The National Environmental Policy Act requires the Los Alamos National Laboratory to periodically prepare a new “Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement (SWEIS) for Continued Operations.”
Please use NukeWatch NM’s recent extensive comments on the Lab’s new draft SWEIS as a resource and citizens’ guide to Lab issues.
Did you know, for example, that:
• LANL’s nuclear weapons production budget has doubled over the last decade?
• The Lab’s so-called cleanup plan is to “cap and cover” some 200,000 cubic yards of radioactive and toxic waste, leaving them permanently buried as a perpetual threat to groundwater?
• There is a planned intentional release of up to 30,000 curies of radioactive tritium gas, all without a public hearing?
Use our lengthy formal comments as a starting point, toolkit or resource for dissecting ongoing and future issues at LANL!
We encourage you to use our comments to ask for follow-up info, either from us here at NukeWatch or from the Lab, and to demand better accountability and transparency! Use as background or briefing material for local and congressional advocacy.
For example:
- Cite or excerpt our comments in future public processes under the National Environmental Policy Act. For example, we are expecting that a nationwide programmatic environmental impact statement for plutonium “pit” bomb core production will be announced soon, the result of a lawsuit in which NukeWatch led.
- Share with those organizing around stopping expanded plutonium pit production and advocating for genuine radioactive and toxic wastes cleanup.
- Learn about LANL’s proposed electrical transmission line across the environmentally and culturally sensitive Caja del Rio and alternatives that were not considered.
- The National Environmental Policy Act itself is under assault by the Trump Administration. We expect environmental justice and climate change issues to be stripped from LANL’s final Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement. This needs to be resisted!
NukeWatch NM argued that the draft SWEIS should be withdrawn and a new one issued because:
• The NNSA has rigged the draft LANL Site-Wide EIS with three self-serving scenarios:
– Expanded nuclear weapons programs (contradictorily called the “No Action Alternative”).
– Yet more expanded nuclear weapons programs (“Modernized Operations Alternative”).
– Yet far more expanded nuclear weapons programs (“Expanded Operations Alternative”).
• A Reduced Operations Alternative must be included.
• The SWEIS’ fundamental justification for expanded nuclear weapons programs is “deterrence.” But “deterrence” has always included nuclear warfighting capabilities that could end human civilization overnight.
• The SWEIS purports to align with U.S. obligations under the 1970 NonProliferation Treaty. That is demonstrably false.
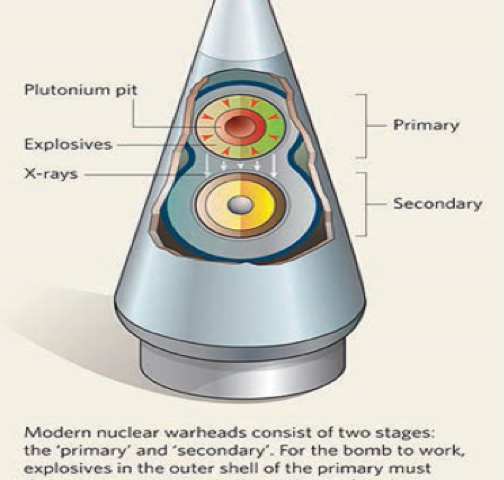
• Future plutonium pit production is NOT to maintain the safety and reliability of the existing nuclear weapons stockpile. Instead, it is for new-design nuclear weapons that could lower confidence in stockpile reliability and/or prompt a return to testing.
• The SWEIS’ No-Action Alternative violates the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA).
• The legally required programmatic environmental impact statement on pit production should be completed first, followed by the LANL SWEIS.
• Plutonium pit reuse should be analyzed as a credible alternative to pit production.
• A recent proposal for a data center at LANL is not in the SWEIS. It raises huge issues of future water and electrical use, the appropriateness of commercial interests at a federal lab, and the possible fusion of artificial intelligence and nuclear weapons command and control.
• Recent Executive Orders could strip the final SWEIS of environmental justice and climate change analyses. This must have clarification.
• Planned tritium releases should be fully analyzed.
• The Electrical Power Capacity Upgrade should be analyzed will all credible alternatives.
• The proposed BioSafety Level-3 facility must have its own standalone EIS.
• All Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board concerns should be addressed and resolved.
• Genuine comprehensive cleanup should be a preferred alternative.
• A new SWEIS should follow a new overdue Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis.