than 77 years ago, we should also reflect on what is about to happen to us today. A proposal is making its way through the federal government that would allow private industry to store tens of thousands of tons of high-level nuclear waste in southeastern New Mexico.
We cannot accept the risk of this prospect and must fight this effort with all that we have.
Downwind and dosed
Half the cast and crew involved with the John Wayne film, The Conqueror, shot in 1954 and released two years later, died of cancer.
Beyond Nuclear | January 19, 2023 beyondnuclear.org
They were the most high-profile victims of the fallout from atomic testing at the Nevada Test Site, which contaminated land, water and people. Although the film location site, in St. George, Utah, was more than 100 miles away, the radiation levels there were so high that when Wayne tested them with a Geiger counter he thought the equipment was broken. As The Guardian described it in a 2015 article, “the United States turned swathes of the desert radioactive during the cold war and denied it.”
Now, a new documentary directed by Mark Shapiro and Douglas Brian Miller — Downwind — is premiering at the Slamdance film festival, telling the stories of St. George citizens and activists harmed by the radioactive fallout from the Nevada Test Site. Libbe HaLevy talks to Shapiro on this week’s Nuclear Hotseat.
Mary Dickson: Downwinders deserve more than a day of recognition
Congress must act to compensate victims of atomic testing.
Salt Lake Tribune | January 18, 2023 sltrib.com
(AP Photo, File) This July 16, 1945, file photo shows an aerial view after the first atomic explosion at Trinity Test Site in New Mexico.Last month, as 2022 drew to a close, Congress approved $857 billion in defense spending under the 2023 National Defense Authorization Act.
I can’t help but be struck by the amount we are putting toward a one-year military budget — $45 billion more than was requested and a full $80 billion more than last year — at the same Downwinders are pushing for an expansion of the exceedingly limited Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA).
It’s been 32 years since RECA was enacted in 1990, and during that time only $2.5 billion has gone toward partial restitution for the harms caused to ordinary citizens by our own government as a result of atmospheric nuclear tests in Nevada. When it comes to defense, there always seems to be a surplus of funds, but not enough for the tens of thousands of unfortunate civilians who became casualties of the production and testing of lethal weapons of mass destruction.
January 27, designated as a National Day of Remembrance for Downwinders, marks the 72nd anniversary of the first nuclear blast at the Nevada Test Site in 1951. All these years later, Downwinders are still fighting for acknowledgement and compensation for the suffering and devastating losses that we’ve endured as a result of radioactive fallout spread across the country.
The ‘East Wind-41’ is the Longest-Range Missile in the World
When people think about how a city is destroyed in a nuclear war, they invariably question where the missile or bomb will have come from.
By Douglas A. McIntyre, 24 WALL ST NEWS | January 26, 2023 24wallst.com
One option, the oldest, is strategic bombers like the B-52. Another is from nuclear submarines. Recently, a Russian submarine that carried nuclear torpedoes was seen near the Arctic Circle. The third threat is intercontinental ballistic missiles that travel thousands of miles carrying multiple warheads. (This is what a nuclear war would do to the world.)
ICBMs are usually launched from inside the borders of the deploying countries. China’s DF-41 can travel 7,456 to 9,321 miles, the greatest distance of any long-range missile, according to Arms Control Association, an organization that promotes effective arms control policies. Russia and the U.S. also have extremely long-range missiles.
For comparison purposes, the longest commercial flight in the world is the Singapore Airlines route from New York City to Singapore, which covers 9,537 miles. People routinely have to fly 7,000 miles or more to reach several cities in Australia.
Mike Pompeo says world has ‘no idea’ how close India and Pakistan came to nuclear war
Former US secretary of state says in his book that Washington’s timely intervention prevented an escalation.
“It took us a few hours – and remarkably good work by our teams on the ground in New Delhi and Islamabad – to convince each side that the other was not preparing for nuclear war,”
Aljazeera | January 25, 2023 aljazeera.com
India and Pakistan came close to a nuclear war in 2019 and Washington’s intervention prevented an escalation, former US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo says in his new memoir.
This happened in February 2019 after New Delhi broke precedent by launching air raids inside Pakistani territory after blaming an armed group there for a suicide bombing that killed 41 Indian paramilitary soldiers in the flashpoint Kashmir region. In response to the attack, Islamabad shot down an Indian warplane, capturing the pilot.
A time of unprecedented danger: It is 90 seconds to midnight
This year, the Science and Security Board of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists moves the hands of the Doomsday Clock forward, largely (though not exclusively) because of the mounting dangers of the war in Ukraine. The Clock now stands at 90 seconds to midnight — the closest to global catastrophe it has ever been.
Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists | January 24, 2023 thebulletin.org
The war in Ukraine may enter a second horrifying year, with both sides convinced they can win. Ukraine’s sovereignty and broader European security arrangements that have largely held since the end of World War II are at stake. Also, Russia’s war on Ukraine has raised profound questions about how states interact, eroding norms of international conduct that underpin successful responses to a variety of global risks.
And worst of all, Russia’s thinly veiled threats to use nuclear weapons remind the world that escalation of the conflict by accident, intention, or miscalculation is a terrible risk. The possibility that the conflict could spin out of anyone’s control remains high.

Continue reading the full 2023 Doomsday Clock statement.
2022 Select Highlighted Press Items
Nuclear Modernization is the ’Absolute Minimum,’ STRATCOM Commander Says | March 8, 2022
US tested hypersonic missile in mid-March but kept it quiet to avoid escalating tensions with Russia | April 4, 2022
Putin’s Nuclear Threats Are a Wake-Up Call for the World | March 15, 2022
Intelligence report determines that Russia's WMD threats will grow as losses mount in Ukraine | March 19, 2022
China and the United States: It’s a Cold War, but don’t panic | March 10, 2022
Russian military doctrine calls a limited nuclear strike “de-escalation.” Here’s why. | March 8, 2022
North Korea says it will strike with nuclear weapons if South attacks | April 4, 2022
Flying Under The Radar: A Missile Accident in South Asia | April 4, 2022
2022 News Articles
New criminal charges filed against Westinghouse official in SC’s nuclear plant failure
“As construction problems mounted, costs rose, and schedules slipped, (and) defendants hid the true status of the project,” the indictment said.
“…Delays and cost overruns — hidden by SCANA officials from the public and state regulators — eventually doomed the effort, making it one of the largest business failures in South Carolina history.”
BY JOHN MONK | August 19, 2021 thestate.com
Acting United States Attorney Rhett DeHart pledges continued efforts in prosecuting those responsible for the failed nuclear site in Fairfield County. BY TRACY GLANTZ
A second high-ranking employee of Westinghouse Electric Corp. is facing criminal charges in connection with the multi-billion dollar failure of the doomed nuclear project in Fairfield County.
Jeffrey Benjamin, a former Westinghouse senior vice president of new plants and projects, faces multiple counts of fraud, according to an 18-page indictment made public Wednesday in U.S. District Court in Columbia.
It is the latest criminal charge in a four-year federal investigation of what went wrong at the highest levels of two substantial American companies — Westinghouse and the former SCANA Corp.
The charges against Benjamin are “for his role in failing to truthfully report information regarding construction of new nuclear units at the V.C. Summer nuclear plant,” Acting U.S. Attorney Rhett DeHart said in a press release.
Benjamin’s alleged cover-up of billions of dollars in losses at Westinghouse’s troubled nuclear plants in South Carolina and Georgia were part of a series of events leading to the company’s bankruptcy in March 2017, according to the indictment.
“The defendant’s misrepresentations and omissions, as well as the associated cover-up, resulted in billions of dollars in losses to (SCANA), ratepayers and investors,” the indictment said.
Benjamin, who was responsible for Westinghouse’s worldwide construction of nuclear reactors, is the fourth person to face criminal charges in connection with the SCANA scandal. The three others — another former Westinghouse employee and two top SCANA officials — all have agreed to plead guilty to various counts of fraud but have not yet been sentenced.
Top Westinghouse Nuclear Executive Charged with Conspiracy, Fraud in 16-Count Federal Indictment
 Department of Justice
Department of JusticeColumbia, South Carolina — Acting United States Attorney for the District of South Carolina M. Rhett DeHart announced today that a Federal Grand Jury has charged former Westinghouse Electric Company Senior Vice President Jeffrey A. Benjamin for his role in failing to truthfully report information regarding construction of new nuclear units at the V.C. Summer nuclear plant.
Benjamin, who served as Senior Vice President for New Plants and Major Projects and directly supervised all new nuclear projects worldwide for Westinghouse during the V.C. Summer project, is charged in a federal indictment with sixteen felony counts including conspiracy, wire fraud, securities fraud, and causing a publicly-traded company to keep a false record.
The charges Benjamin faces carry a maximum of twenty years imprisonment and a $5,000,000 fine.
The indictment alleges that Benjamin was personally involved in communications between Westinghouse and its owners, SCANA and Santee Cooper, regarding the status of the V.C. Summer project.
The indictment further alleges that, throughout 2016 and into 2017, when Westinghouse had direct control over the construction and schedule of the project, Benjamin received information that the V.C. Summer units were materially behind schedule and over budget. Nevertheless, at various times from September 2016 through March 2017, the indictment alleges that Benjamin assured the owners that the units would be completed on schedule and took active steps to conceal from the owners damaging information about the project schedule. During this time period, the owners paid Westinghouse over $600,000,000 to construct the two V.C. Summer units, both of which were ultimately abandoned.
Critics Decry $12 Billion for Nuclear in Infrastructure Bill
Smith in his Monday missive warned a bevy of NNSA endeavors, like pit production and the Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility before it, “have seen massive cost increases, schedule delays, and cancellations of billion-dollar programs. This must end.” Two things, Smith wrote, are vital to the successful modernization of U.S. nuclear weapons: affordability and executability.
By Eric Tegethoff, Producer | August 12, 2021 publicnewsservice.org

BOISE, Idaho — The U.S. Senate has passed a massive infrastructure bill, and buried within the package is $12 billion for the nuclear industry, but critics said the money would be better spent elsewhere.
Half of the money is reserved for nuclear facilities under threat of shutting down due to economic factors. The other half is for research and development, such as on the small modular nuclear reactor model being built in Idaho.
Tim Judson, executive director of the Nuclear Information and Resource Service, said the industry as a whole is struggling, with even the Idaho project being scaled back.
“By propping up the existing reactors and preventing them from being replaced with renewable energy, the nuclear industry’s essentially trying to keep sort of a foothold in the energy system until they can try to ram some of these new reactor projects like the one in Idaho through, if it ever happens,” Judson asserted.
He hopes the U.S. House makes changes to the investments in nuclear. The industry and some environmental groups have touted nuclear energy as an alternative to fossil fuels as the country moves toward clean energy sources.
How the nuclear weapons industry is dominating think tank research
A recent study finds that all major institutions working on nuke policy are getting funds from companies with a vested interest in it.
By Alicia Sanders-Zakre (former Nuclear Watch New Mexico Intern) and Susi Snyder | July 28, 2021 responsiblestatecraft.org
If you read a report about nuclear weapons, odds are it was published by a think tank funded by a company producing nuclear weapons. In our recent study of global nuclear weapons spending, we found that almost all major think tanks working on nuclear weapon issues took money from companies involved in the nuclear weapons industry in 2020 — raising questions about their intellectual independence and moral integrity.
In the report, we include 12 think tanks, picked from the Global Think Tank Index’s top foreign policy think tanks that also publish regularly on nuclear weapons from France, India, the United Kingdom, and the United States. We found the 21 companies that received nuclear weapon contracts gave $10 million in grants to these think tanks in just one year, as reported in the think tanks’ own annual reports and on their websites. This is a systemic issue. It’s not just one think tank, or a few $100,000 grants. Half of the profiled think tanks received up to well over one million dollars in one year from at least nine different companies working on nuclear weapons.
These companies don’t just donate money; key executives also oversee and advise several of these think tanks. Three CEOs of nuclear weapons-producing companies — Guillaume Faury (Airbus), Gregory J. Hayes (Raytheon), and Marillyn A. Hewson (until recently Lockheed Martin) — sit on the advisory board of the Atlantic Council. The Center for New American Security has a similar story: up to $1.8 million received from companies working on nuclear weapons and five board seats for those whose livelihoods are tied to nuclear weapon production.
These links are a problem for two reasons: it raises questions about the think tanks’ independence, and it ties them to companies engaging in immoral activities banned under international law.
Northern New Mexico Activists Hold Events Remembering Hiroshima and Nagasaki
On August 6th and 9th, 1945, the U.S. Government dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan. Over 200,000 people died instantly, while survivors suffered radiation exposure. The harm that was done is formally acknowledged every August at commemoration events around the world. This year, commemoration events were held in Los Alamos on Saturday, August 7th and in Taos on Sunday, August 8th.
On Saturday, at Ashley Pond in Los Alamos, Ken Mayers, chair of the Joan Duffy Santa Fe Chapter of the Veterans for Peace, led a two-hour vigil, “In Remembrance: Hiroshima and Nagasaki – 1945.” http://www.vfp-santafe.org/home.html
Rep. Smith presses Biden to audit pit production as Nuclear Posture Review progresses
Smith in his Monday missive warned a bevy of NNSA endeavors, like pit production and the Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility before it, “have seen massive cost increases, schedule delays, and cancellations of billion-dollar programs. This must end.” Two things, Smith wrote, are vital to the successful modernization of U.S. nuclear weapons: affordability and executability.
By Colin Demarest cdemarest@aikenstandard.com
The chairman of the House Armed Services Committee on Monday urged President Joe Biden to include an audit of plutonium pit production plans and costs in his administration’s broader assessment of U.S. nuclear policy and capabilities.
Writing about the Pentagon’s Nuclear Posture Review, Rep. Adam Smith pressed the president to closely examine pit production — the crafting of nuclear weapon cores, namely in South Carolina and New Mexico — and to “ensure it is both necessary and achievable within the announced cost and schedule.”
“As we near the budgetary heights of the ‘nuclear modernization mountain’ we can ill afford further delays and cost overruns,” wrote the Washington Democrat, who time and again has expressed reservations about pit production in the Palmetto State. He continued: “It is simply acknowledging reality that we must make hard choices.”
Federal law mandates production of 80 plutonium pits per year by 2030 — a rate and date motivated by military demand.
But while National Nuclear Security Administration officials believe production benchmarks in 2024, 2025 and 2026 can be met in New Mexico, at Los Alamos National Laboratory, they do not think a 2030 production target in South Carolina, at the Savannah River Site, is achievable.
Hiroshima and Nagasaki Remembered
We must speak out and call for action, to ensure that the horrific events witnessed in Hiroshima and Nagasaki are never repeated
BY: Chris McDonnell | United Kingdom

It was just after breakfast time on August 6, 1945 when a single B29 super fortress bomber plane of the US Air Force appeared in the clear blue sky above the Japanese city of Hiroshima.
It was about to unleash the most destructive weapon of war yet developed by mankind on the unsuspecting population going about their business in the streets below.
Piloted by Paul Tibbets, the B29 bore the name of his mother on its fuselage nosecone — Enola Gay. Its payload bomb known as Little Boy was the result of years of nuclear research in the United States under the code name of the Manhattan Project. It was the start of the Atomic Age.
In the middle of July the first experimental atomic weapon was detonated at the Alamogordo test range in New Mexico. It created a crater 300 metres in width. It was ironically given the code name “Trinity”. The scene was set for the first use of nuclear weapons in the theatre of war.
Preparations went ahead on the Pacific island of Tinian for the first attack, the city of Hiroshima, with a population well over a quarter of a million people, the designated target.
The bomb was released over the city at 8.15 am that Monday morning and exploded at an altitude of just under 2,000 feet.
The blast equivalent was estimated to be the equivalent of 13 kilotons of TNT, destroying an area of just under 5 square miles. It is likely that 90,000 people lost their lives…
Report: Some Los Alamos nuclear waste too hazardous to move
“In the October report, the safety board said lab personnel had failed to analyze chemicals present in hundreds of containers of transuranic nuclear waste, making it possible for incompatible chemicals to cause a container to explode. Crews also never sufficiently estimated how much radiation would be released by such an event.”
BY: Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com August 2, 2021
Los Alamos National Laboratory has identified 45 barrels of radioactive waste so potentially explosive — due to being mixed with incompatible chemicals — that crews have been told not to move them and instead block off the area around the containers, according to a government watchdog’s report.
Crews have worked to ferret out drums containing volatile compounds and move them to a more secure domed area of the lab after the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board issued a scathing report last year saying there were possibly hundreds of barrels of unstable nuclear waste.
The safety board estimated an exploding waste canister could expose workers to 760 rem, far beyond the threshold of a lethal dose. A rem is a unit used to measure radiation exposure. In its latest weekly report, the safety board said crews at Newport News Nuclear BWXT Los Alamos, also known as N3B — the contractor in charge of cleaning up the lab’s legacy waste — have pegged 60 barrels with volatile mixtures and have relocated 15 drums to the domed area.
Energy Department: Cap rather than clean up Los Alamos lab waste site
A watchdog group called the plan an attempt to save money without considering the potential long-term hazards of keeping highly toxic, slow-decaying waste buried in unlined pits roughly 1,000 feet above a vital groundwater source.
“The aquifer — that’s our main concern,” said Scott Kovac, research and operations director for the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico. “If climate change does affect us and things start drying out, then our aquifer is going to be even more important than it already is. We have to do everything to protect our aquifer that we can.”
Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com | Santa Fe New Mexican July 31, 2021
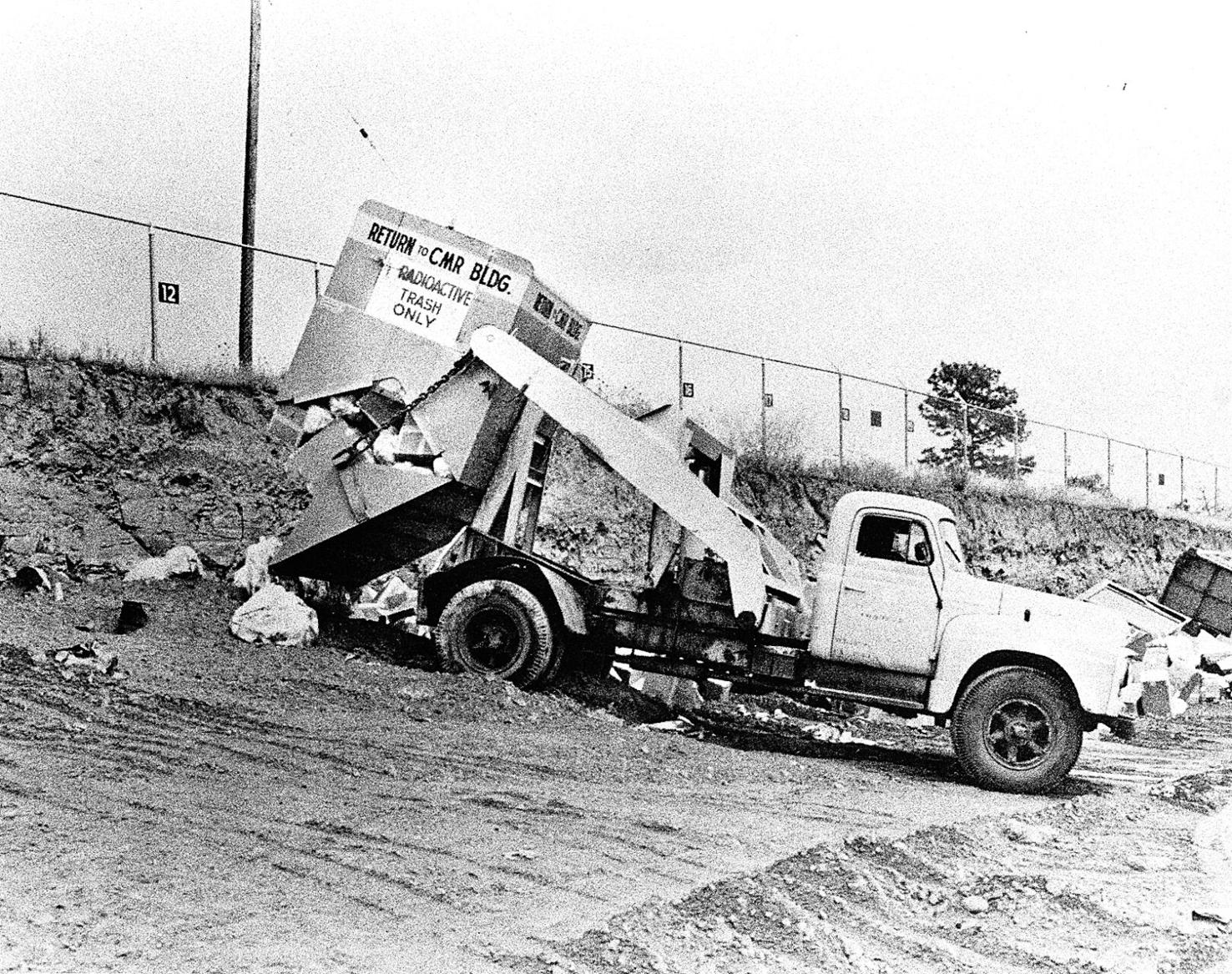

New Mexican file photo
One of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s older nuclear waste disposal sites — a Cold War relic — would be capped and covered rather than cleaned up under a plan put forth by federal officials.
Known as Area C, the 73-year-old dumpsite was shut down in 1974 after taking radioactive waste, caustic chemicals, treatment-plant sludge and a variety of trash, according to records.
U.S. Department of Energy officials propose installing a 2-foot-thick, dirt-and-rock cover they say will safely contain the waste, prevent toxins from leaching into soil and groundwater, and avoid the hazards that excavating the waste would pose to workers and the environment. It also would save hundreds of millions of dollars.
Petition calls for A-bomb victims to be remembered during Olympics
“The moment of silence will also express a commitment to making world peace a reality through the abolition of nuclear weapons.”
KYODO NEWS – Jul 22, 2021 | kyodonews.net
A former mayor of Hiroshima has launched an online petition calling for a moment of silence to be observed during the Tokyo Olympics at the time the atomic bomb was dropped on his western Japan city on Aug. 6.
Tadatoshi Akiba, 78, launched the Change.org campaign on the day International Olympic Committee chief Thomas Bach visited Hiroshima on July 16, amid opposition from some A-bomb survivors who said the visit ahead of the Tokyo Games starting Friday was politically motivated.
“He should have no objections to how important it is to spread the message of Hiroshima and Nagasaki to the world,” Akiba said, noting that Bach came to Hiroshima in spite of the coronavirus pandemic and opposition from many people.

The petition proposes that athletes and people from around the globe observe a moment of silence at 8:15 a.m. on Aug. 6 to remember not only those who perished in the atomic bombings of the two cities, but all victims of war.
Continue reading
Carbon-Free Power Project: Don’t Continue To Delay The Inevitable
“Disclosure of these would go a long way toward improving the credibility of NuScale, UAMPS, and the community boards who are putting their own credibility on the line by subscribing to this project.
We must not forget that our ratepayer and taxpayer monies are being used to underwrite this ambitious project. We are owed transparency in return.”
BY GEORGE CHANDLER, Los Alamos
Los Alamos County Councilors,
I hope you will choose to take this unexpected off-ramp rather than continue to delay the inevitable. The UAMPS CFPP project looks to be slowly dying, apparently because not enough communities believe it to be a viable project, or perhaps because of a lack of transparency. If you choose to continue, then you can make this a better project.
I submitted the questions below to the Utilities Board prior to their July 21 meeting. The Director of the Utilities Department asked CFPP to address these questions at the July 21 meeting, and Mr. Baker and Mr. Hughes did address most of them during their presentation and under questioning by Ms. Walker. Their responses were incomplete, contradictory, and generally unsatisfying. The three of most importance are the Economic Competitiveness Test (ECT), the work on the reactor core being done by Fromatome and Enfission, and the rather curious explanations of the 54% change in output with no design changes.
Waste Isolation Pilot Plant needs more space to dispose of nuclear waste, officials say
“..A 10-year renewal of the permit itself was underway after expiring last year and Don Hancock, nuclear waste program manager at watchdog group Southwest Research and Information Center said any modifications to the permit should be included in the full renewal or wait until after its approval.
He said the DOE aimed to “piecemeal” an expansion of WIPP operations and its lifetime to avoid a discussion on broadening the facility’s purpose and keeping it operational indefinitely.
The current permit called for WIPP to be closed by 2024, but officials speculated it could take as long as until 2050 to complete its mission.”
BY: Adrian Hedden Carlsbad Current-Argus
More underground space is needed to complete the mission at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant to dispose of nuclear waste, contend WIPP officials during a Monday public meeting.
The U.S. Department of Energy was underway with a permit modification request (PMR) that would amend the DOE’s permit with the State of New Mexico to allow for the mining of two new panels where waste would be disposed of along with drifts connecting the panels to the rest of the underground repository.
At WIPP, transuranic (TRU) nuclear waste consisting of clothing items and equipment irradiated during nuclear activities at DOE sites across the country is disposed of via burying in an underground salt deposit.
To achieve this, panels consisting of seven rooms each are mined about 2,000 feet underground where drums of the waste are emplaced, and the salt gradually collapses to permanently entomb the waste.
But due maintenance issues and a three-year shutdown of underground operations in 2014 following an accidental radiological release, portions of three of panels were left unusable and the DOE hoped to mine new panels to finishing burying the waste.
America’s Nuclear Waste Has Nowhere to Go and More Is Coming
“Nuclear power isn’t a silver bullet for our climate problems and there’s a host of issues with constructing new plants. The biggest of which is what to do with the waste. One of the most frequently proposed long term solutions is a geologic repository, a specially designed hole in the ground with thick barriers where large amounts of toxic waste can slowly degrade over hundreds of years.
The problem is that no one can ever agree on where to build a giant and expensive hole to dump nuclear waste that will render the site unusable for generations.”
BY Matthew Gault VICE News

Outside the sleepy Maine town of Wiscasset (population 3,700), armed guards patrol a slab of concrete surrounded by a chain link fence. On the slab is 60 cement and steel canisters containing 550 tons of nuclear waste with nowhere to go according to the Bangor Daily News.
It’s a problem across the country. Nuclear power plants produce waste that’s stored on site in what’s billed as a temporary solution. After decades of promising to move the waste, the Department of Energy (DOE) hasn’t found a more permanent solution. And now, the Pentagon is moving forward with plans to increase the production of plutonium pits, a core component of nuclear weapons, which will produce more highly toxic and radioactive waste.
Nuclear power is incredibly efficient and produces little carbon. A move towards a world based on nuclear power would dramatically cut down on emissions that lead to climate change. But nuclear power produces nuclear waste, a variety of highly toxic substances that will take hundreds of years to become inert.
Nuclear Officials Discuss Modernization of Arsenal in Online Forum
“Officials at the National Nuclear Security Administration have said the earlier estimate of Savannah River meeting its pit production target in 2030 was unrealistic and that it could take until 2035.
Meanwhile, the most recent cost estimate for bringing Savannah River’s pit plant online has swelled to $11 billion from $4.6 billion.”
BY: Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com Jul 20, 2021
A group of nuclear weapons managers agreed Tuesday that making more plutonium cores for warheads will be key to modernizing the nation’s arsenal as a deterrent against rival countries.
But during an online forum, a few of the managers who work at facilities with nuclear weapons programs also delved into a military leader’s assertion in recent months the U.S. is unable to produce a brand-new nuclear weapon, unlike Russia and China.
Peter Heussy, a defense consultant, asked the panel to interpret the comments by Adm. Charles Richard, head of U.S. Strategic Command, based on their work in the field.
“My thinking is: By policy we’re not supposed to be designing new [weapons]. We’re not being asked to do it, either,” said Mark Martinez, who oversees mission support and testing at the Nevada National Security Site.
The current focus is on life extension, Martinez said, referring to the program to replace or upgrade aging components, including the softball-sized plutonium cores — or pits — that detonate warheads.
Plans call for Los Alamos National Laboratory to produce 30 pits by 2026 and Savannah River Site in South Carolina to make 50 pits in the 2030s.
Eastern Idaho nuclear reactor project downsized
Others who support the project worry about its incomplete financial support. All but one council member that day voted to continue Idaho Fall’s 5 MW commitment. But two voiced direct concern over the project not having full subscriptions. Council member Jim Francis was the sole nay vote.
“If this project works out, it’ll be great. I just wish there was a slight bit more security,” he told the Post Register in a phone interview.
A project to build a first-of-its-kind nuclear reactor in eastern Idaho has been significantly downsized.
The initial plan for the Carbon-Free Power Project was to build 12 interconnected miniature nuclear reactor modules to produce a total of 600 megawatts. It would be the first small modular reactor in the United States. After the company tasked with manufacturing the plants said it could make the reactors more power-efficient, planners reduced the project down to six module reactors that could produce 462 MW total.
“After a lot of due diligence and discussions with members, it was decided a 6-module plant producing 462 MW would be just the right size for (Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems) members and outside utilities that want to join,” said LaVarr Webb, UAMPS spokesman.
The decision was made in late June, Webb said.
The project between UAMPS and Portland-based reactor producer NuScale received $1.4 billion from the U.S. Department of Energy last year. The reactor is planned to be built on the DOE’s 890-square mile desert site west of Idaho Falls at Idaho National Laboratory. The plant is expected to be running by 2029.
“A 6-module plant allows us to get to full subscription faster, but we would have reached full subscription regardless,” Webb said of the project’s ability to achieve full financial commitment from partners. “Before joining a next-generation, first-of-a-kind nuclear plant, utilities obviously want to be certain the plant is feasible and will be built. Now that we have made significant progress, including a large cost-share award from the Department of Energy, and NuScale has received design approval from the (Nuclear Regulatory Commission), we’re seeing more and more utilities express interest in the plant.”
So far, Webb said 28 participants have committed to a total of 103 MW. But, he said, “all are currently evaluating whether to increase or decrease” their commitments. He also said “a number of utilities outside of UAMPS are considering” making a commitment.
‘Downwinders’ To Hold Candlelight Vigil In Remembrance Of Trinity Test
BY: DENNIS CARROLL
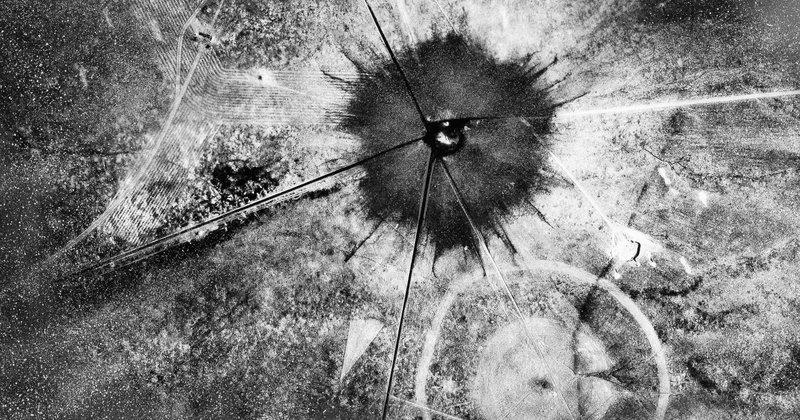
Southern New Mexicans will hold their 12th candlelight vigil in Tularosa Saturday commemorating the 76th anniversary of the Trinity Test, and remembering the suffering and deaths they believe it caused. The test was history’s first detonation of a nuclear device.
KSFR’s Dennis Carroll talks with Tina Cordova, co-founder of the Tularosa Basin Downwinders Consortium, about progress she and supporters have made in their quest for acknowledgement and justice.
Latinos Still Coping with the Fallout of 1st Nuclear explosion
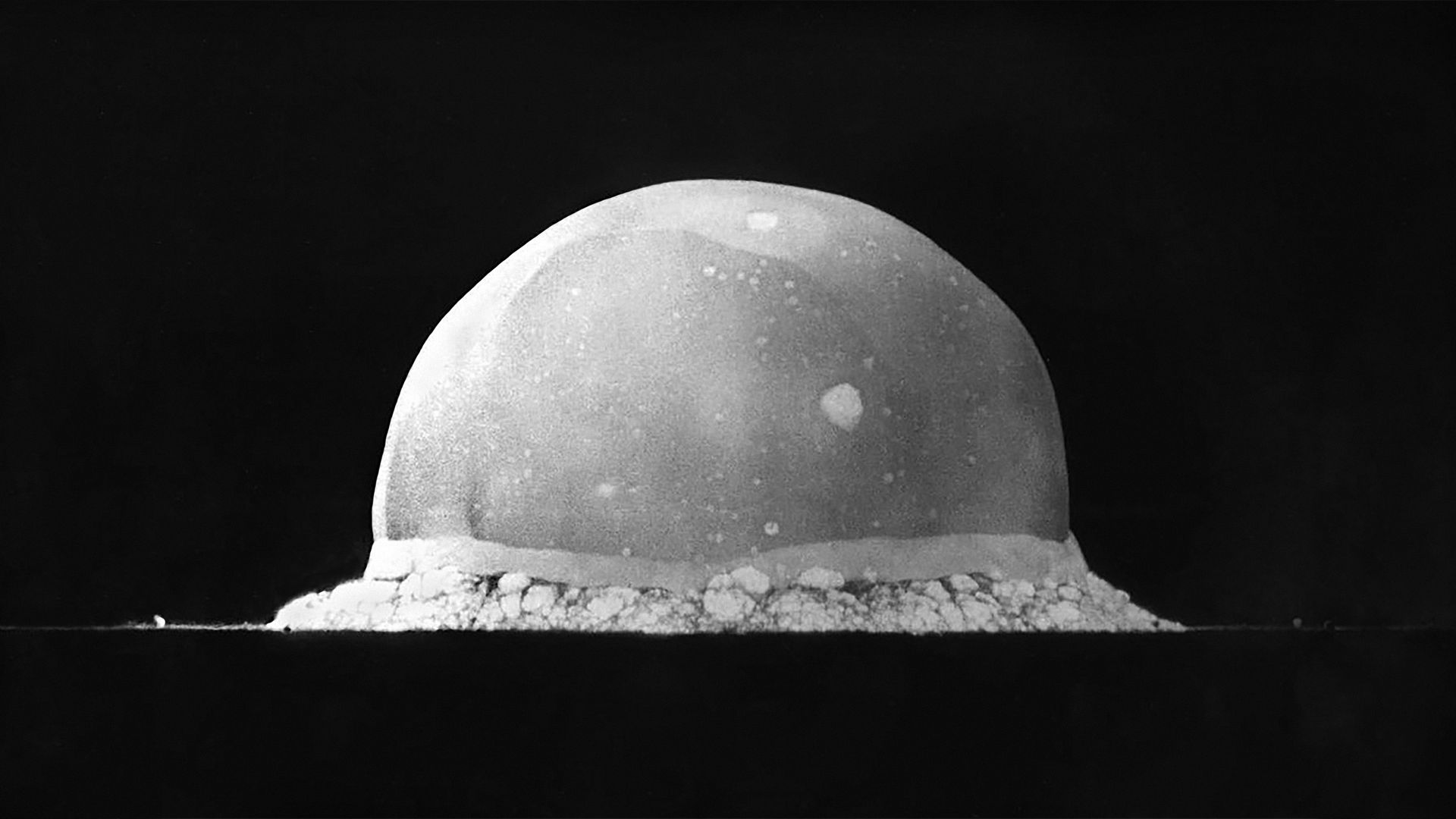

Hispanics and Mescalero Apache tribal members in New Mexico this month are marking the anniversary of the 1945 Trinity Test — an experiment resulting in health problems for generations living near the site of the world’s first atomic bomb explosion.
Why it matters: Descendants of those families use the July 16 anniversary to pressure lawmakers to compensate those who have suffered rare forms of cancer ever since the explosion.
The big picture: Tina Cordova, co-founder of the Tularosa Basin Downwinders, tells Axios that the overlooked residents of southern New Mexico finally are closer to being included in the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act.
- The act is scheduled to sunset on July 15, 2022, but the Hispanic village of Tularosa and the Mescalero Apache Reservation were never included in the law to compensate Americans who lived near and suffered from nuclear testing.
- Cordova said the Tularosa Basin Downwinders expect the U.S. Senate this year to consider a bill to extend the law and include southern New Mexico residents, in addition to Navajo uranium miners and some Idaho residents near other sites.

Sen. Mike Crapo (R-Idaho) plans on introducing a bill later this month that would extend the radiation act and include those forgotten residents, Crapo spokeswoman Melanie B. Lawhorn confirmed to Axios.
- The inclusion comes after decades of protests, vigils, and letter-writing campaigns on behalf of southern New Mexico residents who say their families were unwilling and unacknowledged guinea pigs.
- The proposal is expected to have bipartisan support and is being pushed by Sen. Ben Ray Lujan (D-N.M.).
What happened: On July 16, 1945, in the New Mexico desert, the U.S. Army detonated an atomic bomb developed through the Manhattan Project by scientists at the then-secret community of Los Alamos.
- The bomb exploded at 5:29 a.m., and its thunderous roar during the rainy season knocked people from breakfast tables in Tularosa and sent others on the Mescalero Apache reservation into hiding.
- The Army publicly attributed the sound to a mere ammunition explosion.
- Residents reported black rain and burned cows that passed on radiation poisoning through milk to unsuspecting residents.
- No one told residents of the site’s dangers, and they often picnicked there and took artifacts, including the radioactive green glass known as “trinitite.”
In Memoriam: Priscilla Johnson McMillan, 1928–2021
 A longtime supporter and friend of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, nuclear historian Priscilla Johnson McMillan passed away at 92 on July 7, 2021.
A longtime supporter and friend of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, nuclear historian Priscilla Johnson McMillan passed away at 92 on July 7, 2021.
From the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists:
“Priscilla was generous with her time and intelligence. She was astonishingly knowledgeable about Russia as it emerged from the Cold War and equally modest. She will be greatly missed,” — Kennette Benedict
A 2013 article from the Cambridge Chronicle states, “Since high school, McMillan had been active in politics and supported strengthening the United Nations in the hopes of controlling nuclear weapons.
‘It was the early post-war generation,’ she recalled. ‘We were trying to strengthen the UN so nuclear weapons wouldn’t belong to one country or another.’”
NNSA Los Alamos Shipments to WIPP Resume
BY: WAYNE BARBER
Shipments of transuranic waste to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant from National Nuclear Security Administration operations at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico were set to resume this week after being on hold since an ignition scare in February,…
Feds face suit over plan to build atomic weapons component factory in SC
VIEW NEWS CONFERENCE & PRESS RELEASE ABOVE
(also archived on the Facebook page of the South Carolina Environmental Law Project: https://www.facebook.com/scelp.org)
BY: SAMMY FRETWELL
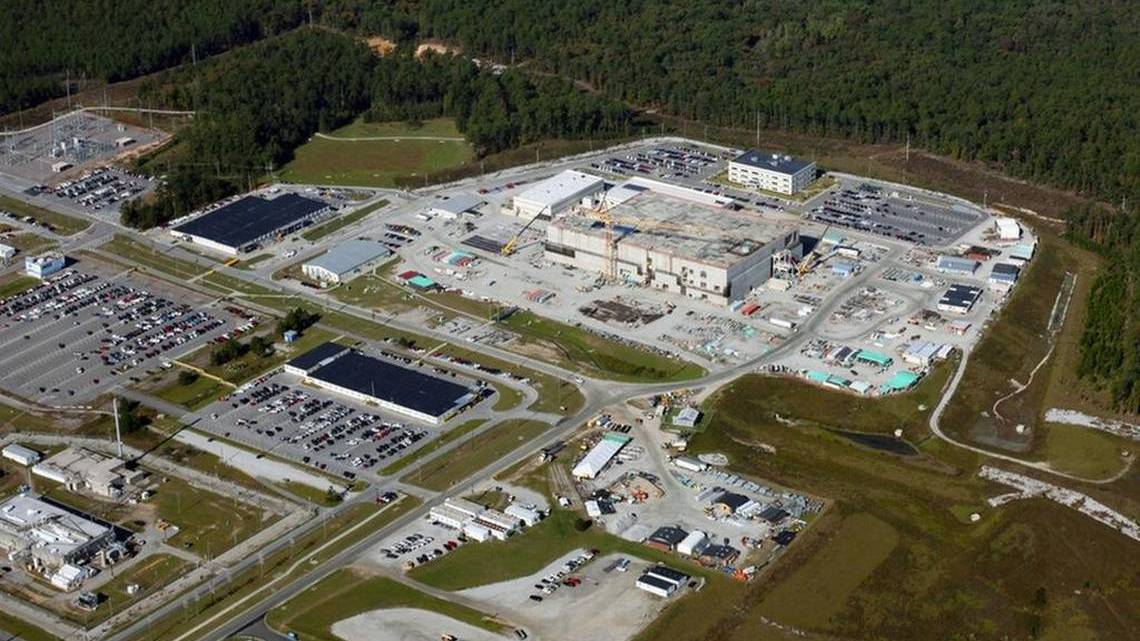

Four public interest groups said Tuesday they are suing the federal government, seeking to stop construction of multi-billion dollar nuclear production factories in South Carolina and New Mexico that would make components for new atomic weapons.
Savannah River Site Watch, Nuclear Watch New Mexico, Tri Valley CARES and the Gullah Geechee Sea Island Coalition are seeking an extensive study, known as a programmatic environmental impact statement, to weigh the effects of new pit plants on the environment and people who live near them.
Federal officials have sought the new plants to update the nuclear arsenal, a prospect that project boosters say could provide 1,000 jobs at the Savannah River Site, the Aiken area weapons complex where a pit factory would be located.
But critics say the promise of jobs isn’t worth the risk of environmental contamination or the cost, now estimated to be about $15 billion for the two plants.
7-acre desert site building at Idaho National Laboratory emptied, awaiting destruction
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) collects waste from across the country. WIPP is the nation’s only repository for the disposal of nuclear waste known as transuranic, or TRU, waste. Most of the waste slated for WIPP disposal comes from the remediation of sites used to produce atomic weapons during World War II and through the Cold War. WIPP’s original planned closure date was 2024.
BY: JOHN ROARK
The Transuranic Storage Area/Retrieval Enclosure at the desert site of Idaho National Laboratory has been emptied and is awaiting demolition according to a Fluor press release. This will be the first building closed as part of a three phase closing of the Advanced Mixed Waste Treatment Projects complex.
The TSA/RE, part of the AMWTP complex, was built over an above-ground waste storage pad which housed Cold War weapons waste. Once covered, Fluor used the facility to characterize, treat, repackage, certify, and ship the waste out of Idaho.
Barrels and boxes of waste, heavy equipment, and metal debris were removed. Over the last 20 years more than 100,000 waste containers have been removed from the facility. Fluor personnel are removing the asphalt floor of the building and will dispose of the material at an on-site landfill, the release said.
Cleanup of the Advanced Mixed Waste Treatment Unit, including solid waste such as trash, tools, and clothes, is part of the 1995 settlement agreement to clean up waste from the Manhattan project and Cold War-era.
The U.S. Nuclear Weapons Program Left ‘a Horrible Legacy’ of Environmental Destruction and Death Across the Navajo Nation
Navajo uranium miners have died of lung cancer and other respiratory illnesses. They weren’t told of the risks, and they want compensation for radiation exposure continued.
BY: Cheyanne M. Daniels, Amanda Rooker
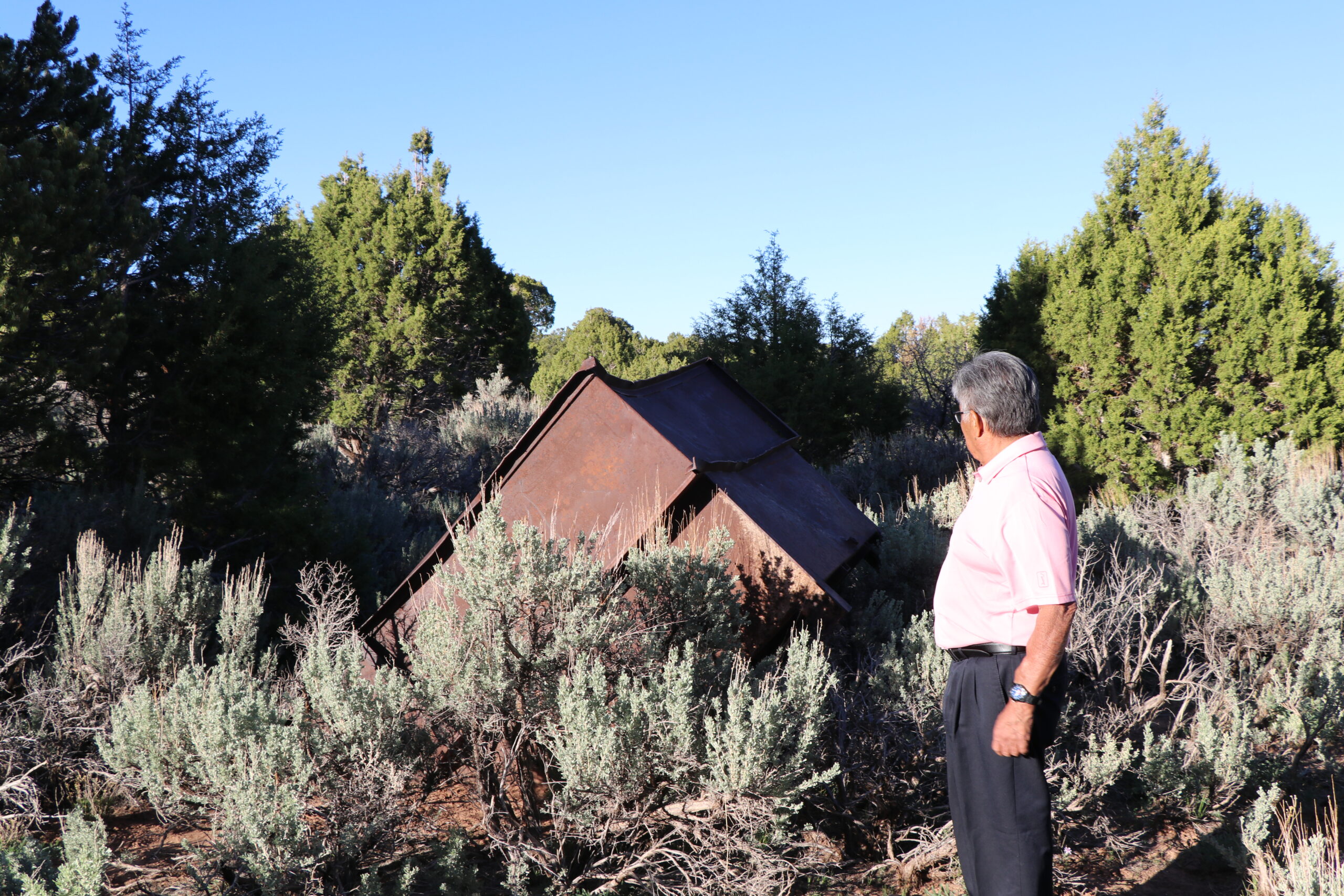

COVE CHAPTER, Ariz.—Phil Harrison walks the Lukachukai mountain range that towers over the Cove Chapter of the Navajo Nation in northeast Arizona. The mountains rise against a clear blue sky, and the red sand is dotted with sagebrush and flowers.
On a clear, warm day in May, he pauses, picks up a sprig of sagebrush and rubs it between his hands. “This is good medicine; it restores your brain,” he says.
He brings the crushed sage to his nose and inhales the sharp scent, holding out his hand and showing the green leaves in his palm. “Boil it, run it through a filter and you can drink that and it restores your memory, provides youth,” he says, then drops the sage and adds, “but I don’t know if this is contaminated.”
He shakes his head and moves on.
Despite the stunning beauty of the 27,000-square-mile Navajo Nation, which encompasses parts of Arizona, New Mexico and Utah, the land is marred by a toxic history: a “horrible legacy” of uranium mining and processing that began in 1944, with the U.S. nuclear weapons program and has slowly killed Navajo miners and their families, littered the land with 523 abandoned mines and tainted pristine aquifers with radioactive ore and the dry air with radioactive dust.
It’s a legacy Harrison is intimately familiar with.
Washington’s Dangerous New Consensus on China
Don’t Start Another Cold War
“Developing a mutually beneficial relationship with China will not be easy. But we can do better than a new Cold War.”
BY: Bernie Sanders
The unprecedented global challenges that the United States faces today—climate change, pandemics, nuclear proliferation, massive economic inequality, terrorism, corruption, authoritarianism—are shared global challenges. They cannot be solved by any one country acting alone. They require increased international cooperation—including with China, the most populous country on earth.
It is distressing and dangerous, therefore, that a fast-growing consensus is emerging in Washington that views the U.S.-Chinese relationship as a zero-sum economic and military struggle. The prevalence of this view will create a political environment in which the cooperation that the world desperately needs will be increasingly difficult to achieve.
It is quite remarkable how quickly conventional wisdom on this issue has changed. Just over two decades ago, in September 2000, corporate America and the leadership of both political parties strongly supported granting China “permanent normal trade relations” status, or PNTR. At that time, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the National Association of Manufacturers, the corporate media, and virtually every establishment foreign policy pundit in Washington insisted that PNTR was necessary to keep U.S. companies competitive by giving them access to China’s growing market, and that the liberalization of China’s economy would be accompanied by the liberalization of China’s government with regard to democracy and human rights.
This position was seen as obviously and unassailably correct. Granting PNTR, the economist Nicholas Lardy of the centrist Brookings Institution argued in the spring of 2000, would “provide an important boost to China’s leadership, that is taking significant economic and political risks in order to meet the demands of the international community for substantial additional economic reforms.” The denial of PNTR, on the other hand, “would mean that U.S. companies would not benefit from the most important commitments China has made to become a member” of the World Trade Organization (WTO). Writing around the same time, the political scientist Norman Ornstein of the conservative American Enterprise Institute put it more bluntly. “American trade with China is a good thing, for America and for the expansion of freedom in China,” he asserted. “That seems, or should seem, obvious.”
Well, it wasn’t obvious to me, which is why I helped lead the opposition to that disastrous trade agreement. What I knew then, and what many working people knew, was that allowing American companies to move to China and hire workers there at starvation wages would spur a race to the bottom, resulting in the loss of good-paying union jobs in the United States and lower wages for American workers. And that’s exactly what happened.
China’s nuclear leak no Chernobyl; we should still worry
The Taishan incident “should be an awakening for China to learn the lessons from Chernobyl and Fukushima, and do some soul-searching.”
BY DAVID FICKLING | BLOOMBERG OPINION (TNS)
Is a nuclear power plant on the edge of China’s 60 million-strong Pearl River Delta megalopolis on the verge of an emergency? It doesn’t look like it — but that doesn’t mean there’s no cause for concern.
The U.S. government has been assessing a report of a leak at the Taishan No. 1 nuclear power plant west of the cities of Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Hong Kong, CNN reported Monday, adding that the situation doesn’t pose a severe safety threat to workers at the plant or the wider public.
A separate statement from Electricite de France SA, or EDF, which owns 30% of the facility and controls Framatome, the company responsible for its maintenance, said there had been an “increase in the concentration of certain noble gases in the primary circuit” of the plant, adding this was a “known phenomenon.”
Don’t fret. There’s nothing in the reports so far to suggest Taishan is anywhere near turning into a Chernobyl, Fukushima or Three Mile Island.
Still, the manner in which the news has emerged suggests a deeper problem that China’s nuclear industry will need to rectify in the years ahead.
Cardinal Cupich: A world without nuclear weapons is ‘not some utopian dream’
“Nuclear weapons pose an existential threat to all life on Earth,” Cupich wrote. “Working toward a world without nuclear weapons, in which vigorous international monitoring and enforcement mechanisms verify compliance, is not some utopian dream. It is, rather, a practical and moral necessity.”
catholicnewsagncy.com June 15, 2021
Ahead of important international meetings this week, Cardinal Blase Cupich of Chicago urged President Joe Biden and other world leaders to work for “a world without nuclear weapons” as a “moral necessity.”
Cardinal Cupich wrote an op-ed published in The Hill on June 11, before Biden and Russian President Vladimir Putin are scheduled to meet on June 16 in Geneva. American and Russian diplomats are expected to begin negotiations on eventually replacing the 2010 New START nuclear arms control treaty, according to Politico. The two nations each control around 6,000 nuclear weapons each – about 90% of the world’s total stockpile.
Cupich wrote that at Thursday’s summit between Biden and Putin, “top on the agenda should be establishing a climate in which the Review Conference can succeed in reducing the nuclear threat.” He argued that the moment “could not be more urgent.”
“Nuclear weapons pose an existential threat to all life on Earth,” Cupich wrote. “Working toward a world without nuclear weapons, in which vigorous international monitoring and enforcement mechanisms verify compliance, is not some utopian dream. It is, rather, a practical and moral necessity.”
The United States and Russia, as the two countries controlling most of the world’s nuclear weapons, “have unique responsibilities in taking the lead to eliminate the nuclear threat,” he said.
Biden Is Going “Full Steam Ahead” on Trump’s Nuclear Weapons Spending Plans
FROM TRUTHOUT truthout.org June 10, 2021
“As President Biden prepares for the G7 and NATO summits and a meeting with Vladimir Putin, we look at how the United States, Russia and other nuclear-armed nations continue to spend billions on nuclear weapons during the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite President Biden’s criticisms of the Trump administration’s nuclear policies during his candidacy, his administration is continuing initiatives to expand the U.S. nuclear arsenal and is seeking $43 billion for nuclear weapons in his new budget. This comes as a new report from the Nobel Prize-winning International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons reveals global spending on nuclear weapons increased during the pandemic, and found the world’s nine nuclear-armed countries spent $72.6 billion on nuclear weapons in 2020, with the United States alone spending $37 billion.
“We’ve been seeing, from year to year, the spending on nuclear weapons has been increasing,” says Alicia Sanders-Zakre, ICAN’s policy and research coordinator (and former Nuclear Watch New Mexico 2019 summer intern). “Despite Biden’s campaign promises of wanting to work for arms control, wanting to work for disarmament, we’re seeing that in reality he’s going full steam ahead with Trump’s legacy nuclear weapons programs and continuing to spend more money on these weapons of mass destruction.”
U.S. must pledge ‘No First Strike’
“The Savannah River pit plant will cost about $11 billion to build, the NNSA said in its latest budget request: nearly two-and-a-half times as much as a preliminary estimate dating back at least to 2018. The Los Alamos pit plant will cost about $4 billion to build, the NNSA estimated in April, quoting figures from the project’s critical decision 1 review. It will cost some $30 billion to operate both plants for about 50 years, the NNSA has estimated.”
By Mary Burton Riseley | Santa Fe New Mexican
A spate of feel-good public relations articles and editorials have been published in the newspaper lately about all the beneficial work Los Alamos National Laboratory does — for example, analyzing the climate effects of wildfire smoke, helping plot the COVID-19 virus response, the economy-boosting relocation of over 500 LANL employees into otherwise unrented, empty office buildings in Santa Fe, and most recently, exploring the use of AI to predict earthquakes. With the exception of the move to Santa Fe, all of these aspects of the lab’s work are welcome.
Thanks especially to Rod Borup for the LANL work on hydrogen engines for commercial trucking.
But I, for one, cannot forget the lab’s core mission confirmed by a public presentation by its director, Thom Mason, on April 29. Always it is nuclear weapons design and development. From 100 percent of its budget in 1945, nuclear weapons work is still 79 percent. Since Rocky Flats has been closed, LANL’s mission has stretched to weapons production.

There have been better times. At the end of Jimmy Carter’s presidential term, nuclear weapons accounted for only 55 percent of LANL’s work, but Ronald Reagan quickly canceled extensive solar and geothermal energy programs. Many of us old-timers remember the vast quantities of expensive experimental solar equipment the late Ed Grothus sold from his lab outlet store, The Black Hole.
Despite the impression given by recent articles, LANL’s fiscal year 2021 budget of $3.68 billion allocates only meager amounts for nonnuclear weapons programs: 8.6 percent for nonproliferation, an estimated 6.8 percent work for others (whatever that may be), 3.1 percent for environmental cleanup, 1.7 percent for science programs, 0.1 percent for renewable energy and zero percent for energy efficiency.
Meanwhile, plutonium from past work continues to contaminate the Pajarito Plateau, as do radioactive chromium, cesium and other toxic radionuclides. This contamination is close to and upstream from Santa Fe. Why was Rocky Flats closed? Because it had so poisoned the earth and water under it that it threatened the well-being of thousands of Colorado residents.
DoE Nuclear Agency Can’t Fully Meet Production Deadline for Warhead Cores, Agency Official Tells Lawmakers
“The Savannah River pit plant will cost about $11 billion to build, the NNSA said in its latest budget request: nearly two-and-a-half times as much as a preliminary estimate dating back at least to 2018. The Los Alamos pit plant will cost about $4 billion to build, the NNSA estimated in April, quoting figures from the project’s critical decision 1 review. It will cost some $30 billion to operate both plants for about 50 years, the NNSA has estimated.”
By: Dan Leone | defensedaily.com
The National Nuclear Security Administration cannot meet a legal requirement to make at least 80 new plutonium cores for intercontinental ballistic missile warheads in 2030, the agency’s acting boss told lawmakers Thursday.
With the planned Savannah River Plutonium Processing Facility (SPPPF) up to five years behind scheduled, “based on our latest information we assess that meeting the 2030 [deadline] … is not going to be achievable,” Charles Verdon, the acting administrator of the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), said in the final minutes of a hearing of the House Armed Services strategic forces subcommittee.
That cat had been part way out of the bag since late May, when Jill Hruby, the Biden administration’s nominee to be the NNSA’s permanent administrator, told the Senate Armed Services Committee that SRPPF at the Savannah River Site in Aiken, S.C., would be as many as five years late.
Verdon’s testimony Thursday, however, clarified that without the SRPPF — to be built from the partially constructed Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility in Savannah River’s F-Area — the NNSA’s other planned pit plant, at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, cannot shoulder the load on its own by 2030.
Both pit plants are eventually supposed to be capable of surging their manufacturing capacity and staff to single-handedly produce the needed 80 pits annually, but the NNSA has not said when that might be possible. The agency did not reply to a request for comment on Thursday.
Biden aims to boost LANL cleanup cash
“That’s good news,” Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said of the plan to get rid of the 35-year-old facility. “Demolishing that building will save the public costs and reduce risks.”
Coghlan at first said he was “pleasantly surprised” to see such a large increase in the budget for cleanup.
“Perhaps better put, flabbergasted,” he added, noting the $107.5 million increase in spending on the task compared to the current fiscal year.
He also noted that the Trump administration had proposed a $100 million decrease in spending on cleanup a year ago, but Congress ultimately kept cleanup spending at LANL at $226 million.
In a news release, Coghlan praised Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham and state Environment Secretary James Kenney for suing DOE over a “continuing pattern of delay and noncompliance” with a 2016 consent order that provided benchmarks for cleanup that LANL has failed to meet.
By T.S. Last / Journal North | Copyright © 2021 Albuquerque Journal June 9, 2021
Los Alamos Lab May Face Greater Demand for Plutonium Pits
“In the end, more than five times could be spent on that building than was spent constructing the $4 billion One World Trade Center — all to manufacture bomb cores, said Jay Coghlan, executive director of nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
Extending renovations by several years is bound to put pressure on the lab to ratchet pit production beyond the current goal, Coghlan said.”
By Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com Jun 8, 2021 | Santa Fe New Mexican
The plutonium pit factory at Savannah River Site in South Carolina will take years longer and cost billions of dollars more to ramp up than previously planned, which could push Los Alamos National Laboratory to make more nuclear bomb cores to fill the gap, watchdog groups say.
For the past three years, plans have called for the Los Alamos lab to produce 30 plutonium warhead triggers by 2026 and Savannah River to make 50 by 2030, but the latter is proving much more costly and nettlesome than anticipated.
Jill Hruby, the nominee to head the National Nuclear Security Administration, said in a U.S. Senate hearing last week that Savannah River might not fully operate until 2035.
And a recently released budget proposal for the country’s nuclear weapons program going into 2022 shows the estimated cost of converting Savannah River Site into a pit plant ballooning to $11 billion from $4.6 billion. A budget note said the estimate could go up.
Rep. Chris Chandler and NMED Sec. James Kenney Unhappy With Progress Of Waste Shipment From LANL
“The poor performance at LANL I think is exactly why we sued the Department of Energy because we believe the DOE and contractor are in violation of the Consent Order, we need to correct that and from a policy perspective, the Department of Energy has prioritized over New Mexico, cleanup at Savannah River, cleanup at Idaho National Labs, cleanup at all these other places and that is unacceptable to the state of New Mexico since we are the only state that holds the geologic repository known as WIPP,” – New Mexico Environment Department Secretary James Kenney
BY MAIRE O’NEILL maire@losalamosreporter.com | The Los Alamos Reporter June 8, 2021
District 43 Rep. Christine Chandler and New Mexico Environment Department Secretary James Kenney on Monday both criticized the Department of Energy’s lack of progress in shipping waste from Los Alamos National Laboratory to the Waste Isolation Pilot Project (WIPP) in Carlsbad. Their comments were made during the Legislative Radioactive & Hazardous Materials Committee meeting. Chandler is the vice chair of that committee.
Eletha Trujillo, Bureau Chief of the Hazardous Waste Planning Division at the state Energy, Minerals and National Resources Department, earlier in the meeting noted that there are two groups from LANL that ship waste – the DOE Environmental Management group and the DOE National Security Administration group.
“The DOE NNSA group had some safety violations back in February – the spark incident that occurred with a barrel at Los Alamos and so they have not been able to do any shipments. They do have material, but they’re not able to ship anything because they’re under a safety hold by the NRC. When they complete their plan and they get approval again from the NRC then the NNSA will be able to ship again. We don’t know when that’s going to happen. Typically the NNSA tends to have more safety violations than Environmental Management,” Trujillo said.
She added that EM has shipped their material and does not have enough material for a full load.
$72.6 billion. That’s how much the nine nuclear-armed states spent on their nuclear weapons in 2020…
during the worst pandemic in a century and when the treaty banning nuclear weapons became law, according to a new ICAN report. It’s an inflation-adjusted increase of $1.4 billion from last year.
But that’s not all. The report, “Complicit: 2020 Global Nuclear Weapons Spending,” dug through thousands of pages of contracts and annual reports to bring you the full picture of nuclear weapons spending. Because it’s not just countries’ governments that are responsible for wasting resources on weapons of mass destruction. Companies, lobbyists and think tanks are all complicit in 2020 spending on nuclear weapons.
In 2020, the report finds that less than a dozen companies got $27.7 billion contracts to work on nuclear weapons. Those companies then turned around and spent $117 million lobbying decision makers to spend more money on defense. And they also spent upwards of $10 million funding most of the major think tanks that research and write about policy solutions about nuclear weapons.
This spending is immoral and contrary to international law. Every actor in the circle is complicit. It’s time to speak up. Tell your country to stop spending money on nuclear weapons and join the TPNW. Protest a company that’s building these weapons near you. Ask think tanks to stop accepting money from the companies building nuclear weapons.
New company sought to operate Waste Isolation Pilot Plant under $3 billion contract
Little change to workforce, operations expected
Adrian Hedden Carlsbad Current-Argus |
A new primary contractor could be coming to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant as the U.S. Department of Energy sought bids from prospective contractors for the management and operations of the nuclear waste site near Carlsbad.
The current holder of the contract Nuclear Waste Partnership began its work at WIPP in 2012 and its contract will expire in September 2021, with an extension carrying the contract through September 2022.
At that point, Vice President of Marketing and Communications at Amentum – NWP’s parent company – Keith Wood said the contractor’s lifetime would end.
“NWP was established to perform the current mission for the current contract,” Wood said. “That company will not be bidding on the next contract. Their sole mission was to perform the work under the current contract.”
Wood declined to comment on if any Amentum-led subsidiaries would bid on the new contract to operate WIPP.
The four-year contract will include six, one-year extension options and was valued at $3 billion over a 10-year performance period.
U.S. Plutonium Pit Costs Rise
“In addition, the Government Accountability Office GAO noted in a report published last September that the NNSA has been unable to plan for and complete major construction projects on time and, over the past two decades, Los Alamos has twice had to suspend laboratory-wide operations after the discovery of significant safety issues.”
By: Kingston Reif | armscontrolnow.org
The Energy Department’s cost to build the infrastructure to produce new plutonium cores for U.S. nuclear warheads could be as high as $18 billion, according to a department estimate and yet-to-be-released internal estimates detailed to Arms Control Today by a congressional source.

A technician at Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico manipulates plutonium as part of the U.S. Stockpile Stewardship Program in 2005. Current plans call for expanding the production of plutonium pits at both Los Alamos and at the Savannah RIver Site in South Carolina. (Photo: U.S. Energy Department)
The updated price tag is nearly two and half times larger than earlier projections and is likely to raise fresh doubts about the affordability of the department’s aggressive plans to sustain and modernize U.S. nuclear warheads and their supporting infrastructure.
The updated estimates are not reflected in the budget plan for the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) that the Trump administration bequeathed to the Biden administration. That means future NNSA weapons program budget requests will require significant increases beyond current plans just to accommodate the growth in the projected cost of pit production.
Plain Talk: On this Memorial Day, consider getting rid of instruments of death
The sad fact is that if the world’s inclination to settle disputes by going to war — whether it be in Iraq or in Israel and Palestine or any of the other dozens of places that teem with hate — results in the use of a nuclear weapon, we won’t have enough people to decorate all the graves.
BY: Dave Zweifel | The Capital Times

AMBER ARNOLD, STATE JOURNAL
Today’s the day we pause to remember the tens of thousands of men and women who paid the ultimate price in service to their country.
When I was a kid this day was known as “Decoration Day.” I remember my grandparents taking us kids to the old cemetery in New Glarus to place flowers and flags, decorations if you please, on the graves of their own departed family members. Two of them had served in the Civil War.
Other folks placed memorials on the gravestones of relatives who had served in World War I, and still others paid their respects to those who gave their lives in the most recent world conflict at the time, World War II.
Today thousands of Americans will also be remembering loved ones killed in Vietnam, then Iraq and Afghanistan and countless other “skirmishes” where our leaders chose to place our young people in harm’s way. Sometimes the cause was good, more often, not so good.
A couple of weeks ago Buzz Davis, a tireless advocate for peace from Stoughton who’s now retired in Arizona, sent along a column he had written that once again calls on all of us to work harder for peace than we consistently do for war.
A Vietnam veteran himself, Davis was a founder of our local Vietnam Veterans for Peace and is still active in the national organization Vets for Peace that spreads the message that we need to find ways to solve our conflicts other than killing each other and filling cemeteries with gravestones to decorate on what we now call Memorial Day.
“Humans have been alive for 200,000 to 300,000 years,” he points out. “Nearly every major discovery has been used to ‘improve’ our ability to kill others.
“From learning how to sharpen sticks, to metal instruments, to explosive power, boats, airplanes, guns, germs and now nuclear reactions — inquisitive men and women ‘discover’ these and, mostly boys, use them to kill others,” he adds.
Nuclear News Archives – 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.