A Grave Problem with South Carolina’s New Nuclear Warhead
In South Carolina, contractors say new plutonium pit warhead waste will be shipped to New Mexico. Is it true?
“The coming showdown over SRNS’s TRU waste underscores what has long been a truism of the US nuclear weapons complex: that the government’s urgency to produce new weapons outstrips its commitment to plan and fund the cleanup of the sites across the American landscape that are contaminated while doing so.”
By Taylor Barnes | January 22, 2026 inkstickmedia.com
On a crisp evening last October, Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS), a federal contractor that hopes to manufacture thousands of cores for new nuclear warheads at a Cold War-era weapons plant in rural South Carolina, put on a public information session at a library in the town of North Augusta. The purpose of the event was to address any concern from locals that its plan to produce 50 plutonium pits per year for 50 years would leave toxic waste, including radioactive refuse known as TRU waste, in and around the 310-square-mile Savannah River Site (SRS) that people in towns like Allendale and Aiken find themselves neighboring.
The session included about 30 presenters whom SRNS employs. They handed out Halloween candy while standing beside posterboards laying out what they described as a “cradle-to-grave” process for TRU waste generated by producing those pits. They described a plan to store batches of radioactive waste for only one year in both existing and to-be-constructed buildings around an abandoned nuclear fuel plant at the SRS. The waste, according to contractor employees and a map they displayed, would then be transported in trucks along Interstate 20 through Atlanta, Birmingham, and Fort Worth before reaching southern New Mexico, where it would be buried in an 2,150-foot-deep salt mine called the Waste Isolation Pilot Project (WIPP). The 1976 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act requires the company to detail those steps, including, crucially, the final “disposition of such wastes,” in order to apply for a local permit to build and operate what SRNS says will be just temporary waste storage buildings at the plant site. An information sheet from SRNS said the company plans for the permit application to be submitted in January and for the new storage buildings to begin construction a year later.
Trump offers states a deal to take nuclear waste
“Governors would effectively be invited to compete for what the administration believes is a once-in-a-generation economic development prize in exchange for hosting the nation’s most politically and environmentally toxic byproduct.”
By Sophia Cai, E&E News by POLITICO | January 21, 2026 eenews.net
The Trump administration wants to quadruple America’s production of nuclear power over the next 25 years and is hoping to entice states to take the nuclear waste those plants produce by dangling the promise of steering massive investments their way.
President Donald Trump’s big bet on amping up nuclear production is not an easy feat, fraught with NIMBY concerns about safety and waste byproducts. The administration hopes to solve at least one of those issues — what to do with toxic nuclear waste — with a program they plan to roll out this week.
Governors would effectively be invited to compete for what the administration believes is a once-in-a-generation economic development prize in exchange for hosting the nation’s most politically and environmentally toxic byproduct.
Energy Secretary Chris Wright has already begun laying groundwork with governors. Over the last two weeks, Wright has met with at least two governors who have expressed interest, according to two officials familiar with the private meetings granted anonymity to discuss them.
Americans Across Party Lines Want the U.S. to Keep Nuclear Limits with Russia, New Poll Finds
YouGov poll commissioned by ReThink Media and the Nuclear Threat Initiative.
“As the last remaining U.S.-Russia nuclear limitations treaty expires on Feb. 5, an overwhelming majority of Americans (91 percent) say the United States should negotiate a new agreement with Russia to either maintain current limits on nuclear weapons or further reduce both countries’ arsenals.”
Nuclear Threat Initiative | January 21, 2026 nti.org
 The poll of 1,000 registered voters also finds that the vast majority of Americans—including 85 percent of those who voted for President Trump—believe the president should agree to Russia’s proposal to continue abiding by the limits imposed by the New START treaty for at least another year after the treaty expires. In addition, 72 percent of registered voters believe that removing all nuclear limits on U.S. and Russian nuclear arsenals would make the United States less secure.
The poll of 1,000 registered voters also finds that the vast majority of Americans—including 85 percent of those who voted for President Trump—believe the president should agree to Russia’s proposal to continue abiding by the limits imposed by the New START treaty for at least another year after the treaty expires. In addition, 72 percent of registered voters believe that removing all nuclear limits on U.S. and Russian nuclear arsenals would make the United States less secure.
When New START expires, it will be the first time in decades that there are no limits capping the number of nuclear weapons for the world’s two largest arsenals. Together, the U.S. and Russia own almost 90 percent of all nuclear weapons in the world.
President Trump recently said he intends to negotiate a better agreement with Russia after New START expires. Previously, he warned that “when you take off nuclear restrictions – that’s a big problem” and made favorable comments about Russia’s one-year offer to voluntarily maintain the treaty’s limits. He repeatedly has warned of the threat posed by nuclear weapons. However, his administration has not yet taken concrete actions to secure a new nuclear limitations agreement with Russia.
Palomares: Reflections of an American, sixty years later
This past Saturday marked 60 years since the 1966 Palomares mid-air crash that left plutonium contamination scattered around the Spanish village. Dr. Michael E. Ketterer, Professor Emeritus of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Northern Arizona University in Flagstaff, AZ, has authored “Palomares: Reflections of an American, sixty years later.” See his English language version here and below and the Spanish version here.
By Michael Ketterer, elDiario | January 17, 2026 eldiario.es

By U.S. Navy, Courtesy of the Natural Resources Defense Council – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by EH101 using CommonsHelper., The original uploader was Asterion at English Wikipedia., 31 May 2007 (original upload date), Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=2630293
During the early morning hours of January 17, 1966, the six-year-old author was in his bed, asleep in the Buffalo, New York suburb of North Tonawanda. During those very same moments, a crash took place between two US planes: a B-52 bomber and a fully loaded KC-135, which were in the midst of refueling the bomber in-flight. The B-52 was crossing the Iberian Peninsula that morning as part of US Air Force’s Strategic Air Command’s daily routes, performing vigilance on the Soviet Union. Three thermonuclear bombs fell to the land, and a fourth fell into the sea, after the collision in the skies over Palomares, a small village located about two kilometers from the Mediterranean, in the province of Almeria, Andalucía in southeastern Spain.
All of that happened before I got out of bed that day.
Two of the bombs were destroyed upon impact, although neither produced a nuclear explosion. Instead, several kilograms of plutonium (Pu) were dispersed on a windy day, onto several square kilometers of the tomato fields and residential zones of Palomares. An additional bomb was found by a local resident; fortunately, it wasn’t significantly damaged since its parachute had opened. On the other hand, the fourth bomb appeared to have been lost in the Mediterranean, and very soon, that was obviously true. The US Air Force’s top priority quickly became to use whatever resources and heroes that were available, for an urgent mission: find the lost bomb before the Soviets could do so. The search and recovery of the bomb became the success story, and the history that was told. That was the lesson learned from Palomares, among the two governments, their military forces, and in the press. The photos of the military commanders from both countries posing with the recovered bomb aboard the USS Petrel are some of the most famous Internet images of Palomares.
Watch BOMBSHELL on PBS American Experience — streaming across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App!
The wait is over! BOMBSHELL is available NOW on PBS American Experience — and will be streaming simultaneously across all PBS-branded platforms, including YouTube, PBS.org and the PBS App.
New Mexico, Department of Energy at odds over cleanup halt at LANL waste site
In a December public meeting, the field office’s manager indicated approval from the Environment Department likely wasn’t needed to defer the study and cleanup of Area C. According to the compliance decree, “NMED approval is not required” in several cases to change the status of an area to deferred, as long as the Department of Energy complied with other requirements.
Environment Department spokesperson Drew Goretzka wrote in an email to The New Mexican a site can be deferred in one of four cases, including if it is involved in active operations and if the amount of time needed for deferment is assessed.
The department doesn’t agree those requirements have been met, Goretzka wrote, “resulting in a breach of the Consent Order.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | January 9, 2026 santafenewmexican.com
 The U.S. Department of Energy has put cleanup of a hazardous waste disposal site at Los Alamos National Laboratory on hold, a decision that seems to have drawn the ire of the New Mexico Environment Department.
The U.S. Department of Energy has put cleanup of a hazardous waste disposal site at Los Alamos National Laboratory on hold, a decision that seems to have drawn the ire of the New Mexico Environment Department.
The state last year was planning to hold a public hearing in early 2026 on how to handle legacy waste left behind at Material Disposal Area C, according to a letter from an official in the Hazardous Waste Bureau.
The Department of Energy, however, had already made up its mind: Any corrective actions at the site would have to wait due to ramped-up operations near Area C. The public hearing is now on hold until the conflict over the deferment of corrective actions is settled, according to an Environment Department spokesperson.
The 11-acre waste site, in use from 1948 to 1974, is located within Technical Area 50 along Pajarito Road. Its six disposal pits were used for various types of waste, including radioactive materials and heavy metals.
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: January 2026
American imperialism:
On the U.S. raid on Venezuela to oust Nicolás Maduro, the Venezuelan president:
Stephen Miller, Donald Trump’s deputy chief of staff for policy and homeland security advisor, told CNN’s Jake Tapper on Monday January 5, 2026:
“We live in a world in which you can talk all you want about international niceties and everything else, but we live in a world—in the real world, Jake—that is governed by strength, that is governed by force, that is governed by power. These are the iron laws of the world that have existed since the beginning of time.”
The “Donroe Doctrine” is a more aggressive Trumpian take on the 1823 Monroe Doctrine, a foreign policy approach focused on unilateral U.S. dominance in the Western Hemisphere. How far does this administration intend to force this new doctrine?
DOE now department of nuclear weapons and Venezuelan oil: The Trump administration engaged the Department of Energy (DOE) and Secretary Chris Wright to oversee the seizure and marketing of Venezuelan oil following the capture of Nicolás Maduro. The U.S. intends to control Venezuelan oil, aiming to sell 30–50 million barrels of accumulated, sanctioned crude to the American people.
Greenland:
Trump describes Greenland as an “absolute necessity” for national security and the defense of the Arctic.
U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent has said that the president believes Greenland is “essential for the Golden Dome missile shield.” https://www.wcvb.com/article/greenland-trump-explainer/70097863
Chicago Tribune Editorial: Tick, tick goes the Doomsday Clock
“It would be madness to resume nuclear testing, let treaties lapse and expand arsenals that already could wipe out the planet. Diplomacy worked for decades, mainly because of an understanding that avoiding nuclear war was essential to humanity’s future. Today’s global leaders need to start acting accordingly.”
By The Editorial Board | Chicago Tribune – January 6, 2026 chicagotribune.com
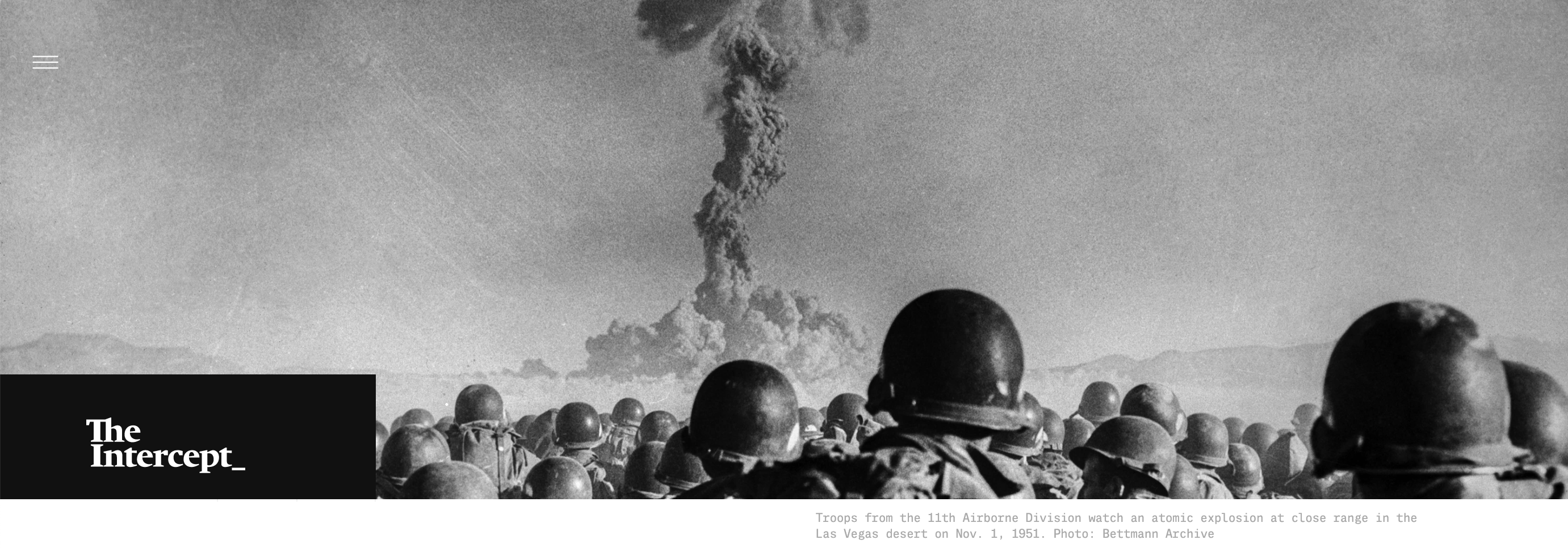
 This month, the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists at the University of Chicago is scheduled to announce whether the hands of its famous Doomsday Clock will move closer to midnight. It feels like a safe bet that Armageddon is drawing nearer today than it has in a long, long time.
This month, the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists at the University of Chicago is scheduled to announce whether the hands of its famous Doomsday Clock will move closer to midnight. It feels like a safe bet that Armageddon is drawing nearer today than it has in a long, long time.
The Doomsday Clock started almost 80 years ago, when physicists who developed the Bomb grew alarmed at its use against Japan to end World War II.
Between the late 1940s and the early 1990s, nuclear war wasn’t a remote possibility: It almost happened, repeatedly, as America and the Soviet Union fought the Cold War. Chicago’s atomic scientists moved the hands of their clock from seven minutes to midnight at its start in 1947 to just two minutes to midnight as of 1953, when the U.S. and Soviets started testing enormously powerful hydrogen bombs.
*The image above differs from the article photo due to usage rights.
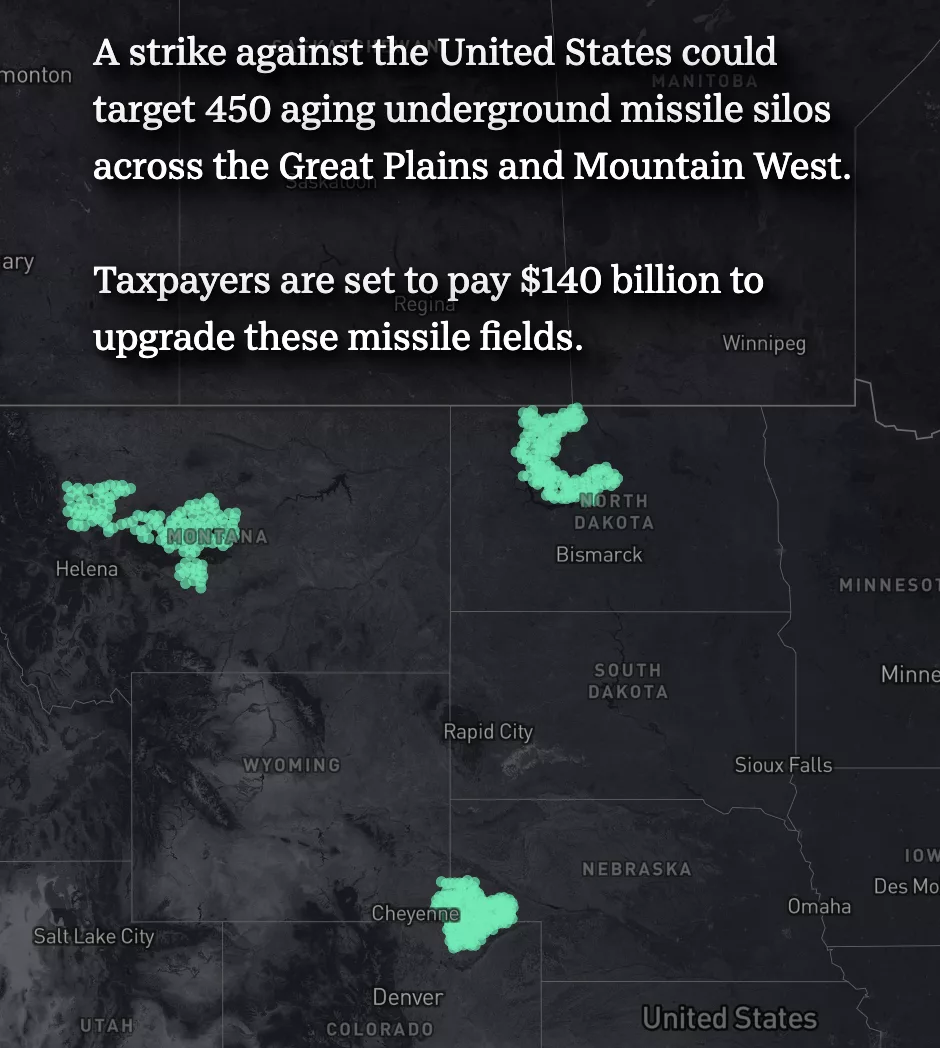
NEW INTERACTIVE PIECE from USA TODAY: THE NUCLEAR SPONGE — & Much More!
Screenshot from USA Today article January 5, 2026 usatoday.com/graphics/interactives/us-nuclear-weapons-expansion-fallout-map/
THE NUCLEAR SPONGE
Fallout maps show what could happen if America’s nuclear missile silos were attacked
By Davis Winkie, Ramon Padilla, Stephen Beard, Karina Zaiets and Carlie Procell, USA TODAY | usatoday.com
U.S. nuclear strategy revolves around the idea of the “triad.” Each of the military’s methods for delivering a nuclear strike represents a leg – the air leg (bomber planes), the sea leg (missile submarines) and the land leg (silo-based intercontinental ballistic missiles).
In recent years, arms control advocates have argued that the land leg of the triad is useless compared with its peers and makes the world a more dangerous place. The root of the debate is the vulnerability of the underground silos: An enemy can – and probably would – destroy them in a first strike against the United States.
Those opposed to land-based nuclear missiles, such as Daryl Kimball of the Arms Control Association, say that this vulnerability would push the president into a “use-or-lose logic” if he or she believed the United States were under nuclear attack. If the president launched a nuclear missile counterattack under a false warning, the results would be catastrophic.
The naysayers also highlight the cost of replacing the existing 1970s-vintage fleet of 400 Minuteman III missiles with the under-development Sentinel missiles, which the Air Force estimated will cost $140 billion (an increase from a 2020 estimate of $78 billion).
Warren, Garamendi Press Energy Secretary on Mismanagement and Taxpayer Waste in Plutonium Pit Production Program
Without transparency, accountability, and action around the pit program, the Department of Energy may be enabling the waste of billions of taxpayer dollars.
“In rushing to production, NNSA has developed an excessively risky program structure, with management concerns around fundamental aspects such as the cost and schedule.”
Sen. Elizabeth Warren and Rep. John Garamendi | warren.senate.gov – garamendi.house.gov
Washington, D.C. — In a new letter, U.S. Senator Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) and Representative John Garamendi (D-Calif.), both members of their respective Armed Services Committees and of the Nuclear Weapons and Arms Control Working Group, are urging Department of Energy Secretary Chris Wright to review the scope of and the need for the nuclear weapon plutonium pit production program, and pause the program’s Savannah River site until the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has established guardrails to prevent additional waste of taxpayer funds.
In August, the Department of Energy (DOE) launched a special study into NSSA’s leadership and management of the plutonium pit production mission. The lawmakers believe that, if properly conducted, the study will find that years of mismanagement have put billions of taxpayer dollars at risk with an unrealistic pit production schedule and goals.
“The Trump administration is blindly spending tens of billions of dollars to produce plutonium pits for nuclear weapons without a real budget or plan,” said Senator Warren. “This program is already years behind schedule and over budget, and Congressman Garamendi and I are urging the Secretary of Energy to conduct a vigorous review to rein in years of waste and mismanagement.”
“For years I have called for Congress to take action to fix the failing plutonium modernization effort. Congress has continued to pour billions of dollars into efforts to restart production with arbitrary targets,” said Congressman Garamendi. “This letter cuts to the core of the matter and asks necessary questions of NNSA, including about the questionable management and faulty assumptions underlying the program. I eagerly await their response, along with the results of the Department of Energy’s 120-day special investigation.”
The lawmakers raise concerns about how, years into this program, it is still unclear what the pit production program’s schedule and full cost will be. The Government Accountability Office recommended NNSA create a master schedule to comply with its best practices, but the agency has yet to produce one…
Livermore Lab Uses Trump Executive Order Gutting Environmental Laws to Push Through Enhanced Plutonium Utilization without Public Input
A November notice from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) erases the previously announced public involvement requirement and thereby fast-tracks increased plutonium use at its Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory after decades of limits protected the public from potential risks.
News from our friends at Tri-Valley CAREs | trivalleycares.org
 First announced In January 2025, the NNSA proposal for “Enhanced Plutonium Facility Utilization” at the Livermore Lab was to include a “Draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement” (SEIS) according to its Federal Register Notice. It specifically stated that, “NNSA will prepare a Draft SEIS. NNSA will announce the availability of the Draft SEIS in the Federal Register and local media outlets. NNSA will hold one or more public hearings for the Draft SEIS. Any comments received on the Draft SEIS will be considered and addressed in the Final SEIS.”
First announced In January 2025, the NNSA proposal for “Enhanced Plutonium Facility Utilization” at the Livermore Lab was to include a “Draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement” (SEIS) according to its Federal Register Notice. It specifically stated that, “NNSA will prepare a Draft SEIS. NNSA will announce the availability of the Draft SEIS in the Federal Register and local media outlets. NNSA will hold one or more public hearings for the Draft SEIS. Any comments received on the Draft SEIS will be considered and addressed in the Final SEIS.”
Now the agency has reneged on this promise, instead fast-tracking directly to a Final SEIS and a Record of Decision without any further opportunity for public input!
DOE using its own land to help pair AI centers, nuclear reactors
The Energy Department wants to build nuclear-powered artificial intelligence data centers on federal land using new public-private partnerships.
By Kelly Livingston and Allison Mollenkamp | rollcall.com
Co-locating advanced nuclear reactors with data centers on DOE sites is part of the Trump administration’s bid to accelerate the development of both technologies, sources say, as research efforts tease out their “symbiotic relationship.” But questions remain about how these projects could affect local communities and the actual timeline for bringing more nuclear power online.
DOE first announced its intention to use federal land for data center development and co-location in early April with a request for information to gauge industry interest. According to the RFI, the department intends to begin construction at the selected DOE sites by the end of the year, with operations beginning by the end of 2027.
Lawmakers introduce bill to cancel $100 million University of Michigan data center grant
The University of Michigan has failed to act transparently or coordinate with local officials on data center project, says state Rep. Jimmie Wilson Jr.
“Eighty-four percent of the lab’s 2026 budget request is for nuclear weapons work, according to the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.”
By Brian Allnutt | planetdetroit.org
Michigan State Rep. Jimmie Wilson Jr. (D-Ypsilanti) introduced legislation Thursday to rescind a $100 million state grant for the University of Michigan and Los Alamos National Laboratory’s data center project in Ypsilanti Township.
The university has been unwilling to offer community benefits or consider another site for the data centers, Wilson said.
“The University of Michigan has not been fully transparent with this project and has refused to collaborate with the Ypsilanti Township officials throughout this planning process,” Wilson said in a statement to Planet Detroit.
Ypsilanti Township officials say the university misled state officials about the size of the project when applying for the $100 million grant, and passed a resolution earlier this month seeking to unwind the funding.
…
Petition highlights Los Alamos’ nuclear weapons work
A petition signed by over 700 University of Michigan employees, faculty, and students urges the school to cancel the $1.2 billion project and halt its partnership with Los Alamos, arguing the project will harm the environment, negatively impact low-income communities, and help advance harmful nuclear weapon and artificial intelligence technologies.
Catholic bishops remind political leaders that nuclear weapons are immoral
On August 5, the two American Cardinals present in Japan delivered stirring words from the Hiroshima World Peace Memorial Cathedral, whose bricks contain ashes from the atomic bomb…
“If our gathering here today is to mean anything, it must mean that in fidelity to all those whose lives were destroyed or savagely damaged on August 6, 80 years ago, we refuse to live in such a world of nuclear proliferation and risk-taking,” said Cardinal Robert McElroy of Washington. “We will resist, we will organize, we will pray, we will not cease, until the world’s nuclear arsenals have been destroyed.”
By John Wester | thebulletin.org
In August, a group of American Catholic Church leaders—including Cardinal Blase Cupich of Chicago, Cardinal Robert McElroy of Washington, DC, Archbishop Paul Etienne of Seattle, and me, the Archbishop of Santa Fe—traveled to Japan to mark the 80th anniversary of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. There, we joined our Japanese counterparts—Bishop Mitsuru Shirahama of Hiroshima, Archbishop Emeritus Mitsuaki Takami of Nagasaki, and Archbishop Michiaki Nakamura of Nagasaki—in commemorating the destruction of their cities. Takami is a hibakusha (atomic bomb survivor); he was in his mother’s womb on August 9, 1945, when his city of Nagasaki was bombed. His maternal aunt and grandmother were both killed in the blast.
Eighty years have passed. But the existential threat posed by nuclear weapons is still with us—and it is growing worse every day. In 2019, Pope Francis elevated the Catholic Church beyond conditional acceptance of so-called deterrence. He declared that the mere possession of nuclear weapons is immoral. Nevertheless, the nuclear powers are now spending enormous sums of money on “modernization” that will keep nuclear weapons virtually forever. Meanwhile, in the United States, taxes are being cut to benefit the rich, and economic inequality and homelessness are exploding. This situation is deeply immoral and counter to the Catholic Church’s teachings on social justice.
SEE MORE ON SANTA FE ARCHBISHOP JOHN WESTER’S MONUMENTAL WORK ON NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT HERE:
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: December 2025
Nuclear weapons:
The government is running on a Continuing Resolution (CR) until the end of January. It’s possible to have another shutdown depending on how tough the Dems want to be. The legislative process is starting to move again, with the annual Defense Authorization Act up first and then appropriations. Both give funding increases to nuclear weapons programs, delivery systems and Trump’s “Golden Dome.”
Cost overruns in nearly all things remains the rule. Golden Dome could cost up to $4 trillion, be destabilizing and never be 100% effective. Putin has already taken steps to circumvent it and China may well be doing the same, particularly with hypersonic delivery systems. The arms race continues, likely to be accelerated by artificial intelligence as well.
Nuclear weapons testing: No specific new developments but this article by ex-LANL Director Sig Hecker is good:
| Lessons From Los Alamos |
| Last month, U.S. President Donald Trump rekindled a decades-old debate about nuclear testing. “Because of other countries testing programs,” he wrote on social media, “I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis…” A return to testing at this time would likely benefit U.S. adversaries more than it would the United States. Worse still, it might rekindle an even greater and broader arms race than in the first few decades of the Cold War. |
| Siegfried Hecker | Foreign Affairs |
| Read More |
Article continued:
“My greatest concern about resuming full-scale nuclear testing is that it will fuel another dangerous arms race at a time when global tensions among the great powers are high. Engaging in another arms race is contrary to Trump’s comment that “it would be great if we could all denuclearize, because the power of nuclear weapons is crazy.”
Instead of suggesting an immediate return to nuclear testing, then, Trump should focus on returning to arms control measures to ensure strategic stability with Russia and with China. Hopefully, these measures would lead to a reduction in U.S. and Russian nuclear forces and reduce incentives for China to increase its arsenal. For nuclear testing, he should help erect the highest possible barriers for any country to test by leading an effort to ratify the CTBT. To settle the question of evasion of low-yield tests or hydronuclear experiments, the president and his counterparts in Beijing and Moscow would need to show the political will to agree on a verifiable low-yield limit. That will almost surely require onsite inspections, which were demonstrated to be possible in 1988.
The bottom line is that even though the United States could derive important benefits from resumed nuclear testing, it would lose more than it stands to gain.”
MESSAGE OF HIS HOLINESS POPE LEO XIV FOR THE LIX WORLD DAY OF PEACE
“The idea of the deterrent power of military might, especially nuclear deterrence, is based on the irrationality of relations between nations, built not on law, justice and trust, but on fear and domination by force.”
From the Vatican, 8 December 2025, vatican.va
“In the relations between citizens and rulers, it could even be considered a fault not to be sufficiently prepared for war, not to react to attacks, and not to return violence for violence. Far beyond the principle of legitimate defense, such confrontational logic now dominates global politics, deepening instability and unpredictability day by day. It is no coincidence that repeated calls to increase military spending, and the choices that follow, are presented by many government leaders as a justified response to external threats. The idea of the deterrent power of military might, especially nuclear deterrence, is based on the irrationality of relations between nations, built not on law, justice and trust, but on fear and domination by force. “Consequently,” as Saint John XXIII had already written in his day, “people are living in the grip of constant fear. They are afraid that at any moment the impending storm may break upon them with horrific violence. And they have good reasons for their fear, for there is certainly no lack of such weapons. While it is difficult to believe that anyone would dare to assume responsibility for initiating the appalling slaughter and destruction that war would bring in its wake, there is no denying that the conflagration could be started by some chance and unforeseen circumstance.”
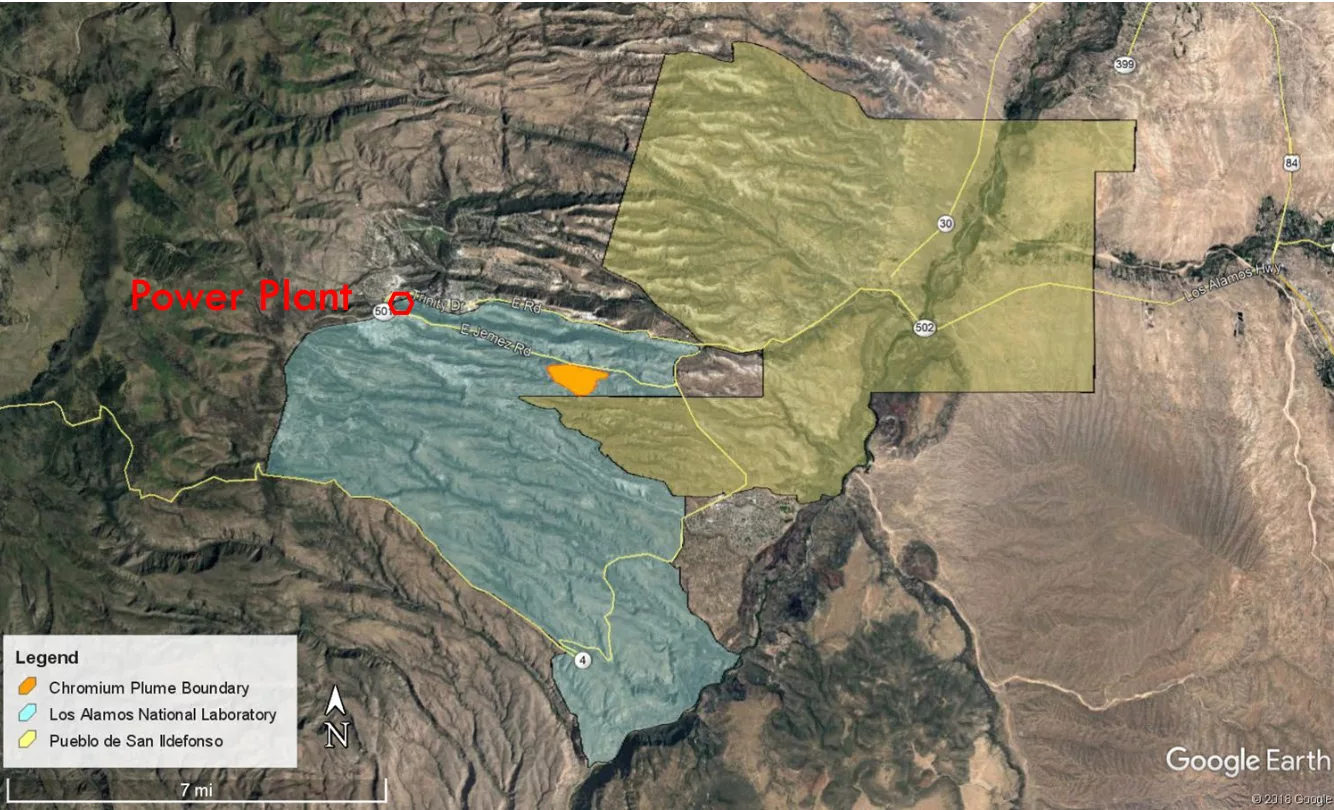
Federal official says further testing needed to determine LANL’s chromium plume migration
“Asked about the difference in opinion between the federal and state agency regarding the sampling, Kunkle said, ‘I can’t answer why we have the disconnect,’ adding that the only sampling done at that monitoring location, called zonal sampling, ‘is really not intended to predict the long term environment or trends in the regional aquifer. That really should be done only with monthly monitoring.’”
By Clara Bates cbates@sfnewmexican.com | santafenewmexican.com
A federal official says more testing is needed to determine whether a toxic chromium plume has seeped into San Ildefonso Pueblo’s groundwater, after the state called groundwater testing “conclusive evidence” the U.S. Department of Energy’s efforts at containment have been “inadequate.”
New Mexico’s Environment Department announced last month hexavalent chromium from Los Alamos National Laboratory had migrated to Pueblo de San Ildefonso land for the first time.
But Jessica Kunkle — the Los Alamos Field Office manager with the U.S. Department of Energy — told state lawmakers on the Radioactive and Hazardous Materials Committee on Monday afternoon the type of groundwater sampling conducted may not have told the whole story. The agency is working with partners to get a monitoring well installed “as quickly as possible,” she said, to get better data.
12/8/25 Los Alamos Legacy Cleanup & Hexavalent Chromium Plume Update
New Air Force Chief Boosts Nuclear Buildup, Moving Away From Deterrence, Experts Warn
“Gen. Ken Wilsbach promotes nuclear “recapitalization” in his first memo to the Air Force — fueling fear of a radical shift away from nukes acting solely as deterrence.”
By: Austin Campbell, The Intercept | theintercept.com

“We will advocate relentlessly for programs like the F-47, Collaborative Combat Aircraft as well as nuclear force recapitalization through the Sentinel program and the B-21,” Wilsbach wrote in a memo dated November 3, referring to planned upgrades to nuclear missiles and stealth bombers.
Experts who spoke to The Intercept said the language signals a doctrinal pivot, prioritizing displays of strength and the buildup of nuclear weaponry over internal repair — an approach that may appeal politically to the Trump administration and Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, but does little to ease the fatigue and distrust spreading among airmen.
…
The Sentinel program Wilsbach referenced is intended to modernize the land-based leg of the nuclear triad, with new missiles, hardened silos, and updated command-and-control infrastructure across missile fields in Wyoming, Montana, and North Dakota. It’s the Air Force’s planned replacement for aging Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile systems. The B-21 Raider is the next-generation stealth bomber designed to replace older strategic bombers like the B-2 and B-1, delivering both conventional and nuclear payloads.
Critics say framing these nuclear modernization efforts as “recapitalization” obscures the ethical and strategic implications of expanding U.S. nuclear capabilities amid declining morale and retention.
“You don’t ‘recapitalize’ genocidal weaponry.”
“The chief of staff’s emphasis on weaponry is disheartening. His description of nuclear weapon ‘recapitalization’ is an abomination of the English language. You don’t ‘recapitalize’ genocidal weaponry. Both the Sentinel missile program and the B-21 bomber are unnecessary systems that could cost as much as $500 billion over the next 20 years,” said William Astore, a retired Air Force lieutenant colonel and military historian.
Los Alamos National Lab (LANL) Town Hall December 3rd, 2025 – Thoughts from Nuclear Watch New Mexico:
The LANL Director mentioned Non-proliferation is a big part of their work. However, the Nuclear Nonproliferation program budget is a mere 6.5% of the total Lab budget (Nuclear Weapons is 84%, with a Billion dollar increase for FY26). https://nukewatch.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/FY26-Lab-Table-spreadsheets-Chart-1.pdf Nuclear Nonproliferation is a valuable program that LANL does well, and its funding should not be cut to provide more money for nuclear weapons production (literally the opposite of nonproliferation). The Nuclear Nonproliferation budget should be increased, especially if the Lab director agrees on its importance. NukeWatch NM is entirely supportive of LANL’s Sealed Sources program, which serves as the nation’s lead for collecting potentially dangerous radioactive materials that are no longer needed, securing them, and ensuring they don’t fall into the wrong hands, protecting communities and enhancing security.
On the discussion of AI missions at the lab:
The lab is partnering with NVIDIA for their hardware and ChatGPT/Open AI for their models. “The goal is to harness the power of the next evolution of high performance computing and apply it to our national security science and technology. Big development on this front is the “genesis” mission…” and in an answer to a question, want to “use artificial intelligence to [for example] help us develop the molecules that could deliver a therapeutic isotope to a cancer cell with high specificity so that when that undergoes radioactive decay the decay products basically kill the cancer cell but no surrounding tissue”
Again, the lab’s nuclear weapons budget ate up almost all else this year – how does the lab propose to work on this kind of work when its’ science budget is less than 1%? How will this advancement of AI be applied to our national security science and technology in terms of nuclear weapons? NukeWatch has serious concerns and questions regarding the tangible risks associated with integrating commercial AI infrastructure to be with active national security and nuclear defense programs. Beyond this, a $1.25 billion advanced computing campus is planned in Michigan to support far-away Los Alamos Lab in high-performance computing and AI research.
Continue reading
Nuclear Watch New Mexico Attends the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability Fall Meeting Nov. 21-23 in Las Vegas, Protesting Nuclear Testing in Nevada & Much More!
Sophie Stroud, Communications and Associate Director, represented NukeWatch at the Alliance for Nuclear Accountability's (ANA) fall meeting Nov. 21-23 in Las Vegas, hosted locally by Ian Zabarte, Principal Man of the Western Shoshone, Secretary of State of the Western Shoshone National Council, and Secretary of the Native Community Action Council (NCAC). The Nevada Test Site, now called the "Nevada National Security Site" and Yucca Mountain are both nuclear sites on Shoshone Land, and nuclear issues continue to threaten the Western Shoshone People. Yucca Mountain is Western Shoshone property with Constitutional protection, and the Department of Energy cannot prove ownership. ANA is a national network made up of 30 organizations whose members live near US nuclear bomb plants and their waste sites. The meeting was scheduled in coordination with the renowned International Uranium Film Festival — uraniumfilmfestival.org. As an organizer of the ANA Meeting as well as the International Uranium Film Festival, NCAC, composed of Shoshone and Paiute peoples, believe these films are a necessary part of the ongoing awareness, witness and resistance to nuclear war, human health and a livable Mother Earth. As 2025 marks the 80th anniversary of the first atomic bombings at the Trinity Site, Hiroshima, and Nagasaki, the world faces a new nuclear arms race that includes nuclear "modernization" of weapons, as well as the fast-tracking of uranium mining for nuclear-powered artificial intelligence data centers.
Friday morning, Nov. 21, the group traveled to the Mercury Exit gate of the Nevada Test Site with banners opposing nuclear weapons and nuclear testing. On October 29, before a meeting in South Korea with Chinese President Xi, President Donald Trump announced on social media that he “instructed the Department of War to start testing [U.S.] Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis” with Russia and China. The post contains various inaccuracies and ambiguity over whether he wants to resume underground nuclear explosive testing — an act the United States, Russia, and China have not undertaken in over 30 years — or continue testing of delivery systems.
Trump Orders Nuclear Weapons Testing for New Nuclear Arms Race
What might Project 2025 mean for N.M.? Non-nuclear cuts at national labs (Updated Dec 1, 2025)
“[The Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025] contemplates pulling funding from any work unrelated to nuclear weapons at Los Alamos National Laboratory, Sandia National Laboratories and sister facility Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California…in New Mexico, some say cutting the labs’ other scientific work would have a devastating economic effect on the state and could ultimately weaken the institutions as a whole.”
“It doesn’t take a nuclear physicist to realize that there could be massive layoffs if this proposal or these ideas were to reach fruition,” said Chandler, who worked in the employment arena for much of her time at the facility. “Now, that might expand the nuclear weapons program to some degree, but it’s not going to absorb the entire workforce.”
“Under the Biden administration, LANL has seen a massive growth in employment as the laboratory ramps up for its production of plutonium pits, the cores of nuclear bombs.”
By Gabrielle Porter and Alaina Mencinger gporter@sfnewmexican.com amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | Updated santafenewmexican.com
Project 2025 — the now-infamous blueprint for a conservative presidency that’s still publicly being held at arm’s length by Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump — proposes all sorts of sweeping policy recommendations, from promoting capital punishment to embracing mass deportations.
But tucked in the 922 pages of its report, “Mandate for Leadership 2025: The Conservative Promise,” is one recommendation that centers squarely on New Mexico.
Trump talk on nuke testing turns focus to New Mexico’s role in decades of blasts
Jay Coghlan, executive director of the nuclear watchdog group Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said Wright’s comments “somewhat” quelled his initial concerns about a renewed explosive nuclear testing program.
But he said claims Russia and China may be conducting small-scale tests known as hydronuclear tests — banned by the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, of which the United States, Russia and China are all signatories — continue to give him pause. He fears rumors about the low-yield tests in other nations could be used to justify a domestic return to testing.
“That, in effect, would give permission to the U.S. [to resume testing],” Coghlan said. “But that would be in violation of the norm of the CTBT.”
Three decades removed from the United States’ last nuclear test, a testing regimen would likely be expensive and time-consuming to start up, Coghlan argued, and could prompt other nuclear powers to follow suit.
It seems likely Russia, at least, would: Following Trump’s post, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced if the United States resumed explosive nuclear testing, the Eastern European nation would follow.
“Then everybody else is going to do it, or virtually everybody else will do it, every other nuclear weapons power,” Coghlan said. “I could just see India and Pakistan champing at the bit to test. And then, of course, there’s North Korea and China.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | November 30, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
It might not have as reverent a name as the Trinity Test or a litany of films made about it. But Project Gnome, a 1961 explosive nuclear test conducted near Carlsbad, is a relic of a bygone era in New Mexico and beyond.
In the 47 years between the Trinity Test and the end of the United States’ explosive nuclear testing in 1992, the nation would perform more than 1,000 such tests — more than any other nuclear nation — with most conducted in Nevada.
New Mexico might not have been the center of the nation’s testing efforts post-Trinity, which marked its 80th anniversary this year, but the state still played a role: Researchers from Sandia National Laboratories and Los Alamos National Laboratory helped design and conduct testing elsewhere, including at the Nevada Test Site and in the Marshall Islands.
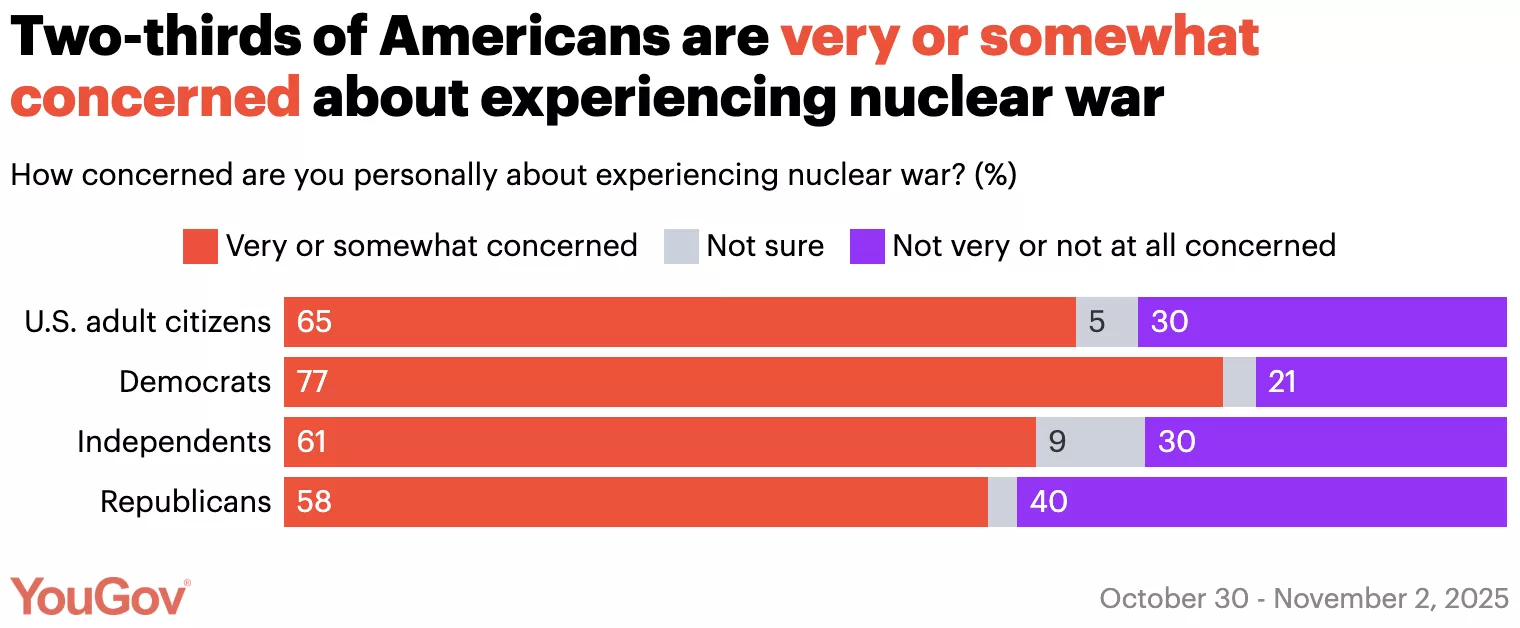
Most Democrats and one-third of Republicans think it’s likely the U.S. will get into a nuclear war in the next decade
A new YouGov poll on nuclear weapons finds that nearly half of Americans believe it’s likely the U.S. will get into a nuclear war in the coming decade, and most are worried about personally experiencing a nuclear war. A majority believe nuclear weapons are making the world less safe, but opinions are mixed on whether the U.S. should dismantle all of its nuclear weapons.
By: Jamie Ballard| November 26, 2025 today.yougov.com
46% of Americans think it’s likely the U.S. will get into a nuclear war within the next 10 years; 37% think this is not very or not at all likely. 57% of Democrats and 37% of Republicans think this is likely.
Department of Energy Seeks to Eliminate Radiation Protections Requiring Controls “As Low As Reasonably Achievable”
An internal Department of Energy (DOE) memorandum eliminates worker and public radiation protection rules known “As Low As Reasonably Achievable” (ALARA). This fundamental departure from decades of accepted health physics practices is being promoted by senior DOE political appointees with little background in health or radiation control. It is marked as “URGENCY: High” under the auspices of the DOE Deputy Secretary, the Under Secretary for Science, and the Administrator of the National Nuclear Security Administration. The memorandum awaits the final signature of DOE Secretary Chris Wright.
The memo’s stated goal is to:
“…remove the ALARA principle from all DOE directives and regulations, including DOE Order 458.1, Radiation Protection of the Public and the Environment, NE [Office of Nuclear Energy] Order 458.1, Radiation Protection of the Public, and, upon completion of the rulemaking process, 10 CFR [Code of Federal Regulations] 835, Occupational Radiation Protection.” [1]
It follows the playbook of the Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025, which called for:
“Set[ting] clear radiation exposure and protection standards by eliminating ALARA (“as low as reasonably achievable”) as a regulatory principle and setting clear standards according to radiological risk and dose rather than arbitrary objectives.” [2]
Lab Chromium Contamination Confirmed on San Ildefonso Pueblo Land
Comprehensive Cleanup Needed Instead of More Nuclear Weapons
The New Mexico Environment Department has announced:
“A toxic chromium plume from Los Alamos National Laboratory has spread beyond Lab boundaries onto Pueblo de San Ildefonso land for the first time, with contamination exceeding state groundwater standards… These new results are conclusive evidence that the U.S. Department of Energy’s efforts to contain the chromium plume have been inadequate.”
In reality, chromium groundwater contamination probably migrated beyond the LANL/San Ildefonso Pueblo boundary long ago, with past Lab maps of the plume “magically’ stopping at the border. In the past, tribal leadership has commented that it was fortunate that the contamination stopped there, but that any future indications of groundwater contamination on Pueblo land could have serious consequences. The San Ildefonso Pueblo is a sovereign Native American tribal government.
As late as the late 1990s the Lab was falsely claiming that groundwater contamination was impossible because underlying volcanic tuff is “impermeable.” [1] This ignored the obvious fact that the Parajito Plateau is heavily seismically fractured, providing ready pathways for contaminant migration to deep groundwater. By 2005 even LANL acknowledged that continuing increasing contamination of the regional aquifer is inevitable.[2] Some 300,000 northern New Mexicans rely upon the aquifer for safe drinking water. The potential serious human health effects (including cancer) caused by chromium contamination was the subject of the popular movie Erin Brockovich.
LANL chromium plume spreads onto San Ildefonso Pueblo land, NMED says
Nuclear Watch New Mexico executive direcor Jay Coghlan sees PF-4 as being a bigger scale — and having bigger risks — than the other aging buildings.
“PF-4 is not unique in being old,” Coghlan said. “However, PF-4 is totally unique in currently being the only facility that can process large amounts of plutonium … particularly including plutonium pit production. I think, in part, that’s why the Safety Board focuses more on PF-4 than, to my knowledge, than any other single individual facility.”
By:Patrick Lohmann | November 13, 2025 sourcenm.com
An underground plume of toxic chromium has spread from Los Alamos National Laboratory to Pueblo de San Ildefonso land, state Environment Department officials announced Thursday.
The discovery marks the first time the plume has been detected within the pueblo boundaries, officials said in a news release, though they added the plume’s spread does not pose imminent threats to drinking water in the pueblo or in Los Alamos County. That’s because the plume is not near any known private or public wells, officials said.
Long-term ingestion of hexavalant chromium can cause serious health problems or increase risk of certain cancers.
US Stands Alone Defying UN Vote on Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
Could the LDS Church end an ongoing nuclear weapons project? These veteran activists think so.
By Thalif Deen, Inter Press Sevice | November 12, 2025 ipsnews.net
UNITED NATIONS, Nov 12 2025 (IPS) – The US took another step backward –to break ranks with the United Nations– when it voted against a draft resolution calling for the entry into force of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT).
The negative vote followed an announcement by President Trump last month that the US plans to resume nuclear testing after a 33-year hiatus. The US stood alone on the UN vote, which was supported by almost all member States in the General Assembly’s First Committee.
The resolution was adopted by an overwhelming majority: with 168 votes in favor, with one against (United States) and 3 abstentions (India, Mauritius, Syria).
During Trump’s first term, the US abstained on the vote. And in other years they had been voting in favour.
Jackie Cabasso, Executive Director, Western States Legal Foundation, which monitors and analyzes U.S. nuclear weapons programs and policies, told IPS the chaos and uncertainty arose from Trump’s factually-challenged social media post that “because of other countries testing programs, I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis.”
The U.S. government’s first ever “No” vote, on the annual UN resolution in support of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT), raises further troubling questions about U.S. intentions.
A Small Town Is Fighting a $1.2 Billion AI Datacenter for America’s Nuclear Weapon Scientists
“Ypsilanti, Michigan resident KJ Pedri doesn’t want her town to be the site of a new $1.2 billion data center, a massive collaborative project between the University of Michigan and America’s nuclear weapons scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratories (LANL) in New Mexico.”
By Matthew Gault | November 10, 2025 404media.co
“My grandfather was a rocket scientist who worked on Trinity,” Pedri said at a recent Ypsilanti city council meeting, referring to the first successful detonation of a nuclear bomb. “He died a violent, lonely, alcoholic. So when I think about the jobs the data center will bring to our area, I think about the impact of introducing nuclear technology to the world and deploying it on civilians. And the impact that that had on my family, the impact on the health and well-being of my family from living next to a nuclear test site and the spiritual impact that it had on my family for generations. This project is furthering inhumanity, this project is furthering destruction, and we don’t need more nuclear weapons built by our citizens.”
At the Ypsilanti city council meeting where Pedri spoke, the town voted to officially fight against the construction of the data center. The University of Michigan says the project is not a data center, but a “high-performance computing facility” and it promises it won’t be used to “manufacture nuclear weapons.” The distinction and assertion are ringing hollow for Ypsilanti residents who oppose construction of the data center, have questions about what it would mean for the environment and the power grid, and want to know why a nuclear weapons lab 24 hours away by car wants to build an AI facility in their small town.
“What I think galls me the most is that this major institution in our community, which has done numerous wonderful things, is making decisions with—as I can tell—no consideration for its host community and no consideration for its neighboring jurisdictions,” Ypsilanti councilman Patrick McLean said during a recent council meeting. “I think the process of siting this facility stinks.”
Harking to the MX, Utahns call on LDS Church President Oaks to speak out against nuclear missile being developed in Utah
Could the LDS Church end an ongoing nuclear weapons project? These veteran activists think so.
THE SALT LAKE TRIBUNE | November 9, 2025 sltrib.com
Decades ago, peace activists helped keep a major nuclear weapons system out of Utah with help from key figures, chiefly Spencer W. Kimball, then the president of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Now some of those same individuals are calling on the church’s newly ascended president, Dallin H. Oaks, to follow in his predecessor’s footsteps and speak out against the federal government’s development of a new generation of nuclear missile, known as Sentinel, partly in the Beehive State.
“The arms race continues,” the group of 12 Utahns and one former resident write in a letter mailed to church headquarters in early October, “and a new moral challenge faces” the leaders of the Utah-based faith.
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: November 2025
Nuclear weapons:
The government shutdown has impact:
National Nuclear Security Agency confirms 152 furloughed at offices in Albuquerque, Los Alamos
Only 14 employees remain at the two sites By: Danielle Prokop-October 22, 2025
The NNSA confirmed 152 New Mexico employees charged with overseeing national laboratories’ nuclear weapons work were furloughed on Oct. 20, 2025. (Courtesy of NNSA)
The federal government this week sent home more than 150 federal New Mexico employees charged with overseeing national laboratories’ nuclear weapons work, with only 14 employees across two sites remaining at work, the National Nuclear Security Agency confirmed to Source NM.
The furloughs include 71 employees at NNSA’s Los Alamos field office and 81 at the Sandia National Laboratories location, NNSA Deputy Director of Communications Laynee Buckels told Source NM in an email. Seven employees remain at each site, working without pay, she said.
The field offices are responsible for “ensuring compliance with federal contracts to manage and operate the national security assets,” according to the NNSA website
To date there doesn’t appear to be furloughs at LANL, whose employees technically work for a contractor rather than the federal government. Congress is not furloughed, but Speaker Mike Johnson has kept the House out of session. As a result, legislation has come to a screeching halt.
Los Alamos’ plutonium facility safety systems need improvement, oversight board says
Nuclear Watch New Mexico executive direcor Jay Coghlan sees PF-4 as being a bigger scale — and having bigger risks — than the other aging buildings.
“PF-4 is not unique in being old,” Coghlan said. “However, PF-4 is totally unique in currently being the only facility that can process large amounts of plutonium … particularly including plutonium pit production. I think, in part, that’s why the Safety Board focuses more on PF-4 than, to my knowledge, than any other single individual facility.”
By Alaina Mencinger amencinger@sfnewmexican.com | November 7, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
An independent oversight agency wants to see improved safety systems at the facility at the heart of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s plutonium pit mission: PF-4.
The Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board reported what it believes to be gaps in a safety analysis drafted for PF-4 and delays in upgrades to safety systems in a letter last month to Energy Secretary Chris Wright.
“Maintaining momentum for these safety infrastructure projects is more important in light of the issues with the safety analysis,” the board wrote in the letter dated Oct. 10. It was signed by former acting chairman Thomas Summers.
LANL Prioritizes Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Core Production Over Safety
The independent Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board recently released its Review of the Los Alamos Plutonium Facility Documented Safety Analysis. It concluded that:
“While LANL facility personnel continue to make important upgrades to the Plutonium Facility’s safety systems, many of those projects have encountered delays due to inconsistent funding and other reasons. DOE and LANL should consider prioritizing safety-related infrastructure projects to ensure that the Plutonium Facility safety strategy adequately protects the public, as the facility takes on new and expansive national security missions.” (Page 24)
In early October 2024, the Department of Energy’s semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) announced with great fanfare that the Los Alamos Lab had produced its first “diamond stamped” plutonium pit for the nuclear weapons stockpile. Tens of billions of taxpayers’ dollars have been sunk into LANL’s long delayed and over budget pit production program. Given no further announcements, it is not currently known whether or not the Lab is meeting its congressionally required production goals. Endemic nuclear safety problems have long been an intractable issue, at one point even forcing a three-year halt to plutonium operations at LANL’s Plutonium Facility-4 (“PF-4”).
In its recent Review, the Safety Board reported:
“The [2009] Plutonium Facility safety basis described very large potential [radioactive] dose consequences to the public following seismic events…. DOE committed to upgrade and seismically qualify the ventilation system, with a particular focus on a specific ventilation subsystem…”
“As the only facility in the DOE complex that can process large quantities of plutonium in many forms, [PF-4] represents a unique capability for the nation’s nuclear deterrent. The Board has long advocated for the use of safety-related active confinement systems in nuclear facilities for the purposes of confining radioactive materials…Passive confinement systems are not necessarily capable of containing hazardous materials with confidence because they allow a quantity of unfiltered air contaminated with radioactive material to be released from an operating nuclear facility following certain accident scenarios. Safety related active confinement ventilation systems will continue to function during an accident, thereby ensuring that radioactive material is captured by filters before it can be released into the environment… (Page 2, bolded emphases added)
AP: Trump appears to suggest the US will resume testing nuclear weapons for first time in 30 years
“For Trump, who has cast Russia as a “paper tiger” for failing to swiftly subdue Ukraine, the message is that Russia remains a global military competitor, especially on nuclear weapons, and that Moscow’s overtures on nuclear arms control should be acted on.”
By MICHELLE L. PRICE and CHRIS MEGERIAN | October 30, 2025 apnews.com
BUSAN, South Korea (AP) — President Donald Trump appeared to suggest the U.S. will resume testing nuclear weapons for the first time in three decades, saying it would be on an “equal basis” with Russia and China.
The Kremlin pointed out that a global ban on nuclear tests has remained in place, but warned that if any country resumes nuclear testing Russia would follow suit.
There was no indication the U.S. would start detonating warheads, but Trump offered few details about what seemed to be a significant shift in U.S. policy.
He made the announcement on social media minutes before he met with Chinese leader Xi Jinping on Thursday in South Korea. He offered little clarity when he spoke to reporters later aboard Air Force One as he flew back to Washington.
The U.S. military already regularly tests its missiles that are capable of delivering a nuclear warhead, but it has not detonated the weapons since 1992. The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, which the U.S. signed but did not ratify, has been observed since its adoption by all countries possessing nuclear weapons, North Korea being the only exception.
REUTERS: Trump tells Pentagon to immediately resume testing US nuclear weapons
“Russia – which tested a new nuclear-powered cruise missile on October 21, held nuclear readiness drills on October 22 and tested a new nuclear-powered autonomous torpedo on October 28 – said it hoped Trump had been properly informed that Moscow had not tested a nuclear weapon itself.”
By Trevor Hunnicutt, Ismail Shakil and Kanishka Singh | October 30, 2025 reuters.com
VIEW THE RECORDING: Santa Fe Ecumenical Conversations Towards Nuclear Disarmament at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Community – Monday, October 27
Archbishop John C. Wester and NukeWatch New Mexico presented a special evening at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Community on Monday, October 27, from 6:00 to 8:00 p.m. MT. Following a presentation from NukeWatch executive director Jay Coghlan on U.S. nuclear weapons “modernization,” the Archbishop shared reflections from his pastoral letter, Living in the Light of Christ’s Peace, and speak about the importance of dialogue and hope in working toward nuclear disarmament.
View the recording at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9LFmQzMoJds&t=1s
Trump Orders Nuclear Weapons Testing for New Nuclear Arms Race
New Plutonium “Pit” Bomb Cores at Los Alamos Lab Could Make It Real
Just minutes before meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping, Trump posted on his Truth Social media platform that “Because of other countries testing programs, I have instructed the Department of War to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis. That process will begin immediately.” House Speaker Mike Johnson soon followed on CNN saying, “I think it is an obvious and logical thing to ensure that our weapons systems work.”
No other countries are currently testing nuclear weapons (the last was by North Korea in 2017). Further, any nuclear weapons tests by the U.S. would be performed by the Department of Energy (whose last test was in 1992), not the Department of War (until recently the Department of Defense). Trump was likely referring to Vladimir Putin’s recent claims of a new nuclear powered cruise missile and a tsunami-causing nuclear-armed torpedo that could threaten America’s coastal cities. In addition, China is dramatically expanding its own fleet of intercontinental ballistic missiles.
But central to all this is the U.S.’ own $2 trillion “modernization” program that will rebuild every nuclear warhead in the planned stockpile with new military capabilities and produce new-design nuclear weapons as well. This so-called modernization program will also build new nuclear weapons production facilities expected to be operational until ~2080, and buy new missiles, subs, and bombers from the usual rich defense contractors, all to keep nuclear weapons forever.
‘Nuclear weapons are blasphemous’: Archbishop Wester continues disarmament push with talk
This event was organized by the “Santa Fe Ecumenical Conversations Towards Nuclear Disarmament” group at the Santa Maria de la Paz parish near the Santa Fe Community College. They kindly invited NukeWatch to speak before Archbishop Wester for what turned out to be a wonderful event. The full recording can be viewed at https://www.youtube.com/@SMDLP/streams
By Cormac Dodd cdodd@sfnewmexican.com | October 28, 2025 santafenewmexican.com
Despite saying he has received a somewhat muted response from the local faithful, Santa Fe’s Catholic archbishop is still pushing nuclear disarmament as vital to humanity’s spiritual well-being and continued existence.
“I think nuclear weapons are blasphemous, because I think nuclear weapons are humanity’s attempt to build a Tower of Babel, an attempt to eat from the apple of the tree of the Garden of Eden, to become like God, to become gods,” Archbishop John C. Wester said in a roughly 30-minute address at Santa Maria de la Paz Catholic Church south of Santa Fe.
“In humility, we must avoid inventing anything that, in a matter of hours, can destroy what God has created,” the leader of the Archdiocese of Santa Fe continued. “The story of Adam and Eve is archetypal, I think: When human beings try to become as God, they lose the Garden of Eden and they must endure the cruel reality of paradise lost.”
The archbishop’s comments followed a journey he undertook to Japan on the 80th anniversary of the U.S. military’s decision to drop atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki toward the end of World War II. He spoke in front of an audience of about 50 people — who gave Wester a standing ovation — at Monday’s event
In a Looming Nuclear Arms Race, Aging Los Alamos Faces a Major Test
The lab where Oppenheimer developed the atomic bomb is the linchpin in the United States’ effort to modernize its nuclear weapons. Yet the site has contended with contamination incidents, work disruptions and old infrastructure.
By Alicia Inez Guzmán | October 28, 2025 The New York Times nytimes.com
In a sprawling building atop a mesa in New Mexico, workers labor around the clock to fulfill a vital mission: producing America’s nuclear bomb cores.
The effort is uniquely challenging. Technicians at Los Alamos National Laboratory must handle hazardous plutonium to create the grapefruit-size cores, known as pits. They do so in a nearly 50-year-old building under renovation to address aging infrastructure and equipment breakdowns that have at times disrupted operations or spread radioactive contamination, The New York Times found.
Now, the laboratory is under increasing pressure to meet the federal government’s ambitions to upgrade the nation’s nuclear arsenal. The $1.7 trillion project includes everything from revitalizing missile silos burrowed deep in five states, to producing new warheads that contain the pits, to arming new land-based missiles, bomber jets and submarines.
But the overall modernization effort is years behind schedule, with costs ballooning by the billions, according to the Congressional Budget Office. In 2018, Congress charged Los Alamos with making an annual quota of 30 pits by 2026, but by last year it had produced just one approved for the nuclear stockpile. (Officials have not disclosed whether more have been made since then.)
*The featured image differs from the article photo due to usage rights.
Why Putin’s ‘invincible’ nuclear-powered missile is more likely to become a disastrous ‘flying Chernobyl’ for Russia
The US abandoned efforts to build nuclear-powered missile weapons during the 1950s arms race with the Soviet Union as a nuclear-powered missile would effectively be a huge radiation risk.
Jeffrey Lewis, a nuclear nonproliferation expert at Middlebury College, described it as a “tiny flying Chernobyl,” referencing the Soviet power plant that melted down and covered a 1,600-mile area with toxic radiation…While Lewis believes the Burevestnik is only capable of subsonic speed and easy to intercept, he warned that Russia’s ambition poses a return to the Cold War era.
“NATO aircraft could intercept it. The problem is that Burevestnik is yet another step in an arms race that offers no victory for either side,” he wrote on X.
By Ronny Reyes | October 28, 2025 nypost.com
Russian strongman Vladimir Putin’s latest threats that Moscow is preparing to deploy its new “invincible” nuclear-powered cruise missile has drawn a rebuke from President Trump and a reminder of America’s own nuclear might.
But experts say the Burevestnik missile could end up being more like a disastrous “flying Chernobyl” for Russia — and proves Putin is actually nervous about the possibility of the US giving Tomahawk cruise missiles to Ukraine.
George Barros, of the Washington-based Institute for the Study of War, described Putin’s ominous Sunday announcement as a form of fear mongering from a Kremlin afraid that the US could give Kyiv a much more conventional weapon — the tried and true Tomahawk.
Russia tested new nuclear-powered Burevestnik cruise missile
“For Trump, who has cast Russia as a “paper tiger” for failing to swiftly subdue Ukraine, the message is that Russia remains a global military competitor, especially on nuclear weapons, and that Moscow’s overtures on nuclear arms control should be acted on.”
By Guy Faulconbridge and Lidia Kelly Tim Balk | October 26, 2025 reuters.com
- Russia tests nuclear-capable Burevestnik missile
- Missile flew for 14,000 km, 15 hours
- Putin says it can pierce any missile defences
Nuclear Weapons Issues & The Accelerating Arms Race: October 2025
Nuclear Weapons Update:
Putin has offered Trump a one-year extension of the numerical cap on strategic nuclear weapons in the new Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty which is 1,550 warheads (however, B52s are counted as one warhead while they can carry a dozen). New START expires in February 2026, which will be the first time the world will be without any nuclear arms control treaties since the mid-1970s. Trump has said it sounded like a good idea.
Note: New START ratification in 2010 provided the opportunity for Republicans in the Senate to attach the condition of $88 billion for nuclear weapons “modernization” that has since metastasized to ~$2 trillion. Nuclear disarmament must be prioritized as the ultimate goal over simply continued arms control.
A mere extension of the numerical cap would not involve Congressional ratification. The extension of New START’s numerical cap is in part to allow for a year in which to begin negotiations for a treaty replacement.
Plutonium Pit Production:
A draft plutonium pit production programmatic environmental impact statement is expected to be released next year in early 2026.
Accelerating Arms Race:
Is North Korea set to become world’s ‘fourth ICBM power’ after missile breakthrough? | Park Chan-kyong | South China Morning Post | September 11, 2025
A new era in North Korea’s missile programme may be dawning, as analysts warn of an imminent test launch of an intercontinental ballistic missile capable of carrying multiple warheads to the US mainland. Fresh from his appearance at China’s Victory Day parade in Beijing last week, North Korean leader Kim Jong-un personally oversaw the trial of a lighter, more robust solid-fuel ICBM engine, state media reported on Tuesday, touting the achievement as a “strategic” breakthrough.
Saudi Arabia signs a mutual defense pact with nuclear-armed Pakistan after Israel’s attack on Qatar | MUNIR AHMED & JON GAMBRELL | AP NEWS | September 18, 2025
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates (AP) — Pakistan’s defense minister says his nation’s nuclear program “will be made available” to Saudi Arabia if needed under the countries’ new defense pact, marking the first specific acknowledgment that Islamabad had put the kingdom under its nuclear umbrella.
Defense Minister Khawaja Mohammad Asif’s comments underline the importance of the pact struck this week between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia, which have had military ties for decades.
The move is seen by analysts as a signal to Israel, long believed to be the Middle East’s only nuclear-armed nation. It comes after Israel’s attack targeting Hamas leaders in Qatar last week killed six people and sparked new concerns among Gulf Arab nations about their safety as the Israel-Hamas war devastated the Gaza Strip and set the region on edge.
Russia suspected of helping North Korea build nuclear submarines, Seoul investigating | Park Chan-kyong | South China Morning Post | September 18, 2025
South Korea is investigating reports that Russia has supplied North Korea with nuclear submarine reactor modules, a move analysts see as highly plausible and one that could mark a breakthrough in Pyongyang’s decades-long push for a nuclear-powered navy… At the 8th Party Congress in January 2021, North Korea declared five core defence goals, including the development of nuclear-powered submarines and submarine-launched strategic nuclear weapons.
China Hardens Military Stance Against U.S. With Nuclear Weapons and Tough Talk | Brian Spegele | The Wall Street Journal| September 18, 2025
China played down its rapidly rising military might for years. In the past few weeks, Beijing has broadcast a steady drumbeat of firepower displays and muscular rhetoric, carrying an unmistakable warning for the U.S… Part of China’s confidence stems from the rapid growth of its firepower. The Pentagon estimates that China’s stockpile of nuclear warheads has more than doubled since 2020, alongside a growing array of options to launch those weapons, from mobile ground-launch systems to increasingly stealthy submarines.
Nuclear News Archive – 2022
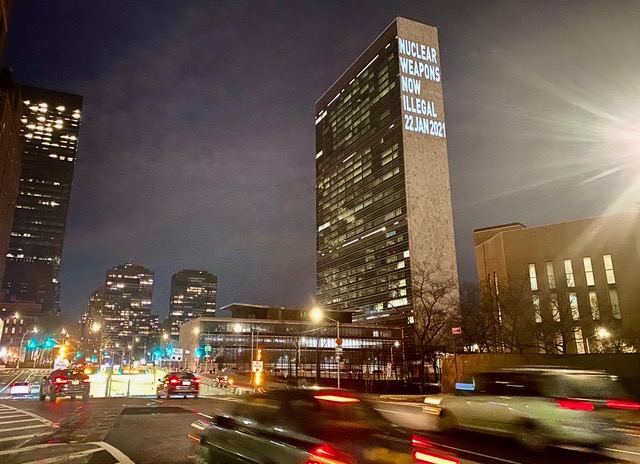
Seeking a world without nuclear weapons
Jan. 22 is the one-year anniversary of the U.N. Treaty on the Abolition of Nuclear Weapons entering into force as international law. Today, 59 countries have ratified the Treaty on the Abolition of Nuclear Weapons, with several more countries on the verge of doing the same. The importance of this cannot be overstated. With more and more countries outlawing everything to do with nuclear weapons, it becomes increasingly harder for the nine countries possessing these weapons to defend their continued existence.
recorder.com | BY SUSAN LANTZ January 22, 2022
For instance, Germany, Norway, Sweden, Belgium, Netherlands, Italy are all likely to sign onto the Treaty on the Abolition of Nuclear Weapons eventually, with strong support already in their populations and parliaments. The United States currently has nuclear weapons in Belgium, Germany and Italy. After these countries ratify the treaty, the United States will be required to remove its weapons.
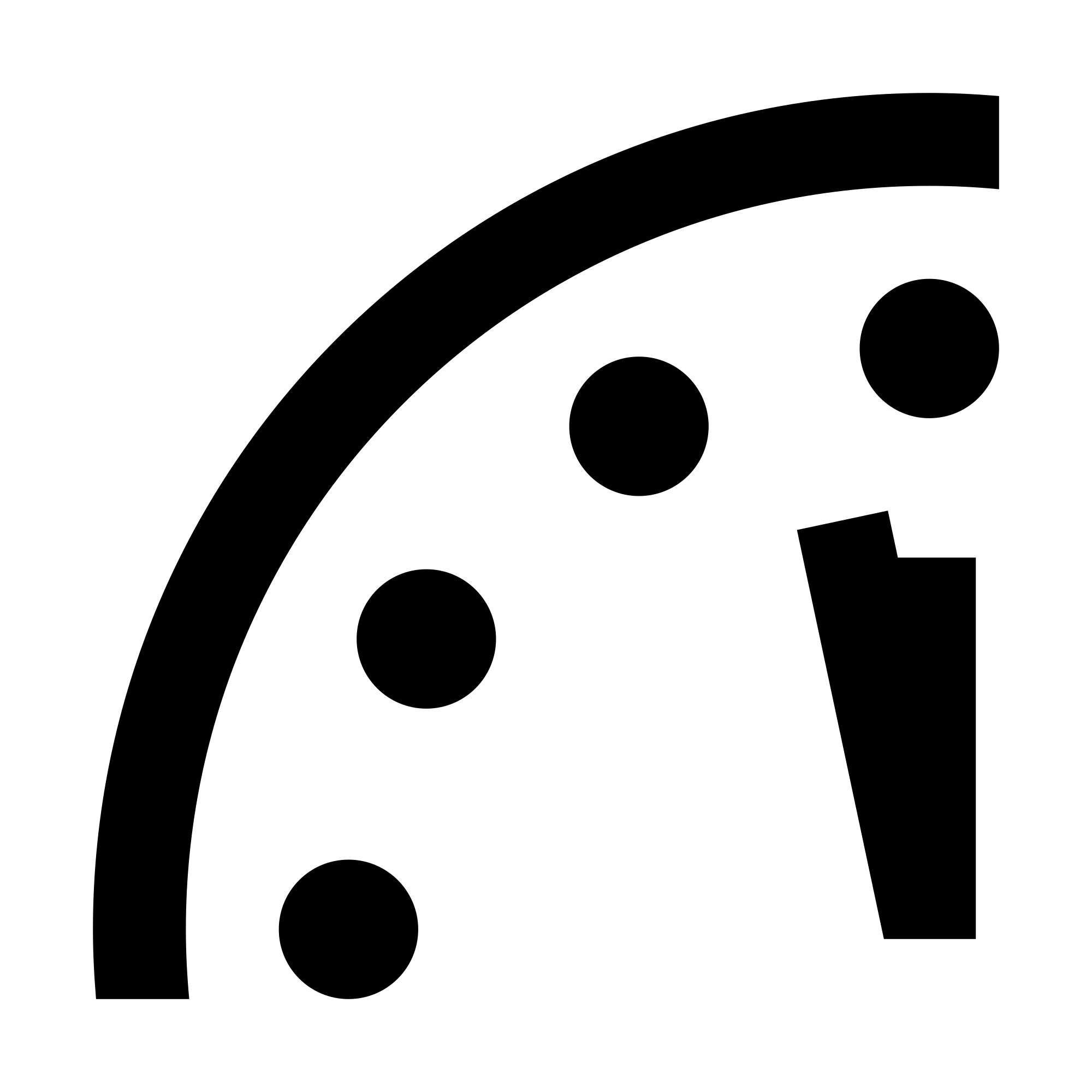
At doom’s doorstep: It is 100 seconds to midnight
2022 Doomsday Clock Statement
It is 100 seconds to midnight
© Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists Science and Security Board | January 20, 2022
To: Leaders and citizens of the world
Re: At doom’s doorstep: It is 100 seconds to midnight
Date: January 20, 2022
Last year’s leadership change in the United States provided hope that what seemed like a global race toward catastrophe might be halted and—with renewed US engagement—even reversed. Indeed, in 2021 the new American administration changed US policies in some ways that made the world safer: agreeing to an extension of the New START arms control agreement and beginning strategic stability talks with Russia; announcing that the United States would seek to return to the Iran nuclear deal; and rejoining the Paris climate accord. Perhaps even more heartening was the return of science and evidence to US policy making in general, especially regarding the COVID-19 pandemic. A more moderate and predictable approach to leadership and the control of one of the two largest nuclear arsenals of the world marked a welcome change from the previous four years.
Still, the change in US leadership alone was not enough to reverse negative international security trends that had been long in developing and continued across the threat horizon in 2021
How Martin Luther King, Jr.’s multifaceted view on human rights still inspires today
The legendary civil rights activist pushed to ban nuclear weapons, end the Vietnam War, and lift people out of poverty through labor unions and access to healthcare.
“It cannot be disputed that a full-scale nuclear war would be utterly catastrophic,” he told Ebony magazine in an interview. “The principal objective of all nations must be the total abolition of war.”
© National Geographic | BY EMILY MARTIN January 17, 2022

Virtual Press Conference & Link to Santa Fe Archbishop John C. Wester’s New Pastoral Letter “Living in the Light of Christ’s Peace: A Conversation Toward Nuclear Disarmament”
Living in the Light of Christ’s Peace – A conversation toward nuclear disarmament
Archbishop John C. Wester’s live press conference to discuss his pastoral letter on the growing need for disarmament.
PASTORAL LETTER
The Time for Nuclear Disarmament is Now
“We need nuclear arms control, not an escalating nuclear arms race.”
Santa Fe New Mexican: MY VIEW JOHN C. WESTER | By John C. Wester santafenewmexican.com | January 15, 2022
In September 2017, I traveled to Japan and visited Hiroshima and Nagasaki. It was a somber, sobering experience as I realized that on Aug. 6, 1945, humanity crossed the line into the darkness of the nuclear age. Historically, the Archdiocese of Santa Fe has been part of a peace initiative, one that would help make sure these weapons would never be used again. I believe it is time to rejuvenate that peace work.
We need to sustain a serious conversation in New Mexico and across the nation about universal, verifiable nuclear disarmament. We can no longer deny or ignore the dangerous predicament we have created for ourselves with a new nuclear arms race, one that is arguably more dangerous than the past Cold War. In the face of increasing threats from Russia, China and elsewhere, I point out that a nuclear arms race is inherently self-perpetuating, a vicious spiral that prompts progressively destabilizing actions and reactions by all parties, including our own country.
US Archbishop Warns of New Nuclear Arms Race
Archbishop of Santa Fe in New Mexico: [Nuclear] Armament a “diabolical spiral”
Source (Translated from German): kathpress.at | January 13, 2022
WASHINGTON, 01/13/2022 (KAP) The Catholic Archbishop of Santa Fe, New Mexico, John Wester, has issued a strong warning of a new nuclear arms race. “We need nuclear arms control, not an escalating nuclear arms race,” he says in a recent pastoral letter, according to the Catholic News Agency (KNA). Nuclear armament is a “diabolical spiral” that endangers everyone.
Wester’s diocese of New Mexico is particularly hard hit by nuclear armaments. Nuclear weapons are manufactured at Los Alamos and at Sandia National Laboratories. The US government stores nuclear weapons at Kirtland Air Force Base in Albuquerque.
New Mexico Church Official Urges Nuclear Disarmament Talks
The head of one of the oldest Roman Catholic dioceses in the U.S. says now is the time to rejuvenate a global conversation about the need for nuclear disarmament and avoiding a new nuclear arms race.”
“We can no longer deny or ignore the extremely dangerous predicament of our human family and that we are in a new nuclear arms race far more dangerous than the first,” he said. “We need nuclear arms control, not an escalating nuclear arms race.”
© Associated Press | By SUSAN MONTOYA BRYAN, Associated Press | January 11, 2022
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. (AP) — The head of one of the oldest Roman Catholic dioceses in the United States says now is the time to rejuvenate and sustain a global conversation about the need for nuclear disarmament and how to develop ways to avoid a new nuclear arms race.
Santa Fe Archbishop John Wester released a lengthy pastoral letter on the subject Tuesday, noting during a virtual news conference that Los Alamos National Laboratory — the birthplace of the atomic bomb — is preparing to ramp up production of the plutonium cores used in the nation’s nuclear arsenal.
Wester called the arms race a vicious spiral.
Archbishop of Santa Fe Issues Pastoral Letter in Support of TPNW
On 11 January 2022, Archbishop John C. Wester of Santa Fe, New Mexico circulated a letter in support of nuclear weapons abolition and the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons to all the parishes in his diocese.
![]() ICAN Campaign News | January 11, 2022
ICAN Campaign News | January 11, 2022
In the letter, Wester outlines the risks and consequences of the new nuclear arms race and highlights the unique role of New Mexico in the U.S. nuclear weapons complex and of the Santa Fe diocese to support nuclear disarmament. He calls for an open dialogue on nuclear disarmament and redirecting resources from the nuclear arms race to peaceful objectives, like cleaning up nuclear contamination and addressing climate change.
New Mexico is at the heart of the U.S. nuclear weapons complex, with two major nuclear weapons laboratories – the Los Alamos and Sandia National Laboratories- located in the state and nearly 40% of the Department of Energy’s nuclear weapons budget allocated for work in New Mexico. It was also the site of the first nuclear test explosion in July 1945 and has the largest repository of nuclear weapons in the country.
The Archdiocese of Santa Fe has a “special responsibility” he states, to support the TPNW and to encourage its active implementation.
“It is the duty of the Archdiocese of Santa Fe, the birthplace of nuclear weapons, to support that Treaty while working toward universal, verifiable nuclear disarmament,” Wester writes.
Waste Isolation Pilot Plant struggles to control costs, per annual performance evaluation
“Conducted by the DOE’s Carlsbad Field Office (CBFO), the evaluation called for improvements in cost control, schedule and risk management, along with work planning and control processes.”
By Adrian Hedden Carlsbad Current-Argus January 12, 2022 currentargus.com
Lingering struggles to complete construction projects on schedule while controlling costs at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant factored into the U.S. Department of Energy’s annual fee allotment to primary contractor Nuclear Waste Partnership (NWP).
NWP earned 67 percent of its potential, performance-based fee – about $10.9 million of about $16.2 million available to the contractor in Fiscal Year 2021.
About $7.6 million of the fee was awarded for specific task incentives with $10.9 million available, and the other $3.3 million came from the subjective portion of the evaluation from a total offering of $5.3 million.
Archbishop Wester to Release Pastoral Letter on Tuesday Calling for Nuclear Disarmament


Pax Christi USA paxchristiusa.org | January 10, 2021
NOTE: The following press release is from the Archdiocese of Santa Fe announcing a press conference on Tuesday, January 11th, where the Archbishop will discuss his pastoral letter, “Living in the Light of Christ’s Peace: A Conversation Toward Nuclear Disarmament”. Pax Christi USA has eagerly anticipated the archbishop’s letter and we wanted to share the release with our membership who can watch the press conference at the link provided in the email. As we approach the 25th anniversary of our statement on the morality of nuclear deterrence, signed by 75 U.S. Catholic bishops in 1998, we welcome this extraordinary, prophetic letter and look forward to the conversation it generates within the U.S. Catholic Church, supporting Pope Francis’ statement at Hiroshima in 2019, “The use of atomic energy for purposes of war is immoral, just as the possessing of nuclear weapons is immoral.”
ALBUQUERQUE – Monday, January 10, 2022 – IMMEDIATE RELEASE – Most Reverend John C.Wester, Archbishop of Santa Fe, will hold a press conference for accredited media to discuss is pastoral letter, “Living in the Light of Christ’s Peace: A Conversation Toward Nuclear Disarmament” on Tuesday, January 11, 2022 at 9:00 a.m. MST via Zoom (https://us02web.zoom.us/j/83010373874?pwd=QTkvTkZpNDRlbDBiNWd3dU9IRnhWUT09). The press conference will be livestreamed at https://youtu.be/kHS2C1wIBeQ.
Archbishop Wester will release his pastoral letter on the urgent need for nuclear disarmament and avoiding a new nuclear arms race. Pope Francis has made clear statements about the immorality of possessing nuclear weapons, moving the Church from past conditional acceptance of “deterrence” to the moral imperative of abolition. The Archdiocese of Santa Fe has a special role to play in advocating for nuclear disarmament given the presence of two nuclear weapons laboratories and the United States of America’s largest repository of warheads located within its boundaries. He therefore believes the archdiocese has a unique role to play in encouraging a future world free of nuclear weapons.
Archbishop Wester states, “The Archdiocese of Santa Fe has a special responsibility not only to support the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, but also to encourage its active implementation.” He goes on to “…invite us to have a conversation together about what it means to follow the risen, nonviolent Jesus who calls us to be peacemakers, put down the sword, and love everyone, even the enemies of our nation.”
Archbishop Wester’s pastoral letter has the support of four Nobel Peace Prize laureates.
Key Lab Used for WWII Atomic Bomb Development Still 14 Years From Clean Up, Maybe More
Watchdog groups said it wasn’t until the state sued in February 2021 that the DOE proposed boosting the cleanup budget at the lab by about one-third. Before that, budgets were flat, with the groups arguing that DOE had no incentive to seek more funding.
“The conclusion I draw from it is the New Mexico Environment Department gets a lot more from the stick than it does from the carrot with respect to making the laboratory and DOE truly committed to comprehensive cleanup,” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
BY CHARLOTTE TRATTNER , NEWSWEEK | January 7, 2022 newsweek.com
Concerns Persist About Pace of Cleanup at US Nuclear Lab
Watchdog groups said it wasn’t until the state sued in February 2021 that the DOE proposed boosting the cleanup budget at the lab by about one-third. Before that budgets were flat, with the groups arguing that DOE had no incentive to seek more funding.
“The conclusion I draw from it is the New Mexico Environment Department gets a lot more from the stick than it does from the carrot with respect to making the laboratory and DOE truly committed to comprehensive cleanup,” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
BY SUSAN MONTOYA BRYAN, Associated Press | January 7, 2022 usnews.com

Officials at one of the nation’s top nuclear weapons laboratories are reiterating their promise to focus on cleaning up Cold War-era contamination left by decades of research and bomb-making.
DOE/NNSA To Start New LANL Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement
During the question and answer period, Nuclear Watch New Mexico executive director Jay Coghlan said he was fascinated to hear that there was some funding allocated for a new SWEIS.
“The last one was in 2008 and it’s woefully outdated. To use NEPA terms, there’s a lot of new information and changed circumstances,” Coghlan said. “…And then there’s the question of the scope of the SWEIS, which would by definition imply it should consider the full range of issues from cleanup to pit production. What more can be said about a new SWEIS for Los Alamos (National Laboratory) at this time because as far as I know this is the first inkling whatsoever that there will be a new one?”
BY MAIRE O’NEILL, LOS ALAMOS REPORTER | January 6, 2022 losalamosreporter.com
Una Introducción a Hanford
El Sitio Nuclear de Hanford es el lugar más contaminado de los EE. UU. ¿Le interesa saber por qué? Pues hay suerte, porque tenemos una presentación que explica este asunto y más. Haga clic para ver el video acerca de la historia y la limpieza del Sitio Nuclear de Hanford. Es una buena manera de aprender más sobre un lugar contaminado pero poco conocido en el estado de Washington. ¡Anímate a verlo!
Yucca Mountain remains in debate over nuclear waste storage
“I’ve always fought misguided efforts to deposit nuclear waste in Nevada, and I’ll keep working with the Nevada delegation to pass my consent-based siting bill that would ensure these dangerous materials are never dumped on our state,” – Catherine Cortez Masto, D-Nev., a former state attorney general who also has fought federal efforts to build a repository at Yucca Mountain.”
Santa Fe New Mexican / Gary Martin Las Vegas Review-Journal | January 1, 2021
LAS VEGAS, Nev. — Mounting opposition to proposed nuclear waste storage sites in Texas and New Mexico has kept Yucca Mountain in Nevada in the national debate over what to do with the growing stockpile of radioactive material scattered around the country.
The Biden administration is opposed to Yucca Mountain and announced plans this month to send waste to places where state, local and tribal governments agree to accept it. That stance is shared by Nevada elected officials, tribal leaders and business and environmental groups.
But until the 1987 Nuclear Waste Policy Act is changed by Congress, the proposed radioactive waste repository 90 miles north of Las Vegas remains the designated permanent storage site for spent fuel rods from commercial nuclear plants.
“That’s what worries me. Until you get a policy in place, it will always be something you have to watch,” U.S. Rep. Dina Titus, D-Nev., told the Las Vegas Review-Journal.
An expert on atomic testing and American politics, Titus as a professor at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas wrote a 1986 book on Nevada’s nuclear past.
As an elected state and congressional lawmaker, she has opposed a permanent storage facility at Yucca Mountain.
Titus introduced legislation in past sessions of Congress that adopts recommendations by a 2012 Blue Ribbon Commission under the Obama administration to send the waste to states that want it.
Spent Fuel: The Risky Resurgence of Nuclear Power
[Letter from Washington]
“In the face of escalating alarm about climate change, the siren song of “clean and affordable and reliable” power finds an audience eager to overlook a business model that is dependent on state support and often greased with corruption; failed experiments now hailed as “innovative”; a pattern of artful disinformation; and a trail of poison from accidents and leaks (not to mention the 95,000 tons of radioactive waste currently stored at reactor sites with nowhere to go) that will affect generations yet unborn.”
BY: Andrew Cockburn © HARPER’S | From the January 2022 Issue
 Last June, Bill Gates addressed a crowd of politicians and reporters in Cheyenne, Wyoming. “Fifteen years ago I assembled a group of experts . . . to solve the dual problems of global energy poverty and climate change,” the sweater-clad multibillionaire declared, speaking by video. “It became clear that an essential tool to solving both is advanced nuclear power.” But the technology, he continued, needed to become safer and less expensive. To this end, he had promised to invest $1 billion in TerraPower, a company he founded in 2008 to develop small modular reactors that can be churned out on an assembly line. He was now happy to announce the construction of a plant on the site of a defunct coal facility in Wyoming.
Last June, Bill Gates addressed a crowd of politicians and reporters in Cheyenne, Wyoming. “Fifteen years ago I assembled a group of experts . . . to solve the dual problems of global energy poverty and climate change,” the sweater-clad multibillionaire declared, speaking by video. “It became clear that an essential tool to solving both is advanced nuclear power.” But the technology, he continued, needed to become safer and less expensive. To this end, he had promised to invest $1 billion in TerraPower, a company he founded in 2008 to develop small modular reactors that can be churned out on an assembly line. He was now happy to announce the construction of a plant on the site of a defunct coal facility in Wyoming.
Gates and other backers extoll the promise of TerraPower’s Natrium reactors, which are cooled not by water, as commercial U.S. nuclear reactors are, but by liquid sodium. This material has a high boiling point, some 1,600 degrees Fahrenheit, which in theory enables the reactor to run at extreme temperatures without the extraordinary pressures that, in turn, require huge, expensive structures. “It’s smaller, cheaper, and inherently safe,” Jeff Navin, the director of external affairs at TerraPower, told me.
Will Construction be Delayed on the New Shaft at WIPP?
“The Environment Department “should be equally considerate towards the judicial review process as it was in the administrative permit modification process, to ensure the courts have sufficient time to review objectively the facts and arguments associated with the appeal.” – Steve Zappe, a member of the Environment Department who worked on WIPP for 17 years.”
Concerned Citizens for Nuclear Safety | December 23, 2021
Two appeals have been filed in the New Mexico Court of Appeals to challenge the decision by New Mexico Environment Department Secretary James Kenney to approve the new shaft at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP). Concerned Citizens for Nuclear Safety filed the second appeal on November 29th. On November 9th, Southwest Research and Information Center and Cynthia Weehler had filed the first appeal. Visit: env.nm.gov/opf/docketed-matters/, scroll down to HWB 21-02 – APPEAL: Waste Isolation Pilot Plant: Class 3 Permit Modification Request, “Excavation of a New Shaft and Associated Connecting Drifts.
SRIC and Weehler also asked Secretary Kenney for a stay, that is, a delay, of shaft construction until the Court of Appeals rules on their appeal. On the stay motion, Secretary Kenney can grant, or deny, or take no action. If he does not grant the stay, or if he takes no action by January 10th, a stay motion then could be filed with the Court of Appeals. Visit: env.nm.gov/opf/docketed-matters/ , scroll down to HWB 21-02 –Waste Isolation Pilot Plant: Class 3 Permit Modification Request, “Excavation of a New Shaft and Associated Connecting Drifts.
Unfortunately, key documents are missing, including the SRIC/Weehler Motion for Stay Pending Appeal, the Hearing Officer’s Report and the Secretary’s Final Order.
The stay motion was supported by three affidavits. Cynthia Weehler stated that she purchased her home near U.S. Highway 285 knowing that the WIPP Permit anticipated that shipments to WIPP would end in 2024. Now, the WIPP expansion plan that requires the new shaft “would result in thousands of additional shipments coming near my house for many decades.” She is very concerned that accidents could result in health effects and “such shipments will reduce my property values.”
 Kathleen Wan Povi Sanchez, an Elder from the Tewa Pueblo of San Ildefonso and among the founding mothers of Tewa Women United, stated in her affidavit that an increase in waste transportation near two schools located on New Mexico Highway 502 would endanger the health of Pueblo children in attendance. Further, “The WIPP expansion plan would result in thousands of new shipments using [] Highway 502 for decades transporting plutonium from the Pantex Plant near Amarillo, Texas to [Los Alamos National Laboratory], and from [Los Alamos] to the Savannah River Site, followed by shipments from that site to WIPP.”
Kathleen Wan Povi Sanchez, an Elder from the Tewa Pueblo of San Ildefonso and among the founding mothers of Tewa Women United, stated in her affidavit that an increase in waste transportation near two schools located on New Mexico Highway 502 would endanger the health of Pueblo children in attendance. Further, “The WIPP expansion plan would result in thousands of new shipments using [] Highway 502 for decades transporting plutonium from the Pantex Plant near Amarillo, Texas to [Los Alamos National Laboratory], and from [Los Alamos] to the Savannah River Site, followed by shipments from that site to WIPP.”
Some LANL plutonium stored in vulnerable containers
An anti-nuclear group said this type of plutonium isn’t explosive but would be hazardous to breathe.
It’s possible the lab made this type of plutonium a lesser priority while ramping up pit production, and now it plans to take big shipments, said Scott Kovac, research and operations director for the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
“That’s a huge amount to accept,” Kovac said. “Now they’re asking NNSA to say that’s OK.”
BY SCOTT WYLAND, THE SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN | December 23, 2021 santafenewmexican.com
Los Alamos National Laboratory wants to store high heat-emitting plutonium in uncertified containers that, if breached in a fire or an earthquake, could expose workers and the public to hazardous doses of radiation, according to a government watchdog’s report.
The lab’s primary contractor seeks a waiver to store large quantities of plutonium-238 in unapproved containers that, if breached, could expose the public to 83 to 378 rem, the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board said in a December report, referring to the unit that measures radiation absorbed in living tissue.
US Still Doesn’t Know How and Where It Will Store Its Growing Pile of Nuclear Waste
The estimated cost of handling the degrading radioactive material is rising steadily — $512 billion at last count.
“DoE is now running up against a statutory limit for how much waste it can store in the space, so it recently changed its counting method to exclude space between storage drums as storage space. New Mexico regulators approved the change but the matter is being challenged in court.
“They knocked a third out of it with a slight of hand. That will allow them a lot more waste,” complains Scott Kovac, operations & research director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico (NWNM), a local anti-nuclear group.”
BY CHARLES PEKOW, EARTH ISLAND JOURNAL | December 23, 2021 earthisland.org
A nuclear watchdog group wants a state commission to nullify its decision on a permit for Los Alamos National Laboratory’s radioactive liquid waste treatment facility, arguing the panel’s former chairwoman backed a ruling favorable to the lab while she sought a job with the federal agency that oversees it.
U.S. Urges Japan Not to Join Nuclear Ban Treaty Meeting
“Germany’s move [planning to to attend the meeting as an observer] has put Japan — which has stated it aspires to a world free of nuclear weapons as the only country to have suffered the devastation of atomic bombings — in the spotlight. Both countries are key U.S. allies that rely on American nuclear forces for protection.”
© KYODO NEWS | December 20, 2021
The United States has urged Japan not to attend as an observer the first meeting of signatories to a U.N. treaty banning nuclear weapons, according to U.S. government sources, reflecting Washington’s opposition to the pact.
The Japanese government has suggested it will come into line with the United States and take a cautious approach to the issue, the sources said. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida told a parliamentary committee on Thursday that Tokyo has no “concrete plans” to attend the meeting as an observer.
The sources said the U.S. administration of President Joe Biden made the request to Japan through diplomatic channels after German political parties announced Nov. 24 that the deal for the new ruling coalition included taking part as an observer at the meeting scheduled for March in Vienna.
Maybe because of the request, Kishida also suggested last week that participation in the meeting would be premature “before building a relationship of trust with President Biden.”
Archbishop calls for nuclear disarming
At least 125 people were present for the service, many bearing roses in honor of the Lady of Guadalupe. Among them was Karen Weber, who said it’s “highly symbolic” for Wester to speak out on the “abolishment of nuclear weapons.”
SANTA FE NEW MEXICAN By Robert Nott rnott@sfnewmexican.com
Looking up at the sky as a young teen one day in Daly City, Calif., Archbishop John C. Wester had one thought as he saw military planes overheard.
Were they ours, or were they Russian planes?
The year was 1962, perhaps the first time nuclear war between the two superpowers seemed likely to erupt as the Cuban Missile Crisis played out and students were taught to prepare for an atomic attack by diving under their desks at schools.
“I don’t think going under our desks was very helpful,” Wester said Sunday in Santa Fe, moments before issuing a call for the world to rid itself its nuclear weapons.
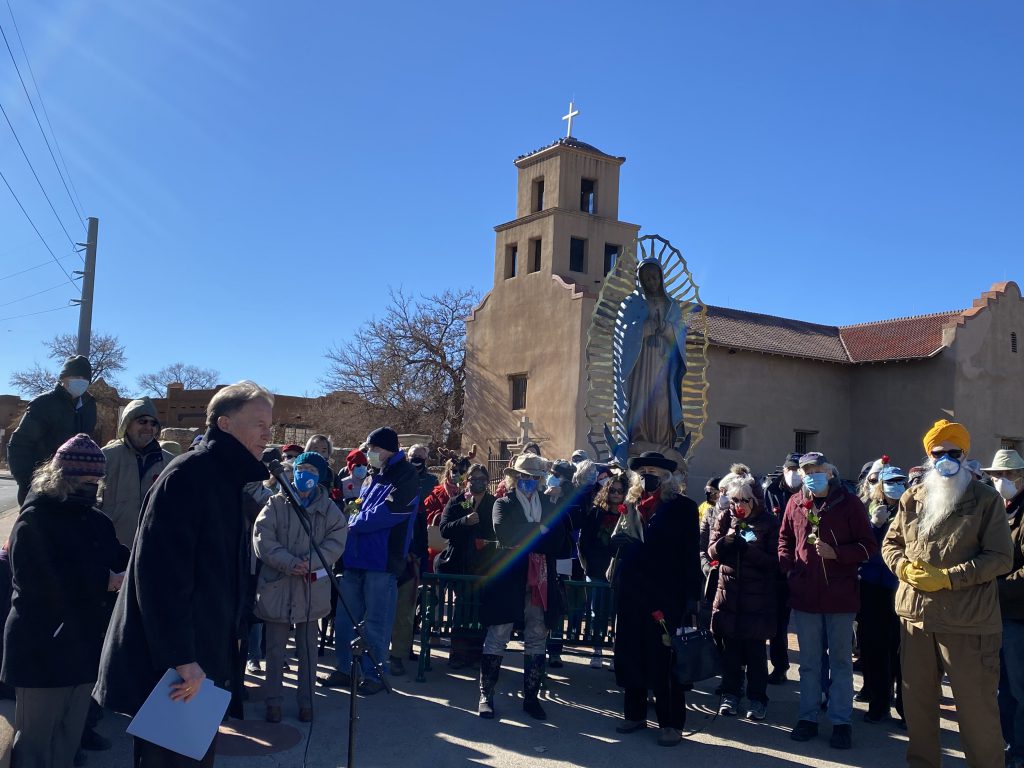

Now, some 60 years later, he said he wants to do more to end the threat of an atomic war. Wester spoke and prayed during a 30-minute prayer service and ceremony at the Shrine of Our Lady of Guadalupe before he unveiled a sign bearing an image of Pope Francis and a quote uttered by the pope in Hiroshima in 2020: “The possession of nuclear arms is immoral.”
Wester said “our archdiocese needs to be facilitating, encouraging an ongoing conversation” about nuclear disarmament.
Why Los Alamos lab is working on the tricky task of creating new plutonium cores
“While the labs work on relearning high-stakes industrial techniques for terrifying weapons, it is estimated that most of the existing warheads will remain fully functional for at least 100 years after first manufacture. Given an arsenal of hundreds of deployed warheads, the stakes of failure to modernize are that, in the event of the worst war humanity has ever known, some warheads might fail to detonate, letting millions live.”
BY KELSEY D. ATHERTON | POPULAR SCIENCE popsci.com December 18, 2021

Plutonium pits, the potent hearts of modern nuclear weapons, degrade over time. As these cores decay, so too does the certainty that they will work as designed when detonated. Los Alamos National Laboratory, the organization that grew out of the Manhattan Project to design and equip the nuclear arsenal of the Cold War, is advancing towards its goal of manufacturing 30 new plutonium pits to go inside nuclear bomb cores by 2026.
The project is both a specific manufacturing challenge, and an opening for the United States to newly consider how many warheads it needs on hand to achieve its stated strategic objectives.
Inside a nuclear warhead, a plutonium pit is crucial to setting off the sequence of reactions that make a thermonuclear explosion. Inside the pit is a gas, like deuterium/tritium, and around the pit is chemical explosive. When the chemical explosive detonates, it compacts the plutonium around the gas until the core is dense enough to trigger a fission reaction. What makes a warhead thermonuclear, as opposed to just atomic, is that this is combined in the same warhead with a uranium core, which creates a fusion explosion.
Hundreds of Scientists Ask Biden to Cut the U.S. Nuclear Arsenal
The letter argued that “by making clear that the United States will never start a nuclear war, it reduces the likelihood that a conflict or crisis will escalate to nuclear war.” And it would demonstrate, they argued, that the United States was committed to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, which obliges the nuclear-armed states to move toward reducing their arsenals.
Written By: Jesus Jiménez © 2021 The New York Times Company The New York Times | December 17, 2021
Nearly 700 scientists and engineers, including 21 Nobel laureates, asked President Joe Biden on Thursday to use his forthcoming declaration of a new national strategy for managing nuclear weapons as a chance to cut the US arsenal by a third and to declare, for the first time, that the United States would never be the first to use nuclear weapons in a conflict.
The letter to Biden also urged him to change, for the first time since President Harry S. Truman ordered the dropping of the atomic bomb over Hiroshima, the American practice that gives the commander in chief sole authority to order the use of nuclear weapons. The issue gained prominence during the Trump administration, and the authors of the letter urged Biden to make the change as “an important safeguard against a possible future president who is unstable or who orders a reckless attack.”
Today I had the honor of delivering a letter on nuclear weapons issues to @POTUS signed by 697 scientists & engineers, including 21 Nobel laureates & 69 members of the National Academies. It recommends four steps to reduce the likelihood of nuclear war: https://t.co/o9ktgLlOxd pic.twitter.com/stjn9BJCCu
— Stephen Young (@StephenUCS) December 16, 2021
Politico-Opinion | Congress Approved $778 Billion for the Pentagon. That Means We Can Afford Build Back Better.
Some senators say Biden’s social and climate bill costs too much, but comparing it to the military spending plan they just passed suggests otherwise.
This week, the families of 61 million children received their final payments under the expanded Child Tax Credit. This credit has kept 10 million children above the poverty line, but it is expiring as the Senate delays a vote to renew it through the Build Back Better Act.
Instead, on the same day these last payments went out, the Senate voted to approve a $778 billion military spending budget — four times as much as the annual cost of the entire Build Back Better plan. Yet we’ve heard endlessly about how it’s Build Back Better that needs to be gutted so we can skimp and save.
Germany’s Baerbock pushes for nuclear disarmament
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock called for a “new momentum” to nuclear disarmament as she met with her Swedish counterpart with an eye toward a review of a non-proliferation treaty.
By Ali Harb Aljazeera aljazeera.com
Germany and Sweden have paired up to find ways to get the world’s nuclear powers to move toward committing to disarmament. The foreign ministers met in Stockholm to plot the way forward ahead of next month’s review of the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
Baerbock has been in talks with her Swedish counterpart Ann Linde and met with the Stockholm Initiative, a group of 16 countries seeking to get rid of nuclear weapons.
“Our joint goal is clear: a world free of atomic weapons,” Baerbock said during a press conference with Linde.
“Our message to the review conference will be clear: Nuclear weapons countries have to push ahead with nuclear disarmament,” read a statement from the initiative, calling for an irreversible, transparent end to nuclear weapons subject to oversight.
Protesters Denounce French Push to Label Nuclear as Sustainable Energy
“By taking the lead of the toxic alliance between fossil gas and nuclear (energy) at a European level, Emmanuel Macron clearly sides with the polluters’ camp. Nuclear is not a green energy: it produces radioactive waste that piles up across the country”
By Reuters | December 14, 2021
PARIS (Reuters) – Demonstrators unfurled a banner declaring “Gas & nuclear are not green” outside France’s foreign ministry on Tuesday in protest at a government drive to label nuclear energy and fossil gas as sectors for climate-friendly investment.
One of the about 20 protesters, wearing a mask of President Emmanuel Macron, chained himself to a gas bottle and a nuclear barrel outside the ministry’s headquarters in Paris. Another held a banner that read “Macron shame on you.”
The European Union is preparing a rulebook on climate friendly investments, which from next year will define which activities can be labelled as green in sectors including transport and buildings.
The EU’s aim is to restrict the green investment label to climate-friendly activities, steer cash into low-carbon projects and stop companies or investors making unsubstantiated environmental claims.
NEW Y-12 CONTRACTORS HAVE HISTORY OF NUCLEAR SAFETY FAILURES, MILLIONS IN PENALTIES AND FINES FOR VIOLATIONS
“The public deserves an explanation,” said Ralph Hutchison, coordinator of the Oak Ridge Environmental Peace Alliance. “Given the persistent criticality safety problems at Y-12, it is astonishing that the National Nuclear Security Administration has turned the management over to Fluor and Amentum, two companies that have racked up millions of dollars in fines in the last two decades for nuclear safety violations.”
immediate release: December 13, 2021
more information: Ralph Hutchison 865 776 5050 / orep@earthlink.net
According to the web site goodjobsfirst.com, which tracks violations in government contracting, AECOM, parent company of Amentum, has been penalized more than $167 million for 114 violations since 2000. Fifty-one of those violations were safety related, for a total of $4.5 million in penalties and fines; of that total, $3,866,250 was assessed for nuclear safety violations.
“From the beginning of October to mid-November, the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board documented nine nuclear safety incidents at Y-12, an average of more than one a week,” Hutchison said. “Unfortunately, this is not an anomaly—Y-12 is consistently plagued by nuclear safety issues, many of them from legacy activities or the ongoing degradation of the buildings used to manufacture nuclear weapons components.
“And the equally sad truth is that contractors at Y-12 have a history of failing to aggressively address issues as they arise. An outside assessment delivered in October noted that Consolidated Nuclear Services declared some cases ‘closed’ even though the actual problem had not been corrected and the cases were, in fact, still open.
Pilgrim Nuclear Plant Will Not Release Contaminated Water In 2022
By CBSBoston.com Staff December 7, 2021
PLYMOUTH (CBS) – The company managing the shutdown of the Pilgrim Nuclear Plant now says it will not release contaminated water into Cape Cod Bay in 2022 as planned.
Holtec International planned to discharge the water sometime early next year.
But in a statement on Monday, they promised to store the water on site through 2022 and search for other options to get rid of it.
“We appreciate and understand the public’s questions and concerns and remain committed to an open, transparent process on the decommissioning of Pilgrim Station focused on the health and safety of the public, the environment, and on-site personnel,” Holtec said in a statement.
Pilgrim went offline in 2019.
House Passes $768 Billion Defense Policy Bill
“I support having by far the strongest military in the world and the good-paying defense jobs in my district that protect our troops,” said Representative Andy Levin, Democrat of Michigan. “But I cannot support ever-increasing military spending in the face of so much human need across our country.”
By: Catie Edmondson The New York Times | December 7, 2021
WASHINGTON — The House on Tuesday overwhelmingly passed a $768 billion defense policy bill after lawmakers abruptly dropped proposals that would have required women to register for the draft, repealed the 2002 authorization of the Iraq war and imposed sanctions for a Russian gas pipeline, in a late-year drive to salvage a bipartisan priority.
The legislation, unveiled hours before the vote, put the Democratic-led Congress on track to increase the Pentagon’s budget by roughly $24 billion above what President Biden had requested, angering antiwar progressives who had hoped that their party’s control of the White House and both houses of Congress would lead to cuts to military programs after decades of growth.
Instead, the measure provides significant increases for initiatives intended to counter China and bolster Ukraine, as well as the procurement of new aircraft and ships, underscoring the bipartisan consensus on Capitol Hill for continuing to spend huge amounts of federal money on defense initiatives, even as Republicans lash Democrats for spending freely on social programs.
Energy Department to spend $15.5M to upgrade route from Los Alamos lab to waste site [WIPP]
“Essentially blessing what DOE was going to have to do anyway in order to expand nuclear weapons activities and waste disposal,” said Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico. “And once again demonstrated the subservience of our state government to the nuclear weapons industry here in New Mexico.”
By Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com Santa Fe New Mexican December 6, 2021 santafenewmexican.com
The N.M. 4 and East Jemez Road intersection in the far northwestern corner of Santa Fe County will be improved as part of a $15.5 million upgrade of routes on which Los Alamos National Laboratory transports nuclear waste to an underground disposal site in Southern New Mexico.
The U.S. Energy Department will spend $3.5 million to improve the intersection, which lies just outside Los Alamos County, and another $12 million to upgrade routes it owns and uses mostly to ship transuranic waste — contaminated gloves, clothing, equipment, soil and other items — to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant near Carlsbad.
REPORT: BIT BY BIT, THE NOOSE IS TIGHTENING AROUND THE NUCLEAR WEAPONS INDUSTRY
Human beings are not necessarily destined to annihilate ourselves.
“…the actual danger of nuclear conflict is now greater than at any point in history.”
By Jon Schwarz THE INTERCEPT December 5, 2021 theintercept.com
FOR YEARS, the Dutch organization PAX has been issuing reports detailing the Armageddon that’s hiding in plain sight. The business of nuclear weapons — and it is in fact a business — does not for the most part take place in secret underground lairs. It is all around us, conducted by corporations and banks that might otherwise make cellphones or cornflakes or autonomous vacuum cleaners.
PAX’s newest paper, “Perilous Profiteering,” should be front-page news around the world. Why it is not is an interesting question.
Nuclear war is still a threat to humanity. It’s true that it’s generally vanished from popular culture and our imagination since the end of the Cold War 30 years ago. What almost no one knows, however, is that many serious observers believe that the actual danger of nuclear conflict is now greater than at any point in history.
The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists invented its Doomsday Clock in 1947 to express how close the world was to self-destruction. It was initially set at seven minutes to midnight. Since then it has varied, being set both closer to and further away from midnight. But today, in 2021, it is the closest it’s ever been: 100 seconds to midnight. The publication’s reasoning can be read here.
Or take it from such anti-peaceniks as former Secretaries of State Henry Kissinger and the late George Shultz. Together they warned for years of the tremendous danger of nuclear war and called for “a world free of nuclear weapons.”
‘Not in my backyard’: The thorny issue of storing German nuclear waste
“Germany is to shut down its last nuclear reactors next year. However, the country still has no place to store the 27,000 cubic metres of highly radioactive material it has already produced, with the amount set to grow as power stations are decommissioned and dismantled. German authorities have set a deadline of 2031 to find a permanent storage location – but for now, the waste is being stored in temporary locations, much to the anger of local residents.”
© FRANCE 24 By: Anne MAILLIET | Nick SPICER france24.com December 4, 2021 / Originally published on:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
One dead, three injured after gas leak at Spanish nuclear plant
A fault in the plant’s fire prevention system caused the gas leak, which was not linked to any radioactive material, the regional fire service posted on Twitter.
MADRID, Nov 24 (Reuters) – One person has died and three have been taken to hospital after a carbon dioxide leak at the Asco nuclear power plant in the Spanish region of Catalonia, local emergency services said on Wednesday.
Shortly afterwards, the fire service said it was preparing to leave the site after checking over the extractor fans with the plant’s staff and ensuring the systems were working properly.
The three people taken to hospital suffered light injuries from carbon dioxide inhalation, emergency services said.
Iran nuclear talks resume with upbeat comments despite skepticism
Russia’s envoy to the talks, Mikhail Ulyanov, said on Twitter they “started quite successfully.” Asked he if was optimistic, Iran’s top negotiator, Ali Bagheri Kani, told reporters: “Yes, I am.”
Vienna, Austria EU, Iranian and Russian diplomats sounded upbeat as Iran and world powers held their first talks in five months on Monday to try to save their 2015 nuclear deal, despite Tehran taking a tough stance in public that Western powers said would not work.
“I feel extremely positive about what I have seen today,” Enrique Mora, the EU official chairing the talks, said after the meeting — the seventh round of talks aimed at reviving a deal under which Iran limited its disputed uranium enrichment program in return for relief from US, EU and UN economic sanctions.
“They have accepted that the work done over the first six rounds is a good basis to build our work ahead,” he said. “We will be of course incorporating the new political sensibilities of the new Iranian administration.”
Nuclear power is never safe or economical
“I hope Sen. Durbin changes his mind about promoting nuclear energy. The real carbon-free sources of electricity are wind and solar.”
Letters to the Editor Chicago Sun Times
I cannot disagree more with the assertion by Sen. Dick Durbin in a recent Sun-Times op-ed that nuclear power is a necessary and viable way to combat climate change.
Electricity production by nuclear power is not, and can never be made, safe and economical.
When nuclear power plants were first touted in the 1950s as a new and safe method for producing electricity, it was said the electricity would be “too cheap to meter.” This is pure nonsense! If it was so safe, why weren’t any power plants built and put on line until passage of the Price-Anderson Act? The law has been amended a number of times and greatly limits the liability of operators of nuclear power plants.
Anything paid out beyond the limits set in Price-Anderson would take years of lawsuits.
Sen. Durbin wrote “It is past time for Congress to step up and develop a comprehensive, consent-based plan to store nuclear waste.” That’s an understatement. Nuclear waste is stored within a half-mile of Lake Michigan at the now-closed Zion nuclear power plant. Why is it close to the source of our drinking water? Because there is nowhere to ship it! Plans to ship such waste to a depository in Yucca Mountain in the southwest fell through when some improperly stored barrels burst into flames, releasing large amounts of high-level radioactive material.
Who does the senator think will agree to a “consent-based plan” when there is no known method of safely storing these dangerous materials for thousands of years, the time it takes for radioactive decay to make it safe for the environment?
Sen. Durbin argued that “we must ensure the nuclear fleet remains safe and economical,” but nuclear power has never been economical. As far as I know, the last time a permit was approved for a new nuclear plant was during the Obama administration. That plant in Georgia is only about half complete, although it was to be finished by now and the cost is already double the initial estimate.
The current “fleet,” as Sen. Durbin called them, of nuclear power plants were designed and engineered to last about 30 to 40 years. Most of our country’s plants are near that age. Their internal systems are constantly bombarded by radioactive particles, making the metal in the systems more brittle and prone to failure every year. Subsidizing them is a waste of taxpayer money and a dangerous gamble with our lives.
I hope Sen. Durbin changes his mind. The real carbon-free sources of electricity are renewables: wind and solar.
George Milkowski, West Ridge
Letters to the Editor: Nuclear energy may not emit carbon, but it isn’t ‘clean’

To the editor: Steven Chu and Ernest Moniz are both professors who served as U.S. Energy secretary. They have more science credentials than most mortals. I am none of those things.
Yet, I was concerned when I read in their piece advocating for the continued use of the Diablo Canyon nuclear plant past the planned 2025 decommissioning that they referred to the electricity it produces as “clean.”
I recognize that they did so in order to differentiate nuclear from energy sources that emit carbon dioxide. However, the lack of carbon emissions notwithstanding, can nuclear energy truly be called clean?
There is the not-so-small matter of spent nuclear fuel. Where does it go? Where will it go? It’s currently in a cooling pool on-site. Owner Pacific Gas and Electric has requested permission to develop a dry cask storage system on-site; it did not estimate how long the spent fuel would be stored there.
Spent fuel is radioactive for a very long time. Whichever way you store it, if anything compromises the containment, the danger is released.
Carbon emissions or none, it is misleading to refer to nuclear energy as clean, especially when it comes to its impact on the environment.
Elise Power, Garden Grove
..
To the editor: I was energized by the piece on the Diablo Canyon nuclear plant. It reminded me of the sad situation at our local San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station.Continue reading
Pilgrim nuclear plant may release 1M gallons of radioactive water into bay. What we know
“Diane Turco, of Harwich, the director of Cape Downwinders, a citizen group that was at the forefront of the effort to close Pilgrim, called any option that included sending radioactive water into the bay “outrageous” and “criminal.” Turco said she has no confidence in the decommissioning process.
“The process has been to allow radioactivity into the environment,” she said. “The answer should be no you can’t do that.””
PLYMOUTH — One of the options being considered by the company that is decommissioning the closed Pilgrim Nuclear Power Station is to release around one million gallons of potentially radioactive water into Cape Cod Bay.
The option had been discussed briefly with state regulatory officials as one possible way to get rid of water from the spent fuel pool, the reactor vessel and other components of the facility, Holtec International spokesman Patrick O’Brien said in an interview Wednesday. It was highlighted in a report by state Department of Environmental Protection Deputy Regional Director Seth Pickering at Monday’s meeting of the Nuclear Decommissioning Citizens Advisory Panel in Plymouth.
“We had broached that with the state, but we’ve made no decision on that,” O’Brien said.
As of mid-December, Holtec will complete the process of moving all the spent fuel rods into casks that are being stored on a concrete pad on the Pilgrim plant site in Plymouth. After that, O’Brien told the panel, the removal and disposal of other components in those areas of the facility will take place and be completed sometime in February.
What to expect as Iran nuclear talks resume next week
“New round of talks unlikely to produce breakthrough but will shed light on posture of new Iranian government, analysts say.”
By Ali Harb Aljazeera aljazeera.com
“We’re going to find out how different these [Iranian] hardliners are from previous hardliners; we’re going to find out if they’re going to be a little softer,” said Negar Mortazavi, an Iranian-American journalist and analyst.
“And we’re also going to find out if the Americans have really realised that they missed an opportunity, and that they should change their position to some extent.”
Proponents of the deal, including Mortazavi, have criticised US President Joe Biden for not moving with urgency to restore the agreement in the first months of his administration, when a more moderate Iranian government headed by former President Hassan Rouhani was in charge.
Six rounds of talks in Vienna between April and June failed to forge a path back into the agreement.
“That golden window of opportunity was short, and the Biden team completely missed it,” Mortazavi told Al Jazeera.
A spin on Kirtland Air Force Base’s (which shares runways with the ABQ International Airport) true mission from the ABQ Journal: “Air Force lab injects $2B into NM’s economy”
The Kirtland Air Force Lab is dedicated to militarizing space, not improving the lives of New Mexico citizens.
As stated by the Arms Control Association in an April 2021 article titled Apes on a Treadmill in Space:
“The United States should recognize that a pattern of continued militarization of space is insufficient to provide the stability on which its economy and its armed forces depend, so the tools of diplomacy and international law should be marshalled too.”
By Kevin Robinson-Avila / Journal Staff Writer – Albuquerque Journal abqjournal.com
Air Force Research Laboratory spending on space and “directed energy” technology like lasers and microwaves boosted the local economy by nearly $2 billion over the past three years, according to a new economic impact report.
Nuclear News Archives – 2021
Consequences of Uranium Mining in the Southwest
Addressing the consequences of uranium mining in the Southwest, Anna Benally said, “When uranium mining came to Navajo Land, we were never told it was unsafe to be around it. We were never told to keep our children from playing near it or keep our livestock from coming around it. We were just happy to have jobs.”
By: Kristin Scheer | Peace Works Kansas City

Uranium mining is still causing problems in the US. This was the topic of Radio Active Magazine on KKFI, 90.1 FM Community Radio, on Feb. 9. Activists from the Multicultural Alliance for a Safe Environment (MASE), based in Albuquerque, NM, joined PeaceWorks-KC leaders for the program.
The MASE activists on the program were Anna Benally, a former uranium mine employee turned activist who is working to heal the land and protect the health of people and livestock, and Susan Gordon, coordinator of MASE. PeaceWorks Board members Ann Suellentrop and myself introduced the MASE leaders and interviewed them. The podcast is online at https://kkfi.org/program-episodes/fighting-uranium-contamination-in-the-southwest/.
Atomic weapons plan risky for SC, lawyers say. Noted legal service joins fray
Savannah River Site Watch, Nuclear Watch New Mexico and Tri-Valley CARES recently retained the Environmental Law Project. They say pit factories are expensive, unnecessary, needlessly threaten the environment, and could leave unused plutonium stranded permanently in places like SRS.
BY: SAMMY FRETWELL | thestate.com FEBRUARY 12, 2021
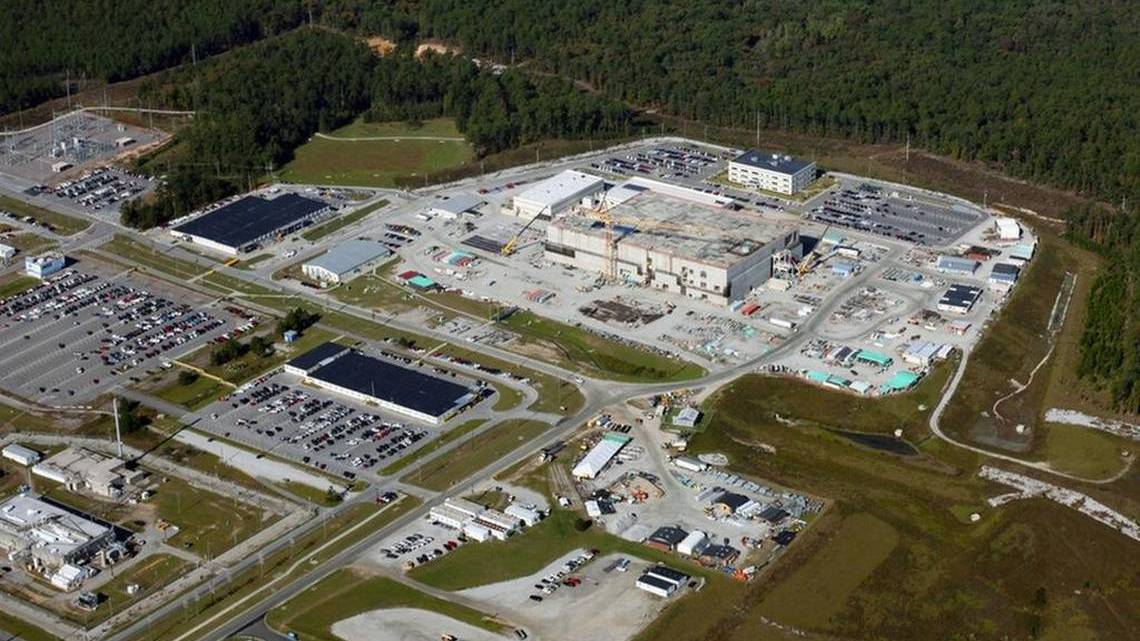

A South Carolina legal service has joined the fight against an atomic weapons components factory at the Savannah River Site, raising the possibility that environmental groups will sue the federal government to stop the effort.
The South Carolina Environmental Law Project, a non-profit service with an extensive record of arguing cases in court, outlined concerns about the factory in a letter this week to the U.S. Department of Energy. The letter called the proposed factory risky and in need of further study.
At issue is a proposal to build a nuclear weapons pit plant that would use plutonium, a deadly long-lived radioactive material, at the Savannah River Site.
The pit factory would produce potentially thousands of jobs, but is drawing opposition from environmental groups in South Carolina, New Mexico and California.
In Santa Fe, protesting LANL’s arrival
Luis Sánchez Saturno / The New Mexican Feb 12, 2021

Los Alamos lab, birthplace of the atomic bomb, STILL under threat from wildfires despite repeated major incidents
“The threat and risks of wildfire to the lab and northern New Mexico will continue to increase because of climate warming, drought and expanded nuclear weapons production,” said Jay Coghlan, director of the group Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
A recent audit by the US Energy Department’s inspector general found that threat-reduction measures such as the maintenance of the lab’s network of fire roads, strategic clearing of vegetation in the surrounding area as well as the production of a coherent preparedness and mitigation plan had not been carried out
Photographic evidence included in the report indicated a tree density of 400 to 500 per acre, 10 times the recommended safe level of 40 to 50 trees per acre.
Audit Raises Concerns About Wildfire Risks at US Nuclear Lab
“The threat and risks of wildfire to the lab and northern New Mexico will continue to increase because of climate warming, drought and expanded nuclear weapons production,” said Jay Coghlan, director of the group Nuclear Watch New Mexico.
BY: SUSAN MONTOYA BRYAN | wokv.com February 10, 2021
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — (AP) — One of the nation’s premier nuclear laboratories isn’t taking the necessary precautions to guard against wildfires, according to an audit by the U.S. Energy Department’s inspector general.
The report comes as wildfire risks intensify across the drought-stricken U.S. West. Climatologists and environmentalists have been warning about worsening conditions across the region, particularly in New Mexico, which is home to Los Alamos National Laboratory and where summer rains failed to materialize last year and winter precipitation has been spotty at best.
The birthplace of the atomic bomb, Los Alamos has experienced hundreds of millions of dollars in losses and damage from major wildfires over the last two decades. That includes a blaze in 2000 that forced the lab to close for about two weeks, ruined scientific projects, destroyed a portion of the town and threatened tens of thousands of barrels of radioactive waste stored on lab property.
Watchdog groups say the federal government needs to take note of the latest findings and conduct a comprehensive review before the lab ramps up production of key plutonium parts used in the nation’s nuclear arsenal.
Los Alamos Nuclear Weapons Lab Opens Office in the City of the Santa Fe (“Holy Faith”) of Peace and Environmental Protection
FEBRUARY 10, 2021
Santa Fe, NM – A Lab press release has announced that “[c]onnections between Los Alamos National Laboratory and the City of Santa Fe will be strengthened with the Laboratory’s opening of a new downtown office” after signing a 10-year lease on a 28,000-square-foot building. The Lab’s press release ignores LANL’s $2.9 billion nuclear weapons production budget (up 33% in one year), its proposed 46% cut to cleanup to $120 million, serious groundwater contamination and recent reports how it has neglected wildfire protection. Two catastrophic wildfires in the last 21 years on or near the Lab blanketed a large portion of northern New Mexico with possibly contaminated smoke.
The City of Santa Fe’s official name is the “La Villa Real de la Santa Fe de San Francisco de Asís” (“The Royal Town of the Holy Faith of Saint Francis of Assisi”), in honor of the beloved saint who preached peace and environmental protection and from whom the present Pope draws his name. Pope Francis has repeatedly called for the abolition of nuclear weapons and while in Japan paid homage to the victims of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings. Those atomic bombs were designed and produced at the Los Alamos Lab.
LANL not serious about wildland fires
BY: T.S. Last / Journal North Copyright © 2021 Albuquerque Journal Feb, 9, 2021
SANTA FE – A recently released report by the Department of Energy’s Office of Inspector General suggests that managers at Los Alamos National Laboratory did not take wildland fire prevention seriously enough, despite two catastrophic wildland fires in the past 20 years that threatened the lab and the town, costing taxpayers millions of dollars.
“Our review found that activities designed to reduce the impact from wildland fire had not been fully implemented at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in accordance with site plans,” says the opening sentence of a 14-page memo from the Inspector General’s office dated Feb. 1.
What’s worse, the report says, some plans were never drafted, and some policies put into place after the Cerro Grande Fire in 2000 and the Las Conchas Fire in 2011 were not being followed.
It adds that lab managers haven’t developed a “comprehensive risk-based approach to wildland fire management,” as required by the Federal Wildland Fire Management Policy. The report also describes a “lack of formality.”
“Specifically, the contractor’s Wildland Fire Plan lacked requirements for documenting wildland fire management activities, and responsibilities for implementation were not well defined,” the report says.
The contractor referred to is Triad National Security LLC, which in November 2019 took over management of the lab, which is tasked with developing and manufacturing parts for nuclear weapons. Previously, Los Alamos National Security LLC had held the management contract since 2006.
It appears evident that some of the problems identified in the report predate Triad’s involvement.
The report says that there are about 2,000 structures, including 13 nuclear facilities, with an estimated value of $14.2 billion on approximately 23,000 acres of lab property.
It notes that the 2000 Cerro Grande Fire, which burned 43,000 acres, including about 7,500 acres of LANL property, resulting in $331 million in damage to the lab alone. That does not include an estimated $15 million in lost productivity per week during a 15-day shutdown and recovery period.
The Cerro Grande Fire was a “crown fire” that burned through the tree canopy and spread quickly, and the report has an entire section on mitigation of crown fires.
Despite recognition of the risk, mitigation measures to reduce the risk of crown fires had not been performed.
LANL Falls Behind on Wildfire Protection While Expanding Nuclear Weapons Production Watchdog Calls for New Site-Wide Environmental Impact Statement
FEBRUARY 9, 2021
Santa Fe, NM – The Department of Energy’s Inspector General is reporting that the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) is falling seriously behind in wildfire protection. This is despite the fact that the 2000 Cerro Grande Fire forced the mandatory evacuation of both LANL and the Los Alamos townsite, burned 3,500 acres of Lab property and came within a half-mile of Area G, its largest waste dump. At the time Area G stored above ground some 40,000 barrels of plutonium-contaminated radioactive wastes. It could have been catastrophic had they burst and sent respirable airborne plutonium across northern New Mexico (inhaled plutonium is a very serious carcinogen).
In 2011 the Los Conchas Fire raced 13 miles in 24 hours to the Lab’s western boundary, where it was stopped along State Highway 4. Both it and the Cerro Grande Fire sent huge plumes of harmful smoke across northern New Mexico, possibly carrying Lab contaminants as well (operation of radioactive air emissions monitoring equipment was suspended during the Cerro Grande Fire).
Report: LANL not managing forests to prevent wildfires
Jay Coghlan, executive director of the nonprofit Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said the lab puts most of its attention on producing nuclear weapons and neglects forest maintenance, despite the disastrous Cerro Grande Fire that destroyed dozens of its structures.
“Nuclear weapons above all,” Coghlan said.”
By Scott Wyland swyland@sfnewmexican.com / sfnewmexican.com Feb 9, 2021
Los Alamos National Laboratory has failed to properly manage its forested lands, increasing the threat of wildfires at lab sites and surrounding areas, according to a federal watchdog.
The lab has not thinned trees or cleared forest debris from many wooded areas, nor has it maintained service roads to ensure safe passage for firefighting crews, boosting the potential for “devastating wildfires” like the Cerro Grande Fire in 2000, the U.S. Energy Department’s inspector general said in a strongly worded report released this week.
The report criticized the lab’s main contractor, Triad National Security LLC, for not following fire management plans and not documenting required yearly activities to prepare for and prevent possible wildfires at the site.
“Our review found that activities designed to reduce the impact from wildland fire had not been fully implemented at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in accordance with site plans,” the report said.
The report comes as the federal Drought Monitor shows Los Alamos County and much of the state as being in exceptional drought — the most severe condition — which raises the risks of wildfires.
Jay Coghlan from Nukewatch New Mexico and Kevin Kamps from Beyond Nuclear discuss the recent developments in Nuclear Weapons proliferation and the new international ban on nuclear weapons.
Living on the Edge also cover reasons why nuclear power may not be the low carbon panacea for transitioning our electric grid that is so widely promoted these days.
Plan to send diluted plutonium to Waste Isolation Pilot Plant moves forward
A plan to dispose of surplus plutonium at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant through a dilution process that would reduce the waste to radiation levels allowable at the facility moved forward at the end of 2020 and the process was expected to continue through 2022.
By: Adrian Hedden | currentargus.com February 8, 2021
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) – an arm of the U.S. Department of Energy – announced in December its intention to draft an environmental impact statement on the project and a public comment scoping was extended until Feb. 18.
Comments on the project can be made to the NNSA via email to SPDP-EIS@NNSA.DOE.GOV with the subject line SPDP EIS Scoping Comment.
The EIS will study the scope of the project and its potential impacts on the environment and DOE operations at numerous sites involved in the storage, down-blending and final disposal of the plutonium.
Radiation Illnesses and COVID-19 in the Navajo Nation
“In Indigenous lands where nuclear weapons testing took place during the Cold War and the legacy of uranium mining persists, Indigenous people are suffering from a double whammy of long-term illnesses from radiation exposure and the COVID-19 pandemic.”
By: Jayita Sarkar, Caitlin Meyer | thebulletin.org February 3, 2021
The COVID-19 pandemic is wiping out Indigenous elders and with them the cultural identity of Indigenous communities in the United States. But on lands that sprawl across a vast area of the American West, the Navajo (or Diné) are dealing not just with the pandemic, but also with another, related public health crisis. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says COVID-19 is killing Native Americans at nearly three times the rate of whites, and on the Navajo Nation itself, about 30,000 people have tested positive for the coronavirus and roughly 1,000 have died. But among the Diné, the coronavirus is also spreading through a population that decades of unsafe uranium mining and contaminated groundwater has left sick and vulnerable.
The Future of War in Biden’s America
Danny Sjursen offers a Bidenesque tour of U.S. militarism.
By: Danny Sjursen Tom’s Dispatch | consortiumnews.com

Hard as it is to believe in this time of record pandemic deaths, insurrection, and an unprecedented encore impeachment, Joe Biden is now officially at the helm of the U.S. war machine. He is, in other words, the fourth president to oversee America’s unending and unsuccessful post-9/11 military campaigns.
In terms of active U.S. combat, that’s only happened once before, in the Philippines, America’s second-longest (if often forgotten) overseas combat campaign.
Yet that conflict was limited to a single Pacific archipelago. Biden inherits a global war — and burgeoning new Cold War — spanning four continents and a military mired in active operations in dozens of countries, combat in some 14 of them, and bombing in at least seven.
Nukes aren’t just for bombers and subs. Here are some unusual ways militaries have also planned to drop the bomb
Throughout the Cold War, the prospect of bombers dropping nuclear bombs and submarines launching nuclear-tipped missiles terrified people around the world. Those were the major delivery methods, but both militaries developed an array of smaller nuclear weapons for tactical use, and planners in those militaries gave very real consideration to using them.
By: Benjamin Brimelow | businessinsider.com Jan 28, 2021
The Special Atomic Demolition Munition (SADM) was small enough to fit into a large backpack but still had a yield of a kiloton. It was intended to be planted by small, specially trained teams that would set a time fuse before attempting to escape.
You can actually view these asinine “backpack nukes” at the National Museum of Nuclear Science & History in Albuquerque. These “small” weapons, many of them more powerful than the nuclear bomb dropped on Hiroshima, would have obliterated any battlefield and irradiated much of the surrounding area.
The Little Boy (15 kilotons) and Fat Man (21 kilotons) atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively, remain the only nuclear weapons used in combat.
Those bombs destroyed the cities, killed or wounded hundreds of thousands of people, and left thousands more with long-term health problems. The carnage and destruction are the first things that come to mind when discussing nuclear weapons.
But nukes weren’t just for destroying cities. Early in the Cold War, the tactical use of nuclear weapons on the battlefield was not only researched extensively but actually considered.
Unknown Impact: County asks Los Alamos National Labs to assess environmental impact before expanding nuclear production
Santa Fe County wants Los Alamos National Laboratories to take stock of its impact on the environment and surrounding communities before pushing ahead with plans to expand.
By Leah Cantor | sfreporter.com Jan 27, 2021
On Tuesday, the Board of County Commissioners unanimously passed a resolution asking the National Nuclear Safety Administration to complete a new site-wide environmental impact statement for LANL in compliance with the National Environmental Policy Act before expanding plutonium pit production.
“The public health and safety is so important,” said Commissioner Anna Hansen, noting that the NEPA process is one of the only avenues for the public to weigh in on what goes on at the labs. “We have a longstanding tradition of promoting democracy and environmental protection in impending nuclear weapons by requesting that local governments be kept fully informed about projects to facilitate large scale production of additional plutonium warheads,” she said.
Yet right now, the labs’ full impact on Northern New Mexico is unknown. It’s been more than a decade since the last time the NNSA produced an EIS for the laboratory, and a lot has changed since then, including regional understanding of wildfire risks and potential water contamination from the labs.
Remembering the Night Two Atomic Bombs Fell—on North Carolina
Sixty years ago, at the height of the Cold War, a B-52 bomber disintegrated over a small Southern town. An eyewitness recalls what happened next.
By: Bill Newcott | nationalgeographic.com PUBLISHED JANUARY 22, 2021
BILLY REEVES REMEMBERS that night in January 1961 as unseasonably warm, even for North Carolina. But it got a lot hotter just before midnight, when the walls of his room began glowing red with a strange light streaming through his window.
“I was just getting ready for bed,” Reeves says, “and all of a sudden I’m thinking, ‘What in the world…?'”
The 17-year-old ran out to the porch of his family’s farm house just in time to see a flaming B-52 bomber—one wing missing, fiery debris rocketing off in all directions—plunge from the sky and plow into a field barely a quarter-mile away.
“Everything around here was on fire,” says Reeves, now 78, standing with me in the middle of that same field, our backs to the modest house where he grew up. “The grass was burning. Big Daddy’s Road over there was melting. My mother was praying. She thought it was the End of Times.”
Like any self-respecting teenager, Reeves began running straight toward the wreckage—until it exploded.
The Doomsday Datavisualizations
[smartslider3 slider=”8″]
In setting the Doomsday Clock, the Bulletin’s Science and Security Board consults widely with colleagues across a range of disciplines and considers qualitative and quantitative information from a wide array of sources. These three visualizations display some of the kinds of public data that are available in the Bulletin’s three coverage areas: nuclear weapons, climate change, and disruptive technology.
The Doomsday Clock is a design that warns the public about existential threats, a metaphor that reminds the world of the perils that must be addressed if humanity is to continue survive. These three data visualizations can be seen as an artistic extension of the original design.
DESIGNED BY PENTAGRAM
Giorgia Lupi, Sarah Kay Miller, Phil Cox,
Ting Fang Cheng, Talia Cotton
In November 2011, the U.S. Senate designated January 27th as a National Day of Remembrance for the Nevada Test Site Downwinders. The Senate recognized the harm caused to Americans from radioactive fallout from the aboveground atomic tests in Nevada, which began on January 27, 1951 and ended on July 17, 1962. Nuclear testing by the U.S. government started in New Mexico with Trinity in July 1945, and the Crossroads Series of three tests followed in the Pacific in 1946. The United States took part in nuclear testing as part of the escalating Cold War arms race, and nuclear weapons proliferated. With each nuclear test, radioactive fallout spread globally.
FOR MORE INFORMATION VIEW LINKS BELOW
Downwinders And The Radioactive West Premieres January 27 at 7PM on PBS Utah
Why a National Day of Remembrance for Downwinders is Not Enough
Congress Introduces Legislation to Expand Compensation for Radiation Exposure
Why a National Day of Remembrance for Downwinders is Not Enough
“A day of recognition is important – these communities deserve to be recognized for the unimaginable sacrifice they unknowingly made to their country. But it is not enough. The best and most important way to honor these victims of the US nuclear weapons program is by compensating them and providing health care for the illnesses and deaths they have suffered.”
BY: LILLY ADAMS GUEST COMMENTARY, UCS | JANUARY 26, 2021, 10:56 AM EST

There’s no question that the US government killed and sickened many of its own people through explosive nuclear testing: estimates of the death toll in the United States from nuclear testing vary widely, from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands. But the harm doesn’t stop there. Other nuclear weapons activities, like uranium mining, production, and waste storage and cleanup, have also caused unknown deaths and illnesses. As is so often the case, the people who have borne the heaviest burden of these activities are often people of color, Indigenous communities, women and children, and those living in poor, rural communities. These people are the largely ignored, often forgotten casualties of the Cold War and the US nuclear weapons program.
The Most Dangerous Situation Humanity Has Ever Faced
“The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists announced Wednesday that the hands of the iconic Doomsday Clock remain at 100 seconds to midnight — as close to the end of humanity as the clock has ever been. The temptation, of course, in a dark hour is to cling to even the faintest signs of light and hope. And the truth is that there are some encouraging signs now emerging. However, we continue to teeter at the brink and moving the Clock away from midnight would provide false hope at a time when urgent action is what is needed.”.
Opinion by Edmund G. Brown Jr. and Robert Rosner / Updated 11:17 AM ET, Wed January 27, 2021
For a year now, the world has been ravaged by the horrors of Covid-19. It has caused millions to lose their jobs, overwhelmed health care systems and dramatically changed how we live. The disease has killed more than 2 million people and infected 100 million around the globe.
Even so, we face fundamentally greater threats to humanity than this pandemic. We refer to the catastrophic dangers which nuclear weapons and climate change pose — dangers that preceded this pandemic and will persist long after it ends. Unfortunately, and unlike the priority given to developing a vaccine against the virus, little progress was made to reduce the danger of the world’s nuclear weapons arsenal or to effectively slow the carbon emissions warming our planet in 2020. The sudden appearance and confused response to the virus makes all too clear how ill-prepared the world can be when it has to deal with an unprecedented threat of global magnitude.
UN Building Lit Up to Celebrate The Nuclear Ban Treaty Entry Into Force January 22
[smartslider3 slider=”6″]
Here are five examples of the type of activities that will be Illegal under international law on 22 January 2021
One of the main problems with talking about nuclear weapons is that it often becomes abstract and hypothetical. Most people barely know which countries have nuclear weapons and do not know to what extent other actors are involved in maintaining and upholding nuclear weapons.
When the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) enters into force on 22 January 2021, that will need to change.

Here are five examples of the kind of activities that will be prohibited under the TPNW and who is currently doing this today. While the treaty will only be legally binding in the countries that have ratified the treaty, it will still create a powerful norm and should lead to increased protests and outrage in countries that haven’t joined the treaty that are behaving in contradiction of this new instrument of international law.
What the treaty prohibits
Article 1 of the treaty prohibits states parties from developing, testing, producing, manufacturing, transferring, possessing, stockpiling, using or threatening to use nuclear weapons, or allowing nuclear weapons to be stationed on their territory. It also prohibits them from assisting, encouraging or inducing anyone to engage in any of these activities.
Treaty Seeks End to Nuclear Madness
It is the beginning of a new movement that will see the elimination of the existential nuclear threat.
Ralph Hutchison, John LaForge | progressive.org
On January 22, the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons will enter into force. The treaty bans the development, production, possession, deployment, testing, use and just about anything else you can imagine related to nuclear weapons.
Fifty years later, nine nuclear-armed militaries possess more than 13,000 nuclear weapons, arsenals that mock their claimed commitment to disarm “at an early date.”
Approved at the United Nations by 122 countries in 2017, and subsequently signed by 86 and ratified by 51 nations, the nuclear weapons ban will join the venerated status of international prohibitions already established against lesser weapons of mass destruction. These earlier agreements include the Geneva Gas Protocol, the Chemical Weapons Convention, the Biological Weapons Convention, the Ottawa Treaty or Mine Ban Convention and the Convention on Cluster Munitions.
Atop the Powerful Budget Committee at Last, Bernie Sanders Wants to Go Big
To the chagrin of Republicans, the democratic socialist senator will play a central role in shepherding Joseph R. Biden Jr.’s agenda through Congress.
“Sanders, the next chairman of the Senate Budget Committee, plans to take a hard look at fraud at the defense budget in his new perch, he tells POLITICO
“You understand you’re talking to the guy who led the effort to lower defense spending by 10 percent,” the Vermont Independent and self-described Democratic Socialist boasted.
You’re talking about the military budget, which is now higher than the next 10 nations combined,” he continued. “You’re talking about the Pentagon budget, which is the only major government agency which has not been able to undertake an independent audit. And I don’t think anyone has any doubt that there’s massive waste and cost overruns in the military budget.”
“I think if you check the record,” he added, “you’ll find that every major defense contractor has been found guilty of collusion and fraud.”
By Alan Rappeport and Jim Tankersley | nytimes.com
Shortly before the 2016 election, Paul D. Ryan of Wisconsin, the Republican nominee for vice president and the speaker of the House, told a group of college Republicans why he thought Democrats winning control of the Senate would be a policy nightmare.
“Do you know who becomes chair of the Senate Budget Committee?” Mr. Ryan asked. “A guy named Bernie Sanders. You ever heard of him?”
Republicans have long feared the prospect of Mr. Sanders, a self-described democratic socialist from Vermont, taking the helm of the powerful committee given his embrace of bigger government and more federal spending with borrowed money. With Democrats reclaiming the Senate, that fear is about to become a reality. Mr. Sanders, the most progressive member of the chamber, will have a central role in shaping and steering the Democrats’ tax and spending plans through a Congress that they control with the slimmest of margins.
Concern grows over massive US cyberattack – New Mexico’s national labs, Los Alamos and Sandia, cited as possible targets among many
Jay Coghlan, executive director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, said the breach escalates the threat of a nuclear catastrophe.
“On top of the dangers that we faced during the Cold War this now raises new concerns…Could our nuclear weapons be hacked for malicious reasons? Could hackers take advantage of LANL’s checkered safety and security record and cause a life threatening event in our own backyard? The sooner we all have a nuclear weapons-free world the safer we will be.”
Copyright © 2020 Albuquerque Journal / BY: T.S. LAST / JOURNAL NORTH
 SANTA FE — While the Department of Energy says that a cyberoffensive was limited to business networks, concerns remain about the depth of the breach and what threat it could still pose to national security and New Mexico’s two national laboratories.
SANTA FE — While the Department of Energy says that a cyberoffensive was limited to business networks, concerns remain about the depth of the breach and what threat it could still pose to national security and New Mexico’s two national laboratories.
Some news reports say that the hacks are believed to have been instigated by a Russian intelligence agency. The reports specifically mention Los Alamos and Sandia national laboratories, where atomic research is conducted, as being vulnerable.
In addition, Los Alamos National Laboratory is tasked with producing plutonium pits, the triggering device in nuclear warheads.
Earlier this week the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued a warning, calling the hack “a grave risk” to federal, state, local and tribal governments, as well as critical infrastructure entities and private sector businesses. It said the suspected breach dates back to at least March.
In a joint statement this week, CISA, the FBI and the director of national intelligence said they were working together to investigate a “significant ongoing cybersecurity campaign.”\
‘Highly skeptical’: House Armed Services chairman concerned about SRS pit production
Biden administration expected to take ‘critical look’ at next-generation warhead, estimated to be twice as explosive as Trident
By: Colin Demarest cdemarest@aikenstandard.com / postandcourier.com
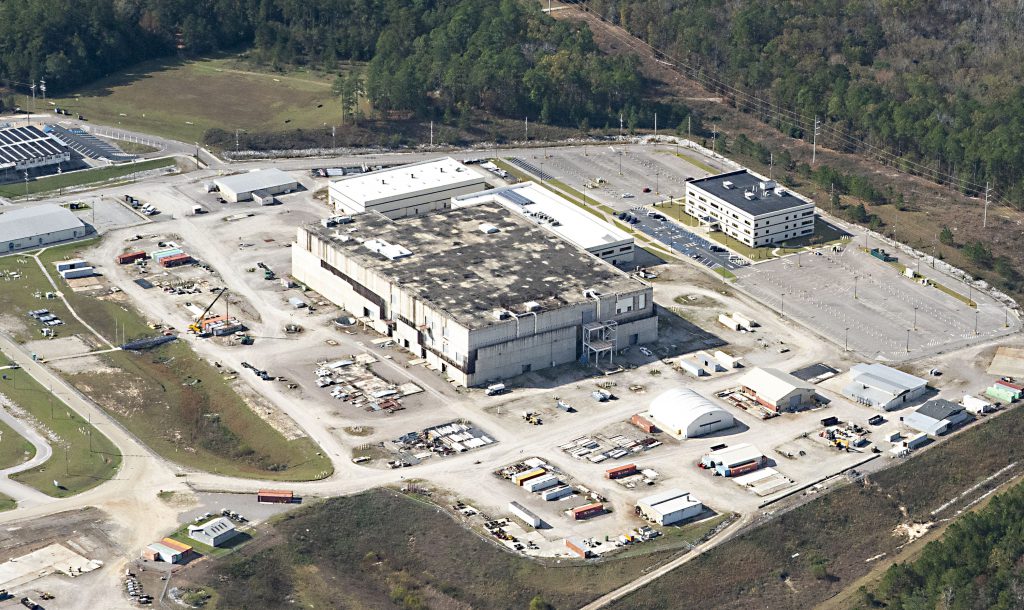

Photo courtesy of High Flyer
Likening the conversion of the failed Mixed Oxide Fuel Fabrication Facility to flipping a bowling alley into a restaurant, U.S. Rep. Adam Smith said he was “highly skeptical that they’re going to be able to turn that building into an effective pit production facility. Highly skeptical.”
US Nuclear Warhead Standoff ‘Has Significant Implications for UK’
Biden administration expected to take ‘critical look’ at next-generation warhead, estimated to be twice as explosive as Trident
By: Dan Sabbagh / theguardian.com

Britain’s most senior defence official admitted there would be “very significant implications” for the future of the Trident nuclear deterrent if Democrats in the US Congress refused to fund a next-generation warhead.
Sir Stephen Lovegrove, permanent secretary at the Ministry of Defence, said that the UK was monitoring the US standoff closely but could not say what impact a refusal to start work on the new W93 warhead would have – or how many billions it would cost.
THE SOFTENING RHETORIC BY NUCLEAR-ARMED STATES AND NATO ALLIES ON THE TREATY ON THE PROHIBITION OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS
BY: TOM SAUER & CLAIRE NARDON / warontherocks.com

Probably the most iconic moment during the negotiations on the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (or “nuclear ban treaty”) was the gathering of a dozen allied ambassadors standing around U.S. Ambassador Nikki Haley in the corridors of the U.N. building in New York, protesting against the ongoing negotiations. While nuclear-armed states and NATO allies remain opposed to the treaty, the tone is softening, and at least two NATO allies are breaking the consensus.