QUOTE OF THE WEEK
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
LANL’s Central Mission: Los Alamos Lab officials have recently claimed that LANL has moved away from primarily nuclear weapons to “national security”, but what truly remains as the Labs central mission? Here’s the answer from one of its own documents:
LANL’s “Central Mission”- Presented at: RPI Nuclear Data 2011 Symposium for Criticality Safety and Reactor Applications (PDF) 4/27/11
Banner displaying “Nuclear Weapons Are Now Illegal” at the entrance in front of the Los Alamos National Lab to celebrate the Entry Into Force of the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty on January 22, 2021
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Follow the Money!
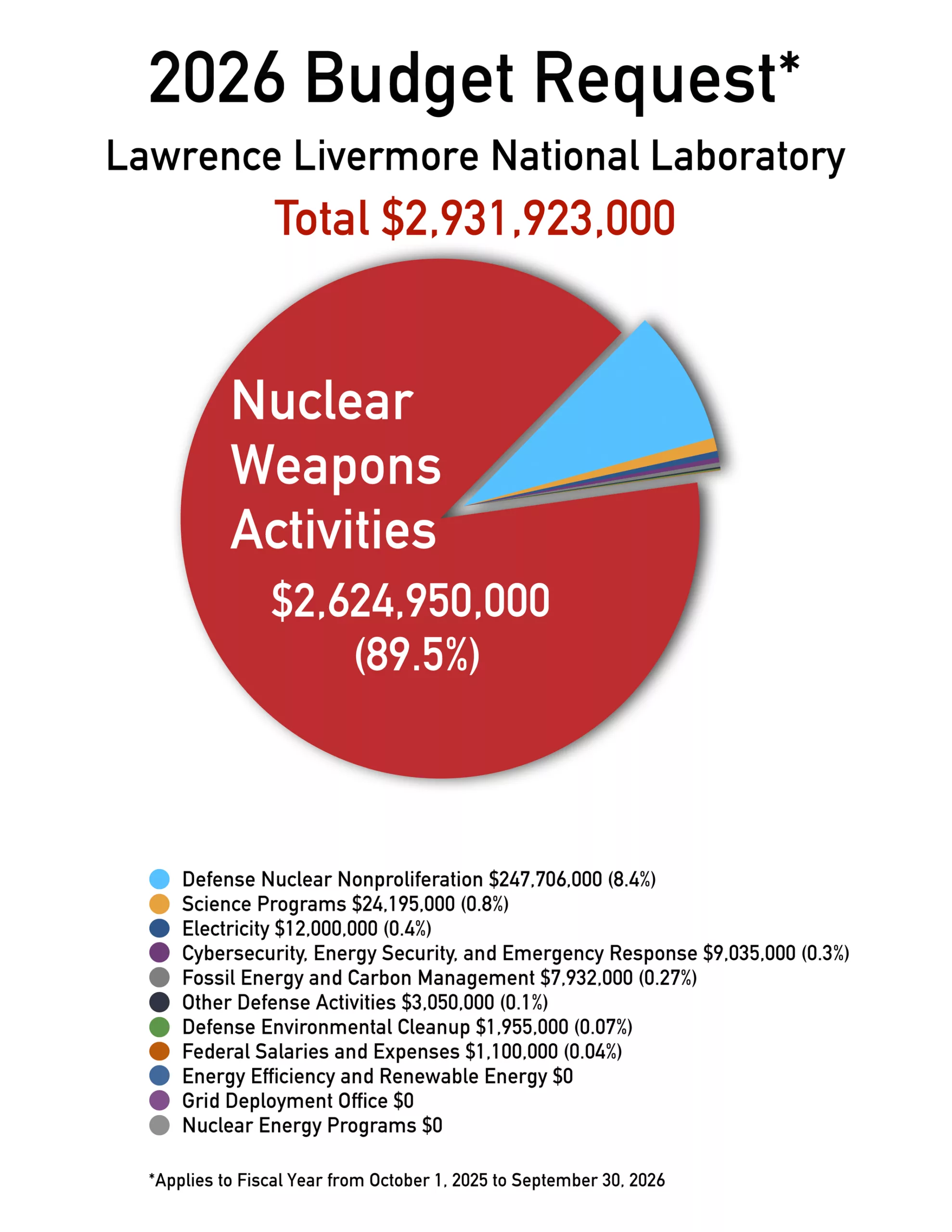
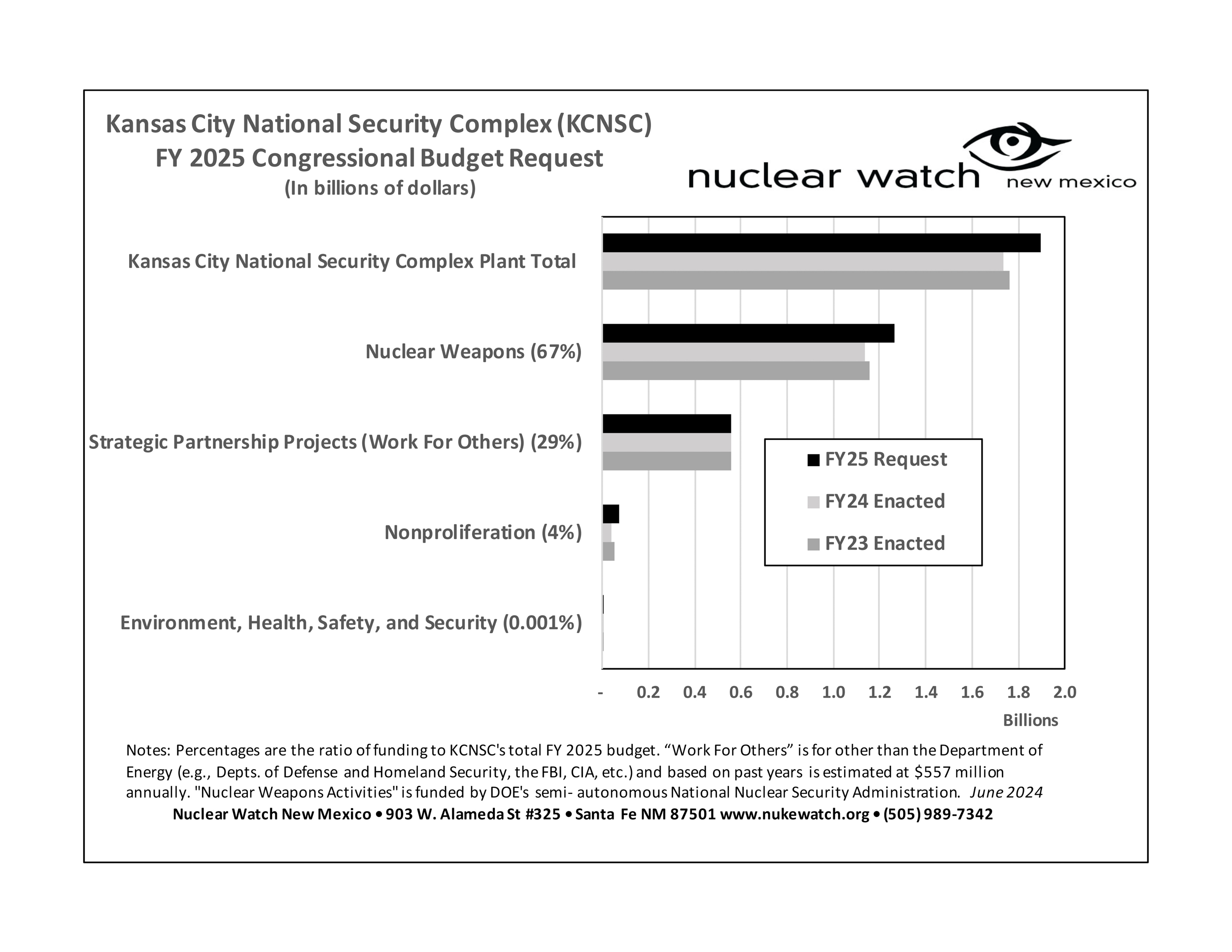
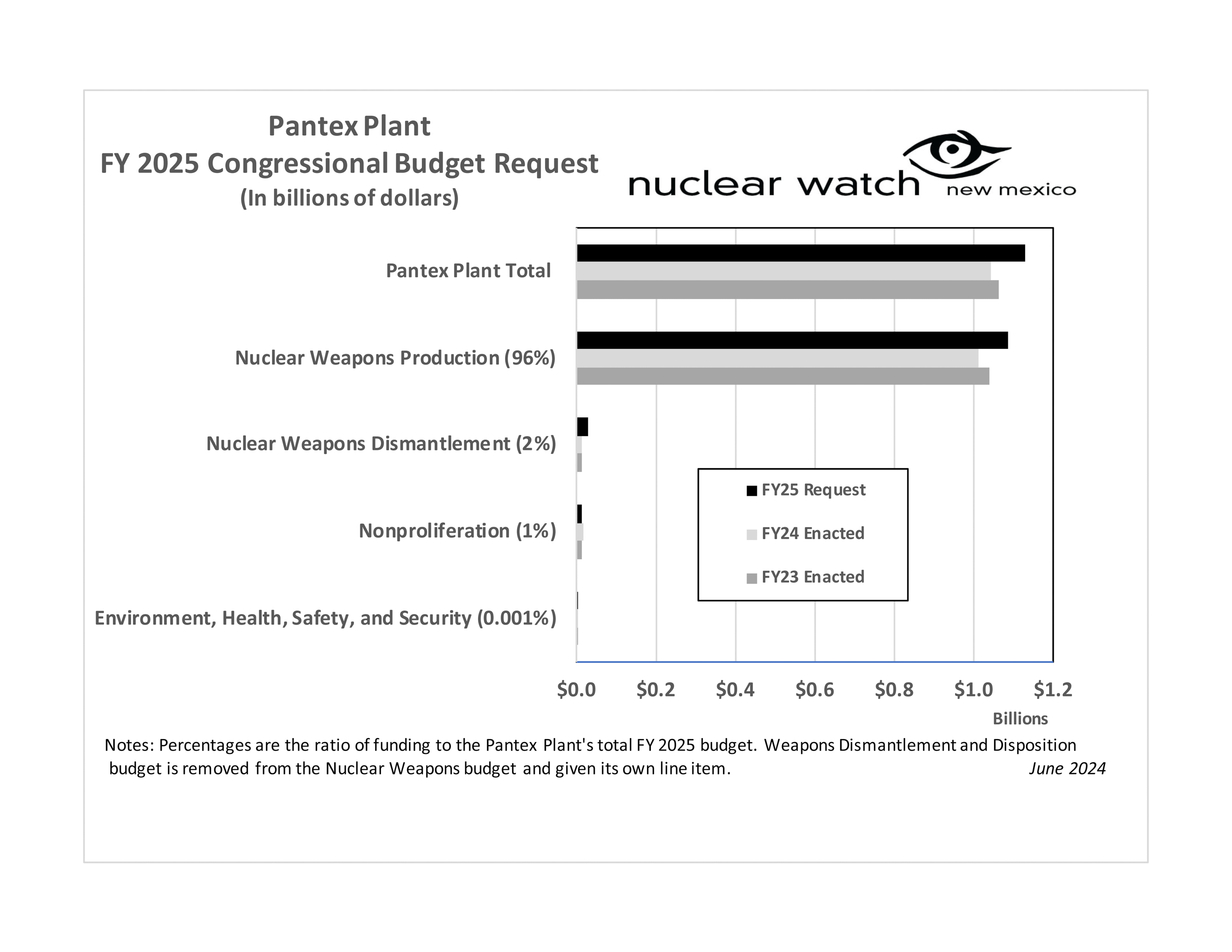
Livermore FY26 Budget Request (Courtesy of Tri-Valley CAREs)
Map of “Nuclear New Mexico”
In 1985, US President Ronald Reagan and Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev declared that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought.”

NEW & UPDATED
4 things to know about the end of the U.S.-Russia nuclear arms treaty
“For the first time in decades, there are no limits on the world’s largest nuclear arsenals. Congress must act now.”
By Austin Headrick, American Friends Service Committee | February 4, 2026 afsc.org
The world changed forever in August 1945, when the United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing an estimated 110,000 to 210,000 people. Scientists, activists, policymakers, and peacebuilders—including organizers at AFSC—have spent the decades since calling for disarmament and an end to all nuclear threats. One crucial result of that work was arms control treaties that limited nuclear arsenals.
But now, that work is being unraveled. On Feb. 5, 2026, the last remaining U.S.-Russia nuclear arms reduction treaty, expired. The New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START) had placed limits on deployed nuclear weapons and created channels for inspections and monitoring.
With the end of the treaty, the guardrails that create transparency and prevent a nuclear arms race end.
Here is what you need to know:
1. The U.S. and Russia hold nearly all the world’s nuclear weapons.
The United States and Russia together possess almost 90% of the world’s nuclear weapons. That is why New START matters even to people far from Washington and Moscow. A world with no limits on the two largest nuclear stockpiles is a more dangerous world.
Without New START, there would be no legally binding guardrails on the two countries’ long-range nuclear weapons for the first time since the first U.S.-Soviet arms control agreements in the early 1970s.
And the risk is not only long-term nuclear development. Without limits, either side could increase the number of nuclear weapons ready to launch relatively quickly by “uploading” additional warheads onto existing missiles, which can fuel pressure for the other side to respond.
2. Arms control makes everyone safer.
New START capped the U.S. and Russia at 1,550 deployed nuclear weapons and limited deployed delivery systems, with an overall limit on launchers and bombers. Those numbers are more than technical details. They limit how many weapons can be used quickly in a crisis.
Continue reading
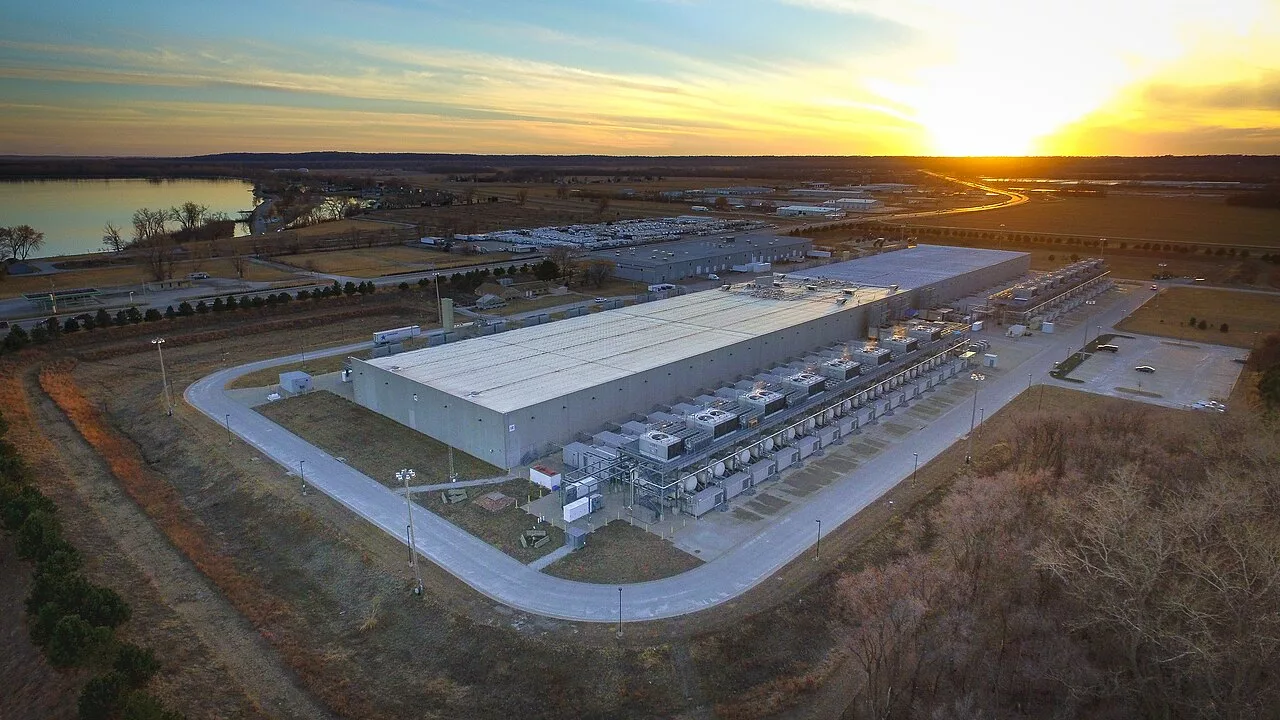
Los Alamos confirms UMich data center to be used for nuclear weapons research
“A representative of Los Alamos National Laboratory confirmed nuclear weapons research will be a priority for its portion of the data center it intends to construct in collaboration with the University of Michigan in Ypsilanti Township.”
By Glenn Hedin, The Michigan Daily | January 30, 2026 michigandaily.com
Patrick Fitch, deputy laboratory director for science, technology, and engineering at Los Alamos, was present at the University’s open house on the project in Ypsilanti Thursday. When The Michigan Daily asked if Los Alamos intended to use its portion of the data center to support nuclear weapons research, Fitch said yes.
“The short answer is yes, because aspects of a nuclear weapon is key to our simulation expertise,” Fitch said. “We want this loop to include large investments in national security, so that spins back into the basic science, and what we learn here — that list of non-nuclear weapons stuff — spins into nuclear weapons.”
The proposed data center has garnered significant opposition from Ypsilanti residents and U-M community members who worry about its potential to negatively impact the surrounding environment and electrical grid, as well the possibility that the facility could be used in the development of nuclear weapons. The University has maintained the facility will not “manufacture” nuclear weapons.
Some activists consider this statement misleading, as data centers are generally used for computing activities and not manufacturing. However, their computing capabilities could be used to support nuclear research in other ways, including in the production of plutonium pits, which serve as the cores of nuclear weapons. While plutonium pits need not be located at a data center, their development requires intensive computing power. Los Alamos has operated under federal directive to modernize the United State’s nuclear arsenal through the development of these pits since 2018.
*The featured image differs from the article photo due to usage rights. Photo: Google Data Center, Council Bluffs Iowa (49062863796).jpg
chaddavis.photography from United States, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Barring last-minute nuclear deal, US and Russia teeter on brink of new arms race
SUMMARY:
• New START treaty set to expire on February 5
• Trump hasn’t responded to Putin’s offer to extend missile limits
• End in sight to more than 50 years of mutual constraints
• Chinese build-up leaves US facing two big nuclear rivals
By Mark Trevelyan and Jonathan Landay | REUTERS, January 29, 2026 reuters.com
LONDON/WASHINGTON, Jan 30 (Reuters) – The United States and Russia could embark on an unrestrained nuclear arms race for the first time since the Cold War, unless they reach an eleventh-hour deal before their last remaining arms control treaty expires in less than a week.
The New START treaty is set to end on February 5. Without it, there would be no constraints on long-range nuclear arsenals for the first time since Richard Nixon and Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev signed two historic agreements in 1972 on the first-ever trip by a U.S. president to Moscow.
It is now 85 seconds to midnight.
On January 27, 2026, the Doomsday Clock was set at 85 seconds to midnight, the closest the Clock has ever been to midnight in its history.
The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists’ Science and Security Board (SASB), which sets the Clock, called for urgent action to limit nuclear arsenals, create international guidelines on the use of AI, and form multilateral agreements to address global biological threats.
Partnership for a World without Nuclear Weapons: Statement on the Fifth Anniversary of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
ALBUQUERQUE—Wednesday, January 21, 2026—The Partnership for a World without Nuclear Weapons released a statement in recognition of the fifth anniversary of the entry into force of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons:
We hope for its further expansion through additional ratifications, now that a majority of the world’s countries have signed the Treaty. In July 2017, the Vatican was the first nation-state to sign and ratify the Treaty as part of its “unwavering commitment to the total elimination of nuclear weapons.”
We condemn the fact that the nuclear weapons powers have never honored their long-held obligations under the 1970 NonProliferation Treaty to enter serious negotiations leading to global nuclear disarmament.
In contrast, the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons was a great step toward the light of peace. The nuclear-armed states have a moral obligation to hear the voices of the majority of the world, and to listen to those who face the threat of annihilation due to the reckless decisions of any one of their nine leaders. Russia’s nuclear saber-rattling over Ukraine makes this clear, while ongoing crises in the Middle East further escalate the risks. Meanwhile, the nuclear weapons powers are engaged in massive “modernization” programs, designed to keep nuclear weapons forever.
The international legal force of the nuclear weapons ban treaty is limited to those states that have formally ratified it. But its moral power does not recognize boundaries between nations, nor lines on a map. The moral power of this Treaty is global and universal. We hope and pray that it will exert moral pressure on the nuclear weapons states to finally honor their disarmament obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty.
On the fifth anniversary of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, we specifically call upon world leaders to demonstrate measurable progress toward nuclear disarmament. Eight decades of nuclear threats are far too long, as evidenced by the horrors documented by the atomic bombing museums in Japan. It is long past time for the nuclear weapons powers to begin to make tangible progress toward that end.
As our close colleague Robert McElroy, Cardinal of Washington, DC, declared last August in Hiroshima on the 80th anniversary of the atomic bombing:
“We refuse to live in a world of nuclear proliferation and risk-taking. We will resist, we will organize, we will pray, we will not cease, until the world’s nuclear arsenals have been destroyed.”
A Grave Problem with South Carolina’s New Nuclear Warhead
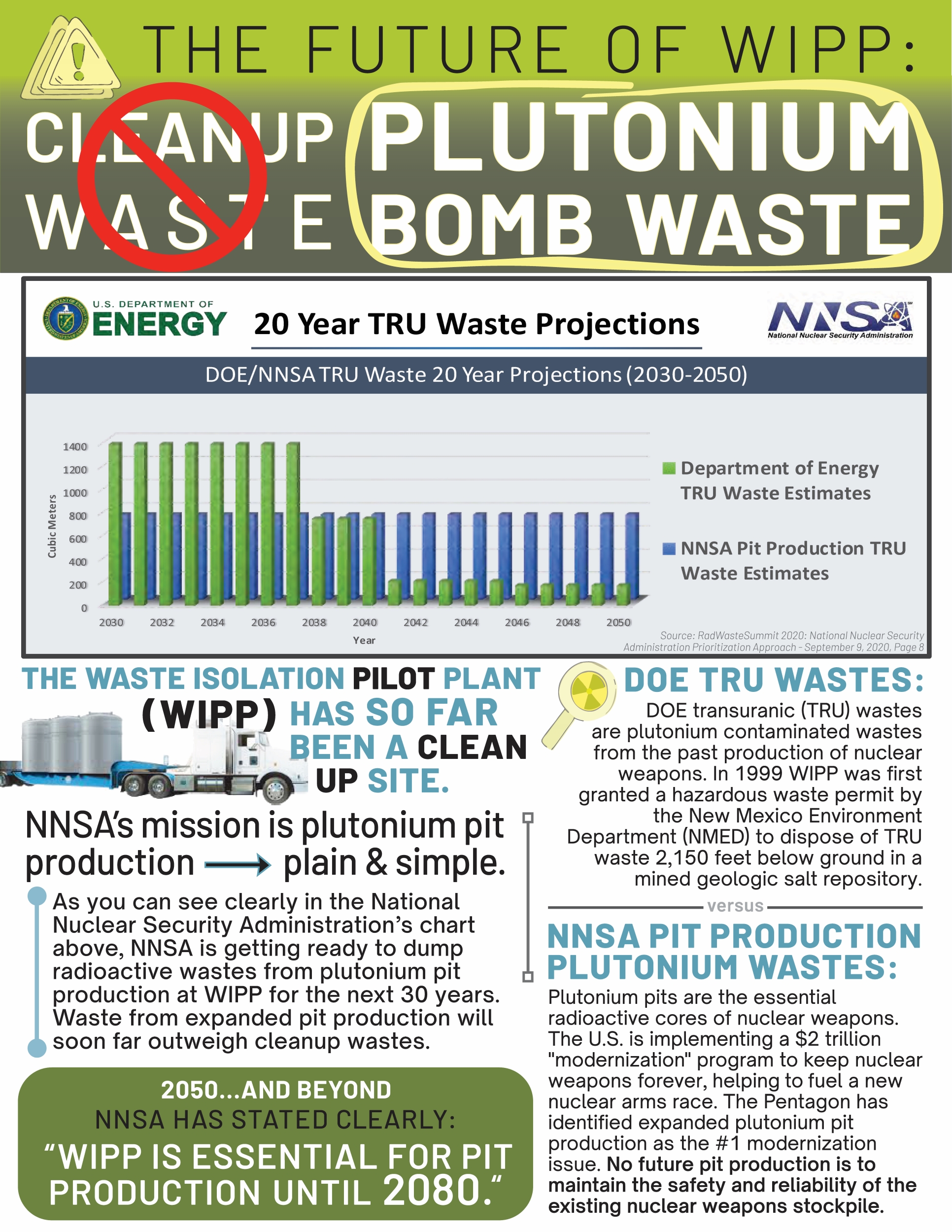
In South Carolina, contractors say new plutonium pit warhead waste will be shipped to New Mexico. Is it true?
“The coming showdown over SRNS’s TRU waste underscores what has long been a truism of the US nuclear weapons complex: that the government’s urgency to produce new weapons outstrips its commitment to plan and fund the cleanup of the sites across the American landscape that are contaminated while doing so.”
By Taylor Barnes | January 22, 2026 inkstickmedia.com
On a crisp evening last October, Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS), a federal contractor that hopes to manufacture thousands of cores for new nuclear warheads at a Cold War-era weapons plant in rural South Carolina, put on a public information session at a library in the town of North Augusta. The purpose of the event was to address any concern from locals that its plan to produce 50 plutonium pits per year for 50 years would leave toxic waste, including radioactive refuse known as TRU waste, in and around the 310-square-mile Savannah River Site (SRS) that people in towns like Allendale and Aiken find themselves neighboring.
The session included about 30 presenters whom SRNS employs. They handed out Halloween candy while standing beside posterboards laying out what they described as a “cradle-to-grave” process for TRU waste generated by producing those pits. They described a plan to store batches of radioactive waste for only one year in both existing and to-be-constructed buildings around an abandoned nuclear fuel plant at the SRS. The waste, according to contractor employees and a map they displayed, would then be transported in trucks along Interstate 20 through Atlanta, Birmingham, and Fort Worth before reaching southern New Mexico, where it would be buried in an 2,150-foot-deep salt mine called the Waste Isolation Pilot Project (WIPP). The 1976 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act requires the company to detail those steps, including, crucially, the final “disposition of such wastes,” in order to apply for a local permit to build and operate what SRNS says will be just temporary waste storage buildings at the plant site. An information sheet from SRNS said the company plans for the permit application to be submitted in January and for the new storage buildings to begin construction a year later.
Trump offers states a deal to take nuclear waste
“Governors would effectively be invited to compete for what the administration believes is a once-in-a-generation economic development prize in exchange for hosting the nation’s most politically and environmentally toxic byproduct.”
By Sophia Cai, E&E News by POLITICO | January 21, 2026 eenews.net
The Trump administration wants to quadruple America’s production of nuclear power over the next 25 years and is hoping to entice states to take the nuclear waste those plants produce by dangling the promise of steering massive investments their way.
President Donald Trump’s big bet on amping up nuclear production is not an easy feat, fraught with NIMBY concerns about safety and waste byproducts. The administration hopes to solve at least one of those issues — what to do with toxic nuclear waste — with a program they plan to roll out this week.
Governors would effectively be invited to compete for what the administration believes is a once-in-a-generation economic development prize in exchange for hosting the nation’s most politically and environmentally toxic byproduct.
Energy Secretary Chris Wright has already begun laying groundwork with governors. Over the last two weeks, Wright has met with at least two governors who have expressed interest, according to two officials familiar with the private meetings granted anonymity to discuss them.
Americans Across Party Lines Want the U.S. to Keep Nuclear Limits with Russia, New Poll Finds
YouGov poll commissioned by ReThink Media and the Nuclear Threat Initiative.
“As the last remaining U.S.-Russia nuclear limitations treaty expires on Feb. 5, an overwhelming majority of Americans (91 percent) say the United States should negotiate a new agreement with Russia to either maintain current limits on nuclear weapons or further reduce both countries’ arsenals.”
Nuclear Threat Initiative | January 21, 2026 nti.org
 The poll of 1,000 registered voters also finds that the vast majority of Americans—including 85 percent of those who voted for President Trump—believe the president should agree to Russia’s proposal to continue abiding by the limits imposed by the New START treaty for at least another year after the treaty expires. In addition, 72 percent of registered voters believe that removing all nuclear limits on U.S. and Russian nuclear arsenals would make the United States less secure.
The poll of 1,000 registered voters also finds that the vast majority of Americans—including 85 percent of those who voted for President Trump—believe the president should agree to Russia’s proposal to continue abiding by the limits imposed by the New START treaty for at least another year after the treaty expires. In addition, 72 percent of registered voters believe that removing all nuclear limits on U.S. and Russian nuclear arsenals would make the United States less secure.
When New START expires, it will be the first time in decades that there are no limits capping the number of nuclear weapons for the world’s two largest arsenals. Together, the U.S. and Russia own almost 90 percent of all nuclear weapons in the world.
President Trump recently said he intends to negotiate a better agreement with Russia after New START expires. Previously, he warned that “when you take off nuclear restrictions – that’s a big problem” and made favorable comments about Russia’s one-year offer to voluntarily maintain the treaty’s limits. He repeatedly has warned of the threat posed by nuclear weapons. However, his administration has not yet taken concrete actions to secure a new nuclear limitations agreement with Russia.
Palomares: Reflections of an American, sixty years later
This past Saturday marked 60 years since the 1966 Palomares mid-air crash that left plutonium contamination scattered around the Spanish village. Dr. Michael E. Ketterer, Professor Emeritus of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Northern Arizona University in Flagstaff, AZ, has authored “Palomares: Reflections of an American, sixty years later.” See his English language version here and below and the Spanish version here.
By Michael Ketterer, elDiario | January 17, 2026 eldiario.es

By U.S. Navy, Courtesy of the Natural Resources Defense Council – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by EH101 using CommonsHelper., The original uploader was Asterion at English Wikipedia., 31 May 2007 (original upload date), Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=2630293
During the early morning hours of January 17, 1966, the six-year-old author was in his bed, asleep in the Buffalo, New York suburb of North Tonawanda. During those very same moments, a crash took place between two US planes: a B-52 bomber and a fully loaded KC-135, which were in the midst of refueling the bomber in-flight. The B-52 was crossing the Iberian Peninsula that morning as part of US Air Force’s Strategic Air Command’s daily routes, performing vigilance on the Soviet Union. Three thermonuclear bombs fell to the land, and a fourth fell into the sea, after the collision in the skies over Palomares, a small village located about two kilometers from the Mediterranean, in the province of Almeria, Andalucía in southeastern Spain.
All of that happened before I got out of bed that day.
Two of the bombs were destroyed upon impact, although neither produced a nuclear explosion. Instead, several kilograms of plutonium (Pu) were dispersed on a windy day, onto several square kilometers of the tomato fields and residential zones of Palomares. An additional bomb was found by a local resident; fortunately, it wasn’t significantly damaged since its parachute had opened. On the other hand, the fourth bomb appeared to have been lost in the Mediterranean, and very soon, that was obviously true. The US Air Force’s top priority quickly became to use whatever resources and heroes that were available, for an urgent mission: find the lost bomb before the Soviets could do so. The search and recovery of the bomb became the success story, and the history that was told. That was the lesson learned from Palomares, among the two governments, their military forces, and in the press. The photos of the military commanders from both countries posing with the recovered bomb aboard the USS Petrel are some of the most famous Internet images of Palomares.
Watch BOMBSHELL on PBS American Experience — streaming across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App!
The wait is over! BOMBSHELL is available NOW on PBS American Experience — and will be streaming simultaneously across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App.
BOMBSHELL examines how the U.S. government manipulated public opinion through propaganda and censorship to justify the use of nuclear weapons and to minimize the human toll. Against this powerful machinery, a small group of journalists—including a Black pool reporter, a Japanese American staffer, a Japanese photographer, and a freelance magazine writer—identified gaps in the official narrative and courageously reported on the human consequences of the atomic bombings.
The Wall Street Journal described BOMBSHELL as offering “lessons for our own age of ascendant AI,” while Foreign Policy called it “provocative history that brings to life the dangers that arise when government secrecy and control overwhelm press freedom.”
New Mexico, Department of Energy at odds over cleanup halt at LANL waste site
In a December public meeting, the field office’s manager indicated approval from the Environment Department likely wasn’t needed to defer the study and cleanup of Area C. According to the compliance decree, “NMED approval is not required” in several cases to change the status of an area to deferred, as long as the Department of Energy complied with other requirements.
Environment Department spokesperson Drew Goretzka wrote in an email to The New Mexican a site can be deferred in one of four cases, including if it is involved in active operations and if the amount of time needed for deferment is assessed.
The department doesn’t agree those requirements have been met, Goretzka wrote, “resulting in a breach of the Consent Order.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | January 9, 2026 santafenewmexican.com
 The U.S. Department of Energy has put cleanup of a hazardous waste disposal site at Los Alamos National Laboratory on hold, a decision that seems to have drawn the ire of the New Mexico Environment Department.
The U.S. Department of Energy has put cleanup of a hazardous waste disposal site at Los Alamos National Laboratory on hold, a decision that seems to have drawn the ire of the New Mexico Environment Department.
The state last year was planning to hold a public hearing in early 2026 on how to handle legacy waste left behind at Material Disposal Area C, according to a letter from an official in the Hazardous Waste Bureau.
The Department of Energy, however, had already made up its mind: Any corrective actions at the site would have to wait due to ramped-up operations near Area C. The public hearing is now on hold until the conflict over the deferment of corrective actions is settled, according to an Environment Department spokesperson.
The 11-acre waste site, in use from 1948 to 1974, is located within Technical Area 50 along Pajarito Road. Its six disposal pits were used for various types of waste, including radioactive materials and heavy metals.
CRITICAL EVENTS
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Nothing Found
It seems we can’t find what you’re looking for. Perhaps searching can help.
Waste Lands: America’s Forgotten Nuclear Legacy
The Wall St. Journal has compiled a searchable database of contaminated sites across the US. (view)
Related WSJ report: https://www.wsj.com
New Nuclear Media: Art, Films, Books & More
Time Zero: 05: The Lab (Part 01)
https://964f6bfd-c857-4667-8d59-615efbd0d7c4.libsyn.com/05-the-lab-part-01
“When the Manhattan Project arrived on the Pajarito Plateau in northern New Mexico, the land was not uninhabited. To establish the highly secretive Site Y, the United States military forcibly removed generations of Nuevomexicano ranchers and blocked regional Indigenous groups from accessing sacred sites. Almost immediately, the lab began detonating massive amounts of explosives, scarring the landscape. Military personnel regularly dumped nuclear waste into local canyon systems that ultimately flowed into the Rio Grande. When World War II came to a close, though, the lab did not.
More than eight decades later, an apocalyptic weapons factory—Los Alamos National Laboratory—still looms over the Pueblos and villages north of Santa Fe. Ninety miles south, Sandia National Laboratory and Kirtland Air Force Base store thousands of nuclear warheads beneath the city of Albuquerque. Both laboratories are expanding in scope and scale.
TELEVISION EVENT Trailer
Television Event is a documentary that follows the dramatic (and sometimes humorous) making and impact of the film The Day After. The 1983 film played a pivotal role in shifting public consciousness around nuclear weapons and, ultimately, President Reagan’s policies. It’s a reminder on the power of art and storytelling to create meaningful change.
The documentary was also reviewed in The New York Times: https://www.nytimes.com/2025/05/30/movies/the-day-after-documentary-television-event.html
More:
In 2023 a book was publishedd about the making of “The Day After”, read the review in Arms Control Today: https://www.armscontrol.org/act/2024-03/book-reviews/apocalypse-television-how-day-after-helped-end-cold-war
As well as: “‘The Day After’: The Arms Control Association’s Forgotten Role.” <https://www.armscontrol.org/act/2019-03/features/day-after-arms-control-associations-forgotten-role> It is a reminder that a few people can, with some luck and good timing, put big things into motion.